FEMA & PMLA | 26 Jul 2022
Why in News?
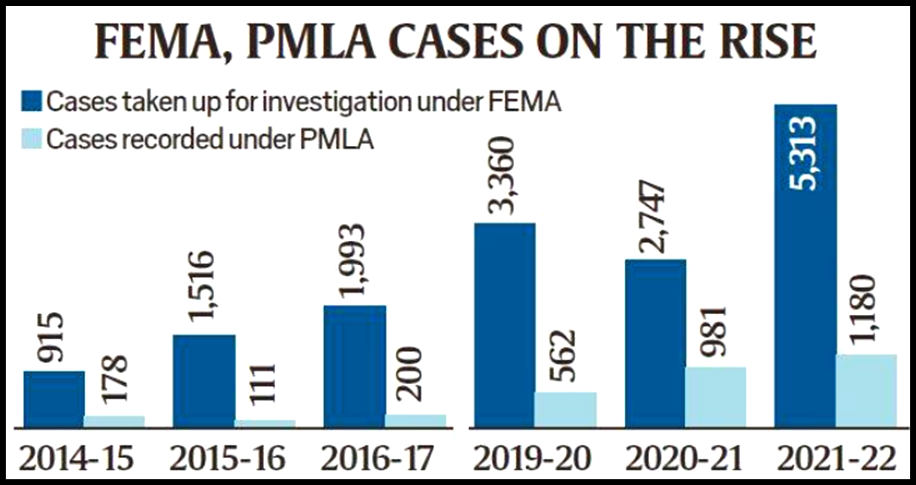
The Directorate of Enforcement (ED) has registered 14,143 cases under FEMA and PMLA between 2019-20 and 2021-22 as compared to 4,913 cases in 2014-15 to 2016-17.
- Year 2021-22 saw the highest number of money laundering and foreign exchange violation cases.
What is Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999?
- The legal framework for the administration of foreign exchange transactions in India is provided by the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999.
- Under the FEMA, which came into force with effect from 1st June 2000, all transactions involving foreign exchange have been classified either as capital or current account transactions.
- Current Account Transactions:
- All transactions undertaken by a resident that do not alter his / her assets or liabilities, including contingent liabilities, outside India are current account transactions.
- Example: payment in connection with foreign trade, expenses in connection with foreign travel, education etc.
- All transactions undertaken by a resident that do not alter his / her assets or liabilities, including contingent liabilities, outside India are current account transactions.
- Capital Account Transactions:
- It includes those transactions which are undertaken by a resident of India such that his/her assets or liabilities outside India are altered (either increased or decreased).
- Example: investment in foreign securities, acquisition of immovable property outside India etc.
- It includes those transactions which are undertaken by a resident of India such that his/her assets or liabilities outside India are altered (either increased or decreased).
- Current Account Transactions:
- Resident Indians:
- A 'person resident in India' is defined in Section 2(v) of FEMA, 1999 as:
- Barring few exceptions, a person residing in India for more than 182 days during the course of the preceding financial year.
- Any person or body corporate registered or incorporated in India.
- An office, branch or agency in India owned or controlled by a person resident outside India.
- An office, branch or agency outside India owned or controlled by a person resident in India.
- A 'person resident in India' is defined in Section 2(v) of FEMA, 1999 as:
What is the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002?
- It forms the core of the legal framework put in place by India to combat Money Laundering.
- The provisions of this act are applicable to all financial institutions, banks (Including RBI), mutual funds, insurance companies, and their financial intermediaries.
- PMLA (Amendment) Act, 2012:
- Adds the concept of ‘reporting entity’ which would include a banking company, financial institution, intermediary etc.
- PMLA, 2002 levied a fine up to Rs 5 lakh, but the amendment act has removed this upper limit.
- It has provided for provisional attachment and confiscation of property of any person involved in such activities.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following groups of items is included in India’s foreign-exchange reserves? (2013)
(a) Foreign-currency assets, Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) and loans from foreign countries
(b) Foreign-currency assets, gold holdings of the RBI and SDRs
(c) Foreign-currency assets, loans from the World Bank and SDRs
(d) Foreign-currency assets, gold holdings of the RBI and loans from the World Bank
Ans: (b)
Explanation:
- Foreign Exchange Reserves are assets kept in reserve by a central bank in foreign currencies.
- According to RBI, Foreign Exchange Reserve in India includes:
- Foreign Currency Assets
- Gold
- SDRs
- Reserve Tranche Position with IMF
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. Discuss how emerging technologies and globalisation contribute to money laundering. Elaborate measures to tackle the problem of money laundering both at national and international levels. (2021)
Q. India’s proximity to the two of the world’s biggest illicit opium-growing states has enhanced her internal security concerns. Explain the linkages between drug trafficking and other illicit activities such as gunrunning, money laundering and human trafficking. What counter-measures should be taken to prevent the same? (2018)