Diyodar Meteorite | 14 Feb 2023
Why in News?
Scientists from Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Ahmedabad, are claiming that the meteorite that crashed in two villages in Banaskantha, Gujarat on August 17, 2022, has been identified as an aubrite.
- The PRL group used a gamma-ray spectrometer to determine the mineral composition of aubrite. The group also classified the meteorite as a monomict breccia.
What are the Major Highlights Related to Aubrite?
- Aubrite meteorite is a coarse-grained igneous rock that formed in oxygen-poor conditions and contains exotic minerals not found on Earth.
- For example, the mineral heideite was first described in the Basti meteorite.
- India has seen hundreds of meteorite crashes, but this is only the second recorded crash of an aubrite. The meteorite has been named the Diyodar meteorite after the taluka in which the villages are located.
- The last crash of an aubrite before this was in Basti, Uttar Pradesh on December 2, 1852.
- Around 90% of the meteorite was composed of orthopyroxene. Pyroxenes are silicates consisting of single chains of silica tetrahedra (SiO 4); orthopyroxenes are pyroxenes with a certain structure.
- Pyroxenes such as diopside and jadeite have been used as gems. Spodumene was historically used as lithium ore. Rocks with pyroxene have also been used to make crushed stone that is used in construction.
- Aubrites have crashed in at least 12 locations worldwide since 1836, including 3 in Africa and 6 in the U.S.
What is a Meteorite?
- About:
- A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from space that survives its passage through the Earth's atmosphere and lands on the Earth's surface.
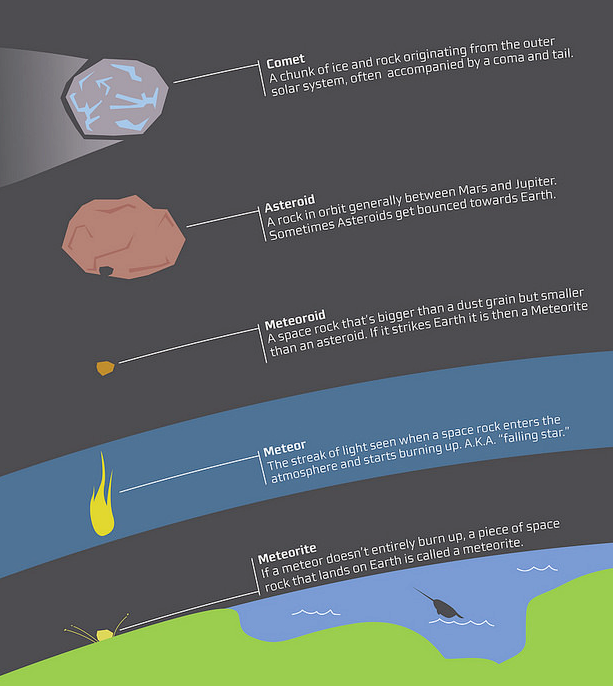
- Difference between Meteor, Meteorite and Meteoroid:
- The difference between a meteor, meteorite and meteoroid is nothing but where the object is.
- Meteoroids are objects in space that range in size from dust grains to small asteroids.
- But when meteoroids enter the Earth’s atmosphere, they are called meteors.
- But if a meteoroid enters the Earth’s atmosphere and hits the ground, it is called a meteorite.
What is a Gamma Ray Spectrometer?
- Gamma ray spectrometers are scientific instruments used to measure the energy distribution of gamma rays emitted by radioactive materials.
- They consist of a detector, electronics, and software to analyse the data.
- The resulting gamma ray spectrum can be used to identify the radioactive isotopes present and their relative abundance.
- Gamma ray spectrometers are used in a variety of applications, including environmental monitoring, geology, and nuclear physics.
- They can be used to detect and measure the radiation emitted by natural sources, such as rocks and soils, as well as anthropogenic sources, such as nuclear power plants and medical facilities.