Important Facts For Prelims
Dhamma Dipa International Buddhist University
- 28 Nov 2022
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Dhamma Dipa International Buddhist University (DDIBU), Buddhism, Schools of Buddhism, Buddhist Texts
For Mains: Significance of Buddhist Councils, Contribution of Buddhism in Indian Culture, Buddhism as way of Soft Diplomacy, Initiatives taken to Promote Buddhism in India
Why in News?
The foundation stone for the Dhamma Dipa International Buddhist University (DDIBU) at Manu Bankul in Sabroom of South Tripura district will be laid on 29th November 2022.
- DDIBU is expected to become the first Buddhist-run university in India to offer Buddhist education along with courses in other disciplines of modern education as well.
What is Buddhism?
- About:
- Buddhism started in India over 2,600 years ago.
- The religion is based upon the teachings, life experiences of its founder Siddhartha Gautam.
- The main teachings of Buddhism are encapsulated in the basic concept of four noble truths or ariya-sachchani and eight-fold path or ashtangika marg.
- Four noble truths:
- Suffering (dukkha) is the essence of the world.
- Every suffering has a cause – Samudya.
- Suffering could be extinguished – Nirodha.
- It can be achieved by following the Atthanga Magga (Eight-Fold Path).
- Eight-Fold Paths: It consists of various interconnected activities related to knowledge, conduct, and meditative practices.
- Right view
- Right intention
- Right speech
- Right action
- Right livelihood
- Right mindfulness
- Right effort
- Right concentration
- Four noble truths:
- The essence of Buddhism is the attainment of enlightenment or nirvana which was not a place but an experience that could be attained in this life.
- There is no supreme god or deity in Buddhism.
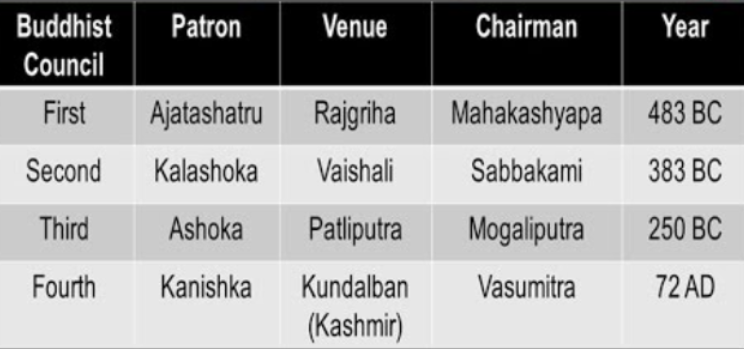
- Buddhist Councils:
- Schools of Buddhism:
- Mahayana (Idol Worship), Hinayana, Theravada, Vajrayana (Tantric Buddhism), Zen.
- Buddhist Texts (Tipitaka):
- Vinaya Pitaka (rules applicable to monastic life), Sutta Pitaka (main teaching or Dhamma of Buddha), Abhidhamma Pitaka (a philosophical analysis and systematization of the teaching).
- Contribution of Buddhism to Indian Culture:
- The concept of ahimsa was its chief contribution. Later, it became one of the cherished values of our nation.
- Its contribution to the art and architecture of India was notable. The stupas at Sanchi, Bharhut, and Gaya are wonderful pieces of architecture.
- It promoted education through residential universities like those at Taxila, Nalanda, and Vikramasila.
- The language of Pali and other local languages developed through the teachings of Buddhism.
- It had also promoted the spread of Indian culture to other parts of Asia.
- UNESCO’s Heritage Sites Related to Buddhism:
- Archaeological Site of Nalanda Mahavihara at Nalanda, Bihar
- Buddhist Monuments at Sanchi, MP
- Mahabodhi Temple Complex at Bodh Gaya, Bihar
- Ajanta Caves Aurangabad, Maharashtra.
- The Buddhist chanting of Ladakh was included in the UNESCO’s Representative List of Humanity's Intangible Cultural Heritage in 2012.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. With reference to Indian history, consider the following texts: (2021)
- Nettipakarana
- Parishishtaparvan
- Avadanashataka
- Trishashtilakshana Mahapurana
Which of the above are Jaina texts?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- The Nettipakarana is a mythological Buddhist scripture, sometimes included in the Khuddaka Nikaya of Theravada Buddhism's Pali Canon.
- Parishishtaparvan is a 12th-century Sanskrit mahakavya by Hemachandra which details the histories of the earliest Jain teachers.
- Avadanasataka is an anthology in Sanskrit of one hundred Buddhist legends, approximately dating to the same time.
- Trishashthilkshana Mahapurana is a major Jain text composed largely by Acharya Jinasena during the rule of Rashtrakuta.
- Hence, option B is correct.
Q2. With reference to Indian history, consider the following pairs: (2021)
| Historical person | Known as | |
| 1. | Aryadeva | Jaina scholar |
| 2. | Dignaga | Buddhist scholar |
| 3. | Nathamuni | Vaishnava scholar |
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) None of the pairs
(b) Only one pair
(c) Only two pairs
(d) All three pairs
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Aryadeva was a Mahayana Buddhist monk, a disciple of Nagarjuna and a Madhyamaka philosopher. Dignaga was an Indian Buddhist scholar and one of the Buddhist founders of Indian logic. Sri Ranganathamuni, popularly known as Sriman Nathamuni (823 CE–951 CE), was a Vaishnava theologian who collected and compiled the Nalayira Divya Prabandham. Hence, only pairs 2 and 3 are correctly matched. First pair is not correctly matched.
- Therefore, option C is correct.
Q3. With reference to the cultural history of India, which one of the following is the correct description of the term ‘paramitas’? (2020)
(a) The earliest Dharmashastra texts written in aphoristic (sutra) style
(b) Philosophical schools that did not accept the authority of Vedas
(c) Perfections whose attainment led to the Bodhisattva path
(d) Powerful merchant guilds of early medieval South India
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Paramita or parami (in Sanskrit and Pali respectively) is a Buddhist term often translated as “perfection”.
- In Mahayana Buddhism, the bodhisattva practices the six paramitas, or transcendent perfections which are generosity, discipline, patience, diligence, meditative concentration, and wisdom.
- Parmitas are described in Buddhist commentaries as noble character qualities generally associated with enlightened beings.
- Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
Q4. Consider the following: (2019)
- Deification of the Buddha
- Treading the path of Bodhisattvas
- Image worship and rituals
Which of the above is/are the feature/features of Mahayana Buddhism?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- The fourth Buddhist Council held at Kundalvana, Kashmir in 72 AD, presided by Vasumitra saw Buddhism divide into two branches, Hinyana and Mahayana.
- Mahayana, literally translates to ‘The Great Vehicle’, whereas supporters of Mahayana Buddhism termed the older tradition of Buddhism as Hinyana (the lesser vehicle).
- Mahayana Buddhists professed the path of the Bodhisattva to attain enlightenment and to help all sentient beings from all sufferings and pain. Hence, 2 is correct.
- This school started believing that the Buddha was the saviour and he was the one who could ensure salvation. Thus, the process of deification of Buddha started. Hence, 1 is correct.
- Besides, the worship of images of the Buddha and rituals became an important part of Buddhist school. Hence, 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option D is the correct answer.
Mains
Q1. Pala period is the most significant phase in the history of Buddhism in India. Enumerate. (2020)
Q2. Early Buddhist Stupa-art, while depicting folk motifs and narrative successfully expounds Buddhist ideals. Elucidate (2016)