Economy
Boosting India's Rubber Industry
- 20 Jan 2025
- 11 min read
For Prelims: Rubber Board, Rubber, National Rubber Policy (NRP) 2019, European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR), EU, European Commission, Deforestation, Forest Degradation, Palm Oil, Non-Tariff Barrier, India-EU FTA, Tropical Tree, Amazon Rainforest, Loamy or Laterite Soil, Agro Management, Mixed Farming, High-Yielding.
For Mains: Initiatives for boosting the rubber industry for meeting global rubber standards.
Why in News?
The Rubber Board has launched new initiatives like Indian Sustainable Natural Rubber (iSNR) and INR Konnect Platform to boost Indian rubber's global prominence and increase domestic production.
- It is in line with the National Rubber Policy (NRP) 2019 that aims to build an environmentally sustainable, globally competitive rubber industry.
What are the Recent Initiatives Taken in India’s Rubber Industry?
- iSNR Initiative: Indian Sustainable Natural Rubber (iSNR) Initiative was launched to meet European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR) standards.
- It facilitates traceability of rubber products with certificates verifying origin and compliance and simplifies the compliance process for stakeholders targeting EU markets.
- It promotes sustainable rubber production while positioning Indian natural rubber as a competitive and responsible choice in the global market.
- INR Konnect Platform: It is a web-based platform aimed at increasing productivity by connecting growers of untapped rubber holdings with interested adopters.
- It targets 20-25% of untapped and neglected plantations in India by absentee landlords to address price drops, and high costs.
- mRube: mRube was launched as the digital marketing platform of Rubber Board to enhance marketing and trade efficiency in the natural rubber sector.
- Subsidy Hike: The government plans to increase subsidies for rubber cultivation in a phased manner.
Note: Absentee landlords own property but don't live or manage it, relying on property managers, tenants, or local agents for maintenance, rent collection, and other operations.
What is EUDR?
- About: EUDR is a legislative framework proposed by the European Commission to address the global issue of deforestation and forest degradation linked to commodity supply chains.
- The regulation aims to reduce the EU's role in driving deforestation and ensure that products linked to deforestation do not enter the European market.
- Mechanism: Traders or operators must demonstrate that their products, when entering the EU market or being exported, do not originate from recently deforested land or contribute to forest degradation.
- Objectives: The primary objectives include:
- Prevent deforestation by ensuring listed products don't contribute to it.
- Reduce carbon emissions by at least 32 million metric tonnes annually.
- Combat forest degradation linked to agricultural expansion of these commodities.
- Commodities Covered: It focuses on commodities such as cattle, wood, cocoa, soy, palm oil, coffee, rubber, and related products (e.g., leather, chocolate, tires, furniture).
- Related Concerns:
- Non-Tariff Barrier: EUDR requires certification that commodities like cattle, soy, and palm oil aren’t from deforested land, which India sees as Non-Tariff Barrier.
- Compliance Burden: Proving goods are deforestation-free imposes additional administrative and operational burdens, especially on SMEs.
- Global Policy Replication: This could lead to global certification schemes becoming the norm creating further pressure on Indian exporters.
- Slowing FTA Negotiations: EUDR has become contentious issues in the ongoing India-EU FTA negotiations.
Rubber Board
- The Rubber Board is a statutory body constituted under the Rubber Act, 1947, for the overall development of the rubber industry in the country.
- It functions under the Ministry of Commerce & Industry of the Government of India.
- The Board's headquarters is situated in Kottayam, Kerala.
- Rubber Research Institute works under the Rubber Board.
What are Key Facts About Rubber?
- About: Rubber is an elastic material derived from the latex or milky sap of certain plant species, primarily the rubber tree (Hevea Brasiliensis).
- This latex is mainly composed of polyisoprene, a polymer, along with various organic compounds.
- Rubber is a tropical tree, native to the Amazon rainforest.
- Production: India is the third largest producer, fourth largest consumer of natural rubber and fifth largest consumer of natural rubber and synthetic rubber together in the world.
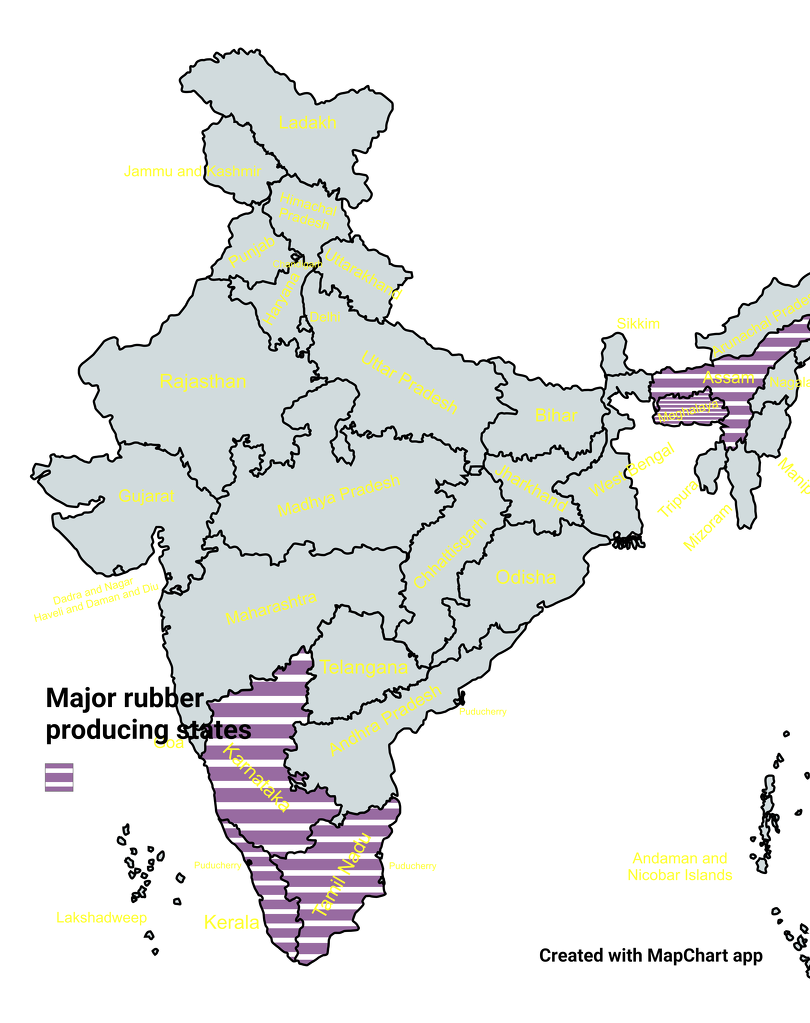
- Kerala (over 90%) is the largest rubber producer in India, followed by Tripura (about 9%).
- Other prominent states/UTs include Karnataka, Assam, Tamil Nadu, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Manipur, Goa, and the Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
- Required Climatic Conditions: It requires temperatures between 20°-35°C and rainfall over 200 cm annually.
- It grows in loamy or laterite soil, sloped or elevated land, requiring cheap, skilled labor for cultivation.
- Trade Scenario: In 2022-23, India exported 3,700 tonnes of Natural Rubber (NR), with the USA, Germany, UAE, UK, and Bangladesh as the largest markets.
- In 2022-23, India imported 5,28,677 tonnes of NR, mainly from Indonesia, Thailand, China, South Korea, and Japan.
What is National Rubber Policy (NRP) 2019?
- About: It is a policy initiative by the Ministry of Commerce & Industry to support production, processing, consumption, and exports.
- Objectives:
- Value Chain Development: Develop the entire rubber industry value chain from cultivation to manufacturing.
- Rubber Area Expansion: Increase natural rubber plantations in non-traditional regions without harming ecosystems.
- Productivity Enhancement: Improve rubber productivity through better agro management practices.
- Domestic Raw Material Supply: Ensure domestic production meets raw material demand.
- Quality Standards: Ensure processed NR meets international quality standards.
- Rubber Product Manufacturing: Strengthen the rubber manufacturing sector and promote exports.
- Policy Interventions:
- National Rubber Status: Recognize NR as an agricultural product to leverage existing policies for income enhancement.
- Production Goals: Achieve 2 million tonnes of NR by 2030 and expand planting areas.
- Value Chain Synchronization: Align activities in NR production, processing, and product manufacturing to boost domestic supply.
Government Initiatives for Promoting Production of Rubber:
- Sustainable & Inclusive Development of Natural Rubber Sector (SIDNRS)
- Rubber Plantation Development Scheme
- Rubber Group Planting Scheme
- 100% Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in Rubber Plantation
- National Rubber Policy 2019
What can be Done to Increase Rubber Production in India?
- Land Diversification: Encouraging farmers to diversify their land use by integrating rubber with other crops in mixed farming systems particularly in North-Eastern states having favorable climatic conditions.
- Scientific Farming: Promoting high-yielding varieties and advanced plantation techniques (such as high-density planting) can help increase production per hectare.
- Research: Increased investment in R&D to develop more disease-resistant, climate-resilient, and high-yielding rubber varieties can play a significant role in improving production.
- Efficient Tapping: Training rubber tappers in efficient methods, like lateral tapping and proper angles, can enhance latex quantity and quality, boosting production.
- Market Access: Expanding market access for Indian rubber and rubber-based products (like rubber-based tires and industrial goods) to global markets can incentivize farmers to produce more rubber.
Conclusion
India is advancing its rubber industry through innovative initiatives like the iSNR, INR Konnect, and mRube platforms, aligned with the National Rubber Policy 2019. These efforts aim to increase domestic production, enhance sustainability, and ensure global competitiveness while tackling challenges like compliance with EUDR and expanding market access.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Evaluate the role of the National Rubber Policy 2019 in strengthening India's rubber industry. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.Which one of the following groups of plants was domesticated in the ‘New World’ and introduced into the ‘Old World’? (2019)
(a) Tobacco, cocoa and rubber
(b) Tobacco, cotton and rubber
(c) Cotton, coffee and sugarcane
(d) Rubber, coffee and wheat
Ans: (a)
Q.Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the Lists: (2008)
| List-I | List-II |
| (Board) | (Headquarters) |
| A. Coffee Board | 1. Bengaluru |
| B. Rubber Board | 2. Guntur |
| C. Tea Board | 3. Kottayam |
| D. Tobacco Board | 4. Kolkata |
Code:
A B C D
(a) 2 4 3 1
(b) 1 3 4 2
(c) 2 3 4 1
(d) 1 4 3 2
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q.Why indentured labour was taken by the British from India to other colonies? Have they been able to preserve their cultural identity over there? (2018)




