Biodiversity & Environment
Amazon Rainforest
- 18 Nov 2022
- 6 min read
For Prelims: Amazon Rainforest, World Wildlife Fund
For Mains: Environment Pollution and Degradation, Conservation
Why in News?
According to a new report ‘Living Amazon Report’ 2022 by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), some 35% of the rainforest is either totally lost or highly degraded.
- The report was released at the 27th Conference of Parties (COP27) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change in Sharm El-Sheikh, Egypt.
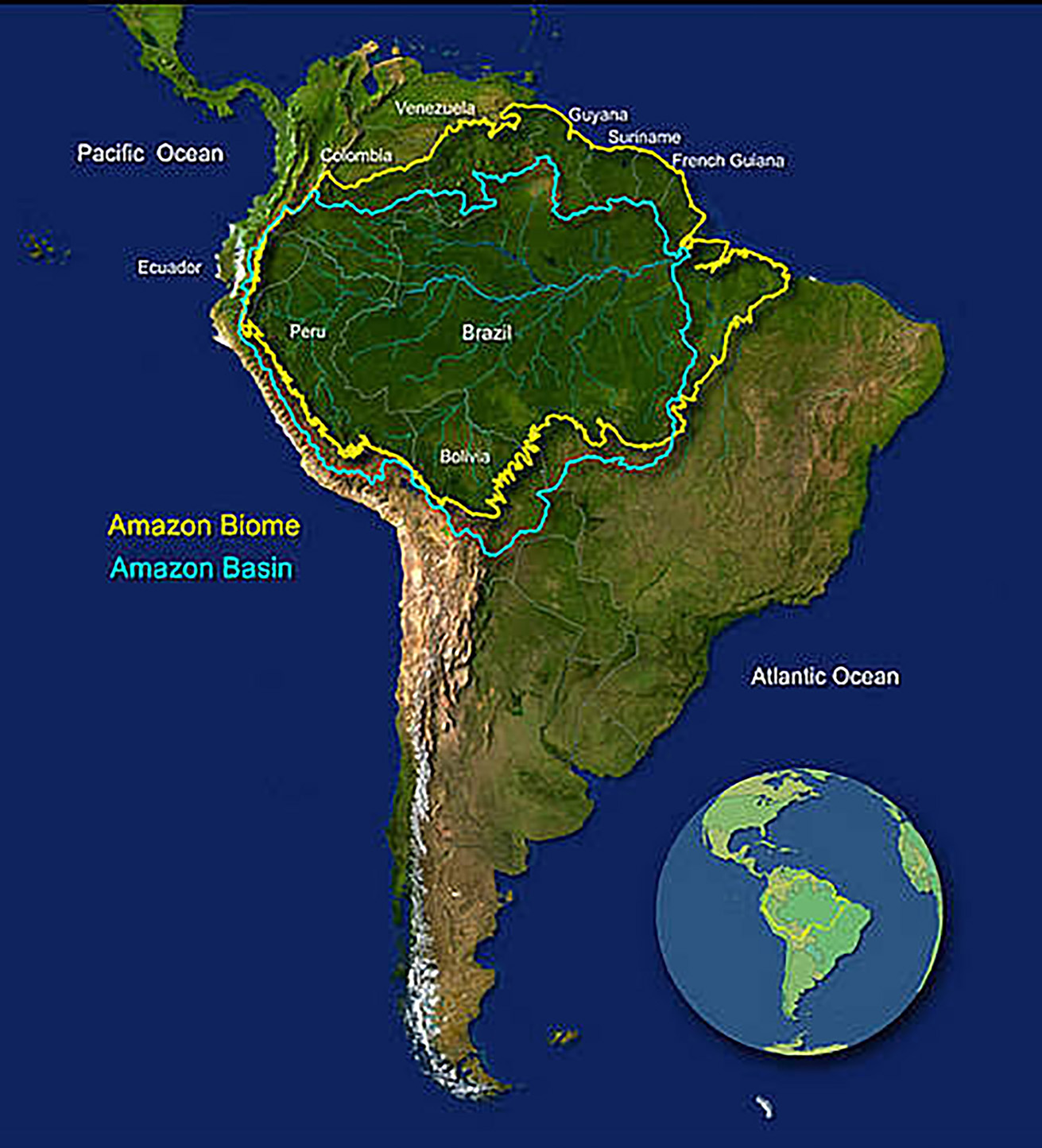
- The report outlined the current status of the Amazon biome and basin, summarised key pressures and drivers of change and outlined a conservation strategy.
What are the Highlights of the Report?
- Vast tracts of the Amazon rainforest, which serve as carbon sinks and the planet’s lungs, are in crisis.
- Some 35% of the rainforest is either totally lost or highly degraded, while another 18% have been converted for other purposes.
- Amazon forests are threatened due to deforestation, fires and degradation.
- Surface water has been lost and rivers are increasingly disconnected and polluted.
- This immense pressure will irreversibly damage the Amazon and the planet in general very shortly.
- Economic activities, most notably extensive cattle ranching and agriculture, illegal activities and poorly planned infrastructure, threaten the region and cause deforestation and degradation throughout the biome, with many areas severely affected.
- Nearly 600 infrastructure projects are in operation along rivers in the Amazon.
- Some 20 planned road projects, 400 operating or planned dams and numerous mining projects continue to dump chemicals such as mercury into the rivers.
What are the Suggestions?
- The protection of the Amazon requires a combination of strategies and approaches that combine conservation requirements with the developmental needs of the countries that comprise it.
- Strategies for effective, integrated landscape management include:
- Conversion-free landscapes
- Sustainably managed forests
- Legal trade
- Ensuring the rights of indigenous peoples, local communities, women and young people.
- These strategies are intended to complement well-managed conservation areas and indigenous territories to form a network of well-conserved landscapes.
- Cross-cutting strategies in three key areas — policies, knowledge generation and communications — are also needed for the conservation and sustainable management of the Amazon biome, its forests and rivers.
- The biome urgently requires effective policies, research and greater awareness of its current status.
What are the Amazon Rainforests?
- These are large tropical rainforests occupying the drainage basin of the Amazon River and its tributaries in northern South America and covering an area of 6,000,000 square km.
- Tropical forests are closed-canopy forests growing within 28 degrees north or south of the equator.
- They are very wet places, receiving more than 200 cm rainfall per year, either seasonally or throughout the year.
- Temperatures are uniformly high - between 20°C and 35°C.
- Such forests are found in Asia, Australia, Africa, South America, Central America, Mexico and on many of the Pacific Islands.
- Comprising about 40% of Brazil’s total area, it is bounded by the Guiana Highlands to the north, the Andes Mountains to the west, the Brazilian central plateau to the south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the east.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched? (2013)
| Geographical Feature | Region | |
| (a) | Abyssinian Plateau | Arabia |
| (b) | Atlas Mountains | North-Western Africa |
| (c) | Guiana Highlands | South-Western Africa |
| (d) | Okavango Basin | Patagonia |
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Abyssinian Plateau is a plateau in Ethiopia (Africa) located at an elevation of 1388 metres above sea level.
- Atlas Mountains are a series of mountain ranges in northwestern Africa, running generally southwest to northeast. It forms the geologic backbone of the countries of the Maghreb (the western region of the Arab world) – Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia.
- Guiana Highlands is the region in northern South America where Brazil, Guyana, and Venezuela meet at Mount Roraima. It is bounded by the Orinoco and Amazon river basins, and by the coastal lowlands of the Guianas.
- The Okavango river basin is the fourth-longest river system in southern Africa. It is an endorheic basin (watershed which does not drain to the sea) found in southwestern Africa.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.