Astronomical Grand Cycles | 20 Mar 2024
Why in News?
A recent study published in the journal Nature Communications has found evidence of erosion in the deep sea linking astronomical grand cycles with the orbits of Earth and Mars, and global warming or cooling.
What are the Key Findings of the Study?
- Astronomical Grand Cycles:
- Geological sedimentary evidence in the deep sea has revealed a newly discovered 2.4-million-year cycle, known as "astronomical grand cycles," linked with the orbits of Earth and Mars.
- The cycle influences global warming or cooling trends and has been detected through erosion patterns in deep-sea sedimentary data.
- Connection Between Mars' Orbit and Earth's Climate:
- The gravity fields of planets in the solar system interfere with each other, leading to changes in their orbital eccentricity (how circular their orbits are).
- The interaction between Earth and Mars' orbits causes variations in the amount of solar radiation received by Earth, resulting in cycles of warming and cooling over 2.4 million years.
- The gravity fields of planets in the solar system interfere with each other, leading to changes in their orbital eccentricity (how circular their orbits are).
- Impact on Climate and Ocean Circulation:
- The vigorous deep-sea circulation driven by eddies (a circular current of water) during warmer cycles could potentially prevent ocean stagnation, even if the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) slows or stops functioning.
- AMOC is a large system of ocean currents that carry warm water from the tropics northwards into the North Atlantic.
- Deep ocean eddies could help provide oxygen to the deep ocean and draw carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into the ocean in a warmer world.
- Intense deep-ocean eddies, described as giant whirlpools, play a vital role in ocean circulation dynamics, these sit at depths of 3,000 to 6,500 meters and where sunlight doesn’t penetrate.
- These eddies contribute to seafloor erosion and the formation of large sediment accumulations known as contourites, resembling snowdrifts in their structure.
- The vigorous deep-sea circulation driven by eddies (a circular current of water) during warmer cycles could potentially prevent ocean stagnation, even if the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) slows or stops functioning.
- Future Research Directions:
- The team plans to gather more data showcasing cycles driven by Earth-Mars interaction, further exploring the dynamics of Earth's climate fluctuations over millions of years.
What are Astronomical Cycles?
- Astronomical cycles refer to periodic variations in the Earth's orbit and orientation towards the Sun that impact the amount of solar radiation received by our planet over long periods.
- These cycles are caused by the gravitational forces between the Earth, Sun, and other planets in the solar system.
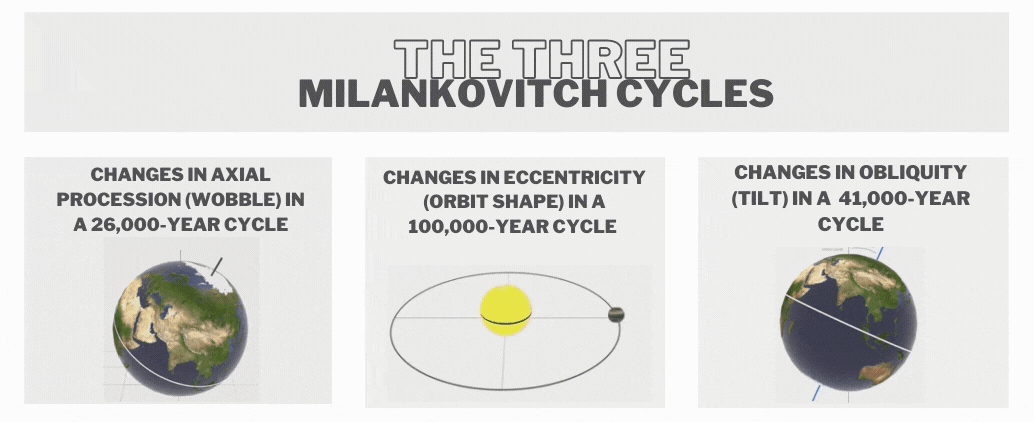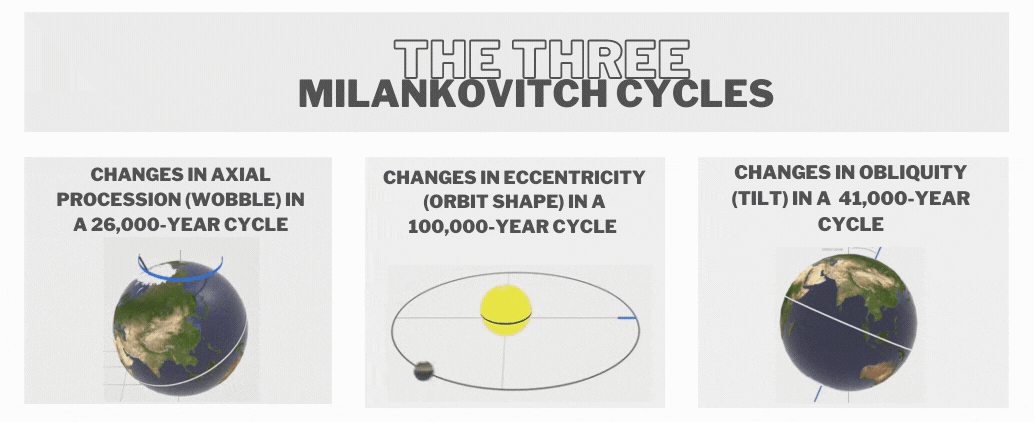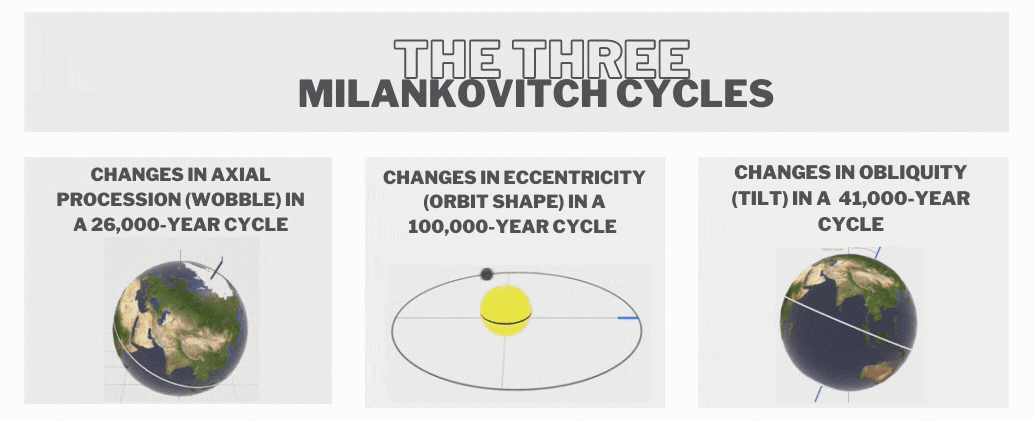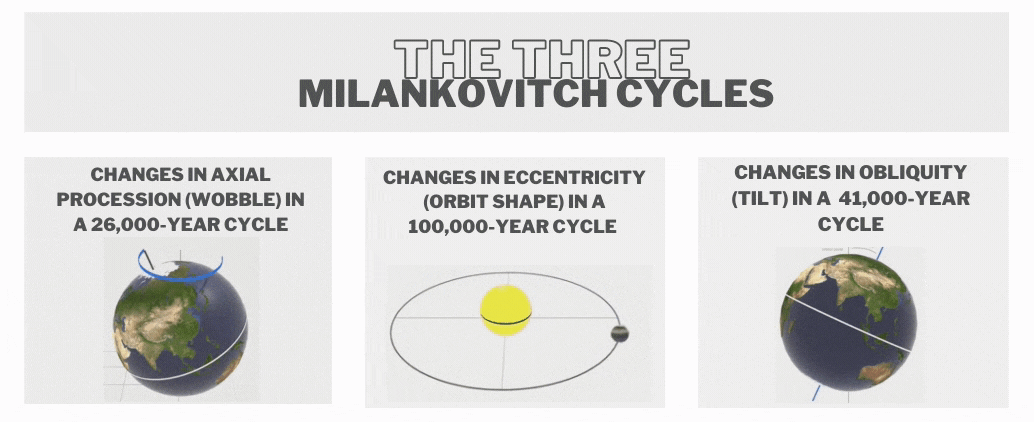
- These cycles were first theorised by Serbian scientist Milutin Milankovitch in the 1920s to explain the cyclical patterns of ice ages on Earth also called Milankovitch cycles, or Milankovitch oscillations.
- Some key astronomical cycles include
- Eccentricity (100,000 years) - Changes in the elliptical shape of Earth's orbit around the Sun.
- Obliquity (41,000 years) - Variations in the tilt of Earth's axis relative to its orbital plane.
- Precession (23,000 years) - The shifting orientation of Earth's axis over time.
- Some key astronomical cycles include
What are the Other Astronomical Influences on Earth's Climate?
- Sunspot Activity:
- Sunspots are dark and cooler patches on the sun that increase and decrease in a cyclical manner.
- The number and intensity of sunspots increase and decrease in a cyclical pattern, typically over an 11-year solar cycle.
- According to some meteorologists, higher sunspot activity and numbers are associated with:
- Cooler and wetter weather patterns on Earth and increased storminess and cloud cover.
- Conversely, periods with fewer sunspots are linked to Warmer and drier conditions globally.
- However, these correlations between sunspot activity and specific weather patterns are not consistently supported by statistically significant evidence.
- Sunspots are dark and cooler patches on the sun that increase and decrease in a cyclical manner.
- Galactic Cosmic Rays:
- Some studies suggest that increased cosmic ray flux from our galaxy could influence cloud formation on Earth, potentially leading to cooling effects.
- However, the magnitude of this effect and the mechanisms involved are still subjects of ongoing research.
- Some studies suggest that increased cosmic ray flux from our galaxy could influence cloud formation on Earth, potentially leading to cooling effects.
- Asteroid/Comet Impacts:
- Major asteroid or comet impacts on Earth, while extremely rare, can inject massive amounts of dust and gasses into the atmosphere, leading to temporary cooling periods.
- The Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction (caused extinction of dinosaurs) around 66 million years ago is thought to have been caused in part by an asteroid impact and associated climate changes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Variations in the length of daytime and nighttime from season to season are due to (2013)
(a) the earth’s rotation on its axis
(b) the earth’s revolution around the sun in an elliptical manner
(c) the latitudinal position of the place
(d) revolution of the earth on a tilted axis
Ans: (d)