Rapid Fire
Ancient Buddhist Sites in Afghanistan
- 25 Apr 2025
- 2 min read
The Taliban, once infamous for destroying historical artifacts like the Buddhas of Bamiyan in 2001, now claim to support the preservation of Afghanistan's ancient heritage sites.
Key Buddhist Sites
- Mes Aynak: Mes Aynak (in Logar province) is a major Buddhist archaeological site discovered in 1963. Occupied from the 1st century BC to the 10th century AD, it includes monasteries, stupas, a Zoroastrian fire temple, a mint, copper smelting workshops, and over 1,000 Buddhist statues, frescoes, and coins.
- Its art reflects Hellenistic, Indian, Persian, and Chinese influences. Situated on the Silk Road, it played a key role in spreading Buddhism from India to China.
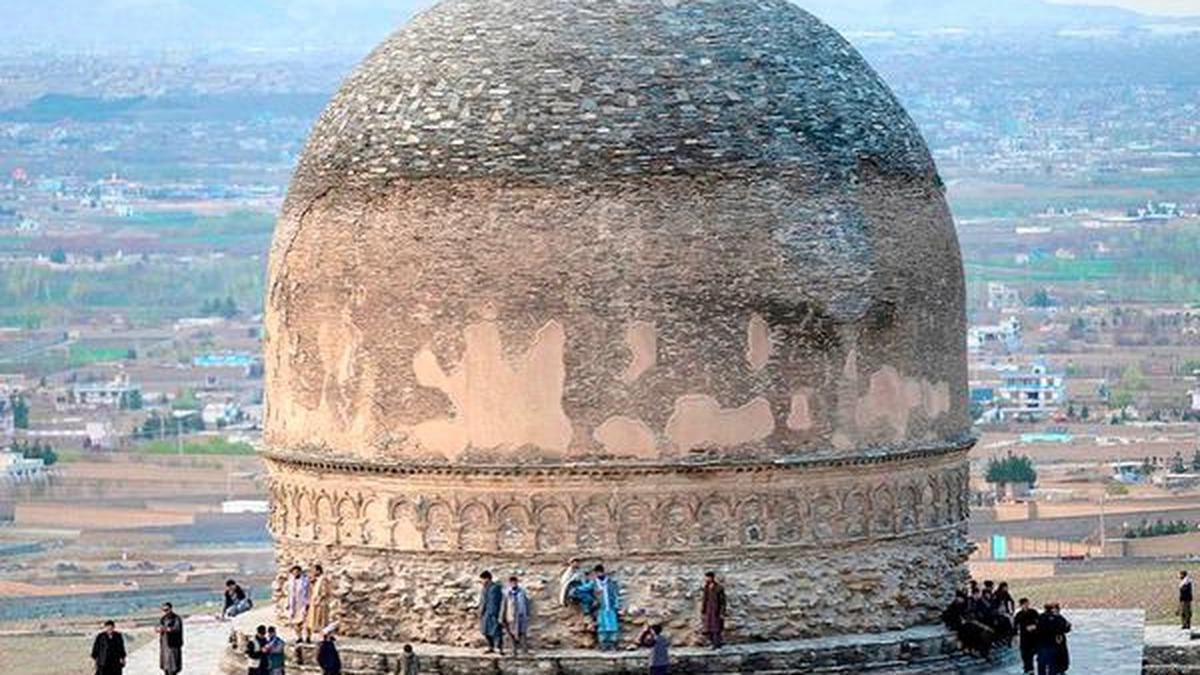
- Shewaki Stupa: The Shewaki Stupa of Kabul is over 20 meters wide and is a major Buddhist-era monument from the 1st to 3rd centuries AD.
- It reflects both Kushan and Hellenistic architectural styles (influenced by Greek culture) and was built with fieldstones, mud, and plaster.
- The stupa, once a key religious and caravan site, was first excavated in 1820 by archaeologists.
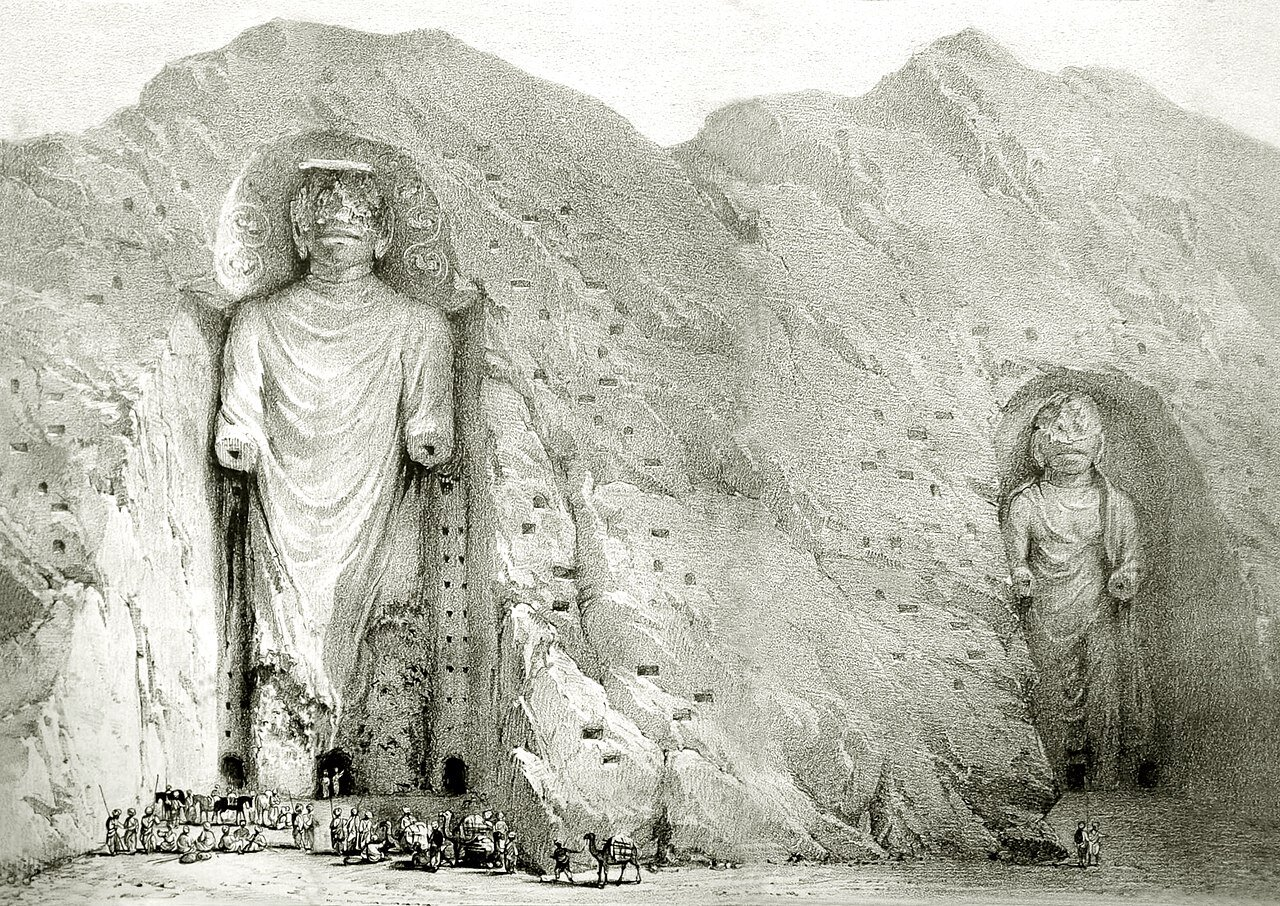
- Bamiyan Buddhas: The 6th century Bamiyan Buddhas were two massive statues, carved into sandstone cliffs in central Afghanistan.
- They belong to Gandharan Buddhist art and reflected Buddhism’s cultural influence from the 1st to 13th centuries.
- Kushan-era Inscriptions: In Laghman Province, archaeologists discovered 2,000-year-old Kushan-era rock niches, Brahmi inscriptions, and winemaking tools, highlighting the empire's vast reach from the Gobi Desert to the Ganga Valley.
| Read More: Bamiyan Buddhas , India’s Engagement with Taliban |