19th East Asia Summit (EAS) | 15 Oct 2024
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister of India attended the 19th East Asia Summit (EAS) in Vientiane, Lao PDR.
What are the Key Highlights of the Visit?
- PM advocated for a development-oriented Indo-Pacific approach over expansionism.
- Reiterated support for Nalanda University and invited EAS members to the Heads of Higher Education Conclave.
- Addressed global challenges like terrorism, cyber, and maritime threats, and stressed dialogue-based conflict resolution.
- PM conveyed his wishes to Malaysia on presiding as the new Chair of ASEAN and expressed India’s full support to it. The present chair of ASEAN is Lao PDR.
What is the East Asia Summit (EAS)?
- Establishment: The EAS was established in 2005 as an Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)-led initiative.
- The EAS is the only leader-led forum in the Indo-Pacific that brings together all key partners to discuss political, security and economic issues of strategic importance.
- The idea of an East Asia Grouping was first proposed by then Malaysian Prime Minister Mahathir Mohamad in 1991.
- The first summit was held in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia on 14th December 2005.
- Objectives: The EAS operates on the principles of openness, inclusiveness, respect for international law, ASEAN centrality, and ASEAN’s role as the driving force.
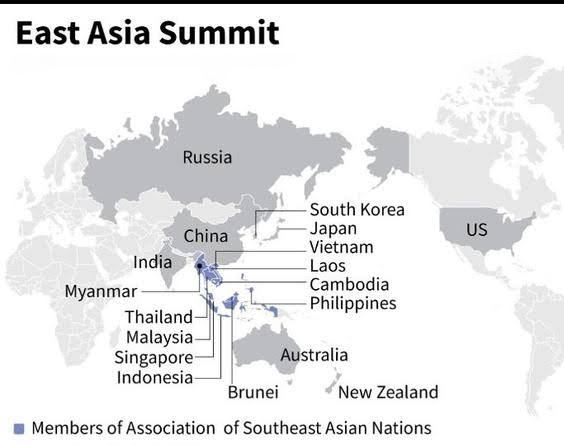
- Members: The EAS is a key forum for strategic dialogue in the Indo-Pacific region, involving 18 countries, including ASEAN members.
- The EAS comprises 18 members, the 10 ASEAN countries (Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam) and eight dialogue partners (Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Russia and the United States).
- Importance:
- Economically: In 2023, EAS members represented approximately 53% of the world's population and accounted for approximately 60% of global GDP.
- India is ASEAN’s seventh-largest trading partner, while ASEAN is India’s fourth-largest partner. In the last ten years India-ASEAN trade had doubled to over USD 130 billion.
- Strategically: Connectivity projects in Southeast Asian countries, both infrastructure and digital, are key to India’s Act East Policy, with major initiatives like the India-Myanmar-Thailand Highway and Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport boosting regional links and coonctivity with Eas Asian Nations.
- Besides, India also engages in capacity-building through the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) programme with Southeast Asian countries like Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam.
- Culturally: Buddhism, a major cultural and religious tradition that connects many Southeast Asian and East Asian nations, originated in India.
- Restoration of Nalanda University and support for the International Buddhist Confederation, enhance India's spiritual and cultural ties with Myanmar, Thailand, and Cambodia, showcasing its commitment to promoting Buddhist traditions.
- Economically: In 2023, EAS members represented approximately 53% of the world's population and accounted for approximately 60% of global GDP.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. India is a member of which among the following? (2015)
- Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation
- Association of South-East Asian Nations
- East Asia Summit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) India is a member of none of them
Ans: (b)
Q. Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(b) 3, 4, 5 and 6
(c) 1, 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2, 3, 4 and 6
Ans: (c)
Q. The term ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership’ often appears in the news in the context of the affairs of a group of countries known as (2016)
(a) G20
(b) ASEAN
(c) SCO
(d) SAARC
Ans: (b)