Indian Economy
Revolutionizing E-Commerce Landscape
This editorial is based on “Watch out, AI and GenAI are transforming e-commerce from the ground up” which was published in The Livemint on 09/05/2024. The article discusses the transformative impact of Generative AI on the e-commerce industry landscape.
For Prelims: E-commerce, Generative AI, Competition Commission of India , Government e-Marketplace, Open Network for Digital Commerce, National E-Commerce Policy, Consumer Protection (E-commerce) Rules 2020, Gross Merchandise Value, FDI in E-commerce.
For Mains: Generative AI in E-Commerce Sector, Major Issues Related to E-Commerce in India.
E-commerce has redefined the shopping experience, allowing consumers to browse and purchase products from the comfort of their homes or on-the-go via mobile devices. This multi-billion dollar industry has witnessed exponential growth, fueled by convenience, wide product assortments, and competitive pricing.
The rise of generative AI technologies like ChatGPT, DALL-E, and Midjourney is rapidly transforming the ecommerce landscape.Generative AI has been shown to drive higher conversion rates and revenue growth of 3-15% for companies investing in the technology. However, Generative AI models can sometimes "hallucinate" and generate incorrect or fabricated information without human oversight.
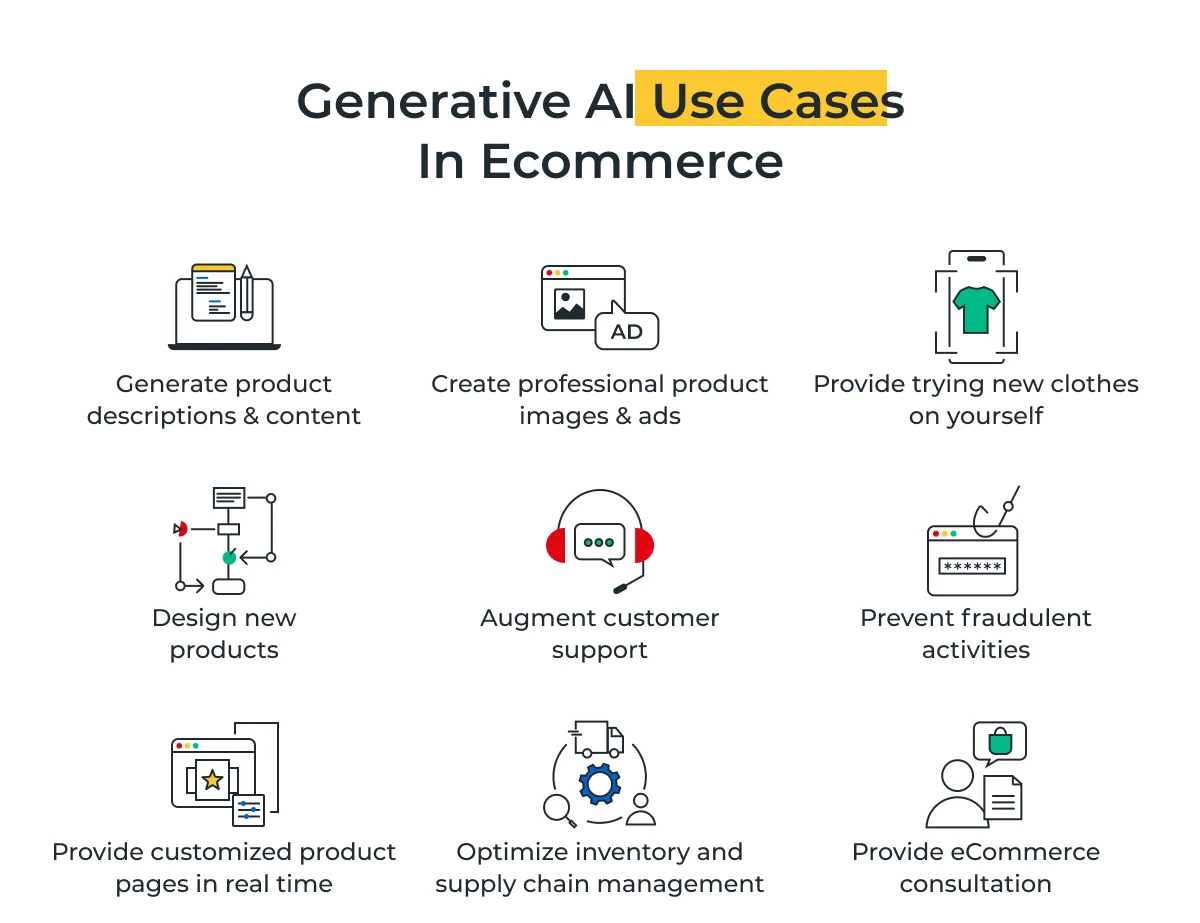
How Generative AI is Revolutionizing the E-Commerce Sector?
- Personalized Product Recommendations: Generative AI can analyze customer data and browsing patterns to provide highly personalized product recommendations.
- New Epsilon research indicates 80% of consumers are more likely to make a purchase when brands offer personalized experiences,
- Automated Product Descriptions and Marketing Content: AI can automatically generate product descriptions, ads, social media posts and more, saving time while maintaining quality.
- 55% of marketers using generative AI for content creation reported improved performance, according to a World Federation of Advertisers study.
- Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimization: By training on historical data, generative AI models can forecast demand patterns and seasonality more accurately than traditional methods.
- This allows ecommerce businesses to optimize inventory levels, reducing costs and preventing stockouts.
- Increased Conversion Rates and Revenue: Businesses investing in generative AI have experienced 3-15% revenue increases and a 10-20% improvement in sales return on an investment, according to McKinsey.
Note: Generative AI is a subset of artificial intelligence that employs algorithms to generate new and unique data or content, mimicking patterns and characteristics learned from analyzing large datasets.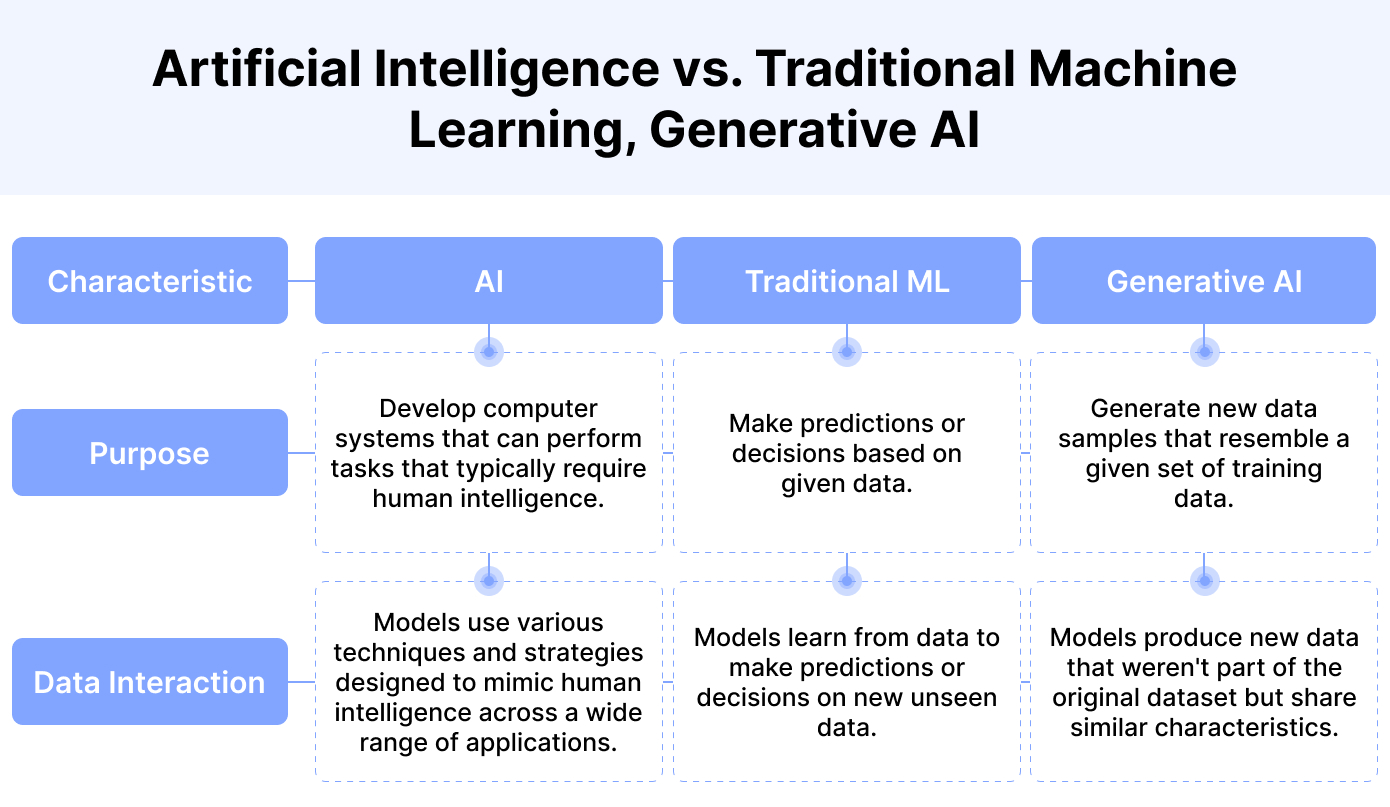
(ML- Machine Learning)
What is the Status of the E-Commerce Sector in India?
- About: The Indian e-commerce industry is projected to reach USD 300 billion by 2030, experiencing significant growth.
- In FY23, the Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) of e-commerce reached USD 60 billion, increasing 22% over the previous year.
- After China and the US, India had the third-largest online shopper base of 150 million in FY21 and is expected to be 350 million by FY26.
- Factors Driving E-Commerce Growth in India:
- Increasing Internet Penetration: With over 821 million users, India was the second-largest internet market in the world. This growing connectivity is a major driver for e-commerce adoption.
- Increasing Footprint in Tier 2 and Tier 3 Cities: . The e-commerce trend is gaining major popularity even in tier-2 and tier- 3 cities as they now make up nearly half of all shoppers and contribute three of every five orders for leading e-retail platforms.
- The e-commerce market’s share of Tier-3 cities grew from 34.2% in 2021 to 41.5% in 2022.
- Rising Middle Class and Disposable Incomes: The size of India’s middle class will nearly double to 61% of its total population by 2047, from 31% in 2020-21 (PRICE Report 2023).
- With increasing disposable incomes, more consumers are shopping online for convenience and access to brands.
- Favorable Demographics: India has a median age of 28 years according to World Population Prospects (WPP), making it one of the youngest populations globally.
- This demographic dividend and tech-savvy population is a significant boost for e-commerce adoption and growth.
- Growth of D2C Brands and Social Commerce: The rise of direct-to-consumer (D2C) brands like boAt, Mamaearth, and Licious has disrupted traditional retail models.
- Social commerce platforms like Meesho are also gaining traction.
- Fintech Solutions for Easier Payments: Digital payment solutions like UPI, mobile wallets, and buy-now-pay-later options have made online transactions more accessible and convenient for Indian consumers.
- The total volume surged to a staggering 65.7 billion transactions in 2023, according to India Digital Payments Report (H2 2023).
- Logistics and Supply Chain Improvements: Investments in logistics infrastructure, warehousing, and last-mile delivery networks by players like Delhivery, Ecom Express, and Xpress Bees have supported e-commerce growth across India.
What are the Major Issues Related to E-Commerce in India?
- Logistics and Supply Chain Inefficiencies: While improving, India's logistics infrastructure still lags, leading to higher costs and delivery delays, especially in remote areas.
- Economic Survey 2022-23 stated that logistics costs in India have been in the range of 14-18% of GDP against the global benchmark of 8%.
- Social and Environmental Impact Concerns: Issues like excessive packaging waste, unethical labor practices in the supply chain, and unsustainable business models raise concerns about the broader ecological and social impact.
- In May 2023, Swiggy delivery partners went on Strike in Chennai, demanding better pay and working conditions.
- Antitrust and Anti-Competitive Practices: Allegations of anti-competitive practices like deep discounting, preferential treatment, and misuse of data by large e-commerce firms threaten a level playing field.
- Example: In 2021, the Competition Commission of India (CCI) imposed a ₹202 crore fine on Amazon for not fully disclosing the Future Group entity deal's scope and purpose.
- Counterfeiting and Piracy Concerns: Proliferation of counterfeit and pirated products on e-commerce platforms not only impacts sales of genuine brands but also endangers consumer safety and trust in the ecosystem.
- Recently, the Crime Branch of Mumbai, seized counterfeit goods worth ₹55,000 being sold as "WoW" products.
- Human Resource Challenges: The rapid growth has created a demand-supply gap for skilled tech, supply chain, and logistics professionals.
What are the Major Government Initiatives Related to E-Commerce?
- Government e-Marketplace (GeM) Portal: Launched in August, 2016, by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry to create an inclusive, efficient, and transparent platform for buyers and sellers to conduct public procurement activities.
- In FY23, procurement crossed Rs. 2 lakh crore.
- Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC): It is an online network launched by the Government of India in 2022, aims to provide equal opportunities to MSMEs to thrive in digital commerce and democratize e-commerce.
- National E-Commerce Policy: The Indian government is poised to unveil a national e-commerce policy, aiming to foster sector growth and boost exports.
- Initially proposed in 2018, a draft of the policy was released in 2019.
- Consumer Protection (E-commerce) Rules 2020: Directed e-commerce companies to display country of origin alongside product listings.
- It also mandated companies to reveal parameters determining product listings on their platforms.
- FDI in E-commerce: Limit of FDI in the E-commerce marketplace model hiked to up to 100% (in B2B models)
- Equalisation Levy Rules 2016 (Amended in October 2020): The equalisation levy aims to ensure a fair share of digital economy tax and avoid double taxation.
- Foreign companies operating e-commerce platforms in India mandated to have Permanent Account Numbers (PAN)
- A 2% tax imposed in FY21 budget on sale of goods or delivery of services through a non-resident e-commerce operator.
What Measures can be Adopted to Revamp the E-Commerce Landscape in India?
- Develop Logistics Parks and Multimodal Hubs: Incentivize the creation of state-of-the-art logistics parks and multimodal logistics hubs through public-private partnerships, leveraging innovative financing models.
- These hubs would integrate different modes of transportation (road, rail, air, and waterways) and provide modern warehousing, packaging, and distribution facilities, streamlining the entire supply chain.
- Foster Rural E-commerce Logistics Startups: Encourage and support the growth of rural e-commerce logistics startups by providing them with access to technology, funding, mentorship, and training.
- These startups could leverage local knowledge and resources to bridge the last-mile delivery gap in remote areas, creating employment opportunities and boosting rural entrepreneurship.
- Implement "Logistics Reverse" and Circular Economy Models: Mandating the use of sustainable packaging materials and promoting the concept of "Logistics Reverse," where e-commerce platforms incentivize customers to return packaging materials for recycling or reuse.
- Additionally, encouraging the adoption of circular economy principles, facilitating the resale, refurbishment, or recycling of products to reduce waste and promote sustainable consumption.
- Establish a Dedicated E-commerce Regulatory Authority: Setting up a dedicated e-commerce regulatory authority or a specialized division within the Competition Commission of India to proactively monitor and address anti-competitive practices, data misuse, and unfair business practices in the e-commerce sector.
- This authority could also oversee the implementation of "Fairness by Design" principles in e-commerce platforms' algorithms and policies.
- Implement Advanced Authentication and Traceability Technologies: Mandating the use of advanced product authentication technologies like RFID tags, QR codes, and blockchain-based traceability systems to combat counterfeiting and ensure product authenticity.
- Collaborate with industry associations and law enforcement agencies to establish a centralized reporting mechanism and a dedicated task force to tackle the sale of counterfeit goods on e-commerce platforms.
- Encourage Gig Talent Pools: Encouraging the development of "Gig Talent Pools," where e-commerce companies can access a curated network of skilled freelancers and independent contractors for short-term or project-based engagements.
- Regulating Generative AI in E-commerce: To maintain competition and ethical practices, regulatory frameworks must mandate transparency in AI-generated content and algorithms.
- E-commerce companies should be required to disclose AI usage and adhere to ethical standards.
- Regular audits and compliance checks will ensure fairness and accountability.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Examine the current state of India's e-commerce industry, highlighting key policy initiatives, challenges, and the sector's impact on the economy. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:
Q. With reference to foreign-owned e-commerce firms operating in India, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2022)
- They can sell their own goods in addition to offering their platforms as market-places.
- The degree to which they can own big sellers on their platforms is limited.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b)2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)