BRICS Expansion: Challenging Western Dominance
This editorial is based on The implications of the expansion of BRICS which was published in The Hindu on 06/09/2023. It talks about the recent expansion of the BRICS along with their efforts to promote cooperation and build institutions outside Western control.
For Prelims: BRICS, New Development Bank, BRICS Contingent Reserve Arrangement
For Mains: Geo-strategic Values of the New BRICS Members, Criticisms Against BRICS, Regional Developments Shaping BRICS Membership Expansion
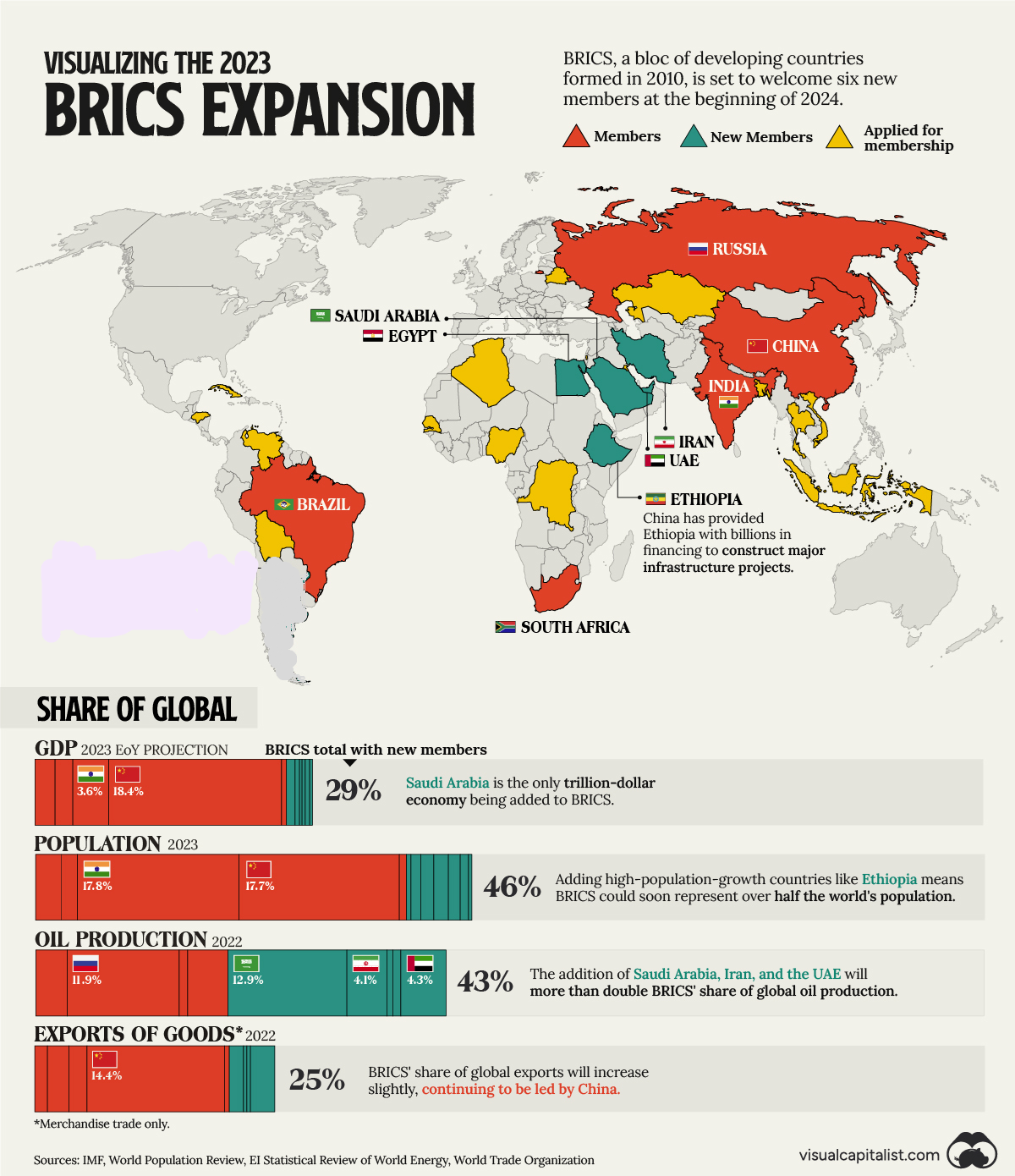
Recently, during the 15th BRICS summit held in Johannesburg, it was announced that the existing five-member BRICS grouping, consisting of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, had taken a significant step by inviting six new countries to join. These new invitees are Iran, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) from West Asia; Egypt and Ethiopia from Africa; and Argentina from Latin America.
BRICS is shaping the future of international relations by advocating for multipolarity, asserting strategic autonomy, and fostering economic cooperation among its diverse members. Amidst criticism from Western commentators, BRICS is carving out a unique path in global politics, making its recent summit a pivotal moment in modern history.
What are the Objectives of BRICS?
- Rejection of Emerging Global Binary Divide: India and other BRICS members reject the idea of an emerging global binary divide, which suggests a world characterised by two opposing and dominant powers, often likened to a new Cold War. They do not agree with this perspective and consider it short-sighted.
- Assertion of Strategic Autonomy: BRICS members, including India, are emphasizing their commitment to asserting their strategic autonomy. This implies that they want to make independent decisions and policies on the global stage, rather than being aligned with any particular superpower or bloc.
- Multipolar World Order: BRICS countries are advocating for a multipolar world order. They envision a world where power and influence are distributed among multiple major players rather than being concentrated in the hands of a few dominant nations.
- Demand for Voice and Respect for Interests: BRICS member nations are demanding that their voices be heard and their interests respected in international affairs. This suggests a desire for a more equitable and inclusive global governance system where the concerns of emerging economies are taken into account.
What are the Views of BRICS Towards West-led Organisations?
- Unequal Voting Power: One of the primary concerns of BRICS nations is the unequal distribution of voting power within institutions like the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank.
- These organisations give more influence to Western countries, particularly the United States and European nations, based on their financial contributions. BRICS members argue that this inequity diminishes their ability to shape policies and decision-making processes.
- Lack of Representation: BRICS nations have argued that the leadership and decision-making bodies of these institutions do not adequately represent the diversity of the global economy. They believe that these institutions should better reflect the economic weight and contributions of emerging economies like themselves.
What are the Criticisms Against BRICS?
- Lack of Shared Vision: Western commentators have criticised BRICS for not having a clear and cohesive shared vision. This implies that the five-member countries may not have a unified and consistent approach to global issues or may not be working towards common objectives.
- Being a "Talk-Shop": BRICS is accused of being primarily a forum for discussion and dialogue rather than an organisation that takes concrete actions or achieves meaningful outcomes.
- In other words, it is seen as a platform where leaders from these countries engage in discussions but do not produce tangible results or solutions.
- No Worthwhile Achievements: Critics argue that BRICS has not produced any substantial or significant achievements that would justify its existence as a bloc. They may contend that the group's activities have not had a meaningful impact on global affairs or have failed to address key challenges effectively.
How BRICS is Challenging this West-led World Order?
- Ongoing and Comprehensive Nature of BRICS Interactions: Since 2009, the BRICS member countries have been holding annual summit meetings. Additionally, the BRICS framework is supported by various ministerial and expert conclaves, implying that it's not just a summit but also a platform for sustained engagement.
- Alternative Institutions: In response to their dissatisfaction with Western-dominated institutions, BRICS nations have taken steps to create alternative financial institutions. The most notable example is the establishment of the New Development Bank (NDB), also known as the BRICS Bank and Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA).
- The NDB aims to provide financing for infrastructure and sustainable development projects in member countries and other emerging economies. This initiative is seen as a way to reduce dependency on Western institutions.
- CRA aims to assist member countries facing short-term balance-of-payments pressures.
- Use of Local Currencies: BRICS members have agreed to encourage the use of local currencies in internal trade and financial transactions among themselves and with other trading partners.
- This demonstrates a desire to reduce reliance on major global currencies like the US dollar and promote the use of their own currencies in international transactions.
- Advocacy for Reform: BRICS nations are advocating for significant reforms in the existing international order. They seek a more representative and fairer global system that takes into account the interests and voices of emerging economies.
- This reform agenda includes calls for changes in international financial institutions and global governance structures.
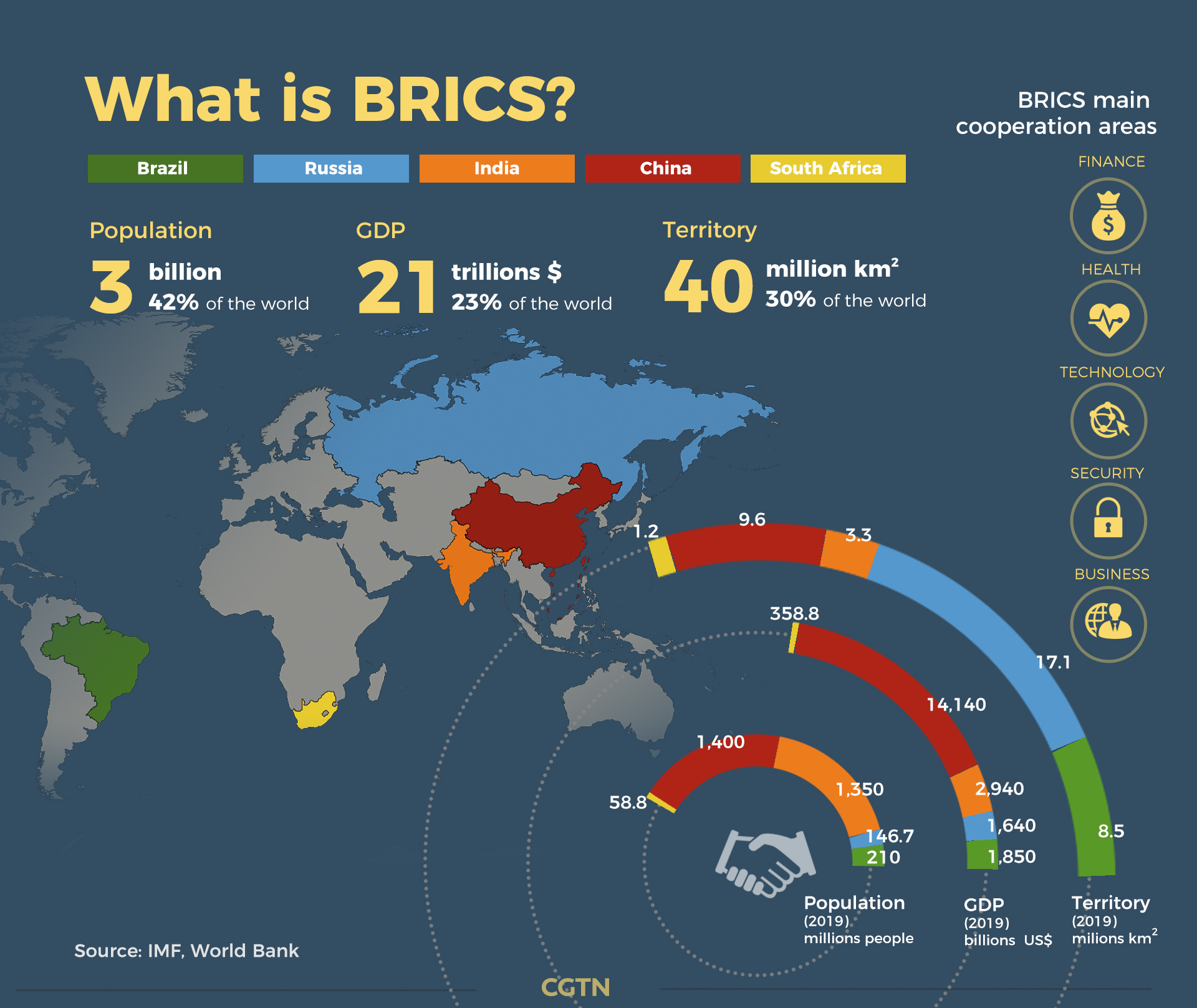
- Increased Economic Influence The BRICS grouping collectively possesses considerable economic power. The expansion of BRICS membership has further boosted its influence. The group represents a significant portion of the world's population, Gross Domestic Product (GDP), global trade, and energy production.
- Energy Sector Impact: The passage highlights the significant impact of BRICS expansion on the energy sector. With the inclusion of new members, BRICS countries collectively produce a substantial share of the world's oil, making them a crucial player in global energy markets. This underscores their potential to shape energy policies and markets.
What are the Geo-strategic Values of the New BRICS Members?
- Energy Resources: The inclusion of new BRICS members from West Asia, such as Saudi Arabia and Iran, is significant due to their substantial energy resources. Saudi Arabia is a major oil producer, and a significant portion of its oil production goes to BRICS countries like China and India.
- Iran, despite facing sanctions, has increased its oil production and exports, primarily directed toward China. This highlights the importance of energy cooperation and trade among BRICS members.
- Diversification of Energy Suppliers: Russia has been a significant supplier of oil to China and India. With the inclusion of Brazil as a new member, Russia is exploring additional markets for its energy exports, which demonstrates the potential for diversified energy sources within BRICS.
- Strategic Geographical Presence: Egypt and Ethiopia are strategically located in the Horn of Africa and the Red Sea region, which is of immense geostrategic importance due to its proximity to critical maritime trade routes. Their presence adds to the geopolitical significance of BRICS in this region.
- Latin American Economic Influence: Argentina, as one of the largest economies in Latin America, would brings economic influence to the BRICS grouping. Latin America has historically been a region of interest for global powers, and Argentina's inclusion would further strengthen BRICS' presence in this part of the world.
- Update: Argentina has formally withdrawn from the expansion of the BRICS bloc.
What are the Regional Developments Shaping BRICS Membership Expansion?
- Independent Foreign Policy: Both Saudi Arabia and the UAE are noted for pursuing independent foreign policy paths, particularly since 2020. This implies that they have sought to assert their sovereignty and make foreign policy decisions that align with their own national interests rather than being heavily influenced by external powers, such as the United States.
- Ending the Qatar Blockade: Saudi Arabia's decision to end the blockade on Qatar in January 2021 is also considered a significant step in this regard. As a result, there was a significant change in the Gulf region, as it signaled a willingness to resolve regional disputes and improve relations with neighboring countries.
- Iran-UAE Relations: UAE has normalised ties with Iran and aims to expand its maritime presence in the Gulf, Gulf of Aden, Red Sea, and Horn of Africa.
- Iran's inclusion in BRICS offers opportunities for regional economic cooperation and the revival of connectivity projects through Chabahar port, which India is involved in.
Conclusion
The expansion of the BRICS group has brought considerable geo-strategic value to the grouping. The BRICS through its current summit has asserted that their "strategic partnership" will be directed at achieving "a more representative, fairer international order". The recent expansion of BRICS's membership has shaped a grouping that is aligned in terms of global perceptions and interests and collectively provides considerable economic clout to the enlarged conclave. The group's efforts to assert their strategic autonomy in a multipolar world order have been described as a "turning point in modern history".
|
Dishti Mains Questions: Discuss the evolving role of BRICS and its expansion in shaping international relations and its strategies to challenge the existing global order. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
- New Development Bank has been set up by APEC.
- The headquarters of the New Development Bank is in Shanghai.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Q. The ‘Fortaleza Declaration’, recently in the news, is related to the affairs of (2015)
(a) ASEAN
(b) BRICS
(c) OECD
(d) WTO
Ans: (b)
Q. With reference to a grouping of countries known as BRICS, consider the following statements: (2014)
- The First Summit of BRICS was held in Rio de Janeiro in 2009.
- South Africa was the last to join the BRICS grouping.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)