India and Greece Relations
For Prelims: India and Greece Strategic Partnership, Tomb of Unknown Soldier, The Grand Cross of the Order of Honour
For Mains: Evolution of India-Greece relations, key areas of cooperation between India and Greece under their strategic partnership
Why in News?
Recently, India and Greece have taken a significant step by upgrading their relationship to a strategic partnership. The partnership aims to double trade, enhance defence and security collaboration, and address shared challenges.
- On this occasion, the Greek President Katerina Sakellaropoulou conferred the Prime Minister(PM) of India with “The Grand Cross of the Order of Honour”.
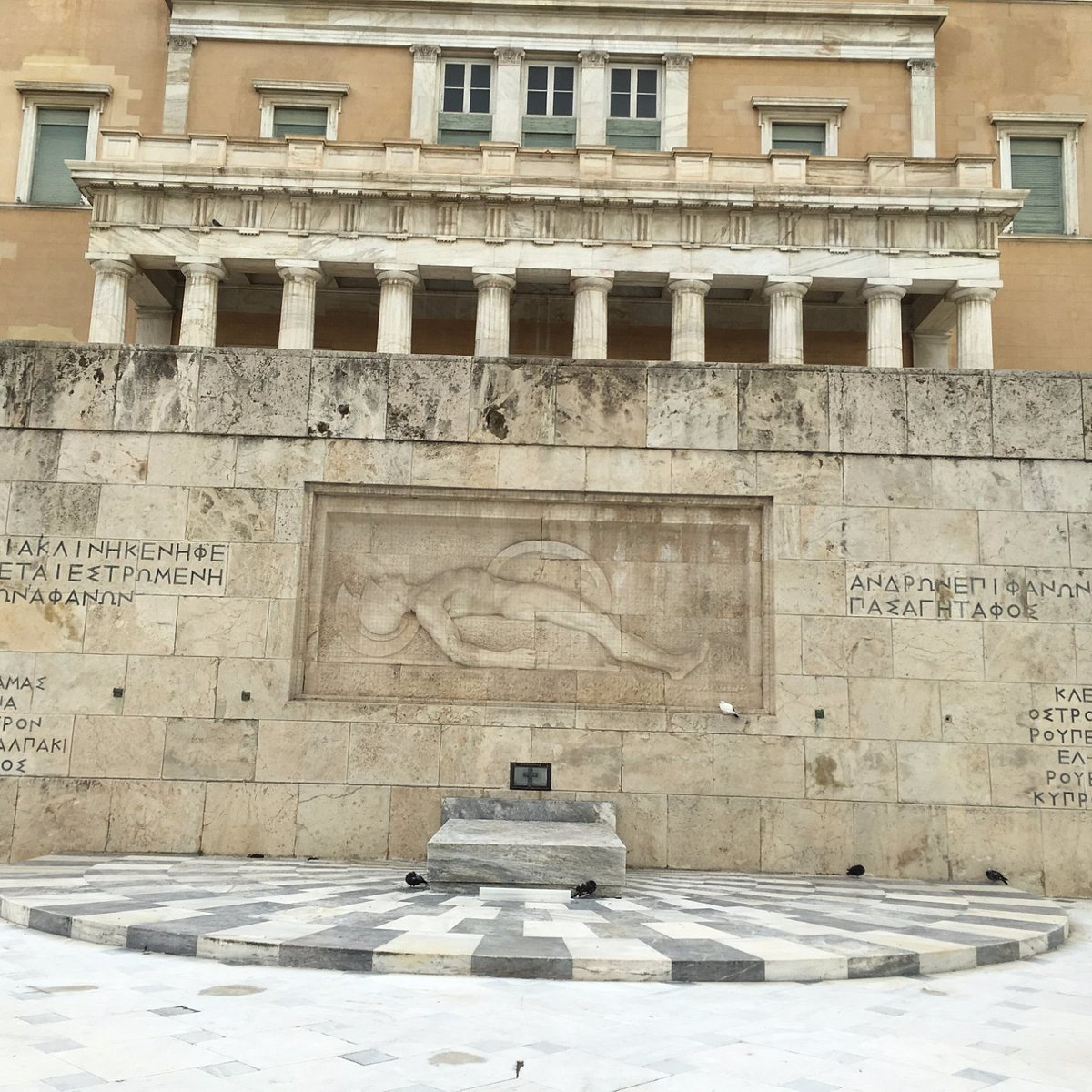
- The Indian PM paid tribute at the ‘Tomb of Unknown Soldier’ in Athens.
What are the Main Areas of Cooperation Under the Strategic Partnership?
- Defence and Security:
- India and Greece agreed to intensify their defence and security cooperation, especially in maritime security, counter-terrorism, cyber security, and the defence industry.
- Decided that there should also be an India-Greece dialogue framework at the level of National Security Advisors (NSAs).
- Maritime Security and Adherence to International Law:
- As leaders of two ancient sea-faring nations with a long-standing maritime outlook, they shared their vision of a free, open and rules-based Mediterranean Sea and Indo-Pacific, in accordance with the law of the sea, in particular the provisions of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and with full respect for the sovereignty, territorial integrity, and freedom of navigation to the benefit of international peace, stability and security.
- Culture and Tourism:
- Both leaders welcomed efforts to promote exchanges in all forms of art.
- They also agreed to encourage joint efforts in preserving and protecting ancient sites and strengthen cooperation within the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
- Trade and investment:
- The two countries also aimed to double bilateral trade by 2030. They agreed to explore new opportunities in sectors such as renewable energy, infrastructure, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and innovation.
- Mobility and Migration Partnership Agreement (MMPA):
- Both leaders agreed that an early finalization of an MMPA would be mutually beneficial, facilitating in particular the free movement of the workforce between the two countries.
- Broad Spectrum of Collaboration:
- Discussions span various domains, including digital payments, shipping, pharmaceuticals, and education.
What is the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier?
- The Tomb of the Unknown Soldier is a war memorial located in Syntagma Square in Athens, Greece.
- It is dedicated to Greek soldiers who lost their lives in various wars.
- The tomb serves as a symbol of remembrance and honour for the sacrifices made by anonymous soldiers.
- It was sculpted between 1930 and 1932 by sculptor Fokion Rok.
What is the Grand Cross of the Order of Honour?
- The Grand Cross of the Order of Honour is the second-highest civilian honour in Greece, after the Grand Cross of the Order of the Redeemer.
- The award was established in 1975 and features the head of goddess Athena on its front side, along with the inscription “ONLY THE RIGHTEOUS SHOULD BE HONORED”.
- The award is given to individuals who have distinguished themselves in the fields of politics, diplomacy, culture, science, or social service, and who have promoted the interests and values of Greece.
How are India's Relations with Greece?
- Historical Linkages:
- India’s contacts with Greece began over 2500 years ago.
- Alexander the Great’s campaign in the 4th century BCE, which reached the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent.
- Diplomatic, trade, and cultural relations between India and Greece were mentioned in Ashoka’s edicts.
- Trading between the Mauryan Kings and Greece is evidenced by coinage and writings.
- Chanakya, in Chandragupta’s Court, records in Arthashastra about the Yavan Ambassador in the Kings’ court named Megasthenes.
- Gandhara art, which flourished in the region of present-day Pakistan and Afghanistan, is believed to be a result of Indian and Greek influences.
- Commercial Relations
- Bilateral trade between India and Greece stood at USD 2 billion in 2022-23.
- India mainly exports aluminum, organic chemicals, fish and crustaceans and iron and steel to Greece, among other things.
- Meanwhile, Greece’s top exports to India are minerals fuels, mineral oils and products, sulphur and aluminium foil.
- India Participated as ‘Honoured Country’ in the 84th Thessaloniki International Fair(TIF), 2019, the largest annual commercial exposition of Greece.
- Political Relations
- Diplomatic relations were established between India and Greece in May 1950. Greece opened its embassy in Delhi in 1950 and India opened its embassy in Athens in 1978.
- Greece has been marked by consistent support to each other on issues of core national interest, such as Kashmir and Cyprus.
- Greece is also favouring United Nation Security Council (UNSC) expansion, with India as a permanent member.
- Defence Relations
- India and Greece's Defence Cooperation accelerated in 1998, which envisages cooperation in areas such as military training, joint exercises, defence industry collaboration, etc.
- Indian Air Force participation in EXERCISE INIOCHOS-23.
- Culture:
- Dimitrios Galanos, a Greek, became the first European Indologist and spent 47 years in India translating many Hindu texts into Greek and compiled a Sanskrit-English-Greek dictionary of over 9000 words.
- A "Dimitrios Galanos" Chair for Hellenic Studies was established at Jawaharlal Nehru University in New Delhi, India in September 2000.
- The Indian Council for Cultural Relations has been offering an annual scholarship for Greek students to study in India.
- Prof. Nicholas Kazanas, a distinguished Greek Indologist, was declared as one of the awardees of the prestigious Padma Shri award on the occasion of the 72nd Republic Day of India in 2021.
- Dimitrios Galanos, a Greek, became the first European Indologist and spent 47 years in India translating many Hindu texts into Greek and compiled a Sanskrit-English-Greek dictionary of over 9000 words.
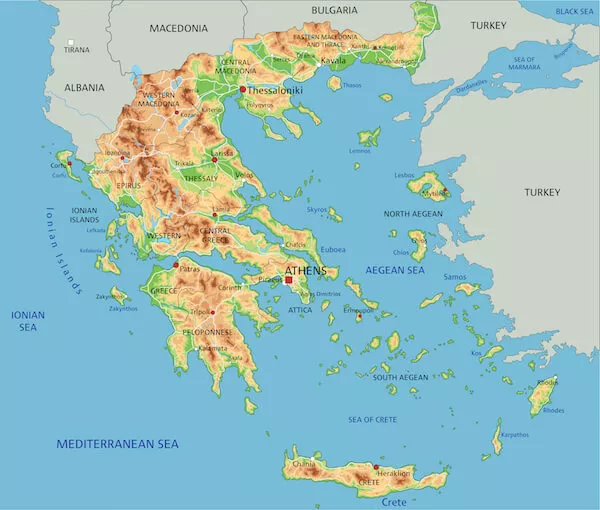
Key Facts about Greece:
- Greece is a country in southern Europe with a long coastline on the Mediterranean Sea. It is bordered by Albania, North Macedonia, Bulgaria, and Turkey.
- Greece is one of the oldest civilizations in the world and is considered the cradle of Western civilization. It is the birthplace of democracy, philosophy, theater, and the Olympic Games.
- Government: Parliamentary Republic.
- Capital: Athens, National
- Language: Greek
- Currency: Euro
- Major Mountains Ranges: Pindus and the Taurus mountains.
- The longest river in Greece is the river Haliacmon.
- Greece's highest mountain is Mount Olympus.
China Releases a Map Asserting Territorial Claims
For Prelims: Aksai Chin Region, Nine-Dash Line, China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), Line of Actual Control (LAC).
For Mains: China Releases a Map Asserting Territorial Claims, its implications on India.
Why in News?
China's government recently unveiled the "2023 edition of the standard map of China," reaffirming its territorial claims over disputed regions.
- The release of the map coincides with China's "National Mapping Awareness Publicity Week," which emphasizes the significance of accurate and consistent mapping.
What are the China's Claims in the New Map?
- Territorial Claims:
- The map incorporates China's territorial claims, encompassing Arunachal Pradesh and the Aksai Chin Region.
- These claims have long been points of contention between China and India.
- The map also features the "Nine-Dash Line," a contentious demarcation that covers the entire South China Sea and underscores Beijing's claims over this strategic maritime region.
- The map also shows the tenth dash line which underlines Beijing’s claims over Taiwan island.
- The map incorporates China's territorial claims, encompassing Arunachal Pradesh and the Aksai Chin Region.
- Renaming of Places:
- China's release of the new map aligns with its previous actions, such as standardizing the names of places in Arunachal Pradesh, including areas close to the state capital.
- Digital Mapping:
- Apart from the physical map, China is set to release digital maps for various applications, including location-based services, precision agriculture, platform economy, and intelligent connected vehicles.
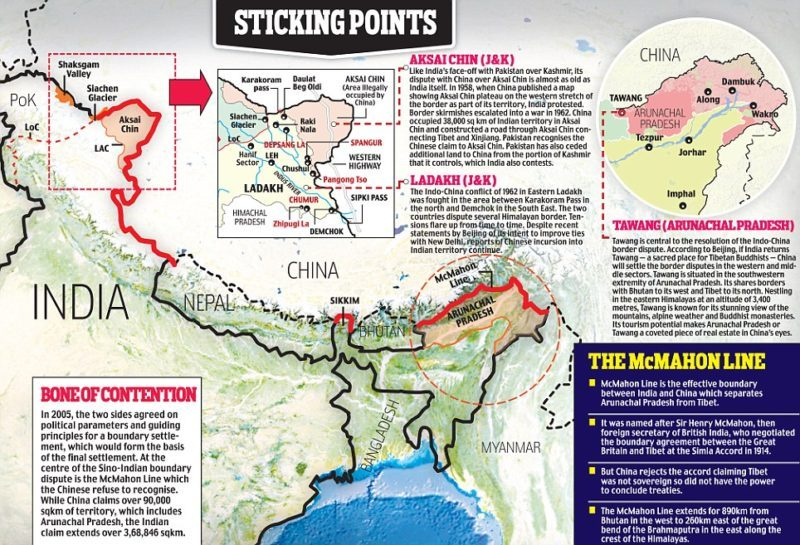
What is the Point of Contention Between India-China Border?
- Background:
- The India-China border dispute refers to the long-standing and complex territorial disputes along their shared border of 3,488 kilometers.
- The main areas of dispute are Aksai Chin, located in the western sector, and Arunachal Pradesh, in the eastern sector.
- Aksai Chin: China administers Aksai Chin as part of its Xinjiang region, while India considers it part of its union territory of Ladakh. The region holds strategic significance due to its proximity to the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) and its potential as a military route.
- Arunachal Pradesh: China claims the entire state of Arunachal Pradesh, referring to it as "South Tibet." India administers this region as a northeastern state and considers it an integral part of its territory.
- No Clear Demarcation: The border between India and China is not clearly demarcated throughout and there is no mutually agreed Line of Actual Control (LAC) along certain stretches.
- LAC came into existence after the 1962 Indo-China war.
- The India-China border is divided into three sectors.
- Western Sector: Ladakh
- Middle Sector: Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand
- Eastern Sector: Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim
- Military Standoffs:
- 1962 Sino-Indian War: The border dispute has led to a number of military standoffs and clashes, including the 1962 Sino-Indian War. Both countries have made efforts to manage the tensions, with various agreements and protocols aimed at maintaining peace along the border.
- Recent Faceoffs: The most serious recent episodes of conflict were in Galwan Valley in Ladakh in 2020 and in Tawang in Arunachal Pradesh in 2022.
- Observers on both sides of the border—the Line of Actual Control (LAC)—agree that the number of serious military confrontations has increased since 2013.
What have been the Border Dispute Settlement Mechanisms?
- Shimla agreement of 1914: To demarcate the boundary between Tibet and North East India, a convention was held at Shimla in 1914, representatives of all three i.e. Tibet, China, and British India.
- After the discussion, the agreement was signed by British India and Tibet but not by the Chinese officials. Presently India recognizes but China rejected both the Shimla agreement and the McMahon line.
- Panchsheel Agreement of 1954: The Panchsheel doctrine clearly indicated the willingness to ‘Respect each other’s sovereignty and territorial integrity’.
- The Agreement on the Maintenance of Peace and Tranquility:
- It was signed in 1993, which called for a renunciation of the use of force, recognition of the LAC, and the resolution of the border issue through negotiations.
- The Agreement on Confidence Building Measures in the Military Field along the LAC:
- It was signed in 1996, which laid down pledges on non-aggression, prior notification of large troop movements, and exchange of maps to resolve disagreements over the LAC.
- The Border Defence Co-operation Agreement:
- It was signed in 2013 following the Depsang Valley incident.
What are the Implications of China's New Map on India?
- Territorial Assertion:
- By incorporating disputed territories into its official map, China is reinforcing its territorial claims, challenging India's sovereignty over Arunachal Pradesh and Aksai Chin, and escalating the border dispute.
- By incorporating disputed territories into its official map, China is reinforcing its territorial claims, challenging India's sovereignty over Arunachal Pradesh and Aksai Chin, and escalating the border dispute.
- Diplomatic Tensions:
- China's actions can lead to diplomatic tensions between the two countries. India has consistently rejected China's territorial claims and will likely respond with reaffirmations of its own claims.
- Impact on Bilateral Relations:
- It can strain India-China relations, affecting cooperation in various areas, including trade, investment, and people-to-people exchanges.
- Regional Balance:
- The border dispute has implications for the broader regional balance of power. It can influence India's strategic alignment with other countries and regional groupings to counter China's influence.
How Should India Tackle China's Territorial and Regional Assertiveness?
- Diplomacy and Dialogue:
- Continue engaging in diplomatic talks with China through established mechanisms like the Special Representative talks and Working Mechanism for Consultation and Coordination (WMCC) on India-China border affairs.
- Emphasize peaceful resolution, adherence to bilateral agreements, and the importance of maintaining peace and stability along the border.
- Strengthen Border Infrastructure:
- Invest in improving border infrastructure, including roads, bridges, airstrips, and communication networks, to enhance mobility and response capabilities for Indian forces.
- Develop logistics hubs and forward bases to ensure swift deployment of troops and supplies in the border regions.
- Enhance Military Preparedness:
- Invest in modernizing the armed forces with advanced equipment, technology, and surveillance capabilities to effectively monitor and respond to any border incidents.
- Focus on enhancing the training and readiness of troops stationed in border areas.
- Regional and Global Partnerships:
- Strengthen partnerships with like-minded countries and regional organizations that share concerns about China's assertiveness in territorial disputes.
- Collaborate on intelligence-sharing, joint military exercises, and coordinated responses to regional challenges.
- Economic and Trade Measures:
- Diversify economic ties to reduce dependence on China and enhance economic resilience.
- Explore trade agreements and partnerships with countries that can provide alternative markets and investment opportunities.
- International Forums:
- Raise the border issue at international forums to garner support for a peaceful resolution based on international norms and principles.
- Uphold international norms and principles related to territorial integrity and dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Continue to engage with international legal experts to present India's case on the border issue.
Conclusion
- China's release of the 2023 edition of its standard map reaffirms its territorial claims over disputed areas like Arunachal Pradesh and the Aksai Chin region.
- This move is consistent with China's assertive approach to its borders and geopolitical interests under President Xi Jinping's leadership.
- The map serves as a reflection of China's ongoing efforts to bolster its territorial claims and geopolitical influence in the region.
Related Infographics: India's Border Dispute With Neighbors
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Siachen Glacier is situated to the (2020)
(a) East of Aksai Chin
(b) East of Leh
(c) North of Gilgit
(d) North of Nubra Valley
Exp:
- The Siachen Glacier is located in the Eastern Karakoram range in the Himalayas, just northeast of Point NJ9842 where the Line of Control between India and Pakistan ends.
- It has the distinction of being the largest glacier outside the polar and subpolar regions.
- It lies to the west of Aksai Chin, north of Nubra Valley, and almost east of Gilgit.
Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. Border management is a complex task due to difficult terrain and hostile relations with some countries. Elucidate the challenges and strategies for effective border management. (2016).
Urban Form of a City to Deal with Heatwaves
For Prelims: Urban Form of a City to Deal with Heatwaves, Heatwaves, Climate Change, Centre for Science and Environment (CSE).
For Mains: Adopting Urban Form of a City to Deal with Heatwaves.
Why in News?
Rising instances of Heatwaves have emerged as a critical issue in India, making it imperative to adopt Urban Form of a City.
- While Larger cities are struggling to deal with Climate Change to improve Livability, the smaller ones are on the brink of explosive growth and require “heat-proof” development.
What is the Urban Form of a City?
- About:
- Every city has a unique combination of natural and human-made infrastructure and the activities resulting from them.
- Closely packed buildings, for instance, will generate shorter trips and hence, less vehicular emissions that pollute the air and trap heat.
- More greenery and water bodies will sequester carbon emissions and cool the ambient environment.
- This combination of green spaces, water bodies and buildings is called the Urban Form of a city, which plays a crucial role in its heat resilience and liveability.
- The Role of Urban Form in Heat Resilience:
- Parameters such as urban morphology, aspect ratio, sky view factor (SVF), blue/green infrastructure (B/GI), floor area ratio (FAR)/floor space index (FSI), and street orientation collectively define a city's urban form and influence its susceptibility to heat.
- A study by the Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) in 2022 investigated the response of diverse urban forms to heat across 10 Indian cities, including Pune, Delhi, Kolkata, Bengaluru, and Jaipur.
- Key findings from the study highlighted potential steps for combating heat in urban India.
- Parameters such as urban morphology, aspect ratio, sky view factor (SVF), blue/green infrastructure (B/GI), floor area ratio (FAR)/floor space index (FSI), and street orientation collectively define a city's urban form and influence its susceptibility to heat.
What are the Findings of the CSE Related to Urban Infrastructure?
- Urban Morphology and Heat Resilience:
- Urban areas characterized by open highrise, open midrise, and compact midrise morphologies with moderate vegetation exhibited lower land surface temperatures (LST) in heat pockets.
- Neighborhoods featuring lowrise buildings suffered 2-4°C higher LST due to sparse vegetation. Large low rise industrial zones are particularly problematic due to heat-trapping roofing materials like asbestos, galvanised iron sheets and plastic sheets.
- Such neighbourhoods can benefit by using better roof materials, reflective paints and green roofs.
- Aspect Ratio:
- Aspect ratio is the ratio of building height and street width. It affects how much heat is trapped by urban surfaces.
- The study shows that the higher the aspect ratio, the lower the LST. This means the narrower the street, the lesser the heat gain. Buildings shade each other and decrease direct exposure of surfaces to the sun.
- Sky View Factor and Heat Trapping:
- The SVF determines heat trapping and dissipation within streets and open spaces. The value of sky view factor lies between 0 and 1. Value 1 means there is none to negligible enclosure. Higher SVF values were associated with a considerable increase in LST.
- Locations with higher SVF, including highways, road intersections, and open parking lots, experienced heightened temperatures.
- Street Orientation and Sun Exposure:
- Street orientation impacts heat gain due to sun exposure and wind speed. North-south-oriented streets had higher LST due to greater sun exposure.
- Streets aligned along the east-west axis were cooler as they received less direct sun exposure.
- Blue / Green Infrastructure:
- Greens play a crucial role in enhancing microclimate of an urban area. They regulate temperature and relative humidity, absorb and decompose pollutants, improve the overall air quality.
- However, the benefits vary widely depending on the kind of greens — grass, shrubs or trees with thick foliage.
- Singapore provides a methodology to calculate effective vegetation cover (EVC) to reduce urban heat island effect and conserve natural resources.
- The CSE study found that a 30% rise in EVC reduces LST by 2-4°C. EVC is better in trees with canopy. LST under trees with thick foliage is about 10°C cooler than LST under palm trees in the same locality.
- Greens play a crucial role in enhancing microclimate of an urban area. They regulate temperature and relative humidity, absorb and decompose pollutants, improve the overall air quality.
What are the Steps to Adopt Urban Form of a City?
- Urban form-based codes can offer context-specific cooling solutions. These codes can tailor zoning regulations to the unique characteristics of a city or neighbourhood. Old markets could feature shaded walkways, temple precincts, cool roofs, and business districts with high EVC (30%).
- Cities must revise their building by-laws and master plans to incorporate the insights from this study and improve heat resilience.
- For instance, Pune's focus on SVF, aspect ratio, effective vegetation cover, and urban morphology could be the model for similar cities.
- Even a modest 1°C temperature decrease could translate into a 2% reduction in a city's power consumption, showcasing the potential impact of effective planning.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. What are the possible limitations of India in mitigating global warming at present and in the immediate future? (2010)
- Appropriate alternate technologies are not sufficiently available.
- India cannot invest huge funds in research and development.
- Many developed countries have already set up their polluting industries in India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Bring out the causes for the formation of heat islands in the urban habitat of the world. (2013)
Equatorial Origin Cyclones and Pacific Decadal Oscillation
For Prelims: Tropical Cyclones, Low Latitude Cyclones, Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO), ENSO
For Mains: Impact of PDO on India, ENSO vs PDO
Why in News?
Equatorial-origin cyclones have been unusually subdued in recent decades.
- However, as per a study published in the journal Nature Communications, the combination of global warming and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) could make such cyclones more frequent in the coming years.
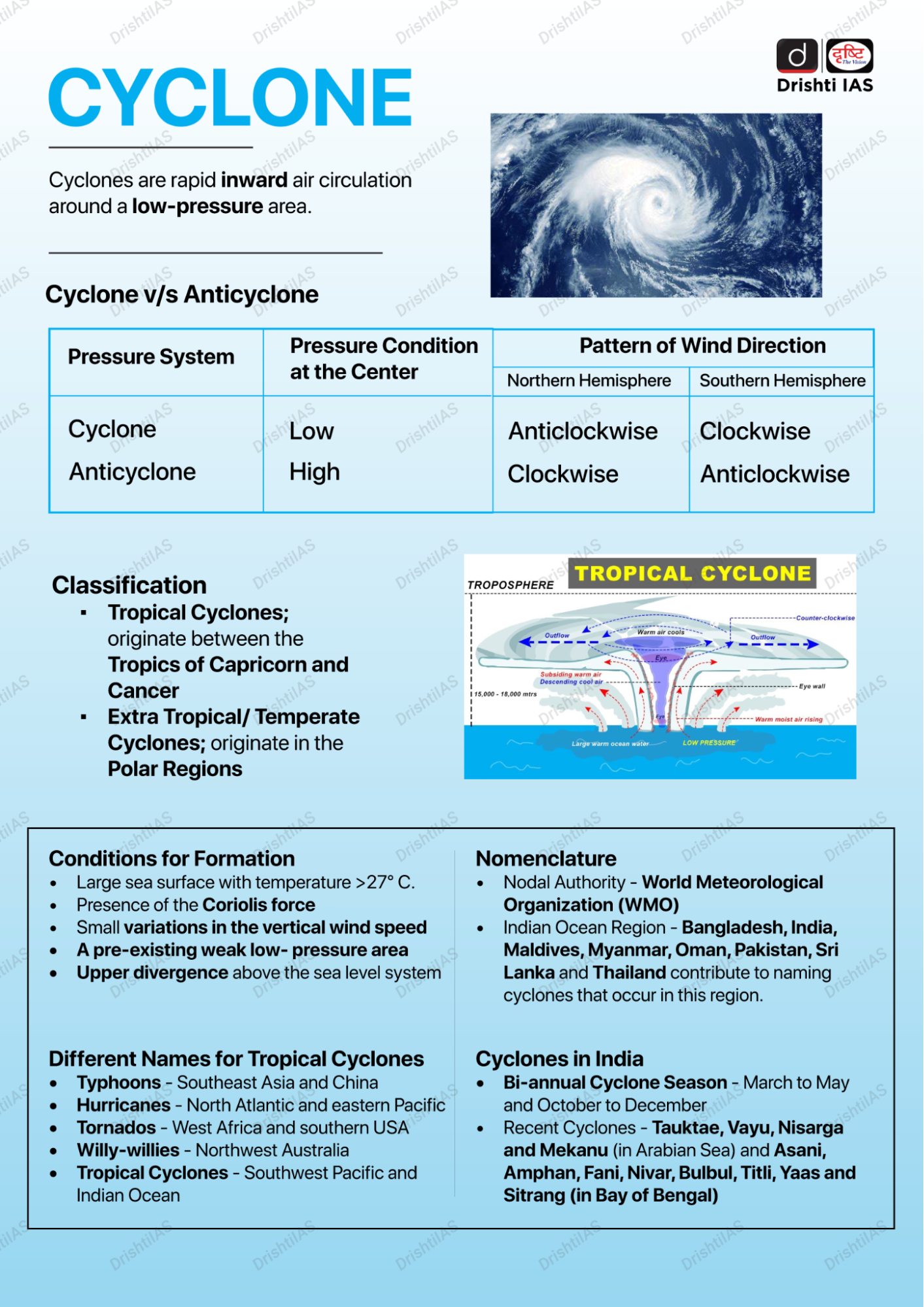
What are Equatorial-Origin or Low Latitude Cyclones?
- Equatorial origin or Low Latitudes Cyclones (LLCs) originate between 5°N and 11°N. These cyclones are much smaller in size than those in higher latitudes but intensify more rapidly.
- Cyclones forming near the equator (low-latitude) is usually rare but when the waters are warm, they can gain more moisture and rise in intensity.
- Majority of cyclones originate in the Western Pacific Ocean.
- Cyclones forming near the equator (low-latitude) is usually rare but when the waters are warm, they can gain more moisture and rise in intensity.
- The last major cyclone of this kind in the Indian neighbourhood was the 2017 Cyclone Ockhi which travelled >2000 km and devastated Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Sri Lanka.
- The north Indian Ocean (NIO) in the post-monsoon season (Oct-Nov-Dec) is a hotbed for LLCs that constitute about 60% of all Tropical Cyclones formed in the NIO (since 1951) but has received relatively less attention.
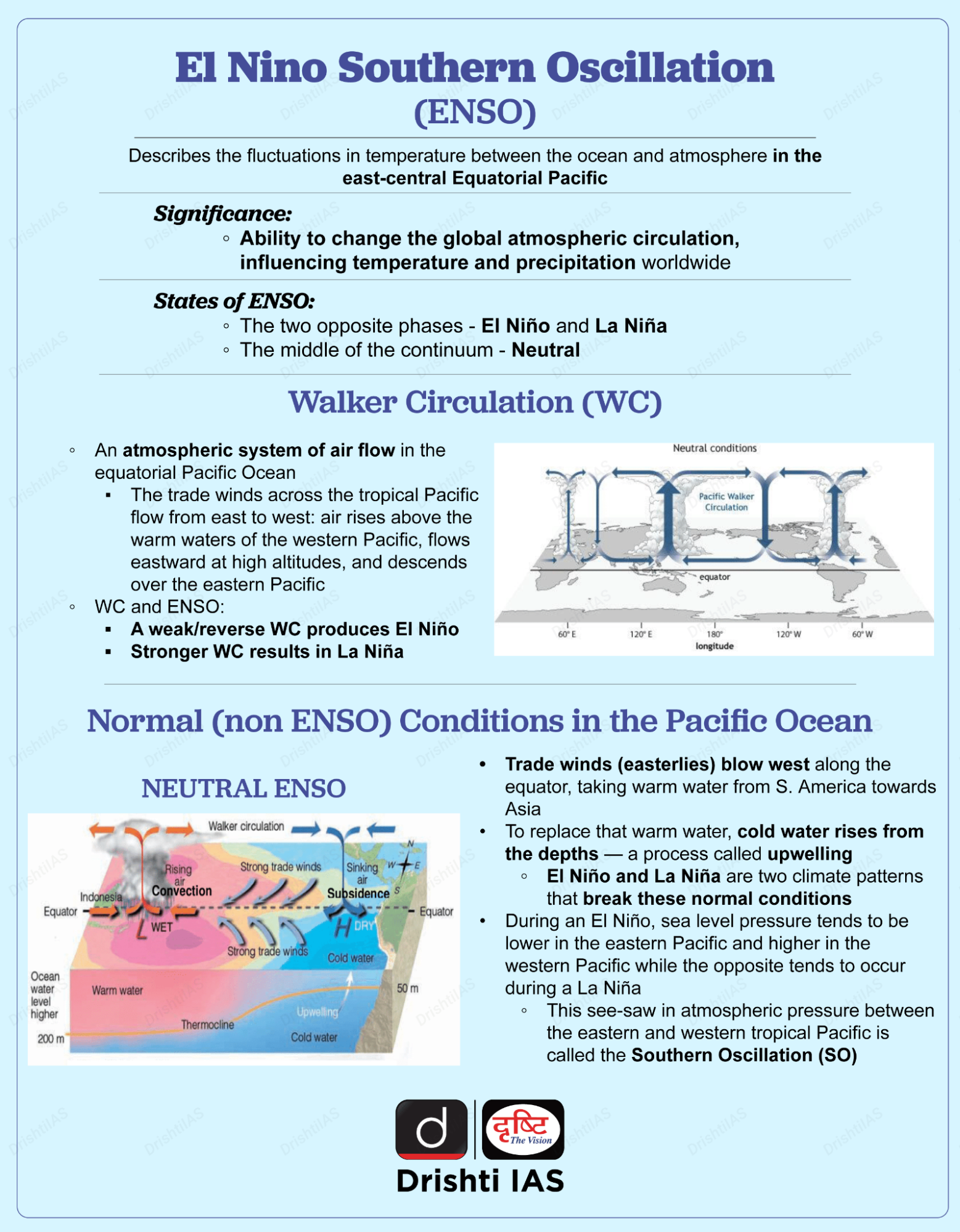
What is Pacific Decadal Oscillation?
- About:
- The Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) is a long-term ocean fluctuation of the Pacific Ocean. It is a cyclical event that repeats every 20-30 years and just like ENSO, has a ‘cool’ and ‘warm’ phase.
- Positive (warm) PDO = cooler west Pacific Ocean and warmer eastern side (vice versa for negative PDO).
- The term PDO was coined in about 1996 by Steven Hare.
- Impact of PDO:
- On Global Climate: PDO phase can have significant implications for the global climate, affecting Pacific and Atlantic hurricane activity, droughts and flooding around the Pacific basin, the productivity of marine ecosystems, and global land temperature patterns.
- On Cyclones: A warmer (positive-phased) PDO implies fewer equatorial-origin cyclones.
- In 2019, the PDO entered a cooler, negative phase and which if continues, could mean more such cyclones in post-monsoon months.
- ENSO and PDO:
- ENSO with a positive PDO is generally not good, however, ENSO with a negative PDO brings more rain to India.
- If both ENSO and the PDO are in the same phase, it is believed that El Niño/La Nina impacts may be magnified.
- PDO vs ENSO:
- El Nino or La Nina events repeat in the Pacific over 2-7 years, however, PDO has a signature for a longer time (on the decadal scale).
- A ‘positive’ or ‘warmer phase’ of a PDO can be known only after several years of measuring ocean temperatures and their interaction with the atmosphere (stage of an ENSO can be determined any year).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. La Nina is suspected to have caused recent floods in Australia. How is La Nina different from El Nino? (2011)
- La Nina is characterised by an usually cold ocean temperature in equatorial Indian Ocean whereas El Nino is characterised by unusually warm ocean temperature in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- El Nino has adverse effect on south-west monsoon of India but La Nina has no effect on monsoon climate.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q. Most of the unusual climatic happenings are explained as an outcome of the El-Nino effect. Do you agree? (2014)
Q. Tropical cyclones are largely confined to the South China Sea, Bay of Bengal and Gulf of Mexico. Why? (2014)
UWW Suspends of Wrestling Federation of India
For Prelims: Wrestling Federation of India, United World Wrestling, Wrestling
For Mains: Role of the Indian government in ensuring the smooth functioning of national sports federations, Discuss the role of sports in enhancing a nation's image and reputation internationally.
Why in News?
The Wrestling Federation of India (WFI), the national governing body for wrestling, has been provisionally suspended by the United World Wrestling (UWW), for not conducting its elections on time.
- This has serious implications for the Indian wrestlers, who will not be able to compete under the national flag in the upcoming World Championships in Serbia.
Why was the WFI Suspended by UWW?
- The UWW has suspended the WFI for violating its constitution, which mandates that all member federations must hold their elections every four years.
- The WFI was supposed to hold its elections in February 2023, but they were delayed due to various reasons, including allegations of sexual harassment, intimidation, financial irregularities, and administrative lapse against the former WFI president and others by some prominent wrestlers.
- The UWW also wanted to protect the athletes and make the federation work properly again.
What are the Other Sports Bodies in India Facing Similar Conflicts?
- FIFA (Fédération internationale de Football Association), the global governing body of football, suspended All India Football Federation of India due to delayed elections in 2002, The ban was lifted subsequently.
- The International Olympic Committee (IOC) and International Hockey Federation (FIH) also warned of potential bans for Indian sports bodies for similar reasons.
- In June 2020, the Indian government revoked recognition of 54 national federations for non-compliance with the National Sports Development Code of India 2011.
Wrestling Federation of India (WFI)
- The WFI is the governing body of wrestling in India. It is headquartered in New Delhi.
- It is recognized by the Government of India and the Indian Olympic Association.
- It organizes various national and international wrestling events, such as the Pro Wrestling League, the National Wrestling Championship, and the Asian Championships.
- The WFI also supports and trains Indian wrestlers who participate in the Olympic Games.
United World Wrestling (UWW)
- UWW is the international governing body for the sport of amateur wrestling. It oversees wrestling at the Olympics and the World Championships.
- UWW is headquartered in Corsier-sur-Vevey, Switzerland.
- UWW was founded in 1912 as the International Federation of Associated Wrestling Styles (FILA). It changed its name to United World Wrestling in 2014.
- UWW has a vision to be globally recognized as an inspiring, innovative, and leading Olympic Federation3. Its mission is to lead the growth of wrestling around the world.
History of the Game of Wrestling in India
- Wrestling in India dates back to the 5th millennium B.C.
- Ancient India practised wrestling known as MallaYudha.
- Bhima from Mahabharata was a renowned wrestler, along with Jarasandha, Keechaka, and Balrama.
- Ramayana also mentions wrestling, with Hanuman as a notable wrestler.
- Wrestling is referred to as "Dangal" in India and is a basic form of wrestling tournament. It's called "kushti" in Punjab and Haryana regions.
- Originally a fitness activity and entertainment for royals, wrestling has evolved into a professional sport.
What is the Impact of the Suspension?
- Wrestlers' Participation:
- According to the UWW, wrestlers and their support personnel can still participate in UWW-sanctioned events, but under the UWW flag rather than the national flag.
- UWW Events:
- Indian wrestlers will be unable to compete under the national flag in UWW events, including the upcoming World Championships in Belgrade, Serbia. Additionally, no Indian national anthem will be played if a wrestler secures a gold medal.
- WFI cannot receive any financial or technical assistance from the UWW.
- Indian Wrestling:
- The suspension tarnishes India’s image and reputation in the international wrestling community. It also demoralizes and disheartens the Indian wrestlers, who have worked hard to prepare for the World Championships and other events.
- Suspension of WFI hinders wrestler’s qualification chances for the 2024 Paris Olympics, as the World Championships are a qualifying event.
- The suspension is a major setback for Indian wrestling, which has been one of the most successful sports for India in recent years. India has won four Olympic medals, 19 World Championship medals, and 69 Asian Championship medals in wrestling since 2008.
Way Forward
- The immediate solution is to conduct the WFI elections as soon as possible and submit the results to UWW for approval.
- The long-term solution is to reform and restructure the WFI, which has been plagued by various problems and controversies for a long time. The WFI should adopt a professional and accountable approach to its functioning, with proper checks and balances, financial audits, grievance redressal mechanisms, etc.
- The WFI should also foster a healthy and harmonious relationship with UWW and other international bodies, and abide by their rules and regulations. The WFI should also cooperate with other national federations and regional associations, and promote the growth and popularity of wrestling in India and abroad.
Legal Insight: Interim Bail in Wrestler Case
Long Read Sequencing and Y Chromosome
For Prelims: Long Read Sequencing, X and Y Chromosomes, DNA
For Mains: Significance of Long Read Sequencing
Why in News?
The new “long-read” sequencing technique has provided a reliable sequence from one end of the Y chromosome to the other.
- The findings published in Nature Journal provide information about the working of sex genes and sperm, the evolution of the Y chromosome, and its possible disappearance in a few million years.
- Earlier, some studies shed light on the role of the Y chromosome in colorectal and bladder cancer, revealing key genetic mechanisms that contribute to tumour progression, immune response, and clinical prognosis.
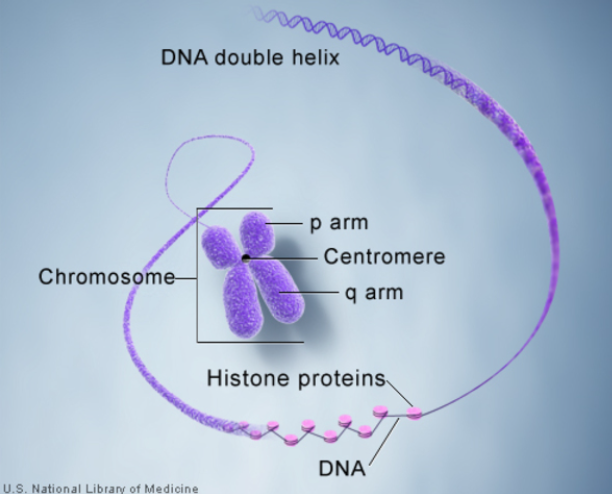
What is the Difference between DNA, Gene, and Chromosome?
- DNA:
- DNA is a long molecule that contains our unique genetic code. DNA is composed of two strands that wrap around each other to form a double helix shape, like a spiral staircase.
- Each strand of DNA is formed of four basic building blocks or ‘bases’: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T).
- Gene:
- Genes are sections of DNA that contain the set of instructions to produce one specific molecule in the body, usually a protein.
- These proteins control how the body grows and works and are responsible for characteristics like eye colour, blood type, or height.
- Each cell contains two sets of genes, one from your mother and one from your father. For ease of storage and access, the genes are packaged up into 46 parcels called chromosomes.
- Genes are sections of DNA that contain the set of instructions to produce one specific molecule in the body, usually a protein.
- Chromosome:
- In the nucleus of each cell, the DNA molecule is packaged into thread-like structures called chromosomes.
- Each chromosome is made up of DNA tightly coiled many times around proteins called histones that support its structure.
- Chromosomes are not visible in the cell’s nucleus - not even under a microscope.
What is the Y Chromosome and Its Related Findings?
- About:
- The Y chromosome is a male-determining chromosome; it bears a gene called SRY (Sex-Determining region Y), which directs the development of a testis in the embryo.
- The Y chromosome is a male-determining chromosome; it bears a gene called SRY (Sex-Determining region Y), which directs the development of a testis in the embryo.
- Y vs X:
- Y is very different from X and the 22 other chromosomes of the human genome; it is small in size and has a lot of DNA sequences that don't seem to contribute to traits (aka "junk DNA") (only 27 compared to about 1,000 on the X) making it difficult to sequence the chromosome.
- Disappearance of Y:
- About 150 mn years ago, the SRY evolved and defined a new proto-Y which degenerated fast enough (losing ~10 active genes per million years).
- If this degradation continues, then in a few million years, the whole human Y chromosome will disappear (as it already has in some rodents).
- Findings of Y Sequencing:
- The Y is the last human chromosome to have been sequenced end-to-end, or T2T (telomere-to-telomere).
- Telomeres are structures made from DNA sequences and proteins found at the ends of chromosomes.
- Some new genes have been discovered, but they are just extra copies of known genes.
- The centromere structure is now known, and the repetitive sequences at the end of the Y have been read.
- Centromere is a region of the chromosome that pulls copies apart when the cell divides.
- The location of the centromere on each chromosome gives the chromosome its characteristic shape and can be used to help describe the location of specific genes.
- The findings are significant for scientists all over the world. It will help in examining the details of Y genes; how SRY and the sperm genes are expressed or where and how repeated sequences originated.
- The Y is the last human chromosome to have been sequenced end-to-end, or T2T (telomere-to-telomere).
What is Long Read Sequencing?
- Long-read sequencing, also called third-generation sequencing, is a DNA sequencing technique that enables the sequencing of much longer DNA fragments than traditional short-read sequencing methods.
- One of the most basic forms of DNA sequencing is Sanger sequencing which can sequence relatively small fragments of DNA (up to 900 base pairs).
- The more modern forms of DNA sequencing are called next-generation sequencing which can efficiently determine longer DNA sequences compared to Sanger sequencing.
- Over the past decade, long-read, single-molecule DNA sequencing technologies have emerged as powerful players in genomics. It can read the DNA sequence of much longer DNA fragments (normal range: 10,000 - 100,000 base pairs).
- While short reads can capture the majority of genetic variation, long-read sequencing allows the detection of complex structural variants that may be difficult to detect with short reads.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. What is Cas9 protein that is often mentioned in the news? (2019)
(a) A molecular scissors used in targeted gene editing
(b) A biosensor used in the accurate detection of pathogens in patients
(c) A gene that makes plants pest-resistant
(d) A herbicidal substance synthesized in genetically modified crops
Ans: (a)
Q. With reference to agriculture in India, how can the technique of ‘genome sequencing’, often seen in the news, be used in the immediate future? (2017)
- Genome sequencing can be used to identify genetic markers for disease resistance and drought tolerance in various crop plants.
- This technique helps in reducing the time required to develop new varieties of crop plants.
- It can be used to decipher the host-pathogen relationships in crops.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only,
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of society? (2021)
National Sports Day 2023
Why in News?
12th National Sports Day was celebrated across India on 29 August.
Why is National Sports Day Celebrated?
- Objective: To commemorate the birth anniversary of hockey legend Major Dhyan Chand.
- First NSD: August 29, 2012.
- Significance: Encourages people of all ages to embrace physical fitness, regular exercise and a healthy lifestyle.
- Serves as a catalyst for developing a robust sports culture in India.
- Highlights of NSD 2023:
- Theme - "Sports are an enabler to an inclusive and fit society".
- National Sports Federations portal launched (for good governance).
Who was Major Dhyan Chand?
- Major Dhyan Chand was a field hockey player who played international hockey from 1926 to 1949.
- He was a three-time Olympic gold medalist who secured gold in the 1928, 1932, and 1936 Olympic editions.
- His exceptional skills in the game made him earn the title ‘magician of hockey.’
- Dhyan Chand, along with his brother Roop Singh, contributed significantly to India's 35-goal tally, earning them the title of ‘hockey twins.’
- In 1934, Dhyan Chand was honoured with the captaincy of the Indian team.
- In 1956, Major Dhyan Chand retired from the army as a Major and was honoured with the Padma Bhushan.
Note:
- Awards named after Major Dhyan Chand:
- Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award (highest sporting honour of India)
- Dhyan Chand Award (highest award for lifetime achievement in sports)
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
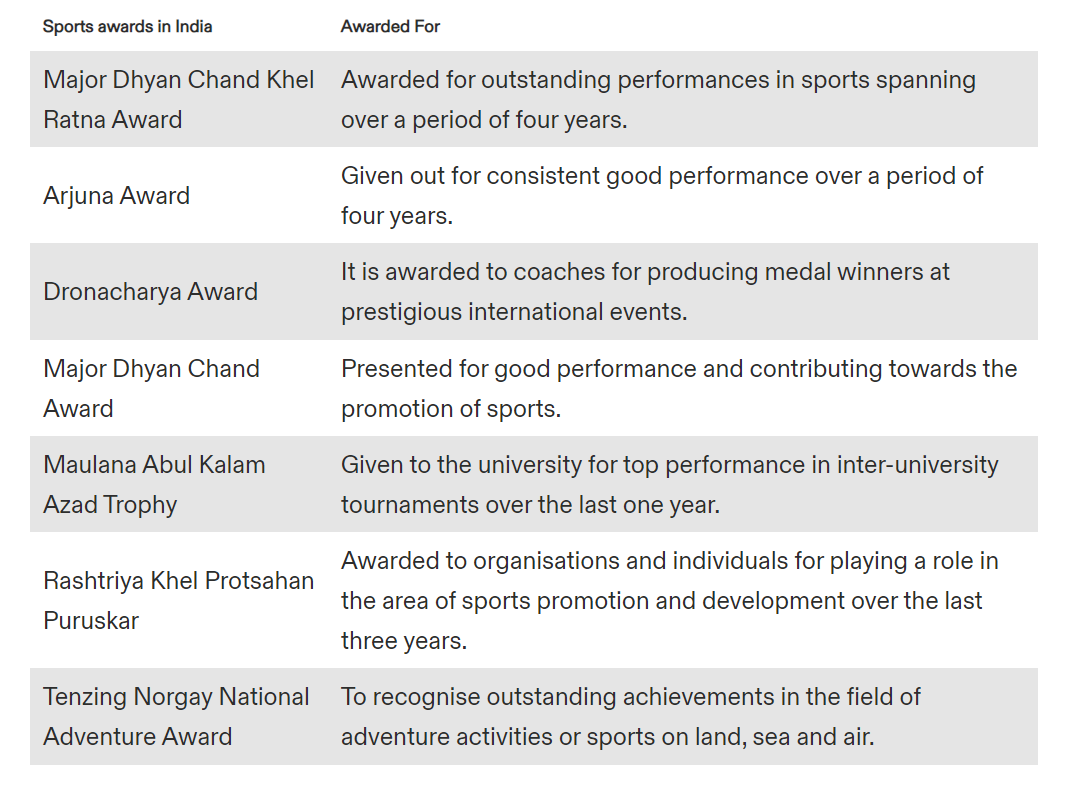
Q. Consider the following pairs with regard to sports awards: (2023)
| 1. Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award | For the most spectacular and outstanding performance by a sportsperson over period of last four years |
| 2. Arjuna Award | For the lifetime achievement by sportsperson |
| 3. Dronacharya Award | To honour eminent coaches who have successfully trained sportspersons or teams |
| 4. Rashtriya Khel Protsahan Puraskar | To recognize the contribution made by sportspersons even after their retirement |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
Ans: (b)
Q. Consider the following statements in respect of the Laureus World Sports Award which was instituted in the year 2000: (2021)
- American golfer Tiger Woods was the first winner of this award.
- The award was received mostly by ‘Formula One’ players so far.
- Roger Federer received this award maximum number of times compared to others.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q. Consider the following statements in respect of the 32nd Summer Olympics: (2021)
- The official motto for this Olympics is ‘A New World’.
- Sport Climbing, Surfing, Skateboarding, Karate and Baseball are included in this Olympics.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Blotting Paper
- Blotting paper absorbs ink through capillary action, a natural process where liquids move to lower surface tension.
- Capillary tubes, tiny channels less than 1mm wide, when in contact with liquids, draw the liquid upward, higher than its outside level.
- Blotting paper, derived from cotton linter, wood, or straw, contains microscopic capillaries formed during its creation. These capillaries quickly soak up ink or water, spreading it across the paper.
- Capillary action also drives plant sap upward and helps oil reach lamp wicks for burning.
India and Kenya Signed a MoU for Collaboration in Shipbuilding
- On a visit to India, the Kenyan Cabinet Secretary for Defence signed an MoU with India’s defence minister for capacity building and collaboration in ship design and construction.
- The two Ministers emphasised on the need for deeper maritime security cooperation in IOR and agreed for a joint training in counter-insurgency and UN peacekeeping domains.
- Kenya is located in East Africa between the Indian Ocean and Lake Victoria.
- Kenya is significant for India in the geopolitics of Western Indian Ocean. It is also an active member of the African Union with whom India has a long-established connection.
Read More: India Kenya Ties, Indian Ocean Region, India Africa Relations