Indian Society
Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India Report 2021: NCRB
For Prelims: National Crime Records Bureau, Reports of NCRB, National and Sectoral Data
For Mains: Population and Associated Issues, Key Findings of the NCRB Report, Reports of NCRB, Functions of NCRB
Why in News?
Recently, the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) released the “Accidental Deaths & Suicides in India Report 2021.”
- The report tabled figures for “Crime Against Women”, “Suicide” and “Crime Rates”.
What are the Report’s findings for Crime Against Women?
- National Figures:
- The rate of crime against women (number of incidents per 1 lakh population) increased from 56.5% in 2020 to 64.5% in 2021.
- 31.8%: Cruelty by husband or his relatives
- 20.8%: Assault on Women with Intent to Outrage her Modesty
- 17.6%: Kidnapping and Abduction
- 7.40%: Rape
- The rate of crime against women (number of incidents per 1 lakh population) increased from 56.5% in 2020 to 64.5% in 2021.
- State:
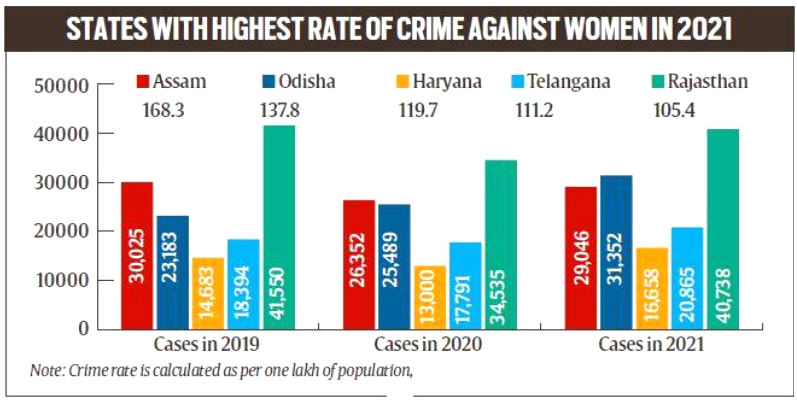
- The highest rate of crime against women in 2021 was registered in Assam 168.3% followed by Odisha, Haryana, Telangana and Rajasthan.
- Rajasthan showed a marginal decrease in the actual number of cases while the three other states (Odisha, Haryana and Telangana) marked an increase.
- In terms of actual number of cases registered in 2021, UP tops the list followed by Rajasthan, Maharashtra, West Bengal and Odisha.
- Nagaland stood out with the lowest number of crimes against women registered in the past three years.
- The highest rate of crime against women in 2021 was registered in Assam 168.3% followed by Odisha, Haryana, Telangana and Rajasthan.
- Union Territories:
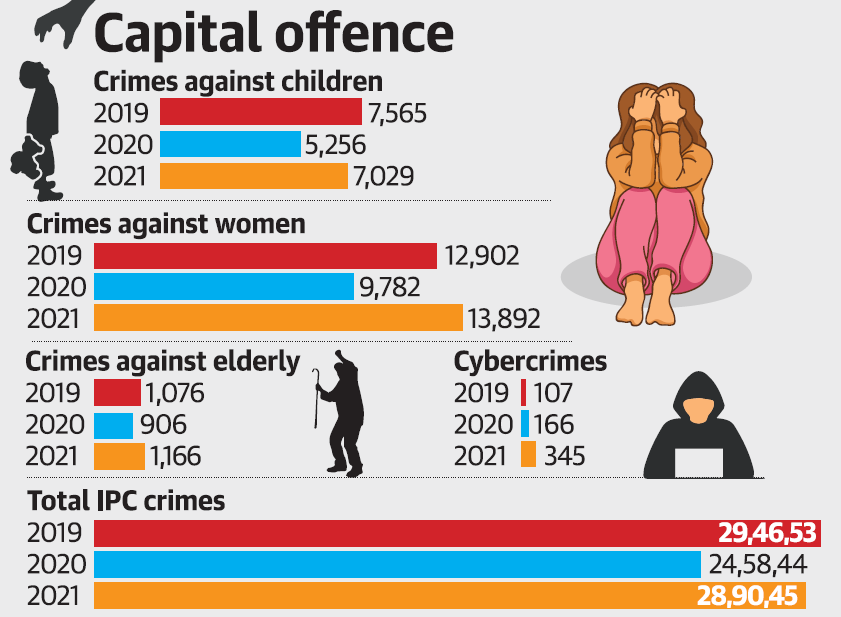
- Among Union Territories, Delhi had the highest rate of crime against women in 2021 at 147.6%.
- Cities:
- Jaipur had the highest rate at over 194%, followed by Delhi, Indore and Lucknow.
- Chennai and Coimbatore (Both in Chennai) had the lowest rate.
- In actual numbers among these cities, Delhi topped in 2021 (13,892) followed by Mumbai, Bengaluru and Hyderabad.
- Jaipur had the highest rate at over 194%, followed by Delhi, Indore and Lucknow.
- Domestic Violence & Dowry Deaths:
- Only 507 cases were registered in the country under the Domestic Violence Act in 2021 — 0.1% of the total cases of crime against women.
- The highest number of cases (270) were filed in Kerala.
- 6,589 cases of dowry deaths were registered in 2021 with the highest number of such deaths registered in UP and Bihar.
- Only 507 cases were registered in the country under the Domestic Violence Act in 2021 — 0.1% of the total cases of crime against women.
What are the Report’s findings for Suicide Rate?
- Daily Wager:
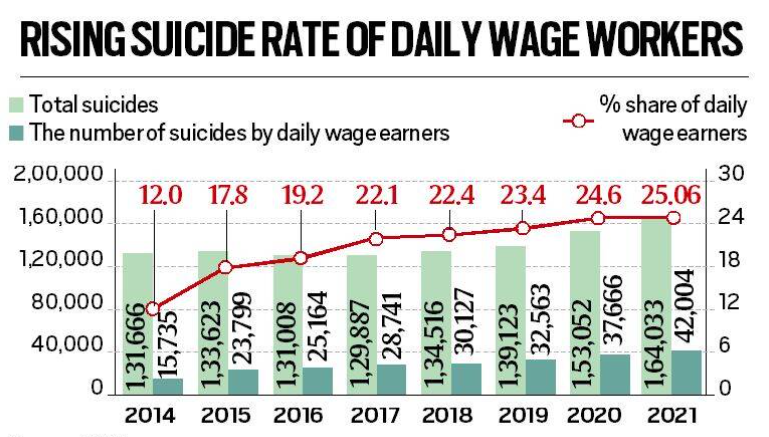
- Daily wage earners remained the largest profession-wise group among suicide victims in 2021, accounting for 42,004 suicides (25.6%).
- The share of daily wagers death by suicide has crossed the quarter mark for the first time.
- At the national level, the number of suicides increased by 7.17% from the years 2020 to 2021.
- However, the number of suicides in the daily wage group rose by 11.52% during this period.
- Farming Sector:
- The overall share of “Persons engaged in farming sector” among the total recorded suicides stood at 6.6% during 2021.
- Profession Wise Distribution:
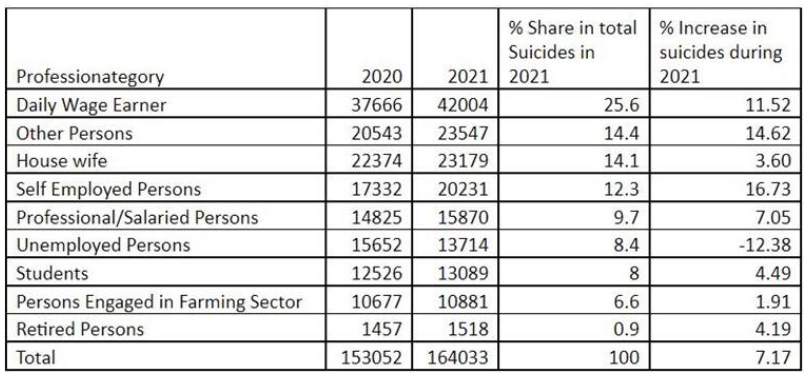
- The highest increase of 16.73% was recorded by “self-employed persons”.
- The “unemployed persons” group was the only one that saw a decline in suicides, with the number dipping by 12.38% from 15,652 in 2020 to 13,714 suicides in 2021.
- Reasons for Suicide:
- 33.2%: Family Problems (other than marriage related problems)
- 4.8%: Marriage Related Problems
- 18.6%: Illness
- State:
- Maharashtra topped the country in terms of the number of suicides reported in 2021 followed by Tamil Nadu and Madhya Pradesh.
- Maharashtra contributed 13.5% to the total number of suicides registered across the country in 2021.
- Maharashtra topped the country in terms of the number of suicides reported in 2021 followed by Tamil Nadu and Madhya Pradesh.
- Union Territories:
- Delhi recorded the highest number of 2,840 suicides.
What are the Report’s findings for Crime Rates?
- About:
- Registered violent crimes such as rape, kidnapping, crimes against children and robberies increased again across India in 2021.
- Pandemic-related restrictions led to a decline in these severe offences in 2020.
- Murders, which did not come down even in 2020, continued to increase last year too.
- Registered violent crimes such as rape, kidnapping, crimes against children and robberies increased again across India in 2021.
- Crime Wise Data:
- Rape cases:
- Increased by 13% (28,046 in 2020)
- Rajasthan had the highest rate of rape for 2021 at 16.4% and topped in actual numbers with 6,337 cases registered in 2021.
- Kidnapping:
- Rose by 20% (84,805 in 2020)
- Murder:
- Increased to 29,272 cases in 2021 from 29,193 in 2020
- Uttar Pradesh registered the highest number of murders followed by Bihar and Maharashtra.
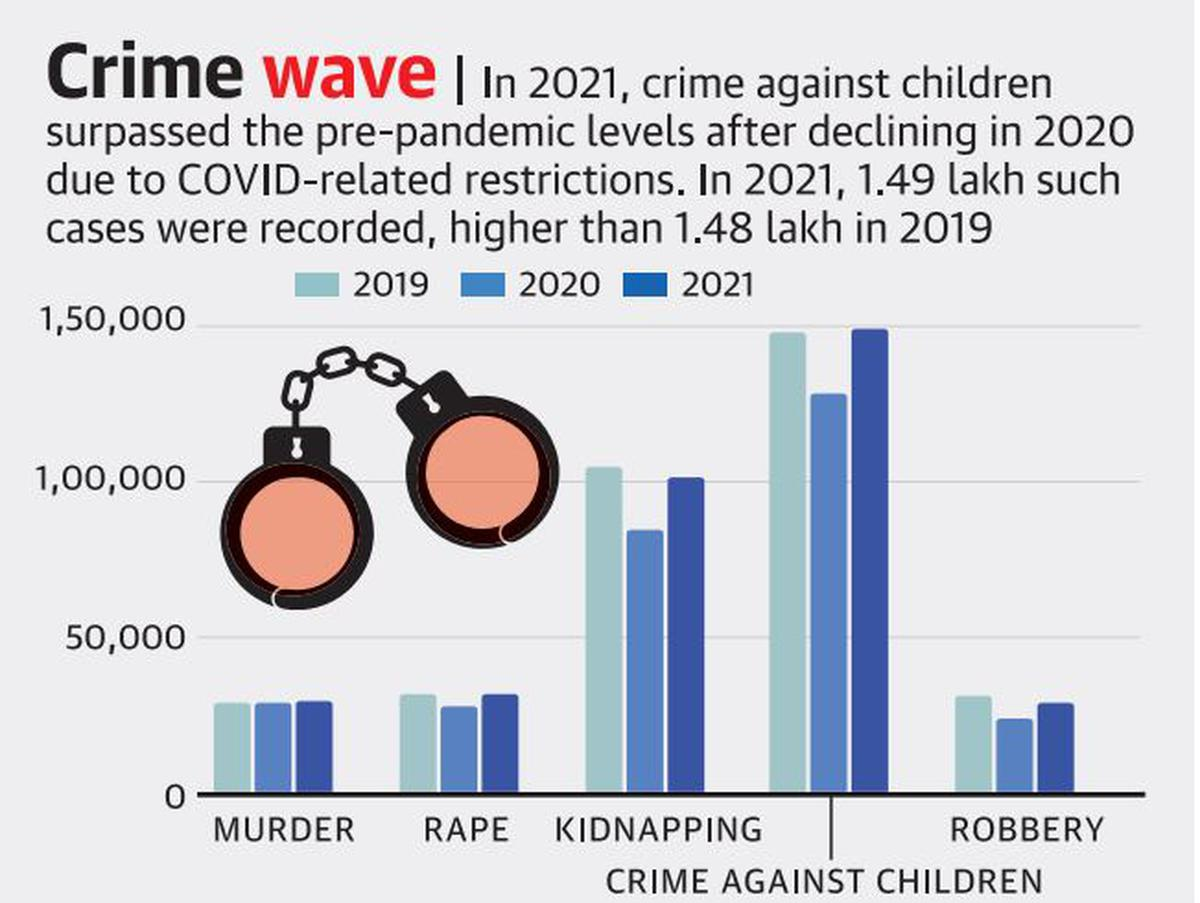
- Crime Against Children:
- Crime against children surpassed the pre-pandemic levels after declining in 2020 due to Covid-related restriction.
- In 2021, 1.49 lakh such cases were recorded, higher than 1.48 lakh in 2019.
- Sikkim has the highest rate of sexual offences against children followed by Kerala, Meghalaya, Haryana and Mizoram.
- Rape cases:
- Covid-19 Violations Dips:
- The decline in overall crimes in 2021 can be attributed to a sharp decrease in cases registered under “disobedience to order duly promulgated by a public servant (Section 188 of IPC).
- Such cases were registered mainly over violations of COVID-19 norms. They were also recorded under ‘Other IPC Crimes’ and ‘Other State Local Acts.’
- The number of cases filed under Section 188 of the IPC has almost halved from 6.12 lakh cases in 2020 to 3.22 lakh in 2021.
- The decline in overall crimes in 2021 can be attributed to a sharp decrease in cases registered under “disobedience to order duly promulgated by a public servant (Section 188 of IPC).
What is the National Crime Records Bureau?
- About:
- NCRB, headquartered in New Delhi, was set-up in 1986 under the Ministry of Home Affairs to function as a repository of information on crime and criminals so as to assist the investigators in linking crime to the perpetrators.
- It was set up based on the recommendations of the National Police Commission (1977-1981) and the MHA’s Task Force (1985).
- Functions:
- The Bureau has been entrusted to maintain National Database of Sexual Offenders (NDSO) and share it with the States/UTs on regular basis.
- NCRB has also been designated as the Central Nodal Agency to manage technical and operational functions of the ‘Online Cyber-Crime Reporting Portal’ through which any citizen can lodge a complaint or upload a video clip as evidence of crime related to child pornography, rape/gang rape.
- The responsibility of implementation of the Inter-operable Criminal Justice System (ICJS) has also been given to the NCRB.
- ICJS is a national platform for enabling integration of the main IT system used for delivery of Criminal Justice in the cuntry.
- It seeks to integrate the five pillars of the system viz Police (through Crime and Criminal Tracking and Network Systems), e-Forensics for Forensic Labs, e-Courts for Courts, e-Prosecution for Public Prosecutors and e-Prisons for Prisons.
- Major Publications:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Q. Why do some of the most prosperous regions of India have an adverse sex ratio for women? Give your arguments. (2014)


Ethics
Civil Servants and Social Media
For Mains: Pros and Cons related to the use of Social Media by Civil Servants
Why in News?
Several civil servants-retired and serving-even advocated some sort of restrictions on social media accounts of civil servants as they may hinder work.
What are the Pros and Cons related to the use of Social Media by Civil Servants?
- Pros:
- Accessible to the Common People:
- Civil servants have become accessible to the common people and public service delivery issues have been resolved through the use of social media.
- Created Positive outlook:
- Social media has also created a positive outlook towards an institution long perceived as opaque and inaccessible.
- Increased Awareness:
- Social media has increased awareness among people about government policies and programmes.
- Opportunity to Shape Public Discourse:
- It provides an opportunity for bureaucrats to shape the public discourse and engage with the public while being politically neutral.
- The use of social media helps minimise blind obedience among bureaucrats at a time when politicians tend to receive the advice they want to hear from bureaucrats.
- Accessible to the Common People:
- Cons:
- Anonymity:
- Anonymity has been a hallmark of Westminster bureaucracies, including in India.
- Public service anonymity is the convention that ministers answer to Parliament and to the public for government actions without naming the public servants who provided advice or who carried out the administrative action.
- In a world where public governance has become the norm, remaining habitually anonymous is counterproductive.
- Anonymity has been a hallmark of Westminster bureaucracies, including in India.
- Dominance of Values:
- Further, values are becoming more dominant than facts in public policymaking.
- And both values and facts are getting reshaped due to fake news and systematic propaganda within public policy circles as well.
- As a result, the bureaucracy, which is expected to serve as a repository of facts and epitome of public values, shouldn't be expected to govern privately.
- Institutionalisation of Social Media:
- The use of social media is gradually getting institutionalised in many Westminster system-based countries.
- During the Brexit debate in the U.K., many civil servants shaped public debate through the use of social media even while remaining politically neutral.
- In India, civil servants haven’t reflected on this aspect of digital bureaucracy.
- Anonymity and opaqueness have already been watered down through the Right to Information Act of 2005, but they continue to be prominent features.
- Accessibility and Accountability:
- In India, the role of social media in bureaucracy has taken a different direction.
- Social media is getting used by civil servants for self-promotion.
- Through their selective posts and promotion of these posts by their social media fans, civil servants create a narrative of their performance, which is justified in the name of accessibility and accountability.
- There is a wrong notion getting entrenched in the public consciousness that social media is the way to access civil servants and make them accountable.
- Anonymity:
Way Forward
- Improving Public Policy:
- Bureaucrats should use social media to improve public policies. If they don’t use social media appropriately, their role as independent advisers stands threatened.
- Social media may have improved accessibility and accountability, but it is important to note that civil servants are at an advantage to share the information they want and respond to those they want.
- It is not a formal set-up where accessibility and accountability are based on uniformity of treatment.
- Social media accountability is no alternative to institutional and citizen-centric accountability.
- It is, in fact, partly unethical to use social media during office hours and justify it when some people who have travelled long distances are waiting outside the office.
- Use of Social Media to bring Facts to Light:
- It is high time that not only should social media be used to bring forth facts but the achievements also need to be road-showed.
- This is a part of the larger context to combat the negativity that seems to be becoming all pervasive.
- #Nexusofgood is a movement in that direction, which is a movement to identify, understand, appreciate, replicate and scale good work that is being done by civil servants and society as a whole.
- The idea is to evolve an alternative narrative to the negativity that is becoming all pervasive in social media and other mediums of communication. Such negativity is impacting the thoughts and actions of a large number of people.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. ‘The current internet expansion has instilled a different set of cultural values which are often in conflict with traditional values.’ Discuss. (2020)


Governance
OTT Platforms
For Prelims: OTT Platforms, Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules 2021
For Mains: Increasing importance of OTT Platforms and Its Implications
Why in News?
Recently, a report was released by SBI Research, which said that the OTT (Over-The-Top) market is set to become a Rs 12,000-crore industry by 2023, up from Rs 2,590 crore in 2018.
What are the Findings?
- Statistics:
- The OTT market is expected to reach Rs 11,944 crore by 2023, up from Rs 2,590 crore in 2018, logging in a compound annual growth of 36%.
- OTT has already chipped away 7-9 % of the entertainment industry share and revenue, and is consistently growing with over 40-odd players and offering original media content in all languages.
- There are over 45 crore OTT subscribers today in the country and this is expected to reach 50 crores by end-2023.
- The pay-per-view segment stood at 3.5 crore in 2018 and is on course to touch 8.9 crore this year and touch 11.7 crore in 2027.
- Pay-per-view is a pay television or webcast program that allows viewers to buy activities to watch on a private telecast.
- Video downloads were 4.2 crore and 7.7 crore, 8.6 crore, while video streaming at 1.9 crore, 6.8 crore, and 10.8 crore, respectively during this period.
- Growth Drivers:
- This strong growth is led by affordable high-speed mobile Internet, doubling of Internet users, increased adoption of digital payments and discounted price offered by global players.
- Covid-led lockdowns which completely shut cinemas.
- Implications:
- This may lead to a repeat of the sudden death of the VCR/VCP/DVD industry that boomed in the 1980s, with the exponential rise of multiplexes since the early 2000s across metro/urban areas.
- It can be noted that the 1980s saw the exponential rise in video cassette recorders/players (VCRs/VCPs) that for the first time challenged the established modes and models of viewing a movie.
- The rise of OTT is expected to eat into cinemas' profits as over 50 % of the people use OTTs more than 5 hours a month.
- It is expected that OTT platforms' expansion into education, health, and fitness will additionally cement its future.
- It has unlocked new routes for content creators, and the audience has begun to understand it as more than just a medium of enjoyment.
- This may lead to a repeat of the sudden death of the VCR/VCP/DVD industry that boomed in the 1980s, with the exponential rise of multiplexes since the early 2000s across metro/urban areas.
What are OTT platforms?
- OTT, or over-the-top platforms, are audio and video hosting and streaming services which started out as content hosting platforms, but soon branched out into the production and release of short movies, feature films, documentaries and web-series themselves.
- These platforms offer a range of content and use artificial intelligence to suggest to users the content they are likely to view based on their past viewership on the platform.
- Most OTT platforms generally offer some content for free and charge a monthly subscription fee for premium content which is generally unavailable elsewhere.
- Premium content is usually produced and marketed by the OTT platform themselves, in association with established production houses which historically have made feature films.
- Examples: Netflix, Disney+, Hulu, Amazon Prime Video, Hulu, Peacock, CuriosityStream, Pluto TV, and so many more.
What are the laws regulating OTT platforms?
- In February 2022, the government had notified the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules 2021 to regulate OTT platforms.
- The rules establish a soft-touch self-regulatory architecture with a Code of Ethics and three-tier grievance redressal mechanism for OTT platforms.
- Every publisher should appoint a Grievance Officer based in India for receiving and redressing grievances in 15 days.
- Also, every publisher needs to become a member of a self-regulating body. Such a body will have to register with the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting and address grievances that have not been resolved by the publisher within 15 days.
- The Ministry of Information Broadcasting and the Inter-Departmental Committee constituted by the Ministry constitute the third-tier Oversight Mechanism
- They provide for self-classification of the content without any involvement of Central Board of Film Certification.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Q. COVID-19 pandemic has caused unprecedented devastation worldwide. However, technological advancements are being availed readily to win over the crisis. Give an account of how technology was sought to aid management of the pandemic. (2020)


International Relations
Maritime Security
For Prelims: Maritime Security, Yuan Wang 5, Government’s Initiatives
For Mains: Significance of Maritime Security, Challenges in Maritime Security, Government’s Initiatives
Why in News?
Recently, Sri Lanka’s envoy in India said India-Sri Lanka should build a framework to discuss maritime concerns like the Chinese satellite and missile tracking ship, the Yuan Wang 5 in Hambantota Port.
What is Yuan Wang 5?
- Yuan Wang 5:
- It is a third-generation vessel of the Yuan Wang series that entered service in 2007.
- This series of ships include "space tracking ships involved in supporting the manned space programme".
- It has the ability to track satellites and intercontinental missiles.
- Hambantota Port:
- Hambantota International Port Group is a Public Private Partnership and a Strategic Development Project between the Government of Sri Lanka and China Merchants Port Holdings (CMPort).
- This port was given to China by Sri Lanka on a 99-year lease after Sri Lanka failed to repay Chinese loans.
- It is seen as a case of Chinese "debt trap" Diplomacy.
What is the need for Maritime Security in India?
- About:
- Maritime security doesn’t have a commonly agreed definition.
- It classifies issues in the maritime domain comprising national security, marine environment, economic development, and human security.
- Besides the world's oceans , it also deals with regional seas, territorial waters, rivers and ports.
- Maritime security doesn’t have a commonly agreed definition.
- Significance:
- Maritime security is of utmost significance to the world community as there are maritime concerns ranging from piracy at sea to illegal immigration and weapon smuggling.
- It also deals with threats of terrorist attacks and environmental catastrophes.
- For India, maritime security is an important aspect of national security as it has a coastline of over 7,500 km.
- With advancement in technology, physical threats in the maritime region have now been overshadowed by technological threats.
- India’s exports and imports have remained mostly across the shipping lanes of the Indian Ocean. Therefore, securing Sea Lanes of Communication (SLOCs) have been an important issue for India in the 21st century.
- Maritime security is of utmost significance to the world community as there are maritime concerns ranging from piracy at sea to illegal immigration and weapon smuggling.
- Chinese presence:
- In 2019, the Chinese research vessel Shiyan 1, was seen near the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- In August 2020, in the middle of the ongoing conflict in eastern Ladakh on the Sino-Indian border, China sent its Yuan Wang class research vessel into the Indian Ocean.
What are India’s Initiatives for Maritime Security?
- Security and Growth for All (SAGAR) Policy:
- India’s SAGAR policy is an integrated regional framework, unveiled by Indian Prime Minister during a visit to Mauritius in March 2015. The pillars of SAGAR are:
- India’s role as a net security provider in the Indian Ocean region (IOR).
- India would continue to enhance the maritime security capacities and economic resilience of friendly countries in IOR.
- A more integrated and cooperative focus on the future of the IOR, which would enhance the prospects for the sustainable development of all countries in the region.
- The primary responsibility for peace, stability and prosperity in the IOR would be on those “who live in this region”.
- India’s SAGAR policy is an integrated regional framework, unveiled by Indian Prime Minister during a visit to Mauritius in March 2015. The pillars of SAGAR are:
- Mission SAGAR:
- Launched in May 2020, 'Mission Sagar’ was India’s initiative to deliver Covid-19 related assistance to the countries in the Indian Ocean Littoral states. The countries included were Maldives, Mauritius, Madagascar, Comoros and Seychelles.
- Under ‘Mission Sagar’, the Indian Navy has been deploying its ships to send medical and humanitarian aid to the counties in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) and beyond.
- Launched in May 2020, 'Mission Sagar’ was India’s initiative to deliver Covid-19 related assistance to the countries in the Indian Ocean Littoral states. The countries included were Maldives, Mauritius, Madagascar, Comoros and Seychelles.
- Abiding by the International Law:
- India accepted an United Nations Convention for the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) tribunal award on the maritime boundary arbitration between India and Bangladesh.
- It envisaged contributing a new impulse to effective international economic cooperation among the littoral states of the Bay of Bengal (BIMSTEC).
- Data Sharing:
- Sharing data on threats to commercial shipping is an important component of enhancing maritime security.
- In this context, India established an International Fusion Centre (IFC) for the Indian Ocean region in Gurugram in 2018.
- IFC is jointly administered by the Indian Navy and Indian Coast Guard.
- IFC serves the objective of generating Maritime Domain Awareness on safety and security issues.
Way Forward
- India to Adopt Multi-Pronged Approach:
- For India, only a robust military strategy to counter China is not enough, it will have to be a multipronged approach including infrastructure component, the technology related aspect.
- In the Indian Ocean, India must maintain its preeminence and assertiveness, deter China from operating in regions that are significant to India.
- India must cooperate and improve ties with its partners to gain an influence over the Pacific region because it is where China is highly unstable and sensitive.
- India’s maritime policies have to be mated against China.
- Matching China’s Levels of Infrastructure Projects:
- China is planning to build a port in Israel, antagonizing the USA.
- It has ports in Djibouti in Africa and also in Gwadar in Pakistan near Iran and its Belt and Road Initiative has its reach in Europe.
- Indian strategy will have to match the Chinese level of the effort which it is making in the African countries by building infrastructures.
- Development of Indian infrastructure is essential for the country's economic development and growth. As India adopted a growth-led economic policy, India needs to develop our maritime infrastructure, be it in developing our ports and harbours, connectivity, logistics etc.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following in respect of Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS). (2017)
- Inaugural IONS was held in India in 2015 under the chairmanship of the Indian Navy.
- IONS is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime co-operation among navies of the littoral states of the Indian Ocean Region.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Explanation:
- The ‘Indian Ocean Naval Symposium’ (IONS) is a voluntary initiative that seeks to increase maritime cooperation among navies of the littoral States of the Indian Ocean Region by providing an open and inclusive forum for discussion of regionally relevant maritime issues. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- It provides a forum to increase maritime security cooperation, and promote friendly relationships among the member nations.
- The inaugural IONS-2008 was held in New Delhi, India in Feburary, 2008. The Chief of the Naval Staff, Indian Navy was designated as the Chairman of IONS for the period 2008-10. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q1. Project ‘Mausam’ is considered a unique foreign policy initiative of Indian government to improve relationship with its neighbours. Does the project have a strategic dimension? Discuss. (2015)
Q2. With respect to the South China sea, maritime territorial disputes and rising tension affirm the need for safeguarding maritime security to ensure freedom of navigation and overflight throughout the region. In this context, discuss the bilateral issues between India and China. (2014)


Geography
Pakistan’s Devastating Floods
For Prelims: Geographical Phenomena, Flood, Trade between India and Pakistan.
For Mains: Causes of floods, Impact on life and economy.
Why in News?
India will be extending humanitarian assistance to Pakistan to deal with the Devastating Flood that occurred because of Pakistan’s Monster Monsoon.
- The climate crisis is the prime reason for the devastating scale of flooding in Pakistan, which has killed more than 1,000 people and affected 30 million.
What is the Indian Assistance to Pakistan?
- The aid will be the first time since 2014 that India will be extending aid to Pakistan on account of a natural disaster.
- In the past, India extended assistance to Pakistan for the floods in 2010, and for the earthquake in 2005.
How has been the Bilateral Trade between India and Pakistan?
- In 2021, Pakistan allowed the import of cotton and sugar from India, partially reversing a two-year old decision to suspend all trade with India.
- The decision to cancel trade was taken by the Pakistan government in August, 2019, days after the Indian government amended Article 370 and reorganised Jammu and Kashmir.
- Over the years, India has had a trade surplus with Pakistan, with much less imports than exports and trade has always been linked to politics.
- India’s exports to Pakistan fell around 16% to USD 1.82 billion in 2016-17 as compared to 2015-16 after relations deteriorated in the aftermath of the Uri terror attack and the Indian Army’s surgical strikes on militant launchpads in Pakistan-occupied Kashmir in 2016.
- Despite continuing tensions, trade between the two countries grew marginally in subsequent years.
What caused the Severe Flood in Pakistan?
- Extremely Wet monsoon:
- The current flood is a direct result of an extremely wet monsoon season this year.
- The same southwest monsoon that brings the bulk of India’s annual rainfall causes rain in Pakistan as well.
- The monsoon season in Pakistan, however, is a little shorter than in India. That is because the rain-bearing monsoon winds take time to travel northward from India into Pakistan.
- There’s been a 400% increase in average rainfall in areas like Baluchistan and Sindh, which led to extreme flooding.
- Extreme Heat:
- In May 2022, Pakistan consistently saw temperatures above 45 degrees Celsius (113 Fahrenheit).
- Warmer air holds more moisture — about 7% more per degree Celsius (4% per degree Fahrenheit) — and that eventually comes down, in this case in torrents.
- Instead of just swollen rivers flooding from extra rain, Pakistan is hit with another source of flash flooding.
- The extreme heat accelerates the long-term glacier melting then water speeds down from the Himalayas to Pakistan in a dangerous phenomenon called glacial lake outburst floods.
- ENSO:
- The El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) appears to be in its La Niña phase.
- “La Niña is behaving very strongly in some metrics and is a significant factor for enhancing monsoonal rains.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. The frequency of urban floods due to high intensity rainfall is increasing over the years. Discussing the reasons for urban floods, highlight the mechanisms for preparedness to reduce the risk during such events. (2016)


International Relations
Falkland Islands
For Prelims: Location of Falkland Island and its Neighborhood, Conflict of Falkland Islands.
For mains: Effect of Policies & Politics of Countries on India's Interests, India and its Neighborhood, Conflict of Falkland Islands.
Why in News?
Recently, India extended support to Argentina's campaign to restart international negotiation on the Falklands Territorial Issue.
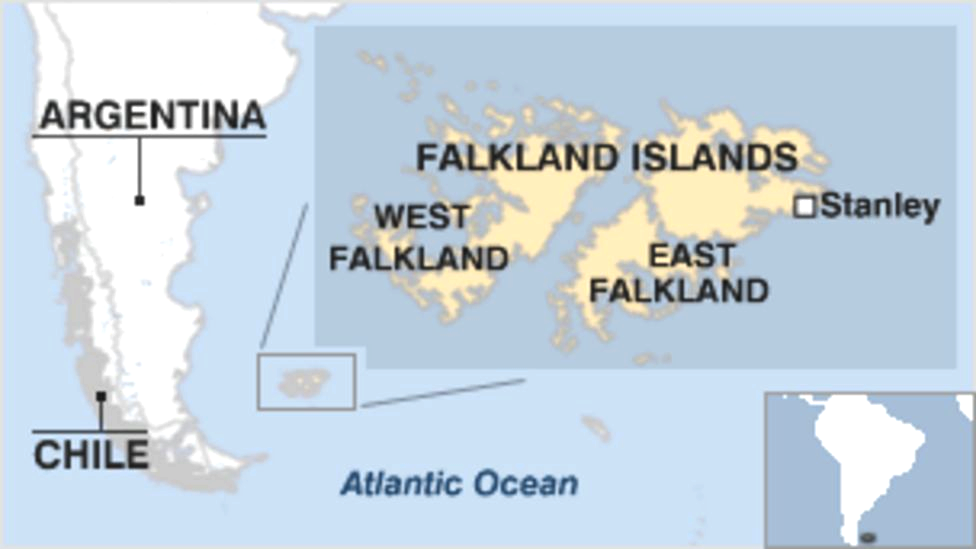
Where is Falkland Island?
- Falkland Islands, also called Malvinas Islands or Spanish Islas Malvinas, internally self-governing overseas territory of the United Kingdom in the South Atlantic Ocean.
- It lies about 300 miles northeast of the southern tip of South America and a similar distance east of the Strait of Magellan.
- The capital and major town is Stanley, on East Falkland, there are also several scattered small settlements as well as a Royal Air Force base that is located at Mount Pleasant.
- The two main islands, East Falkland and West Falkland, and about 200 smaller islands.
- The government of the Falkland Islands also administers the British overseas territory of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, including the Shag and Clerke rocks.
What is the History of the Falkland Islands?
- The British, in 1765, were the first to settle West Falkland, but they were driven off in 1770 by the Spanish, who had bought out the French settlement about 1767.
- The British outpost on West Falkland was restored in 1771 after threat of war, but then the British withdrew from the island in 1774 for economic reasons, without renouncing their claim to the Falklands.
- Spain maintained a settlement on East Falkland (which it called Soledad Island) until 1811.
- In 1820 the Argentina Government, which had declared its independence from Spain in 1816, proclaimed its sovereignty over the Falklands.
- In 1831 the US warship destroyed the Argentine settlement on East Falkland in reprisal for the arrest of three US ships that had been hunting seals in the area.
- In early 1833, a British force expelled the few remaining Argentine officials from the island without firing a shot. In 1841, a British civilian lieutenant governor was appointed for the Falklands, and by 1885 a British community of some 1,800 people on the islands was self-supporting.
- Argentina regularly protested Britain’s occupation of the islands.
- After World War II (1939-45) the issue of sovereignty over the Falkland Islands shifted to the United Nations (UN) when, in 1964, the islands’ status was debated by the UN committee on decolonization.
- In 1965, the UN General Assembly approved a resolution inviting Britain and Argentina to hold discussions to find a peaceful solution to the dispute.
- These protracted discussions were still proceeding in February 1982, but in April Argentina’s military government invaded the Falklands.
- This act started the Falkland Islands War, which ended 10 weeks later with the surrender of the Argentine forces at Stanley to British troops who had forcibly reoccupied the islands.
- Although Britain and Argentina reestablished full diplomatic relations in 1990, the issue of sovereignty remained a point of contention.
- In the early 21st century Britain continued to maintain some 2,000 troops on the islands.
- In January 2009 a new constitution came into effect that strengthened the Falklands’ local democratic government and reserved for the islanders their right to determine the territory’s political status. In a referendum held in March 2013, islanders voted nearly unanimously to remain a British overseas territory.
What are the Bases of Different Claims on the Island?
- Argentina based its claim to the Falklands based on an official document of 1493 modified by the Treaty of Tordesillas (1494), by which Spain and Portugal had divided the New World between themselves, on succession from Spain, on the islands’ proximity to South America, and on the need to end a colonial situation.
- Britain based its claim on its “open, continuous, effective possession, occupation, and administration” of the islands since 1833 and its determination to apply to the Falklanders the principle of self-determination as recognized in the United Nations Charter.
- Britain asserted that, far from ending a colonial situation, Argentine rule and control of the lives of the Falklanders against their wishes would in fact create one.


Governance
Integration of ODOP with ONDC
For Prelims: UPSC, IAS, One District One Product, Open Network for Digital Commerce, Initiatives Related to Food Processing Sector, Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro food processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme, Atma Nirbhar Abhiyan, Self Help Groups (SHGs).
For Mains: Significance of One District One Product Initiatiative, Ways to Improve Agricultural Marketing.
Why in News?
Recently, Union Minister called for the integration of One District One Product (ODOP) initiative with Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC).
- ONDC would help in further expanding the frontiers of ODOP by bringing buyers and sellers together on a democratic platform.
- It will help bring prosperity to the remotest regions of the nation.
What is the ODOP Approach?
- About:
- ODOP is an approach adopted under the Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro food processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme.
- It will provide for the framework for value chain development and alignment of support infrastructure of the PMFME scheme. There may be more than one cluster of ODOP products in one district.
- There may be a cluster of ODOP products consisting of more than one adjacent district in a State.
- The States would identify food products for districts keeping in view the existing clusters and availability of raw material.
- The ODOP could be a perishable produce based or cereal based or a food item widely produced in an area. E.g., mango, potato, pickle, millet-based products, fisheries, poultry, etc.
- Certain other traditional and innovative products including waste to wealth products could be supported under the Scheme.
- For example, honey, minor forest products in tribal areas, traditional Indian herbal edible items like turmeric, amla, haldi, etc.
- Significance:
- Adopting a cluster approach will help in the development of specific agriproducts in districts having a comparative advantage.
- It would lead to easing in providing common facilities and other support services.
What is the PMFME Scheme?
- About:
- Launched under Atma Nirbhar Abhiyan, Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro food processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme aims to enhance the competitiveness of existing individual micro-enterprises in the unorganised segment of the food processing industry and to promote formalisation of the sector and provide support to Farmer Producer Organisations, Self Help Groups, and Producers Cooperatives along their entire value chain.
- The scheme adopts the One District One Product (ODOP) approach to reap the benefit of scale in terms of procurement of inputs, availing common services and marketing of products.
- It is being implemented over a period of five years from 2020-21 to 2024-25.
- Funding:
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme with an outlay of Rs. 10,000 crore.
- The expenditure under the scheme would be shared in 60:40 ratio between Central and State Governments, in 90:10 ratio with North Eastern and Himalayan States, 60:40 ratio with UTs with legislature and 100% by Centre for other UTs.
Way Forward
- ODOP should form a part of international exhibitions, events, meetings and conferences to enhance international exposure of products.
- There is a need for simplifying, streamlining and fast tracking the GI tagging process.
- Flagship programs of the government such as Startup India, Make in India, district as export hubs etc. should be converged with the vision of ODOP.
- Students of eminent institutions like NIFT, NID and IIFT should engage to find creative methods to amplify ODOP.
- Branding of the ODOP products, most of which are natural and eco-friendly as sustainable and good for the planet should be one of the agendas.
- The list of Geographical Indication (GI) tagged products needs to be expanded by simplifying, streamlining and fast tracking the GI tagging process.


Important Facts For Prelims
Russia-China Cooperation in the Arctic
Why in News?
Recently, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) Warned Russia's Military built up and Chinese interest in Arctic Region.
- As per various reports, China has deepening strategic partnership with Russia in the Arctic Region.
What are the Concerns Regarding the Cooperation?
- Russian Military Build-up:
- Russia has set up a new Arctic Command and has opened hundreds of new and former Soviet-era Arctic military sites, including airfields and deep-water ports.
- Significant Russian military build-up with new bases, new weapons systems and also using the High North as a test bed for their most advanced weapons, including hypersonic missiles.
- Russia has set up a new Arctic Command and has opened hundreds of new and former Soviet-era Arctic military sites, including airfields and deep-water ports.
- China’s Claim:
- China has declared itself a near-Arctic state. Further, China plans to build the world’s largest icebreaker and is spending tens of billions of dollars on energy, infrastructure and research projects in the north.
- Climate Change:
- As climate change thaws more ice, it is predicted to open up more waterways enabling deeper penetration in the area.
- Further, these channels can be exploited by nations as they explore new shipping routes that could be a gamechanger in trade, cutting down longer and costlier journeys around the globe.
- As climate change thaws more ice, it is predicted to open up more waterways enabling deeper penetration in the area.
- Conflict with US’s Interest:
- While China is not an Arctic nation, its deepening strategic partnership with Russia and increased cooperation in the Arctic has worried the US which thinks this pairing is against American values and interests.
Is there any cooperation among Nations in the Arctic?
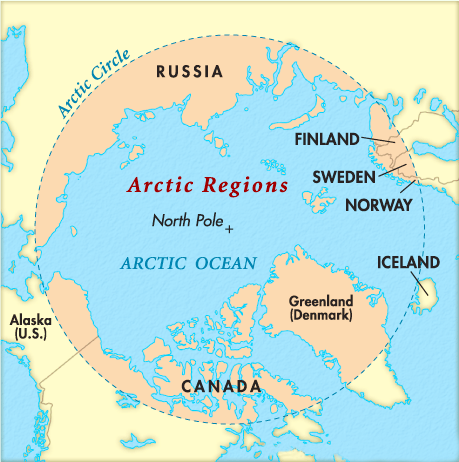
- There are eight Arctic nations - The US, Canada, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, and Russia.
- These are part of the Arctic Council, an intergovernmental forum that was formed to promote cooperation in the region.
- On three occasions, the Arctic States have negotiated legally binding agreements. these are -
- Agreement on Cooperation on Aeronautical and Maritime Search and Rescue in the Arctic (signed 2011),
- Agreement on Cooperation on Marine Oil Pollution Preparedness and Response in the Arctic (signed 2013),
- Agreement on Enhancing International Arctic Scientific Cooperation (signed 2017).
What is the Relevance of Arctic Region for India?
- About:
- India’s interests in the Arctic region are scientific, environmental, commercial as well as strategic.
- India became the observer of Arctic Council in 2013 and its membership as an observer was renewed in 2018 for another five years.
- The National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India, is the nodal agency for India’s Polar research programme, which includes Arctic studies.
- India’s Ministry of External Affairs provides the external interface to the Arctic Council.
- Research Station:
- India’s engagement with the Arctic dates back to 1920 with the signing of the Svalbard Treaty in Paris.
- Since July 2008, India has a permanent research station in the Arctic called Himadari at NyAlesund, Svalbard Area in Norway.
- It has also deployed a multi-sensor moored observatory called IndARC in the Kongsfjorden fjord since 2014.
- Impacts on India:
- The Arctic influences atmospheric, oceanographic and biogeochemical cycles of the earth’s ecosystem.
- Moreover, the Arctic is vulnerable to climate change and global warming.
- The effects are manifested by the loss of sea ice, ice caps, and warming of the ocean and atmosphere.
- It will lead to lowering of salinity levels, rising temperature differential between land and oceans in the tropical regions, drying of subtropical areas and increase in precipitation at higher latitudes.
- The Arctic influences atmospheric, oceanographic and biogeochemical cycles of the earth’s ecosystem.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following countries: (2014)
- Denmark
- Japan
- Russian Federation
- United Kingdom
- United States of America
Which of the above are the members of the ‘Arctic Council’?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 4 and 5
(d) 1, 3 and 5
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- The ‘Arctic Council’ is the leading intergovernmental forum promoting cooperation, coordination and interaction among the Arctic States, Arctic indigenous communities and other Arctic inhabitants on common Arctic issues, in particular on issues of sustainable development and environmental protection in the Arctic.
- The 1996 Ottawa Declaration established the ‘Arctic Council’. The Declaration lists the following countries as members of the Arctic Council: Canada, the Kingdom of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, the Russian Federation, Sweden and the United States. Hence, 1, 3 and 5 are correct.
- The Arctic Council’s mandate, as articulated in the Ottawa Declaration, explicitly excludes military security.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. How do the melting of the Arctic ice and glaciers of the Antarctic differently affect the weather patterns and human activities on the Earth? Explain. (2021)


Important Facts For Prelims
Registry to Check Bank Fraud
Why in News?
Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) considering setting up a fraud registry to create a database of fraudulent websites, phones and various methods used by fraudsters.
What are the Key Highlights of the Fraud Registry?
- About:
- The Registry’s database will help prevent fraudsters from repeating the fraud as the websites or phone numbers would be blacklisted.
- The Payment system participants will be provided access to this registry for near-real-time fraud monitoring.
- Create Awareness:
- The aggregated fraud data will be published to educate customers on emerging risks.
- Ombudsman Scheme:
- Under this scheme around 4.18 lakh complaints were received during 2021-22 as against 3.82 lakh in the previous year.
- About 97.9% of cases were cleared in 2021 as compared to 96.5% in 2020.
- About 39% of the complaints received by the RBI during the last financial year were related to digital transactions.
- Other Related Initiatives:
- The integrated consumer grievance redressal mechanism for addressing service deficiencies in banking, NBFCs and digital payment systems.
- One Nation One Ombudsman:
- Prime Minister launched the One Nation One Ombudsman to make the alternate dispute redressal mechanism simpler and more responsive to the customers of regulated entities.
What is Banking Ombudsman Scheme?
- About:
- The scheme was launched for resolving customer grievances in relation to services provided by entities regulated by RBI in an expeditious and cost-effective manner.
- It amalgamates three ombudsman schemes of RBI - banking ombudsman scheme of 2006, ombudsman scheme for NBFCs of 2018 and ombudsman scheme of digital transactions of 2019.
- The unified ombudsman scheme will provide redress of customer complaints involving deficiency in services rendered by RBI regulated entities viz. banks, NBFCs (Non banking Financial Companies) and pre-paid instrument players if the grievance is not resolved to the satisfaction of the customers or not replied within a period of 30 days by the regulated entity.
- It also includes non-scheduled primary co-operative banks with a deposit size of Rs 50 crore and above.
- The integrated scheme makes it a “One Nation One Ombudsman’ approach and jurisdiction neutral.
- The scheme was launched for resolving customer grievances in relation to services provided by entities regulated by RBI in an expeditious and cost-effective manner.
Who is an Ombudsman?
- A government official who deals with complaints made by ordinary people against public organizations. This concept of Ombudsman arrived from Sweden.
- It means an officer appointed by the Legislature to handle complaints against a service or administrative authority.
- In India an Ombudsman is appointed to resolve grievances in the following sectors.
- Insurance Ombudsman
- Income Tax Ombudsman
- Banking Ombudsman
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the institution of Banking Ombudsman in India, which one of the statements is not correct? (2010)
(a) The Banking Ombudsman is appointed by the Reserve Bank of India
(b) The Banking Ombudsman can consider complaints from Non-Resident Indians having accounts in India
(c) The orders passed by the Banking Ombudsman are final and binding on the parties concerned
(d) The service provided by the Banking Ombudsman is free of any fee
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- The Banking Ombudsman Scheme is an expeditious and inexpensive forum for bank customers for resolution of complaints relating to certain services rendered by banks. It was launched in 2006, and was recently amended in 2017.
- All Scheduled Commercial Banks, Regional Rural Banks and Scheduled Primary Co-operative Banks are covered under the Scheme.
- Banking Ombudsman is appointed by the Reserve Bank from among its officers of the rank of Chief General Manager or General Manager. They shall have tenure not exceeding 3 years at a time.
- Any person aggrieved by the final orders of the Banking Ombudsman can approach the Appellate Authority. The Appellate Authority is vested with the Deputy Governor of the RBI.
- The Banking Ombudsman can consider complaints from Non-Resident Indians having accounts in India in relation to their remittances from abroad, deposits and other bank-related matters.
- The service provided by the Banking Ombudsman is free of any fee.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer