Call for Safer and Healthier Working Environments: ILO
For Prelims: Safer and Healthier Working Environments, International Labour Organization, Asia-Pacific region, World Congress on Safety and Health at Work (WCSHW).
For Mains: Safer and Healthier Working Environments: ILO, Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
Why in News?
Recently, the ILO (International Labour Organization) has released a report titled ‘A Call for Safer and Healthier Working Environments’, which will be discussed at the 23rd World Congress on Safety and Health at Work (WCSHW) in Sydney, Australia.
- The WCSHW, first held in 1955, is one of the largest international conferences for work health and safety. It aims to connect global leaders in safety and harm prevention from over 120 countries.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Annual Deaths:
- Approximately 30 lakh (3 million) workers globally die each year due to work-related accidents and diseases.
- More than 63% of these deaths occur in the Asia-Pacific region.
- Major Causes of Deaths:
- Long working hours (55 hours or more per week) led to the most fatalities in 2016, accounting for nearly 7.45 lakh deaths.
- Exposure to occupational particulate matter, gases, and fumes resulted in around 4.5 lakh deaths.
- Occupational injuries caused approximately 3.63 lakh deaths.
- Fatal Occupational Injury Rate (FOIR):
- Sectors such as mining and quarrying, construction, and utilities were identified as the most hazardous globally based on fatal occupational injury rates.
- The FOIR is a statistical measure used to quantify the number of deaths resulting from work-related accidents or injuries within a specific occupational group, industry, or geographic region over a specified period.
- ILO Conventions:
- So far 79 out of the 187 member countries have ratified the ILO Occupational Safety and Health Convention, while 62 countries have ratified the Promotional Framework for Occupational Safety and Health Convention, 2006.
- India has not ratified both the conventions.Recently, in the wake of Uttarkashi tunnel incident , the Central Trade Unions had urged the Union government to ratify the conventions.
- So far 79 out of the 187 member countries have ratified the ILO Occupational Safety and Health Convention, while 62 countries have ratified the Promotional Framework for Occupational Safety and Health Convention, 2006.
- Work-Related Diseases:
- A significant portion of work-related deaths (26 lakh) is attributed to work-related diseases, including circulatory diseases, malignant neoplasms (Cancerous tumours), and respiratory diseases.
- Changing trends in diseases due to occupational exposure, such as increased cases of trachea, bronchus, and lung cancers attributable to chromium exposure, and rising cases of mesothelioma due to asbestos exposure.
- Decrease in Certain Health Risks:
- Deaths due to exposure to asthmagens and particulate matter, gases, and fumes have decreased by over 20%.
- Recommendations:
- ILO called for five categories of “Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work” for ensuring safety and health at work. These principles include:
- Freedom of association and the effective recognition of the right to collective bargaining
- Elimination of all forms of forced or compulsory labor
- Abolition of child labor
- Elimination of discrimination in respect of employment and occupation
- A safe and healthy working environment
- ILO called for five categories of “Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work” for ensuring safety and health at work. These principles include:
What is the International Labor Organization?
- It is the only tripartite United Nation (UN) agency. It brings together governments, employers and workers of 187 member States (India is a member), to set labour standards, develop policies and devise programmes promoting decent work for all women and men.
- It received the Nobel Peace Prize in 1969.
- It was established in 1919 by the Treaty of Versailles as an affiliated agency of the League of Nations and became the first affiliated specialized agency of the UN in 1946.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. International Labour Organization’s Conventions 138 and 182 are related to (2018)
(a) Child Labour
(b) Adaptation of agricultural practices to global climate change
(c) Regulation of food prices and food security
(d) Gender parity at the workplace
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- In 2017, the Union Cabinet, GoI approved ratification of the Minimum Age Convention, 1973 (No. 138) and the Worst Forms of Child Labour Convention, 1999 (No. 182) of the International Labour Organization (ILO).
- Convention No. 138: India is the 170th ILO Member state to ratify Convention No. 138, which requires state parties to set a minimum age under which no one shall be admitted to employment or work in any occupation, except for light work and artistic performances.
- Convention No. 182: India also became the ILO’s 181st Member state to ratify Convention No. 182. This calls for the prohibition and elimination of the worst forms of child labour, including slavery, forced labour and trafficking; the use of children in armed conflict; the use of a child for prostitution, pornography and in illicit activities (such as drug trafficking); and hazardous work.
- These all are in line with the Child Labour (Prohibition and Regulation) Amendment Act, 2016, which completely prohibits employment or work of children below 14 years in any occupation or process and also prohibits the employment of adolescents (14 to 18 years) in hazardous occupations and processes.
- Additionally, the Child Labour (Prohibition and Regulation) Central Rules, as recently amended, for the first time provide for a broad and a specific framework for the prevention, prohibition, rescue and rehabilitation of child and adolescent workers.
- With ratification of the two core ILO Conventions, India has ratified six out of eight core ILO Conventions. Four other conventions relate to abolition of forced labour, equal remuneration and no discrimination between men and women in employment and occupation.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Centre Exempts CERT-In from Ambit of RTI Act
For Prelims: Right to Information Act, 2005, Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In), Cyber Security
For Mains: Right to Information (RTI) Act, Transparency & Accountability, Cyber Security
Why in News?
The Centre, through the Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT), has recently issued a notification exempting the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) from the purview of the Right to Information Act, 2005.
- CERT-In, will now operate outside the scope of the RTI Act,2005 limiting public access to information about its activities and functioning.
How was CERT-In Exempted?
- The Centre has used its powers given under Section 24(2) of the RTI Act to exempt CERT-In from the purview of the transparency law.
- Section 24(2) of the RTI Act, 2005 allows the Central Government to change the Schedule by adding or removing intelligence or security organizations established by the Government.
- However, the subsection does not apply to the information pertaining to the allegations of corruption and human rights violations, not to the cases where such allegations are made.
- Moreover, the information related to the allegations of human rights violations can only be provided after the approval of the Central Information Commission.
- Section 24(2) of the RTI Act, 2005 allows the Central Government to change the Schedule by adding or removing intelligence or security organizations established by the Government.
- The Centre can amend the Second Schedule through a notification in the Official Gazette. However, every such notification shall be laid before each House of Parliament.
- Similar powers have been given to the state government under Sub-section 4 of Section 24 of the RTI Act.
- Using those powers, the Centre has included CERT-In in the Second Schedule of the RTI Act, alongside 26 other intelligence and security organizations that are already exempted from the Act.
- The list includes prominent intelligence and security organizations such as Intelligence Bureau, Directorate of Revenue Intelligence, Directorate of Enforcement, Narcotics Control Bureau, and others.
What is CERT-In?
- About:
- Functions of CERT-In:
- According to the Information Technology Amendment Act 2008, CERT-In has been designated to serve as the national agency to perform the following functions in the area of cyber security:
- Collection, analysis and dissemination of information on cyber incidents.
- Forecast and alerts of cyber security incidents.
- Emergency measures for handling cyber security incidents.
- Coordination of cyber incident response activities.
- Issue guidelines, advisories, vulnerability notes and whitepapers relating to information security practices, procedures, prevention, response and reporting of cyber incidents.
- Such other functions relating to cyber security as may be prescribed.
- According to the Information Technology Amendment Act 2008, CERT-In has been designated to serve as the national agency to perform the following functions in the area of cyber security:
- Importance for India:
- CERT-In is important for India because it helps to protect the country’s critical information infrastructure and digital assets from cyber-attacks.
- It also helps to enhance the cyber resilience and readiness of the country’s various sectors, such as government, defence, banking, telecom, etc.
- It also contributes to the national security and economic development of the country by promoting a safe and secure cyber environment.
What is the Right to Information Act, 2005?
- About:
- Enacted in 2005, the RTI Act is a legislative framework granting Indian citizens access to information held by public authorities.
- Its foundation lies in Article 19(1)(a) of the Constitution, ensuring freedom of speech and expression.
- The act replaced the Freedom of Information Act 2002.
- Constitutional Backing:
- Derived from Article 19(1)(a), the RTI Act is considered a fundamental right, as established in the Raj Narain vs. State of Uttar Pradesh case.
- Time Period and Exemptions:
- In normal course, information to an applicant is to be supplied within 30 days, or 48 hours if related to life or liberty.
- Section 8(1) outlines exemptions, covering national security, strategic state matters, foreign relations, and more.
- In normal course, information to an applicant is to be supplied within 30 days, or 48 hours if related to life or liberty.
- Implementation:
- The Public Information Office (PIO) is a pivotal component of the RTI Act’s implementation.
- A PIO is a designated officer within a public authority who acts as a bridge between citizens seeking information and the government organization holding that information.
- The Public Information Office (PIO) is a pivotal component of the RTI Act’s implementation.
- Appellate Authority:
- If dissatisfied with the PIO's response, citizens can appeal to the First Appellate Authority within the same public authority. Further appeals can be made to the Central or State Information Commission if needed.
- Recent Amendments in RTI Act:
- Amendment in 2023:
- Recently, section 44 (3) of the Digital Personal Data Protection Act 2023 modified Section 8 (1)(j) of the RTI Act, creating an exemption for all personal information from disclosure and removing the previously established exceptions that permitted the release of such information.
- Right to Information (Amendment) Act, 2019:
- Altered tenure and conditions of Chief Information Commissioner (CIC) and Information Commissioners (ICs).
- ICs' terms made subject to central government prescription (currently set for 3 years, not the previous fixed 5-year term).
- Salary, allowances and other service conditions of the CIC and an ICs (of centre as well as states) shall be such as prescribed by the central government.
- Eliminated provisions for deduction of pension or retirement benefits for previous government service at the time of CIC and ICs' appointment.
- Altered tenure and conditions of Chief Information Commissioner (CIC) and Information Commissioners (ICs).
- Amendment in 2023:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. The Right to Information Act is not all about citizens’ empowerment alone, it essentially redefines the concept of accountability.” Discuss. (2018)
Rat-Hole Mining
For Prelims: Rat-Hole Mining, Silkyara-Barkot Tunnel, National Green Tribunal (NGT).
For Mains: Rat-Hole Mining, Environmental pollution and degradation, Challenges Related to Indian Himalayan Region.
Why in News?
Recently, Rat Hole Mining method has been used to evacuate 41 workers who were trapped inside Uttarakhand's Silkyari tunnel.
What is Rat-Hole Mining?
- About:
- Rat hole mining is a method of extracting coal from narrow, horizontal seams, prevalent in Meghalaya.
- The term “rat hole” refers to the narrow pits dug into the ground, typically just large enough for one person to descend and extract coal.
- Once the pits are dug, miners descend using ropes or bamboo ladders to reach the coal seams. The coal is then manually extracted using primitive tools such as pickaxes, shovels, and baskets.
- Types:
- Side-Cutting Procedure: In the side-cutting procedure, narrow tunnels are dug on the hill slopes and workers go inside until they find the coal seam.
- The coal seam in the hills of Meghalaya is very thin, less than 2 m in most cases.
- Box-Cutting: In Box-cutting, a rectangular opening is made, varying from 10 to 100 sqm, and through that a vertical pit is dug, 100 to 400 feet deep.
- Once the coal seam is found, rat-hole-sized tunnels are dug horizontally through which workers can extract the coal.
- Side-Cutting Procedure: In the side-cutting procedure, narrow tunnels are dug on the hill slopes and workers go inside until they find the coal seam.
- Concerns:
- Rat hole mining poses significant safety and environmental hazards. The mines are typically unregulated, lacking safety measures such as proper ventilation, structural support, or safety gear for the workers.
- The process is not only perilous for the miners but also detrimental to the environment. Rat-hole mining has been linked to a host of ecological issues, such as the acidification of rivers, Land Degradation, Deforestation, and Water Pollution.
- The acidic runoff from these mines, known as Acid Mine Drainage (AMD), has been particularly harmful, degrading water quality and reducing biodiversity in affected water bodies.
- Despite attempts by authorities to regulate or ban such practices, they often persist due to economic factors and the absence of viable alternative livelihoods for the local population.
Why was Rat-Hole Mining Banned?
- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) banned rat-hole mining in 2014 for being unscientific, but the practice continues to be rampant.
- Several accidents have resulted in deaths of rat-hole miners in the Northeastern state.
- In 2018, 15 men involved in illegal mining were trapped inside a flooded mine. Only two bodies could be recovered in the course of the rescue operation that lasted for more than two months.
- Another such accident took place in 2021 when five miners were trapped in a flooded mine. Three bodies were found before rescue teams called off the operation after a month. Add to this the environmental pollution caused by this method.
- Mining, however, is a key source of revenue for the state government. The Manipur government has challenged the NGT ban, arguing that there is no other feasible mining option for the region.
- A panel appointed by Meghalaya High Court in 2022 found rat-hole mining continues unabated in Meghalaya.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. “In spite of adverse environmental impact, coal mining is still inevitable for development”. Discuss.(2017)
Fibre Optic Cables
For Prelims: Fibre Optic Cables, Optical Fibres, Charles Kao, Total Internal Reflection, National Mission on Quantum Technologies and Applications.
For Mains: Fibre Optic Cables, Evolution of Internet, Challenges in Fibreisation, Government’s Initiative.
Why in News?
With the increasing demand for high-speed internet connections Optical Fibres have been materialized into the present-day reality of high-speed data transmission.
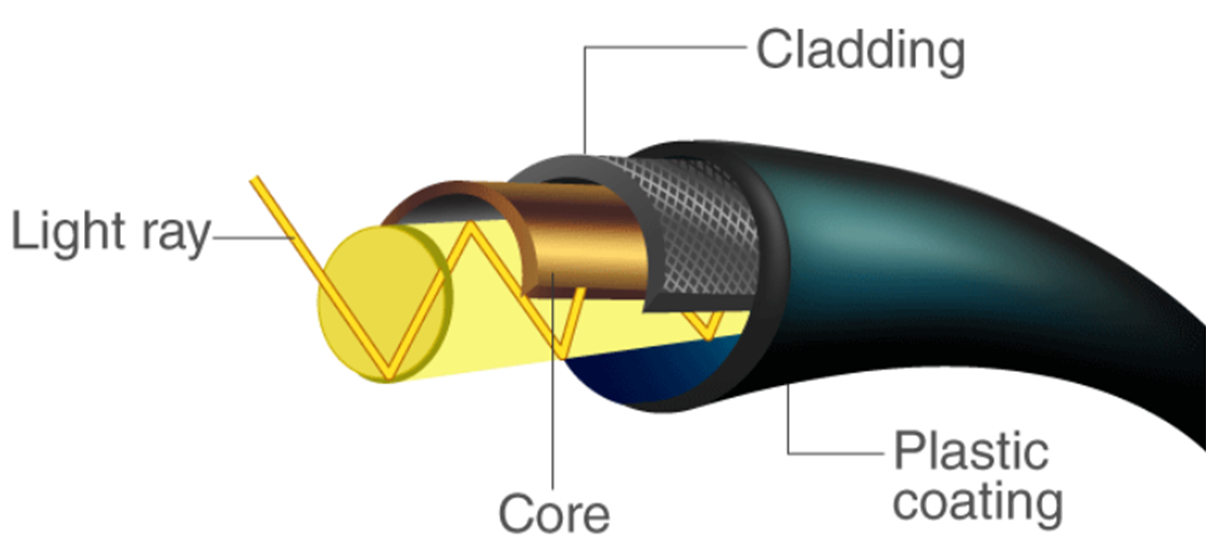
What is an Optical Fibre?
- About:
- Optical Fibres are thin, cylindrical strands composed of glass, with a diameter typically comparable to that of a human hair.
- These fibres possess the remarkable ability to transmit various forms of information, including text, images, audio, video, phone calls, and any data that can be digitized, across vast distances at speeds approaching that of light.
- They are strong, lightweight, and remarkably flexible, making them suitable for burial underground, submersion underwater, or coiling around a spool.
- Almost 60 years ago, physicist Charles Kao proposed the concept of using glass Fibres as a superior medium for telecommunications, superseding the prevalent copper wires.
- His groundbreaking contributions to Fibre optic communication earned him a share of the 2009 Nobel Prize in Physics.
- Working:
- Principle of Total Internal Reflection: The phenomenon of Total Internal Reflection (TIR) forms the basis for guiding light within optical Fibres.
- If light travels from a higher refractive index medium (like glass) to a lower one (such as air) at a specific angle, it may not exit the medium but be entirely reflected back within it. This phenomenon is called TIR.
- Signal Encoding: Information is encoded into optical signals as rapidly blinking light pulses, typically representing binary digits (zeros and ones).
- These optical signals are fed into one end of an optical Fibre, where they travel by reflecting and bouncing between the glass walls due to total internal reflection.
- Signal Transport: The optical Fibre carries the encoded signals across several kilometers without significant loss of signal integrity.
- At the destination, a receiver reproduces the encoded information from the transmitted optical signal.
- Principle of Total Internal Reflection: The phenomenon of Total Internal Reflection (TIR) forms the basis for guiding light within optical Fibres.
- Benefits:
- High Speed: Fibre provides more bandwidth and has standardized performance up to 10 Gbps and beyond, something that it is impossible to achieve when using copper.
- More bandwidth means that Fibre can carry more information with far greater efficiency than copper wire.
- Range of Transmission: Since data travels in the form of light in Fibre-optic cables, very little signal loss occurs during transmission and data can move at higher speeds and greater distances.
- Not susceptible to interference: Fibre-optic cable is also much less susceptible to noise and electromagnetic interference than copper wire.
- It is so efficient, in fact, that roughly 99.7% of the signal reaches the router in most cases.
- Durability: Fibre-optic cable is completely immune to many environmental factors that affect copper cable.
- The core is made of glass, which is an insulator, so no electric current can flow through.
- High Speed: Fibre provides more bandwidth and has standardized performance up to 10 Gbps and beyond, something that it is impossible to achieve when using copper.
What is the Current Scenario of Fibre Optics in India?
- Fibre optics technology has since been widely used in telecommunication, medical science, laser technology, and sensing.
- With a goal to securing communication and promoting quantum science, the Government of India announced a national mission in the Union Budget of 2020. The proposed budget for this ‘National Mission on Quantum Technologies and Applications’ is Rs 8,000 crore over a period of five years.
- The possibilities of fibre optic networks are growing at an accelerated rate, reaching all the way into our homes. Along with quantum optics, fibre optic communication stands on the cusp of a new era.
NITI Ayog Releases CCUS Policy Framework
For Prelims: Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS), CO2 emissions, NITI Aayog, Carbon Taxes, IPCC, Cap-and-Trade systems.
For Mains: About Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS), Significance of CCUS Process, Challenges associated with CCUS, Way Forward.
Why in News?
Recently, experts from research and academia highlighted the need for investment both from the government and industry in Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS) and the importance of leading experts in the field to work collaboratively towards India’s net zero targets through CCUS.
What is Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS)?
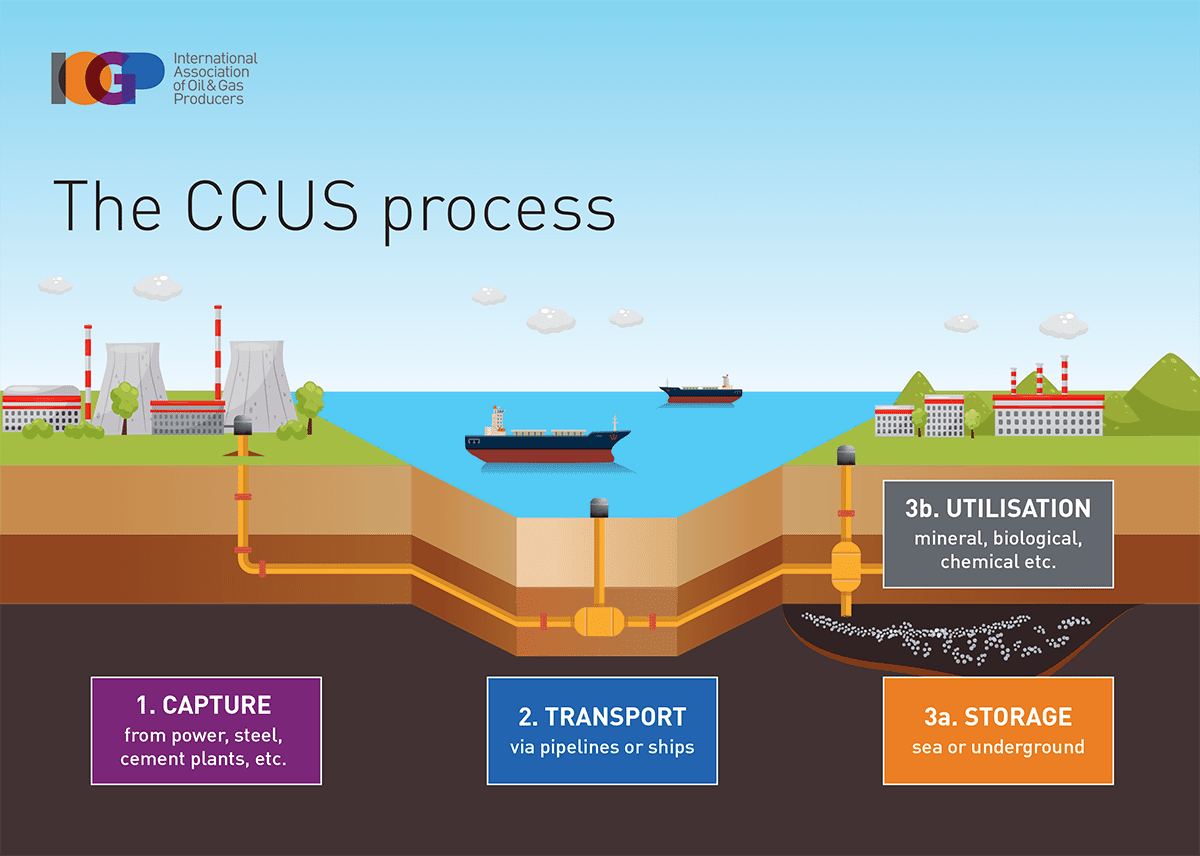
- About: CCUS is a set of technologies and processes aimed at mitigating carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions generated from large-scale point sources like power plants, industrial facilities, and refineries.
- Objective: The primary goal of CCUS is to prevent CO2 from being released into the atmosphere. It is considered a crucial strategy for the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions from industries.
- Process: The process involves three main steps:
- Capture: This step involves capturing CO2 emissions at their source before they are released into the air.
- There are various capture technologies, including post-combustion capture, pre-combustion capture, and oxy-fuel combustion.
- Transport: This step involves moving compressed CO2 by ship or pipeline from the point of capture to the point of storage.
- Storage: The transported CO2 is stored in underground geological formations which include depleted oil and gas fields or deep saline aquifers.
- Utilization: Once captured, the CO2 can be utilized in various ways rather than being released. This may include using CO2 in industrial processes, such as manufacturing chemicals or fuels.
- Capture: This step involves capturing CO2 emissions at their source before they are released into the air.
What is Significance of the CCUS?
- Strategic Role in Decarbonization:
- In its report titled 'Policy Framework and Deployment Mechanism for Carbon Capture, Utilisation, and Storage in India,' NITI Aayog emphasizes the significance of CCUS as a strategy for reducing emissions. particularly in hard-to-abate sectors.
- Hard-to-abate industries include categories like steel, cement, and petrochemicals.
- The IPCC emphasizes that the deployment of CCUS technologies is crucial for achieving net zero emissions globally.
- In its report titled 'Policy Framework and Deployment Mechanism for Carbon Capture, Utilisation, and Storage in India,' NITI Aayog emphasizes the significance of CCUS as a strategy for reducing emissions. particularly in hard-to-abate sectors.
- Energy Security:
- The incorporation of CCUS into the energy mix provides flexibility to the energy grid.
- CCUS facilitates low-carbon electricity and hydrogen production. Hydrogen produced through CCUS serves as a direct substitute for fossil fuels.
- This diversity enhances energy security, aligning with the growing priorities of governments worldwide.
- Industrial Applications of CCUS
- Concrete and Cement Industrial Sectors: In the concrete and cement industry, CCUS technology captures CO2 emitted during the firing of limestone and clay. The recovered CO2 is then injected into concrete mixtures can enhance its strength and durability, a process known as carbonation.
- Basic Chemicals and Fuel Industrial Sectors: CCUS serves as a source of CO2 for synthetic gas production, which is essential for the further production of bio-jet fuel, aligning with sustainable aviation fuel initiatives.
- Fine Chemicals Sector: The fine chemicals industry employs CCUS by capturing carbon dioxide (CO2), blending it with biomass, and subsequently transforming it into oxygenated compounds like high-functional plastics.
- Cost-Effective Solution:
- CCUS allows industries to continue using existing infrastructure, such as power plants and manufacturing facilities, reducing the need for significant capital investments in new, low-carbon alternatives.
What are the Challenges associated with CCUS?
- High Initial Costs:
- Implementing CCUS on a large scale necessitates significant infrastructure development, including pipelines for transporting captured CO2 and suitable storage sites. This poses logistical challenges and requires substantial investments
- Technological Maturity:
- CCUS technologies are in the initial phases of development and have not yet been widely deployed. Additionally, there are gaps in knowledge and experience when it comes to implementing and operating CCUS technologies.
- Competition with Renewable Energy:
- CCUS competes for attention and resources with renewable energy technologies. Some argue that investments in renewables may offer a more direct and sustainable path to decarbonization
- Absence of Regulatory Framework:
- The absence of clear and supportive regulatory frameworks can impede CCUS deployment. Ambiguities in regulations regarding liability, long-term responsibilities, and environmental standards may hinder investment.
- The economic viability of CCUS projects depends on various factors, including the price of carbon, government incentives, and the availability of funding.
Way Forward:
- Policy and Regulatory Support: Governments should establish clear and supportive regulatory frameworks for CCUS projects. This includes addressing issues related to liability, long-term responsibilities, environmental standards, and permitting processes.
- Financial Incentives: Providing financial incentives, subsidies, and tax credits can encourage private-sector investment in CCUS projects. Implementing carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems, can make CCUS more economically viable.
- Infrastructure Development: Governments and industries should invest in the necessary infrastructure for CCUS, including pipelines for CO2 transport and suitable storage sites.
- Capacity Building: Investing in education and training programs can address the knowledge and skill gaps in CCUS technology. Developing a skilled workforce is essential for the successful deployment and operation of CCUS projects.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q.Which one of the following statements best describes the term ‘Social Cost of Carbon’? (2020)
(a) It is a measure, in monetary value, of the long-term damage done by a tonne of CO2 emissions in a given year.
(b) requirement of fossil fuels for a country to provide goods and services to its citizens, based on the burning of those fuels.
(c) efforts put in by a climate refugee to adapt to livein a new place.
(d) contribution of an individual person to the carbon footprint on the planet Earth.
Ans: A
Mains
Q.Should the pursuit of carbon credits and clean development mechanisms set up under UNFCCC be maintained even though there has been a massive slide in the value of a carbon credit? Discuss with respect to India’s energy needs for economic growth.(2014)
NASA's Psyche Spacecraft
Why in News?
NASA's Psyche spacecraft, currently journeying over 16 million kilometers away in space, recently achieved a groundbreaking feat by successfully firing a laser signal at Earth.
- It took off on 13th October, 2023, launching from the Kennedy Space Center via a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket.
What is NASA’s Psyche Mission?
- About: The Psyche mission aims to explore the asteroid Psyche, located between Mars and Jupiter.
- Psyche is a rare metallic asteroid believed to be the exposed nickel-iron core of an early planet.
- This mission offers a unique opportunity to directly study a planetary core, providing invaluable insights into the formation of terrestrial planets like Earth.
- Objectives:
- Core Identity: Determine if Psyche is a core or unmelted material.
- Surface Age Assessment: Analyze relative ages of different regions on Psyche's surface.
- Composition Comparison: Compare elemental composition with Earth's core.
- Formation Conditions: Determine if Psyche's formation conditions were more oxidizing or reducing than Earth's core.
- Topography Characterization: Study Psyche's surface features.
- Scientific Instruments:
- Multispectral Imager: Capture images across different wavelengths.
- Gamma Ray & Neutron Spectrometer: Analyze elemental composition.
- Magnetometer: Measure magnetic fields. Confirmation of a remanent magnetic field at Psyche would be strong evidence that the asteroid formed from the core of a planetary body.
- X-band Gravity Science Investigation: Study gravitational effects of Asteroid on spacecraft.
- Deep Space Optical Communication (DSOC): Test laser-based communication technology using near-infrared wavelengths for faster data transmission between the spacecraft and Earth.
What is the Significance of Deep Space Optical Communications?
- Psyche is the inaugural spacecraft equipped with a NASA's Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) transceiver.
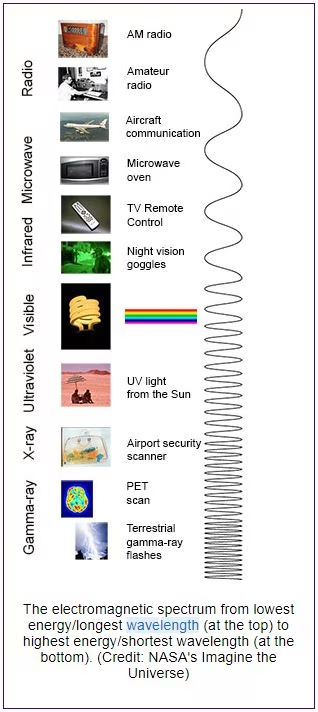
- The DSOC technology encodes data in near-infrared light photons instead of radio waves.
- It is poised to enable data rates at least ten times higher than current radio systems, facilitating enhanced imaging, extensive scientific data transmission, and even video streaming.
- It will facilitate faster data transmission than current space communication tech which predominantly relies on radio waves due to their propagation capabilities, enabling them to traverse through various mediums and obstacles.
- Near-infrared waves, while useful for specific applications, lack radio waves' penetration and distance capabilities.
- The distinction lies in the fact that near-infrared waves have shorter wavelengths, as opposed to radio waves, which feature the longest wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum.
- However, limitations in data transmission rates prompt the quest for better technology.
- Near-infrared waves, while useful for specific applications, lack radio waves' penetration and distance capabilities.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Satellites used for telecommunication relay are kept in a geostationary orbit. A satellite is said to be in such an orbit when: (2011)
- The orbit is geosynchronous.
- The orbit is circular.
- The orbit lies in the plane of the Earth’s equator.
- The orbit is at an altitude of 22,236 km.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Night Sky Sanctuary in Ladakh
Why in News?
The Government of India, recently announced the upcoming establishment of South East Asia's first Night Sky Sanctuary in Ladakh.
What are the Key Points Related to Night Sky Sanctuary in Ladakh?
- It will be located at Hanle village in Eastern Ladakh as a part of Changthang Wildlife Sanctuary.
- It is being set up with the help of Indian Institute of Astrophysics Bengaluru, which is affiliated to the Department of Science & Technology, Govt of India.
- Spread over 1,073 square kilometers, it is adjacent to the Indian Astronomical Observatory, the second-highest optical telescope in the world.
- It will boost Astro-tourism in India and will be one of the world’s highest-located sites for optical, infra-red, and gamma-ray telescopes.
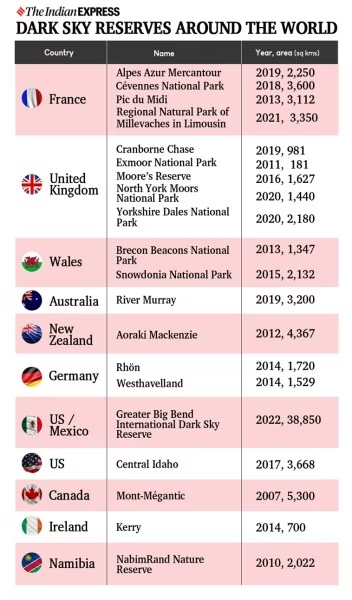
What are the Major Types of Dark Sky Places?
- The International Dark Sky Association, a U.S.-based non-profit, designates places as International Dark Sky Places, Parks, Sanctuaries and Reserves, depending on the criteria they meet:
- Dark Sky Parks: These are conservation areas, publicly or privately owned, that implement effective outdoor lighting practices and offer programs centered around experiencing dark skies.
- Dark Sky Sanctuaries: These are extremely remote and often the darkest places on Earth. They require stringent conservation measures due to their fragile state.
- Dark Sky Reserves: These reserves have a defined dark "core" zone surrounded by populated areas. Policies are implemented to safeguard the darkness of the core zone while accommodating nearby communities.
- Urban Night Sky Places: These urban sites strive to provide an authentic night time experience despite significant artificial light. Here focus is on creating environments where people can still appreciate the night sky.
- Dark Sky Communities: Cities and towns recognized for their quality outdoor lighting ordinances and efforts to educate residents about the significance of preserving dark skies.
What Makes Ladakh a Suitable Site for Night Sky Sanctuary?
- Ladakh's high elevation, cold desert terrain, and sparse population, situated at approximately 3,000 meters above sea level, create an ideal environment for astronomical observatories.
- Also, the absence of extensive urban areas preserve the natural darkness in Ladakh and contributes to minimal Light Pollution, fostering ideal conditions for Night Sky Sanctuary.
Ayushman Arogya Mandir: Transforming Healthcare
The Union Government has decided to rename the existing Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centres (AB-HWCs) as ‘Ayushman Arogya Mandir’ with the tag-line ‘Arogyam Parmam Dhanam’.
- Ayushman Bharat aims to shift from selective healthcare to offering a full spectrum of services, covering preventive, promotive, curative, rehabilitative, and palliative care. It comprises two components:
- First: The creation of 1,50,000 Health & Wellness Centres (HWCs) for free Comprehensive Primary Health Care, emphasizing wellness and a wider array of services at the community level.
- Second: Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY), extends health insurance of Rs. 5 lakhs per year to over 10 crore impoverished families for secondary and tertiary care.
- The HWCs aim to provide an extensive range of services encompassing non-communicable diseases, palliative and rehabilitative care, oral, eye, and ENT care, mental health support, and initial care for emergencies and trauma, along with free essential drugs and diagnostics.
Read more: Ayushman Bharat
Aadhaar Privacy and Marital Rights
The High Court of Karnataka recently highlighted that marriage does not give one spouse the right to access the other's Aadhaar data without a fair hearing.
- The court dismissed the notion that marriage merges the identities of spouses, firmly stating that each individual's right to privacy remains paramount.
- Emphasizing the necessity of following due procedure under Section 33 of the Aadhaar (Targeted Delivery of Financial and Other Subsidies, Benefits & Services) Act, 2016, the court dismissed the notion that marriage merges the identities of spouses, firmly stating that each individual's right to privacy remains paramount.
Read more: Right to Privacy
Michael Douglas honored with the Satyajit Ray Lifetime Achievement Award
Recently, Hollywood actor and producer Michael Douglas was honored with the prestigious Satyajit Ray Lifetime Achievement Award for Excellence in Cinema at the 54th International Film Festival of India (IFFI) in Goa.
- His profound impact on cinema resonates through iconic roles, from his Academy Award-winning portrayal as Gordon Gekko in Wall Street to gripping performances in films like Fatal Attraction, The American President, Basic Instinct, Traffic, and Romancing the Stone, among many others.
- As a UN Messenger of Peace, his commitment to global issues includes advocacy for disarmament, nuclear non-proliferation, and halting illicit arms trade.
Read More: 54th International Film Festival of India
4th Edition of ASEAN India Grassroots Innovation Forum (AIGIF)
India along with 10 ASEAN Member States (AMS) were represented by 200 participants, at the 4th edition of the annual ASEAN India Grassroots Innovation Forum (AIGIF) that was launched in Langkawi, Malaysia on 28th November 2023.
- The AIGIF is an annual programme focused on fostering a strengthened relationship between India and AMS on the premise of cooperation in Science, Technology and Innovation (STI).
- While on one side it aims to give exposure to social innovations in different countries, it also strengthens governance in the grassroots innovation ecosystem.
Read More: ASEAN