Governance
India Smart Cities Award Contest 2022
For Prelims: India Smart Cities Award Contest 2023, Smart Cities Mission, Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC), Centrally Sponsored Scheme, Ease of Living Index, Municipal Performance Index.
For Mains: India Smart Cities Award Contest, Smart Cities Mission.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) has announced the India Smart Cities Award Contest (ISAC) 2022 under the Smart Cities Mission (SCM), that felicitated 66 winners in various categories.
- Indore, Madhya Pradesh, and Chandigarh emerged as top performers in the ISAC 2022 awards, securing recognition for their excellence in different areas of urban development.
What are the Key Highlights of ISAC 2022?
- National Smart City Award:
- Indore secured the prestigious national smart city award, reflecting its exceptional progress in urban development strategies, followed by Surat and Agra.
- Indore's commitment to sanitation, water supply, and urban environment earned it recognition as a leader in these vital areas.
- Indore secured the prestigious national smart city award, reflecting its exceptional progress in urban development strategies, followed by Surat and Agra.
- State Award:
- Madhya Pradesh received the state award for its comprehensive approach to fostering smart city initiatives within its borders.
- Madhya Pradesh is followed by Tamil Nadu and Rajasthan.
- Union Territory (UT) Award:
- Chandigarh was honored with the UT award, acknowledging its efforts to transform itself into a model smart city.
- Other Categories:
- Coimbatore took the top spot for built environment,
- Ahmedabad for the culture and Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC) category,
- Jabalpur for economy,
- Chandigarh for governance and mobility,
- Indore for sanitation, water and urban environment,
- Vadodara for social aspects,
- Hubbali Dharwad for the innovative idea category and Surat for Covid innovation category.
What is ISAC?
- The ISAC recognizes and rewards the cities, projects and innovative ideas that are promoting sustainable development across the 100 smart cities, as well as stimulating inclusive, equitable, safe, healthy and collaborative cities, thus enhancing quality of life for all.
- The ISAC has witnessed three editions in 2018, 2019 and 2020.
- The fourth edition of the ISAC was launched in April 2022 during the ‘Smart Cities-Smart Urbanization’ event in Surat, Gujarat.
- The ISAC 2022 award had a two-stage submission process consisting of ‘Qualifying Stage’, which involved overall assessment of the city’s performance, and the ‘Proposal Stage’ which required the smart cities to submit their nominations for six award categories.
- Project Awards: 10 different themes,
- Innovation Awards: 2 different themes,
- National/Zonal City Awards,
- State Awards,
- UT Award, and
- Partners Awards, 3 different themes.
- The ISAC 2022 award had a two-stage submission process consisting of ‘Qualifying Stage’, which involved overall assessment of the city’s performance, and the ‘Proposal Stage’ which required the smart cities to submit their nominations for six award categories.
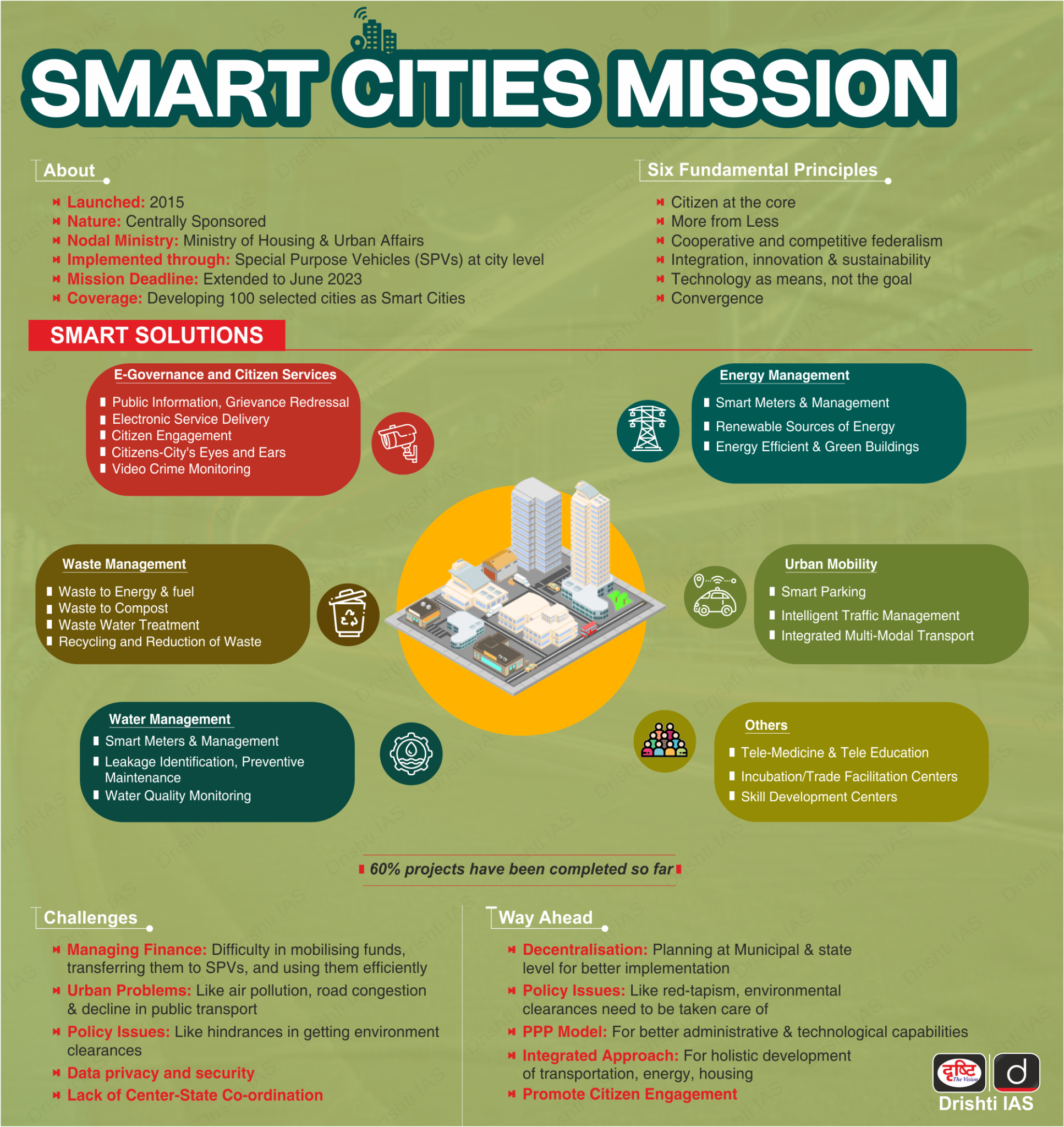
What is a Smart Cities Mission?
- About:
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, launched in June 2015 to transform 100 cities to provide the necessary core infrastructure and clean and sustainable environment to enable a decent quality of life to their citizens through the application of "Smart Solutions".
- The mission aims to meet the aspirations of India’s population living in cities through various urban development projects.
- Features:
- Among its strategic components is ‘area-based development’, which includes city improvement (retrofitting), city renewal (redevelopment) and city extension (greenfield development), plus a pan-city initiative in which ‘smart solutions’ are applied covering larger parts of the city.
- Key focus areas of the scheme include construction of walkways, pedestrian crossings, cycling tracks, efficient waste-management systems, integrated traffic management and assessment.
- The scheme also assesses various indices to track urban development such as the Ease of Living Index, Municipal Performance Index, City GDP framework, Climate Smart Cities assessment framework, etc.
- Achievements:
- Integrated Command and Control Centers (ICCC): One of the pivotal achievements of the Smart Cities Mission is the establishment of ICCC in all 100 smart cities.
- These centers serve as the operational hubs for urban management, utilizing technology to enhance various aspects of city operations. Notably, ICCCs have contributed to improvements in crime tracking, citizen safety, transport management, waste management, water supply, and disaster preparedness.
- Sectoral Progress: The Smart Cities Mission encompasses a wide array of projects across sectors, including mobility, energy, water, sanitation, public spaces, social infrastructure, and governance.
- Smart Mobility: Completion of 1,174 projects.
- Smart Energy: Successful completion of 573 projects.
- Water Supply, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH): Over 1,162 projects completed.
- Public Spaces: Development of more than 1,063 public spaces.
- Integrated Command and Control Centers (ICCC): One of the pivotal achievements of the Smart Cities Mission is the establishment of ICCC in all 100 smart cities.
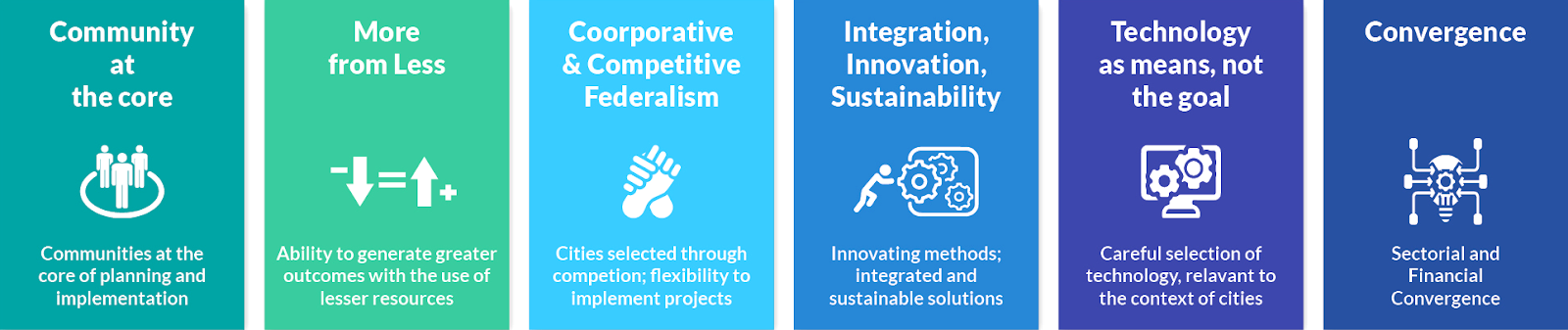
What is a Smart City?
- There is no standard definition or template of a smart city. In the context of our country, the six fundamental principles on which the concept of Smart Cities is based are:
What are the other Initiatives Related to Urban Development?
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With a brief background of quality of urban life in India, introduce the objectives and strategy of the ‘Smart City Programme.’ (2016)
Indian Economy
Inflation And Current Outlook of Indian Economy
For Prelims: Inflation And Current Outlook of Indian Economy, Retail Inflation, Reserve Bank of India, Monetary Policy, GDP (Gross Domestic Product), Supply Chain.
For Mains: Inflation And Current Outlook of Indian Economy, Impact of Inflation on Na Economy.
Why in News?
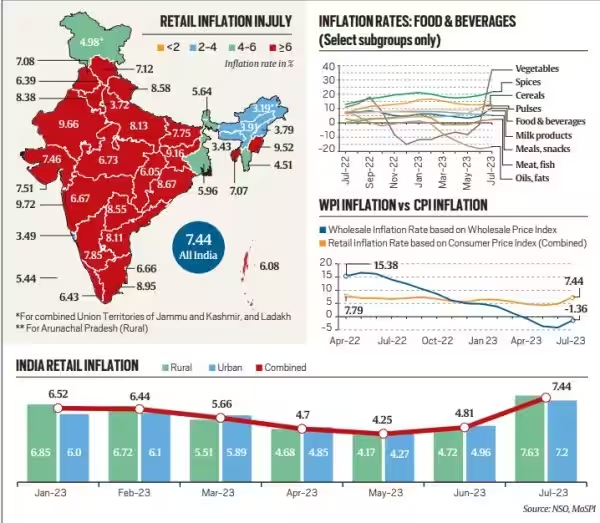
July 2023 witnessed a notable increase in Retail Inflation, reaching 7.44%, creating Goldilocks scenario for India, making investors and savers uncertain about the economic situation.
- A Goldilocks Scenario describes an ideal state for an economy whereby the economy is not expanding or contracting by too much. A Goldilocks economy has steady economic growth, preventing a recession, but not so much growth that inflation rises by too much.
What is the Current Economic Scenario of India and Projections?
- GDP Projection:
- The projected GDP (Gross Domestic Product) growth for 2023-24 is 6.5%, while the benchmark Sensex index stands currently at 65,000 points.
- However, if inflation remains high, it could affect returns on stock market investments.
- Gold and bank deposit rates, on the other hand, are expected to remain stable in the coming months.
- The projected GDP (Gross Domestic Product) growth for 2023-24 is 6.5%, while the benchmark Sensex index stands currently at 65,000 points.
- Inflation Projection:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) anticipates inflation to stay above 5% until the first quarter of 2024-25, potentially reaching 6.2% in the current quarter (July-Sept) 2023, exceeding the RBI's comfort level of 4%.
- Food Price Pressures:
- Food prices are expected to remain elevated for a few more months. July's data reveals a surge in vegetable prices (37.3%), along with inflation in cereals, pulses (both 13%), spices (21.6%), and milk (8.3%).
- It is expected that government interventions and fresh crop arrivals will eventually ease this pressure.
- Interest Rates and Monetary Policy:
- Due to the higher inflation projections, the possibility of a rate cut has been postponed to the next Fiscal Year (2024-25).
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is likely to maintain policy rates in the upcoming meeting, with the first rate cut potentially occurring in the following fiscal year.
- Market Outlook:
- Despite inflation and high interest rates, India's market has performed well.
- Supported by strong earnings prospects and stable macro conditions, India has outperformed other markets.
What is the Impact of Such Rising Inflation on the Indian Economy?
- Impact on Markets:
- When inflation is high, stock prices are undervalued, and the value of gold increases. Rising inflation reduces purchasing power, leading to lower real earnings.
- Additionally, higher inflation results in higher Interest Rates, affecting the cost of equity.
- The RBI's series of repo rate hikes since April 2022 has contributed to an overall increase in lending rates, affecting various types of loans.
- Income Redistribution:
- Inflation can impact different groups within society unevenly. Creditors may lose out, as the value of the money they receive from debtors decreases.
- Conversely, debtors could benefit by repaying loans with money that is worth less than when they borrowed it.
- International Competitiveness:
- High inflation in one country can lead to a decrease in its international competitiveness. If domestic prices rise faster than those in trading partner countries, the country's exports may become less attractive on the global market.
- Wage-Price Spiral:
- Inflation can sometimes trigger a cycle of rising wages and prices. Workers demand higher wages to keep up with rising costs, and businesses pass on those higher costs to consumers in the form of higher prices. This cycle can perpetuate inflation.
Way Forward
- Given the concerns about rising inflation, the government and the RBI need to work together to manage inflationary pressures. This could involve targeted measures to stabilize food prices, improve Supply Chain efficiency, and maintain a cautious monetary policy.
- The government should focus on maintaining a balanced budget, reducing unnecessary expenditure, and boosting revenue generation through reforms and measures that promote economic growth.
- The RBI should continue to adopt a vigilant and data-driven monetary policy approach. This may involve adjusting interest rates to manage inflation while also considering the impact on economic growth.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 With reference to Indian economy, demand-pull inflation can be caused/increased by which of the following?
- Expansionary policies
- Fiscal stimulus
- Inflation-indexing of wages
- Higher purchasing power
- Rising interest rates
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (a)
Q.2 Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The weightage of food in Consumer Price Index (CPI) is higher than that in Wholesale Price Index (WPI).
- The WPI does not capture changes in the prices of services, which CPI does.
- Reserve Bank of India has now adopted WPI as its key measure of inflation and to decide on changing the key policy rates.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Biodiversity & Environment
State of India’s Birds 2023 Report
For Prelims: State of India’s Birds 2023 Report, IUCN (International Union for the Conservation of Nature), Western Ghats, Asian Koel, Migratory Birds, Climate Change.
For Mains: State of India’s Birds 2023 Report.
Why in News?
Recently, the State of India’s Birds (SoIB) 2023 was released, which highlighted that despite thriving a few bird species, there is a substantial decline in numerous bird species.
- the SoIB 2023 is a first-of-its-kind collaborative effort of 13 government and non-government organisations, including the Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS), Wildlife Institute of India (WII), and Zoological Survey of India (ZSI), Wildlife Trust of India (WTI), Worldwide Fund for Nature–India (WWF–India) among others, which evaluates the overall conservation status of the most regularly occurring bird species in India.
What are the Methodologies Used in the Report?
- This report is based on data collected from approximately 30,000 birdwatchers.
- The report relies on three primary indices to assess bird populations,
- Long-term trend (change over 30 years)
- Current annual trend (change over the past seven years)
- Distribution range size within India
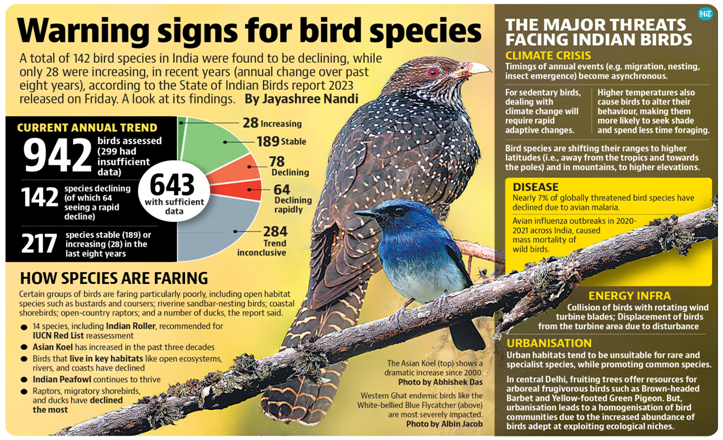
- Among the 942 bird species assessed, the report indicates that many could not have their long-term or current trends accurately established.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Status:
- For the 338 species with identified long-term trends, 60% have experienced declines, 29% are stable, and 11% have shown increases.
- Among the 359 species with determined current annual trends, 39% are declining, 18% are rapidly declining, 53% are stable, and 8% are increasing.
- Positive Trends: Increasing Bird Species:
- Despite the general decline, there are some positive trends among certain bird species.
- The Indian Peafowl, for instance, the national bird of India, is showing a remarkable increase in both abundance and distribution.
- This species has expanded its range into new habitats, including high-altitude Himalayan regions and rainforests in the Western Ghats.
- The Asian Koel, House Crow, Rock Pigeon, and Alexandrine Parakeet are also highlighted as species that have demonstrated a notable increase in abundance since the year 2000.
- The Indian Peafowl, for instance, the national bird of India, is showing a remarkable increase in both abundance and distribution.
- Despite the general decline, there are some positive trends among certain bird species.
- Specialist Birds:
- Bird species that are “specialists’’ – restricted to narrow habitats like wetlands, rainforests, and grasslands, as opposed to species that can inhabit a wide range of habitats such as plantations and agricultural fields – are rapidly declining.
- The “generalist’’ birds that can live in multiple habitat types are doing well as a group.
- “Specialists, however, are more threatened than generalists.
- Grassland specialists have declined by more than 50%.
- Birds that are woodland specialists (forests or plantations) have also declined more than generalists, indicating a need to conserve natural forest habitats so that they provide habitat to specialists.
- Migrant and Resident Birds:
- Migratory Birds, especially long-distance migrants from Eurasia and the Arctic, have experienced significant declines by more than 50% – followed by short-distance migrants.
- Shorebirds that breed in the Arctic have been particularly affected, declining by close to 80%.
- By contrast, resident species as a group have remained much more stable..
- Diet and Decline Patterns:
- Dietary requirements of birds have also shown up in abundance trends. Birds that feed on vertebrates and carrion have declined the most.
- Vultures were nearly driven to extinction by consuming carcasses contaminated with diclofenac.
- White-rumped Vultures, Indian Vultures, and Red-headed Vultures have suffered the maximum long-term declines (98%, 95%, and 91%, respectively).
- Dietary requirements of birds have also shown up in abundance trends. Birds that feed on vertebrates and carrion have declined the most.
- Endemic and Waterbird Declines:
- Endemic species, unique to the Western Ghats and Sri Lanka biodiversity hotspot, have experienced rapid declines.
- Of India's 232 endemic species, many are inhabitants of rainforests, and their decline raises concerns about habitat preservation.
- Ducks, both resident and migratory, are declining, with certain species like the Baer’s Pochard, Common Pochard, and Andaman Teal being particularly vulnerable.
- Riverine sandbar-nesting birds are also declining due to multiple pressures on rivers.
- Endemic species, unique to the Western Ghats and Sri Lanka biodiversity hotspot, have experienced rapid declines.
- Major Threats:
- The report highlighted several major threats – including Forest Degradation, urbanization, and energy infrastructure – that bird species face across the country.
- Environmental pollutants including veterinary drugs such as nimesulide still threaten vulture populations in India.
- Impacts of Climate Change (such as on migratory species), avian disease, and illegal hunting and trade are also among the major threats.
- Other Species:
- Sarus Crane has rapidly declined over the long term and continues to do so.
- Of the 11 species of woodpeckers for which clear long-term trends could be obtained, seven appear stable, two are declining, and two are in rapid decline.
- The Yellow-crowned Woodpecker, inhabiting widespread thorn and scrub forests, has declined by more than 70% in the past three decades.
- While half of all bustards worldwide are threatened, the three species that breed in India – the Great Indian Bustard, the Lesser Florican, and the Bengal Florican – have been found to be most vulnerable.
What are the Recommendations?
- There is a need to conserve specific groups of birds. For instance, the report found that grassland specialists have declined by more than 50% – indicating the importance of protecting and maintaining grassland ecosystems.
- Systematic monitoring of bird populations over long periods of time is critical to understanding small-scale changes in bird populations.
- It is becoming clearer the need for more research to understand the reasons behind the declines or increases.
- The report's findings emphasize the importance of habitat preservation, addressing pollution, and understanding the dietary requirements of birds in order to reverse the decline of bird populations and ensure a healthier ecosystem.
What Can be done to Ensure the Viable Population of the Birds in the Ecosystem?
- Habitat Conservation and Restoration:
- Protect and preserve natural habitats, such as forests, wetlands, grasslands, and coastal areas, that are essential for birds' nesting, feeding, and breeding.
- Restore degraded habitats by planting native vegetation and removing invasive species that can threaten bird populations.
- Protected Areas and Reserves:
- Establish and manage protected areas and wildlife reserves where birds can thrive without human disturbances.
- Implement regulations and guidelines to prevent habitat destruction and disturbances in these areas.
- Reducing Pollution:
- Control pollution sources, including air and water pollution, that can harm bird populations directly or through the contamination of their food sources.
- Promote sustainable practices to minimize pollution in urban and industrial areas.
- Mitigating Climate Change:
- Address climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable energy sources.
- Support habitat corridors that allow birds to move and adapt to changing climatic conditions.
- Limiting Human Disturbances:
- Educate the public about the importance of minimizing disturbances to nesting and feeding sites, particularly during breeding seasons.
- Establish buffer zones around sensitive bird habitats to reduce human interference.
What Measures Have Been Taken to Safeguard Different Bird Species?
- National Action Plan for the Conservation of Migratory Birds (2018-2023)
- Transboundary protected areas for conservation of species like Tigers, Asian elephants, Snow Leopard, the Asiatic Lion, the one-horned rhinoceros, and the Great Indian Bustard.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
- India has taken several steps to conserve vultures like imposing a ban on the veterinary use of diclofenac, establishment of Vulture breeding centres, etc.
Science & Technology
Somatic Genetic Variants
For Prelims: Genome sequencing, Cancer, Somatic Genetic Variants, Germline cells, DNA replication.
For Mains: Harnessing Somatic Genetic Variants for Human Health Advancement
Why in News?
Recent advances in genome sequencing unveil the impact of somatic genetic variants on human health, from cancer development to immune disorders, driving innovation in disease detection and treatment strategies.
What are Somatic Genetic Variants?
- About:
- Somatic genetic variants also known as somatic mutations refer to alterations in the DNA sequence that occur specifically within the cells of an individual's body (somatic cells), excluding the germline cells (sperm and egg cells).
- Somatic genetic mutations occur after birth during development and are not inherited from parents.
- Somatic Mutation Progression:
- The human genome consists of 23 pairs of chromosomes, inherited from each parent, forming the blueprint of our genetic identity.
- Following the fertilization of an egg cell by a sperm cell, the resultant single cell amalgamates genetic material from both parents.
- Through subsequent rounds of division, this initial cell proliferates extensively, ultimately generating the countless trillions of cells constituting the human body.
- During the process of DNA replication, the incorporation of errors is notably minimized by error-correcting proteins. Nevertheless, a minute error rate persists and occurs at different times, contributing to the emergence of somatic genetic mutations.
- As cells continue to renew and replace old ones throughout life, errors keep occurring, leading to the gradual accumulation of somatic mutations over time.
- This is why differences in genetic makeup are observed between different tissues in the body as people get older.
- The human genome consists of 23 pairs of chromosomes, inherited from each parent, forming the blueprint of our genetic identity.
- Influence of Somatic Genetic Variants on Human Health:
- Cancer Development: Somatic genetic variants can drive the uncontrolled cell growth and division characteristic of cancer, leading to tumor formation.
- Neurological Disorders: Accumulated somatic mutations in brain cells can contribute to neurological conditions, affecting cognitive and motor functions.
- Aging and Tissue Function: Gradual accumulation of somatic mutations with age can impair tissue function and contribute to age-related diseases.
- Immune System Dysfunction: Somatic variants can disrupt immune cell development and function, leading to autoimmune disorders and immunodeficiencies.
- Harnessing Somatic Genetic Variants for Human Health Advancement:
- Disease Biomarkers: Somatic variants can serve as diagnostic and prognostic markers for diseases.
- Detecting specific mutations can aid in early disease detection and predicting disease progression.
- Precision Medicine: Knowledge of an individual's somatic mutations allows personalized treatment plans.
- Tailoring therapies to a patient's unique genetic makeup can enhance treatment outcomes.
- Aging and Longevity: Studying somatic mutations associated with aging can shed light on the aging process and age-related diseases, potentially leading to interventions for healthier aging.
- Solution of Genetic Disease: In some instances, somatic mutation brings a deleterious change to a normal one, a phenomenon known as revertant mosaicism.
- E.g., Around 10% of cases of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, a rare genetic immunodeficiency, have been found to have revertant mosaicism, as a result alleviating the severity of the disease in many individuals.
- Disease Biomarkers: Somatic variants can serve as diagnostic and prognostic markers for diseases.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q.1 With reference to agriculture in India, how can the technique of ‘genome sequencing’, often seen in the news, be used in the immediate future? (2017)
- Genome sequencing can be used to identify genetic markers for disease resistance and drought tolerance in various crop plants.
- This technique helps in reducing the time required to develop new varieties of crop plants.
- It can be used to decipher the host-pathogen relationships in crops.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q2. Consider the following statements: (2022)
- DNA Barcoding can be a tool to:
- Assess the age of a plant or animal.
- Distinguish among species that look alike.
- Identify undesirable animal or plant materials in processed foods.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
International Relations
China and Bhutan Meet to Delimit Boundary
For Prelims: India-Bhutan Relations, Treaty of Friendship in 1949
For Mains: Challenges in India-Bhutan Relations, Chinese Challenge in the Region
Why in News?
Recently, China and Bhutan held the 13th Expert Group Meeting (EGM) in Beijing, focusing on boundary delimitation. The meeting marked the establishment of a Joint Technical Team on the Delimitation of the China-Bhutan Boundary.
- As both nations aim to expedite boundary resolution, this move holds implications for the broader regional context, including India.
What are the Key Highlights of the 13th Expert Group Meeting Meeting?
- Both nations expressed their commitment to expedite efforts towards achieving a resolution on the disputed boundary.
- Plans were laid out for the upcoming 14th round of boundary talks to maintain the encouraging pace.
- The meeting addressed the implementation of the Three-Step Road Map, reflecting the commitment to follow the outlined strategy for expediting boundary negotiations.
How Recent Developments in China-Bhutan Relations Concerning India?
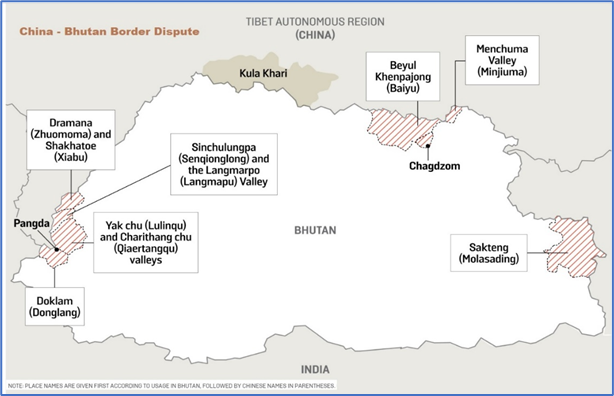
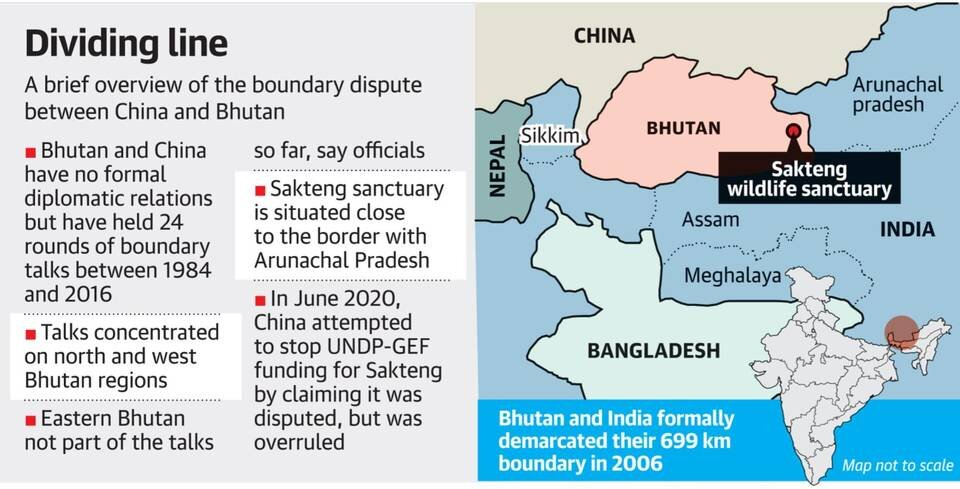
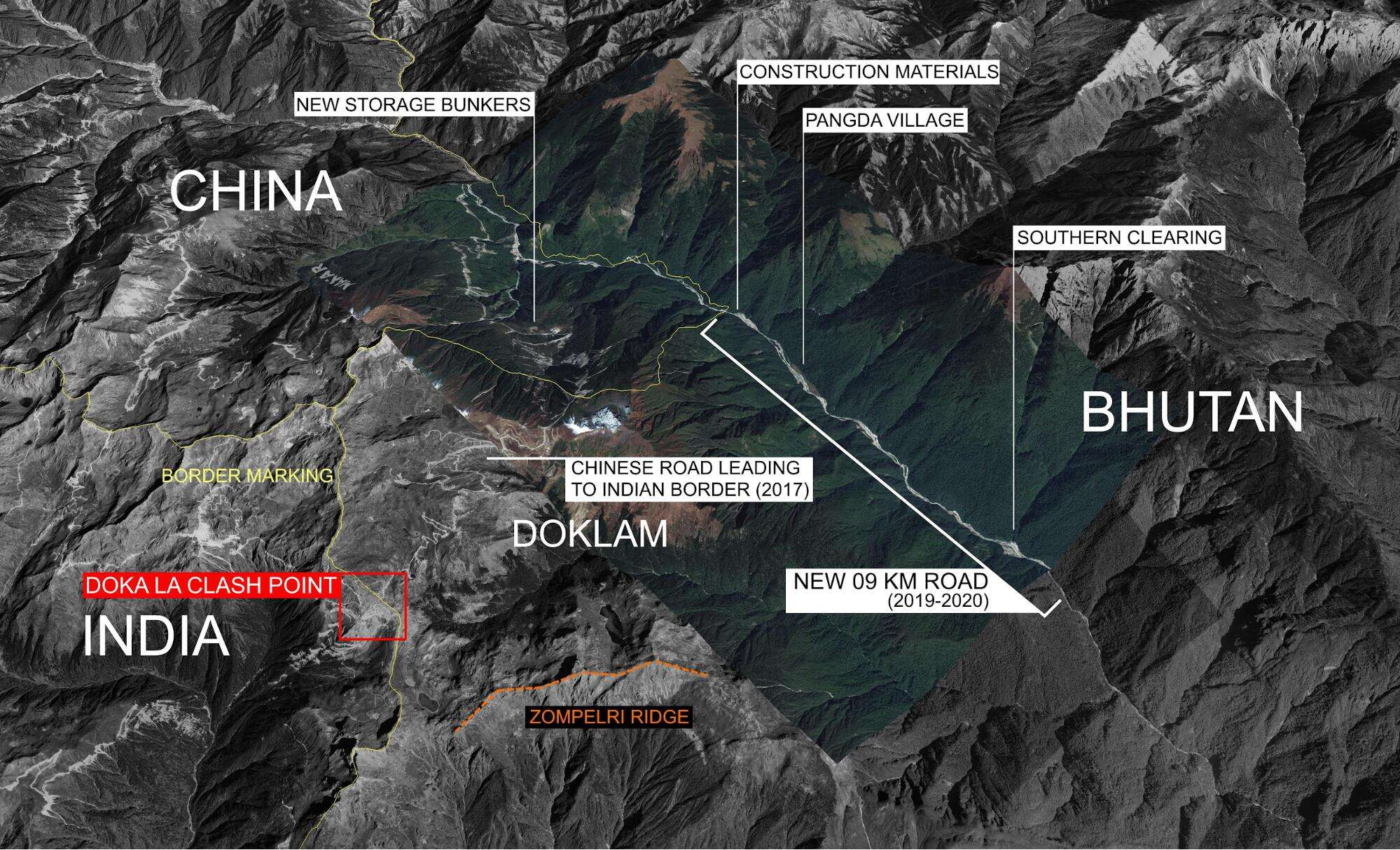
- Recent developments of China and Bhutan could affect India’s strategic interests, especially in the Doklam tri-junction, where India, Bhutan, and China meet.
- China has also revived its claim to the eastern region of Bhutan, known as Sakteng (Wildlife Sanctuary), which borders the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh.
- China considers Arunachal Pradesh as part of its territory and calls it “South Tibet”. China’s claim to Sakteng could be seen as a pressure tactic to force Bhutan to accept its terms on the boundary issue, as well as to challenge India’s sovereignty over Arunachal Pradesh.
- Bhutan is one of India's closest allies in the region, and India has long provided economic and military support to Bhutan. However, in recent years, China has been increasing its economic and diplomatic ties with Bhutan, which could potentially weaken India's influence in the region.
How have been India’s Relations with Bhutan?
- Historical and Cultural Ties:
- India and Bhutan share a common cultural heritage, rooted in Buddhism, Hinduism, and other traditions.
- A number of Bhutanese pilgrims travel to Bodh Gaya, Rajgir, Nalanda, Sikkim, Udayagiri, and other Buddhist sites in India.
- Bhutan was one of the first countries to recognize India’s sovereignty and independence in 1947 and has supported its development and modernization ever since.
- Strategic and Security Cooperation
- India and Bhutan signed a Treaty of Friendship in 1949, which was revised in 2007, to establish peace and non-interference in each other’s internal affairs.
- India has provided Bhutan with assistance in areas such as defence, infrastructure, and communication, which has helped to maintain Bhutan's sovereignty and territorial integrity.
- In 2017, during the Doklam standoff between India and China, Bhutan played a crucial role in allowing Indian troops to enter its territory to resist Chinese incursions.
- Economic and Development Partnership:
- The India-Bhutan Agreement on Trade, Commerce, and Transit (signed in 1972 and revised in 2016) establishes a free trade regime between the two countries.
- India is Bhutan’s largest trading partner. India also provides economic aid and assistance to Bhutan’s socio-economic development, especially in the sectors of agriculture, irrigation, infrastructure, energy, health, education, and culture.
- India’s top exports to Bhutan are petrol & diesel, passenger cars, rice, wood charcoal, cellphones, soya-bean oil, excavators, electric generators and motors, parts for turbines, and transport vehicles.
- India’s top imports from Bhutan are electricity, betel nut, oranges, semi-finished products of iron or non-alloy steel, boulders, etc.
- India is the leading source of investments in Bhutan, comprising 50% of the country’s total FDI.
- Hydropower Cooperation:
- This hydropower cooperation comes under the 2006 Agreement on Cooperation in Hydropower.
- India has agreed to assist Bhutan in the development of a minimum of 10,000 MW of hydropower and import of surplus electricity from the same by 2020.
- Four hydroelectric projects (HEPs)- Chhukha, Kurichu, Tala, and Mangdechhu totaling 2136 MW are already operational in Bhutan and are supplying electricity to India.
- Two HEPs Punatsangchhu-I and, Punatsangchhu-II in Inter-Governmental mode are under various stages of implementation
- This hydropower cooperation comes under the 2006 Agreement on Cooperation in Hydropower.
- Multilateral Partnership:
- Both of them share multilateral forums such as South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC), BBIN (Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, and Nepal), BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation) etc.
- People-to-People Contacts:
- About 50,000 Indian citizens are working in Bhutan, mainly in the construction sector, education and technical consultants involved in infrastructure projects.
- India is the most popular educational destination for Bhutanese students.
- India and Bhutan also exchange cultural delegations, artists, scholars, exhibitions, festivals, etc. to promote cultural understanding and appreciation.
What are the Challenges in the India-Bhutan Relations?
- China's increased presence in Bhutan, especially along the disputed border, raises alarms in India due to strategic implications.
- India and Bhutan share a 699 km border, mostly peaceful, but recent Chinese border incursions, like the 2017 Doklam standoff, have caused tensions among India, China, and Bhutan, potentially affecting India-Bhutan relations.
- Bhutan's economy relies heavily on hydropower, with India playing a crucial role in its development. Concerns in Bhutan about terms of some projects favoring India have led to public opposition.
- India is Bhutan’s largest trading partner and source of tourists. However, there have been some frictions over trade and tourism policies between the two countries.
- For instance, Bhutan has expressed concerns over the environmental impact of trade and tourism on its fragile ecology and culture and proposed to levy entry charges on Indian tourists.
- According to All India Surveys of Higher Education (AISHE), the number of Bhutanese students receiving tertiary education in India declined to just 3.8% of all international students from 7% a decade ago.
Way Forward
- Collaborating on regional multilateral platforms to promote stability and shared interests.
- Encouraging transparent communication between India, Bhutan, and China to mitigate border tensions.
- Addressing concerns over hydropower projects through dialogue and fair terms to benefit both nations.
- India and Bhutan could establish a joint committee to collaboratively formulate sustainable policies that balance economic interests with ecological and cultural preservation.
- India can help Bhutan in the areas of education and skill development by providing scholarships to Bhutanese students and training programs to enhance the skills of Bhutanese professionals.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. Border management is a complex task due to difficult terrain and hostile relations with some countries. Elucidate the challenges and strategies for effective border management. (2016).
Social Justice
Post-Hospitalization Mortality in Covid-19 Patients
For Prelims: Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), Covid-19
For Mains: How can healthcare systems address the post-covid-19 mortality
Why in News?
Recently, a new study conducted by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has shed light on the post-hospitalization mortality rate among former Covid-19 patients.
- The study's comprehensive examination of factors such as comorbidities(more than one disease or condition at the same time), age, and vaccination sheds light on vulnerabilities and emphasizes the importance of managing health conditions to reduce mortality risk.
What are the Key Highlights From the Study?
- Mortality Rate and Participant Demographics:
- The study examined 14,419 former Covid-19 patients across 31 Indian medical centers.
- The observed mortality rate one year after hospital discharge is 6.5%.
- Around 50% of patients who died, passed away within 28 days of hospital discharge.
- The risk of mortality decreases as time elapses after discharge.
- The elderly age group (60+) with comorbidities is particularly vulnerable to mortality.
- The study examined 14,419 former Covid-19 patients across 31 Indian medical centers.
- Prevalence of Post-Covid-19 Conditions:
- 17.1% of participants experienced Post-Covid-19 conditions, including lethargy, breathlessness, cognitive abnormalities, and difficulty in concentrating.
- Focus on All-Cause Mortality:
- The study primarily concentrated on all-cause mortality, rather than attributing deaths solely to Covid-19.
- All-cause mortality encompasses various causes of death, including comorbidities and other factors.
- Vaccination and Disease Severity:
- Vaccination confers approximately 60% protection before Covid-19 infection.
- Vaccines contribute to reducing disease severity during hospitalization.
- Vulnerabilities Leading to Higher Mortality:
- Comorbidity, age, and gender were identified as factors influencing mortality risk.
- Individuals with one comorbid condition are over 9 times more likely to die.
- Men faced a 1.3-fold higher risk, and aged 60 and above were associated with a 2.6-fold higher risk.
- The study underscores the importance of managing comorbidities to reduce mortality risk.
- Children's Vulnerability:
- Children aged 0 to 18 faced a 5.6 times higher risk of death between four-week and one-year follow-ups.
- Risk 1.7-fold higher in the first four weeks post hospitalization.
- Children with serious health conditions like cancer and kidney disorders had a higher chance of passing away.
- Children aged 0 to 18 faced a 5.6 times higher risk of death between four-week and one-year follow-ups.
- Limitations of the Study:
- The study did not examine long Covid symptoms.
- The operational definition of Post Covid Condition (PCC) used in this study is not an exact match with the definitions provided by either the World Health Organization (WHO) or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention(CDC), the national public health agency of the United States.
- WHO definition for PCC says that we have to wait for three months and then check if the symptoms persist for two months, it says long covid symptoms persist post-three months after initial infection.
- Long Covid-19, as defined by the CDC, encompasses various ongoing health problems post-Covid-19 infection, starting from at least four weeks after infection. However, the ICMR study only did a symptomatic assessment at four weeks’ time, not after that.
Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR):
- ICMR is the apex body in India for the formulation, coordination, and promotion of biomedical research.
- ICMR was established in 1911 as the Indian Research Fund Association (IRFA) and was renamed as ICMR in 1949.
- ICMR is funded by the Government of India through the Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Its mandate is to conduct, coordinate and implement medical research for the benefit of the Society; translating medical innovations into products/processes and introducing them into the public health system.
- ICMR also collaborates with international organizations, such as WHO, United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), etc., on various health research projects and programs.
- ICMR has also supported human resource development and capacity building in biomedical research through various schemes and programs.
Mains
Q. COVID-19 pandemic accelerated class inequalities and poverty in India. Comment. (2020)
Governance
Performance of the Fast Track Special Court
For Prelims: Fast Track Courts, Justice in Sexual Offense Cases, Protection of Children from Sexual Offenses (POCSO) Act, 2012, Indian Penal Code (IPC), UN Convention on the Rights of the Child in 1992.
For Mains: Fast Track Courts for Justice in Sexual Offense Cases.
What are the Fast Track Special Courts (FTSCs)?
- Background (Scheme for Fast Track Courts):
- Fast track courts (FTCs) were first recommended by the Eleventh Finance Commission in 2000 "to substantially bring down, if not eliminate, pendency in the district and subordinate courts over the next five years".
- Following the report, the Centre created 1,734 additional courts in different states for a period of five years. In 2011, the central government stopped funding fast-track courts.
- Following the December 2012 Gangrape and murder case, the Union Government set up a 'Nirbhaya Fund', amended the Juvenile Justice Act, 2015 and set up fast-track Mahila Courts (a Special Court).
- Some other states such as Uttar Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Bihar etc. also set up FTCs for rape cases thereafter.
- Fast track courts (FTCs) were first recommended by the Eleventh Finance Commission in 2000 "to substantially bring down, if not eliminate, pendency in the district and subordinate courts over the next five years".
- About Fast Track Special Courts (FTSCs):
- FTSCs are dedicated courts expected to ensure swift dispensation of justice. They have a better clearance rate as compared to the regular courts and hold speedy trials.
- In 2019, the government approved a scheme for setting up 1,023 FTSCs across the country for expeditious disposal of pending rape cases under the Indian Penal Code (IPC) and crimes under the POCSO Act.
- It also strengthens the deterrence framework for sexual offenders.
- FTSCs are dedicated courts expected to ensure swift dispensation of justice. They have a better clearance rate as compared to the regular courts and hold speedy trials.
- Performance:
- As of June 2023, the FTSCs have successfully disposed of more than 1.74 lakh cases related to rape and POCSO Act.
- This reflects the significant impact of these specialized courts in providing speedy justice to the victims of sexual offences.
- 763 FTSCs are currently functional across 29 States and Union Territories.
- Among these, 412 courts are exclusive POCSO Courts.
- As of June 2023, the FTSCs have successfully disposed of more than 1.74 lakh cases related to rape and POCSO Act.
What are the Challenges Related to Fast Track Special Court?
- Inadequate Infrastructure and Low Disposal Rate:
- Special courts in India often suffer from the same challenges as regular courts, as they are usually designated rather than established as new infrastructure.
- This leads to overburdened judges who are assigned other categories of cases in addition to their existing workload without the necessary support staff or infrastructure.
- Consequently, the disposal rate of cases in these special courts slows down.
- According to data from the Ministry of Law and Justice till May 2023, Delhi's FTSCs have a disposal rate of only 19%, which is one of the lowest in the country.
- Limited Jurisdiction:
- These courts are established with a specific jurisdiction, which can limit their ability to deal with related cases. This can lead to delays in justice delivery and a lack of consistency in the application of laws.
- Ideally, cases in these special courts should be disposed of within a year. However, as of May 2023, Delhi had only disposed of 1,049 cases out of a total of 4,369 pending cases. This indicates a significant lag in meeting the target.
- These courts are established with a specific jurisdiction, which can limit their ability to deal with related cases. This can lead to delays in justice delivery and a lack of consistency in the application of laws.
- Vacancies and Lack of Training:
- The lack of judges due to vacancies affects the courts' capacity to handle cases effectively.
- As of 2022, lower courts across India had a vacancy rate of 23%.
- Regular judges from normal courts are often deputed to work in FTSCs.
- However, these courts require judges with specialized training to handle cases quickly and effectively.
- The lack of judges due to vacancies affects the courts' capacity to handle cases effectively.
- Prioritization of Certain Offences Over Others:
- The establishment of special courts in India is often determined by ad-hoc decisions made by both the judicial and executive branches of government.
- This approach means that certain categories of offences are arbitrarily prioritised for faster disposal over others.
What are the Initiatives to Curb Women and Child Abuse?
Way Forward
- Adequate infrastructure, including courtrooms, support staff, and modern technology, should be provided to FTSCs to ensure smooth and efficient operations.
- Additional funding should be allocated for the establishment and maintenance of these specialized courts.
- To enhance the disposal rate, FTSCs should focus on strict case management, reducing unnecessary delays caused by adjournments, and ensuring the timely presentation of evidence.
- Specialized training for judges and support staff can help streamline procedures and enhance the speed of proceedings.
- Efforts should be made to fill vacancies promptly and ensure that judges with relevant expertise are assigned to these courts.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q.1 Examine the main provisions of the National Child Policy and throw light on the status of its implementation. (2016)
Q.2 We are witnessing increasing instances of sexual violence against women in the country. Despite existing legal provisions against it, the number of such incidences is on the rise. Suggest Some innovative measures to tackle this menace. (2014)
Important Facts For Prelims
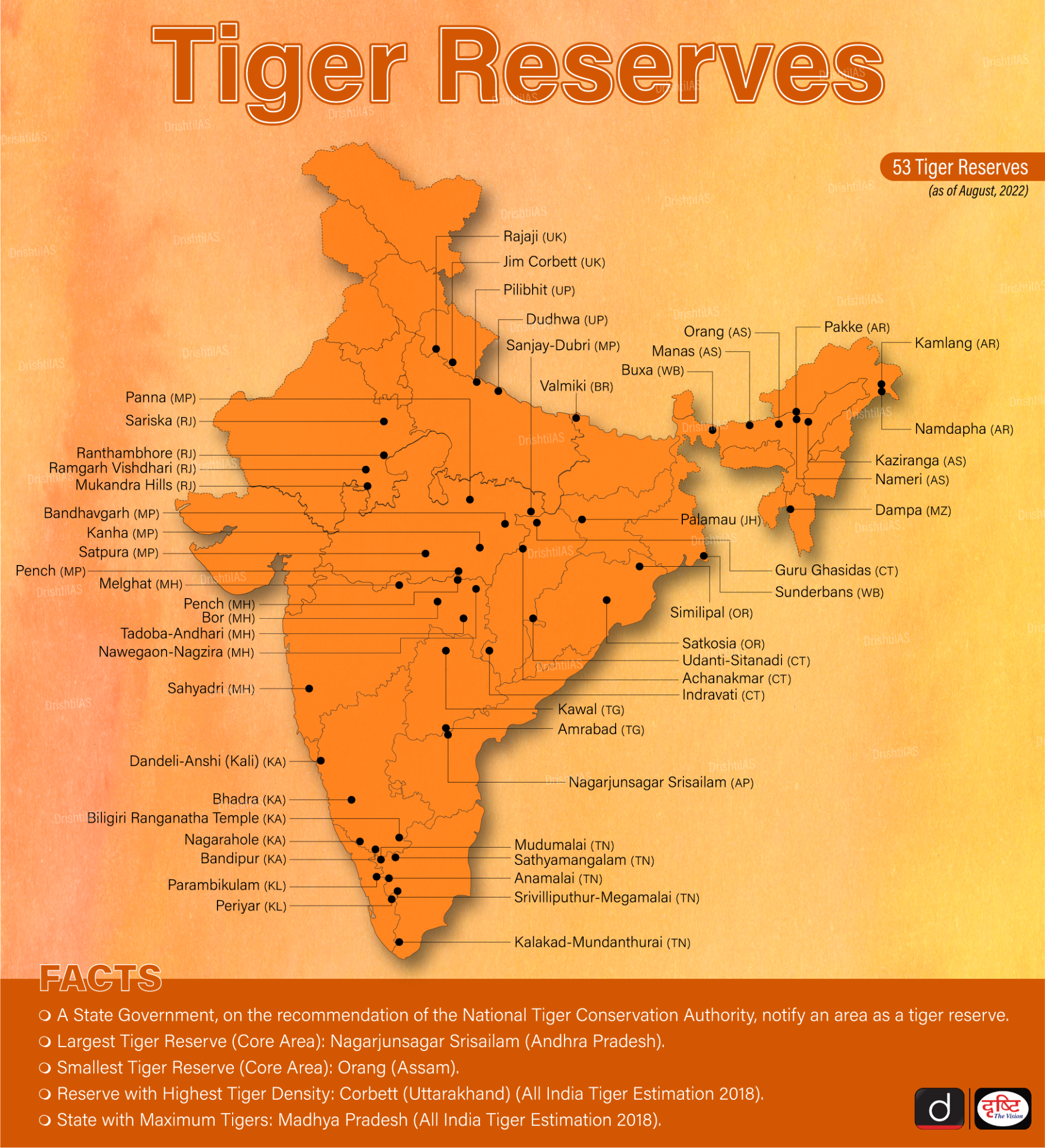
Dholpur-Karauli: India’s 54th Tiger Reserve
Why in News?
National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has given its approval for the establishment of the Dholpur-Karauli Tiger Reserve in the state of Rajasthan.
- It has secured its position as the fifth tiger reserve in the state of Rajasthan following Mukundra Hills, Ramgarh Vishdhari, Ranthambore, and Sariska.
What are Tiger Reserves?
- A protected area designated for the conservation of the striped big cats (tigers) is referred to as Tiger Reserve. However, a tiger reserve may also be a national park or wildlife sanctuary.
- For Example: The Sariska Tiger Reserve is also a national park. It is so because the place was originally created as a national park and later dedicated to tiger conservation.
- Tiger Reserves are notified by State Governments as per provisions of Section 38V of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 on advice of the National Tiger Conservation Authority.
- Presently, India accommodates a total of 54 Tiger Reserves (with the most recent addition being the Dholpur-Karauli Tiger Reserve).
Note:
- India is home to 75% of the world’s tiger population. As per the latest report on the Status of Tigers in India, the tiger count in the country has surged to 3,167 as of 2022.
- Project Tiger is an ongoing centrally sponsored program of the Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change that provides government assistance to tiger states for tiger conservation in designated tiger reserves
What is the National Tiger Conservation Authority?
- About:
- The NTCA is a statutory body under the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change constituted under enabling provisions of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, as amended in 2006, for strengthening tiger conservation.
- Objectives:
- Providing statutory authority to Project Tiger so that compliance of its directives becomes legal.
- Fostering accountability of Center-State in management of Tiger Reserves, by providing a basis for MoU with States within our federal structure.
- Addressing livelihood interests of local people in areas surrounding Tiger Reserves.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Consider the following protected areas: (2012)
- Bandipur
- Bhitarkanika
- Manas
- Sunderbans
Which of the above are declared Tiger Reserves?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Q2. From the ecological point of view, which one of the following assumes importance in being a good link between the Eastern Ghats and the Western Ghats? (2017)
(a) Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
(b) Nallamala Forest
(c) Nagarhole National Park
(d) Seshachalam Biosphere Reserve
Ans: (a)
Important Facts For Prelims
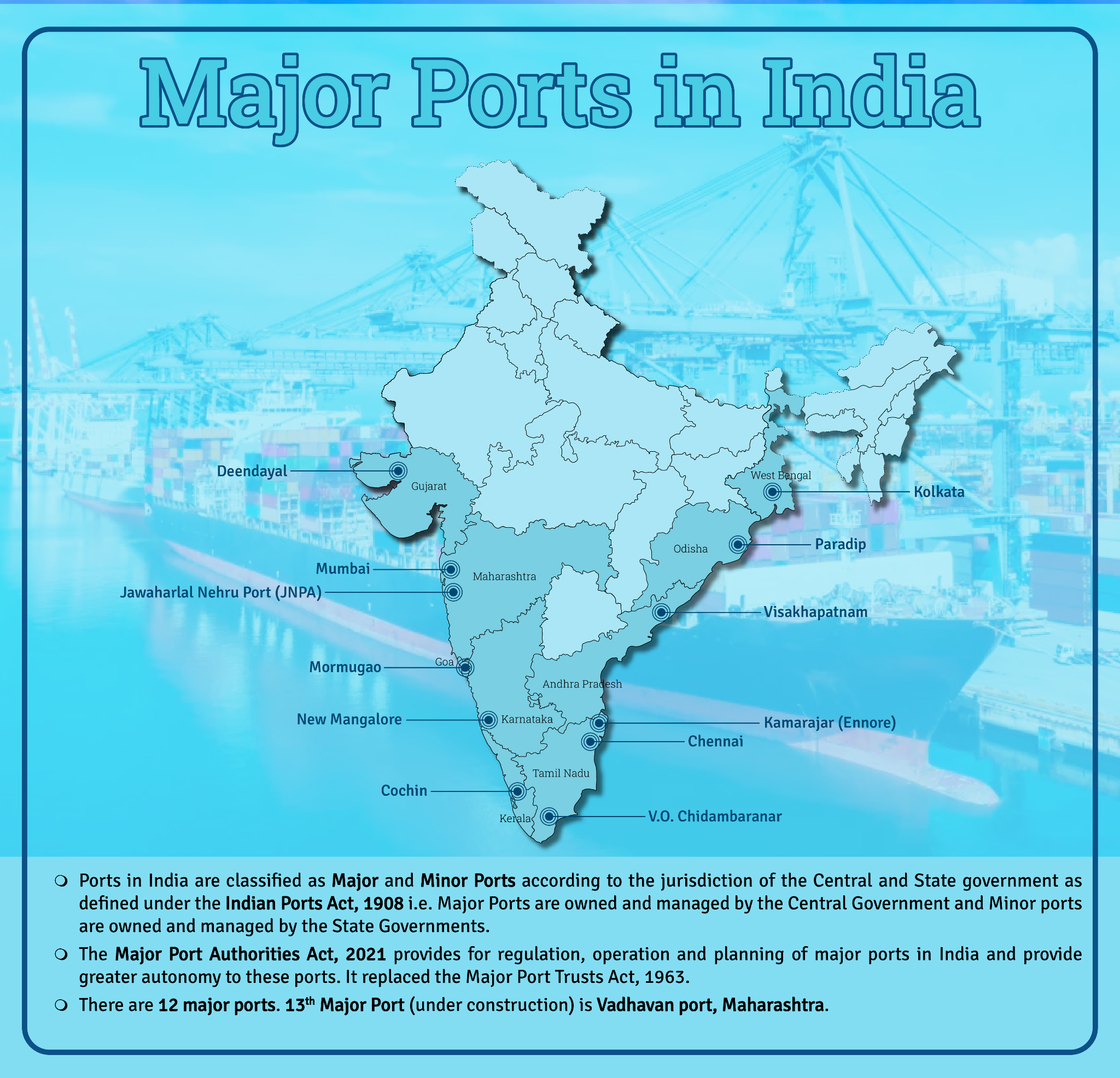
Container Terminal Project at Deendayal Port
Why in News?
Recently, the Deendayal Port Authority and Dubai-based DP World, a multinational logistics company, partnered for the Mega Container Terminal Project at Tuna Tekra, Gujarat. The initiative was initiated by India's Ministry of Ports, Shipping & Waterways (MoPSW).
- With the aim to enhance port capacity, foster multimodal logistics, and promote global connectivity, this venture signifies a pivotal step in public-private partnership.
What are the Key Highlights of Container Terminal?
- The terminal will have an annual capacity to handle 2.19 million twenty foot equivalent units (TEUs) with capability to handle next-generation vessels carrying more than 18,000 TEUs.
- Mega Container Terminal Project is fully compliant with the green port guidelines.
- The terminal will connect Northern, Western and Central India with the Global market.
- The project aligns with India’s Vision 2047 to quadruple port handling capacity.
- The terminal will be a part of the National Infrastructure Pipeline complementing PM Gati Shakti.
- The Container Terminal is expected to transform the economic landscape of Kutch, with the creation of several ancillary services like warehousing, etc. and also result in the creation of direct and indirect employment opportunities.
What are the Key Points About Deendayal Port?
- Deendayal Port, also known as Kandla port, is one of the twelve Major Ports in India and is located on the West Coast of India, in the Gulf of Kutch in the State of Gujarat.
- Deendayal Port primarily services northern India, including the landlocked Jammu and Kashmir, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan.
- Deendayal Port’s journey began in 1931 with the construction of RCC Jetty by Maharao Khengarji. After the independence of India in 1947, Deendayal Port emerged to be India’s No. 1 Port in the year 2007-08 and has retained the top position for the 14th consecutive year since then.
- In 2016, Deendayal Port created history by handling 100 MMT cargo in a year – the first Major Port to achieve this milestone.
- It is the largest port in India by volume of cargo handled.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Consider the following pairs:
| Port | Well known as |
| 1. Kamarajar Port | First major port in India registered as a company |
| 2. Mundra Port | Largest privately owned port in India |
| 3. Visakhapatnam Port | Largest container port in India |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
(a) Only one pair
(b) Only two pairs
(c) All three pairs
(d) None of the pairs
Explanation: (b)
- Kamarajar Port, formerly known as Ennore Port, is the first major port in India registered as a company and is the only corporatized major port in India. Hence, pair 1 is correctly matched.
- It was declared as the 12th major port of India in March 1999 and incorporated as Ennore Port Limited under the Companies Act, 1956 in October 1999.
- It is located on the Coromandel Coast about 24 km north of Chennai Port, Tamil Nadu.
- Mundra Port is India's largest commercial port located on the northern shores of the Gulf of Kutch near Mundra, Kutch district, Gujarat. It is owned and operated by Adani Ports and Special Economic Zone Limited (APSEZ), which is a part of Adani Group.
- It was established in 1998 as a private sector port and became operational in October 2001. It handles various types of cargo such as containers, bulk, break-bulk, liquid, chemicals, automobiles, etc. Hence, pair 2 is correctly matched.
- Visakhapatnam Port, located on the east coast of India in Andhra Pradesh, is not the largest container port in India. It is one of the oldest and largest major ports in India, handling various types of cargo such as iron ore, coal, petroleum products, fertilisers, containers, etc.
- The largest container port in India is Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust (JNPT), located near Mumbai in Maharashtra. Hence, pair 3 is NOT correctly matched.
Q. In India, the ports are categorized as major and nonmajor ports. Which one of the following is a nonmajor port? (2009)
(a) Kochi (Cochin)
(b) Dahej
(c) Paradip
(d) New Mangalore
Ans: (b)
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
India's Current Account Deficit Narrows Amid Trade Shifts
India's Current Account Deficit (CAD) is being influenced by shifts in trade patterns. The deficit is expected to decrease to around USD 10 billion or 1% of the GDP in the April-June quarter of 2023-24, down from USD 18 billion or 2.1% in the same period of 2022-23.
- CAD is a crucial economic indicator that quantifies the difference between a country's earnings from foreign trade and its expenditures on imports of goods and services, including transfer payments.
- A CAD arises when a nation's imports exceed its exports, leading to an outflow of currency and often necessitating foreign borrowing to bridge the gap.
- A low CAD can be seen as a positive economic indicator because it often implies that the country's economy is self-sustaining and is able to finance its external commitments without straining its resources.
- It can also indicate that the country is competitive in international trade and has a balanced approach to its imports and exports.
Read more: Current Account Deficit
Public Declarations Not Necessary for Marriages: Supreme Court
Recently, the Supreme Court has declared that not all marriages necessitate a public declaration or solemnization. Also, the court approved a Tamil Nadu law that allowed “self-respect” marriages and affirmed that lawyers can officiate at 'self-respect marriages' between consenting adults.
- Through a state amendment in 1967, Section 7-A of the Hindu Marriage Act, applicable to Tamil Nadu, provides legal recognition to self-respect or reformist marriages among Hindus.
- These marriages can be solemnized in the presence of relatives, friends, or other individuals and allow couples to marry without a formal public ceremony and empower advocates to conduct such unions in private settings.
- The court's ruling upholds an individual's right to choose a life partner without external interference, in accordance with Article 21 of the Indian Constitution.
- Solemnizing marriage without a Brahmin priest was the prime objective of the Self Respect Movement started by E.V. Ramaswamy Naicker (Periyar) in 1925.
Read more: Hindu Marriage Act, Article 21, Supreme Court.
Exploring Consciousness in Artificial Intelligence
Researchers have developed a checklist based on neuroscience-based theories that could help assess whether an Artificial Intelligence(AI) system is conscious.
- The study suggests that the rapid progress in the field of AI has raised the possibility that conscious AI systems could be built in the near future.
- However, human-like behaviors can make it difficult to judge the true level of engagement by AI systems.
- Being conscious means experiencing consciousness or having the potential for it.
- "Conscious" is different from "sentient" which refers to having senses.
- No AI system appears to be a strong candidate for consciousness at present.
- Microsoft's study: GPT-4 AI can think and use common sense like humans.
- Researchers believe assessing AI consciousness is scientifically doable, and the authors provided initial evidence that many of the indicator properties can be implemented in AI systems using current techniques.
Read more: India and Generative AI
Kampala Declaration on Climate Change
A significant step has been taken by 48 African countries to adopt the Kampala Ministerial Declaration on Migration, Environment, and Climate Change (KDMECC) to address the interconnection between human mobility and climate change on the continent.
- The decision was discussed at a Conference of States co-hosted by Kenya and Uganda. The initiative was supported by the International Organization for Migration (IOM) and the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- IOM was born in 1951 out of the chaos and displacement of Western Europe following the Second World War.
- Africa is highly vulnerable to climate change's impacts, leading to increased migration due to extreme weather events.
- KDMECC Originally signed by 15 African states in Kampala, Uganda, in July 2022. The KDMECC-AFRICA is expected to be signed by Member States during the Africa Climate Summit in Nairobi on September 4, 2023.
- The Declaration is the first comprehensive, action-oriented framework led by Member States to address climate-induced mobility in a practical and effective manner.
- The KDMECC-AFRICA will ensure that all voices, including those of youth, women, and persons in vulnerable situations are the priority of the expanded declaration.