Forest Conservation Amendment Bill 2023
For Prelims: Forest Conservation Amendment Bill 2023, Supreme Court, Forest Conservation Rules, Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980, Van (Sanrakshan Evam Samvardhan) Adhiniyam, 1980.
For Mains: Forest Conservation Amendment Bill 2023.
Why in News?
Recently, the Forest (Conservation) Amendment Bill 2023 has been passed by the Lok Sabha, and it aims to bring significant changes to the Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980, which is a crucial central statute for the conservation of forests in India.
What is the Background?
- After Independence, vast areas of forest land were designated as reserved and protected forests.
- However, many forested areas were left out, and areas without any standing forests were included in 'forest' lands.
- In Godavarman case, 1996, the Supreme Court suspended the felling of trees across the country, and ruled that the FC Act would apply to all land parcels that were either recorded as 'forest' or resembled the dictionary meaning of forest.
- In June 2022, the government amended the Forest Conservation Rules to propose a mechanism to allow developers to raise plantations "over land on which the (FC) Act is not applicable" and to swap such plots against subsequent requirements of compensatory afforestation.
What are the Key Provisions of the Forest (Conservation) Amendment Bill 2023?
- Scope of the Act:
- The Bill broadens the scope of the Act by inserting a Preamble.
- The Act's name was changed to Van (Sanrakshan Evam Samvardhan) Adhiniyam, 1980 to reflect the potential of its provisions.
- Applicability on Various Lands:
- The Act, which was initially applied to notified forest land, was later extended to revenue forest land and lands recorded as forest in government records.
- The amendments seek to streamline the application of the Act to recorded forest lands, private forest lands, plantations, etc.
- Exemptions:
- The Bill proposes certain exemptions to encourage afforestation and plantation outside forests.
- 0.10 ha of forest land has been proposed to provide connectivity for habitation and establishments located on the side of roads and railways, up to 10 ha of land proposed for security related infrastructure and up to 5 ha of forest land in Left Wing Extremism Affected Districts for public utility projects.
- These exemptions include strategic projects related to national security within 100 km of the International Borders, Line of Actual Control (LAC), Line of Control (LoC) etc.
- Provisions for Development:
- The Bill extends existing provisions of the Principal Act relating to assignment of forest land, on lease to private entities, to Government companies as well.
- This will facilitate development projects and ensure uniformity in the implementation of the Act.
- New Forestry Activities:
- The amendments add new activities such as infrastructure for frontline forest staff, ecotourism, zoo, and safari into the array of forestry activities for the conservation of forests. Surveys and investigations in forest areas will not be considered non-forestry activities.
- Climate Change Mitigation and Conservation:
- It aims to ensure that such areas contribute to India's efforts in combating climate change by being recognized as part of its forest conservation efforts and contribute to India’s international commitments like Net Zero Emission by 2070
- Empowering Local Communities:
- The Bill encourages activities like establishment of zoos, safaris, and ecotourism, which will be owned by the government and set up in approved plans outside Protected Areas.
- These activities not only raise awareness about forest conservation and wildlife protection but also create livelihood opportunities for local communities, integrating them with overall development.
What are the Concerns Related to the Bill?
- Objection on Hindi Name:
- There were objections to the Act’s new name (which is now in hindi) on the grounds that it was “non-inclusive” and left out many among the “(non-Hindi speaking) population both in South India and also in the North-East.
- Impact on Ecologically Sensitive Areas:
- The proposed exemptions in the Bill, particularly those related to strategic projects near international borders, have raised concerns about the potential clearance of forests in ecologically sensitive areas, such as the Himalayan, trans-Himalayan, and northeastern regions.
- Bill, 2023 (FCA) will erase the rights of indigenous communities living on India’s borders.
- Without appropriate "assessment and mitigation plans," such clearances could threaten biodiversity and trigger extreme weather events.
- The proposed exemptions in the Bill, particularly those related to strategic projects near international borders, have raised concerns about the potential clearance of forests in ecologically sensitive areas, such as the Himalayan, trans-Himalayan, and northeastern regions.
- Limited Applicability:
- The Bill restricts the legislation's ambit only to areas recorded as forests on or after October1980. This exclusion may result in leaving out significant sections of forest land and biodiversity hot spots from the Act's purview, allowing them to be potentially sold, diverted, cleared, and exploited for non-forestry purposes.
- Concurrent List and Center-State Balance:
- Some State governments have argued that forest conservation falls under the Concurrent List, which means both the Center and States have a role in the matter.
- They believe that the proposed amendments could tilt the balance towards the Center and may impact the rights and authority of the State governments in forest conservation matters.
Way Forward
- There is a need to conduct a thorough and comprehensive assessment of the proposed amendments and their potential impacts on forests, biodiversity, and local communities.
- This assessment should consider ecological, social, and environmental factors and involve input from diverse stakeholders, including experts, NGOs, tribal communities, and State governments.
- Continue engaging in meaningful consultation and dialogue with all stakeholders to understand their perspectives and address their concerns. This will promote transparency, inclusivity, and better decision-making.
Empowering India's Senior Citizens
For Prelims: SAGE Portal, SACRED Portal, Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana , Silver economy
For Mains: Significance of empowering senior citizens, Role of the government in facilitating silver economy
Why in News?
Recently, the Minister of State for the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment provided valuable insights into the accomplishments of the Seniorcare Ageing Growth Engine(SAGE) Portal and Senior Able Citizens for Re-Employment in Dignity (SACRED) Portal the significant contributions made under the Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana (AVYAY).
- These initiatives have been instrumental in addressing the needs and concerns of India's senior citizens, fostering innovation, providing employment opportunities, and ensuring the overall well-being of the elderly population.
What is SAGE Portal?
- The SAGE Portal serves as a catalyst to attract entrepreneurs and start-ups to invest in the "silver economy" segment, fostering innovation in elderly care solutions.
- SAGE provides convenient "one-stop access" for stakeholders, including senior citizens and their families, to discover and access a wide range of products and services catering to their needs.
- The government plays a crucial role as a facilitator, enabling the elderly to access the products and services offered by identified start-ups through the SAGE Portal.
- Selected start-ups or start-up ideas receive equity support of up to Rs. 1 crore per project through the Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI).
- The government ensures that the total government equity in the start-up does not exceed 49%.
Silver Economy
- The silver economy is the system of production, distribution and consumption of goods and services aimed at using the purchasing potential of older and ageing people and satisfying their consumption, living and health needs.
- The silver economy is analyzed in the field of social gerontology (study of aging) not as an existing economic system but as an instrument of ageing policy and the political idea of forming a potential, needs-oriented economic system for an aging population.
- Its main element is gerontechnology (Technology pertaining to aged people) as a new scientific, research and implementation paradigm.
What is SACRED Portal?
- SACRED Portal empower senior citizens and provide them with opportunities for re-employment.
- This portal specifically targets citizens aged 60 years and above, focusing on the needs and requirements of this age group.
- The portal provides opportunities for senior citizens to find suitable jobs and work options that match their preferences and skills.
- The SACRED Portal employs a virtual matching system that aligns the preferences of senior citizens with private enterprises seeking experienced individuals.
- Through job opportunities, the SACRED Portal helps senior citizens attain financial security and reduces their dependence on external support.
What is Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana (AVYAY)?
- About:
- The AVYAY aims to provide holistic support for senior citizens.
- Components:
- Integrated Programme for Senior Citizens (IPSrC):
- This component grants aid to implementing agencies to run and maintain Senior Citizens Homes, offering shelter, food, medical care, and entertainment opportunities for indigent senior citizens.
- State Action Plan for Senior Citizens (SAPSrC):
- States and Union Territories receive grant-in-aid to create a pool of trained geriatric caregivers, conduct special cataract drives, and implement other state-specific welfare activities for indigent senior citizens.
- Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana (RVY):
- This component provides eligible senior citizens suffering from age-related disabilities with assisted living devices, enhancing their bodily functions and overcoming their disabilities.
- Elderline - National Helpline for Senior Citizens (NHSC):
- The Elderline offers a toll-free helpline (14567) to provide free information, guidance, emotional support, and field intervention in cases of abuse, ensuring an improved quality of life for senior citizens.
- Senior-care Ageing Growth Engine (SAGE): This component aims to encourage youth to think about the problems of the elderly and come up with innovative ideas for elderly care and promote them into start-ups by providing equity support.
- Integrated Programme for Senior Citizens (IPSrC):
- Outcomes:
- Nearly 1.5 lakh beneficiaries are staying in the Senior Citizen homes.
- During the last 3 financial years a total of Rs. 288.08 crore grants in aid released and number of beneficiaries is 3,63,570.
- Improved quality of life and social integration for indigent elderly individuals.
- Promotion of an inclusive society that values and respects senior citizens.
- Economic growth through the development of the "silver economy" and employment generation.
What are the Other Initiatives Related to Elderly in India?
Welfare Schemes for the Minority Communities
For Prelims: Pre-Matric Scholarship Scheme,Post-Matric Scholarship Scheme,Pradhan Mantri Virasat Ka Samvardhan, Minority Communities
For Mains: Welfare schemes related to minority communities, Issues Related to Minorities
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Minority Affairs, shared significant achievements and insights about the various schemes and initiatives implemented by the government for the welfare and upliftment of minority communities in India.
What are the Various Schemes for the Welfare of Minority Communities in India?
- Educational Empowerment Schemes:
- Pre-Matric Scholarship Scheme:
- It is a centrally funded scholarship scheme for students in all states, which is open every year.
- Aims to provide financial assistance to students from minority communities studying in classes 1 to 10.
- Helps in covering educational expenses and encouraging minority students to pursue education.
- Post-Matric Scholarship Scheme:
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme and implemented through State Government and UT administration.
- Provides scholarships to minority students studying in classes 11 and 12 and pursuing undergraduate and postgraduate courses.
- Supports students in pursuing higher education and enhancing their career prospects.
- National Means Cum-Merit Scholarship Scheme (NMMSS):
- It is the Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) which was launched in 2008.
- Focuses on providing financial assistance to meritorious minority students with limited financial resources.
- Encourages academic excellence and ensures equal opportunities for deserving students.
- Education Loan Scheme by National Minorities Development & Finance Corporation (NMDFC):
- NMDFC offers an Education Loan Scheme to students belonging to minority communities, including the Jain community.
- Concessional credit is provided for pursuing technical and professional courses with a maximum course duration of 5 years.
- Educational loans of up to ₹20.00 lakh are available for 5-year courses in India and ₹30.00 lakh for 5-year courses abroad.
- Pre-Matric Scholarship Scheme:
- Employment and Economic Empowerment Schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri Virasat Ka Samvardhan (PMVIKAS):
- Aims to preserve and promote the rich cultural heritage of minority communities.
- Supports traditional crafts, art forms, and cultural practices to empower artisans and craftsmen.
- NMDFC Scheme:
- Provides concessional loans to minorities to support their economic ventures and entrepreneurship.
- Enables economic self-reliance and promotes sustainable livelihoods.
- Pradhan Mantri Virasat Ka Samvardhan (PMVIKAS):
- Special Schemes:
- Jiyo Parsi:
- A unique scheme aimed at reversing the population decline of the Parsi community in India.
- Implements measures to encourage Parsi families to have more children and sustain their community's cultural legacy.
- Qaumi Waqf Board Taraqqiati Scheme (QWBTS) and Shahari Waqf Sampatti Vikas Yojana (SWSVY):
- Focuses on the development and utilization of waqf properties for the welfare of minority communities.
- Enhances infrastructure and facilities in waqf properties to serve the community better.
- Jiyo Parsi:
- Infrastructure Development Schemes:
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK):
- Aims at creating better infrastructure in minority-concentrated areas.
- Provides improved amenities, healthcare facilities, education centers, and skill development opportunities.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram (PMJVK):
Minority Communities in India:
- About:
- Muslims, Sikhs, Christians, Buddhists, and Zoroastrians (Parsis) have been notified as minority communities under the National Commission for Minorities Act, 1992.
- In 2014, Jains were also notified as a minority community.
- As per the Census 2011, the percentage of minorities in the country is about 19.3% of the total population of the country.
- The population of Muslims are 14.2%; Christians 2.3%; Sikhs 1.7%, Buddhists 0.7%, Jain 0.4% and Parsis 0.006%.
- Muslims, Sikhs, Christians, Buddhists, and Zoroastrians (Parsis) have been notified as minority communities under the National Commission for Minorities Act, 1992.
- Constitutional Provisions:
- The term "minority" is not defined in the Indian Constitution. However, the Constitution recognizes only religious and linguistic minorities.
- Article 29: It provides that any section of the citizens residing in any part of India having a distinct language, script or culture of its own, shall have the right to conserve the same.
- Article 30: Under the article, all minorities shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.
- Article 350-B: Originally, the Constitution of India did not make any provision with respect to the Special Officer for Linguistic Minorities. But, the Seventh Constitutional Amendment Act of 1956 inserted Article 350-B in the Constitution.
- Parliamentary Provisions:
- National Commission for Minorities Act, 1992: It defines a minority as “a community notified as such by the Central government.'
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In India, if a religious sect/community is given the status of a national minority, what special advantages it is entitled to? (2011)
- It can establish and administer exclusive educational institutions.
- The President of India automatically nominates a representative of the community to Lok Sabha.
- It can derive benefits from the Prime Minister’s 15-Point Programme.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- At present Muslims, Sikhs, Buddhists, Jains, Christians, and Parsis (Zoroastrians) are notified as minority religious communities by GoI. There are certain special advantages that these communities are entitled by the Constitution of India as well as various other legislative and administrative measures.
- Article 30 of the Indian Constitution upholds the right of religious and linguistic minorities to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice. Hence, statement 1 is correct. There is no provision for the President of India to automatically nominate a member of a minority religious community to the Lok Sabha. This provision was earlier available for members of Anglo-Indian community under Article 331 of the Constitution. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Religious minorities can derive benefits from the Prime Minister’s 15-Point Programme. The programme was launched in 2005 to ensure the welfare of minorities in the fields of education, skill development, employment and prevention of communal conflicts. Hence, statement 3 is correct. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Left Wing Extremism in India
For Prelims: National Policy and Action Plan to address Left Wing Extremism 2015, Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015, SAMADHAN Initiative.
For Mains: Issues Associated with Left Wing Extremism in India.
Why in News?
In a recent announcement, the Ministry for Home Affairs revealed that starting from 2022, India is maintaining separate data for incidents involving Left Wing Extremists.
- LWE has been a significant security challenge in India for several decades, particularly in regions affected by civil unrest and armed conflicts.
What is Left Wing Extremism?
- About:
- Left-wing extremism, also known as left-wing terrorism or radical left-wing movements, refers to political ideologies and groups that advocate for significant societal and political change through revolutionary means.
- LWE groups may target government institutions, law enforcement agencies, or private property to further their agenda.
- The LWE movement in India originated in a 1967 uprising in Naxalbari, West Bengal.
- Status in India:
- Union Home Ministry has stated that violence related to LWE had come down by 76% in 2022 as compared to 2010
- Also, there has been a decrease in the geographical spread of violence as only 46 districts reported LWE-related violence in 2021, compared to 96 districts in 2010.
- Union Home Ministry has stated that violence related to LWE had come down by 76% in 2022 as compared to 2010
- Responsible Factors for LWE: The 2006 D Bandopadhyay Committee identified governance gaps and extensive discrimination against tribals in economic, socio-political, and cultural spheres as the primary causes of Naxalism's proliferation.
- Socio-economic Disparities: India has significant socio-economic disparities, with large sections of the population living in poverty and facing issues such as, unemployment, and lack of access to basic amenities.
- Left-wing extremist groups have historically capitalized on these grievances and used them to gain support among the marginalized communities.
- Land Alienation and Displacement: The issue of land rights and land alienation has been a major concern for many rural communities in India.
- The development projects and acquisition of land for industrial purposes have sometimes led to the displacement of local communities without adequate compensation or rehabilitation.
- This has been a focal point of Naxalite agitation.
- The development projects and acquisition of land for industrial purposes have sometimes led to the displacement of local communities without adequate compensation or rehabilitation.
- Adivasi Rights: India is home to a significant number of Adivasis, who are indigenous communities with their distinct cultures and traditions.
- Left-wing extremist groups often advocate for Adivasi rights and resist perceived exploitation of their resources and displacement from their ancestral lands.
- Socio-economic Disparities: India has significant socio-economic disparities, with large sections of the population living in poverty and facing issues such as, unemployment, and lack of access to basic amenities.
- Government Initiatives:
- 'National Policy and Action Plan to address Left Wing Extremism 2015: The plan adopted a comprehensive approach that involved various facets of governance, security, and development.
- It aims to enhance the capabilities of security forces to combat LWE and contain its spread.
- It ensures that the rights and entitlements of local communities are safeguarded, thereby reducing grievances that fuel extremist ideologies.
- It also focuses on socio-economic development in affected regions to address the root causes of extremism and improve the lives of local communities.
- Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015: The Juvenile Justice Act, enacted in 2015, plays a crucial role in protecting children affected by LWE, particularly those in distress situations, including:
- Children in Conflict with Law (CCL): Children involved in illegal activities related to LWE are provided with care and protection through this act.
- Children in Need of Care and Protection (CNCP): Children who are victims of or affected by armed conflicts, civil unrest, or natural calamities are recognized as needing care and protection under this act.
- Criminal Prosecution: The act makes it clear that any non-state, self-styled militant group or outfit recruiting or using children for any purpose will face criminal prosecution.
- SAMADHAN: It is the one-stop solution for the LWE problem. It encompasses the entire strategy of government from short-term policy to long-term policy formulated at different levels. SAMADHAN stands for-
- S- Smart Leadership,
- A- Aggressive Strategy,
- M- Motivation and Training,
- A- Actionable Intelligence,
- D- Dashboard Based KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) and KRAs (Key Result Areas),
- H- Harnessing Technology,
- A- Action plan for each Theatre,
- N- No access to Financing.
- 'National Policy and Action Plan to address Left Wing Extremism 2015: The plan adopted a comprehensive approach that involved various facets of governance, security, and development.
Way Forward
- Community Engagement and Dialogue: There is a need to foster open channels of communication between the government, security forces, and affected communities.
- Also, there is a need to encourage community leaders, NGOs, and religious institutions to play a role in mediating conflicts and addressing local issues.
- Youth Entrepreneurship and Startup Incubation: Establish entrepreneurship and startup incubation centers in affected regions to encourage young people to channel their energy and creativity into business ventures.
- This can provide an alternative path to economic growth and self-sufficiency.
- Ecological and Sustainable Development Initiatives: Introduce projects that focus on sustainable development and conservation of natural resources in areas affected by extremism.
- By involving local communities in environmental protection efforts, a sense of ownership and responsibility can be fostered, leading to reduced extremism.
- Empowering Local Peace Ambassadors: Identify and empower influential individuals within communities who are committed to promoting peace and countering extremist narratives.
- Provide them with resources and support to spread messages of harmony and understanding.
- Social Impact Bonding: Introduce social impact bonds to attract private investments in social initiatives focused on countering extremism.
- Investors will receive returns based on the success of these initiatives, creating incentives for impactful programs.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. The persisting drives of the government for development of large industries in backward areas have resulted in isolating the tribal population and the farmers who face multiple displacements. With Malkangiri and Naxalbari foci, discuss the corrective strategies needed to win the Left-Wing Extremism (LWE) doctrine that affected citizens back into the mainstream of social and economic growth. (2015)
Fast Radio Bursts
Fast Radio Bursts
Why in News?
Recently, an international team of astronomers studied repeating Fast Radio Bursts (FRB), FRB 20190520B, using the Green Bank Telescope in the U.S. and the Parkes Observatory in Australia. The report was published in the journal Science.
What are Fast Radio Bursts?
- They are mysterious emissions of radio light (or Radio Waves) that come from the far reaches of the universe.
- FRBs reach Earth from faraway galaxies, emitting as much energy in a millisecond as the sun does over weeks.
- They are the brightest radio bursts found in nature.
- Astrophysicists have only been able to 'see' FRBs momentarily using large radio telescopes, but their precise origins and causes are unknown.
- Some FRBs are 'one-off' phenomena, while others are repeaters, flashing earth intermittently.
What are the Key Highlights of the Study?
- Highly Variable Faraday Rotation Measure:
- The astronomers discovered that the Faraday rotation measure of the repeating FRB 20190520B was highly variable and reversed direction twice.
- This measure is an indicator of the FRB's magnetic field strength.
- The astronomers discovered that the Faraday rotation measure of the repeating FRB 20190520B was highly variable and reversed direction twice.
- Binary Star System:
- The variation in the FRB's magnetic field strength and the direction of the reversal led the researchers to conclude that the FRB source is likely orbiting a binary star system, where the companion star is possibly a massive star or a black hole.
- This led to the raising of the possibility that "all repeating FRBs could be in binaries." However, further monitoring and research are required to confirm this hypothesis.
- The variation in the FRB's magnetic field strength and the direction of the reversal led the researchers to conclude that the FRB source is likely orbiting a binary star system, where the companion star is possibly a massive star or a black hole.
- Turbulent Magnetized Plasma Environment:
- The observed changes in the magnetic field and electron density around the FRB source suggest the presence of a turbulent magnetized plasma environment.
- This environment likely influences the behavior of the FRB signals.
- The observed changes in the magnetic field and electron density around the FRB source suggest the presence of a turbulent magnetized plasma environment.
- Importance of Radio Telescopes:
- The study underscores the significance of advanced radio telescopes in studying FRBs and other intergalactic phenomena.
- These telescopes, such as the Very Large Array and the Deep Synoptic Array-110, enable precise localization of FRBs and provide valuable data for understanding their sources and characteristics.
- Unraveling Cosmic Mysteries:
- The study emphasizes the role of radio astronomy in unraveling cosmic mysteries and deepening our understanding of the universe.
World Hepatitis Day
Why in News?
World Hepatitis Day (WHD) takes place every year on 28th July bringing the world together under a single theme to raise awareness of the global burden of viral hepatitis and to influence real change.
What are the Key Points Related to WHD?
- Theme 2023: One life, one liver.
- Significance:
- On this day, communities, people, and politicians may learn about the many varieties of hepatitis, as well as about preventative strategies, testing, and treatment choices.
- It promotes global advocacy and cooperation in the fight against the rising number of hepatitis-related diseases and fatalities.
What is Hepatitis?
- About:
- The word hepatitis refers to any inflammation of the liver — the irritation or swelling of the liver cells from any cause.
- It can be acute (inflammation of the liver that presents with sickness — jaundice, fever, vomiting) or chronic (inflammation of the liver that lasts more than six months, but essentially showing no symptoms).
- Causes:
- Usually caused by a group of viruses known as the “hepatotropic” (liver directed) viruses, including A, B, C, D and E.
- Other viruses may also cause it, such as the varicella virus that causes chicken pox.
- SARS-CoV-2, the virus causing Covid-19 may injure the liver too.
- Other causes include drugs and alcohol abuse, fat buildup in the liver (fatty liver hepatitis) or an autoimmune process in which a person’s body makes antibodies that attack the liver (autoimmune hepatitis).
- Types of Hepatitis:
- Hepatitis A virus (HAV): It is an inflammation of the liver that can cause mild to severe illness.
- It is transmitted through ingestion of contaminated food and water or through direct contact with an infectious person (sex practices).
- Almost everyone recovers fully from hepatitis A with a lifelong immunity (few people with HAV could die from fulminant hepatitis).
- A safe and effective vaccine is available to prevent hepatitis A.
- Hepatitis B virus (HBV): It is a viral infection that attacks the liver and can cause both acute and chronic disease.
- It is most commonly transmitted from mother to child during birth, in early childhood, during sex with an infected partner, unsafe injections.
- Hepatitis B can be prevented by vaccines.
- Hepatitis C virus (HCV): The virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging in severity from a mild illness to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and cancer.
- It is a bloodborne virus and most infection occurs through exposure to unsafe health care, blood transfusions, injection drug use and sexual practices.
- Direct-acting antiviral medicines (DAAs) can cure more than 95% of persons with hepatitis C infection, but access to diagnosis and treatment is low.
- There is currently no effective vaccine against hepatitis C.
- Hepatitis D virus (HDV): It is a virus that requires hepatitis B virus (HBV) for its replication. It affects globally nearly 5% of people who have a chronic infection with HBV.
- Hepatitis B and D can infect people together (co-infection) or one after the other (super-infection). This is more common in native people, dialysis patients and drug users. Having both viruses is very bad for the liver and can cause cancer or death.
- Hepatitis D infection can be prevented by hepatitis B immunization, but treatment success rates are low.
- Hepatitis E virus (HEV): It is an inflammation of the liver caused by infection with the HEV. It is found worldwide, but most common in East and South Asia.
- The virus is transmitted via the fecal-oral route, principally via contaminated water.
- A vaccine to prevent hepatitis E virus infection has been developed and is licensed in China but is not yet available elsewhere.
- Hepatitis A virus (HAV): It is an inflammation of the liver that can cause mild to severe illness.
What are the Government Initiatives to Tackle Hepatitis?
- National Viral Hepatitis Control Program:
- The Program aims to end viral hepatitis as a public health threat by 2030 in the country.
- India's Universal Immunization Programme (UIP):
- Hepatitis B is included under India's UIP which provides free of cost vaccination against eleven vaccine-preventable diseases i.e., Tuberculosis, Diphtheria, Pertussis, Tetanus, Polio, Pneumonia and Meningitis due to Haemophilus Influenzae type b (Hib), Measles, Rubella, Japanese Encephalitis (JE) and Rotavirus diarrhoea.
Standard Model of Particle Physics and Electric Dipole Moment
Why in News?
Some physicists are doing experiments to find flaws in a theory called the Standard Model of particle physics with taking electron dipole moment into consideration.
What is the Standard Model of Particle Physics?
- About:
- The Standard Model of particle physics is a theoretical framework that describes the fundamental particles and their interactions.
- It incorporates three of the four fundamental forces of nature: electromagnetism, the weak nuclear force, and the strong nuclear force, while gravity is not included in this model.
- Components:
- Elementary Particles: The model classifies particles into two main categories: fermions and bosons.
- Fermions: These are particles that make up matter. They are further divided into two groups:
- Quarks: The building blocks of protons and neutrons, among other particles.
- Leptons: Include particles like electrons.
- Bosons: These particles are responsible for mediating the fundamental forces between fermions. It includes Photons, W and Z bosons, Gluons, Higgs boson.
- Limitations:
- It does not account for dark matter and dark energy, which are significant components of the universe.
- It doesn’t know why the Higgs boson is so heavy or why gravity is so much weaker than the other fundamental forces.
- It also does not provide a quantum theory of gravity, which is needed to understand phenomena such as black holes and the Big Bang.
- It does not account for dark matter and dark energy, which are significant components of the universe.
How does the Electron Play an Important Role in Testing the Standard Model?
- The electron is one of the simplest and most precisely measured particles in nature. It has a negative electric charge, a spin (a form of intrinsic angular momentum) and a mass, but no other known properties.
- According to the Standard Model, the electron should have a spherical shape, meaning that its positive and negative charges are distributed evenly around its center.
- This implies that it has no electric dipole moment (EDM), which is a measure of how its charges are separated along its spin axis.
- Therefore, measuring the EDM of the electron is a sensitive way to test the validity of the Standard Model and to probe for new physics beyond it.
What is Electric Dipole Moment?
- An EDM is a concept in physics that describes the separation of positive and negative charges within an object, creating a dipole. It is a vector quantity that measures the strength and direction of this charge separation.
- The strength of the dipole depends on how big the charges are and how far apart they are from each other.
- Electric dipoles are relevant in understanding the behavior of molecules, atoms, and even tiny particles that make up matter.
- Scientists study electric dipole moments to explore important questions, like why there is more matter than antimatter in the universe, and to search for new physics beyond our current understanding.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q1. The terms ‘Event Horizon’, ‘Singularity’, ‘String Theory’ and ‘Standard Model’ are sometimes seen in the news in the context of (2017)
(a) Observation and understanding of the Universe
(b) Study of the solar and the lunar eclipses
(c) Placing satellites in the orbit of the Earth
(d) Origin and evolution of living organisms on the Earth
Ans: (a)
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
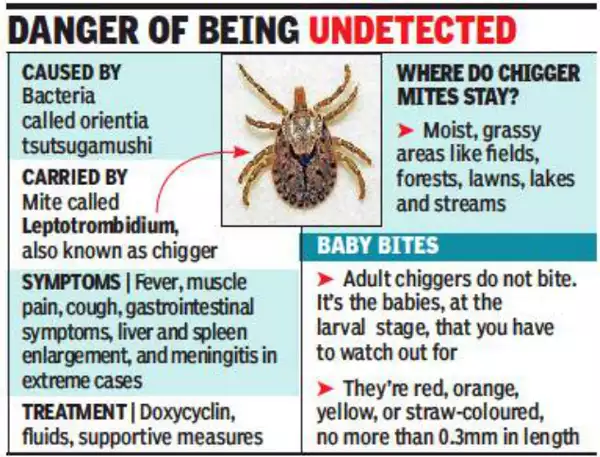
Scrub Typhus
The Kerala Health department has issued an alert against scrub typhus in Alappuzha, Kerala.
- About: Scrub typhus, also known as bush typhus, caused by a bacteria called Orientia tsutsugamushi.
- Spread: It is spread to people through bites of infected chiggers (larval mites).
- Humans mostly get the disease when bitten by chiggers present on the body of animals such as rats, rabbits, mice, and squirrels.
- Affected Areas: Rural areas of Southeast Asia, Indonesia, China, Japan, India, and northern Australia
- Treatment: Antibiotics. No vaccine available.
Read More: Scrub Typhus
Hygroelectricity
A team at the University of Massachusetts (UMass) Amherst published a paper declaring they had successfully generated a small but continuous electric current from humidity in the air which is called Hygroelectricity.
Significance:
- Hygroelectricity has the potential to be a renewable and sustainable energy source as it relies on the continuous availability of atmospheric moisture.
- Unlike traditional power generation methods that may rely on finite resources, hygroelectricity could provide a consistent source of energy from ambient environmental conditions.
Read More: Renewable Energy
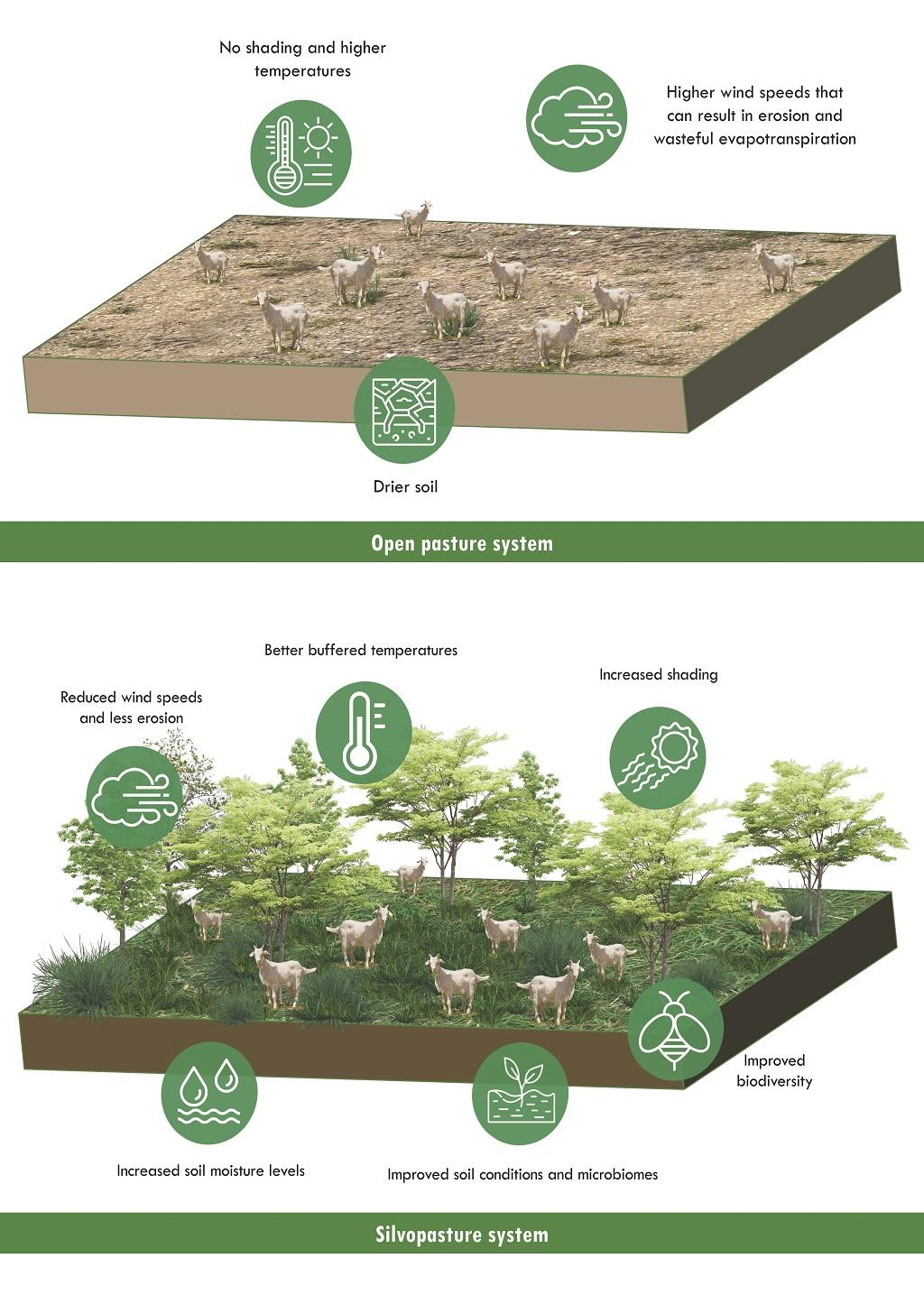
Silvopasture System
Silvopasture is an ancient and proven practice that harmoniously integrates trees, forage and livestock on the same land.
Benefits of Silvopasture system:
- Trees in silvopasture act as potent natural carbon sinks, capturing five to ten times more carbon than treeless pastures, without compromising productivity.
- It also regulates local climatic conditions, buffering against temperature and wind extremes, providing a favourable living environment for livestock.
- Trees in silvopasture aid nutrient cycling, enhance soil stability and quality, and combat erosion through their extensive root systems. Silvopasture is a sustainable land-use practice that can improve the health and productivity of the land over the long term.
Read More: Soil Erosion, Deforestation
Herbig-Haro 46/47
NASA recently released a high-resolution image from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), showing two actively forming stars known as Herbig-Haro 46/47.
- These young stars are hidden within an orange-white blob surrounded by gas and dust, indicating their early stages of growth.
- They will give insights into the mass accumulation of stars over time.
- Observing the orange lobes helps understand how stars ejected and consumed gas, shaping the lobes over thousands of years.
JWST:
- It is a large, infrared telescope designed to observe the most distant objects in the universe. It is the successor to the Hubble Space Telescope.
- It is a collaboration between NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
Read More: James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), Objects in Space