International Relations
Partners in Blue Pacific
For Prelims: Partners in the Blue Pacific, G7, Blue Water Navy, Exclusive Economic Zones, Solomon Island, Belt and Road Initiative
For Mains: Pacific Islands Countries, Significance of the Pacific Island Countries, India-PICs Relations, China's Ties in the Pacific Island Countries
Why in News?
Recently, US and its allies- Australia, New Zealand, Japan and the United Kingdom — have launched a new initiative called ‘Partners in the Blue Pacific’ for “effective and efficient cooperation” with the region’s small island nations.
- Areas where PBP aims to enhance cooperation include “climate crisis, connectivity and transportation, maritime security and protection, health, prosperity, and education”.
What is the Partners in the Blue Pacific (PBP) initiative?
- The PBP is a five-nation “informal mechanism” to support Pacific islands and to boost diplomatic, economic ties in the region.
- It speaks of enhancing “prosperity, resilience, and security” in the Pacific through closer cooperation.
- It means that through the PBP, these countries together and individually will direct more resources towards the Pacific Island Countries to counter China’s aggressive outreach.
- The initiative members will “elevate Pacific regionalism”, and forge stronger ties with the Pacific Islands Forum (PIF).
What is Pacific Islands Forum (PIF)?
- The Pacific Islands Forum is the region’s premier political and economic policy organization.
- Founded in 1971, it comprises 18 members: Australia, Cook Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, Fiji, French Polynesia, Kiribati, Nauru, New Caledonia, New Zealand, Niue, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Republic of Marshall Islands, Samoa, Solomon Islands, Tonga, Tuvalu, and Vanuatu.
What is the Significance of the Pacific Region?
- Largest Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs):
- The islands are divided on the basis of physical and human geography into three distinct parts- Micronesia, Melanesia and Polynesia.
- Despite their small land area, the islands are spread out over a wide swath of the Pacific Ocean.
- As a result, though they are some of the smallest and least populated states, they have some of the largest Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs) in the world.
- Economic Potential:
- Large EEZs have a great deal of economic potential since they can be used to exploit the wealth of fisheries, energy, minerals, and other marine resources present there.
- Hence, they prefer to be identified as Big Ocean States, rather than Small Island States.
- In fact, Kiribati and FSM, both PICs, have EEZs larger than that of India.
- Role in Major Power Rivalry:
- The major powers of the colonial era competed with each other to gain control over these strategic territories.
- The Pacific islands also acted as one of the major theatres of conflict during the Second World War- between imperial Japan and the US.
- Potential Vote Bank:
- The Pacific Island Countries (PICs), bound together by shared economic and security concerns, account for as many votes in the United Nations, and act as a potential vote bank for major powers to mobilise international opinion.
- Strategic Importance:
- In its 2019 strategy report, the US Department of Defence called the Indo-Pacific the “single most consequential region for America’s future”.
- Spanning a vast stretch of the globe from the west coast of the United States to the western shores of India, the region is home to the world’s most populous state (China), most populous democracy (India), and largest Muslim-majority state (Indonesia), and includes over half of the earth’s population.
- Among the 10 largest standing armies in the world, 7 reside in the Indo-Pacific; and 6 countries in the region possess nuclear weapons.
- Nine of the world’s 10 busiest seaports are in this region, and 60% of global maritime trade transits through Asia, with one-third of global shipping passing through the South China Sea alone.
- In its 2019 strategy report, the US Department of Defence called the Indo-Pacific the “single most consequential region for America’s future”.
How is China trying to transform its ties in the Pacific?
- As China signed a security pact with Solomon Islands, the deal flagged serious concerns about the Chinese military getting a base in the southern Pacific, close to the US island territory of Guam, and right next to Australia and New Zealand.
- China’s quest to dominate crucial shipping lanes pushed 10 Pacific nations to endorse a game-changing agreement called the “Common Development Vision”.
- Common Development Vision is a comprehensive strategic partnership featuring mutual respect and common development, to build a closer China-Pacific Island Countries community with a shared future.
- The vision is to follow cooperative and sustainable security measures and promote regional peace - strengthening dialogue and cooperation in governance and cybersecurity.
- China and the US are among 21 PIF dialogue partners, but this year the regional forum had decided not to engage with the dialogue partners in-person during the Fiji meet.
- Apart from the vast marine richness of the PICs, the Taiwan factor plays a major role in China’s Pacific calculus.
- China, which considers Taiwan to be a breakaway territory, is preparing for what seems like an inevitable military invasion.
- The PICs are located geostrategically in what is referred to by China as its ‘Far Seas’, the control of which will make China an effective Blue Water capable Navy, an essential prerequisite for becoming a superpower.
- A Blue Water Navy is one that has the capacity to project itself over a much bigger maritime area than its maritime borders.
What is being done by the US and its allies to counter China?
- Before launching the PBP, the US and its partners started the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF), a trade-boosting play in the region with 13 nations-
- Australia, Brunei, India, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, Fiji and Vietnam.
- G7 announced a plan- Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII) to rival China’s Belt and Road Initiative by promising to raise 600 billion dollars to fund development projects in low and middle-income countries.
What are the Highlights of the India-PICs Relations?
- About:
- India’s interaction with the PICs is still largely driven by the presence of sizable Indian Diaspora in the region.
- Nearly 40% of Fiji’s population is of Indian origin and about 3000 Indians live in Papua New Guinea at present.
- In terms of institutional engagements, India participates in the Pacific Island Forum (PIF) as one of the key dialogue partners of the Forum.
- The most important development in facilitating India’s interaction with the PICs in recent years has been the formation of an action-oriented Forum for India and Pacific Islands Cooperation (FIPIC).
- FIPIC, a multinational grouping, was launched in 2014.
- Areas of Cooperation:
- Blue Economy:
- The PICs with their resource-rich EEZs can be attractive sources of natural resources like Liquefied natural gas (LNG) and hydrocarbons to fuel India’s growing economy and can also provide new markets.
- India can engage with these countries particularly, given its own emphasis on the idea of ‘Blue Economy’.
- Climate Change and Sustainable Development:
- The geography of these island countries makes them vulnerable to the adverse effects of climate challenges.
- The increasing soil salinity due to the rising sea level threatens the low-lying island states, also giving rise to the problem of displacement.
- Therefore, climate change and sustainable development are crucial areas of concern where a closer partnership can be developed for effective and concrete solutions.
- Blue Economy:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. ‘Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action’, often seen in the news, is: (2015)
(a) a strategy to tackle regional terrorism, an outcome of a meeting of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
(b) a plan of action for sustainable economic growth in the Asia-Pacific Region, an outcome of the deliberations of the Asia-Pacific Economic Forum
(c) an agenda for women’s empowerment, an outcome of a World Conference convened by the United Nations
(d) a strategy to combat wildlife trafficking, a declaration of the East Asia Summit
Ans: (c)
- The Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action is a global commitment to achieve equality, development and peace for women worldwide. It was adopted in September, 1995 at the Fourth World Conference on Women held in Beijing. It builds upon consensus and progress made at earlier UN Conferences, particularly the Conference on Women in Nairobi in 1985.
- The Platform for Action is an agenda for women's empowerment. It aims at accelerating the implementation of the Nairobi Forward-looking Strategies for the Advancement of Women and at removing all the obstacles to women’s active participation in all spheres of public and private life through a full and equal share in economic, social, cultural and political decision-making.]
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer
International Relations
48th G-7 Summit
For Prelims: G7, Clean Energy Technology, Ethanol Blending, Foreign Direct Investment, Low-Carbon Technology
For Mains: Market of Clean Energy Technology in India, Important International Institutions
Why in News?
Recently, at the 48th G7 Summit, Indian Prime Minister invited the G7 Nations to tap into the huge market for clean energy technologies emerging in the country.
- Germany holds the presidency of the G7 in 2022.
- The German Presidency has invited Argentina, India, Indonesia, Senegal and South Africa to the G7 Summit.
What is Group of Seven (G7)?
- It is an intergovernmental organisation that was formed in 1975.
- The bloc meets annually to discuss issues of common interest like global economic governance, international security and energy policy.
- The G7 countries are the UK, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan and the US.
- All the G7 countries and India are a part of G20.
- The G7 does not have a formal charter or a secretariat. The presidency, which rotates among member countries each year, is in charge of setting the agenda. Sherpas, ministers and envoys hammer out policy initiatives before the summit.
- As of 2022, G7 countries make up 10% of the world’s population, 31% of global GDP, and 21% of global carbon dioxide emissions, according to the Summit website. China and India, the two most populous countries with among the largest GDP figures in the world, are not part of the grouping.
- In all G7 countries, annual public sector expenditure exceeded revenue in 2021. Most G7 countries also had a high level of gross debt, especially Japan (263% of GDP), Italy (151%) and the US (133%).
- The G7 countries are important players in global trade. The US and Germany in particular are major export nations. Both sold goods worth well over a trillion US dollars abroad in 2021.
What are the Other Highlights of G7 Summit?
- PGII:
- G7 announced the collective mobilization of 600 billion dollars by 2027 under Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII) to deliver “game-changing” and “transparent” infrastructure projects to developing and middle-income countries.
- LiFE Campaign:
- Indian Prime Minister highlighted Global Initiative for LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) campaign.
- The goal of this campaign is to encourage an eco-friendly lifestyle.
- Indian Prime Minister highlighted Global Initiative for LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) campaign.
- Stand on Russia-Ukraine Crisis:
- Russia-Ukraine crisis has pushed the energy prices to a record high, Indian Prime Minister addressed the need for equal energy distribution amongst the population of rich and poor nations.
- On Russia-Ukraine war, Prime Minister reiterated his stand that there must be an immediate end to the hostilities and a resolution should be reached by choosing the path of dialogue and diplomacy.
What is Clean Energy Technology?
- About:
- It refers to any process, product or service that reduces negative environmental impacts through significant energy efficiency improvements, sustainable use of resources or environmental protection activities.
- Clean energy technologies also endure economic growth by enhancing the supply of energy demand and tackling environmental challenges and their impacts due to the use of other conventional sources of energy and their impacts due to the use of other conventional sources of energy.
- Clean technology includes a broad range of technology related to recycling, renewable energy (Wind power, solar power, biomass, hydropower, geothermal, biofuels, etc.), information technology, green transportation, electric motors, green chemistry, lightning, greywater, etc.
- Emerging Market for Clean Technology in India:
- Governmental Regulations:
- With a more active media and awareness of people towards the environment, India is driven towards adopting a pro-environment stance in all its development strategies.
- Adopting Newer & Cleaner Technologies:
- The adoption of newer and cleaner technologies will help India in leap frogging into the sustainable growth pathway as the Indian economy grows at an unprecedented rate.
- Global Climate Negotiations:
- The current global negotiations on climate change have put pressure on rapidly developing economies like India to adopt green technologies.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI):
- The Indian market offers strong business prospects for foreign investors.
- India’s growing economy and surging demand for clean power to strengthen energy security and reduce pollution, as well as ongoing sector reforms, is making India one of the most attractive destinations in the world for environmentally-friendly investments.
- Low-carbon Technologies:
- India is particularly well placed to become a global leader in renewable batteries and green hydrogen.
- Other low-carbon technologies can create a market worth up to 80 billion dollars in India by 2030.
- Governmental Regulations:
- Development in India:
- India has achieved the target of 40% energy-capacity from non-fossil sources and 10% Ethanol-blending in petrol.
- India has the world's first fully solar power operated airport.
- India is one of the largest energy producing countries from renewable sources. In the electricity sector, renewable energy (excluding large hydro) accounted for 20% of the total installed power capacity.
What are the Benefits of Clean Energy?
- Clean energy provides a variety of environmental and economic benefits, including a reduction in air pollution.
- A diverse clean energy supply also reduces the dependence on imported fuels.
- Renewable clean energy also has inherent cost savings, as there is no need to extract and transport fuels, such as with oil or coal, as the resources replenish themselves naturally.
- Other industrial benefits of a clean energy mix are the creation of jobs to develop, manufacture and install the clean energy resources of the future.
International Relations
Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII)
For Prelims: Build Back Better World (B3W), PGII, BRI ,China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), Silk Road Economic Belt, Climate Sustainability Fund, Hambantota Port in Sri Lanka
For Mains: Pillars of PGII, Benefits to India from PGII , Belt Road Initiative
Why in News?
Recently, at the 48th G-7 Summit, the U.S. along with G7 allies unveiled the ambitious Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII).
What is the Background?
- The U.S. along with its allies had announced the launch of the Build Back Better World (B3W) in 2021 with the aim of narrowing the 40 trillion dollar infrastructure gap in the developing world.
- Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment is therefore a relaunch of the B3W plan.
- The PGII is being seen as the G7’s counter to China’s multi-trillion dollar Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) to build connectivity, infrastructure, and trade projects in Asia, Europe, Africa, and Latin America.
What is Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment?
- About:
- PGII is a “values-driven, high-impact, and transparent infrastructure partnership to meet the enormous infrastructure needs of low and middle-income countries
- And support the United States and its allies economic and national security interests.
- Under the PGII, G7 will mobilize 600 billion dollars by 2027 to deliver “game-changing” and “transparent” infrastructure projects to developing and middle-income countries.
- U.S. President announced the country’s pledge to channel 200 billion USD in grants, public financing, and private capital over the next five years for the PGII.
- The European Commission President declared Europe’s pledge of mobilizing 300 billion euros for the partnership over the same period.
- PGII is a “values-driven, high-impact, and transparent infrastructure partnership to meet the enormous infrastructure needs of low and middle-income countries
- Pillars of PGII:
- First: G7 grouping aims to tackle the climate crisis and ensure global energy security through clean energy supply chains.
- Second: The projects will focus on bolstering digital Information and Communications technology (ICT) networks facilitating technologies such as 5G and 6G internet connectivity and cybersecurity.
- Fibre-optic cable project to link Europe and Latin America.
- Third: The projects aim to advance gender equality and equity.
- Gender Equality: It requires equal enjoyment by women and men of socially-valued goods, opportunities, resources and rewards.
- Gender Equity: It recognizes that each person has different circumstances and allocates the exact resources and opportunities needed to reach an equal outcome.
- Fourth: The project stresses upgrading global health infrastructure.
- The U.S International Development Finance Corporation (DFC), along with the G7 nations and the EU are disbursing a 3.3 million USD technical assistance grant to build a vaccine facility in Senegal.
- The European Commission’s Global Gateway initiative is also undertaking projects supporting the PGII such as mRNA vaccine plants in Latin America.
- Benefits to India:
- U.S. International Development Finance Corporation (DFC) will invest up to USD 30 million in Omnivore Agritech and Climate Sustainability Fund.
- Climate Sustainability Fund: It is an impact venture capital fund that invests in entrepreneurs building the future of agriculture, food systems, climate, and the rural economy in India.
- The Fund seeks to invest in companies that increase food security and promote both climate resilience and climate adaptation in India and it will also improve the profitability and agricultural productivity of smallholder farms.
- Omnivore Agritech: It is a technology driven agricultural practice that will increase agricultural prosperity and transform food systems to make farming more resilient and sustainable.
- It includes farmer platforms, precision agriculture, Agri-biotech etc.
- U.S. International Development Finance Corporation (DFC) will invest up to USD 30 million in Omnivore Agritech and Climate Sustainability Fund.
How will PGII Counter China’s BRI?
- Projects:
- PGII has laid focus on climate action and clean energy, while China has built large coal-fired plants under BRI along with solar, hydro, and wind energy projects.
- Funding:
- PGII aims to build projects through grants and investments. China builds BRI’s projects by extending large, low-interest loans to countries that have to usually be paid over 10 years.
- While the G7 has pledged 600 billion USD by 2027, It has been estimated that China’s overall funding for BRI by that time could reach 1.2 USD to 1.3 trillion USD with the actual funding being higher. Under the PGII, large private capital will be also mobilized while China’s BRI is majorly state-funded.
- Transparency:
- While G7 leaders emphasized ‘transparency’ as the cornerstone of PGII projects, the BRI has faced criticism for making countries sign confidential tenders for extending massive loans, leaving countries indebted to China.
- For instance, after the BRI’s flagship 62 billion USD China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, Pakistan owes Beijing a large proportion of its foreign debt.
- PGII aims to build projects through grants and investments.
- While G7 leaders emphasized ‘transparency’ as the cornerstone of PGII projects, the BRI has faced criticism for making countries sign confidential tenders for extending massive loans, leaving countries indebted to China.
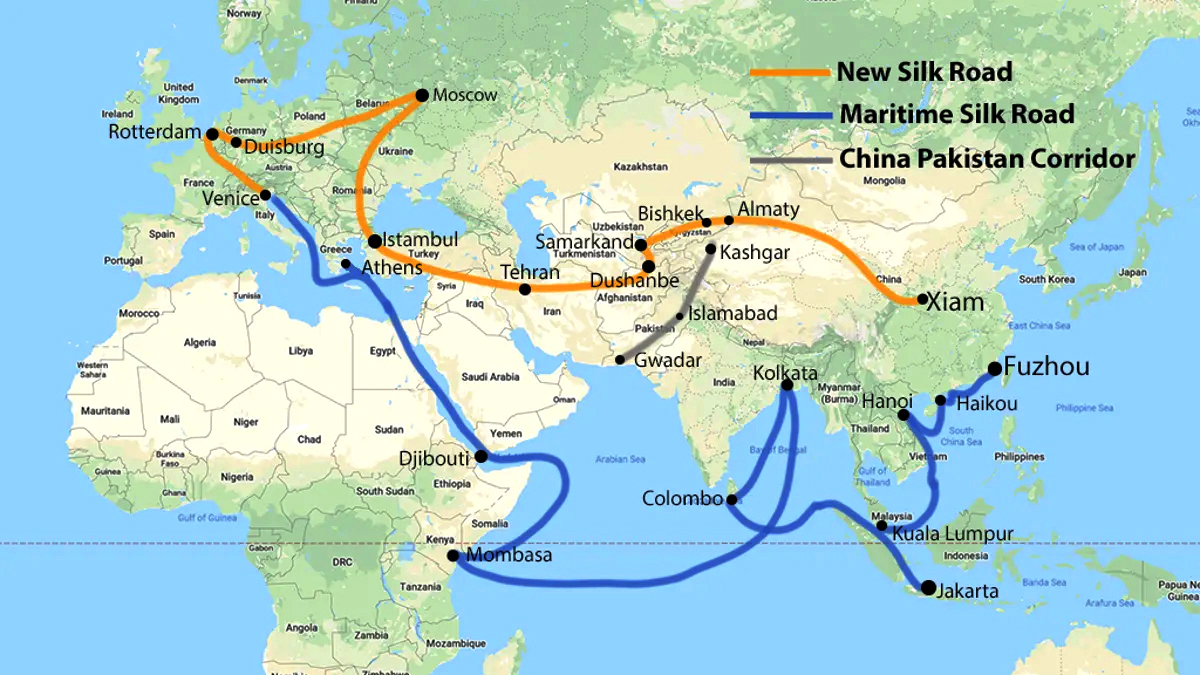
What is the Belt & Road Initiative (BRI)?
- About:
- Belt & Road Initiative (BRI) is an ambitious project that focuses on connectivity and cooperation among multiple countries spread across the continents of Asia, Africa, and Europe. BRI spans about 150 countries (China’s Claim).
- Initially announced in the year 2013, the project involves building networks of roadways, railways, maritime ports, power grids, oil and gas pipelines, and associated infrastructure projects.
- The project covers two parts.
- Silk Road Economic Belt: It is land-based and is expected to connect China with Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and Western Europe.
- 21st Century Maritime Silk Road: It is sea-based and is expected to connect China’s southern coast to the Mediterranean, Africa, South-East Asia, and Central Asia.
- Belt & Road Initiative (BRI) is an ambitious project that focuses on connectivity and cooperation among multiple countries spread across the continents of Asia, Africa, and Europe. BRI spans about 150 countries (China’s Claim).
- Significance of BRI For China:
- The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is the most emblematic of China’s economic and industrial might, as of its ambitions for global, political and strategic influence.
- As infrastructure spending at home became less sustainable, China has shifted the emphasis to boost the global competitiveness of domestic businesses.
- The large infrastructure investments in the least developed and developing countries have enabled China to leverage its influence around the world, potentially altering the established rules of the global order and challenging western powers.
- BRI will strengthen China’s presence in the Eurasian region and put it in a commanding position over Asia’s heartland.
- Criticism:
- Western critics have attacked the initiative as new colonialism, or the Marshal Plan for the 21st century.
- BRI is also being seen as a part of China’s debt trap policy, wherein China intentionally extends excessive credit to another country with the intention of extracting economic or political concessions from the debtor country.
Why has India not joined BRI?
- China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) is one of the flagship projects of BRI which is seen by India as infringing its sovereignty.
- CPEC can aid Pakistan’s legitimacy in the Kashmir dispute.
- China is building roads and infrastructure in the disputed territory of Gilgit-Baltistan, which is under Pakistan’s control but which India claims as a part of Jammu and Kashmir.
- If the CPEC project gets implemented successfully, this would hamper India’s strategic interests in the South Asian region. It will serve Beijing's strategic ambition to encircle India.
- China’s increasing footprints in the South Asian region is detrimental to India’s strategic hold e.g., construction of the Hambantota Port in Sri Lanka provided China with a critical strategic location in the Indian Ocean.
Economy
International MSMEs Day
For Prelims: MSME, MSME Day and Significance, Efforts to Promote MSMEs
For Mains: Significance of MSME for Indian Economy
Why in News?
International MSME Day is observed every year on 27th June all over the world to highlight the significance of MSMEs and how they play a crucial role in being the backbone of the country’s economy.
- Earlier, Ministry for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises has launched the MSME (Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises) Sustainable (ZED-Zero Defect Zero Effect) Certification Scheme.
What are the Key Points?
- History:
- The United Nations (UN) designated 27th June as Micro, Small and Medium-sized Enterprises Day through a resolution passed in the UN General Assembly in April 2017.
- In May 2017, a program titled 'Enhancing National Capacities for Unleashing Full Potentials of MSMEs in Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in Developing Countries was launched.
- It has been funded by the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development Sub-Fund of the United Nations Peace and Development Fund.
- Theme for 2022:
- Resilience and Rebuilding: MSMEs for Sustainable Development.
- The theme mainly highlights that for the socio-economic development of a country Micro-Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises is a necessary component.
- Resilience and Rebuilding: MSMEs for Sustainable Development.
- Objectives:
- World MSME Day 2022 recognizes the potential of MSMEs and their role in strengthening the economies globally.
- It also aims to raise public awareness regarding the contribution of MSMEs to global economic growth and sustainable development.
- Significance:
- As per the United Nations, the formal and informal MSMEs account for 70 % of the total employment and 50 % of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- Moreover, MSMEs make up 90 % of all the firms. With such a significant contribution to the country’s economy, MSMEs are essential for the job creation, innovation and productivity growth.
- However, despite being a key player in generating jobs, MSMEs worldwide face challenges in working conditions, productivity, and informality apart from the lack of support from the governments and administrations.
- World MSME Day is celebrated to unlock the potential of such enterprises and also to utilize it for bolstering the global economy.
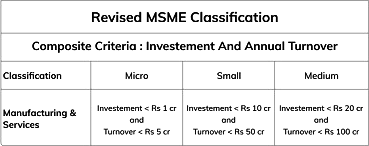
What is MSME?
- About:
- Micro-Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises are the organizations that do not usually employ more than 250 employees, however, are responsible for creating more than two-thirds of all jobs globally.
- Role of MSME in Indian Economy:
- They are the growth accelerators of the Indian economy, contributing about 30% of the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- In terms of exports, they are an integral part of the supply chain and contribute about 48% of the overall exports.
- MSMEs also play an important role in employment generation, as they employ about 110 million people across the country.
- Interestingly, MSMEs are intertwined with the rural economy as well, as more than half of the MSMEs operate in rural India.
What are the Related Initiatives?
- The Micro Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act: It was notified in 2006 to address policy issues affecting MSMEs as well as the coverage and investment ceiling of the sector.
- Prime Minister’s Employment Generation programme (PMEGP): It is a credit linked subsidy scheme, for setting up of new micro-enterprises and to generate employment opportunities in rural as well as urban areas of the country.
- Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries (SFURTI): It aims to properly organize the artisans and the traditional industries into clusters and thus provide financial assistance to make them competitive in today's market scenario.
- A Scheme for Promoting Innovation, Rural Industry & Entrepreneurship (ASPIRE): The scheme promotes innovation & rural entrepreneurship through rural Livelihood Business Incubator (LBI), Technology Business Incubator (TBI) and Fund of Funds for start-up creation in the agro-based industry.
- Interest Subvention Scheme for Incremental Credit to MSMEs: It was introduced by the Reserve Bank of India wherein relief is provided upto 2% of interest to all the legal MSMEs on their outstanding fresh/incremental term loan/working capital during the period of its validity.
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for Micro and Small Enterprises: Launched to facilitate easy flow of credit, guarantee cover is provided for collateral free credit extended to MSMEs.
- CHAMPIONS portal: It aims to assist Indian MSMEs march into the big league as National and Global CHAMPIONS by solving their grievances and encouraging, supporting, helping and hand holding them.
- MSME Innovative Scheme: It ensures support through guidance, financial support, technical support, and more to MSMEs to scale up.
- Udyam Registrations Portal: This new portal assists the government in aggregating the data on the number of MSMEs in the country.
- MSME SAMBANDH: It is a Public Procurement Portal. It was launched to monitor the implementation of the Public Procurement from MSEs by Central Public Sector Enterprises.
Governance
Increase in NREGS demand
For Prelims: NREGS (National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme)
For Mains: Working of NREGS, its challenges and the way forward
Why in News?
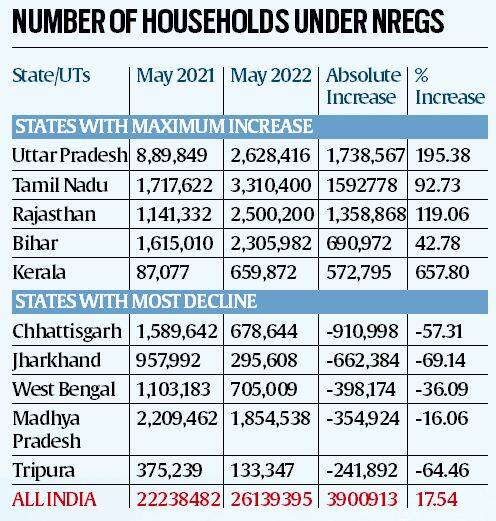
In May 2022, 2.61 crore households worked under the NREGS (National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme), which is 17.39% more than in the same month last year.
What are the Key Findings?
- There was a rise in demand for NREGS after the dip in April. In April 2022, 1.86 crore families availed the NREGS, which is 12.27% lower than the number recorded in April last year.
- The number of households that availed the NREGS is lower than May 2020, when the demand sharply rose to 3.30 crore as migrant workers returned to their villages in wake of lockdown during the first wave of Covid-19.
- But it is higher than the 2.10 crore figure recorded in May 2019 (pre-pandemic times).
- In terms of states, Uttar Pradesh saw the maximum increase in terms of the absolute increase in the number of families availing the NREGS, followed by Tamil Nadu.
- Whereas, the maximum decline was recorded in Chhattisgarh followed by Jharkhand.
What is NREGS?
- The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), also known as Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MNREGS) is legislation enacted on 25th August, 2005.
- It provides a legal guarantee for one hundred days of employment in every financial year to adult members of any rural household willing to do public work-related unskilled manual work at the statutory minimum wage.
- The Ministry of Rural Development (MRD) is monitoring the entire implementation of this scheme in association with state governments.
- This act was introduced with an aim of improving the purchasing power of the rural people, primarily semi or unskilled work to people living below poverty line in rural India. It attempts to bridge the gap between the rich and poor in the country.
- According to the law roughly one-third of the stipulated work force must be women.
- The registered person can submit an application for work in writing (for at least fourteen days of continuous work) either to Panchayat or to Programme Officer.
- Employment will be provided within a radius of 5 km. And if it is beyond 5 km, an extra wage will be paid.
- A majority of the works that are notified under NREGS are related to agricultural and allied activities, besides the works that facilitate rural sanitation projects in a major way.
- NREGS is a demand-driven wage employment programme and resource transfer from the Centre to the states is based on the demand for employment in each state.
- It provides a legal guarantee for wage employment by providing allowances and compensation both in cases of failure to provide work on demand and delays in payment of wages for work undertaken.
- In May 2021, the Ministry of Rural Development launched the National Mobile Monitoring Software (NMMS) app, a new application meant for “improving citizen oversight and increasing transparency” in National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (NREGA) works.
What have been the Outcomes of NREGS?
- In the past 15 years, it has created more than 31 billion person-days of employment.
- In the last 15 years, the government has invested more than Rs 6.4 lakh crore in this demand-driven programme.
- In the rural sections of the nation, more than 30 million water conservation-related assets have been developed since 2006.
What are the Challenges?
- Low wage rates: NREGS wages are currently around Rs. 180 per day, which is far below the market rate. For almost a decade, the wages have been adjusted only for inflation, ignoring the average wage rate for the same kind of work. And right now, they have fallen below the minimum wage rate in 23 states, leading to a dip in participation.
- Late Payments: Another issue is that despite the scheme mandating that workers be paid within 15 days; these people often don’t get paid at all. The past few financial years have opened with a large balance of wage arrears- nearly Rs. 10,000 crores in 2019–20. According to the government’s portal, over 30% of wage requests have been pending since October 2019.
- Corruption: The biggest issue with the scheme is that even if the funding allocation increases, it’s very hard to root out corrupt middlemen from the system.
- Wasteful work: Most officials simply offer pointless busy work that adds no value to the agricultural infrastructure in the country. It’s like asking people to dig holes and fill them up in order to tick a box.
Way Forward
- The government could look at linking the wages to a consumption-based index- one that is revised annually, the idea is that this way the wage workers can be compensated adequately based on their consumption needs. This may be a better approach.
- Need to leverage technology to tackle corruption and reduce the issue of late payments through efficient management of resources.
Biodiversity & Environment
Commonwealth adopts ‘Living Lands Charter’
For Prelims: Commonwealth Nations, Living Lands Charter
For Mains: Living Land Charter, Conservation
Why in News?
Recently, the Commonwealth members have agreed to voluntarily dedicate ‘living land’ in their respective countries to future generations, in line with the strategy set for the United Nations Decade on Ecosystem Restoration.
- The 'Living land’ charter was announced at the conclusion of the 2022 Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting (CHOGM) in Kigali (Rwanda).
What is the United Nations Decade on Ecosystem Restoration?
- The United Nations Decade on Ecosystem Restoration runs from 2021 to 2030.
- Its purpose is to promote the United Nation's environmental goals.
- Specifically, to facilitate global cooperation for the restoration of degraded and destroyed ecosystems.
- It calls for protection and revival of ecosystems across the world.
What is the Living Land Charter?
- The non-binding ‘Living Lands Charter’ mandates that member countries will safeguard global land resources and arrest land degradation while acting against climate change, biodiversity loss and towards sustainable management.
- The Living Lands Charter helps to encapsulate the combined effort to hold the global average temperature increase to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
- The charter aims to achieve climate goals through a mixture of policy influence, financing, technical assistance, governance and sharing knowledge across nations.
- Commonwealth governments have been asked to submit their emission reduction targets by 23rd September, 2022.
- It is aimed to support member countries to effectively deliver their commitments under the three Rio conventions — UN Convention on Biological Diversity, UN Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) and UN Framework Convention on Climate Change.
What are the Highlights of the CHOGM 2022?
- The Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting is a biennial summit meeting of the heads of government from all Commonwealth nations.
- CHOGM2022 was taken place in Rwanda, with theme: ‘Delivering a Common Future: Connecting, Innovating, Transforming.'
- It has raised more than USD 4 billion in pledges for the battle against malaria and other tropical diseases.
- There have been 24 CHOGMs since 1971, with the most recent one taking place in the United Kingdom (UK) in 2018.
What is the Commonwealth?
- It is an international intergovernmental organization of countries that were mostly former territories of the British Empire and dependencies.
- It was established by the London Declaration in 1949.
- Queen Elizabeth II is the head of the Commonwealth.
- Many countries from Africa, Asia, Americas, Europe and the Pacific have joined the commonwealth.
- The current membership includes 56 Countries. The membership is based on free and equal voluntary co-operation.
- The two African countries, Gabon and Togo, were admitted to the Commonwealth of Nations, as its 55th and 56th members, respectively, at the CHOGM 2022.
- It is Headquartered in London.
Geography
High-grade lithium discovered in Nigeria
For Prelims: High Grade Lithium, spodumene and lepidolite, Electric Vehicles
For Mains: Applications of Lithium, Lithium in India, Steps taken by India to reduce import of Lithium
Why in News?
Recently, High-grade Lithium has been discovered in Nigeria.
- Greenbushes mine in Western Australia is the largest hard-rock Lithium mine in the world.
- The largest importers of lithium are South Korea, China, Japan, US and Belgium.
What are the Key Highlights of Lithium?
- About:
- Lithium is an element and in nature tends to concentrate sufficiently in the two minerals, spodumene and lepidolite.
- They are usually found in specialised rocks called rareCand greisens.
- The Geological Agency described lithium as high grade because it is found with 1-13% oxide content. Normally exploration begins at levels as low as 0.4%.
- Grade (in %) is a measure of the concentration of lithium in the minerals and or rocks that contain it.
- Therefore, the higher the grade the more the economic viability. Higher grades are very rare for metals like lithium.
- Applications:
- Special Glasses and Ceramics:
- Lithium disilicate (Li2Si2O5) is a chemical compound that is a glass ceramic.
- It is widely used as a dental ceramic due to its strength, machinability and translucency.
- Alloy Making:
- Lithium metal is used to make useful alloys.
- For example, with lead to make ‘white metal’ bearings for motor engines, with aluminium to make aircraft parts, and with magnesium to make Armour plates.
- Lithium metal is used to make useful alloys.
- Rechargeable batteries:
- Lithium is used in rechargeable batteries for mobile phones, laptops, digital cameras and electric vehicles. Lithium is also used in some non-rechargeable batteries for things like heart pacemakers, toys and clocks. The different types of batteries are:
- Lithium-cobalt oxide battery: It is used in consumer electronics and is being applied in electric vehicles. It is relatively cheap.
- Lithium-nickel-manganese-cobalt: It is a newer, higher performing range of battery chemistry. It is mainly developed for the electronic vehicle market but is finding a wider use because of its increasing cost effectiveness.
- Lithium iron phosphate: It is the safest technology with relatively high performance but relatively expensive. It is very popular in China.
- Lithium-nickel-cobalt-aluminium oxide: It is developed to reduce cobalt consumption and is known as a solid performer and of reasonable cost. It is also becoming popular outside China.
- Lithium is used in rechargeable batteries for mobile phones, laptops, digital cameras and electric vehicles. Lithium is also used in some non-rechargeable batteries for things like heart pacemakers, toys and clocks. The different types of batteries are:
- Special Glasses and Ceramics:
- High Demand:
- Due to the growing interest in clean energy, the demand for lithium has skyrocketed as most countries draw plans to phase out fossil fuel and switch to zero emission electric vehicles.
- Lithium production globally grew from 28,100 metric tonnes in 2010 to 86,000 in 2019. The challenge will be in supplying the market with enough lithium.
- Due to the growing interest in clean energy, the demand for lithium has skyrocketed as most countries draw plans to phase out fossil fuel and switch to zero emission electric vehicles.
- Lithium in India:
- Researchers at the Atomic Minerals Directorate (under India’s Atomic Energy Commission) have estimated lithium reserves of 14,100 tonnes in a small patch of land surveyed in Southern Karnataka’s Mandya district.
- Also, to be India’s first ever Lithium deposit site.
- Researchers at the Atomic Minerals Directorate (under India’s Atomic Energy Commission) have estimated lithium reserves of 14,100 tonnes in a small patch of land surveyed in Southern Karnataka’s Mandya district.
What are the Steps taken by India to reduce import of Lithium?
- India has adopted a multi-modal strategy to reduce its dependence on imported lithium and give fresh impetus to the growth of the local electric vehicles (EV) industry.
- State-run Khanij Bidesh India Ltd (KABIL) is working with the authorities in Argentina, Chile, Australia and Bolivia for acquiring lithium and cobalt mines overseas.
- These nations are rich in lithium reserves.
- The country is also working on urban mining where recycled materials remain in circulation and this reduces the dependency on fresh lithium inputs. This will further bring down the requirement for imports.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which one of the following pairs of metals constitutes the lightest metal and the heaviest metal, respectively? (2008)
(a) Lithium and mercury
(b) Lithium and osmium
(c) Aluminium and osmium
(d) Aluminium and mercury
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Light metals are metals of low atomic weight while heavier elements generally have high atomic weight.
- Osmium is a hard metallic element which has the greatest density of all known elements. Osmium has an atomic weight of 190.2 u and its atomic number is 76.
- Lithium having an atomic number 3 and atomic weight of 6.941u is the lightest known metal.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Important Facts For Prelims
Dak Karmayogi
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Communications has launched ‘Dak Karmayogi, an e-learning portal of the Department of Posts.
- To recognise the good performance of employees of Department of Posts, Meghdoot Awards were also conferred in eight different categories. Meghdoot Award was introduced in the year 1984. This is the highest award of Department of Posts at National level for overall performance and excellence.
What is Dak Karmyogi?
- About:
- This portal has been developed ‘In-House’ under vision of ‘Mission Karmayogi’, which was conceptualized by Prime Minister with a view to bring efficiency efficiency of bureaucracy with ‘Minimum Government’ and ‘Maximum Governance’.
- The Portal will enable the trainees to access the uniform standardized training content online or in blended campus mode to enable them to effectively deliver a number of G2C (Government to Citizen) services for enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Objective:
- To provide better services by upgrading employees and Gramin Dak Sevaks.