India and Vietnam Relations
For Prelims: Indian Ocean Region, INS Kirpan, Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief, India's Act East Policy,Mekong-Ganga Cooperation, United Nations Security Council, Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, UNCLOS.
For Mains: Areas of Cooperation Between India and Vietnam
Why in News?
India gifted the indigenously built in-service missile corvette INS Kirpan to Vietnam. It reflects India's commitment to deepening defense cooperation and cementing its role as Vietnam's 'Preferred Security Partner' in the Indian Ocean Region.
What is INS Kirpan?
- INS Kirpan is a Khukri class missile corvette, commissioned into the Indian Navy on January 12, 1991.
- The Khukri class corvettes are equipped with Diesel Engines assembled in India, under license by Kirloskar Group. Around 65% of the ship contains indigenous parts.
- It boasts a speed more than 25 knots and is equipped with various armaments, making it highly versatile in performing multiple roles, including coastal and offshore patrol, surface warfare, coastal security, anti-piracy, and Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations.
What are the Areas of Cooperation Between India and Vietnam?
- About:
- India had established the Consul General’s office in Hanoi as early as 1956.
- Vietnam established its diplomatic mission in 1972.
- India had stood by Vietnam in opposing US intervention in that country at the cost of embittering Indo-US relations.
- India was the Chairman of the International Commission for Supervision and Control (ICSC), which was formed pursuant to the Geneva Accord of 1954 to facilitate the peace process in Vietnam.
- In 1992, India and Vietnam established extensive economic ties, including oil exploration, agriculture and manufacturing.
- In July 2007, relations between the two countries were elevated to the level of ‘Strategic Partnership’.
- In 2016, bilateral relations were further elevated to a “Comprehensive Strategic Partnership”
- India had established the Consul General’s office in Hanoi as early as 1956.
- Economic Cooperation:
- Mekong-Ganga Cooperation (MGC): As members of MGC, India and Vietnam have been working to enhance ties between India and Southeast Asian nations and promote development cooperation.
- Trade and Investment: In financial year 2021-22, bilateral trade between India and Vietnam posted a growth of 27% and reached USD 14.14 billion.
- India one of the top 8th trading partners of Vietnam. While vietnam is the 15th largest trading partner of India and the fourth in Southeast Asia.
- Capacity Building: India provides training programs and scholarships under the Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) to Vietnam, contributing to Vietnam's socio-economic development.
- Political Backing: India and Vietnam have supported each other in various international forums and organizations, demonstrating their commitment to global cooperation.
- Vietnam has backed India's bid to become a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) and join the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC).
- Multilateral Cooperation:
- India and Vietnam closely cooperate in various regional forums such as ASEAN, East Asia Summit, Asia Europe Meeting (ASEM) besides UN and WTO.
- Defense Cooperation:
- High-Speed Patrol Boats: In September 2014, India extended a Line of Credit (LoC) of USD 100 million to procure 12 high-speed patrol boats for the Vietnamese border guard force.
- In 2016, an additional USD 500 million defense LoC was extended to Vietnam.
- Also, Joint Vision Statement on India-Vietnam defense partnership towards 2030 was signed in June 2022.
- Vietnam-India Bilateral Army Exercise: Ex VINBAX
- High-Speed Patrol Boats: In September 2014, India extended a Line of Credit (LoC) of USD 100 million to procure 12 high-speed patrol boats for the Vietnamese border guard force.
- Maritime Security and Cooperation:
- Freedom of Navigation: Both countries firmly support freedom of navigation and overflight, as well as lawful commerce in national waters, in accordance with international laws, particularly UNCLOS.
- South China Sea Code of Conduct: India and Vietnam emphasize that the Code of Conduct on the South China Sea should be consistent with relevant UN conventions and respect the legitimate rights and interests of nations not participating in the discussions.
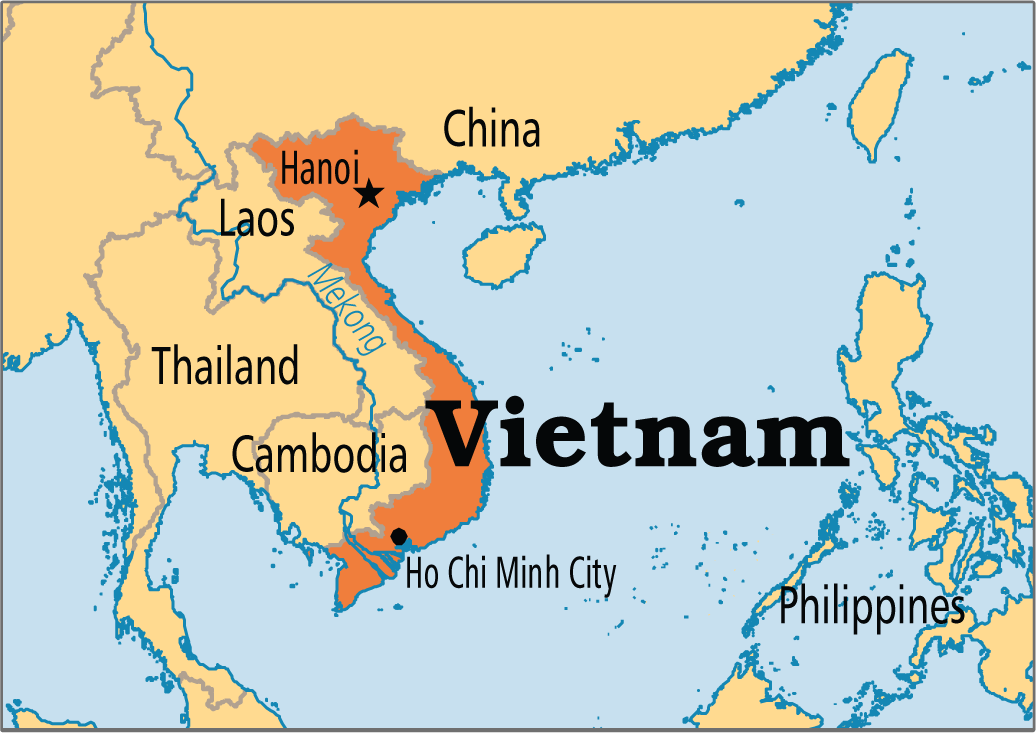
Facts About Vietnam
- Location: Southeast Asia, bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea to the east and south.
- Capital: Hanoi
- Largest Rivers: The Mekong in the south and the Red in the north, end at the South China Sea.
- Currency: Vietnamese Dong (VND)
- Independence: Declared on September 2, 1945, from French colonial rule.
- Historical Events: Vietnam War (1955-1975) involving the US and North and South Vietnam: Reunification of North and South Vietnam in 1976.
- Festivals: Tet Nguyen Dan (Lunar New Year) and Vu Lan (Hungry Ghost Festival).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In the Mekong-Ganga Cooperation, an initiative of six countries, which of the following is/are not a participant/ participants? (2015)
- Bangladesh
- Cambodia
- China
- Myanmar
- Thailand
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 5
Ans: (c)
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2020)
| River | Flows into | |
| 1. | Mekong | Andaman Sea |
| 2. | Thames | Irish Sea |
| 3. | Volga | Caspian Sea |
| 4. | Zambezi | Indian Ocean |
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2 and 4 only
Ans: (c)
- Mekong River, originating in the icy headwaters of the Tibetan highlands, flows through the steep canyons of China, known as the upper basin, through lower basin countries Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, and Cambodia, before fanning an expansive delta in Vietnam and emptying into the South China Sea. Hence, pair 1 is not correctly matched.
- River Thames, the longest river in England, flows 215 miles from the Cotswolds to the North Sea. The main tributaries of Thames are Buscot, Reading, and Kingston. Hence, pair 2 is not correctly matched.
- The Volga River, the longest river in Europe, runs through Russia with its delta flowing into the Caspian Sea just south of the Kazakhstan border. Hence, pair 3 is correctly matched.
- The Zambezi is the fourth-largest river after the Congo/Zaire, Nile and Niger in Africa. It rises in the Kalene hills in north-western Zambia and flowseastwards for about 3000 km to the Indian. Hence, pair 4 is correctly matched. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Controlled Human Infection Studies and Ethical Concerns
For Prelims: Controlled Human Infection Studies , Malaria, Dengue, Vaccines
For Mains: Indian Council of Medical Research Guidelines, Ethical Concerns Related to Controlled Human Infection Studies
Why in News?
The Indian Council of Medical Research’s (ICMR) Bioethics Unit has drafted a consensus policy statement addressing the ethical aspects of Controlled Human Infection Studies (CHIS), opening the door for its potential implementation in India.
What is Controlled Human Infection Studies and Related Ethical Concerns?
- About:
- Benefits of CHIS Implementation: ICMR recognizes that CHIS has the potential to provide numerous benefits for medical research and public health:
- Insights into Disease Pathogenesis: CHIS can offer unique insights into how diseases develop and progress, leading to a deeper understanding of infectious diseases.
- Accelerated Medical Interventions: By allowing researchers to study disease progression more rapidly, CHIS can expedite the development of new treatments and vaccines.
- Cost-effective and Efficient Outcomes: CHIS requires smaller sample sizes compared to large clinical trials, making it a more cost-effective research model.
- Contributions to Public Health Response: Findings from CHIS can inform public health responses, healthcare decision-making, and policy development.
- Understanding disease dynamics through CHIS can enhance preparedness for future pandemics.
- Community Empowerment: Involving communities in CHIS research can empower them to take ownership of their health and participate actively in healthcare initiatives.
- Ethical Challenges:
- Deliberate Harm and Participant Protection: Exposing healthy volunteers to pathogens raises concerns about potential harm to participants.
- Inducement and Compensation: Determining appropriate compensation for participants in CHIS can be challenging.
- Offering too much compensation might unduly induce people to participate, potentially compromising informed consent.
- Conversely, offering inadequate compensation might exploit vulnerable individuals.
- Third-party Risk: The risk of disease transmission to third parties beyond the research participants is a concern.
- Justice and Fairness: There is a concern that CHIS may disproportionately involve participants from low-income or marginalized communities.
Way Forward
- Ethical Considerations: The first step is to establish an independent ethics committee to evaluate the CHIS protocols thoroughly.
- The committee should consist of experts in relevant fields, including medical ethics, infectious diseases, and legal representatives, to ensure that participant safety and rights are protected throughout the process.
- Informed Consent and Withdrawal: Volunteers should be fully informed about the risks involved in participating in CHIS.
- Informed consent should be obtained, and participants should have the right to withdraw at any time without penalty.
- Risk Minimization and Medical support: Measures should be in place to minimize the risk to participants.
- This includes close medical monitoring during the trial and access to appropriate medical care and treatment if any participant becomes ill.
PM-DevINE Scheme
Why in News?
The Union Ministry for the Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region provided recent updates on the Prime Minister's Development Initiative for North Eastern Region (PM-DevINE).
What is PM-DevINE?
- The Genesis of PM-DevINE:
- The PM-DevINE scheme as a Central Sector scheme, was introduced as a part of the Union Budget 2022-23.
- The Cabinet granted approval for the PM-DevINE scheme on 12th October 2022. It has been granted 100% Central funding, ensuring that resources are directly allocated to the development initiatives.
- It will be implemented by Ministry of Development of North-East Region.
- Objectives of PM-DevINE:
- Infrastructure Development: In line with the spirit of PM GatiShakti, PM-DevINE aims to fund infrastructure projects in a cohesive manner, ensuring seamless connectivity and accessibility across the NER.
- Supporting Social Development Projects: Recognizing the unique needs and challenges of the NER, the scheme endeavors to support social development projects that address critical issues and improve the overall quality of life for the region's inhabitants.
- Empowering Youth and Women: PM-DevINE seeks to create livelihood opportunities specifically targeting the youth and women of the NER, enabling them to participate actively in the region's development and progress.
- Budget Allocation:
- The scheme received an initial allocation of Rs. 1500 crore in the Union Budget 2022-23.
- Over the 4-year period from 2022-23 to 2025-26, which aligns with the remaining years of the 15th Finance Commission period, the scheme has an overall outlay of Rs. 6,600 crore.
- A state-wise, project-wise list of projects approved during FY 2022-23 has been laid out, with each project tailored to address the specific needs of the respective states.
What are Other Initiatives Related to Development of Northeast Region?
- North East Industrial Development Scheme (NEIDS)
- North Eastern Council (NEC)
- North East Road Sector Development Scheme
- Connectivity Projects: Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Project (Myanmar) and Bangladesh-China-India-Myanmar (BCIM) Corridor.
- Bharatmala Pariyojana ( 5,301 km road stretches in NER for improvement)
- North East has been kept as a priority area under RCS-UDAN (to make flying more affordable).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Cross-border movement of insurgents is only one of the several security challenges facing the policing of the border in North-East India. Examine the various challenges currently emanating across the India- Myanmar border. Also, discuss the steps to counter the challenges. (2019)
Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2021
For Prelims: Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2021, Convention on Biological Diversity, National Biodiversity Authority, Intellectual Property Rights, AYUSH.
For Mains: Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2021.
Why in News?
Recently, the Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2021 has been passed in the Lok Sabha.
What is the Background?
- The Biological Diversity Act, 2002 was enacted in response to India's commitments under the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) of 1992.
- The CBD recognizes that countries have the right to control their biological resources and sets the stage for regulating access to these resources based on national legislation.
- To effectively manage biological resources and associated traditional knowledge, the Act establishes a three-tier structure:
- the National Biodiversity Authority (NBA) at the national level
- State Biodiversity Boards (SBBs) at the state level
- Biodiversity Management Committees (BMCs) at the local level.
- In December 2021, the Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2021 was introduced in Lok Sabha to amend the 2002 Act.
- The amendments are designed to align the Act with current needs and developments, while supporting sustainable biodiversity conservation and utilization in India.
What are the Key Provisions of the Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2021?
| Provisions | The Biological Diversity Act, 2002 | Amendments to the 2002 Act |
| Access to Biological Resources | The Act requires anyone seeking to access biological resources or associated knowledge in India to obtain prior approval or inform the regulatory authority about their intent. | The Bill modifies the classification of entities and activities that require intimation, while also introducing exemptions to certain cases. |
| Intellectual Property Rights | Concerning Intellectual Property Rights (IPR), the Act currently demands NBA approval before applying for IPR related to biological resources from India. | The Bill suggests that approval will be required before the actual grant of the IPR, not during the application process. |
| Exempting AYUSH Practitioners | It seeks to exempt registered AYUSH medical practitioners and people accessing codified traditional knowledge, among others, from giving prior intimation to State biodiversity boards for accessing biological resources for certain purposes. | |
| Benefit Sharing |
The Act mandates benefit sharing, which involves sharing both monetary and non-monetary benefits with those who conserve biodiversity or hold traditional knowledge associated with it. NBA determines the terms of benefit sharing when granting approvals for various activities. |
The Bill removes the applicability of benefit sharing requirements from research, bio-survey, and bio-utilisation. |
| Criminal Penalties | The Act imposes criminal penalties, including imprisonment, for offenses such as not obtaining approval or intimation for specific activities. | The Bill, on the other hand, decriminalizes these offenses and introduces fines ranging from one lakh to fifty lakh rupees instead. |
What are the Concerns Related to the Biological Diversity (Amendment) Bill, 2021?
- Favoring Industry over Conservation:
- Critics argue that the amendments seem to prioritize industry interests rather than focusing on biodiversity conservation, which goes against the spirit of the CBD.
- The CBD emphasizes sharing benefits from biodiversity use with the communities that have conserved it for generations.
- The amendments may weaken the framework for benefit-sharing and community involvement.
- Decriminalization of Violations:
- The Bill proposes to decriminalize violations, removing the power of the NBA to file FIRs against parties that do not comply with regulations.
- This may weaken the enforcement of biodiversity protection laws and hinder efforts to deter illegal activities.
- Exemption for Domestic Companies:
- Only "foreign-controlled companies" would need to seek permission for using biodiversity resources. This could potentially create loopholes for domestic companies with foreign shareholding to bypass the approval process, raising concerns about unchecked exploitation of biodiversity.
- Limited Benefit Sharing:
- The inclusion of "codified traditional knowledge" exempts certain users, including practitioners of Indian systems of medicine, from the need to share benefits.
- This may lead to profiteering domestic companies avoiding their responsibility to share profits with the communities holding traditional knowledge.
- Ignoring Conservation Issues:
- Critics argue that the amendments do not adequately address the challenges faced by biodiversity conservation in India.
- The Bill appears to focus more on reducing regulations and facilitating business interests, raising concerns about the potential negative impact on biodiversity and traditional knowledge holders.
Way Forward
- There is a need to strike a balance between promoting economic development and ensuring the sustainable conservation of India's biodiversity.
- There is a need to engage in transparent and inclusive consultations with various stakeholders, including local communities, indigenous people, conservationists, scientists, and industry representatives.
- This will help ensure that all perspectives are considered in the decision-making process and that the amendments align with the principles of biodiversity conservation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2023)
- In India, the Biodiversity Management Committees are key to the realization of the objectives of the Nagoya Protocol.
- The Biodiversity Management Committees have important functions in determining access and benefit sharing, including the power to levy collection fees on the access of biological resources within its jurisdiction.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Biodiversity Governance in India: India’s Biological Diversity Act 2002 (BD Act), is in close synergy with the Nagoya Protocol and aims to implement provisions of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
- The Nagoya Protocol sought to ensure commercial and research utilisation of genetic resources led to sharing its benefits with the government and the community that conserved such resources.
- Under Section 41(1) of the Biological Diversity Act, 2002, every local body in the State shall constitute a Biodiversity Management Committee within its area of jurisdiction. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- The main function of the BMC is to prepare People’s Biodiversity Register (PBR) in consultation with local people. The BMC shall be responsible for ensuring the protection of the knowledge recorded in PBR, especially to regulate its access to outside persons and agencies.
- In addition to preparation of the People’s Biodiversity Register (PBR), the BMCs in their respective jurisdiction shall also be responsible for the following :-
- Conservation, sustainable use and access and benefit sharing of biological resources.
- Regulation of access to the biological resources and/ or associated Traditional Knowledge, for commercial and research purposes.
Mains
Q. How is the Government of India protecting traditional knowledge of medicine from patenting by pharmaceutical companies? (2019)
Flash Floods in Himachal Pradesh
For Prelims: Flash Floods in Himachal Pradesh, Monsoon, Flash Floods, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Indian Meteorological Department, Western Disturbances.
For Mains: Flash Floods in Himachal Pradesh.
Why in News?
The 2023 Monsoon rain in Himachal Pradesh has brought severe Flash Floods in many regions causing unprecedented loss of lives and assets.
What are Flash Floods?
- About:
- They are sudden surges in water levels generally during or following an intense spell of rain.
- These are highly localised events of short duration with a very high peak and usually have less than six hours between the occurrence of the rainfall and peak flood.
- The flood situation worsens in the presence of choked drainage lines or encroachments obstructing the natural flow of water.
- They are sudden surges in water levels generally during or following an intense spell of rain.
- Causes:
- It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, tropical storm, or meltwater from ice or snow flowing over ice sheets or snowfields.
- Flash Floods can also occur due to Dam or Levee Breaks, and/or Mudslides (Debris Flow).
How have been the Instances of Precipitation in Himachal Pradesh (HP)?
- In the Himalayas, there is a noticeable pattern of increased precipitation occurring in shorter periods of time.
- The IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) 6 report has clearly stated that the Himalayas and coastal regions of India will be the hardest hit by climate change.
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) data shows that the normal rainfall during this period is expected to be between 720mm and 750 mm. However, in certain instances, it has exceeded 888 mm in 2010 and 926.9 mm in 2018.
- In 2023, the precipitation in HP so far has been attributed to the combined effect of the South-West Monsoon with Western Disturbances.
- The total rainfall from June to date was 511 mm.
What are the Factors of Such Flash Floods in Himachal Pradesh?
- Developmental Model Led by Liberalization:
- Himachal Pradesh's development model brought progress and ranked second in social development for mountainous regions.
- Liberalization led to fiscal reforms, self-reliance, however increased exploitation of natural resources, causing ecological impacts.
- Hydropower Projects:
- Uncontrolled construction of the Hydropower Projects has turned mountain rivers into mere streams.
- The diversion of water through tunnels and disposal of excavated material (muck) along riverbeds exacerbate the impact during periods of heavy rainfall or cloudbursts.
- Improper disposal of muck not only creates a favorable situation for landslides during the rainy season but also clogs river valleys with heavy sediments dumped by humans, leading to water diversion, overflow, and, consequently, floods.
- Tourism and Road Expansion:
- Tourism-driven Road expansion has led to four-lane and two-lane road transformations, bypassing essential geological studies.
- Vertical cutting roads of mountains during road construction has resulted in landslides and damage to existing roads during even normal rainfall, exacerbating destruction during heavy rain or floods.
- Earlier there were terraced and curved roads in mountains which were somewhat safer against landslides, but the vertical roads are more susceptible to landslides and erosion.
- Cement Plants:
- Massive cement plant establishment and extensive mountain cutting have altered land use patterns, reducing the land's water absorption capacity, and contributing to flash floods during rainfall.
- Changes in Crop Patterns:
- The shift to cash crop and horticulture economies over traditional cereal farming, which have implications for transportation to markets within short timeframes, since they are perishable in nature.
- Hasty road construction for cash crops or larger farm fields without proper land cutting and drainage leads to rapid swelling of rivers during rainfall, further contributing to the floods.
What are the Government Initiatives to Tackle Flash Floods?
- National Flood Risk Mitigation Project (NFRMP)
- National Disaster Management Plan (NDMP).
- National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA).
- India Meteorological Department (IMD)
- National Flood Management Programme
- Rashtriya Barh Ayog (National Flood Commission) 1976
Way Forward
- Institute a Commission of Inquiry involving major stakeholders, empowering local communities over their assets, and insuring assets to facilitate quicker rebuilding. Adequate changes in infrastructure planning are crucial to avert disasters while considering the reality of climate change.
- With climate change as a reality, humans should not add to the problem, but make adequate changes in infrastructure planning to avert disasters that the State has been witnessing for some time.
Black Holes and Quantum Mechanics
Why in News?
Recently, research conducted by a team of scientists from S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences, an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and Technology, has delved into the intriguing realm of black holes and their interaction with quantum mechanics.
- This exploration holds the potential to provide valuable insights into the unification of two significant scientific theories: quantum mechanics and the general theory of relativity, propounded by Einstein.
- The study focuses on atoms freely falling into a black hole and the novel quantum effects on the radiation emitted in this process.
Note:
- General Theory of Relativity: Albert Einstein's theory explains how objects move around massive ones. A fundamental consequence of the general theory of relativity is the existence of a black hole.
- Quantum Theory: The study of tiny particles' behavior, like atoms, at the smallest level.
- Einstein's Principle of Equivalence: The idea that nature's laws are the same in a small region with gravity as without it.
- Hawking Radiation: It is a theoretical concept proposed by Stephen Hawking, which suggests that black holes can emit radiation due to quantum effects near the event horizon known as Hawking radiation.
What are the Key Highlights of Study?
- Radiation from atoms falling into black holes exhibits similarities to Hawking radiation.
- The investigation reveals that the radiation is generated from two-level atoms, unlike the radiation emitted by black holes as predicted by Hawking.
- The study introduces the concept of "horizon brightened acceleration radiation entropy" (HBAR entropy) to quantify the amount of disorder in the emitted radiation.
- The HBAR entropy follows the area law with logarithmic leading order area corrections and inverse order of area subleading corrections.
- The findings uphold Einstein's Principle of Equivalence in a general setting, providing valuable insights into the interplay of quantum mechanics and general relativity in black hole scenarios.
- The study adds to our understanding of the mysterious world of quantum effects in black holes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following phenomena: (2018)
- Light is affected by gravity.
- The Universe is constantly expanding.
- Matter warps its surrounding space-time.
Which of the above is/are the prediction/predictions of Albert Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity, often discussed in media?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Ocular Burns in Children
Why in News?
A new study sheds light on the major role played by "chuna" or slaked lime in causing ocular burns among children in the Indian subcontinent.
- Most individuals with acute ocular burns were male, constituting over 80% among adults and over 60% among children.
What is Slaked Lime?
- About:
- Slaked lime (Ca (OH)2), is obtained by mixing quicklime (calcium oxide) with water, resulting in a chemical reaction that produces calcium hydroxide.
- The process of slaking quicklime with water is highly exothermic, generating a significant amount of heat.
- It has a high pH value, making it highly alkaline and caustic.
Note:
- Alkali is the Base that dissolved in water. Base refers to a type of chemical substance that has a high pH value, typically above 7 on the pH scale.
- Alkalis are also known as bases and are characterized by their ability to neutralize acids, producing salts and water in the process.
- Common examples of alkalis include sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and potassium hydroxide (KOH).
- Acid is a type of chemical substance that has a low pH value, usually below 7 on the pH scale. Acids are characterized by their ability to release hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution. They can react with metals, carbonates, and bases to form salts and water.
- Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
- Application:
- Slaked lime has been used for various applications throughout history, including in construction and agriculture.
- It is traditionally used as a chuna (a binding agent) in the preparation of paan, a popular traditional chewable mixture in South and Southeast Asia.
- Issue:
- Loose and poorly sealed packets of chuna are posing a risk of ocular burns. An exploding packet of chuna can cause alkali to encounter a person's eyes, resulting in chemical burns to the ocular surface and potentially causing severe damage.
- Chemical burns to the corneal limbus, the specialized stem cell-rich area of the cornea, can impair its ability to repair itself, leading to long-term vision issues.
- Children At Risk:
- Alkalis accounted for 38% of all ocular burns, with chuna being the most common alkali agent, responsible for 32% of all alkali burns among children due to their close contact with chuna in households and in fireworks.
Note: Ocular burns refer to injuries caused by exposure of the eye to harmful chemicals, intense heat, or radiation, resulting in damage to the eye's surface or internal structures.
Ocular burns can be caused by various substances, such as acids, alkalis, solvents, or even exposure to high-energy sources like welding arcs or lasers.
STARFIRE Algorithm
Why in News?
Recently, Scientists at Raman Research Institute (RRI), an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and Technology have developed an algorithm names STARFIRE to tackle unwanted Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) in space, enriching data obtained from space-based astronomy missions.
What is STARFIRE?
- About:
- Simulation of TerrestriAl Radio Frequency Interference in oRbits around Earth (STARFIRE) is an advanced algorithm developed to estimate and map unwanted RFI signals in space.
- The STARFIRE algorithm can estimate and identify the RFI emitted by various sources, including FM radio stations, Wi-Fi networks, mobile towers, radar, satellites, and communication devices.
- This innovative algorithm has the potential to revolutionize space-based Astronomy missions and enrich the data obtained from such missions in the future.
- To develop this algorithm, scientists utilized data on FM transmitter stations from six countries, including Canada, the USA, Japan, Australia, Germany, and South Africa.
- Simulation of TerrestriAl Radio Frequency Interference in oRbits around Earth (STARFIRE) is an advanced algorithm developed to estimate and map unwanted RFI signals in space.
- Applications:
- Enhancing Radio Astronomy:
- STARFIRE helps astronomers study the early Universe by estimating and mapping unwanted RFI signals in space.
- It enables the tuning of radio antennas within the 40 to 200 Mega Hertz (MHz) range to detect the 21-cm hydrogen line, revealing secrets about the cosmos.
- Optimal Instrument Design:
- The algorithm assists in designing instruments for space-based Astronomy missions that can operate optimally even in the presence of RFI.
- This leads to improved data collection and analysis for future missions.
- Supporting PRATUSH Mission:
- STARFIRE is utilized in missions like Probing ReionizATion of the Universe using Signal from Hydrogen (PRATUSH), aimed at studying the birth of stars and galaxies in the Universe using the 21-cm hydrogen line from the far side of the moon.
- The algorithm plays a key role in fine-tuning antennas and instrument components for successful data gathering.
- Orbit Selection:
- The algorithm's capability extends to aiding orbit selection for future space missions.
- It identifies low RFI orbits, particularly in the ~100 MHz frequency range, making them suitable for various scientific experiments.
- Flexibility and Versatility:
- STARFIRE offers flexibility to adjust the properties of transmitting and receiving antennas.
- This enables including astrophysical radio signals from our own galaxy and the cosmos, leading to more meaningful experimental results.
- Potential for Wide Range of Applications:
- The generic mathematical formulation of the STARFIRE code makes it adaptable for various applications, benefiting missions with low RFI orbits.
- Enhancing Radio Astronomy:
Radio Frequency Interference (RFI):
- RFI is a type of electromagnetic interference (EMI) that affects devices or circuits that operate with radio frequencies.
- RFI in space can affect the quality and reliability of satellite communications, navigation, and remote sensing systems.
- RFI can also interfere with the scientific observations and measurements of space-based instruments, such as radio telescopes and radars.
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Vibrant Villages Programme
Recently, the Ministry of Home Affairs provided valuable insights into the Vibrant Villages Programme (VVP) during a written reply in the Rajya Sabha.
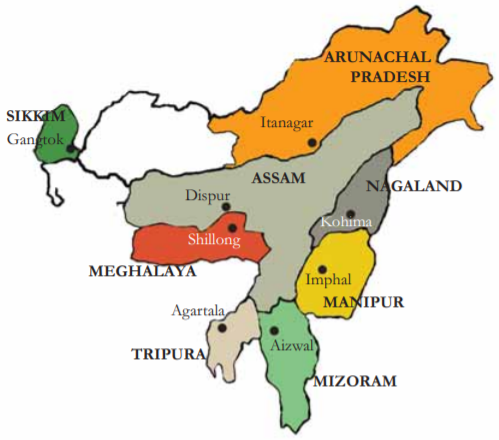
- VVP is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme approved on 15th February 2023 and officially launched on 10th April 2023. focusing on the comprehensive development of select villages in 46 blocks across 19 districts abutting the northern border in Arunachal Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Uttarakhand, and UT of Ladakh.
- The program aims to create livelihood opportunities through tourism promotion, cultural heritage preservation, skill development, entrepreneurship, and development of cooperative societies, including agriculture and cultivation of medicinal plants/herbs.
- Interventions under the program include road connectivity, housing, village infrastructure, renewable energy, television & telecom connectivity, and more, with the objective of providing sufficient incentives for people to stay in the selected villages.
- Additionally, under the Border Area Development Programme (BADP), essential infrastructure projects have been approved in census villages/towns, semi-urban, and urban areas located within 0-10 km distance from the first habitation at the International Boundary (IB) in 16 states and 2 UTs abutting land borders.
- Specific villages in Kinnaur and Lahul & Spiti districts of Himachal Pradesh, as well as Chamoli, Uttarkashi, and Rudraprayag districts, have been selected for the VVP.
Read more: Vibrant Villages Programme
Lithium Ore in Jammu and Kashmir
Recently, the Ministry of Coal, Mines, and Parliamentary Affairs provided important details regarding the Geological Survey of India's G3 stage mineral exploration project and the significant discovery of lithium ore in the Salal-Haimna areas of Reasi District, Jammu & Kashmir.
- An inferred resource (G3) of 5.9 million tonnes of lithium ore has been confirmed in the region.
- Geological Survey of India (GSI) is a geo-scientific organisation that was established in 1851 to find coal deposits and now provides national geo-science information and mineral resource assessment.
- The GSI is an attached office to the Ministry of Mines and has its headquarters in Kolkata and has six regional offices located at Lucknow, Jaipur, Nagpur, Hyderabad, Shillong and Kolkata. Every state has a state unit.
- The decision regarding auctioning of the Lithium mineral block in Jammu & Kashmir will be taken up by the Government of Jammu and Kashmir.
Read more: GSI Discovers Lithium Resources in J&K
Indian Army Inaugurates First PAEC for Aadhaar Services
- Indian Army inaugurated its inaugural Permanent Aadhaar Enrolment Centre (PAEC) recently, at the 1 Central Base Post Office (CBPO) in New Delhi.
- The establishment of the PAEC marks a crucial milestone for the tri-services personnel and their dependents, as it will offer Aadhaar-related services, including enrolment and updation, at 48 identified locations across the country through the Field Post Offices (FPOs).
- The PAEC's comprehensive coverage, including both Field and Peace locations, ensures that all army personnel, including those stationed in remote areas, can conveniently avail themselves of the Aadhaar services.
Read more: Aadhar and its Voluntary Use, Indian Army
National Coal Index (NCI) Shows Significant Decline
- The National Coal Index (NCI) has shown a significant decline of 33.8% in May 2023 compared to May 2022. This decline is an indication of a robust supply of coal in the market.
- NCI is a price index that combines coal prices from all sales channels, including notified prices, auction prices and import prices.
- Established with the base year as fiscal year 2017-18, it serves as a reliable indicator of market dynamics, providing valuable insights into coal price fluctuations.
Read more: National Coal Index