Implementing Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework
For Prelims: Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF), Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC-AR 6), Conference of the Parties (COP), Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
For Mains: Impact and relevance of Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework on conservation of environment and nature.
Why in News?
Recently, the 25th meeting of the Subsidiary Body on Scientific, Technical and Technological Advice (SBSTTA-25) in Nairobi, Kenya concluded with recommendations aimed at facilitating the transition from agreement to action following the adoption of the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (KMGBF) in December 2022.
- The meeting primarily focused on creating a progress monitoring mechanism, while also addressing the implications of assessments conducted by the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) and the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC AR6), among other matters.
What is Subsidiary Body on Scientific, Technical and Technological Advice (SBSTTA)?
- Article 25 of the Convention on Biological Diversity establishes an open-ended intergovernmental scientific advisory body known as the Subsidiary Body on Scientific, Technical and Technological Advice (SBSTTA).
- Its purpose is to provide the Conference of the Parties (COP) and, as appropriate, its other subsidiary bodies, with timely advice relating to the implementation of the Convention.
What Was the Recent SBSTTA-25 Meeting About ?
- IPBES Reports on Invasive Species and Biodiversity Valuation:
- The recent IPBES report has highlighted the critical role that invasive species play in driving the extinction of plants and animals. Additionally, the Methodological Assessment Report on Diverse Values and Valuation of Nature, as well as the Thematic Assessment Report on the Sustainable Use of Wild Species, were discussed.
- These findings shed light on the intricate relationship between biodiversity and the impact of invasive species.
- IPCC AR6 Findings on Biodiversity and Climate Change:
- The findings from the IPCC AR6 report were also a focal point of discussion. The report underscores that climate change is the primary driver of biodiversity loss and emphasizes the capacity of biodiversity to support climate adaptation, resilience, mitigation, and disaster risk reduction.
- This connection between biodiversity and climate change has significant implications for global environmental management.
- Converging Crises
- During the meeting, experts recognized that biodiversity loss, climate change, ocean acidification, desertification,land degradation, invasive alien species, and pollution are interconnected crises.
- Recommendations:
- To address these challenges coherently and effectively, the group finalized 15 key points for presentation at the 16th meeting of the Conference of the Parties (COP16) to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
- This approach aligns with the goals of the Convention, the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework, and other global initiatives such as the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change and the 2030 Agenda on Sustainable Development.
- Moreover, the meeting emphasized the importance of utilizing the work of other multilateral agencies, including the World Health Organization and the Food and Agriculture Organization, to enhance scientific and technical guidance in implementing the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework.
What is Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework?
- About:
- The Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) was adopted during the fifteenth meeting of the Conference of the Parties (COP)-15 of CBD following a four year consultation and negotiation process.
- This historic Framework, which supports the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals and builds on the Convention’s previous Strategic Plans, sets out an ambitious pathway to reach the global vision of a world living in harmony with nature by 2050.
- 30 by 30 Target:
- The declaration made a reference to the '30 by 30' target which is a key proposal being debated at the COP15, that would afford 30% of the Earth’s land and oceans protected status by 2030.
- Main Targets:
- The framework consists of four goals for 2050 and 23 targets for 2030.
- The four goals are:
- Conserve and restore biodiversity.
- Ensure sustainable use of biodiversity.
- Share benefits fairly and equitably.
- Enable transformative change.
- The 23 Targets are:
- The four goals are:
- The framework consists of four goals for 2050 and 23 targets for 2030.
Kunming Biodiversity Fund
- China has also pledged to inject USD 233 million into a new fund to protect biodiversity in developing countries. The fund is being referred to by China as Kunming Biodiversity Fund.
- Further, some rich country donors say a new fund for conservation is unnecessary because the United Nations’ Global Environment Facility already helps developing nations finance green projects.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. “Momentum for Change: Climate Neutral Now” is an initiative launched by (2018)
(a) The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
(b) The UNEP Secretariat
(c) The UNFCCC Secretariat
(d) The World Meteorological Organisation
Ans: (c)
Q. What is/are the importance/importances of the ‘ United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification' ? (2016)
- It aims to promote effective action through innovative national programmes and supportive international partnerships.
- It has a special/particular focus on South Asia and North Africa regions, and its Secretariat facilitates the allocation of major portions of financial resources to these regions.
- It is committed to a bottom-up approach, encouraging the participation of local people in combating the desertification.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Global Tax Evasion Report 2024
For Prelims: Global Tax Evasion Report 2024, Tax Evasion, European Union Tax Observatory, Global Minimum Tax.
For Mains: Global Tax Evasion Report 2024, Inclusive growth and issues arising from it.
Why in News?
Recently, the European Union Tax Observatory has released 'Global Tax Evasion Report 2024' highlighting several critical issues related to tax evasion, the Global Minimum Tax (GMT) on billionaires, and measures to combat tax evasion.
- The report investigates the effects of international reforms adopted over the past 10 years, such as the automatic international exchange of bank information, and the international agreement on a global minimum tax for MNCs, among other issues.
What is Tax Evasion?
- Tax evasion is the illegal act of not paying taxes that one owes to the government by underreporting income, inflating deductions, hiding money in offshore accounts, or using other fraudulent means to reduce one's tax liability.
- It is a deliberate and unlawful attempt to reduce tax obligations by misrepresenting or concealing financial information.
What are the International Reforms to Combat Tax Evasion?
- Global Minimum Tax (GMT):
- A GMT applies a standard minimum tax rate to a defined corporate income base worldwide.
- The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) developed a proposal featuring a corporate minimum tax of 15% on foreign profits of large multinationals, which would give countries new annual tax revenues of USD 150 billion.
- In October 2021, a group of 136 countries, including India, set a minimum global tax rate of 15% for MNCs and sought to make it harder for them to avoid taxation.
- The framework of GMT aims to discourage nations from tax competition through lower tax rates that result in corporate profit shifting and tax base erosion.
- Automatic Exchange of Information:
- The automatic exchange of information was introduced in 2017 to fight offshore tax evasion by wealthy individuals.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Challenges in Curbing Offshore Tax Evasion:
- Offshore tax evasion has decreased over the past decade. In 2013, 10% of the world's GDP was stored in global tax havens, but now only 25% of this wealth remains untaxed.
- However, challenges remain, including non-compliance by offshore financial institutions and limitations in the automatic exchange of bank information.
- Tax Rates Equivalent to 0%:
- Global billionaires have effective tax rates equivalent to 0% to 0.5% of their wealth, due to the frequent use of shell companies to avoid income taxation.
- US billionaires have an effective tax rate equivalent to 0.5% of their wealth and French billionaires a tax rate of zero.
- Profit Shifting by MNCs:
- Multinational corporations (MNCs) have shifted around USD 1 trillion to tax havens in 2022, equivalent to 35% of the profits they earned outside their headquarters countries.
- The report red-flagged the trend of “Greenwashing the Global Minimum Tax” wherein MNCs can use ‘green’ tax credits for low carbon transition to reduce their tax rates way below the minimum of 15%.
- Importance of Policy Choices:
- Tax evasion, wealth concealment, and profit shifting to tax havens are not natural occurrences but results of policy choices or the failure to make necessary choices.
- There is a need to evaluate the consequences of tax policies and make improvements for sustainable tax systems.
- Recommendations:
- The report advocates for a global minimum tax on billionaires, proposing a rate of 2% of their wealth. Institute mechanisms to tax wealthy people who have been long-term residents in a country and choose to move to a low-tax country.
- This measure is seen as essential for governments worldwide to increase their revenue, address wealth inequality, and fund critical services like education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
- Reform the international agreement on minimum corporate taxation to implement a rate of 25% and remove the loopholes in it that foster tax competition.
- Implement unilateral measures to collect some of the tax deficits of multinational companies and billionaires in case global agreements on these issues fail.
- Move towards the creation of a Global Asset Registry to better fight tax evasion.
- Strengthen the application of economic substance and anti-abuse rules.
- The report advocates for a global minimum tax on billionaires, proposing a rate of 2% of their wealth. Institute mechanisms to tax wealthy people who have been long-term residents in a country and choose to move to a low-tax country.
What is the Difference Between Income and Wealth Taxes?
- Wealth taxes are assessed on the wealth stock, or the total amount of net wealth owned by a taxpayer, whereas income taxes are levied on the flow from the wealth stock.
- Example of a wealth tax: Estate taxes, gift taxes, and inheritance taxes are examples of one-time or infrequently assessed wealth taxes.
What are the Government Measures to Curb Tax Evasion?
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. The term ‘Base Erosion and Profit Shifting’ is sometimes seen in the news in the context of (2016)
(a) mining operation by multinational companies in resource-rich but backward areas
(b) curbing of the tax evasion by multinational companies
(c) exploitation of genetic resources of a country by multinational companies
(d) lack of consideration of environmental costs in the planning and implementation of developmental projects
Ans: (b)
Biomass Co-Firing In Thermal Power Plants
For Prelims: Crop Residue Management (CRM), Biomass Co-Firing, National Capital Region (NCR), Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM), Thermal Power Plants (TPP), Stubble Burning.
For Mains: Impact and relevance of Biomass Co-Firing on conservation of environment and nature.
Why in News?
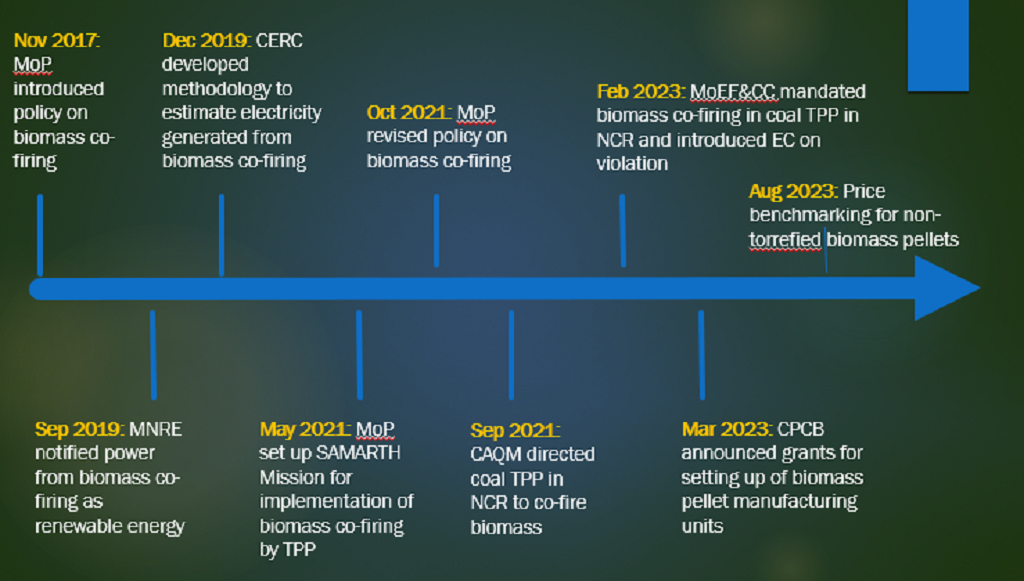
In recent years, the government has tried to tackle the issue of stubble burning by bringing the focus on ex-situ mechanisms of handling biomass or crop residue management (CRM) such as biomass co-firing and production of bio-CNG.
- The Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) conducted a survey-based study in 2022 to understand the on-ground progress of the policy implementation on co-firing biomass in coal-fired thermal power plants in the National Capital Region (NCR).
What Are the Highlights of the Survey Conducted by CSE ?
- Limited Biomass Co-Firing Progress:
- The study found that, as of the end of 2022, co-firing was sporadic, with most plants only conducting trial runs. Unfortunately, the situation has not significantly improved since then. Only three plants reported increased biomass co-firing from December 2022 to August 2023.
- Reasons for Delay in Biomass Co-Firing Implementation:
- CSE investigated the reasons behind the delay in implementing the mandated 5% co-firing by coal thermal power plants (TPP) in the NCR and adjoining areas.
- The Harduaganj Thermal Power Plant attributed its success in co-firing biomass to a consistent and affordable biomass supply. However, they acknowledge that the supply chain needs further strengthening.
- In contrast, Haryana Power Generation Corporation Limited (HPGCL) faced challenges due to technical limitations and a shortage of torrefied biomass pellet manufacturers.
- Mahatma Gandhi Thermal Power Plant faced technical limitations of only being able to co-fire up to 1.5% biomass pellets instead of 5% as mandated and would need significant investments to increase biomass co-firing to the mandated level, impacting electricity tariffs.
- Talwandi Saboo TPP struggled to find vendors for its plant due to the absence of established technology for manufacturing torrefied biomass pellets.
- CSE investigated the reasons behind the delay in implementing the mandated 5% co-firing by coal thermal power plants (TPP) in the NCR and adjoining areas.
- Efforts to Overcome Supply Challenges:
- Several plants, like Indira Gandhi TPP, have initiated measures to address the supply challenge by issuing tenders for raw materials to set up in-house pellet manufacturing units and also explored partnerships and in-house manufacturing for biomass pellets.
- Challenges in Implementing Biomass Co-Firing for Farm Fire Reduction:
- Despite government directives and efforts to enhance pellet manufacturing capacity, the study suggests that biomass co-firing may not significantly reduce farm fires.
- Timely planning and a coordinated approach, from tendering by coal TPPs to crop residue procurement by pellet manufacturers, are essential to effectively address stubble burning, which is time-sensitive.
What is Biomass Co-firing?
- About:
- Biomass co-firing is the practice of substituting a part of the fuel with biomass at coal thermal plants.
- Biomass co-firing stands for adding biomass as a partial substitute fuel in high efficiency coal boilers.
- Coal and biomass are combusted together in boilers that have been designed to burn coal. For this purpose, the existing coal power plant has to be partly reconstructed and retrofitted.
- Co-firing is an option to convert biomass to electricity, in an efficient and clean way, and to reduce GHG (Greenhouse Gases) emissions of the power plant.
- Biomass co-firing is a globally accepted cost-effective method for decarbonising a coal fleet.
- India is a country where biomass is usually burnt on the field which reflects apathy towards resolving the problem of clean coal using a very simple solution that is readily available.
- Co-firing 5 to 7% biomass pellets in thermal power plants can prevent 38 million tonnes of carbon dioxide every year, as per the Finance Minister in the budget speech in 2022.
- Agro Residues for Biomass Pellet Production:
- The Ministry of Power has identified various surplus agro residues that can be utilized for biomass pellet production. These include:
- Crop Residues:
- Agro-residues from crops such as Paddy, Soya, Arhar, Gwar, Cotton, Gram, Jawar, Bajra, Moong, Mustard, Sesame, Til, Maize, Sunflower, Jute, Coffee, etc.
- Shell Waste:
- Waste products like Groundnut Shell, Coconut Shell, Castor Seed Shell, etc.
- Crop Residues:
- The Ministry of Power has identified various surplus agro residues that can be utilized for biomass pellet production. These include:
- Additional Biomass Sources:
- Bamboo and its by-products, horticulture waste, and other biomass materials like Pine Cone/Needle, Elephant Grass, Sarkanda, etc.
What are the Government Interventions Related to Biomass Co-firing?
- Financial Assistance:
- The MNRE and Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) have introduced Finance Assistance Schemes to support biomass pellet manufacturing units.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has approved 'Biomass pellet manufacturing' as an eligible activity under Priority Sector Lending (PSL), fostering financial viability for such endeavors.
- Procurement and Supply Chain:
- A dedicated Procurement Provision of Biomass Category has been established on the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) portal.
- Ministry of Power has introduced a Revised Model Long-Term Contract for Biomass Supply, ensuring a consistent supply chain.
- The provision of Udyam Aadhaar on the National Single Window System streamlines administrative processes for biomass-related projects.
- The Udyam Aadhaar registration process is based on the concept of self-declaration, enabling MSMEs to register themselves for free and obtain the Udyam Aadhaar number.
Way Forward
- Ensuring a Steady Supply of Biomass to Power Plants:
- Steady supply of biomass to power plants can be ensured by developing a reliable supply chain that can transport biomass from source to plant.
- This could involve partnering with farmers, forestry companies, or other biomass suppliers to secure a steady supply of biomass.
- Steady supply of biomass to power plants can be ensured by developing a reliable supply chain that can transport biomass from source to plant.
- Building Infrastructure and Logistics:
- Developing the necessary infrastructure and logistics to transport, store, and process biomass is critical to the success of biomass co-firing.
- This could involve building new storage facilities, upgrading transportation networks, or investing in new processing technologies.
- Developing the necessary infrastructure and logistics to transport, store, and process biomass is critical to the success of biomass co-firing.
- Robust Regulatory Framework:
- The Biomass Co-firing Policy needs to be backed by a strong policy and regulatory framework that provides incentives and support for biomass co-firing.
- It also includes developing specialized boilers, burners, and control systems that can handle the unique characteristics of biomass, as well as retrofitting existing equipment to accommodate biomass co-firing.
- The Biomass Co-firing Policy needs to be backed by a strong policy and regulatory framework that provides incentives and support for biomass co-firing.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following: (2019)
- Carbon monoxide
- Methane
- Ozone
- Sulphur dioxide
Which of the above are released into the atmosphere due to the burning of crop/biomass residue?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)
Q. With reference to the usefulness of the by-products of sugar industry, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2013)
- Bagasse can be used as biomass fuel for the generation of energy.
- Molasses can be used as one of the feedstocks for the production of synthetic chemical fertilizers.
- Molasses can be used for the production of ethanol.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
The Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023
For Prelims: Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023, IPC (Indian Penal Code), Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC), Indian Evidence Act, Supreme Court, Adultery, National Judicial Data Grid.
For Mains: The Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023, Amendments, Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Why in News?
Recently, a Parliamentary Committee has reviewed the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS) 2023 Bill, proposing significant changes to India's Criminal Justice System, recommendations including a gender-neutral provision criminalizing adultery.
- The BNS Bill, introduced by the Ministry of Home Affairs, seeks to replace the colonial-era IPC (Indian Penal Code).
What are the Key Highlights of the Proposed Changes in BNS?
- Adultery and Gender-Neutral Provision:
- The parliamentary committee has recommended including a gender-neutral provision that criminalizes Adultery.
- This move comes after the Supreme Court (SC) declared Section 497 of the Indian Penal Code (IPC), which criminalized adultery, as unconstitutional in 2018.
- The panel seeks to protect the institution of marriage but in a gender-neutral way.
- The parliamentary committee has recommended including a gender-neutral provision that criminalizes Adultery.
- Non-Consensual Sex and Bestiality:
- The committee is considering a clause to criminalize non-consensual sex between men, women, or transpersons, as well as acts of bestiality.
- This indicates an effort to address various forms of sexual offenses comprehensively.
- Definition of Terms:
- The committee has suggested better definitions for terms like "community service" and "life imprisonment" in the bill.
- Positive Changes:
- The new draft code has included the removal of Section 124A (Sedition) and provisions for prosecuting offenses committed in foreign countries.
What are the Arguments for Legalizing and Criminalizing Adultery?
- Legalizing Adultery:
- Individual Autonomy and Privacy: The Supreme Court, in Joseph Shine vs. The Union of India, 2018 judgment recognized the importance of individual autonomy and the right to privacy.
- Legalizing adultery acknowledges the right of adults to make decisions about their personal relationships without state interference.
- The court said that the 158-year-old law was unconstitutional and is violative of Article 21 (Right to life and personal liberty) and Article 14 (Right to equality).
- Doctrine of Curvature: Section 497 of the IPC (Indian Penal Code) is based on the Doctrine of Coverture.
- This doctrine, not recognised by the Constitution, holds that a woman loses her identity and legal right with marriage, is violative of her fundamental rights.
- Human Liberty: According to the Supreme Court (SC), Marriage does not mean ceding autonomy of one to the other.
- Ability to make sexual choices is essential to human liberty. Even within private zones, an individual should be allowed her choice.
- The SC observes that "Society imposes impossible virtues on a woman, raises her to a pedestal. Confines her to spaces. Objectifies her and says she should be pure. But society has no qualms to commit rape, honour killings, sex-determination and infanticide".
- Deterrence Effect: Legalization could eliminate the chilling effect of the law on individuals who may be reluctant to leave abusive or unhappy marriages due to the fear of legal consequences.
- It might encourage open communication and resolution of marital issues.
- Reducing Judicial Burden: Adultery cases used to burden the legal system. Legalizing it can free up the courts to address more pressing issues and cases.
- Criminalizing Adultery:
- Preservation of Marital Sanctity: Adultery can harm the institution of marriage, leading to broken families and emotional trauma for the spouse and children. Criminalizing it can be seen as a means to protect the sanctity of marriage.
- Gender Protection: It is argued that criminalizing adultery is a means to protect women from unfaithful spouses who might otherwise abandon them, leaving them economically vulnerable.
- Moral and Societal Values: It is argued that the adultery law upholds traditional moral and societal values, which are still important to many in Indian society.
- Criminalizing adultery could be viewed as a way to protect and preserve the family structure, which is considered a fundamental building block of society.
Way Forward
- Creating awareness about the implications of adultery on families and relationships can help individuals make informed decisions about their personal lives.
- Encouraging couples to seek marriage counseling and mediation in cases of marital discord can be a proactive approach to resolving issues before they lead to adultery. Promoting the availability and accessibility of such services can be beneficial.
- There is a need to promote alternative dispute resolution mechanisms, such as arbitration and mediation, to help couples resolve issues related to infidelity or marital discord outside of the court system.
SIM Cards
For Prelims: SIM Cards, Smartphones, Climate Change, Antimicrobial Resistance, International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI), Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM), Universal Integrated Circuit Card (UICC), Mobile Equipment (ME), eSIM.
For Mains: Impact and relevance of eSIM cards in fulfilling the objectives of Digital India Mission while taking care of privacy and security.
Why in News?
In contemporary times, the usage of smartphones have outgrown other electronic devices so much that an important component of smartphones, i.e. Subscriber Identification Module (SIM) Cards need apt description.
What is a SIM Card?
- About:
- A SIM card is a tiny integrated circuit or microchip that plays a vital role in identifying subscribers on a cellular network. It can be thought of as an individual's ID card within the vast city of a cellular network.
- This ID card carries a unique identification number known as the international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI), which is used to locate and confirm the identity of the subscriber when others try to reach them on the network.
- Essential Role in Network Access:
- When it comes to connecting a mobile phone to a cellular network adhering to the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) standard, a SIM card is mandatory. This connection relies on a special authentication key (SAK) that serves as a digital lock and key mechanism.
- Each SIM card stores SAK, but it's inaccessible through the user's phone. Instead, when the phone communicates with the network, it 'signs' the signals using this key, allowing the network to verify the legitimacy of the connection.
- It's important to note that duplicating a SIM card is feasible by accessing and copying this authentication key onto multiple cards.
- Each SIM card stores SAK, but it's inaccessible through the user's phone. Instead, when the phone communicates with the network, it 'signs' the signals using this key, allowing the network to verify the legitimacy of the connection.
- When it comes to connecting a mobile phone to a cellular network adhering to the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) standard, a SIM card is mandatory. This connection relies on a special authentication key (SAK) that serves as a digital lock and key mechanism.
- Information Storage:
- Beyond its primary role in network access, a SIM card also serves as a storage unit for various data. It stores not only the IMSI but also the integrated circuit card identifier, the subscriber's location area identity, and a list of preferred networks for roaming.
- Additionally, SIM cards can contain essential emergency contact numbers, and, space permitting, store the subscriber's contacts and SMS messages.
- This compact chip plays a pivotal role in the functionality and security of mobile communication on GSM-based networks.
How Does a SIM Card Work?
- SIM Card Standard:
- SIM cards adhere to the ISO/IEC 7816 international standard, which is overseen by the International Organisation for Standardisation and the International Electrotechnical Commission.
- Pin Functions and Standards:
- The metal contacts on a SIM card are segmented into pins, each serving a specific purpose. These roles for each pin are defined by the ISO/IEC 7816-2 standard
- In fact, there are 15 pins in total, each specifying various functions of the SIM card.
- The metal contacts on a SIM card are segmented into pins, each serving a specific purpose. These roles for each pin are defined by the ISO/IEC 7816-2 standard
- SIM Card's Network Role:
- When a subscriber dials a recipient's number, the phone sends data through the network, authenticated by the key on the SIM card.
- This data is then sent to a telephone exchange. If the recipient is connected to the same exchange, their identity is confirmed, and the call is directed to them.
How have SIM cards changed?
- Evolution of Smart Cards:
- The history of smart cards, which include SIM cards, traces back to the late 1960s. Over the years, these smart cards underwent significant changes in size and architecture, spurred by the advancements in technology described by Moore's law.
- Moore’s law is the observation that the number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years, making computers faster and cheaper over time.
- The history of smart cards, which include SIM cards, traces back to the late 1960s. Over the years, these smart cards underwent significant changes in size and architecture, spurred by the advancements in technology described by Moore's law.
- SIM Card Standards and Development:
- The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) played a pivotal role by formulating the GSM Technical Specification for SIM cards.
- It covered aspects ranging from physical features like operating temperature and contact pressure to authentication and data access characteristics.
- Transition and Compatibility:
- The term 'SIM card' once referred to both the hardware and software, up until the 2G networks. However, with the arrival of the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System and 3G networks, a shift occurred.
- 'SIM' came to represent only the software, while the hardware was labeled the Universal Integrated Circuit Card (UICC).
What is an eSIM?
- Evolution of SIM Cards: From Physical to eSIM:
- Unlike its physical predecessors, the eSIM's software is loaded onto a permanent, non-removable UICC in the mobile device during the manufacturing process. Notable devices, like Google Pixel 2, 3, 4, and the iPhone 14 series, support eSIM functionality.
- With eSIM, users no longer need to physically replace SIM cards when switching or joining networks. Instead, network operators can remotely reprogram the eSIM.
- Different Benefits of eSIM Technology:
- eSIM technology offers several advantages. Firstly, it's considered environmentally friendly because it eliminates the need for additional plastic and metal for physical SIM cards, due to its reprogrammable nature.
- Secondly, eSIMs enhance security by preventing separate access to the SIM application and making duplication more challenging for potential malicious actors.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which among the following do/does not belong/ belongs to the GSM family of wireless technologies? (2010)
(a) EDGE
(b) LTE
(c) DSL
(d) Both EDGE and LTE
Ans: (c)
Q. With reference to communication technologies, what is/are the difference/differences between LTE (LongTerm Evolution) and VoLTE (Voice over Long-Term Evolution)? (2019)
- LTE is commonly marketed as 3G and VoLTE is commonly marketed as advanced 3G.
- LTE is data-only technology and VoLTE is voice only technology.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Role of Dust Suppressants in Mitigating Air Pollution
Why in News?
Recently, Dust suppressants have gained significant attention as a potential solution to reduce dust-related pollution especially in cities like Delhi where air pollution remains a critical concern.
What are Dust Suppressants?
- About:
- Dust suppressants are typically composed of calcium or magnesium salts, which are mixed with water and then sprayed on roads.
- This mixture effectively suppresses dust, providing longer-lasting relief from particulate matter in the air.
- Efficacy:
- The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) study indicated that the application of dust suppressants, when mixed with water, is more effective at controlling pollution than traditional methods, such as water spraying.
- The study observed up to a 30% reduction in dust concentration (including PM10, PM2.5, and PM1) for construction sites and roads following the use of dust suppressants.
- In 2019, the CPCB recommended the use of dust suppressants on excavated earth surfaces, construction and demolition waste piles, and access roads in construction areas.
- The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) study indicated that the application of dust suppressants, when mixed with water, is more effective at controlling pollution than traditional methods, such as water spraying.
Note: Air pollution is the presence of harmful substances in the Earth's atmosphere, originating from natural and human-made sources, which adversely affect air quality, human health, and the overall environment.
What are the Other Recent Technological Interventions to Curb Air Pollution?
- Ionisation Technology for Pollution Reduction: This technology aims to neutralize pollutants through ionization processes, enhancing air quality in specific areas.
- Wind Augmentation and Air Purifying Unit (WAYU): It can be positioned in an industrial complex, residential complexes, and schools in the vicinity of traffic road intersection/divider to tackle air pollution.
- This device works on two principles i.e. Wind generation for dilution of air pollutants and active pollutants removal.
- Medium/Large-Scale Smog Towers: These towers are substantial air purifiers targeting the reduction of particulate matter and pollutants on a larger scale.
- Indigenous Photonic System for Air Quality Monitoring: The Department of Science and Technology (DST) is developing an indigenous photonic system for real-time remote air quality monitoring, improving data accuracy for informed pollution management.
What are the Government Initiatives to Combat Air Pollution?
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
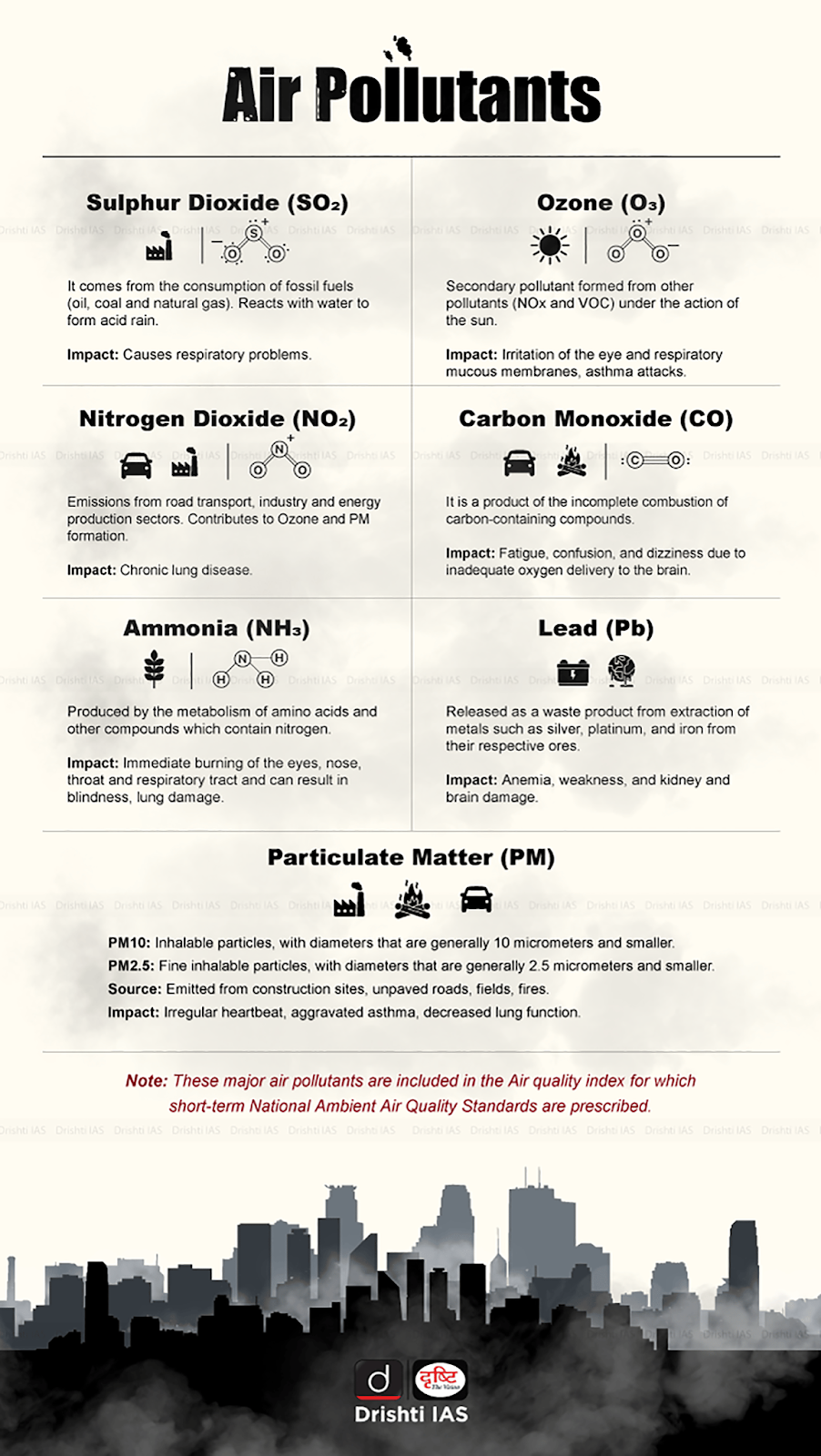
Q. In the cities of our country, which among the following atmospheric gases are normally considered in calculating the value of the Air Quality Index? (2016)
- Carbon dioxide
- Carbon monoxide
- Nitrogen dioxide
- Sulfur dioxide
- Methane
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Describe the key points of the revised Global Air Quality Guidelines (AQGs) recently released by the World Health Organisation (WHO). How are these different from its last update in 2005? What changes in India’s National Clean Air Programme are required to achieve revised standards? (2021)
Marsquake
Why in News?
- Recently, scientists have revealed the causes of the largest recorded marsquake. This finding holds scientific importance and carries implications for forthcoming Mars exploration by providing fresh insights into the geology and seismic events of the Red Planet.
What are the Recent Findings Related to Marsquake?
- A Marsquake, or Martian earthquake, is a seismic event occurring on Mars. In 2022, a significant marsquake with a magnitude of 4.7 was recorded.
- Initial suspicion was a meteoroid impact due to similar seismic signals from past meteoroid-caused quakes.
- Space agencies like Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), European Space Agency, China National Space Administration, and the UAE Space Agency collaborated on a groundbreaking project to search for a crater on Mars.
- The search found no impact crater, leading to the conclusion that the marsquake resulted from internal tectonic forces, indicating increased seismic activity.
- The cause was attributed to the accumulated stresses within Mars' crust, evolving over billions of years due to differential cooling and shrinking rates in different regions.
- This discovery has implications for future Mars exploration, aiding in the identification of safe landing sites and areas to avoid for astronauts.
What are the Major Facts Related to Mars?
- Mars, the fourth planet from the Sun, takes its name from the Roman God of war. It is often referred to as the "Red Planet" due to its distinctive reddish appearance. This reddish coloration is primarily attributed to the presence of a significant amount of iron oxide, commonly known as rust, in its surface rocks and soil.
- Mars, being the second smallest planet in our solar system after Mercury, boasts a diameter of approximately 6,791 kilometers, making it about half the size of Earth.
- It possesses two moons, known as Phobos and Deimos.
- The planet experiences extreme cold, with equatorial temperatures reaching 20°C and polar regions plunging as low as -140°C due to its greater distance from the sun.
- Mars is home to Olympus Mons, the tallest volcano in our solar system, roughly three times the height of Mount Everest.
- A Martian day is 24 hours and 37 minutes, slightly longer than an Earth day, but a Martian year lasts nearly twice as long, spanning 687 Earth days due to its extended orbit around the Sun.
- Mars' axis of rotation is tilted 25 degrees with respect to the plane of its orbit around the Sun. This is similar to Earth, which has an axial tilt of 23.4 degrees.
- Mars has distinct seasons, but they last longer than seasons here on Earth.
What Missions Have Been Sent to Mars?
- India’s Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) or Mangalyaan (2013)
- ExoMars rover (2021) (European Space Agency)
- Tianwen-1: China's Mars Mission (2021)
- UAE’s Hope Mars Mission (UAE’s first-ever interplanetary mission) (2021)
- Mars 2 and Mars 3 (1971) (Soviet Union)
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO
- is also called the Mars Orbiter Mission
- made India the second country to have a spacecraft orbit the Mars after USA
- made India the only country to be successful in making its spacecraft orbit the Mars in its very first attempt
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations
Why in News?
- Recently, in response to the allegations raised by the Canadian Foreign Minister regarding India's purported violation of diplomatic protocols, the Indian Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) emphasized that India's actions are consistent with the provisions outlined in Article 11.1 of the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations.
What is the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations?
- About:
- The Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations (1961) is established to define fundamental principles and terms governing how countries must treat each other's diplomatic representatives.
- It was adopted on 14th April 1961 by the United Nations Conference on Diplomatic Intercourse and Immunities held at the Neue Hofburg in Vienna, Austria.
- It aims to foster friendly relations and maintain effective communication channels between nations.
- Today, 193 countries have ratified the convention.
- India ratified it through the Diplomatic Relations (Vienna Convention) Act of 1972.
- The Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations (1961) is established to define fundamental principles and terms governing how countries must treat each other's diplomatic representatives.
- Major Provisions:
- A key principle of the Convention is diplomatic immunity. It grants diplomats exemption from certain laws and taxes in the host country where they are posted. It ensures that diplomats can fulfill their duties without fear, threat, or intimidation.
- According to Article 29 of the Convention, diplomats are not subject to arrest or detention. The host country must accord the diplomatic agent the appropriate level of respect and is responsible for undertaking all necessary measures to prevent any form of harm or violation to the diplomat's person, liberty, or dignity.
- Article 11.1 of the Convention empowers the host country to establish reasonable and appropriate limits on the size of a foreign diplomatic mission, taking into consideration the prevailing conditions and circumstances in the host nation, as well as the unique requirements of the particular diplomatic mission.
- Article 9 of the Convention allows the receiving State to declare the head of the mission or any member of the diplomatic staff persona non grata or unwelcome without the need for an explanation, and this notification can be made at any time.
- A key principle of the Convention is diplomatic immunity. It grants diplomats exemption from certain laws and taxes in the host country where they are posted. It ensures that diplomats can fulfill their duties without fear, threat, or intimidation.
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Raising Day of Indo-Tibetan Border Police
The Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP), is a dedicated force responsible for safeguarding India's borders with Tibet (China). The Prime Minister praised their unwavering determination and courage on their raising day (24th October), acknowledging their vital role in protecting the nation's border security and integrity.
- The ITBP is a specialized mountain force of India, which was established on 24th October 1962, soon after the India-China war which was initially meant for deployment along the India-China border.
- ITBP was initially raised under the Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) Act, 1949. However, in 1992, parliament enacted the ITBP Act and the rules were framed in 1994.
- However, over the years, ITBP has also been deployed for various internal security duties, including anti-Naxal operations. The force is known for its expertise in high-altitude rescue and mountaineering operations.
Read More: Central Armed Police Forces
ICT Labs for PM Shri Schools
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) labs and Smart Classrooms for PM Shri schools are to be introduced in Haryana for adopting modern technology in the classrooms which will enhance the quality of education and provide a better learning experience to the students.
- ICT labs and Smart Classrooms bridge urban-rural digital gap, providing equal education opportunities.
- PM Shri is a centrally sponsored scheme for upgradation and development of more than 14500 Schools across the country which aims at strengthening the selected existing schools from amongst schools managed by Central Government/ State/UT Government/ local bodies.
- It will showcase all components of the National Education Policy 2020 and act as exemplar schools and also offer mentorship to other schools in their vicinity.
Read More: Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing (DIKSHA), Digital India Mission
Ball Lightning
Ball lightning, a rare natural event, is a luminous sphere that typically appears near lightning strikes.
- It can penetrate closed windows and is usually accompanied by a hissing sound, and has a lifetime of several seconds.
- The color is quite variable and the ball often ends with an explosion. However, it is not usually destructive.
- Also, it is sometimes called globe lightning, these spheres are thought to be composed of plasma, an ionized state of matter with freely moving ions.
Supreme Court Rectifies Long-standing Employment Issue
In a recent landmark decision, the Supreme Court has rectified a 30-year-old injustice in a public employment case.
- The Court invoked its powers under Article 142 of the Constitution, ordering the concerned department to appoint an individual to a probationary position for 10 years.
- Article 142 of the Constitution grants the Supreme Court the unique authority to deliver "complete justice" in situations where the law or statutes may not offer a remedy.
- SC held that a public employer, which falls under the 'state' category as per Article 12 of the Constitution, cannot dismiss a candidate from job consideration without a valid and justifiable reason.
- The ruling underscores the importance of clear and fair eligibility criteria from the outset of a selection process and reaffirms the principle of non-discrimination in public employment.
Read more: Supreme Court