Indian Economy
Open Network for Digital Commerce
For Prelims: Open Network for Digital Commerce, UPI, Initiatives related to e-Commerce
For Mains: Significance of Open Network for Digital Commerce
Why in News?
Recently, the government has launched the pilot phase of Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) with an aim to “democratise” the country’s fast growing digital e-commerce space that is currently dominated by the two U.S.-headquartered firms — Amazon and Walmart.
What is ONDC?
- About:
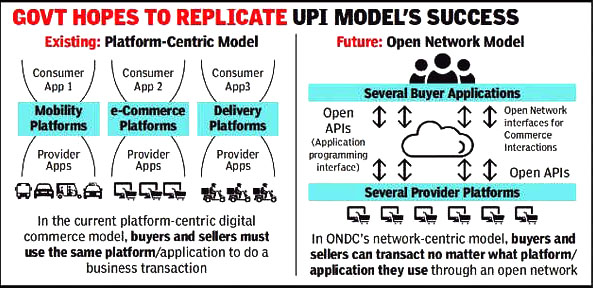
- ONDC is a freely accessible government-backed platform that aims to democratise e-commerce by moving it from a platform-centric model to an open network for buying and selling of goods and services.
- Under ONDC, it is envisaged that a buyer registered on one participating e-commerce site (for example, Amazon) may purchase goods from a seller on another participating e-commerce site (for example, Flipkart).
- Presently, buyers and sellers have to be on the same app for a transaction which happens through the same platform. For example, a buyer needs to go to Amazon, to buy a product from a seller on Amazon.
- It is a not-for-profit organisation that will offer a network to enable local digital commerce stores across industries to be discovered and engaged by any network-enabled applications.
- The open network concept extends beyond the retail sector, to any digital commerce domains including wholesale, mobility, food delivery, logistics, travel, urban services, etc.
- It is neither an aggregator application nor a hosting platform, and all existing digital commerce applications and platforms can voluntarily choose to adopt and be a part of the ONDC network.
- The ONDC aims at promoting open networks developed on open-sourced methodology, using open specifications and open network protocols, independent on any specific platform.
- Implementation of ONDC, which is expected to be on the lines of Unified Payments Interface (UPI) could bring various operational aspects put in place by e-commerce platforms to the same level.
- The project to integrate e-commerce platforms through a network based on open-source technology has been tasked to the Quality Council of India.
- Open source refers to a software program or platform with source code that is readily accessible and which can be modified or enhanced by anyone. Open source access grants users of an application permission to fix broken links, enhance the design, or improve the original code.
- ONDC is a freely accessible government-backed platform that aims to democratise e-commerce by moving it from a platform-centric model to an open network for buying and selling of goods and services.
- Benefits:
- The ONDC will standardise operations like cataloguing, inventory management, order management and order fulfilment, hence making it simpler and easier for small businesses to be discoverable over network and conduct business.
- Potential Issues:
- Experts have pointed out some likely potential issues such as getting enough number of e-commerce platforms to sign up, along with issues related to customer service and payment integration.
What is the Significance?
- On ONDC, buyers and sellers may transact irrespective of the fact that they are attached to one specific e-commerce portal.
- This could give a huge booster shot to smaller online retailers and new entrants.
- However, if mandated, this could be problematic for larger e-commerce companies, which have their own processes and technology deployed for these segments of operations.
- ONDC is expected to digitise the entire value chain, standardise operations, promote inclusion of suppliers, derive efficiency in logistics and enhance value for consumers.
- The platform envisages equal-opportunity participation and is expected to make e-commerce more inclusive and accessible for consumers as they can potentially discover any seller, product or service by using any compatible application/platform, thus increasing their freedom of choice.
- It will enable transactions of any denomination, thus making ONDC a truly ‘open network for democratic commerce’.
- Over the next five years, the ONDC expects to bring on board 90 crore users and 12 lakh sellers on the network, enabling 730 crore additional purchases.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to ‘Quality Council of India (QCI)’, consider the following statements: (2017)
- QCI was set up jointly by the Government of India and the Indian Industry.
- Chairman of QCI is appointed by the Prime Minister on the recommendations of the industry to the Government.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans (c)
Exp:
- The Quality Council of India was set up jointly by the Government of India and the Indian Industry represented by the three premier industry associations, i.e., Associated Chambers of Commerce and Industry of India, Confederation of Indian Industry and Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- It was set up to establish and operate national accreditation structure and promote quality through National Quality Campaign.
- The Council plays a pivotal role at the national level in propagating, adoption and adherence to quality standards in all important spheres of activities including education, health care, environment protection, governance, social sectors, infrastructure sector and such other areas of organized activities that have significant bearing on improving the quality of life and wellbeing of the citizens of India.
- The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (Ministry of Commerce and Industry), is the nodal ministry for QCI.
- It is governed by a Council of 38 members with equal representations of government, industry and consumers.
- Chairman of QCI is appointed by the Prime Minister on the recommendation of the industry to the government. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Governance
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban
For Prelims: Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY)- Urban, Geotagging
For Mains: PMAY-U, Welfare Schemes, Government Policies and Interventions
Why in News?
Recently, Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY)- Urban has completed seven years of successful implementation.
- With a total investment of Rs 8.31 Lakh Crore, PMAY-U has so far sanctioned 122.69 lakh houses, out of which more than 1 crore houses have been grounded and over 61 lakh houses have been completed and delivered to the beneficiaries.
What is Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban?
- About:
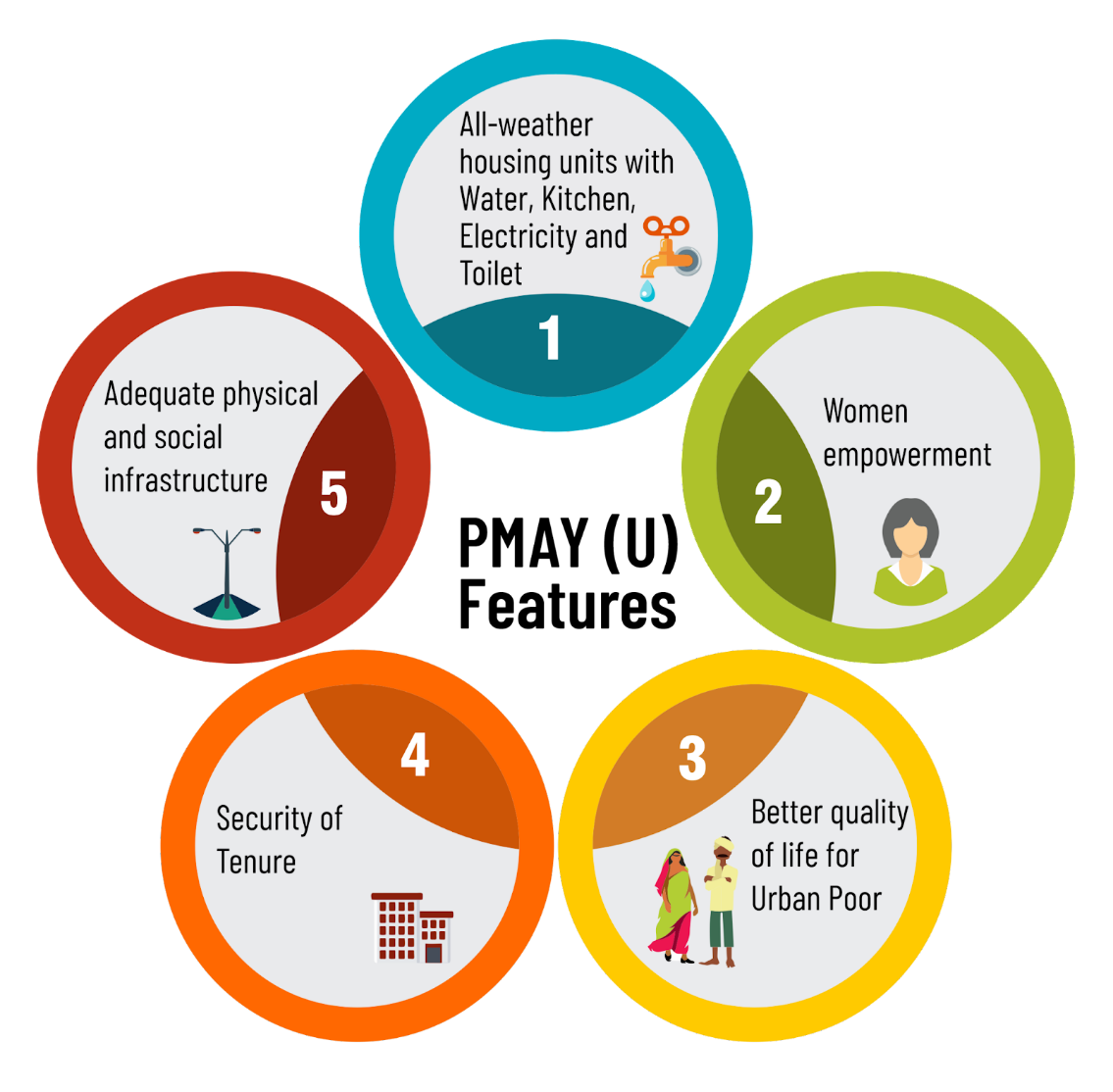
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) falls under the Government’s mission - Housing for All by 2022 for urban housing being implemented by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- It makes home loans affordable for the urban poor by providing a subsidy on the Interest Rate of a home loan during repayment by way of EMI (Equated Monthly Installments).
- Beneficiaries:
- The Mission addresses urban housing shortage among the EWS/LIG and MIG categories including the slum dwellers.
- Economically Weaker Section (EWS) - with a maximum annual family income of Rs. 3,00,000.
- Low Income Group (LIG) - with maximum annual family income of Rs. 6,00,000) and
- Middle Income Groups (MIG I & II) - with a maximum annual family income of Rs. 18,00,000)
- A beneficiary family will comprise husband, wife, unmarried sons and/or unmarried daughters.
- The Mission addresses urban housing shortage among the EWS/LIG and MIG categories including the slum dwellers.
- Four Verticals of PMAY-U:
- In Situ Slum Redevelopment (ISSR):
- This vertical will be implemented with the concept “Land as a resource” with private sector participation for providing houses to eligible slum dwellers.
- Slum: It is a compact area of at least 300 people or about 60 - 70 households of poorly built congested tenements in an unhygienic environment usually with inadequate infrastructure and lacking in proper sanitary and drinking water facilities
- This vertical will be implemented with the concept “Land as a resource” with private sector participation for providing houses to eligible slum dwellers.
- Affordable Housing through Credit Linked Subsidy (CLSS):
- Beneficiaries of EWS, LIG, MIG (I &II) seeking housing loans from Banks, Housing Finance Companies and other such institutions for acquiring, new construction or enhancement of houses are eligible for an interest subsidy of:
- 6.5% on loan amount up to Rs. 6 Lakh
- 4% on loan amount up to Rs. 9 Lakh
- 3% on loan amount up to Rs. 12 Lakh
- Beneficiaries of EWS, LIG, MIG (I &II) seeking housing loans from Banks, Housing Finance Companies and other such institutions for acquiring, new construction or enhancement of houses are eligible for an interest subsidy of:
- Affordable Housing Through Partnership (AHP):
- An affordable housing project can be a mix of houses for different categories but it will be eligible for Central Assistance, if at least 35% of the houses in the project are in the EWS category.
- Beneficiary-led individual house construction (BLC):
- Central Assistance up to Rs. 1.5 lakh per EWS house is provided to eligible families belonging to EWS categories for individual house construction/ enhancement.
- In Situ Slum Redevelopment (ISSR):
- Demand-driven Approach:
- PMAY-U adopts a demand-driven approach strengthening the ethos of cooperative federalism, housing shortage is decided based on demand assessment by States/Union Territories (UTs).
- The Mission is implemented as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) except the CLSS vertical of the PMAY-U which is being implemented as a Central Sector Scheme.
- Central Sector Schemes are 100% funded by the Union government and implemented by the Central Government machinery.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) a certain percentage of the funding is borne by the States and the implementation is by the State Governments.
- Geotagging:
- Geotagging is a process of adding geographical identification to various media like photography.
- Under the PMAY-U guidelines, it is mandatory for the state government to ensure that all houses built under the scheme are geotagged to the Bhuvan HFA (housing for all) application.
- Bhuvan is an Indian Geo Platform developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- It is a web-based application which allows users to access various map related services.
- Under the PMAY-U guidelines, it is mandatory for the state government to ensure that all houses built under the scheme are geotagged to the Bhuvan HFA (housing for all) application.
- Geotagging is a process of adding geographical identification to various media like photography.
- Women Empowerment:
- The Mission promotes Woman Empowerment by providing the ownership of houses in the name of a female member or in joint names.
- Preference is also given to women (with overriding preference to widows, single women), persons belonging to Scheduled Castes/Scheduled Tribes/Other Backward Classes, Minorities, Persons with disabilities and Transgender.
- Initiatives under PMAY-U:
- Affordable Rental Housing Complexes (ARHCs) :
- It is a sub-scheme under PMAY-U.
- This will provide ease of living to urban migrants/ poor in the Industrial Sector as well as in non-formal urban economies to get access to dignified affordable rental housing close to their workplace.
- Global Housing Technology Challenge :
- It aims to identify and mainstream a basket of innovative construction technologies from across the globe for the housing construction sector that are sustainable, eco-friendly and disaster-resilient.
- CLSS Awas Portal (CLAP):
- It is a common platform where all stakeholders i.e., MoHUA, Central Nodal Agencies, Primary Lending Institutions, Beneficiaries and Citizens are integrated in a real-time environment.
- The portal facilitates processing of applications along with tracking of subsidy status by beneficiaries.
- Affordable Rental Housing Complexes (ARHCs) :
Biodiversity & Environment
National Air Quality Resource Framework of India
For Prelims: NARFI, Air Pollution
For Mains: Health, Conservation
Why in News?
Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government inaugurated the National Mission on "National Air Quality Resource Framework of India (NARFI)".
- NARFI has been developed by the National Institute of Advanced Studies (NIAS), Bengaluru.
What is NARFI?
- About:
- The NARFI is an information mechanism to help decision-makers in government, municipalities, start-ups and in the private sectors to address air pollution issues in different climatic zones of India.
- Research-based audited Information and industry-oriented solutions will be shared in an easy-to-understand format.
- The short-term basic training modules tailored for different groups such as active ground level staff in government establishments, implementers, media and policymakers, would be an integral part of the framework.
- Objectives:
- To help enrich communication and enhance general awareness, leading to self-mitigation.
- Modules: The NARFI will evolve around the following five modules:
- THEME-1: Emission Inventory, Air Shed, and Mitigation
- THEME-2: Impacts on Human Health and Agriculture
- THEME-3: Integrated Monitoring, Forecasting and Advisory Framework
- THEME-4: Outreach, Social Dimension, Transition Strategy and Policy
- THEME-5: Solutions, Public-Industry Partnership, Stubble Burning & New Technologies.
- Significance:
- It will will enable knowledge creation, developing infrastructure and industrial structures and studying its effects on human health in the country.
- It will provide an all-inclusive guide to collecting air quality data, studying its impact and implementing science-based solutions.
What is Air Pollution?
- About:
- Air pollution is contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere.
- Household combustion devices, motor vehicles, industrial facilities and forest fires are common sources of air pollution.
- Pollutants:
- Pollutants with the strongest evidence for public health concern include particulate matter (PM), Ozone (O3), Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and Sulphur dioxide (SO2).
- These pollutants are capable of penetrating deep into lung passageways and entering the bloodstream causing cardiovascular, cerebrovascular and respiratory impacts.
- Sources of Air Pollution:
- Burning of Fossil Fuels: Most of the pollutants are produced by burning fossil fuels or wood, for driving, heating, power plants and industry.
- Several man-made factors, vehicular emissions, construction dust, garbage burning causes severe pollution.
- The particles can be made of black carbon, nitrates, sulphates, ammonia or mineral dust.
- Agriculture & Allied Sources: Farming is one such source of pollution, with ammonia from livestock manure and fertilisers blowing into cities and forming particles, particularly in spring time when crops are sown and muck is spread.
- Further, stubble burning is also one of the major sources of air pollution in northern India, especially in winters.
- Natural Sources: Apart from it, there are some natural sources of outdoor air pollution such as dust storms.
- Burning of Fossil Fuels: Most of the pollutants are produced by burning fossil fuels or wood, for driving, heating, power plants and industry.
- Related Initiatives:
- Graded Response Action Plan
- SAFAR (System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research)
- The Commission for Air Quality Management in National Capital Region (NCR) and Adjoining Areas.
- Bharat Stage (BS) VI norms.
- Dashboard for Monitoring Air Quality.
- National Clean Air Programme.
- National Air Quality Index (AQI).
- Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981.
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following: (2011)
- Carbon dioxide
- Oxides of Nitrogen
- Oxides of Sulphur
Which of the above is/are the emission/emissions from coal combustion at thermal power plants?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- Coal based power plants are the major contributor of the atmospheric air pollution and contribute significantly to global warming and adverse health effects which can ultimately lead to diseases like lung cancer.
- Toxic compounds released from the burning of coal include:
- Oxides of Carbon (COx ), Carbon Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; hence, 1 is correct.
- Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx), hence, 2 is correct.
- Oxides of Sulphur (SOx ), hence, 3 is correct.
- Fly Ash
- Trace elements like Mercury, Cadmium and lead are also emitted which are also hazardous for health.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Indian Polity
NITI Aayog
For Prelims: NITI Aayog
For Mains: NITI Aayog, Significance and Concerns
Why in News?
NITI (National Institution for Transforming India) Aayog CEO Amitabh Kant is set to leave and will be replaced by former Secretary of the Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation - Parameswaran Iyer.
What is NITI Aayog?
- Background:
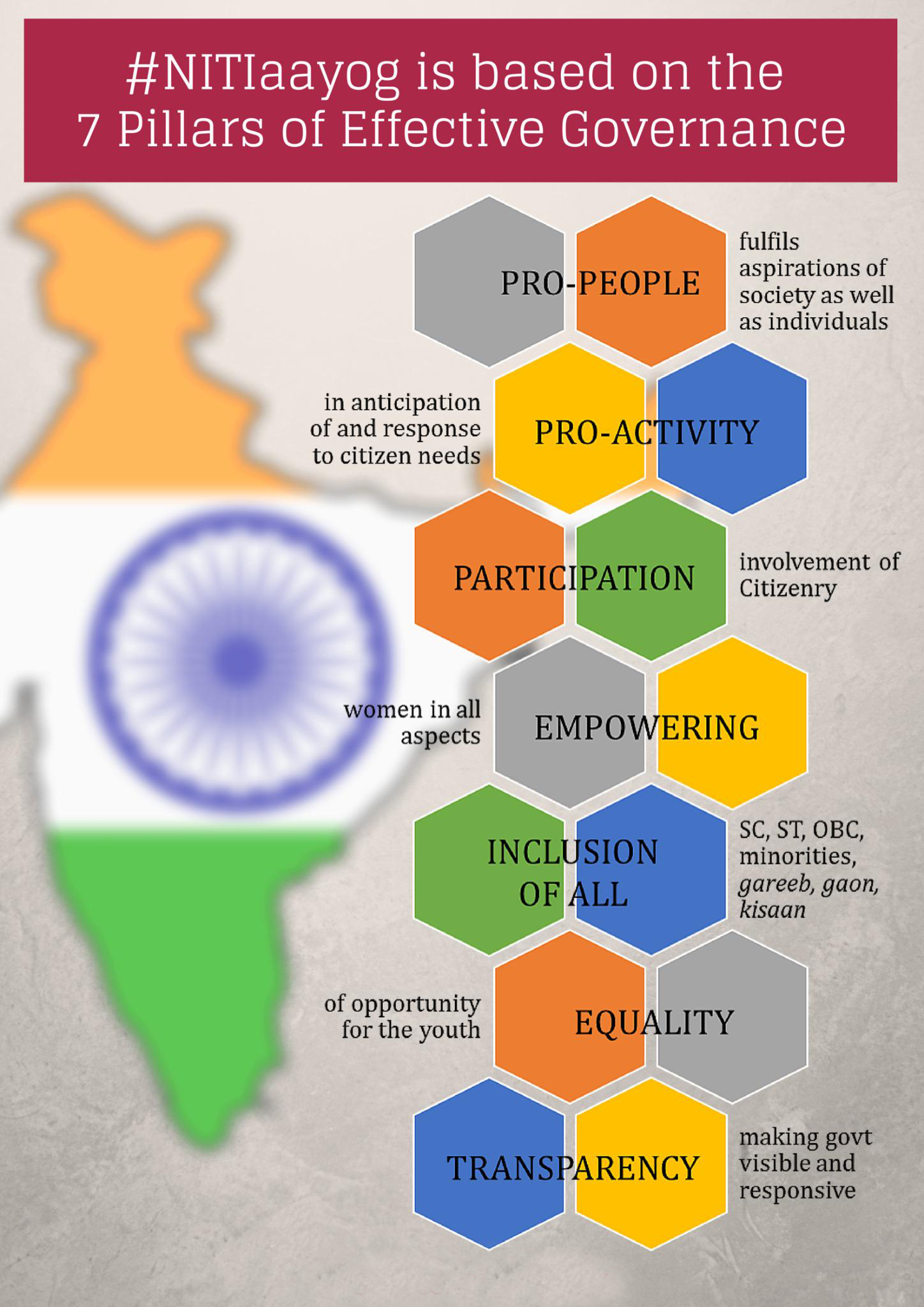
- Planning Commission was replaced by a new institution – NITI Aayog on 1st January, 2015 with emphasis on ‘Bottom –Up’ approach to envisage the vision of Maximum Governance, Minimum Government, echoing the spirit of ‘Cooperative Federalism’.
- It has two Hubs.
- Team India Hub acts as interface between States and Centre.
- Knowledge and Innovation Hub builds the think-tank acumen of NITI Aayog.
- Composition:
- Chairperson: Prime minister
- Vice-Chairperson: To be appointed by Prime-Minister
- Governing Council: Chief Ministers of all states and Lt. Governors of Union Territories.
- Regional Council: To address specific regional issues, Comprising Chief Minister and Lt. Governors Chaired by the Prime Minister or his nominee.
- Ad-hoc Membership: Two members in ex-officio capacity from leading Research institutions on a rotational.
- Ex-Officio membership: Maximum four from the Union council of ministers to be nominated by the Prime Minister.
- Chief Executive Officer: Appointed by the Prime-minister for a fixed tenure, in the rank of Secretary to Government of India.
- Special Invitees: Experts, Specialists with domain knowledge nominated by the Prime Minister.
- Objectives:
- To foster cooperative federalism through structured support initiatives and mechanisms with the States on a continuous basis, recognizing that strong States make a strong nation.
- To develop mechanisms to formulate credible plans at the village level and aggregate these progressively at higher levels of government.
- To ensure, on areas that are specifically referred to it, that the interests of national security are incorporated in economic strategy and policy.
- To pay special attention to the sections of our society that may be at risk of not benefiting adequately from economic progress.
- To provide advice and encourage partnerships between key stakeholders and national and international like-minded Think Tanks, as well as educational and policy research institutions.
- To create a knowledge, innovation and entrepreneurial support system through a collaborative community of national and international experts, practitioners and other partners.
- To offer a platform for resolution of inter-sectoral and inter-departmental issues in order to accelerate the implementation of the development agenda.
- To maintain a state-of-the-art Resource Centre, be a repository of research on good governance and best practices in sustainable and equitable development as well as help their dissemination to stakeholders.
| NITI Aayog | Planning Commission |
| It serves as an advisory Think Tank. | It served as extra-constitutional body. |
| It draws membership from a wider expertise. | It had limited expertise. |
| It serves in spirit of Cooperative Federalism as states are equal partners. | States participated as spectators in annual plan meetings. |
| Secretaries to be known as CEO appointed by Prime- Minister. | Secretaries were appointed through usual process. |
| It focuses upon ‘Bottom-Up’ approach of Planning. | It followed a ‘Top-Down’ approach. |
| It does not possess mandate to impose policies. | Imposed policies on states and tied allocation of funds with projects it approved. |
| It does not have powers to allocate funds, which are vested in Finance Minister. | It had powers to allocate funds to ministries and state governments. |
Why is the Creation of NITI Aayog is Significant?
- The 65 year-old Planning Commission had become a redundant organization. It was relevant in a command economy structure, but not any longer.
- India is a diversified country and its states are in various phases of economic development along with their own strengths and weaknesses.
- In this context, a ‘one size fits all’ approach to economic planning is obsolete. It cannot make India competitive in today’s global economy.
What are the Related Concerns and Challenges?
- NITI Aayog has no powers in granting discretionary funds to states, which renders it toothless to undertake a transformational intervention.
- It acts as an advisory body only that advises the government on various issues without ensuring the enforceability of its ideas.
- NITI Aayog has no role in influencing private or public investment.
- Politicization of the organization has been in recent times.
- NITI Aayog has been transformed into a glorified recommendatory body which lacks the requisite power to bring positive change in the government’s actions.
What are the Initiatives of NITI Aayog?
- SDG India Index
- Composite Water Management Index
- Atal Innovation Mission
- SATH Project.
- Aspirational District Programme
- School Education Quality Index
- District Hospital Index
- Health Index
- Agriculture Marketing And Farmer Friendly reform Index
- India Innovation Index
- Women Transforming India Awards
- Good Governance Index
Way Forward
- Equipping the planning body with requisite powers so that it can effect change.
- Allocation of adequate resources is needed.
- It can be made legally accountable to the legislature for its inability to meet the targets. This would bring in more accountability.
- Ensure the planning body remains a non-partisan institution.
- Bureaucratic inertia need to be shaken, specializing it and fixing the accountability on basis of performance.
Governance
Draft Guidelines to Regulate Child Participation in the Entertainment Industry
For Prelims: Guidelines to Regulate Child Protection within the Entertainment Industry, Child and Adolescent Labour Act, 1986, Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act, 2012, and the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015
For Mains: Issues Relating to Children
Why in News?
The National Commission for the Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) has published draft Guidelines to Regulate Child Protection within the Entertainment Industry.
- The “Guidelines to Regulate Child Participation in the Entertainment Industry” were issued by the Commission in 2011. The new draft increases the scope of the guidelines to cover social media and Over the Top (OTT) platforms for the first time.
What are the Key Highlights of the New Guidelines?
- Permission of the District Magistrate:
- Any producer of any audio-visual media production or any commercial event involving the participation of a child will now need to obtain the permission of the District Magistrate where the activity is to be performed.
- Producers will also have to run a disclaimer saying measures were taken to ensure there has been no abuse, neglect or exploitation of children during the entire process of the shooting.
- Stringent Penal Provisions:
- The commission has further included stringent penal provisions for violating the guidelines, including imprisonment, and has mandated that child artists and children being used in entertainment need to be registered with District Magistrates.
- Provisions of Various Acts:
- Parents who are using children to make money have to be held accountable. There are different Acts protecting children — the provisions of these Acts have now been included in the guidelines.
- Provisions under the Juvenile Justice Act, 2015, Child Labour Amendment Act, 2016, Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act, 2012, Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules, 2021, etc., have been included in the guidelines.
- Various penalties for offences have been prescribed under different acts including Child and Adolescent Labour Act, 1986, Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act, 2012, and the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015.
- Scope:
- The scope of the new guidelines will cover TV programmes including but not limited to reality shows, serials, news and informative media, movies, content on OTT platforms, content on social media, performing arts, advertising and any other kind of involvement of children in commercial entertainment activities.
- Prohibited Roles:
- The guidelines prohibit children being cast in roles or situations that are inappropriate,
- Consideration has to be given to the child’s age, maturity, emotional or psychological development and sensitivity, a child cannot be exposed to ridicule, insult or discouragement, harsh comments or any behaviour that could affect his/her emotional health.
- Children cannot be shown imbibing alcohol, smoking or using any other substance or shown to be indulging in any sort of antisocial activity and delinquent behaviour.
- No child can be engaged in any situation involving nudity.
- Presence of Guardian:
- At least one parent or legal guardian or a known person has to be present during a shoot, and for infants a registered nurse needs to be present along with the parent or legal guardian.
- Prohibited Harmful Lighting, Contaminated Cosmetics:
- A minor, especially below the age of six years, shall not be exposed to harmful lighting, irritating or contaminated cosmetics.
- Medical Fitness Certificate:
- Every person involved in production who may be in contact with children will have to submit a medical fitness certificate ensuring that they are not carrying obvious contagious disease and police verification of the staff also needs to be carried out.
- Ensure Child’s Education:
- The producer also needs to ensure the child’s education under the Right to Education (RTE) Act, 2009 to ensure no discontinuity from school or lessons as well as adequate and nutritious food, water for the children during the process of production and medical facilities.
- One Shift per Day:
- A child shall only participate in one shift per day, with a break after every three hours.
- Income of the Child Deposited in a Fixed Deposit:
- At least 20% of the income earned by the child from the production or event shall be directly deposited in a fixed deposit account in a nationalised bank in the name of the child which may be credited to the child on attaining majority.
- Content Created by the Child or his Family/Guardian:
- Content created by the child or his family/guardian shall be treated as children working in a family enterprise as provided under Section 3(2)(a) of the Child Labour and Adolescent Labour Act, 1986.
What are the Constitutional Provisions Related to Children?
- The Constitution guarantees to every child the right to live with dignity (Article 21), the right to personal liberty (Article 21), the right to privacy (Article 21), the right to equality (Article 14) and/or the right against discrimination (Article 15), the right against exploitation (Article 23 & 24).
- Right to free and compulsory elementary education for all children in the 6–14-year age group (Article 21 A)
- The Directive Principles of State Policy, and in particular Article 39(f), cast an obligation on the State to ensure that children are given opportunities and facilities to develop in a healthy manner and in conditions of freedom and dignity and that childhood and youth are protected against exploitation and against moral and material abandonment.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which of the following are envisaged by the Right against Exploitation in the Constitution of India? (2017)
- Prohibition of traffic in human beings and forced labour
- Abolition of untouchability
- Protection of the interests of minorities
- Prohibition of employment of children in factories and mines
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Articles 23 and 24 under Part III (Fundamental Rights) of the Constitution deal with the Right against exploitation.
- Article 23 provides for the prohibition of traffic in human beings and forced labour. It states that traffic in human beings and begar and other similar forms of forced labour are prohibited and any contravention of this provision shall be an offence punishable in accordance with law. Hence, 1 is correct.
- Article 24 provides for the prohibition of employment of children in factories, etc. It states that no child below the age of fourteen years shall be employed to work in any factory or mine or engaged in any other hazardous employment. Hence, 4 is correct.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer
Indian Economy
Card Tokenisation
For Prelims: RBI, Card Tokenisation, Card-on-File
For Mains: Reports of RBI, Card Tokenisation, Card-on-File
Why in News?
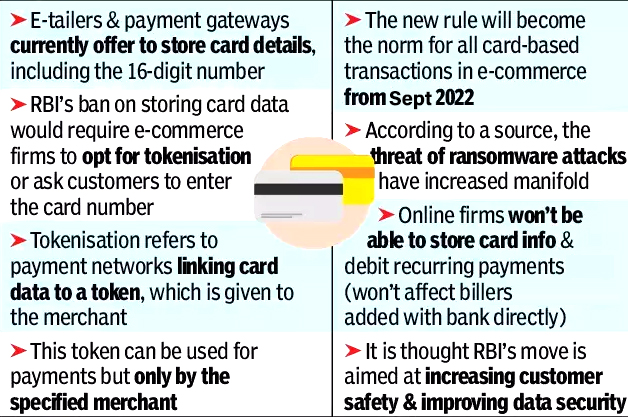
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) extended the timeline for tokenisation of debit and credit cards by three months till 30th September, 2022 to avoid disruption and inconvenience to cardholders.
- After 30th September, no entity in the card transaction or payment chain, other than the card issuers and card networks, should store the CoF (Card-on-File data or storage of actual card data) and any such data stored previously will be done away with.
What is Tokenisation and Card-on-File?
- Tokenisation: It refers to replacement of actual credit and debit card details with an alternate code called the “token”, which will be unique for a combination of card, token requestor and device.
- A tokenised card transaction is considered safer as the actual card details are not shared with the merchant during transaction processing.
- Customers who do not have the tokenisation facility will have to key in their name, 16-digit card number, expiry date and CVV each time they order something online.
- As of now, about 19.5 crore tokens have been created. Opting for CoFT (creating tokens) is voluntary for the cardholders.
- Card-on-File: A CoF transaction is a transaction where a cardholder has authorised a merchant to store the cardholder’s Mastercard or Visa payment details.
- The cardholder then authorises that same merchant to bill the cardholder’s stored Mastercard or Visa account.
- E-commerce companies and airlines and supermarket chains normally store card details in their system.
Why is Tokenisation of Cards Required?
- Many entities involved in an online card transaction chain store card data like card number and expiry date — Card-on-File (CoF) for undertaking transactions in future. While this practice does render convenience, availability of card details with multiple entities increases the risk of card data being stolen or misused.
- There have been instances where such data stored by merchants have been compromised.
- Many jurisdictions do not mandate Additional Factor of Authentication (AFA) for authenticating card transactions, stolen data in the hands of fraudsters may result in unauthorised transactions and resultant monetary loss to cardholders. Within India as well, social engineering techniques can be employed to perpetrate frauds using such data.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) acts as a ‘bankers’ bank. This would imply which of the following? (2012)
- Other banks retain their deposits with the RBI.
- The RBI lends funds to the commercial banks in times of need.
- The RBI advises the commercial banks on monetary matters.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 2 and 3 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
- The origin of the Reserve Bank of India can be traced to 1926, when the Royal Commission on Indian Currency and Finance (also known as the Hilton- Young Commission) recommended the creation of a central bank for India to separate the control of currency and credit from the Government and to augment banking facilities throughout the country. The Reserve Bank of India Act of 1934 established the Reserve Bank.
- Role of RBI as a Bankers’ Bank and Supervisor
- RBI holds a part of the cash reserves of banks, lends them funds for short periods and provides them with centralized clearing and cheap and quick remittance facilities. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- The RBI is authorized statutorily to require scheduled commercial banks to deposit with it a stipulated ratio of their Net Demand Time Liabilities (NDTL). Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- As a Banker to Banks, the Reserve Bank also acts as the ‘lender of last resort’. It can come to the rescue of a bank that is solvent but faces temporary liquidity problems by supplying it with much needed liquidity when no one else is willing to extend credit to that bank.
- The RBI is supposed to function as the lender of the last resort.
- RBI also supervise and advise the commercial banks in monetary matters. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Governance
Children and Adolescents in Need of Education Support
For Prelims: Education Cannot Wait (ECW), UNESCO
For Mains: State of Educational system of the world
Why in News?
The United Nations global fund for education in emergencies and protracted crises, Education Cannot Wait (ECW), released a report that indicates the number of crisis-impacted school-aged children requiring educational support has grown from an estimated 75 million in 2016 to 222 million.
What are the Major Highlights of the Report?
- The study indicates that as many as 78.2 million are out of school, and close to 120 million are in school, but not achieving minimum proficiency in math or reading. In fact, just one in ten crisis-impacted children attending primary or secondary education are actually achieving these proficiency standards.
- The analysis indicates that 84% of the out-of-school crisis-impacted children are living in areas with protracted crises. The vast majority of these are in countries specifically targeted through ECW’s ground-breaking multi-year investments, including Afghanistan, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Mali, Nigeria, Pakistan, Somalia, South Sudan, Sudan and Yemen.
- The war in Ukraine is pushing even more children out of school, with recent estimates indicating the conflict has impacted 5.7 million school-aged children.
- Around 119.6 million children living in crisis-prone areas attended school but did not achieve minimum proficiency in mathematics or reading.
- #222 Million Dreams: To respond to this pressing global education crisis, ECW and strategic partners launched the #222MillionDreams resource mobilization campaign in Geneva.
- The campaign calls on donors, the private sector, philanthropic foundations and high-net-worth individuals to urgently mobilize more resources to scale up ECW’s investments, which are already delivering quality education to over 5 million children across more than 40 crisis-affected countries.
What is Education Cannot Wait (ECW)?
- About:
- It is the United Nations global, billion-dollar fund for education in emergencies and protracted crises.
- It is administered under UNICEF’s financial, human resources, and administrative rules and regulations; operations are run by the Fund’s own independent governance structure.
- Mission:
- ECW works to generate greater shared political, operational and financial commitment to meet the educational needs of millions of children and youth affected by crises, with a focus on more agile, connected and faster response that spans the humanitarian-development continuum to lay the ground for sustainable education systems.
Geography
Residual Flood Damage under Intensive Adaptation
For Prelims: Flood Management, NDMA
For Mains: Residual Flood Damage under Intensive Adaptation, Climate Change
Why in News?
According to a new Study published, Residual Flood Damage under Intensive Adaptation, the risk of river flooding is expected to increase with climate change and socioeconomic development.
- Residual flood damage under intensive adaptation tries to estimate the global cost of employing adaptive flood measures depending on local economic scenarios and cost adaptation measures by trying to quantify the cost of Residual Flood Damage (RFD).
What is RFD?
- RFD refers to the unavoidable increases in flood damage even under an adaptation strategy based on feasible adaptation costs.
- Adaptation strategy in the context of floods includes infrastructural measures employed to mitigate flood risks.
- RFD is the part of total Expected Annual Damage (EAD).
- The expected annual damage is the average of flood damages calculated over a number of events.
- It is calculated by subtracted past EAD (1970-2000) and future EAD estimates (set to 1000 years).
What are the Findings?
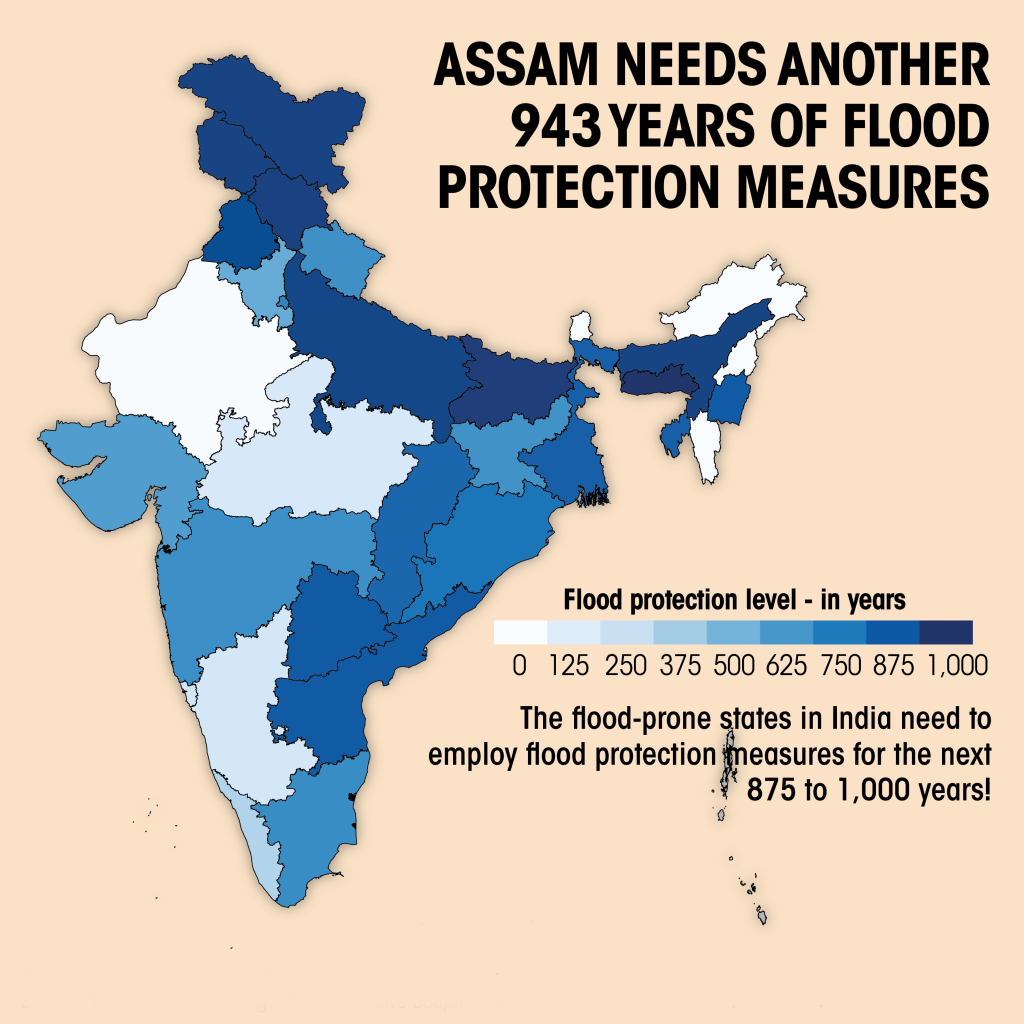
- Assam will need 943 years of flood protection measures to prevent a crisis like the one it is witnessing if its pace of preparedness and climate adaptation doesn’t increase.
- In 2022, the flooding started as early as May, with 62% above average rainfall from March-May — a 10-year high.
- Currently, 33 of Assam’s 35 districts have been affected due to flooding along the Brahmaputra basin. Over 4.2 million people have been affected by floods this year, while over 100,000 hectares of cropland have been damaged as of June 20.
- Other flood-prone states like Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Meghalaya will need 966, 935 & 996 years respectively.
- In India, riverine floods — considered one of the major natural disasters — have become synonymous with economic losses. The total flood-related losses in the country were estimated to be over Rs 37 lakh crores from 1953-2017, according to the Central Water Commission.
- RFD in South Asia is estimated to be around USD 4 million and adaptive costs around USD 3 million.
- RFD (as a part of the gross domestic product) remained high in eastern China, northern parts of India and the central regions of the African continent.
- RFD can be reduced with shorter construction periods or lower adaptation costs, implying the need for immediate and appropriate adaptation actions, including enhanced financial support for high-risk regions.
What is Flood?
- About:
- It is an overflowing of water onto land that is normally dry. Floods can happen during heavy rains, when ocean waves come on shore, when snow melts quickly, or when dams or levees break.
- Damaging flooding may happen with only a few inches of water, or it may cover a house to the rooftop. Floods can occur within minutes or over a long period, and may last days, weeks, or longer. Floods are the most common and widespread of all weather-related natural disasters.
- Flash floods are the most dangerous kind of floods, because they combine the destructive power of a flood with incredible speed.
- Flash floods occur when heavy rainfall exceeds the ability of the ground to absorb it.
- They also occur when water fills normally dry creeks or streams or enough water accumulates for streams to overtop their banks, causing rapid rises of water in a short amount of time.
- They can happen within minutes of the causative rainfall, limiting the time available to warn and protect the public.
- Measures:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. La Nina is suspected to have caused recent floods in Australia. How is La Nina different from El Nino? (2011)
- La Nina is characterized by a usually cold ocean temperature in equatorial Indian Ocean whereas El Nino is characterized by unusually warm ocean temperature in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- El Nino has adverse effect on south-west monsoon of India but La Nina has no effect on monsoon climate.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- Normally, when the tropical eastern South Pacific Ocean experiences high pressure, the tropical eastern Indian Ocean experiences low pressure. But in certain years, there is a reversal in the pressure conditions and the eastern Pacific has lower pressure in comparison to the eastern Indian Ocean. This periodic change in pressure conditions is known as the Southern Oscillation (SO).
- A feature connected with the SO is the El Nino phenomenon in which a warm ocean current flows past the Peruvian Coast, in place of the cold Peruvian current, every 2 to 5 years. The presence of El Nino leads to an increase in sea-surface temperatures and weakening of the trade winds in the region. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The result of El Nino is:
- Rain on the western coast of South America
- Drought in Northern Australia, Indonesia and India
- Storms and Hurricanes in the East Pacific
- Coral bleaching
- The La-Nina episode represents periods of below average sea-surface temperature across the east central Equatorial Pacific.
- Global climate La Nina impacts tend to be opposite those of El Nino impacts. In the tropics, ocean temperature variations in La Nina also tend to be opposite those of El Nino. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- During La Nina, things are same as in a “normal” year, but the two things – Cold Peru Current and Trade Winds become even “stronger”. This results into too many fishes on the Peruvian coast and too much rain in Indonesia and Australia.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Important Facts For Prelims
Vertical Launch Short Range Surface to Air Missile
Why in News?
Recently, Vertical Launch Short Range Surface to Air Missile (VL-SRSAM) was successfully flight-tested by Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Indian Navy from an Indian Naval Ship at Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur off the coast of Odisha.
Key Points
- About:
- VL-SRSAM has been designed and developed jointly by three facilities of the Defence Research and Development Organisation for deployment of Indian Naval warships.
- The missile has the capability of neutralizing various aerial threats at close ranges including sea-skimming targets.
- Sea skimming is a technique many anti-ship missiles and some fighter or strike aircraft use to avoid radar and infrared detection.
- Design:
- The missile has been designed to strike high-speed airborne targets at the range of 40 to 50 km and at an altitude of around 15 km.
- Its design is based on Astra missile which is a Beyond Visual Range Air to Air missile.
- Astra ("weapon") is India's first air-to-air all weather beyond-visual-range active radar homing air-to-air missile, developed by the Defence Research and Development Organization.
- A Beyond-Visual-Range missile (BVR) is an air-to-air missile that is capable of engaging at ranges of 20 nautical miles or beyond.
- Features:
- Cruciform wings: They are four small wings arranged like a cross on four sides and give the projective a stable aerodynamic posture.
- Thrust Vectoring: It is the ability to change the direction of the thrust from its engine, control the angular velocity and the attitude of the missile.
- Thrust is the force which moves an aircraft through the air.
- Canisterised system: The inside environment is controlled, thus making its transport and storage easier and improving the shelf life of weapons.
Naval Warfare
- It is a combat in and on the sea, the ocean, or any other battlespace involving a major body of water such as a large lake or wide river.
- Defence Mechanism:
- Chaffs:
- It is a countermeasure technology used worldwide to protect naval ships from enemy’s radar and Radio Frequency (RF) missile seekers.
- Missiles to counter Anti-Ship missiles:
- These systems have to have a swift detection mechanism and quick response to warships.
- Chaffs:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. What is “Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD)”, sometimes seen in the news? (2018)
(a) An Israeli radar system
(b) India’s indigenous anti-missile programme
(c) An American anti-missile system
(d) A defence collaboration between Japan and South Korea.
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Terminal High Altitude Area Defence (THAAD) is an American anti-missile system designed to intercept and destroy short and medium-range ballistic missiles during their “terminal” phase of flight when they are falling towards the target.
- They have the ability to intercept missiles inside and outside the atmosphere.
- It is interoperable with other ballistic missile defence systems and is highly mobile and deployable worldwide.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q. From which one of the following did India buy the Barak anti-missile defence systems? (2008)
(a) Israel
(b) France
(c) Russia
(d) USA
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Barak-8 is a supersonic, vertically-launched short range air defence system, with an operational range of about 5 to 100 km.
- It was designed and developed by Israel to protect its economic zones and strategic facilities from various threats.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer
Important Facts For Prelims
Vanijya Bhawan and Niryat Portal
Why in News?
Prime Minister has launched Vanijya Bhawan and NIRYAT (National Import-Export Record for Yearly Analysis of Trade) Portal.
What is Vanijya Bhawan?
- Vanijya Bhawan is the new premises of the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Vanijya Bhawan, which is constructed near the India Gate (New Delhi) will be used by the two departments under the Ministry i.e. Department of Commerce and the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
What is NIRYAT Portal?
- NIRYAT (National Import-Export Record for Yearly Analysis of Trade) is developed as a one-stop platform for the stakeholders to get all the necessary information that is related to India’s foreign trade.
- India exported a total of USD 670 billion- Rs. 50 lakh crores in 2021. Exports are vital to a country’s progress.