Sea Ice Loss and Climate Disruptions
For Prelims: Arctic Sea, Antarctic Sea, Ocean Temperature, Solar Radiation, Ocean Salinity, Ocean Circulation, Jhelum, Karewa, Gujjar-Bakarwal.
For Mains: Sea ice loss and its impact on ocean and climate, Impact of retreating glaciers on India.
Why in News?
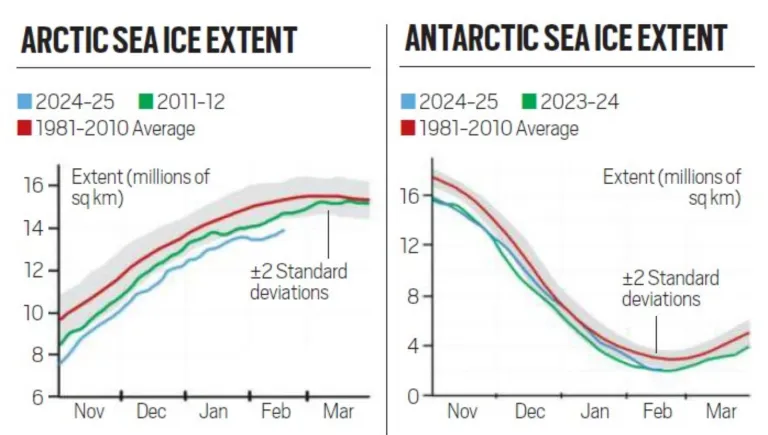
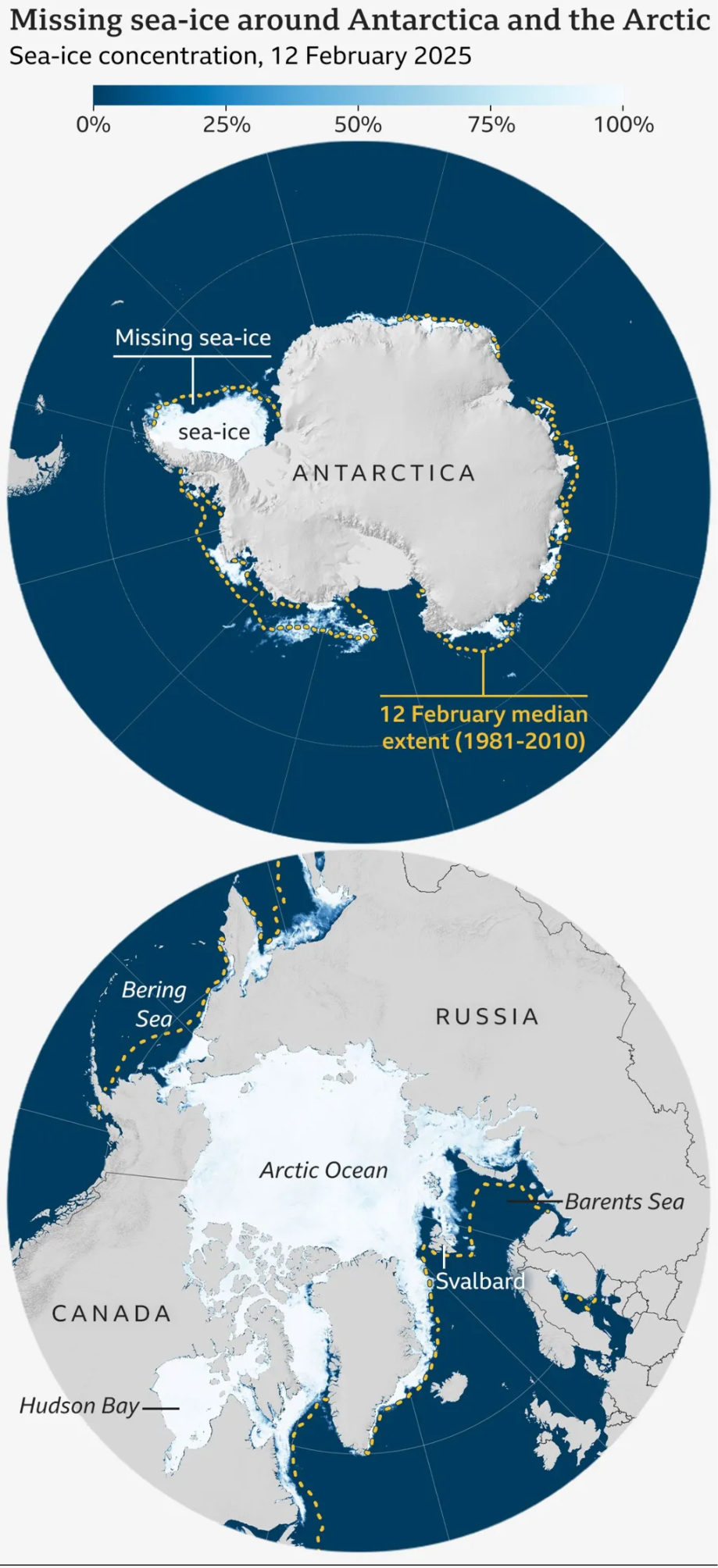
According to the US National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), global sea ice cover combining Arctic and Antarctic sea ice dropped to 15.76 million sq km in February 2025.
- According to NASA, between 1981 and 2010 the Arctic sea ice shrank by 12.2% per decade.
- In addition, Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) in India is adversely affected by retreating of Himalayan glaciers.
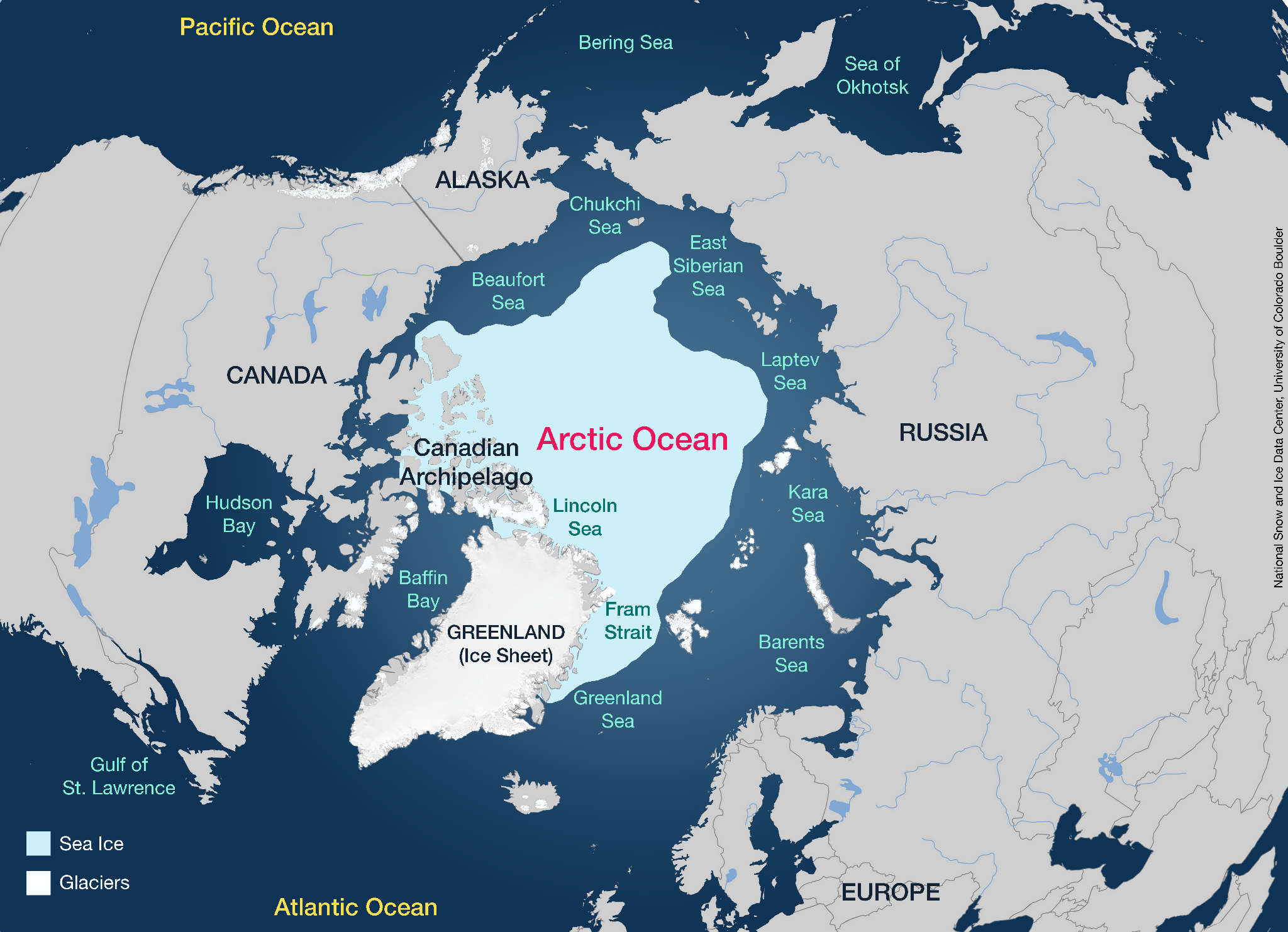
What is Sea Ice?
- About: Sea ice is free-floating polar ice that expands in winter, melts in summer, and partly persists year-round.
- It is found mainly in the Arctic Ocean and Antarctica Ocean.
- Features: Sea ice forms from frozen saltwater, unlike icebergs, glaciers, and ice sheets, which originate on land.
- As sea ice forms, most of the salt is expelled, making sea ice less salty than seawater.
- The remaining salt content gets trapped in tiny pockets, giving the ice a porous structure.
| Click Here to Read: What are Glaciers? |
What are the Reasons for Drop in Arctic and Antarctic Sea Ice Cover?
- Delayed Freezing: Unusually warm ocean temperatures slowed the cooling process, delaying ice formation. E.g., slow ice formation around the Hudson Bay (northeastern Canada).
- Marine Heatwaves (MHWs): Arctic MHWs and heated Gulf Streams carry excess heat toward the Arctic and intensify Arctic ice loss by melting sea ice.
- Ice-Breaking Winds: Storms in the Barents Sea and Bering Sea fragmented ice, making it more vulnerable to melting.
- Antarctic sea ice is particularly vulnerable to ice-breaking winds as it floats in the ocean that can be easily broken by winds, unlike landlocked Arctic ice. E.g., Colossus A23a is a massive Antarctic iceberg that has been floating in the Southern Ocean since 2020.
- Thinning Ice: Over the years, Arctic ice has become thinner and more fragile, making it more susceptible to breaking due to storms and temperature fluctuations.
- Higher air temperatures led to the melting of the edges of the Antarctic ice sheet (ice shelves) which extend over the ocean.
- Higher Air Temperatures: Regions like Svalbard, Norway, experienced above-normal temperatures, leading to additional sea ice loss.
- Increased air and water temperatures towards the end of the southern hemisphere summer accelerated ice melting in the Antarctic region.
What are the Consequences of the Drop in Arctic and Antarctic Sea Ice Cover?
- Increased Global Warming: Less sea ice cover means that more water is getting exposed to the Sun and more heat (solar radiation) absorption by water, leading to a further rise in temperature of water.
- Polar sea-ice has already lost around 14% of its natural cooling effect due to the decline in bright and reflective ice since the early-to-mid 1980s.
- Disruption of Global Ocean Circulation: Melting sea ice releases freshwater, reducing ocean salinity and surface water density.
- This slows ocean circulation, disrupting marine ecosystems and global climate patterns.
- Loss of Climate Regulation: Sea ice cools the planet by reducing evaporation and heat loss to the atmosphere by creating an insulating cap across the ocean surface. Less ice weakens this effect, speeding up climate change.
- Extreme Weather Events: Thinner ice and warmer temperatures may increase the frequency and intensity of storms.
How J&K is Impacted by Retreating of Himalayan Glaciers?
|
Formation of Ice Caps on Earth
- The research, published in Science Advances, challenges the assumption that Earth will naturally return to a cooler climate if emissions are halted.
- Historically, the planet has preferred warm, high-CO₂ conditions.
- The research has identified the following factors responsible for formation of icecaps on Earth.
- Low Volcanic CO₂ Emissions: Reduced greenhouse gases limited warming.
- Increased Carbon Storage: Forests absorbed more CO₂.
- Chemical Weathering: CO₂ reacted with rocks, further reducing atmospheric carbon.
- Geography: Widely dispersed continents and large mountain ranges increased rainfall, accelerating carbon removal and promoting cooling and glaciation.
Conclusion
The rapid decline in global sea ice is accelerating climate change, disrupting ocean circulation, and increasing extreme weather events. In India, particularly in Jammu and Kashmir, glacier melting is causing severe water shortages, agricultural losses, wetland shrinkage, and forced migration. Urgent climate action and sustainable policies are essential to mitigate these impacts.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Examine the consequences of glacial melting on India’s water security, agriculture, and livelihoods. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following statements is/are correct about the deposits of ‘methane hydrate’? (2019)
- Global warming might trigger the release of methane gas from these deposits.
- Large deposits of ‘methane hydrate’ are found in Arctic Tundra and under the sea floor.
- Methane in the atmosphere oxidizes to carbon dioxide after a decade or two.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Why is India taking keen interest in the resources of the Arctic region? (2018)
Q. How does the cryosphere affect global climate? (2017)
Stagnation of India’s Patent Growth
For Prelims: Intellectual Property Rights, World Intellectual Property Organization, Venture capital
For Mains: Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) in India, Digital Patent Filing and AI in IPR Protection
Why in News?
India's Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) ecosystem has grown significantly over the past decade. However, patent applications stagnated in 2024, with very few approvals, raising concerns that low private-sector Research and Development (R&D) investment is limiting innovation.
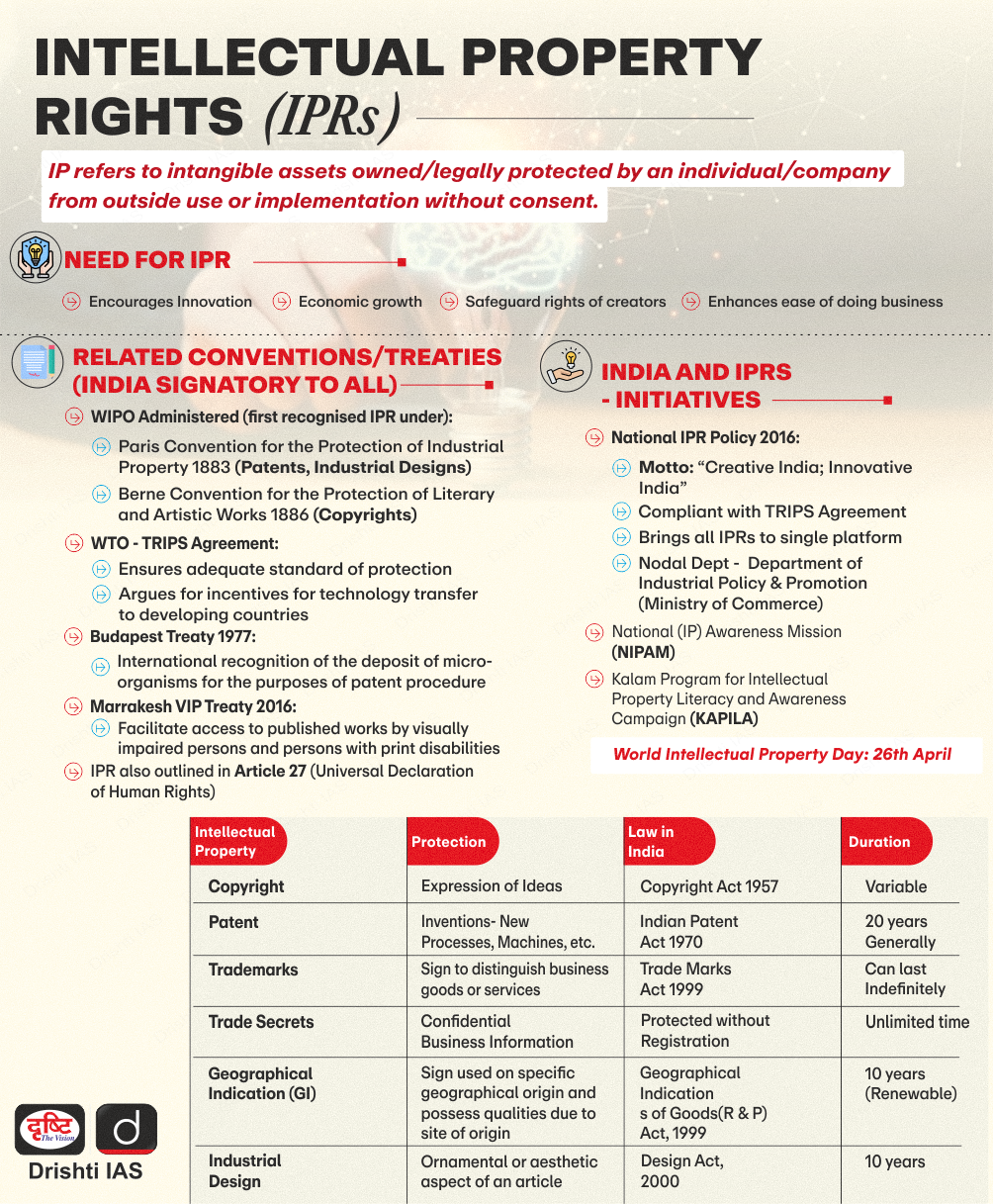
What are the Key Trends in India's IPR Ecosystem?
- Increase in Patents: India now ranks 6th globally in terms of patent applications, with 64,480 patent filings in 2023.
- Patent applications grew from 42,951 (2013-14) to 92,168 (2023-24), with grants rising due to backlog clearance.
- In 2013-14, 25.5% of patent applications were from Indian residents, which increased to 56% in 2023-24.
- Earlier, patent filings were dominated by foreign multinational corporations, but Indian applicants are now filing more patents.
- However, in 2024-25, 78,264 patent applications and 26,083 grants indicate a lower approval rate.
- Trademarks: According to the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) 2024 report, India ranked 4th globally in trademark filings after the US, China, and Russia.
- Trademark applications in India have indeed grown significantly from around 2 lakh in 2016-17 to approximately 4.8 lakh in 2023-24. However, the rate of increase has slowed.
- Industrial Design: 36.4% increase in industrial design applications, driven by textiles, tools & machines, and health sectors.
- Manpower: The patent office workforce increased from 272 in 2014-15 to 956 currently, but still lags behind China (13,704) and the US (8,132).
What are the Challenges in India’s Patent Ecosystem?
- Low R&D Investment: India’s R&D spending is just 0.65% of GDP (compared to the US (3.6%), China (2.4%), Singapore (2.2%)).
- The private sector contributes only 36% to R&D, whereas it accounts for 79% in the US and 77% in China.
- Many Indian companies operate at a global scale but invest little in R&D, limiting patent filings.
- High Dependence on Foreign Patents: Despite rising domestic filings, foreign entities dominate Patent approvals (74.46% in 2022), far exceeding China’s 12.87%.
- India remains reliant on imported technology, leading to a trade deficit and reduced self-reliance in innovation.
- Manpower Shortage: Patent examination capacity is limited due to a lack of skilled examiners. Fewer examiners lead to long processing delays and lower patent approval rates.
- On average, it takes about 58 months to grant a patent in India, compared to 21 months in the US.
- Quality of Patent Applications: Domestic patent filings lag in approvals due to poor-quality applications, weak research, plagiarized content, and lack of resources in startups.
- Weak IP Enforcement: Patent infringement cases are rising in India, but weak enforcement and judicial backlogs hinder effective protection.
- Indian firms often lack the expertise to navigate the global IP system effectively. In the digital age, easy copying, anonymous infringers, and cross-border piracy further complicate IP enforcement.
Way Froward
- Ease of Patent Filing: Streamlining digital patent processing with AI-driven IP infringement detection systems can increase patent filling.
- Tax incentives for corporate R&D spending and increased venture capital funding can drive deep-tech advancements and boost patent filings.
- Enforcement and Legal Framework: Set up specialized IP courts to resolve patent disputes faster. Increase penalties for copyright infringement to deter violations under Copyright Act 1957.
- Global Partnerships for Innovation: Participate in global patent treaties like the Riyadh Design Law Treaty to simplify cross-border filings and attract foreign investment in strengthening India's IP ecosystem.
- IP Awareness: Integrate IP education into curricula and conduct awareness programs in universities and businesses.
- Encourage joint R&D projects with international institutions like WIPO to enhance the quality and quantity of domestic patent filings.
|
Drishti Mains Question: India has shown remarkable growth in IP filings, yet challenges persist. Critically analyze the key factors affecting India’s IPR ecosystem. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- According to the Indian Patents Act, a biological process to create a seed can be patented in India.
- In India, there is no Intellectual Property Appellate Board.
- Plant varieties are not eligible to be patented in India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q. With reference to the ‘National Intellectual Property Rights Policy’, consider the following statements:(2017)
- It reiterates India’s commitment to the Doha Development Agenda and the TRIPS Agreement.
- Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion is the nodal agency for regulating intellectual property rights in India.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. In a globalized world, Intellectual Property Rights assume significance and are a source of litigation. Broadly distinguish between the terms—Copyrights, Patents and Trade Secrets. (2014)
NEP 2020 and Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan
For Prelims: Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan, National Education Policy (NEP 2020), PM SHRI, Right to Education Act, 2009, PARAKH, NISHTHA, PM e-VIDYA, DIKSHA, Vidya Samiksha Kendra, SDG, Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
For Mains: Key features of Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan and the National Education Policy (NEP 2020) and federal issues arising from their implementation.
Why in News?
The Union Government has withheld Tamil Nadu’s central share of Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan funds for opposing the National Education Policy (NEP 2020).
Why Tamil Nadu Opposes NEP 2020?
- Language Policy Dispute: NEP 2020 mandates a three-language policy (Tamil, English, and a regional language), which Tamil Nadu views as an imposition of the center's policy.
- Tamil Nadu follows a two-language formula (Tamil and English) since 1968.
- Undermining State Autonomy: Tamil Nadu sees the Centre’s push for uniform NEP implementation as an infringement on its autonomy, weakening cooperative federalism.
- Education is on the Concurrent List, requiring flexibility and state-level adaptability.
- Tamil Nadu is drafting its own State Education Policy to suit its socio-linguistic and economic context.
- Call for a Pragmatic Approach: Tamil Nadu argues that central schemes like Samagra Shiksha and PM SHRI should be delinked from NEP 2020.
- Funding should be based on performance indicators rather than policy compliance.
What is the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020?
- About: NEP 2020 replaced the 34-year-old NEP of 1986 and aimed to bridge gaps in quality, equity, and access to education at all levels.
- Based on the recommendations of Dr K Kasturirangan committee, it prioritizes foundational literacy, a holistic curriculum, multilingual learning, and integration of vocational and academic pathways.
- Key Provisions:
- Structural Reforms: NEP 2020 replaced the 10+2 system with a 5+3+3+4 structure, aligning education with the developmental needs of children aged 3 to 18 years.
|
Stage |
Duration |
Ages (Grades Covered) |
Key Features |
|
Foundational Stage |
5 years |
Ages 3-8 (Preschool & Grades 1-2) |
Play-based learning |
|
Preparatory Stage |
3 years |
Grades 3-5 |
Introduction of formal learning methodologies |
|
Middle Stage |
3 years |
Grades 6-8 |
Experiential and multidisciplinary learning |
|
Secondary Stage |
4 years |
Grades 9-12 |
Flexibility in subject choices |
- Experiential Learning: NEP 2020 emphasizes experiential learning through internships, field visits, and real-world projects to bridge theory and practice.
- NEP promotes technology integration through digital literacy, online platforms, and tech-enabled classrooms to enhance learning.
- Teacher Training: NEP 2020 emphasizes continuous professional development to equip teachers for evolving educational needs.
- Key Initiatives:
- PM SHRI scheme: It aims to develop 14,500 ideal schools to serve as role models.
- NIPUN Bharat Mission: It was launched to ensure foundational literacy and numeracy by Grade 2.
- PARAKH: PARAKH (Performance Assessment, Review, and Analysis of Knowledge for Holistic Development) have been introduced to monitor learning outcomes.
- NISHTHA: NISHTHA (National Initiative for School Heads' and Teachers' Holistic Advancement) teacher training program launched to equip educators with skills aligned with NEP’s transformative goals.
- Major Achievements:
- Foundational Stage Curriculum: The National Curriculum Framework for the Foundational Stage (NCF-FS) introduced the Jadui Pitara kit to promote play-based learning for children aged 3-8.
- Regional Language Inclusion: AICTE-approved engineering and medical courses are now available in regional languages, with JEE and NEET conducted in 13 languages for better accessibility.
- Four-Year Undergraduate Program (FYUP): Over 105 universities have adopted the FYUP, offering multiple exit options and greater flexibility in higher education.
- Global IITs: IIT-Madras opened a campus in Zanzibar (Tanzania) and IIT-Delhi is planning a campus in Abu Dhabi (UAE).
- Digital Learning: PM e-VIDYA and DIKSHA platforms promote digital learning for universal access, while Vidya Samiksha Kendra provides real-time data on educational progress.
- Challenges:
- Integration of the 5+3+3+4 Structure: Aligning state curricula and training teachers for new methods remains a challenge, with foundational textbooks for some grades only recently prepared.
- Pending Legislation: NEP 2020 proposes merging UGC, AICTE, and NCTE into a single higher education regulator, but the legislative framework is still pending.
- Lack of Uniform Monitoring: Although evaluation efforts are ongoing, there are no standardized assessment metrics across states to measure NEP's impact effectively.
What is Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan?
- About: Introduced in the Union Budget 2018-19, Samagra Shiksha is a comprehensive program covering education from pre-nursery to Class 12 to ensure equitable learning outcomes.
- Key Features:
- Integration of Schemes: It subsumes three earlier schemes:
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA): Focused on universal primary education.
- Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA): Aimed at secondary education.
- Teacher Education (TE): Focused on training teachers.
- Sector-Wide Development Approach: It streamlines implementation across all levels (state, district, and sub-district) instead of fragmented project-based objectives.
- Alignment with SDGs: Ensures free, equitable, and quality education (SDG 4.1) while eliminating gender disparities and ensuring access for vulnerable groups (SDG 4.5).
- Implementation: It is a centrally sponsored scheme (CSS) implemented through a single State Implementation Society (SIS) at the State/UT level.
- SIS is a state-registered body implementing CSS and development programs.
|
Click Here to Read: |
Conclusion
The withholding of Samagra Shiksha funds highlights the tension between the Centre and Tamil Nadu over NEP 2020, reflecting broader issues of federalism, linguistic autonomy, and education policy implementation. Ensuring educational progress requires a collaborative approach that respects state-specific needs while maintaining national development goals.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What are the key features of National Education Policy (NEP 2020). Critically analyze the impact of NEP 2020 on federalism. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. National Education Policy 2020 is in conformity with the Sustainable Development Goal-4 (2030). It intends to restructure and reorient the education system in India. Critically examine the statement. (2020)
Solar Coronal Holes
The study has revealed that Indian astronomers have accurately estimated the thermal and magnetic field structures of solar coronal holes (SCH).
What are Solar Coronal Holes?
- About: Coronal Holes are large, dark regions on the Sun that are cooler and less dense than the surrounding plasma. It was first discovered in the 1970s by X-ray satellites.
- Occurrence:
- They occur in areas where the Sun's magnetic field is open to interplanetary space, allowing high-speed solar wind (geomagnetic storm) to escape.
- Open magnetic field lines are magnetic field lines that do not form closed loops but extend outward into space without returning to their source.
- Coronal holes are most prevalent during the declining phase of a solar cycle and are typically found near the Sun's poles.
- They occur in areas where the Sun's magnetic field is open to interplanetary space, allowing high-speed solar wind (geomagnetic storm) to escape.
- Properties of Coronal Holes:
- Uniform Temperature: Coronal holes maintain a consistent temperature across latitudes, indicating a deep origin within the Sun.
- Magnetic Field Variation: Magnetic field strength increases from the solar equator to the poles, likely influenced by Alfvén wave disturbances.
- Alfvén wave disturbances are low-frequency oscillations in the magnetic field and ions of a plasma that can cause fluctuations in the solar wind and geospace.
- Impacts of SCH:
- Impact on Space Weather: The high-speed solar wind from coronal holes interacts with Earth’s magnetic field, causing geomagnetic storms that can disrupt satellites, GPS, and communication networks.
- Effect on Indian Monsoon: The study suggests that, along with sunspots, the radiative effects of coronal holes influence Indian monsoon rainfall variability.
- Ionospheric Disturbances: Coronal hole activity affects Earth's ionosphere, impacting radio wave propagation and telecommunication systems.
Sunspots
- Sunspots are dark areas on the sun's surface that are caused by strong magnetic fields. They are cooler than the surrounding areas of the sun, making them appear darker on the surface of the Sun (photosphere).
- Coronal holes and sunspots differ in location, magnetic field, and visibility.
| Read More: What is a Geomagnetic Storm? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question:
Q. If a major solar storm (solar flare) reaches the Earth, which of the following are the possible effects on the Earth? (2022)
- GPS and navigation systems could fail.
- Tsunamis could occur at equatorial regions.
- Power grids could be damaged.
- Intense auroras could occur over much of the Earth.
- Forest fires could take place over much of the planet.
- Orbits of the satellites could be disturbed.
- Shortwave radio communication of the aircraft flying over polar regions could be interrupted.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5 only
(b) 2, 3, 5, 6 and 7 only
(c) 1, 3, 4, 6 and 7 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7
Ans: (c)
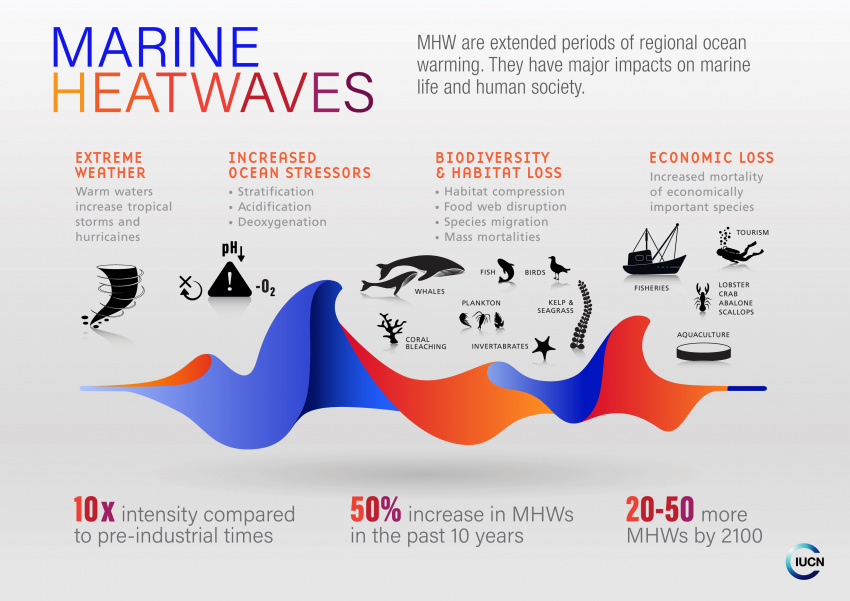
Impact of Marine Heatwaves on Arctic Wildlife
Why in News?
A study warns that Arctic marine heatwaves (MHWs) are causing higher mortality, and lower reproductive rates risks in marine mammals.
What are the Key Findings of the Study?
- Increased Mortality & Reproductive Decline: Arctic and Subarctic marine mammals like whales, seals, and walruses face higher death rates and reduced calf production due to MHWs.
- Rising temperatures lead to toxic algal blooms (rapid increase in algae in a body of water), spread of diseases (e.g., avian influenza in polar bears), and prey migration, affecting food availability.
- Distribution & Human-Wildlife Conflict: Shifts in prey distribution compel species to migrate or risk starvation, increasing their chances of becoming entangled in fishing gear.
What are the Key Facts About Marine Heatwaves?
- About: MHWs are extreme oceanic weather events characterized by a sudden rise in sea surface temperature (3-4°C above average) for at least five days, potentially lasting weeks or longer.
- These events can cover small coastal areas or extend across entire ocean basins.
- Key Causes of MHWs: Climate change, driven by anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions, has increased global ocean temperatures by 1.5°C over the past century.
- Disruptions in oceanic currents, such as El Niño, amplify heat retention, while Arctic ice loss exposes more ocean surface to solar radiation, accelerating warming.
- Unusual weather patterns, shifts in atmospheric circulation, and storm activities further trigger MHWs.
- Impact:
- Ocean Life: MHWs cause mass fish deaths and habitat destruction. Higher ocean temperatures lead to widespread coral bleaching (e.g., 2005 Caribbean bleaching event).
- Rising temperatures wipe out kelp forests, promote invasive species, and alter wildlife migration.
- Extreme Weather Events: MHWs intensify storms, leading to stronger hurricanes, cyclones, and severe flooding.
- Humans: They disrupt fisheries and global seafood supply, threatening the livelihoods of coastal communities that rely on coral reefs.
- Economic losses mount as MHWs force species migration, impacting tourism and fishing industries.
- Ocean Life: MHWs cause mass fish deaths and habitat destruction. Higher ocean temperatures lead to widespread coral bleaching (e.g., 2005 Caribbean bleaching event).
- Projected Trends: MHWs are expected to occur 50 times more often by 2100 compared to pre-industrial times.
- The Arctic and tropical regions are most vulnerable due to their existing temperature extremes.
- Mitigation and Adaption to MHWs: Stricter Paris Agreement policies are needed to limit ocean warming.
- Early warning systems can help fisheries and coastal communities prepare for MHWs.
- Expanding Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) and protecting key habitats like kelp forests, seagrass meadows, and coral reefs will safeguard marine life.
What are the Key Facts About the Arctic Region?Click here to Read: Arctic Region |
|
Drishti Mains Question: What are Marine Heatwaves, and how do they impact marine biodiversity and climate stability? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to Ocean Mean Temperature (OMT), which of the following statements is/are correct? (2020)
- OMT is measured up to a depth of 26ºC isotherm which is 129 meters in the south-western Indian Ocean during January-March.
- OMT collected during January-March can be used in assessing whether the amount of rainfall in monsoon will be less or more than a certain long term mean.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
SC Strikes Down NMC Rule
In Anmol vs Union of India Case, 2024, the Supreme Court (SC) ruled National Medical Commission’s (NMC) guideline requiring candidates with disabilities to have “both hands intact with intact sensations and sufficient strength” for MBBS admission as arbitrary, discriminatory, and unconstitutional.
- This requirement was held to be antithetical to the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Act, 2016, Article 41 of the Constitution and United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD).
- Article 41 secures the right to work, to education, and to public assistance in cases of unemployment, old age, sickness and disablement.
- The SC ruled that the functional assessment of a candidate’s abilities should take precedence over rigid eligibility criteria.
- The SC held that NMC’s Assessment Board failed to meet the standards set in two landmark judgments:
- Omkar Ramchandra Gond Case, 2024: It ruled that mere disability quantification is insufficient, functional ability must be assessed.
- Om Rathod vs Director General of Health Services Case, 2024: It emphasized opportunities for PwD candidates, prioritizing functional competency over physical attributes.
- The SC urged NMC to revise disability admission guidelines in line with the Constitution, RPwD Act, UNCRPD, and SC judgments.
| Read More: Enhancing Accessibility for Persons with Disabilities |
Bharat Tex 2025
The Prime Minister addressed the Bharat Tex 2025 event, which is a global platform for engagement, collaboration, and policy discussions in the textile sector in which over 120 countries participated.
India’s Textile Sector:
- India’s textile industry contributes 2.3% to GDP, 12% to exports, 13% to industrial production and employs 45 million, second only to agriculture.
- India is the 6th largest textile exporter globally (after China, EU, Vietnam, Bangladesh, and Turkey) and world’s 2nd largest producer of textiles and garments.
- India's textile exports increased 7% from 2023 to 2024, reaching Rs 3 lakh crore, with a target of Rs 9 lakh crore by 2030.
Challenges in Textile Sector:
- India's textile sector faces high cotton dependence (60%), competition from Bangladesh & Vietnam, logistics inefficiencies (costs at 13-14% of GDP compared to China’s 8%) and environmental concerns from fast fashion.
- Government Initiatives for Textile Sector:
- Mega Integrated Textile Region and Apparel (MITRA) Parks
- Mission for Cotton Productivity: To facilitate improvements in productivity and sustainability of cotton farming.
- GI tagging for Handloom Products: E.g. Uppada Jamdani Sarees, Muga Silk of Assam, Kashmir Pashmina etc.
- Samarth Scheme
| Read More: India's Garment Export Sector |
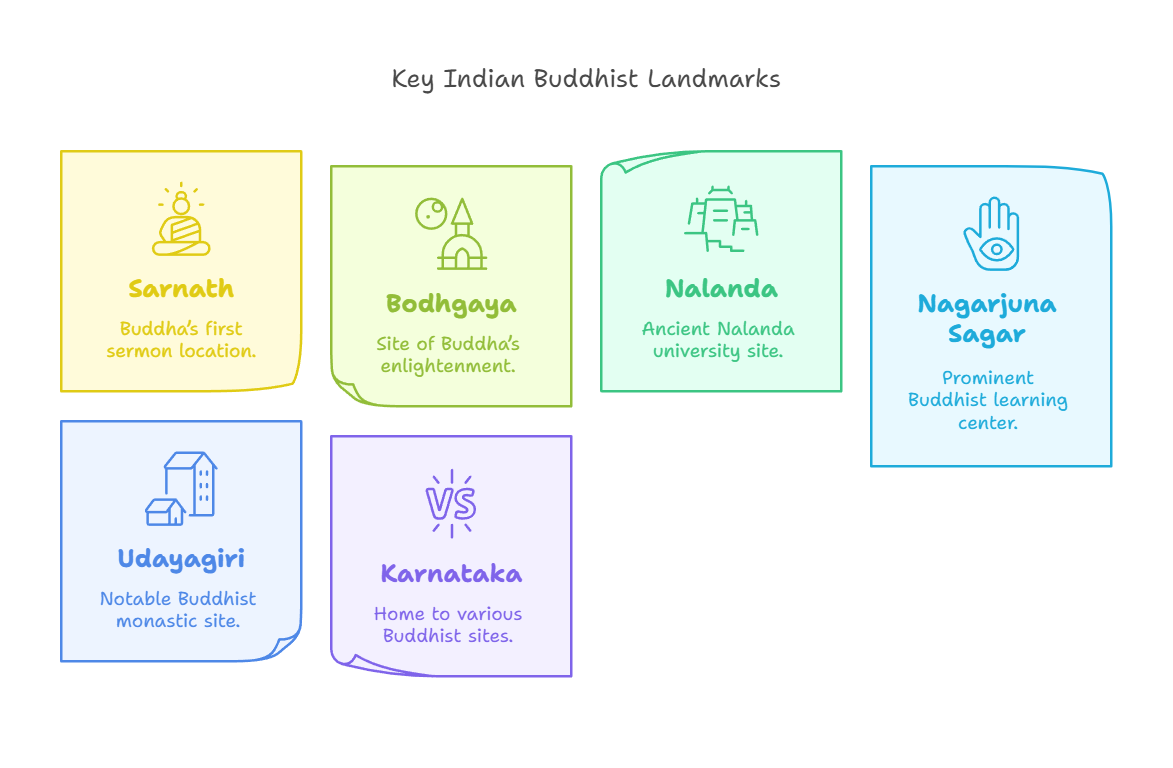
Trination Buddhist Motorcycle Expedition
The Heartfulness Lord Buddha Trination Tri-Services Motorcycle Expedition started in February 2025 in Lumbini (birthplace of Lord Buddha), Nepal.
- It is a historic initiative uniting Nepal, India, and Sri Lanka through their shared Buddhist heritage.
- Key Indian Buddhist landmarks on the route include:
- The expedition is organized with the International Buddhist Confederation (IBC), Land Port Authority of India (Ministry of Home Affairs) and Nalanda University, Rajgir.
- Key Buddhist sites in Sri Lanka include Anuradhapura, Polonnaruwa, Dambulla etc.
| Read More: Buddhism in India |
DBT’s North Eastern Programme
The Department of Biotechnology (DBT)’s North Eastern Programme is driving a biotechnology-led transformation in India’s North East Region (NER).
- DBT’s North Eastern Programme: Initiated in 2010-2011, the DBT has since allocated 10% of its annual budget to biotech programmes in NER, focusing on enhancing education, research, and bio-entrepreneurship.
- Enabled R&D projects, benefiting researchers and students, and 6 biotech hubs established across NER to support research and training.
- DBT introduced Biotechnology Labs in Senior Secondary Schools (BLiSS) to promote biotechnology education. Additionally, the Visiting Research Professorship (VRP) programme engages top scientists to drive advancements in biotechnology across NER institutions.
- DBT also supports farmers through initiatives like the DBT-North East Centre for Agricultural Biotechnology (DBT-NECAB).
- Major Achievements: The “Patkai” rice variety, developed by Assam Agricultural University, integrates blight resistance (protection against bacterial blight disease) from Improved Samba Mahsuri (rice variety).
- A Lateral Flow Assay (LFA) for rapid brucellosis (bacterial infection) detection in livestock was standardized, improving disease diagnostics.
- Additionally, the Pig Disease Diagnosis Expert System (PDDES), a mobile application, was developed to assist veterinarians and farmers in diagnosing and managing pig diseases.
| Read more: India's Biotech Revolution |
NOVA 1
Recent research suggests that genetics played a key role in the evolution of human speech, with scientists linking the NOVA1 (Neuro-Oncological Ventral Antigen 1) gene to the development of spoken language.
- NOVA1:
- NOVA1 is a gene that produces a protein found in most mammals, playing a key role in processing genetic information, brain development, and neuron activity.
- Modern humans have a unique variant of this gene, distinguishing it from those found in Neanderthals and Denisovans (ancient human species).
- NOVA 1 Role in Speech Evolution:
- Scientists in an experiment replaced the NOVA1 variant in mice with the human version using CRISPR gene-editing.
- The modified mice showed distinct vocalizations, with altered distress calls in infants and more complex social squeaks in males, indicating that the gene influenced communication.
- FOXP2:
- FOXP2 is also a gene linked to speech and language. It is found in both humans and Neanderthals, while NOVA1 is unique to Homo sapiens, making it more likely to explain human speech evolution.
| Read More: ecDNA Challenging Genetics Principles |