Indian Polity
Women’s Reservation Bill 2023
For Prelims: Parliament and State legislative Assemblies, Delhi Special Status, Reservation Provisions and Affirmative policies.
For Mains: Inter-relationship between reservation provisions for Lok Sabha and State Assemblies, Differences of Delhi Legislative Assembly with respect to other State Assemblies
Why In News?
Recently, the Lok Sabha (LS) and Rajya Sabha (RS), both passed Women's Reservation Bill 2023 (128th Constitutional Amendment Bill) or Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam.
- The bill reserves one-third of the seats in Lok Sabha, State legislative assemblies and the Delhi assembly. This will also apply to the seats reserved for SCs (Scheduled Castes) and STs (Scheduled Tribes) in Lok Sabha and State Legislatures.
What is the Background and Need for this Bill?
- Background:
- The discussion upon the reservation of women reservation bill is prevalent since the tenure of Former Prime Minister Shri Atal Bihari Vajpayee in 1996.
- As the then Government lacked a majority, the Bill could not have been approved.
- Earlier Attempts at Reserving Seats for Women:
- 1996: First Women Reservation Bill was introduced in the Parliament.
- 1998 – 2003: Government tabled the Bill on 4 occasions but failed.
- 2009: Government tables the bill amid protests.
- 2010: The Union Cabinet passes the Bill and RS passes it.
- 2014: The Bill was expected to be tabled in LS.
- Need:
- There are 82 women Member of Parliaments in LS (15.2%) and 31 women in RS(13%).
- While the number has increased significantly since the 1st Lok Sabha (5%) but is still far lower than in many countries.
- According to recent UN Women data, Rwanda (61%), Cuba (53%), Nicaragua (52%) are the top three countries in women representation. Bangladesh (21%) and Pakistan (20%) as well are ahead of India in case of female representation.
- There are 82 women Member of Parliaments in LS (15.2%) and 31 women in RS(13%).
What are the Key Features of the Bill?
- Reservation for Women in Lower House:
- The Bill provided for inserting Article 330A to the constitution, which borrows from the provisions of Article 330, which provides for reservation of seats to SCs/STs in the Lok Sabha.
- The Bill provided that reserved seats for women may be allotted by rotation to different constituencies in states or Union Territories.
- In the seats reserved for SCs/STs, the Bill sought to provide one-third of the seats to be reserved for women on rotational basis.
- The Bill provided for inserting Article 330A to the constitution, which borrows from the provisions of Article 330, which provides for reservation of seats to SCs/STs in the Lok Sabha.
- Reservation for Women in State Legislative Assemblies:
- The Bill introduces Article 332A, which mandates the reservation of seats for women in every state Legislative Assembly. Additionally, one-third of the seats reserved for SCs and STs must be allocated for women, and one-third of the total seats filled through direct elections to the Legislative Assemblies shall also be reserved for women.
- Reservation for Women in NCT of Delhi ( New clause in 239AA):
- Article 239AA to the constitution grants special status to the Union Territory of Delhi as national capital with regards to its administrative and legislative functioning.
- Article 239AA(2)(b) was amended by the bill accordingly to add that the laws framed by parliament shall apply to the National Capital territory of Delhi.
- Commencement of Reservation (New article - 334A):
- The reservation will be effective after the census conducted after the commencement of this Bill has been published. Based on the census, delimitation will be undertaken to reserve seats for women.
- The reservation will be provided for a period of 15 years. However, it shall continue till such date as determined by a law made by Parliament.
- Rotation of Seats:
- Seats reserved for women will be rotated after each delimitation, as determined by a law made by Parliament.
What are the Arguments Against the Bill?
- The Bill merely reads that it shall come into effect “after an exercise of delimitation is undertaken for this purpose after the relevant figures for the first Census taken after commencement of the Bill is undertaken. It doesn’t specify the cycle of elections from which women will get their due share.
- The current Bill does not provide women’s reservation in the Rajya Sabha and State Legislative Councils. The Rajya Sabha currently has lower representation of women than the Lok Sabha. Representation is an ideal that must be reflected in both the Lower and Upper Houses.
Note: - The Bill also borrowed from the provisions of Article 334 of the constitution which mandated the parliament to review the provisions of reservation after 70 years of the laws coming into existence. But in the case of the Women's reservation Bill, the Bill provided for the sunset clause of 15 years for the reservation provisions for the women to get reviewed by the parliament.
Legal Insights: Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam
Governance
National Higher Education Qualifications Framework
For Prelims: National Higher Education Qualifications Framework (NHEQF), National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, Academic Bank of Credits
For Mains: Initiatives related to Education, Regulation of Higher Education in India
Why in News?
University Grants Commission (UGC) has finalised the National Higher Education Qualifications Framework (NHEQF) to standardise qualifications and promote academic mobility.
- However, the implementation of this framework has raised concerns due to the presence of multiple guidelines, and frameworks, leading to confusion among stakeholders.
What is the National Higher Education Qualifications Framework ?
- Background:
- The movement to specify frameworks for higher education qualifications gained momentum across the world in the late 1990s, but India remained without an NHEQF.
- The idea was deliberated at the 60th meeting of the Central Advisory Board of Education in 2012, which assigned the responsibility to the UGC.
- About:
- The UGC has formulated the NHEQF with the aim of facilitating transparency and comparability of higher education qualifications at all levels. The framework has been issued for all educational institutes to adopt.
- The NHEQF is based on the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which envisages a new and forward-looking vision for India’s higher education system.
- The UGC has formulated the NHEQF with the aim of facilitating transparency and comparability of higher education qualifications at all levels. The framework has been issued for all educational institutes to adopt.
- Main Features:
- The framework categorizes education into eight levels, with the first four being part of the National School Education Qualification Framework (NSEQF) and the latter four pertaining to higher education qualifications (level 4.5 to level 8), each with a corresponding level descriptor that specifies the learning outcomes, the volume of learning, and the qualification type and title.
- The NHEQF provides the guidelines for the development and implementation of programmes of study, such as the programme learning outcomes, the course learning outcomes, the curriculum design, the pedagogy, the assessment, and the feedback.
- The credit framework document of the UGC mandates that each semester must have a minimum of 20 credits.
- This document suggests that one credit must comprise 15 hours of direct and 30 hours of indirect teaching. This means that students are required to study for a minimum of 900 hours per semester or close to 10 hours a day.
- Qualification types are broad and discipline-independent, including certificates, diplomas, bachelor's degrees, master's degrees, and PhDs. The NHEQF also includes qualifications from technical and vocational education and professional and technical education programs, excluding medical and legal education, all within one framework.
- It establishes the quality assurance mechanism such as the roles and responsibilities of the regulators, the higher education institutions, and the external agencies, as well as the processes and criteria for the approval, monitoring, and evaluation of programmes and qualifications.
What are the Issues with the NHEQF?
- Multiplicity of Guidelines:
- The UGC has prescribed two separate frameworks - the NHEQF and the National Credit Framework.
- Higher educational institutions are separately required to implement the Academic Bank of Credits as a mandated modality for recognizing, accepting, and transferring credits across courses and institutions.
- The presence of multiple regulations impinges on higher education qualifications.
- Ambiguity:
- The NHEQF provides exit requirements, but it doesn't clearly explain eligibility conditions and pathways through which a student can enter a program at a particular level.
- The absence of clear eligibility conditions and pathways may lead to confusion among students and institutions.
- The NHEQF provides exit requirements, but it doesn't clearly explain eligibility conditions and pathways through which a student can enter a program at a particular level.
- Lack of Consensus:
- Disciplines such as agriculture, law, medicine, and pharmacy may be under the jurisdiction of separate regulators, but they could have been included in the NHEQF through consensus across various regulatory bodies.
- The lack of consensus may lead to a fragmented higher education system and impede academic mobility.
- Degrees Within a Degree:
- The framework appears to create a hierarchy, allowing certain students who hold four-year undergraduate degrees with a minimum CGPA of 7.5 to be eligible for admission to PhD programmes.
- This approach may lead to elitism, as academic performance is often influenced by socioeconomic conditions.
- The framework appears to create a hierarchy, allowing certain students who hold four-year undergraduate degrees with a minimum CGPA of 7.5 to be eligible for admission to PhD programmes.
- Equating Postgraduate Diplomas and Undergraduate Programs:
- The NHEQF creates issues by equating postgraduate diplomas with four-year undergrad programs, causing confusion, especially for degrees like B.Ed (could be completed in one, two or four years is confusing).
- This framework's attempt to standardise qualifications on a scale of 4.5 to 10 complicates categorizing degrees that don't fit neatly, making it hard to determine their level.
- The NHEQF creates issues by equating postgraduate diplomas with four-year undergrad programs, causing confusion, especially for degrees like B.Ed (could be completed in one, two or four years is confusing).
- Influence of International Models:
- The NHEQF draws heavily from the European Bologna process and Dublin descriptors.
- The Bologna Process is a series of agreements between European countries to ensure the quality and comparability of higher education qualifications.
- The Dublin descriptors are a system of qualifications frameworks for evaluating students for bachelor's, master's, and doctoral degrees.
- India's higher education system is more complex and diverse than the European model. The NHEQF's development could benefit from broader consultations with Indian states.
- The NHEQF draws heavily from the European Bologna process and Dublin descriptors.
Way Forward
- Merge the NHEQF and the National Credit Framework into a single comprehensive framework to reduce confusion and streamline the qualification standards.
- Engage in wider and more intense consultations with the States to better reflect the diversity and complexity of India's higher education system.
- Develop learning outcomes tailored to the Indian higher education system, considering socio-cultural and socio-economic factors.
- Recognise that learning outcomes should not solely focus on employability but also on holistic personal and societal development.
- Review the eligibility criteria for admission to Ph.D. programs to prevent making the higher education system elitist.
- Establish a mechanism for ongoing monitoring and evaluation of the NHEQF to make necessary adjustments as the higher education landscape evolves.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following provisions of the Constitution does India have a bearing on Education? (2012)
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Rural and Urban Local Bodies
- Fifth Schedule
- Sixth Schedule
- Seventh Schedule
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 2 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans- (d)
Mains
Q1. National Education Policy 2020 is in conformity with the Sustainable Development Goal-4 (2030). It intends to restructure and reorient the education system in India. Critically examine the statement. (2020)
Q2. How have digital initiatives in India contributed to the functioning of the education system in the country? Elaborate on your answer. (2020)
Science & Technology
Gravitational Instabilities and Galaxy Evolution
For Prelims: Gravitational Instabilities and Galaxy Evolution, Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), Gravitational Instabilities, Spitzer Photometry and Accurate Rotation Curves (SPARC).
For Mains: Gravitational Instabilities and Galaxy Evolution.
Why in News?
Recently, a study has been conducted by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA), aiming to comprehend the relationship between Gravitational Instabilities and Galaxy Evolution.
Note:
- Gravitational Instabilities refer to a fundamental physical phenomenon that occurs in astrophysical systems, particularly in celestial bodies like galaxies, stars, and planetary systems.
- These instabilities are driven by the force of gravity and play a crucial role in shaping the structure, evolution, and dynamics of these cosmic entities.
What is the Methodology of the Study?
- Researchers compared star formation rates, gas fractions, and time scales for gravitational instability growth in nearby galaxies by analysing the stability levels of a sample of 175 galaxies from the Spitzer Photometry and Accurate Rotation Curves (SPARC) database.
- The study investigated how stability levels in galaxies are regulated, including the potential role of dark matter. It sought to determine whether stars and gas can self-regulate stability levels.
- They compared stability levels in nearby galaxies with those observed at high redshifts, which are considered precursors to galaxies in the local universe.
Redshift:
- Scientists measure cosmic distances via redshift, the extent to which light is shifted towards the red (lower energy) part of the electromagnetic spectrum during its long journey across the universe.
- The greater the distance, the higher the redshift.
What are the Key Highlights of the Study?
- Spiral Galaxies:
- Spiral galaxies, such as the Milky Way, exhibited specific characteristics.
- They had a higher median star formation rate, lower stability, reduced gas fraction, and a smaller time scale for the growth of gravitational instabilities.
- Spiral galaxies, such as the Milky Way, exhibited specific characteristics.
- Conversion of Gas to Stars:
- In spiral galaxies with lower stability, gravitational instabilities efficiently convert a significant amount of gas into stars.
- This process led to the depletion of gas reservoirs in these galaxies.
- In spiral galaxies with lower stability, gravitational instabilities efficiently convert a significant amount of gas into stars.
- Star Formation Mechanism:
- The galaxies with marginal stability levels undergo intense star formation activity for a short time scale, depleting gas reserves.
- In contrast, highly stable galaxies exhibit slower and gradual star formation processes over longer time scales, converting available gas into stars.
- Future & Significance:
- There is a need for future investigations into the impact of gravitational instabilities on the morphological evolution of galaxies across different redshifts.
- These insights are crucial for understanding fundamental processes in galaxy formation and evolution.
Biodiversity & Environment
Elephant Corridors
For Prelims: Elephant corridors, Project Elephant, World Elephant Day
For Mains: Significance of elephant corridors in wildlife conservation, Initiatives related to elephant conservation.
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian government identified 62 new elephant corridors, marking a significant milestone in the nation's commitment to wildlife conservation. This brings the total number of such corridors to 150, a remarkable increase from the 88 registered in 2010.
What are the Key Highlights About Elephant Corridors?
- About:
- Elephant corridors can be described as a strip of land that enables elephant movement between two or more friendly habitats.
- The corridors were reported by respective state governments and ground validation methods were used to verify them.
- State Wise Distribution:
- According to the report, West Bengal leads with 26 corridors, constituting 17% of the total.
- East central India contributes 35% (52 corridors), while the North East region has 32% (48 corridors).
- Southern India has 21% (32 corridors), and northern India has the lowest with 12% (18 corridors).
- Status of Corridor Use:
- Elephant corridor report released by the central government showed a 40% increase in elephant corridors across 15 elephant range states in India.
- 19% of corridors (29) show a decrease in use, and 10 require restoration due to impairment.
- Decreased use is attributed to habitat fragmentation and destruction.
- Reasons for Increase in Corridors:
- Elephants have expanded their ranges in the Vidarbha region of Maharashtra and southern Maharashtra bordering Karnataka.
- Elephant corridors have increased in these areas.
- Elephants have also been seen in increased numbers in Madhya Pradesh and northern Andhra Pradesh.
- Elephants have expanded their ranges in the Vidarbha region of Maharashtra and southern Maharashtra bordering Karnataka.
Elephants
- Elephants in India:
- Elephants are keystone species as well as the Natural Heritage Animal of India.
- India has the largest number of wild Asian Elephants. The elephant population in the country is estimated to be over 30,000.
- Karnataka has the highest elephant population in India.
- Conservation Status:
- Convention of the Migratory Species (CMS): Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of threatened species:
- Asian Elephant: Endangered
- African Forest Elephant: Critically Endangered
- African Savanna Elephant: Endangered
- Conservative Efforts:
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to Indian elephants, consider the following statements: (2020)
- The leader of an elephant group is a female.
- The maximum gestation period can be 22 months.
- An elephant can normally go on calving till the age of 40 years only.
- Among the States in India, the highest elephant population is in Kerala.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 3 and 4 only
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The elephant herd is led by the oldest and largest female member (known as the matriarch). This herd includes the daughters of the matriarch and their offspring. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Elephants have the longest-known gestational (pregnancy) period of all mammals, lasting up to 680 days (22 months). Hence, statement 2 is correct. Females between 14 - 45 years may give birth to calves approximately every four years with the mean interbirth intervals increasing to five years by age 52 and six years by age 60. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
- As per the Elephant Census (2017), Karnataka has the highest number of elephants (6,049), followed by Assam (5,719) and Kerala (3,054). Hence, statement 4 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Biodiversity & Environment
State of the Rhino 2023
For Prelims: Types of Rhinos,World Rhino Day, State of the Rhino Report
For Mains: Conservation Efforts for Wildlife
Why in News?
Recently, the International Rhino Foundation (IRF) published the report, State of the Rhino, 2023 which documents current population estimates and trends for the five surviving rhino species in Africa and Asia.
- Every year, World Rhino Day is observed on 22th September to spread awareness for all five species of rhino and work being done to save them.
- It was first announced by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) - South Africa in 2010.
What are the Key Findings of the Report ?
- Major Threats:
- Poaching, Habitat Loss: Poaching still threatens all five rhino species and has increased in several regions that had not previously been targeted.
- South Africa continues to battle devastating poaching losses of its white rhinos.
- Black rhino populations are increasing despite constant poaching pressure.
- Climate Change:
- In Africa, climate change-induced drought is causing myriad detrimental impacts.
- In Asia dramatically increased precipitation and longer monsoon periods could cause more direct deaths of rhinos and humans alike.
- Changing weather conditions and landscapes can also trigger an increase in invasive plant species, crowding out or overtaking native rhino food plants and causing general habitat degradation.
- Poaching, Habitat Loss: Poaching still threatens all five rhino species and has increased in several regions that had not previously been targeted.
- Status of Rhino:
- Javan Rhinos:The status and whereabouts of 12 of the approximately 76 remaining Javan rhinos is unknown.
- Sumatran Rhinos: Signs of Sumatran rhinos are increasingly hard to find, creating more uncertainty about their population in the wild.
- White Rhinos: 2,000 white rhinos from “World’s Largest Rhino Farm” will now be rewilded throughout Africa.
- Bright Spots:
- Greater one-horned rhinos in India and Nepal continue to thrive due to strong protection .
- Black rhinos in Africa are rebounding in the past few decades at a strong growth rate despite still significant poaching losses.
- With the right interventions, all five rhino species can rebound and thrive in our ever changing world.
- Recommendations:
- Implement a holistic strategy to safeguard rhinos by addressing poaching, habitat protection, community involvement, capacity building, demand reduction, advocacy, and wildlife trafficking disruption.
What are the Conservation Efforts by India ?
- Translocation: Rhino translocations to Manas National Park set for the beginning of 2023 were rescheduled for 2024 while security measures were reinforced after a poached rhino was discovered in January.
- Rhino Corridor: In 2022, the Assam government finalized the addition of approximately 200 sq km to Orang National Park in north-central Assam, more than doubling the size of this protected area and key rhino habitat.
- With this added land, Orang National Park is now connected to Burhachapori Wildlife Sanctuary in the east, completing the creation of a linked corridor between all the protected areas in Assam that hold rhinos: Manas National Park, Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary, Orang National Park, the Laokhowa and Burhachapori Wildlife Sanctuaries and Kaziranga National Park.
- New Delhi Declaration on Asian Rhinos: India, Bhutan, Nepal, Indonesia and Malaysia have signed a declaration for the conservation and protection of the species.
- DNA Profiles of all Rhinos: The project will help in curbing poaching and gathering evidence in wildlife crimes involving rhinos
- National Rhino Conservation Strategy: It was launched in 2019 to conserve the greater one-horned rhinoceros.
- Indian Rhino Vision 2020: It was an ambitious effort to attain a wild population of at least 3,000 greater one-horned rhinos spread over seven protected areas in the Indian state of Assam by the year 2020.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Asiatic lion is naturally found in India only.
- Double-humped camel is naturally found in India only.
- One-horned rhinoceros is naturally found in India only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Important Facts For Prelims
Recovering RNA From Extinct Tasmanian Tiger
Why in News?
In recent years, researchers have successfully retrieved DNA (DeoxyriboNucleic Acid), from ancient animals and plants, with specimens dating back over 2 million years. However, A recent study represents the first instance where RNA (Ribonucleic Acid), a molecule less stable than DNA, has been extracted from extinct species such as the Tasmanian Tiger.
Note:
The ability to extract, sequence and analyze old RNA could boost efforts by other scientists toward recreating extinct species. Recovering RNA from old viruses also could help decipher the cause of past pandemics.
What is the Difference Between DNA and RNA?
|
Characteristic |
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) |
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) |
|
Sugar Component |
Deoxyribose |
Ribose |
|
Nitrogenous Bases |
Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), Thymine (T) |
Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), Uracil (U) |
|
Number of Strands |
Double-stranded (usually) |
Single-stranded (usually) |
|
Structure |
Forms a double helix |
Generally single-stranded |
|
Bases Pairing |
A pairs with T, C pairs with G |
A pairs with U, C pairs with G |
|
Function |
Stores genetic information |
Carries genetic information, protein synthesis |
|
Location |
Found in the nucleus of cells, mitochondria, and chloroplasts |
Found in the nucleus, cytoplasm, and ribosomes |
|
Stability |
Stable and less prone to degradation |
Generally less stable, more susceptible to degradation |
|
Role in Protein Synthesis |
Serves as a template for mRNA synthesis |
Serves as a template for protein synthesis |
|
Types |
Mainly exists as genomic DNA and mitochondrial DNA |
Several types, including messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) |
What are the Key Facts About Tasmanian Tiger?
- The Tasmanian tiger, or thylacine (a dog headed pouched dog) was an exclusively carnivorous marsupial that is considered to be extinct (also the IUCN status).
- It is also known as the Tasmanian Wolf and bears some resemblance to a dog, with its distinguishing features being the dark stripes beginning at the rear of its body and extending into its stiff tail and abdominal pouch.
- It was confined to Tasmania in recent times and disappeared from mainland Australia over 2000 years ago, mainly because of over-hunting by humans, diseases and competition from the Dingo (Canis lupus), a wild dog native to Australia.
UPSC CSE PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS (PYQs)
Q. Consider the following statements : (2017)
- DNA Barcoding can be a tool to:
- assess the age of a plant or animal.
- distinguish among species that look alike.
- identify undesirable animal or plant materials in processed foods.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 2 and 3
Ans: D
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Joint Call to Action for Forests Towards 2030
The Collaborative Partnership on Forests (CPF), consisting of 16 global organisations chaired by the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), has introduced the Joint Call to Action for Forests towards 2030.
- Their objective is to emphasise the urgent need for increased action and political commitment in implementing forest solutions to align with the UN mandated Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- The initiative encompasses four key areas: Implementation and action; data, science, and innovation; finance for forests; and communication and awareness-raising.
Read more: Sustainable Development Goals
Agumbe's Rainfall Dominance Wanes as New Rain Gauges Emerge
Agumbe Rainforest Complex (ARC), in Karnataka long renowned for its exceptional rainfall and often referred to as the 'Cherrapunji of the South,' is losing its historical status due to the installation of new rain gauges in the region.
- While Agumbe has been a rain gauge site for over a century, recent installations in areas like Nadpal and Mudradi have revealed higher rainfall levels, pushing Agumbe down the ranking.
- A rain gauge is a meteorological instrument used to measure the amount of precipitation, typically rainfall, that falls over a specific period of time in a particular location
- These new gauges, operational since 2022, show that Agumbe received 6,251.5 mm of rain in 2022-2023, making it the third-highest in Karnataka.
- Despite these changes, Agumbe's rainfall data remains valuable for researchers studying biodiversity, hydrology, and the unique habitat of the King Cobra.
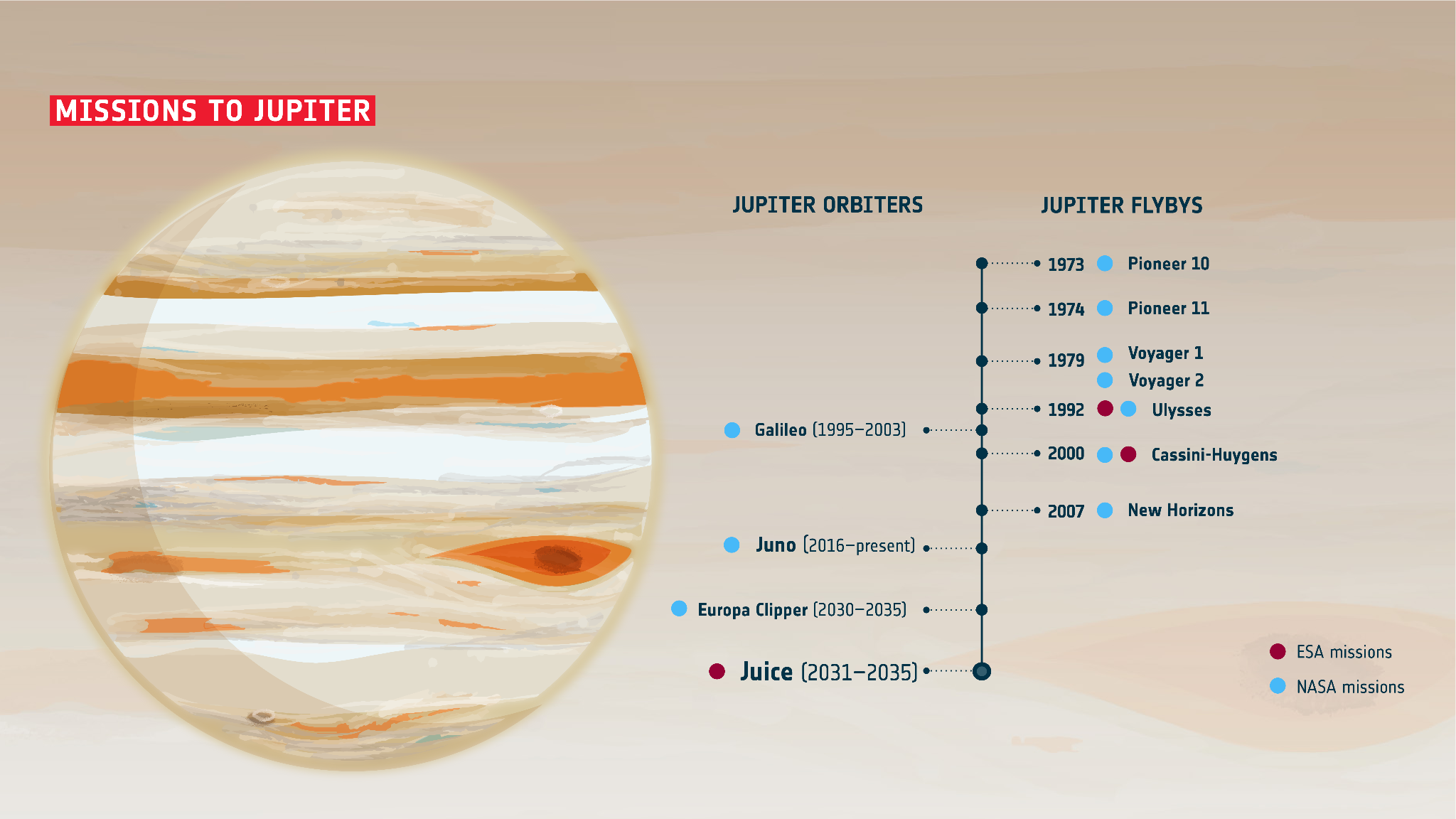
Juno
Juno is a solar-powered NASA spacecraft that makes long, looping orbits around giant planet Jupiter.
- Juno was launched on 5th August, 2011.The spacecraft traveled roughly 3 billion kilometers before arriving at Jupiter in 2016.
- Juno conducted its 53rd close flyby of Jupiter, capturing a remarkable image of Jupiter and its volcanic moon Io, on 31st July 31, 2023.
- Io is known for its intense volcanic activity, with hundreds of erupting volcanoes spewing molten lava and sulfurous gasses.
- It is slightly larger than Earth's Moon, and is tidally locked to Jupiter and completes both its rotation on its axis and orbit around Jupiter in approximately 1.8 Earth days.