Governance
Pre-draft National Curriculum Framework for School Education
- 11 Apr 2023
- 9 min read
For Prelims: National Curriculum Framework for School Education, Modular Board Exams, National Education Policy 2020.
For Mains: Features of National Education Policy 2020, Major Issues Related to the Education Sector in India, Government Initiatives Related to Educational Reforms.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Education released a pre-draft version of the National Curriculum Framework for School Education and has sought feedback from diverse stakeholders.
- The pre-draft was formulated by a committee led by K Kasturirangan, a former head of the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO).
What is the National Curriculum Framework?
- About:
- NCF is one of the key components of the New Education Policy(NEP) 2020, that enables and energizes this transformation, informed by the aims, principles, and approach of NEP 2020.
- The NCF has undergone four revisions in the past - in 1975, 1988, 2000, and 2005. The proposed revision, if implemented, would be the fifth iteration of the framework.
- Four Sections of NCF:
- NCF for School Education
- NCF for Early Childhood Care and Education (Foundational Stage)
- NCF for Teacher Education
- NCF for Adult Education
- Objective:
- It aims to help in positively transforming the school education system of India as envisioned in NEP 2020, through corresponding positive changes in the curriculum including pedagogy.
- It aims to realize the highest quality education for all children, consistent with realizing an equitable, inclusive, and plural society as envisaged by the Constitution of India.
What is NCF for School Education?
- About:
- The National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCF-SE) is developed based on the vision of the NEP 2020, and to enable its implementation.
- The formulation of NCF-SE will be undertaken by the NCERT. The NCFSE document shall henceforth be revisited and updated once every 5-10 years, considering the frontline curriculum.
- Objectives:
- The NCFSE serves as a guideline for developing syllabi, textbooks, and teaching practices in India.
- Its objectives include shifting from rote (memorization by repetition) learning, connecting education to real-life situations, making examinations more flexible, and enriching the curriculum beyond textbooks.
- The NCFSE also aims to make learning enjoyable, child-centered, and self-reliant, and promote democratic values. It provides guidelines for counseling secondary school students and is mandated for all age groups.
What is the Pre-draft National Curriculum Framework for School Education?
- About:
- The document covers the curriculum framework for children aged 3 to 18 years and seeks feedback from students, parents, teachers, educators, experts, scholars, and professionals.
- Key Features:
- Learning via 6 Pramana's:
- Pratyaksa, interpreted as perception through five senses;
- Anumana, which uses inferences to come to new conclusions;
- Upamana, which is knowing through analogy and comparison;
- Arthapatti, which involves knowing through circumstantial implication,
- Anupalabdhi, which includes perception of non-existence,
- Sabda, which is “something an individual can only directly know a fraction of all reality"
- Panchakosha Vikas for Moral Development:
- Indian education system emphasizes a holistic approach that fosters moral development, cultural understanding, and social awareness among children.
- This is achieved through a five-fold development approach that includes traditional practices like yoga, a balanced diet, and cultural activities.
- Teachings from Indian History:
- Education in India encourages questioning and debates to stimulate critical thinking and open-mindedness, as exemplified by the Upanishads.
- Additionally, Indian history education identifies and explains important phases of the Indian national movement against British rule, with special reference to the Gandhian and subaltern movements, to promote national identity and social justice.
- Teaching the concepts of different religious and philosophical traditions, including Buddhism, Jainism, and Vedic philosophies, to promote cultural diversity and interfaith understanding.
- No Exams till Class 2:
- It proposes that explicit tests and exams are not suitable assessment tools for children in classes up to 2 and recommends introducing written tests only from class 3 onwards to avoid imposing additional burden on the child.
- Curriculum for Secondary Stage:
- For Grade 10 certification, students will have to take two essential courses from humanities, maths and computing, vocational education, physical education, arts education, social science, science, and interdisciplinary areas.
- In Grades 11 and 12, students will be offered choice-based courses in the same disciplines for more rigorous engagement.
- This phase of the Secondary Stage would be divided into semesters and each choice-based course would be for a semester.
- Students must complete 16 choice-based courses to complete Grade 12.
- Modular Board Exams will be offered as opposed to a single exam at the end of the year, and the result will be based on the cumulative result of each exam.
- Arts and Interdisciplinary Areas:
- Arts education will include music, dance, theatre, sculpture, painting, set design, and scriptwriting, while interdisciplinary areas will include knowledge of India, traditions, and practices of Indian knowledge systems.
- Learning via 6 Pramana's:
- Significance:
- The National Curriculum Framework for School Education is significant because it provides a roadmap for the education of children in India, which includes multiple educative approaches and learning-teaching material for different stages of school education.
- The framework emphasizes the importance of including values and their "rootedness" in India, including content, language learning, academic approaches, philosophical basis, aims, and epistemic approach.
What are the Other Government Initiatives Related to Educational Reforms?
- National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning.
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan
- PRAGYATA
- Mid Day Meal Scheme
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao
- PM SHRI Schools
What is the National Education Policy 2020?
- About:
- The NEP 2020 is a comprehensive framework for education reform in India that was approved in 2020, aiming to bring significant changes in the education system of India by providing a holistic and multidisciplinary approach to education.
- Features of the NEP 2020:
- Universalization of education from preschool to secondary level.
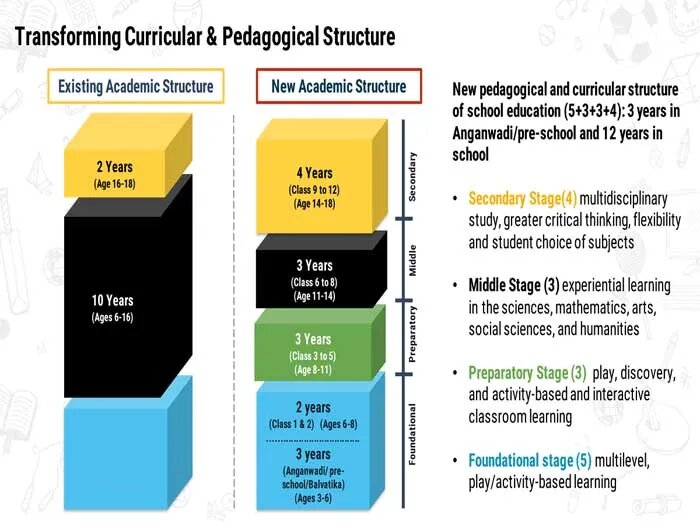
- Introduction of a new pedagogical and curricular structure based on cognitive and socio-emotional development of students.
- Emphasis on the development of foundational literacy and numeracy skills in primary education.
- Increased focus on research and development in education.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- As per the Right to Education (RTE) Act, to be eligible for appointment as a teacher in a State, a person would be required to possess the minimum qualification laid down by the State Council of Teacher Education concerned.
- As per the RTE Act, for teaching primary classes, a candidate is required to pass a Teacher Eligibility Test conducted in accordance with the National Council of Teacher Education guidelines.
- In India, more than 90% of teacher education institutions are directly under the State Governments.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 3 only
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. National Education Policy 2020 is in conformity with the Sustainable Development Goal-4 (2030). It intends to restructure and reorient education system in India. Critically examine the statement. (2020)