International Relations
India–Saudi Arabia Relations
For Prelims: Foreign Direct Investment, National Anti-Doping Agency, EX-SADA TANSEEQ, Bilateral Haj Agreement
For Mains: India’s Foreign Policy and Strategic Partnerships, India-Saudi Arabia Relations, India’s strategic alliances within the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
Why in News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi paid a state visit to the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and chaired the 2nd meeting of the India-Saudi Arabia Strategic Partnership Council (SPC).
What are the Key Outcomes of the India-Saudi Arabia Bilateral Engagement?
- New Ministerial Committees: The 2nd Leaders’ Meeting of the SPC, led to the creation of two new Ministerial Committees on Defence Cooperation and Tourism & Cultural Cooperation.
- The SPC now operates through four key committees: Political, Consular & Security Cooperation; Defence Cooperation; Economy, Energy, Investment & Technology; and Tourism & Cultural Cooperation.
- High Level Task Force on Investment (HLTF): Saudi Arabia's commitment to invest USD 100 billion in India spans sectors like energy, infrastructure, tech, and health.
- The HLTF has facilitated collaboration on establishing two refineries in India and achieved progress in taxation, boosting future investment cooperation.
- MoUs/Agreements Signed:
- Space Cooperation: MoU between Saudi Space Agency and Department of Space of India for cooperation in space activities for peaceful purposes.
- Health Cooperation: Saudi Arabia signed MoU with India to foster cooperation in healthcare.
- Anti-Doping Cooperation: MoU between the Saudi Arabian Anti-Doping Committee (SAADC) and the National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA) (India) on anti-doping education and prevention.
- Postal Cooperation: Agreement between Saudi Post Corporation (SPL) and Department of Posts, India on cooperation in inward surface parcel services.
How have India–Saudi Arabia Relations Developed Over the Years?
- Diplomatic and Strategic Relations: India and Saudi Arabia established diplomatic ties in 1947, with key milestones including the Delhi Declaration (2006) and the Riyadh Declaration (2010) during PM Manmohan Singh’s visit, which elevated ties to a Strategic Partnership.
- In 2019, PM Narendra Modi’s 2nd visit led to the formation of the SPC.
- Economic Cooperation:
- Trade: India is Saudi Arabia’s 2nd largest trade partner, while Saudi Arabia ranks as India’s 5th largest.
- In FY 2023-24, bilateral trade stood at USD 42.98 billion, with Indian exports at USD 11.56 billion and imports at USD 31.42 billion.
- Investments: Indian investments in Saudi Arabia total around USD 3 billion, focusing on sectors like IT, telecom, pharma, and construction.
- Saudi investments in India amount to USD 10 billion, led by Public Investment Fund (PIF).
- Saudi Arabia occupies the 20th position in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) equity inflows into India with a cumulative FDI amount of USD 3.22 billion from 2000- 2024.
- Trade: India is Saudi Arabia’s 2nd largest trade partner, while Saudi Arabia ranks as India’s 5th largest.
- Energy Partnership: In FY 2023-24, Saudi Arabia was India’s 3rd largest source of crude oil, which accounted for 14.3% of India’s total crude imports.
- It was also the 3rd largest Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) supplier, contributing 18.2% to India’s total LPG imports.
- Defence Partnership: The first India-Saudi joint land exercise, EX-SADA TANSEEQ, was held in India in 2024, and the bilateral naval exercise ‘Al Mohed Al Hindi’ has also been conducted.
- Cultural Relations: India and Saudi Arabia signed the Bilateral Haj Agreement 2024, allocating a quota of around 1.75 lakh Indian pilgrims. The agreement also supports India’s initiative to allow women pilgrims without a Mehram.
- Yoga gained popularity in Saudi Arabia after being recognized as a sports activity in 2017. In 2018, Ms. Nouf Al-Marwaai received the Padma Shri for promoting yoga in Saudi Arabia.
- The 2.6 million-strong Indian community in Saudi Arabia is the largest expatriate community in the Kingdom and is the ‘most preferred community’.
What are the Key Challenges in India–Saudi Arabia Relations?
- Labour Welfare Concerns: Reports of poor working conditions, delayed wages, and exploitation are common among Indian blue-collar workers in Saudi Arabia.
- Restrictive Labour Laws like the Kafala system (which ties workers' legal status to their employer) limit mobility and rights.
- Worsening Trade Deficit: India’s trade deficit with Saudi Arabia touched nearly USD 20 billion in 2023–24, driven by crude oil imports. While the Saudi economy is diversifying under Vision 2030, it remains oil-dependent.
- India’s reliance on Saudi oil makes their trade ties vulnerable to global price shifts, increasing the trade imbalance
- Saudi Arabia’s Foreign Policy and Regional Instability: Saudi Arabia’s military actions in Yemen, the Qatar blockade, and involvement in Syria destabilize the Gulf, complicating India’s security and economic interests in the region.
- Saudi-Iran rivalry creates a diplomatic challenge for India, which has strategic ties with both, especially in energy security and regional cooperation.
- Saudi Arabia’s shift towards stronger ties with China and Pakistan challenges India’s traditional alignment with the US, complicating India’s efforts to balance its strategic relationship with Saudi Arabia and its broader regional alliances.
What are the Key Areas for Strengthening Relations Between India and Saudi Arabia?
- Green Energy Collaboration: With Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 aiming for diversification, India’s expertise in solar and green hydrogen opens doors for joint renewable energy projects.
- Saudi Arabia’s vast deserts hold great potential for solar power, and through the International Solar Alliance, both nations could create the world’s largest solar zone, driving sustainable energy and global clean energy exports.
- Technology and Innovation Partnership: India’s IT and AI expertise, combined with Saudi Arabia’s tech innovation drive, offers a unique opportunity to co-develop a "Digital Silk Road", focusing on next-gen financial systems and AI solutions.
- A joint AI and FinTech Innovation Lab in Riyadh or Bengaluru could drive investment and create cutting-edge solutions for the Middle East and Asia.
- Enhance the Strategic Partnership: The IMEC (India-Middle East Economic Corridor) offers a strategic opportunity for seamless connectivity in trade, energy, and services, transforming the region into a global economic powerhouse.
- By developing ultra-modern trade and shipping hubs will boost both countries' positions in global trade networks.
- Utilizing GCC Platforms: As Saudi Arabia shifts towards a more assertive foreign policy, India’s diplomatic channels within the GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council) can help facilitate collaboration on regional stability and peace efforts, especially in the context of evolving relations with Iran and other regional powers.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the strategic significance of the India-Saudi Arabia Strategic Partnership. How does the evolving relationship align with India’s foreign policy objectives? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following is not a member of ‘Gulf Cooperation Council’? (2016)
(a) Iran
(b) Saudi Arabia
(c) Oman
(d) Kuwait
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) is an alliance of 6 countries in the Arabian Peninsula – Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. Iran is not a member of the GCC.
- It was established in 1981 to promote economic, security, cultural and social cooperation between the members and holds a summit every year to discuss cooperation and regional affairs.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. The question of India’s Energy Security constitutes the most important part of India’s economic progress. Analyse India’s energy policy cooperation with West Asian countries. (2017)


International Relations
Tightening Student Visa Norms
For Prelims: Visa, Remittances, University Grant Commision, GIFT City, Vienna Convention
For Mains: Impact of Foreign Education Policies on Domestic Education Systems, India’s Soft Power and Global Influence
Why in News?
Indian students are facing a sharp drop in visa issuances and increasing visa revocations in the US, alongside tightening visa norms in Australia, disrupting academic plans and career aspirations.
What are the Concerns Regarding Indian Student Visas?
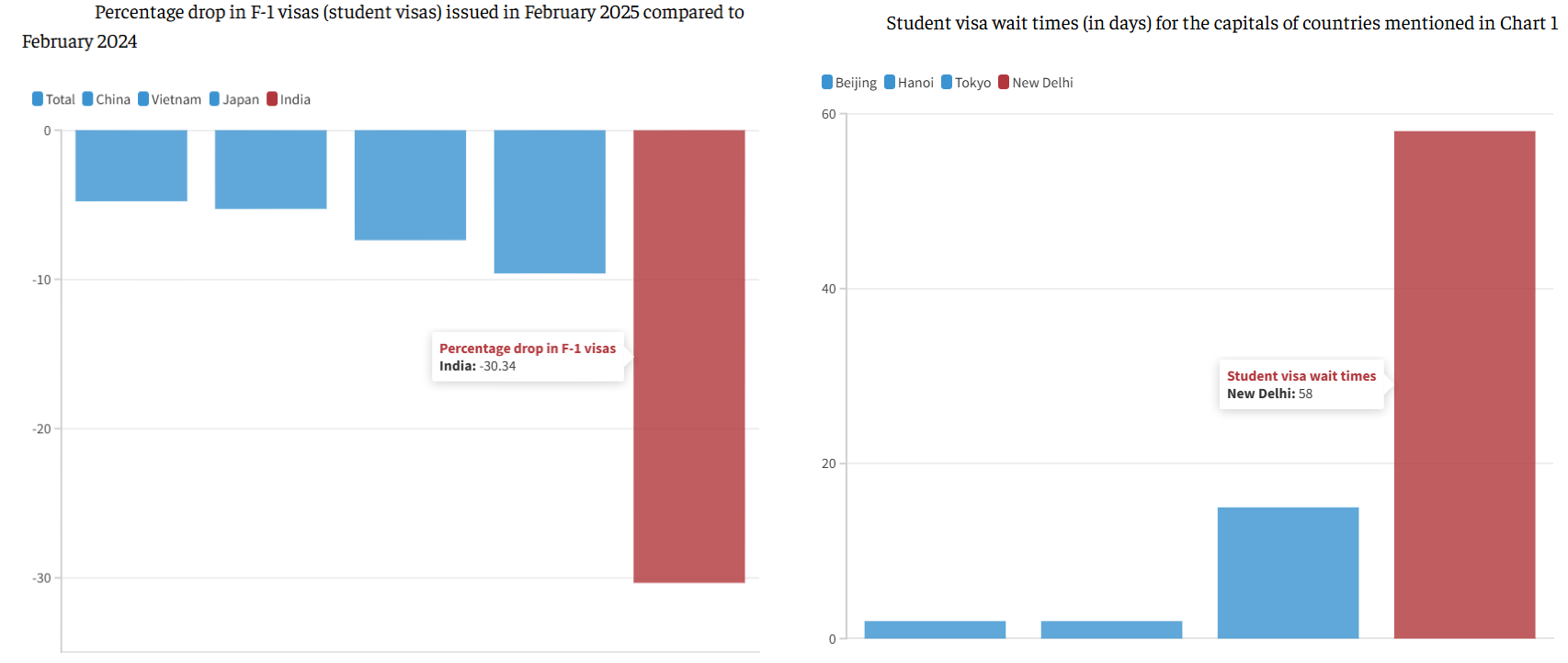
- Sharp Decline in Visa Issuance: In February 2025, the US recorded a 30% drop (590 to 411 visas) in F-1 student visas issued to Indian nationals compared to February 2024.
- This decline is disproportionately higher than the global average decrease of 4.75%, and significantly steeper than the drops for other top countries such as China (5.2%), Japan (9.6%), and Vietnam (7.4%).
- Visa wait times are also significantly longer for Indian students, averaging 58 days in Delhi, compared to just 2–15 days in East Asian capitals.
- Surge in Visa Terminations and Revocations: According to a survey by the American Immigration Lawyers Association (AILA), 50% of international students whose US visas were revoked in early 2025 were Indian nationals.
- The revocations were largely driven by the US State Department’s AI-based “Catch and Revoke” programme, which monitors social media and police databases, raising concerns over fairness, transparency, and diplomatic fallout.
- Legal and Financial Hardship: Students facing revocation must undergo complex legal procedures to restore their SEVIS (Student and Exchange Visitor Information System) status.
- Many have filed lawsuits, but the costs are prohibitive, and delays can cause students to lose academic terms, jobs, and scholarships.
- Targeted Visa Scrutiny: Reports suggest Australia has increased visa scrutiny for applicants from five Indian states Punjab, Haryana, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, and Bihar.
- This has sparked fears of profiling and unfair generalisations against Indian applicants from these regions.
What are the Potential Implications of Indian Student Visa Issues?
- Weakening of India’s Soft Power: India, along with China, is one of the two largest sources of international students but is facing setbacks due to a decline in US visas and stricter norms in Australia.
- These disruptions weaken India’s soft power and global presence in key fields like AI, climate science, and biotechnology.
- Risk to India’s Demographic Dividend: With 65% of India’s population under 35, access to global education is crucial for skill development. Visa curbs and revocations hinder opportunities, impacting long-term productivity and innovation.
- Decline in Remittances: In 2024, India received a record USD 129.1 billion in remittances, driven partly by Indian students in advanced economies.
- Stricter visa norms could reduce student migration and remittances, potentially impacting India's economy.
- SEVIS Removals: Unlike visa revocations, which prevent re-entry into the U.S. but do not automatically terminate a student's legal status, SEVIS removals bring swift and severe consequences, including the loss of employment eligibility and complications for dependents like spouses and children.
- Middle-class aspirants relying on loans or savings are most affected, experiencing both economic and emotional distress.
- Human Capital Drain and Redirection: The shift away from traditional destinations (U.S., Australia) toward emerging hubs like the Nordic countries and South Korea, alters the trajectory of India’s global talent flow.
- This re-routing affects network building, diaspora influence, and strategic industry placements, particularly in Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM), healthcare, and research.
- Pressure on Domestic Higher Education Infrastructure: As international avenues shrink, demand for quality institutions in India is expected to rise sharply.
- This may strain already limited Tier-I universities (IITs, IIMs, AIIMS) and push the University Grant Commission and All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) to fast-track capacity building and accreditation reforms under National Education Policy, 2020.
What Strategies Can Mitigate Indian Student Visa Challenges?
- Leveraging Diplomatic Instruments: The Vienna Convention on Consular Relations (1963) empowers Indian missions to protect the interests of Indian citizens abroad. This legal provision should be more actively used to assist students facing visa issues.
- Strengthen the Emigration Act, 1983 to bring student visa consultancies under its ambit, making registration, accountability, and penalties enforceable for false promises or forged documents.
- Emergency Student Safety Net: Set up an Overseas Education Protection Fund (OEPF) under the MEA to assist students facing visa revocation, tuition loss, or forced deportation.
- Enhance Domestic Higher Education: India should incentivize top-tier foreign universities to set up campuses or offer joint-degree programs, as per the 2022-23 Union Budget, which allows world-class institutions to operate in GIFT (Gujarat International Finance Tec-City) City.
- Simultaneously, Indian universities, under NEP 2020, should adopt reforms like dual-degree programs, international faculty exchange, and establish Multidisciplinary Education and Research Universities (MERUs) to create a world-class education ecosystem.
- Digital Registry for Students: India should create a voluntary digital student registry for real-time visa tracking and embassy support.
- Indian embassies can develop an AI-based system, similar to the US "Catch and Revoke" program, to monitor students’ digital profiles and social media for early alerts on visa risks.
- Regulating Education Consultancies: India must tighten regulations on education consultancies by enforcing stricter registration, audits, and penalties for fraud, ensuring students are not misled.
- The Ministry of Education should launch awareness campaigns and provide a verified list of reputable consultancies to reduce scams.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the implications of tightening visa norms for Indian students. What measures can the Indian government take to address these challenges? |


Important Facts For Prelims
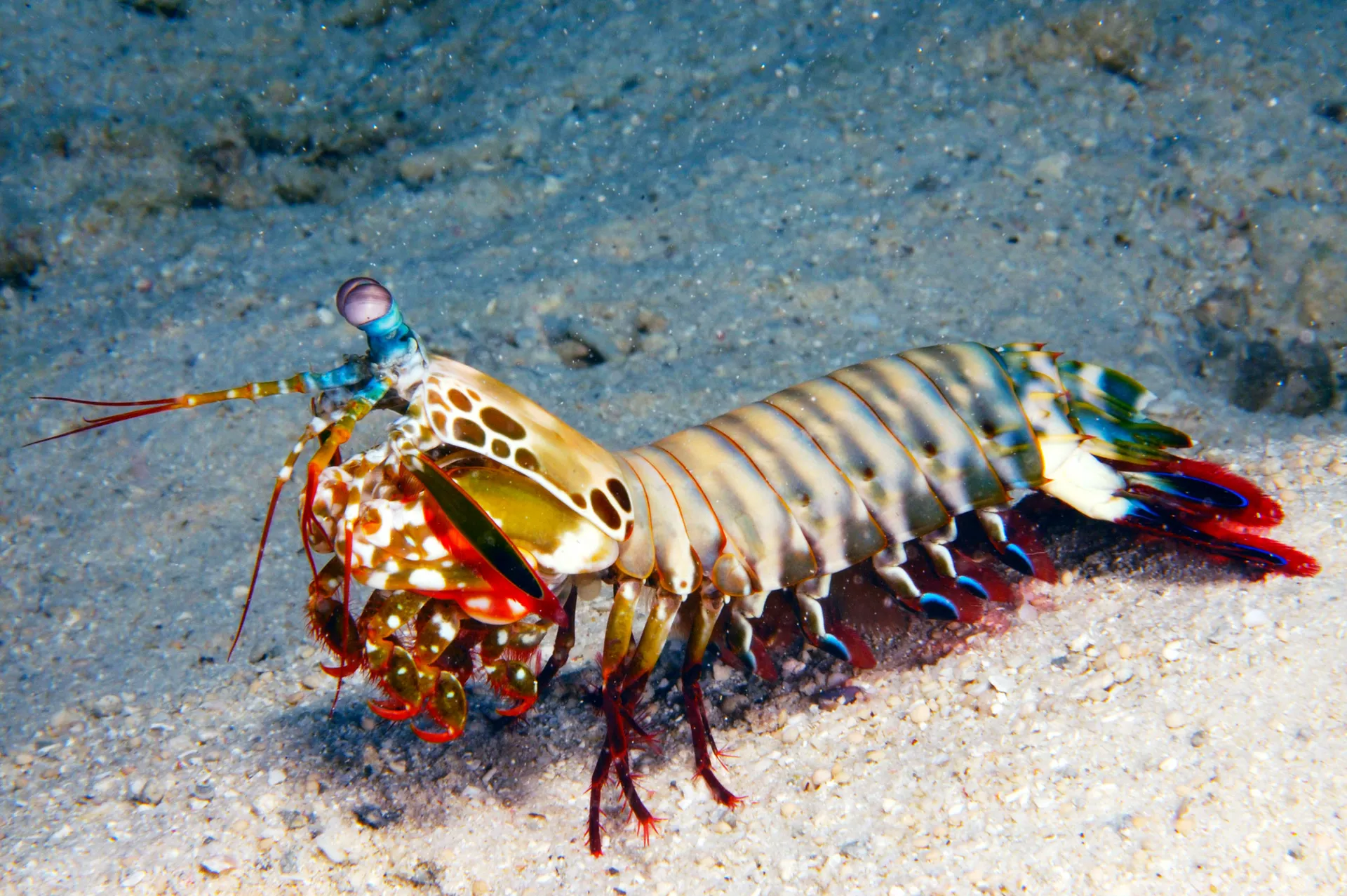
Mantis Shrimp and Metamaterials
Why in News?
A new study has revealed that the mantis shrimp’s hammer-like limb delivers powerful blows and also uses a natural recoil-dampening system, challenging previous beliefs about metamaterials and energy control.
- This work not only highlights the evolutionary genius of the mantis shrimp, but also opens new frontiers in material science and bioengineering.
What are the Key Research Findings on Mantis Shrimps?
- Researchers found that the mantis shrimp's striking appendage acts as a natural phononic metamaterial (materials that block or control mechanical waves like sound or vibrations).
- The club structure provides dual mechanical advantages—it both withstands force and controls energy propagation.
- Its hierarchical structure includes:
- A hydroxyapatite surface (a hard mineral also found in human bones and teeth) that disperses impact
- Spring-like tendons (elastic structures that help absorb shock)
- Biopolymer fibers arranged in a periodic pattern (repeating natural fibers that reduce impact damage from repeated strikes)
- The study confirms that nature has evolved metamaterials, changing how scientists understand biological material design.
What are Mantis Shrimps?
- About:
- Mantis shrimp are ancient marine crustaceans belonging to the order Stomatopoda, closely related to crabs and lobsters.
- With over 450 known species, they range in size from 10 cm to nearly 46 cm.
- Despite their name, they are not true shrimp but are distinguished by their vibrant colors, complex behavior, and powerful hunting appendages.
- Mantis shrimp are ancient marine crustaceans belonging to the order Stomatopoda, closely related to crabs and lobsters.
- Habitat:
- Mantis shrimp inhabit warm, shallow tropical and subtropical waters, particularly in the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
- They live in self-dug burrows within seabeds—smashers in harder substrates and spearers in soft ones—near coral reefs.
- Mantis shrimp inhabit warm, shallow tropical and subtropical waters, particularly in the Indian and Pacific Oceans.
- Hunting Mechanisms: Mantis shrimp are categorized into two main types based on their hunting adaptations:
- Spearers: Possess spiny, barbed forelimbs used to impale soft-bodied prey like fish, squid, and worms.
- Smashers: Have heavily calcified, club-like appendages capable of delivering one of the fastest strikes in the animal kingdom, used to break open hard-shelled prey like snails, crabs, and clams.
- Ecological and Scientific Significance: Their club mechanism has inspired biomimicry in armor and aerospace engineering
- Eye structure is influencing optical sensor and cancer detection technology
- They help control prey populations in reef ecosystems and contribute to nutrient cycling.
- Researchers are also investigating methods to convert trapped mechanical energy into other usable forms, potentially leading to energy-harvesting applications.
What are Metamaterials?
- About: Metamaterials are artificially engineered materials designed to exhibit properties not found in nature.
- Their unique behaviour arises from their internal structure and arrangement, not from the base materials they’re made of.
- Key Properties:
- They often display unusual electromagnetic properties, such as a negative refractive index.
- This makes them valuable in fields like optics, telecommunications, and electromagnetism.
- Their behaviour is comparable to materials like graphite, diamond, and graphene—which all consist of carbon but differ drastically due to structural arrangement.


Important Facts For Prelims
Quantum Gravity Gradiometer
Why in News?
A team of National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) scientists has proposed deploying a Quantum Gravity Gradiometer (QGG) onboard a satellite in low-Earth orbit to detect minute gravitational variations on Earth.
- This would allow for precise monitoring of the planet’s subsurface mass distribution, aiding in climate studies and enhancing national security.
What is a Gravity Gradiometer?
- Gravity: It is a natural force of attraction between two objects that have mass. It pulls objects toward each other and is responsible for keeping planets in orbit, causing objects to fall to the ground, and giving weight to physical bodies.
- Gravity is directly proportional to an object's mass and varies depending on the mass distribution of the Earth. These variations are too subtle to detect without sensitive instruments.
- Gravity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between two objects (as the distance increases, the gravitational pull weakens).
- Gravity Gradiometer: It is a highly sensitive scientific instrument used to measure the variation in gravitational acceleration over a specific distance.
- Based on Newton’s second law (F = ma), the Gravity Gradiometer detects variations in gravitational force and acceleration caused by changes in local mass distribution.
- A faster fall means more mass below (e.g., mountains), while a slower fall suggests less mass (e.g., air pockets or oil reserves).
Note: Newton’s second law states that the force acting on a body is equal to its mass multiplied by its acceleration (F = ma).
What is a Quantum Gravity Gradiometer (QGG)?
- About: A QGG measures the differences in gravitational acceleration at different points in space. It detects how gravity changes due to variations in mass distribution on Earth or other celestial bodies.
- Working: The QGG cools atoms to near absolute zero (0 kelvin, or -273.15 °C), causing them to behave like waves. Lasers manipulate these atoms, and their phase shift becomes sensitive to gravitational forces.
- It then measures gravitational differences as small as 10⁻¹⁵ m/s², enabling the detection of minute variations in gravity.
- Potential Applications: The QGG can detect the gravitational pull of large landforms like the Himalayas, as their mass creates a stronger gravitational force. It measures these variations to provide precise data on their mass.
- It can track shifts in water, ice, and land masses, which is crucial for studying climate change and glacial melt.
- Additionally, QGG can help identify underground hydrocarbons, minerals, and aquifers, supporting resource exploration.
- It can also monitor strategic infrastructure, and geological threats, enhancing national security.
- QGG can be used in archaeology and heritage conservation for the non-destructive detection of buried ruins or ancient structures without excavation.
- It also boosts advancements in quantum sensors, satellite tech, and geophysics.
| Read more: Quantum Nature of Gravity |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following phenomena: (2018)
- Light is affected by gravity.
- The Universe is constantly expanding.
- Matter warps its surrounding space-time.
Which of the above is/are the prediction/predictions of Albert Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity, often discussed in media?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)


Rapid Fire
CCI Approves Google’s Antitrust Settlement
The Competition Commission of India (CCI) has approved Google’s settlement proposal in the Android TV case, under Section 48A(3) of the Competition Act, 2002, marking a significant resolution under the Competition Commission of India (Settlement) Regulations, 2024.
- Case Background: The case under Section 19(1)(a) of the Competition Act, 2002, alleged that Google abused its dominant position in the Android TV market by bundling the Play Store with its Android TV OS and restricting alternative Android versions.
- Section 19(1)(a) of the Competition Act, 2002, empowers the CCI to investigate alleged violations of Section 3 (anti-competitive agreements) or Section 4 (abuse of dominant position).
- Investigation Findings: CCI found Google dominant in Smart TV OS and App Store markets in India, using unfair practices to stifle competition and innovation.
- Settlement Process: Under Section 48A(3) of the Competition Act, 2002 ( deals with settlement process), Google agreed to a settlement by removing bundling requirements, allowing OEMs to develop non-Google Android devices, and paying a settlement fee of Rs 20.24 crore.
- CCI: It is a statutory body established by the Government of India in 2009 to enforce the Competition Act, 2002.
- This Act replaced the Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Act, 1969 (MRTP Act) on the recommendations of the Raghavan Committee(1999).
- The CCI also replaced the Competition Appellate Tribunal (COMPAT) with the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT).
- The Competition Act, 2002 (amended in 2023) empowers the CCI to address violations through the Commitment and Settlement Regulations, 2024, allowing enterprises to offer commitments or pay a settlement fee.
| Read more: Google Faces Antitrust Complaints in the US and India |


Rapid Fire
World Earth Day 2025
World Earth Day is celebrated every year on 22nd April with the mission of broadening, educating, and activating environmental movements worldwide.
- Theme for 2025: "Our Power, Our Planet”-- It calls on everyone to unite for renewable energy and to work toward tripling clean energy capacity by 2030.
World Earth Day
- The first Earth Day was observed in 1970 after Senator Gaylord Nelson witnessed the catastrophic effects of an oil spill in California.
- Nelson initiated a movement that brought over 20 million Americans together to rally for environmental reforms.
- This pivotal day led to the passing of significant environmental legislation in the US, including the creation of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
- In 1990, Earth Day became a global event with 200 million people and 141 countries participating.
- Significance: It also offers an opportunity to celebrate green initiatives around the world and highlight ongoing efforts toward environmental protection.
| Read More: Celebrating Earth Day, Strengthening India's Environmental Governance |


Rapid Fire
Exercise Desert Flag-10
India participated in Exercise Desert Flag-10, a premier multinational air combat exercise hosted by the United Arab Emirates (UAE) Air Force.
- The exercise includes air forces from Australia, Bahrain, France, Germany, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, South Korea, Turkey, the UK, and the US.
- The exercise aims to enhance interoperability, operational synergy, and mutual understanding through complex air combat scenarios and exchange of global best practices.
- The Indian Air Force (IAF) deployed MiG-29 and Jaguar aircraft, showcasing its frontline combat capabilities.
- India’s Exercises with the UAE: Desert Cyclone (Land-based Military Exercise), Desert Eagle (Bilateral Air Force Combat Exercise), Zayed Talwar (Bilateral Naval Exercise), and Desert Knight (Trilateral Air Force Exercise with France).
| Read more:India-UAE Ties: From Tradition to Transformation |