Infographics
Governance
Anti-Maritime Piracy Bill
For Prelims: Anti-Maritime Piracy Bill, Exclusive Economic Zone, UN Convention on the Law of Sea
For Mains: Features and Challenges of Anti-Maritime Piracy Bill, UN Convention on the Law of Sea
Why in News?
Recently, Rajya Sabha passed the Anti-Maritime Piracy Bill which the government said would provide an effective legal instrument to combat Maritime Piracy.
- The security of sea lanes of communication is critical as more than 90% of India’s trade takes place by sea routes and more than 80% of the country’s hydrocarbon requirements was sea-borne.
What are the Key Features of the Bill?
- About:
- The Bill provides for prevention of maritime piracy and prosecution of persons for such piracy-related crimes.
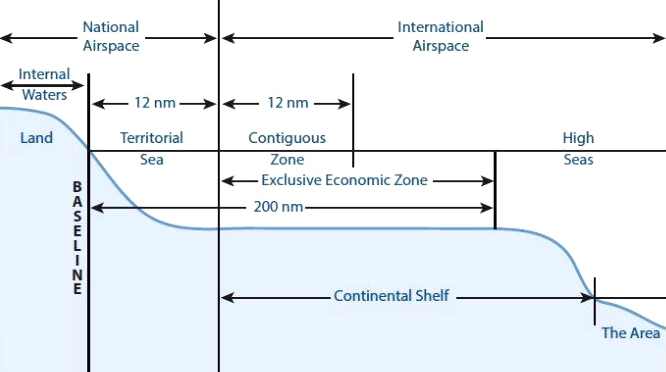
- It will apply to all parts of the sea adjacent to and beyond the limits of the Exclusive Economic Zone of India, i.e., beyond 200 nautical miles from the coastline.
- The Bill brings into law the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- The Bill provides for prevention of maritime piracy and prosecution of persons for such piracy-related crimes.
- Definition of Piracy:
- It defines piracy as any illegal act of violence, detention, or destruction committed against a ship, aircraft, person or property, for private purposes, by the crew or passengers of a private ship or aircraft. Such acts may be carried out in the high seas (beyond the Exclusive Economic Zone of India) or any place outside the jurisdiction of India.
- Inciting or intentionally facilitating such acts would also qualify as piracy.
- It includes any other act that is considered as piratical under international law.
- Piracy also includes voluntary participation in the operations of a pirate ship or aircraft used for piracy.
- It defines piracy as any illegal act of violence, detention, or destruction committed against a ship, aircraft, person or property, for private purposes, by the crew or passengers of a private ship or aircraft. Such acts may be carried out in the high seas (beyond the Exclusive Economic Zone of India) or any place outside the jurisdiction of India.
- Penalties:
- An act of piracy will be punishable with:
- Imprisonment for life; or
- Death, if the act of piracy causes or attempts to cause death.
- An attempt to commit, aid, support, or counsel an act of piracy will be punishable with up to 14 years of imprisonment, and a fine.
- Participating, organising, or directing others to participate in an act of piracy will also be punishable with up to 14 years of imprisonment, and a fine.
- Offences will be considered extraditable. This means that the accused can be transferred to any country for prosecution with which India has signed an extradition treaty.
- In the absence of such treaties, offences will be extraditable on the basis of reciprocity between the countries.
- An act of piracy will be punishable with:
- Jurisdiction of the Courts:
- The central government, in consultation with the Chief Justice of the concerned High Court, may notify Sessions Courts as the Designated Courts under this Bill.
- The Designated Court will try offences committed by:
- A person in the custody of the Indian Navy or Coast Guard, regardless of his nationality.
- A citizen of India, a resident foreign national in India, or a stateless person.
- The Court will not have jurisdiction over offences committed on a foreign ship unless an intervention is requested by:
- The country of origin of the ship.
- The ship-owner.
- Any other person on the ship.
- Warships and government-owned ships employed for non-commercial purposes will not be under the jurisdiction of the Court.
What are the Key Challenges in the Bill?
- Under the Bill, if a person, while committing an act of piracy causes or seeks to cause death, he will be punished with death.
- This implies a mandatory death penalty for such offences.
- The Supreme Court has held that mandatory death penalty for any offence is unconstitutional as it violates Articles 14 and 21 of the Constitution.
- However, Parliament has passed laws providing for mandatory death penalty for some offences. Example: Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989 (SC/ST Act).
- The Bill provides for imprisonment of up to 14 years if a person participates in an act of piracy. Committing an act of piracy (which includes voluntarily participating in the operation of a pirate ship or aircraft) is punishable with life imprisonment.
- As these circumstances may overlap, it is unclear how the punishment would be determined in such cases.
- The Bill will apply to all parts of the sea adjacent to and beyond the limits of the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of India, i.e., beyond 200 nautical miles from the coastline.
- The question is whether the Bill should cover the EEZ also, that is the area between 12 nautical miles and 200 nautical miles (from the coastline of India).
What is the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea?
- The UNCLOS, 1982 is an international agreement that establishes the legal framework for marine and maritime activities.
- It is also known as Law of the Sea. It divides marine areas into five main zones namely- Internal Waters, Territorial Sea, Contiguous Zone, Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) and the High Seas.
- It is the only international convention which stipulates a framework for state jurisdiction in maritime spaces. It provides a different legal status to different maritime zones.
- It provides the backbone for offshore governance by coastal states and those navigating the oceans.
- It not only zones coastal states’ offshore areas but also provides specific guidance for states’ rights and responsibilities in the five concentric zones.
- In 1995, India ratified the UNCLOS.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. With reference to the ‘Trans-Pacific Partnership’, consider the following statements: (2016)
- It is an agreement among all the Pacific Rim countries except China and Russia.
- It is a strategic alliance for the purpose of maritime security only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Q2. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC)’, consider the following statements: (2015)
- It was established very recently in response to incidents of piracy and accidents of oil spills.
- It is an alliance meant for maritime security only.
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. With respect to the South China sea, maritime territorial disputes and rising tension affirm the need for safeguarding maritime security to ensure freedom of navigation and overflight throughout the region. In this context, discuss the bilateral issues between India and China. (2014)
Agriculture
Innovation in Agriculture
Prelims: Artificial Intelligence, Precision Agriculture, Machine Learning, National e-Governance Plan in Agriculture.
Mains: Need of IoT and AI in Agriculture.Why in News?
Recently, the government of India has taken various initiatives related to Agriculture by using Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- IoT is a computing concept that describes the idea of everyday physical objects being connected to the internet and being able to identify themselves to other devices.
What is the Need for IoT and AI in the Agriculture Sector?
- Even as agriculture remains a priority sector accounting for the livelihoods of around 58 % of the country's population, adoption of technology in the sector is at a transitory juncture and faces several challenges across the value chain.
- These challenges require disruptive interferences which can be provided by technological solutions such as the IoT and AI etc.
- Adoption of AI technologies can pave the way for higher production with the optimum utilization of available resources and facilitate predictive analysis, crop health management, enhance quality and traceability among others.
- The adoption of innovative and transformative smart farming practices in the country is gradually becoming a major trend.
- Globally technology advancements in recent years are re-engineering both the upstream and downstream segments of the agri value chain, which makes it important to adapt innovation in Agriculture.
- Cutting-edge technologies in AI such as IoT, ML (Machine Learning), cloud computing, statistical computing, deep learning, Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) can enable the Agriculture Sector to overcome the challenges of productivity, quality, traceability and carbon emission with enhanced profitability.
What is the Usage of AI in Agriculture?
- Analyzing Farm Data:
- Farms produce hundreds of thousands of data points on the ground daily. With the help of AI, farmers can now analyze a variety of things in real-time such as weather conditions, temperature, water usage or soil conditions collected from their farm to better inform their decisions.
- Farmers are also using AI to create seasonal forecasting models to improve agricultural accuracy and increase productivity.
- Precision Agriculture:
- Precision agriculture uses AI technology to aid in detecting diseases in plants, pests, and poor plant nutrition on farms.
- AI sensors can detect and target weeds and then decide which herbicides to apply within the right buffer zone.
- This helps to prevent over-application of herbicides and excessive toxins that find their way in our food.
- It would increase productivity by introducing precision agriculture.
- Tackling the Labour Challenge:
- With fewer people entering the farming profession, most farms are facing the challenge of a workforce shortage.
- One solution to help with this shortage of workers is AI agriculture bots. These bots augment the human labour workforce and are used in various forms. For example:
- These bots can harvest crops at a higher volume and faster pace than human labourers, more accurately identify and eliminate weeds, and reduce costs for farms by having around the clock labour force.
- Additionally, farmers are beginning to turn to chatbots for assistance. Chatbots help answer a variety of questions and provide advice and recommendations on specific farm problems.
What are the Related Initiatives taken?
- National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber Physical Systems (NM-ICPS):
- It was launched in 2018 by the Ministry of Science and Technology with an outlay of Rs. 3,660.00 crore for a period of five years to encourage innovation in new age technologies.
- Under the Mission, 25 Technology Innovation Hubs (TIHs) have been set up in premier institutes of national importance across the country in advanced technology verticals.
- The Mission can act as an engine of growth that would benefit national initiatives in health, education, energy, environment, agriculture, strategic cum security, and industrial sectors, Industry 4.0, SMART Cities, Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) etc.
- Digital India initiatives:
- Under the Digital India initiatives government has set up Centres of Excellence on Internet of Things with the objective to enable India to emerge as an innovation hub in IoT through democratization of innovation and realization of prototypes.
- One of the focus areas of Centres of Excellence on IoT is on Agri-tech and it connects various entities such as startups, enterprises, venture capitalists, government and academia.
- National e-Governance Plan in Agriculture:
- Funding is given to State Governments for Digital Agriculture projects using emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML), IoT, Block chain etc.
- Innovation and Agri-Entrepreneurship Development:
- This programme is operational under Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) from 2018-19 with the objective to promote innovation and entrepreneurship by providing financial support and nurturing the incubation ecosystem.
- In this connection, five Knowledge Partners (KPs) and 24 Agribusiness Incubators (R-ABIs) have been appointed across the country. The five KPs are:
- National Institute of Agricultural Extension Management (MANAGE), Hyderabad.
- National Institute of Agricultural Marketing (NIAM) Jaipur.
- Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) Pusa, New Delhi.
- University of Agriculture Science, Dharwad, Karnataka.
- Assam Agriculture University, Jorhat, Assam.
Way Forward
- With the recent reforms in the agriculture sector, there is a likelihood of increased investments in contract farming and infusion of technology for better yields and productivity.
- This will further push the adoption of AI in agriculture. Further, in order to help these AI solutions, scale increased investments needed, both from the public and private sector.
- A huge surge in the emergence of agritech start-ups is being witnessed in India, driven by advanced technology penetration coupled with a conducive policy environment.
- This can only be seen as a starting point for the penetration of advanced technologies like AI, ML, IoT and Blockchain in the agriculture ecosystem.
- These collective technologies come as a great boon to the agricultural sector which is heavily reliant on unpredictable climatic conditions.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Years Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Q.2 When the alarm of your smartphone rings in the morning, you wake up and tap it to stop the alarm which causes your geyser to be switched on automatically. The smart mirror in your bathroom shows the day’s weather and also indicates the level of water in your overhead tank. After you take some groceries from your refrigerator for making breakfast, it recognises the shortage of stock in it and places an order for the supply of fresh grocery items. When you step out of your house and lock the door, all lights, fans, geysers and AC machines get switched off automatically. On your way to office, your car warns you about traffic congestion ahead and suggests an alternative route, and if you are late for a meeting, it sends a message to your office accordingly. (2018)
In the context of emerging communication technologies, which one of the following terms best applies to the above scenario?
(a) Border Gateway Protocol
(b) Internet of Things
(c) Internet Protocol
(d) Virtual Private Network
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. How is science interwoven deeply with our lives? What are the striking changes in agriculture triggered off by science-based technologies? (2020)
Governance
Rashtriya Gokul Mission
For Prelims: Rashtriya Gokul Mission and related Iinitiatives, Rashtriya Pashudhan Vikas Yojana, Gokul Grams
For Mains: Initiatives to Promote Livestock Sector
Why in News?
Recently, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying announced that employment will be given to more than 50 lakh farmers.
- Under Rashtriya Gokul Mission (RGM) there is a scheme to provide subsidy on cow/buffalo/pig/chicken/goat breeding farms and silage making units of which 50% subsidy will be given by the Government of India. Also, 3% interest subvention on the loan amount can also be taken under the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) scheme.
What is Rashtriya Gokul Mission?
- About:
- It is being implemented for development and conservation of indigenous bovine breeds since December 2014.
- The scheme is also continued under umbrella scheme Rashtriya Pashudhan Vikas Yojna from 2021 to 2026 with a budget outlay of Rs.2400 crore.
- Nodal Ministry:
- Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying
- Objectives:
- To enhance productivity of bovines and increasing milk production in a sustainable manner using advance technologies.
- To propagate use of high genetic merit bulls for breeding purposes.
- To enhance Artificial insemination coverage through strengthening breeding network and delivery of Artificial insemination services at farmers doorstep.
- To promote indigenous cattle & buffalo rearing and conservation in a scientific and holistic manner.
- Significance:
- The RGM will result in enhanced productivity and benefit of the programme, percolating to all cattle and buffaloes of India especially with small and marginal farmers.
- This programme will also benefit women in particular since over 70% of the work involved in livestock farming is undertaken by women.
- Components:
- Availability of High genetic Merit Germplasm
- Extension of Artificial Insemination Network
- Development and Conservation of indigenous Breeds
- Skill Development
- Farmers Awareness
- Research Development and Innovation in Bovine Breeding
- Implementing Agency:
- Rashtriya Gokul Mission will be implemented through the “State Implementing Agency (SIA viz Livestock Development Boards).
- Significant Initiatives:
- Gopal Ratna Awards:
- For farmers maintaining the best herd of Indigenous Breed and practicing best management practices.
- Kamdhenu Awards:
- For best-managed Indigenous herd by Institutions/Trusts/ NGOs/ Gaushalas or best-managed Breeders’ societies.
- Gokul Grams:
- RGM envisages the establishment of integrated cattle development centers, ‘Gokul Grams’ to develop indigenous breeds including up to 40% nondescript breeds (belonging or appearing to belong to no particular class or kind) with objectives to:
- Promote indigenous cattle rearing and conservation in a scientific manner.
- Propagate high genetic merit bulls of indigenous breeds.
- Optimize modern Farm Management practices and promote Common Resource Management.
- Utilize animal waste in an economical way i.e., Cow Dung, Cow Urine.
- Recently, funds have been released for setting up of 16 Gokul Grams.
- RGM envisages the establishment of integrated cattle development centers, ‘Gokul Grams’ to develop indigenous breeds including up to 40% nondescript breeds (belonging or appearing to belong to no particular class or kind) with objectives to:
- National Kamdhenu Breeding Centre (NKBC):
- It is being established as a Centre of Excellence to develop and conserve Indigenous Breeds in a holistic and scientific manner.
- E-Pashu Haat:
- It is a web portal which provides information on pet cattle, trading of bovine animals that were not offered on any other platform in the country.
- Nakul Prajnan Bazaar:
- An e-market portal connecting breeders and farmers, for quality- disease-free bovine germplasm.
- Pashu Sanjivni:
- An animal wellness program encompassing the provision of animal health cards (‘Nakul Swasthya Patra’) along with unique identification and uploading data on National Database.
- Advanced Reproductive Technology (ART):
- Including Assisted Reproductive Technique- IVF/Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer (MOET) and sex-sorted semen technique to improve the availability of disease-free female bovines.
- National Bovine Genomic Center for Indigenous Breeds (NBGC-IB):
- It will be established for selection of breeding bulls of high genetic merit at a young age using highly precise gene-based technology.
- AHIDF Scheme:
- AHIDF of Rs.15000 crore has been set up under Atma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyan stimulus package for incentivizing investments by individual entrepreneurs, private companies, MSME, Farmers Producers Organizations (FPOs) and Section 8 companies to establish:
- the dairy processing and value addition infrastructure,
- meat processing and value addition infrastructure and
- Animal Feed Plant.
- AHIDF of Rs.15000 crore has been set up under Atma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyan stimulus package for incentivizing investments by individual entrepreneurs, private companies, MSME, Farmers Producers Organizations (FPOs) and Section 8 companies to establish:
- Gopal Ratna Awards:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Years Question (PYQ)
Q. Livestock rearing has a big potential for providing non-farm employment and income in rural areas. Discuss suggesting suitable measures to promote this sector in India. (2015)
Indian Economy
SAMARTH Scheme
For Prelims: Handloom, Integrated Skill Development Scheme, Scheme for Integrated Textile Park (SITP), Power-Tex India, Silk Samagra Scheme, Amended Technology Upgradation Fund Scheme (ATUFS), National Handloom Day
For Mains: Growth & Development, Inclusive Growth
Why in News?
Under the SAMARTH Scheme of Textile Ministry, more than 13,235 artisans have been trained in the last three years.
What is the Samarth Scheme all about?
- About:
- Samarth (Scheme for Capacity Building In Textile Sector) is a flagship skill development scheme approved in continuation to the Integrated Skill Development Scheme for 12th Five Year Plan (FYP), Cabinet Committee of Economic Affairs.
- The office of the Development Commissioner (Handicrafts) is implementing the SAMARTH to provide skill training to handicraft artisans under the component ‘Skill Development in Handicrafts Sector’ of National Handicrafts Development Programme (NHDP).
- Objectives:
- To provide demand-driven, placement-oriented skilling programmes to incentivize the efforts of the industry in creating jobs in the organized textile and related sectors to promote skilling and skill up-gradation in the traditional sectors through respective sectoral divisions/organizations of the Ministry of Textile.
- To provide livelihood to all sections of the society across the country.
What is the Status of the Textile Sector in India?
- About:
- Textiles & garments industry is a labour intensive sector that employs 45 millions people in India and is second only to the agriculture sector in terms of employment.
- India’s textiles sector is one of the oldest industries in the Indian economy, and is a storehouse and carrier of traditional skills, heritage and culture.
- It can be divided into two segments:
- The unorganised sector is small scale and uses traditional tools and methods. It consists of handloom, handicrafts and sericulture (Production of silk).
- The organised sector uses modern machinery and techniques and consists of the spinning, apparel and garments segment.
- Other Schemes of the Textile Sector:
- Scheme for Integrated Textile Park (SITP): Launched in 2005, it aims to provide the industry with world-class state of the art infrastructure facilities for setting up their textile units.
- Power-Tex India: It is an all-inclusive scheme that's made for the development of the power loom sector which further addresses the unheard needs of the power loom sector.
- Silk Samagra Scheme: It focuses on improving the quality and productivity of domestic silk thereby reducing the country’s dependence on imported silk.
- Amended Technology Upgradation Fund Scheme (ATUFS): It is a credit linked Capital Investment Subsidy (CIS) scheme to catalyze capital investments for technology upgradation and modernization of the textile industry.
- National Handloom Day: National Handloom Day is observed every year on 7th August to mark the importance of the handloom weaving community in India.
- National Technical Textile Mission: The mission aims to position India as a global leader in Technical Textiles by increasing the domestic market size from USD 40 billion to USD 50 billion by 2024.
Note
- On the occasion of International Women’s Day 2022, the Union Minister for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), launched a Special Entrepreneurship Promotion Drive for Women -"SAMARTH".
- Through this initiative, the Ministry of MSME is focusing on providing Skill Development and Market Development Assistance to women.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Years Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The value of Indo-Sri Lanka trade has consistently increased in the last decade.
- “Textile and textile articles” constitute an important item of trade between India and Bangladesh.
- In the last five years, Nepal has been the largest trading partner of India in South Asia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Indian Economy
State of the Economy Report: RBI
For Prelims: Inflation, Equity Flow, War in Ukraine, Oil Prices, Base Effect, Debt Distress.
For Mains: State of the Economy Report: RBI.
Why in News?
Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has released a report titled- “State of the Economy”, which warns of a darkening global outlook.
What are the Highlights of the Report?
- Darkening Global Outlook:
- The balance of risks gets increasingly tilted towards a darkening global outlook for 2023, the year that will bear the brunt of monetary policy actions of this year.
- Emerging Market Economies:
- Emerging market economies (EMEs) appear precarious, having battled currency depreciations and capital outflows in addition to slowing growth and high inflation.
- Energy Prices:
- An unease hangs over energy prices, for now, Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) plus stayed its hand in cutting production, but an oil price cap threatens to unleash disruptive financial forces, with hedge funds already cutting net long positions in crude contracts.
- Despite moderation in global commodity markets, climate change and the war in Ukraine are set to keep food prices at higher than pre-pandemic levels.
- Debt:
- Debt distress is rising, with a surge in default rates and an appreciating US dollar – the principal currency in which debt is denominated – although more recently it has tumbled down from 20-year highs.
- Indian Growth Outlook:
- Inflation:
- Inflation may be slightly down, but it is certainly not out.
- Inflation is likely to moderate in 2023 from current levels, but it would remain well above targets in most economies.
- The easing of inflation is primarily driven by the sharp moderation in food inflation. The index declined by 11 bps month-on-month (m-o-m), which along with a favorable Base Effect.
- Domestic Drivers:
- The near-term growth outlook for the Indian economy is supported by domestic drivers.
- Domestic economic activity remained resilient in November and early December of 2022.
- The outlook for private consumption and investment is looking up, although relatively higher inflation in rural areas is muting spending in those regions.
- Headline inflation moderated by 90 basis points to 5.9 % in November 2022 driven by a fall in vegetables prices even as core inflation remained steady at 6 %.
- The near-term growth outlook for the Indian economy is supported by domestic drivers.
- Equity Inflow:
- Equity markets touched a string of new highs during November buoyed by strong portfolio flows to India.
- Waning input cost pressures, still buoyant corporate sales and turn-up in investments in fixed assets are heralding the beginning of an upturn in the capex cycle in India which will contribute to a speeding up of growth momentum in the Indian economy.
- Future Prospects:
- In December 2022, as India engages in setting out its priorities and deliverables under its G20 Presidency, there is a sense that perhaps it's time for India in the centre of the world’s stage has arrived.
- As the third largest economy in PPP (Purchasing power parities) terms, and the 5th largest in terms of market exchange rates, India accounts for 3.6 % of G20 GDP while its share in real (PPP) terms is much higher at 8.2 %.
- In 2023, India is projected to be among the fastest growing economies within G20.
- India’s priorities under the G20 Presidency encapsulate a vision of unity and interconnectedness. They will also reflect the priorities of the global South: One Earth, One Family, One Future.
- Inflation:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Years Question (PYQ)
Q.1 The Reserve Bank of India regulates the commercial banks in matters of (2013)
- liquidity of assets
- branch expansion
- merger of banks
- winding-up of banks
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 4 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)
Q.2 With reference to inflation in India, which of the following statements is correct? (2015)
(a) Controlling the inflation in India is the responsibility of the Government of India only
(b) The Reserve Bank of India has no role in controlling the inflation
(c) Decreased money circulation helps in controlling the inflation
(d) Increased money circulation helps in controlling the inflation
Ans: (c)
Q.3 Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The weightage of food in Consumer Price Index (CPI) is higher than that in Wholesale Price Index (WPI).
- The WPI does not capture changes in the prices of services, which CPI does.
- Reserve Bank of India has now adopted WPI as its key measure of inflation and to decide on changing the key policy rates.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Science & Technology
National Mathematics Day
Prelims: Srinivasa Ramanujan, Critical Thinking, UNESCO, Ramanujan number.
Mains: Contributions of Srinivasa Ramanujan, Achievements of Indians in Science & Technology
Why in News?
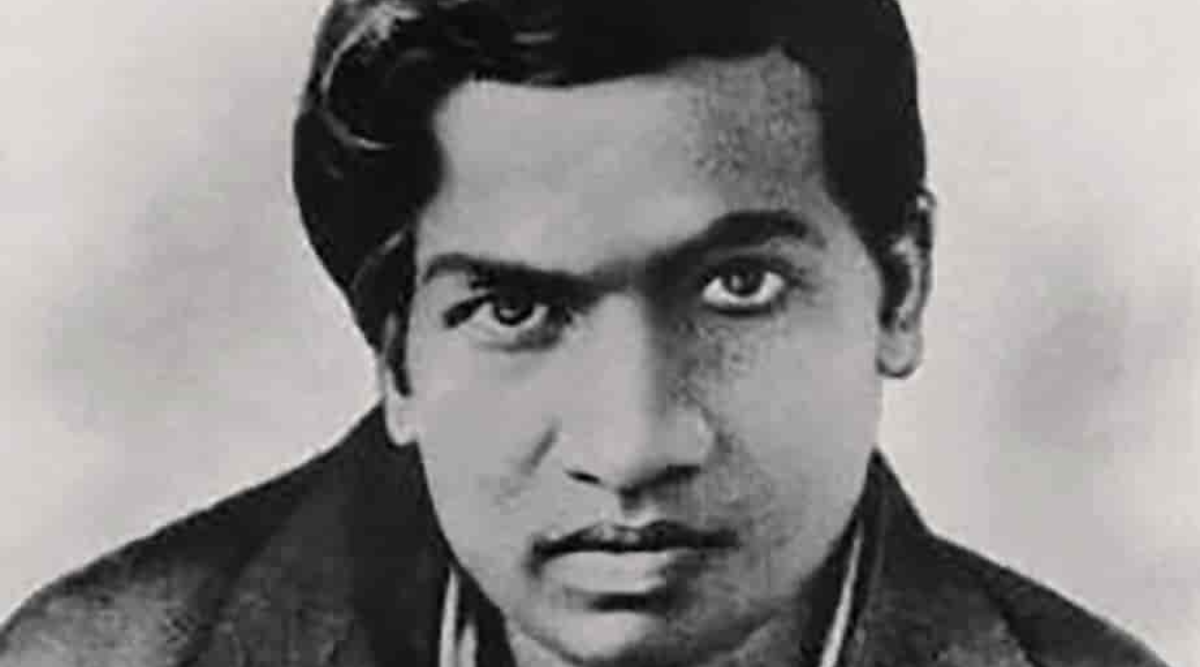
National Mathematics Day (NMD) has been celebrated every year on 22nd December to mark the birth anniversary of Srinivasa Ramanujan.
- On the 125th birth anniversary of Ramanujan, NMD was announced by the then-Indian Prime Minister Manmohan Singh in 2012.
- The day is celebrated annually with the aim to make people aware of the importance of mathematics and advancements and developments made in the field.
Who was Srinivasa Ramanujan?
- About:
- Born on 22nd December, 1887 in Erode, Tamil Nadu.
- In 1903, he secured a scholarship to the University of Madras but lost it the following year because he neglected all other subjects in pursuit of mathematics.
- In 1911, Ramanujan published the first of his papers in the Journal of the Indian Mathematical Society.
- In 1913, he began a correspondence with the British mathematician Godfrey H. Hardy which led to a special scholarship from the University of Madras and a grant from Trinity College, Cambridge.
- In 1918, he was elected to the Royal Society of London.
- Ramanujan was one of the youngest members of Britain's Royal Society and the first Indian to be elected a Fellow of Trinity College, Cambridge University.
- Contributions to Mathematics:
- Formulas and Equations:
- Ramanujan compiled around 3,900 results consisting of equations and identities. One of his most treasured findings was his infinite series for Pi.
- He gave several formulas to calculate the digits of Pi in many unconventional ways.
- Game Theory:
- He discovered a long list of new ideas to solve many challenging mathematical problems, which gave a significant impetus to the development of game theory.
- His contribution to game theory is purely based on intuition and natural talent and remains unrivalled to this day.
- Ramanujan’s Book:
- One of Ramanujan’s notebooks was discovered by George Andrews in 1976 in the library at Trinity College. Later the contents of this notebook were published as a book.
- Ramanujan number:
- 1729 is known as the Ramanujan number.
- It is the smallest number which can be expressed as the sum of two different cubes in two different ways.
- 1729 is the sum of the cubes of 10 and 9 - cube of 10 is 1000 and cube of 9 is 729 adding the two numbers results in 1729.
- 1729 is also the sum of the cubes of 12 and 1, cube of 12 is 1728 and cube of 1 is 1 adding the two results in 1729.
- Other Contributions:
- Ramanujan’s other notable contributions include hypergeometric series, the Riemann series, the elliptic integrals, mock theta function, the theory of divergent series, and the functional equations of the zeta function.
- Death: He died on April 26th, 1920, at the age of 32, just after returning to India after a long illness.
- Formulas and Equations:
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. A recent movie titled The Man Who Knew Infinity is based on the biography of (2016)
(a) S. Ramanujan
(b) S. Chandrasekhar
(c) S.N. Bose
(d) C.V. Raman
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- ‘The Man Who Knew Infinity’ is a movie based on the biography of S. Ramanujan (1887-1920), an Indian mathematician, known for his immense contribution in mathematical analysis. He was a fellow of the Royal Society.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Important Facts For Prelims
Samudrayaan Mission
Why in News?
According to the Ministry of Earth Science, the Samudrayaan Mission is expected to be realised by year 2026.
What is Samudrayaan Mission?
- About:
- The mission is aimed at sending three personnel to 6000-metre depth in a vehicle called ‘MATSYA 6000’ for the exploration of deep-sea resources like minerals.
- ‘MATSYA 6000’ vehicle is being designed and developed by National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT), Chennai under Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- It has an endurance of 12 hours under normal operation and 96 hours in case of emergency for human safety.
- It is India’s first unique manned ocean mission and is a part of the Rs 6000-crores Deep Ocean Mission.
- The mission is aimed at sending three personnel to 6000-metre depth in a vehicle called ‘MATSYA 6000’ for the exploration of deep-sea resources like minerals.
- Significance:
- The manned submersible will allow scientific personnel to observe and understand unexplored deep-sea areas by direct intervention.
- It will also boost the Central government's vision of 'New India' that highlights the Blue Economy as one of the ten core dimensions of growth.
- India has a unique maritime position, a 7517 km long coastline, which is home to nine coastal states and 1,382 islands.
- For India, with its three sides surrounded by the oceans and around 30% of the nation's population living in coastal areas and coastal regions play a major economic factor.
- It supports fisheries and aquaculture, tourism, livelihoods, and blue trade.
What is the Deep Ocean Mission?
- It was approved in June 2021 by the Ministry of Earth Sciences. It aims to explore the deep ocean for resources, develop deep-sea technologies for sustainable use of ocean resources, and support the Blue Economy Initiatives of the Indian Government.
- The cost of the Mission has been estimated at Rs. 4,077 crores over a five-year period and will be implemented in phases.
What are the Other Related Initiatives?
- India-Norway Task Force on Blue Economy for Sustainable Development: It was inaugurated jointly by both the countries in 2020 to develop and follow up joint initiatives between the two countries.
- Sagarmala Project: The Sagarmala project is the strategic initiative for port-led development through the extensive use of IT enabled services for modernization of ports.
- O-SMART: India has an umbrella scheme by the name of O-SMART which aims at regulated use of oceans, marine resources for sustainable development.
- Integrated Coastal Zone Management: It focuses on conservation of coastal and marine resources, and improving livelihood opportunities for coastal communities etc.
- National Fisheries Policy: India has a National Fisheries policy for promoting 'Blue Growth Initiative' which focuses on sustainable utilization of fisheries wealth from marine and other aquatic resources.
Important Facts For Prelims
BF.7 Variant of the Coronavirus
Why in News?
The current surge in Covid-19 infections in China, is believed to be driven by the BF.7 sub-variant of Omicron that is circulating over there.
What is the BF.7 Variant of Coronavirus?
- The dominant virus strain in China is BF.7, a sub-variant of Omicron that has been in circulation for over a year now.
- There are over 500 Omicron sub-variants currently in circulation.
- BF.7 is the name for the BA.5.2.1.7, which itself has evolved from the BA.5 sub-variant.
- BF.7 is not unique to China.
- It accounted for over 5% of the cases in the US in October, 2022 and over 7% of the cases in the UK.
- When viruses mutate, they create lineages and sub-lineages— like the main trunk of the SARS-CoV-2 tree sprouting branches and sub-branches.
- A research study reported that the BF.7 sub-variant has a 4.4-fold higher neutralisation resistance than the original D614G variant— meaning that in a lab setting, antibodies from a vaccinated or infected individual were less likely to destroy BF.7 than the original Wuhan virus that spread worldwide in 2020.
- A higher neutralisation resistance means there is a higher likelihood of the variant spreading in a population and replacing other variants.
How are New Variants Formed?
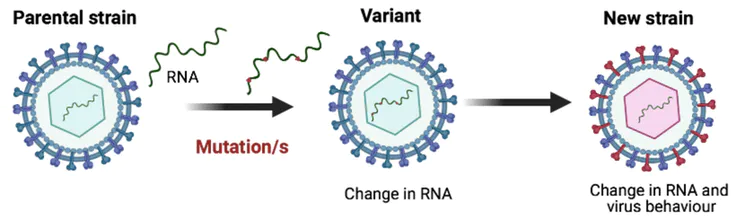
- When a virus multiplies, it doesn’t always manage to produce an exact copy of itself.
- This means that, over time, the virus may start to differ slightly in terms of its genetic sequence.
- Any changes to the viral genetic sequence during this process is known as a Mutation.
- Viruses with new mutations are sometimes called Variants. Variants can differ by one or multiple mutations.
- When a new variant has different functional properties to the original virus and becomes established in a population, it is sometimes referred to as a New Strain of the virus.
- All strains are variants, but not all variants are strains.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Years Question (PYQ)
Q. In the context of vaccines manufactured to prevent COVID-19 pandemic, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Serum Institute of India produced COVID-19 vaccine named Covishield using mRNA platform.
- Sputnik V vaccine is manufactured using vector-based platform.
- COVAXIN is an inactivated pathogen-based vaccine.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- COVISHIELD vaccine is based on the platform which uses a recombinant, replication-deficient chimpanzee adenovirus vector encoding the SARS-CoV-2 Spike (S) glycoprotein. Following administration, the genetic material of part of coronavirus is expressed which stimulates an immune response. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Sputnik V is the world's first registered vaccine based on a well-studied human adenovirus vector platform. It has been approved for use in 71 countries with a total population of 4 billion people. The vaccine is named after the first Soviet space satellite. The vaccine’s efficacy is 97.6%, based on the analysis of data on the incidence of coronavirus among Russians vaccinated with both vaccine components between December 5, 2020 and March 31, 2021. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Covaxin is an inactivated viral vaccine. This vaccine is developed with Whole-Virion Inactivated Vero Cell-derived technology. They contain inactivated viruses, which cannot infect a person but still can teach the immune system to prepare a defence mechanism against the active virus. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- Hence, option (b) is correct.
Important Facts For Prelims
Three Sites in Tentative List of World Heritage Sites
Why in News?
Recently, three sites- Gujarat’s Vadnagar town and the iconic Sun Temple at Modhera, and the Rock-cut Sculptures of Unakoti in Tripura have been added to the tentative list of United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) World Heritage Sites.
What are the Key Facts about Three Sites?
- Vadnagar:
- It is located in the Mehsana district in Gujarat is a city with deep historical roots.
- Also called Chamatkarpur, Anandpur, Snehpur and Vimalpur, the city of Vadnagar was mentioned in the Puranas as well.
- Home to many archaeological treasures, Vadnagar is famous for its torans, a pair of 12th century Solanki-era columns, 40 feet tall and built in red and yellow sandstone to celebrate a war victory.
- In 640 AD, Chinese Buddhist traveller, Hiuen Tsang visited the city, and is said to have mentioned it in his travelogue.
- During excavations in 2008-09, ruins of a Buddhist monastery were also unearthed in Vadnagar.
- Vadnagar is home to Tanariri Performing Arts College, named so to honour the valour of two sisters, Tana and Riri, who had sacrificed their lives when asked by Akbar to sing in his court, which was against their custom.
- It is located in the Mehsana district in Gujarat is a city with deep historical roots.
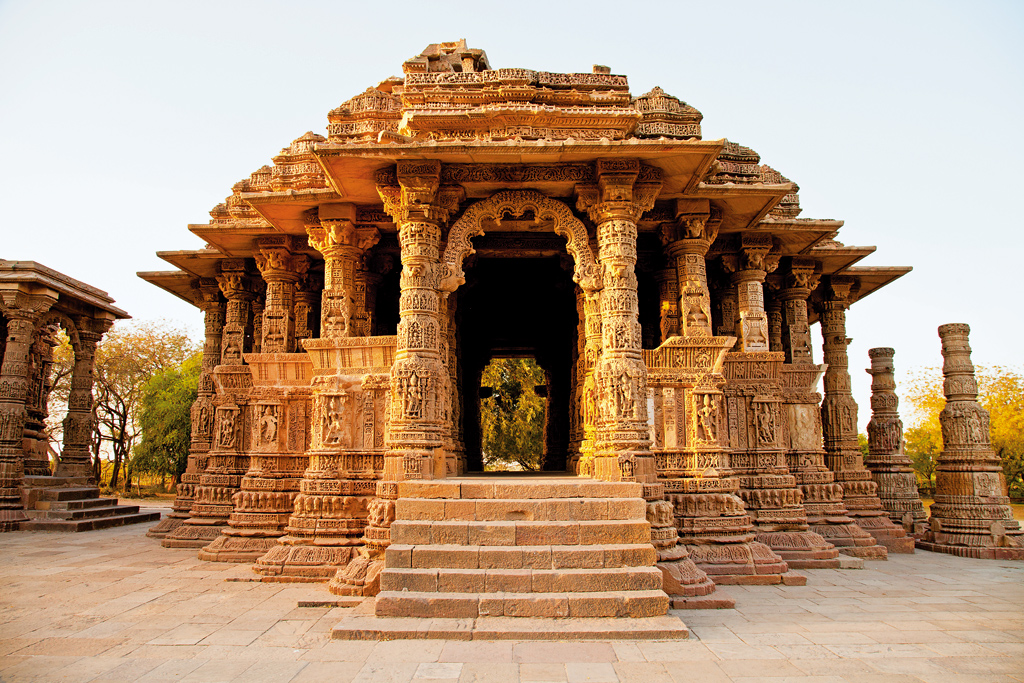
- Modhera Sun Temple:
- The Sun Temple at Modhera is located on the left bank of the river Pushpavati, a tributary of river Rupan in Becharaji taluka of Mehsana district.
- The temple description states that it is built in Maru-gurjara architectural style, consists of the main temple shrine (garbhagriha), a hall (gadhamandapa), an outer hall or assembly hall (Sabhamandapa or rangamandapa) and a sacred pool (Surya Kunda), which is now called Ramakunda.
- Ramakunda is a massive rectangular stepped tank perhaps the grandest temple tank in India.
- Every year, at the time of the equinoxes, the sun shines directly into this central shrine of the temple.
- Rock-cut Sculptures of Unakoti:
- It is Shaivite pilgrimage and dates back to 7th or 9th century if not earlier.
- Unakoti means one less than a crore and it is said that these many rock cut carvings are available here.

- As per Hindu mythology, when Lord Shiva was going to Kashi along with one crore gods and goddesses, he made a night halt at this location.
- He asked all the gods and goddesses to wake up before sun rise and proceed for Kashi.
- It is said that in the morning, except Shiva himself, no one else could get up so Lord Shiva set out for Kashi himself cursing the others to become stone images.
- As a result, we have one less than a crore stone images and carvings at Unakoti.
- The images found at Unakoti are of two types, namely rock-carved figures and stone images.
- Among the rock cut carvings, the central Shiva head and gigantic Ganesha figures deserve special mention.
- The central Shiva head is known as ‘Unakotiswara Kal Bhairava’.
- On each side of the head-dress of the central Shiva, there are two full size female figures – one of Durga standing on a lion and another female figure on the other side.
- In addition, three enormous images of Nandi Bull are found half buried in the ground.
- Among the rock cut carvings, the central Shiva head and gigantic Ganesha figures deserve special mention.
- Every year a big fair popularly known as ‘Ashokastami Mela’ is held in the month of April which is visited by thousands of pilgrims.
What is UNESCO’s Tentative List?
- UNESCO’s tentative list is an inventory of properties which each state party intends to consider for nomination.
- As per Operational Guidelines, 2019 of UNESCO, it is mandatory to put any monument/site on the tentative list for one year before it is considered for the final nomination dossier.
- Once the nomination is done, it is sent to the World Heritage Centre (WHC).
- India now has now 52 sites on the tentative list.
What is World Heritage Site?
- World Heritage Site refers to any of various areas or objects inscribed on the UNESCO’s World Heritage List.
- The sites are designated as having “outstanding universal value” under the Convention Concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage 1972.
- It provides a framework for international cooperation in preserving and protecting cultural treasures and natural areas throughout the world.
- There are three types of sites: Cultural, Natural, and Mixed.
- Cultural heritage sites include hundreds of historic buildings and town sites, important archaeological sites, and works of monumental sculpture or painting.
- Natural heritage sites are restricted to those natural areas that have excellent ecological and evolutionary processes, unique natural phenomena, habitats of rare or endangered species etc.
- Mixed heritage sites contain elements of both natural and cultural significance.
- India has 40 world heritage sites, including 32 cultural properties, 7 natural properties and 1 mixed site. The latest one included are Harappan city of Dholavira and Kakatiya Rudreshwara (Ramappa) Temple.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q1. Which one of the following statements is correct? (2021)
(a) Ajanta Caves lie in the gorge of Waghora river.
(b) Sanchi Stupa lies in the gorge of Chambal river.
(c) Pandu-lena Cave Shrines lie in the gorge of Narmada river.
(d) Amaravati Stupa lies in the gorge of Godavari river.
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Ajanta is a series of rock-cut caves in the Sahyadri ranges (Western Ghats) on Waghora river near Aurangabad in Maharashtra. There are a total of 29 caves (all Buddhist) of which 25 were used as Viharas or residential caves while 4 were used as Chaitya or prayer halls. This UNESCO World Heritage Site is a collection of paintings, sculptures and temples of Buddhist art, constructed from 200 BC to 500 AD. India’s best-preserved group of Buddhist monuments, known as Sanchi Stupa, is located in west-central Madhya Pradesh. It lies in an upland plateau region, just west of the Betwa River and about 5 miles (8 km) southwest of Vidisha. It was designated a UNESCO World Heritage site in 1989.
- The Buddhist monument Pandavleni Caves, also known by the name Pandu Lena caves and Trirashmi caves are a group of 24 rock-cut caves. They are located on the north face of Trivashmi hill of Nasik city. Nasik city is situated on the banks of river Godavari.
- Amravati Stupa illustrates Lord Buddha in a human form, subduing an elephant. The stupa is taller than the Sanchi stupa and has high platforms, extending in the four cardinal directions, along with a huge circular dome. Amravati Stupa is situated near river Krishna.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Q2. Consider the following pairs: (2019)
| Famous Place | River | |
| 1. | Pandharpur | Chandrabhaga |
| 2. | Tiruchirappalli | Cauvery |
| 3. | Hampi | Malaprabha |
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Pandharpur is a holy place of Shri Vitthal and Shri Rukmini. It is also known as the Southern Kashi of India and Kuldaivat of Maharashtra State. The Chandrabhaga (Bhima) river flows through the city. Hence, pair 1 is correctly matched.
- Tiruchirappalli, situated on the banks of the river Cauvery, is the fourth largest city in Tamil Nadu. It was a citadel of the early Cholas which later fell to the Pallavas. Hence, pair 2 is correctly matched.
- Hampi is a UNESCO World Heritage Site in India located near Hospet town in the Karnataka State. It is situated on the southern bank of the Tungabhadra River. Hence, pair 3 is not correctly matched.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.