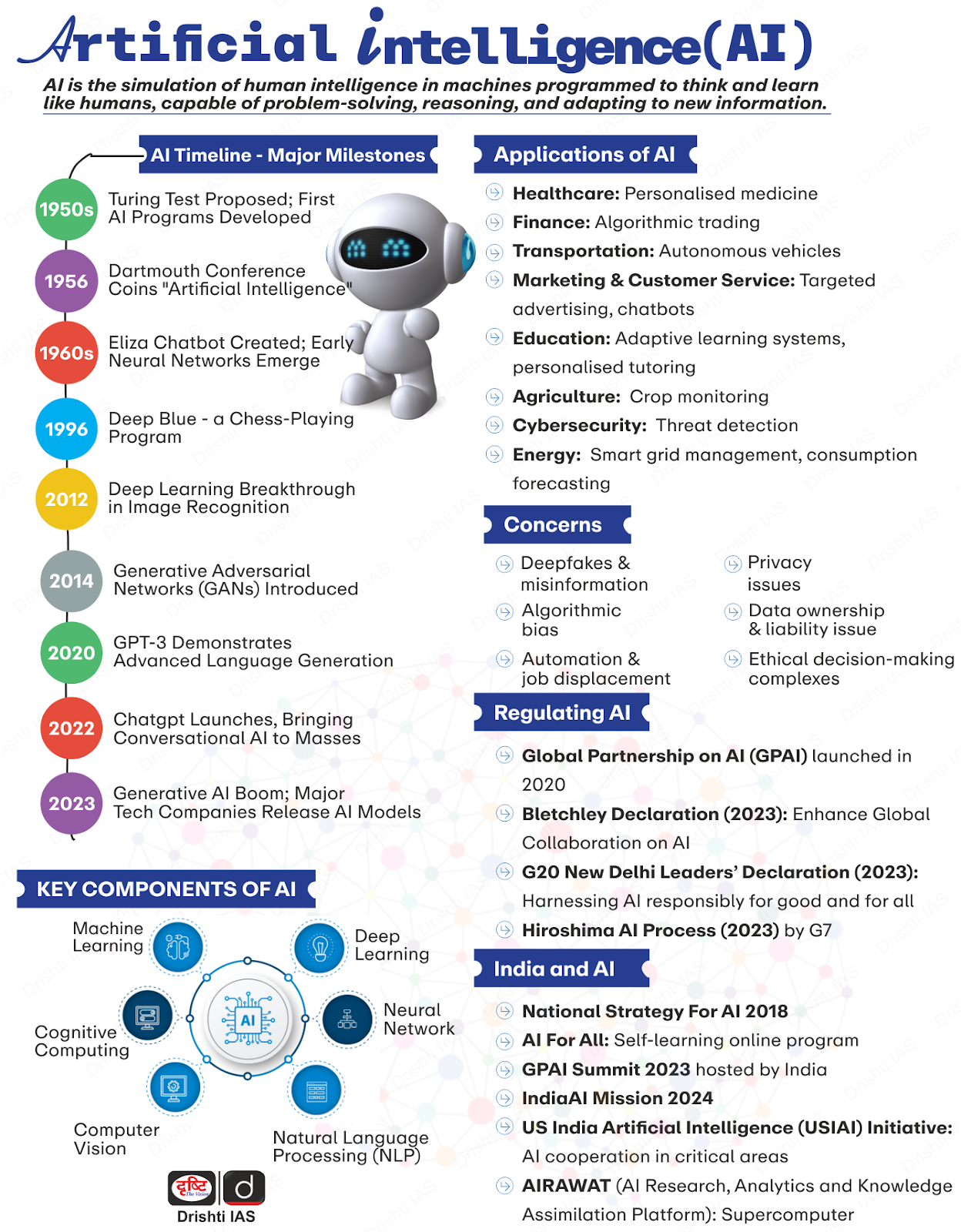
India-Qatar Strategic Partnership
For Prelims: Gulf Cooperation Council, Liquefied Natural Gas, Gulf, Za’ir-Al-Bahr
For Mains: India-Qatar Bilateral Relations, Mutual significance of India and Qatar, India’s Role in West Asia
Why in News?
Sheikh Tamim Bin Hamad Al Thani, the Amir of Qatar, visited India to enhance bilateral ties, focusing on trade, energy, and investment.
- Both nations committed to doubling trade to USD 28 billion and increasing Qatari investment in India.
What are the Key Highlights of the Visit?
- Elevation to Strategic Partnership: Qatar and India have upgraded their bilateral relations to a strategic partnership, aiming to deepen cooperation in various sectors, including trade, investment, energy, and security.
- Target for Bilateral Trade: India and Qatar have set an ambitious target to double bilateral trade from USD 14 billion to USD 28 billion by 2030.
- Qatar’s Investment Commitment: Qatar’s sovereign wealth fund has invested USD 1.5 billion in India and committed an additional USD 10 billion in sectors like infrastructure, renewable energy, and emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning.
- Avoidance of Double Taxation: A Revised Agreement for Avoidance of Double Taxation was also exchanged, which will foster economic and financial collaboration.
- Status of a Free Trade Agreement (FTA): Both nations discussed the possibility of a FTA.
- Negotiations are ongoing for an FTA between India and the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), which includes Qatar.
- Infrastructure: Discussed the operationalization of India’s Unified Payment Interface (UPI) in Qatar and the expansion of Qatar National Bank’s presence in India through GIFT (Gujarat International Finance Tec-City) City.
- Israel-Palestinian Conflict: India reaffirmed its support for a two-state solution.
Why is Qatar Important for India?
- Energy Cooperation: In FY 2022-23, Qatar was India's largest Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) supplier, providing over 48% of total LNG imports, and the top liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) supplier, accounting for 29% of LPG imports.
- This stable and uninterrupted energy partnership is vital as India transitions to cleaner energy sources and reduces reliance on coal, helping meet both climate goals and growing energy demands.
- Strategic Cooperation: Qatar is a key partner in India’s Look West policy (converted to "Link and ACT West"), strengthening ties with the GCC countries, including the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Oman, and Kuwait, to enhance energy security and trade.
- Geopolitical Significance: Qatar's role as a mediator in key geopolitical issues, like Afghanistan and the Israel-Palestine conflict, allows India to engage in regional matters indirectly.
- Qatar's close ties with the US on Middle East peace efforts, also offer India a platform for engagement with the US on regional issues.
- Counterterrorism Cooperation: India and Qatar share common interests in combating terrorism and extremism, with Qatar's strategic location enabling India's collaboration on counterterrorism and maritime security in the Gulf (as the Gulf region fulfilled 55.3% of India's total crude oil demand in 2022–23).
India-Qatar Bilateral Relations
- Defense Cooperation: India-Qatar defense ties include training, naval visits, biennial Doha International Maritime Defence Exhibition and Conference (DIMDEX) participation, and the bilateral maritime exercise Za’ir-Al-Bahr (Roar of the Sea).
- Trade: Bilateral trade between India and Qatar in 2023-24 stood at USD 14.08 billion, with India's exports at USD 1.7 billion and imports at USD 12.3 billion.
- India is among the top three largest export destinations for Qatar (along with China and Japan) and among the top three sources of Qatar’s imports (along with China and the US).
- Qatar primarily exports LPG, LNG, chemicals, petrochemicals, and aluminium to India, while India exports a variety of goods, including cereals, iron, steel, textiles, and machinery.
- Investment: Over 15,000 Indian companies operate in Qatar, with USD 450 million invested by Indian firms.
- Cultural Cooperation: Regular cultural exchanges occur under the 2012 Cultural Cooperation Agreement, with Qataris admiring India's diversity. The year 2019 was celebrated as India-Qatar Year of Culture.
- Indian Community: Over 835,000 Indians reside in Qatar, forming the largest expatriate community (27% of the population).
|
Drishti Mains Question: How do India’s engagements with Qatar and other Gulf countries align with its "Link and Act West" policy? Evaluate the role of West Asia in India’s economic and strategic interests. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Prelims
Q. Which of the following is not a member of ‘Gulf Cooperation Council’? (2016)
(a) Iran
(c) Oman
(b) Saudi Arabia
(d) Kuwait
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. The question of India’s Energy Security constitutes the most important part of India’s economic progress. Analyse India’s energy policy cooperation with West Asian countries. (2017)
Microfinance Sector in India
For Prelims: Microfinance Institutions (MFIs), Financial Inclusion, SHGs, Co-operative Societies, Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS), Companies Act, 2013, NBFC-MFIs, Reserve Bank of India
For Mains: Significance of microfinance institutions in financial inclusion, poverty alleviation, and sustainable economic development in India.
Why in News?
The microfinance sector in India has played a pivotal role in financial inclusion by providing credit to underserved households. However, rising concerns over credit expansion underscore the need for stronger regulations and responsible lending.
What are Microfinance Institutions (MFI)?
- About:
- MFIs are financial companies that provide small loans and other financial services to people who don't have access to banking facilities.
- Objective:
- It aims to empower low-income and unemployed individuals by fostering self-sufficiency.
- It plays a crucial role in financial inclusion, particularly benefiting marginalized groups, including women, by promoting social equity and economic empowerment.
- Regulatory Framework: The RBI regulates MFIs under the NBFC-MFI framework (2014), which covers client protection, borrower safeguards, privacy, and credit pricing.
- Business Models in Microfinance: Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and Microfinance Institutions (MFIs)
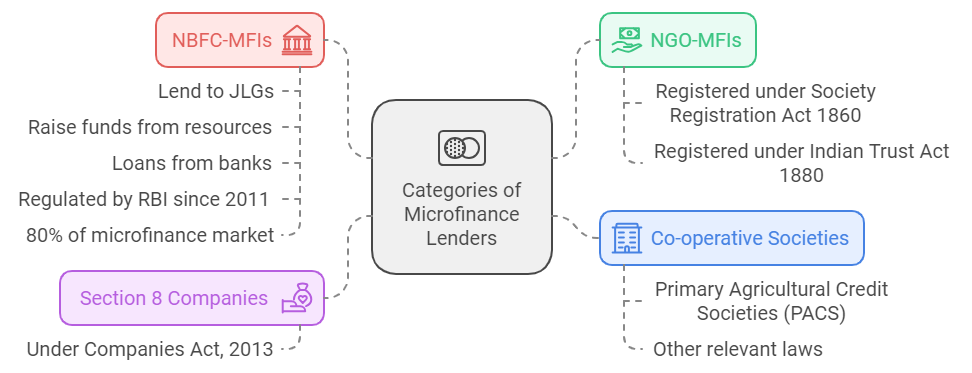
- Categories of Microfinance Lenders:
- MFIs in India:
- As of 31st March 2024, India's microfinance sector comprises 168 MFIs across 29 states, 4 UTs, and 563 districts, serving over 3 crore clients with a loan portfolio of Rs 4.33 lakh crore.
What are the Challenges for Microfinance Institutions (MFIs)?
- Profitability and Economic Sustainability: MFIs rely on subsidies, face high operating costs, and limited capital access. Most MFIs cover costs but only a third are truly profitable after capital expenses.
- To cover costs, they charge high interest rates, which can burden borrowers.
- Regulatory Gaps: The RBI framework mandates household income and liability assessments, but lack of documentary proof and delayed credit bureau data hinder accurate evaluation, especially by unregulated lenders.
- Rising Competition: More regulated and unregulated players in the sector have increased credit supply, sometimes without stringent due diligence.
- Poor Model Selection: MFIs in India mainly use the SHG or JLG lending models whose effectiveness is often questioned and also their selection is often random rather than scientific reasoning.
- The choice of the lending model impacts the repayment burden on weaker sections and affects the long-term sustainability of MFIs.
- Gender Bias: Women face significant barriers in accessing financial services and are 15-20% less likely than men to have a bank account or access formal credit.
- However, studies indicate that women have a 17% higher loan repayment rate compared to men.
RBI Guidelines on Microfinance Lending (2022)
- Microfinance loans are collateral-free for households with annual incomes up to Rs 3 lakh.
- Lenders must ensure flexible repayment policies and assess household income.
- The cap on the number of lenders per borrower is removed, but loan repayments cannot exceed 50% of monthly income.
- The requirement for NBFC-MFIs to maintain 75% of their loan portfolio in microfinance (reduced from 85%).
- Entities must report income discrepancies and household income details.
- No prepayment penalties; late fees apply only to overdue amounts.
What are the Government Schemes Related to Microfinance?
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY)
- Self-Help Group (SHG) - Bank Linkage Program
- Credit Guarantee Fund for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE)
What are the Proposed Reforms for Sustainable Growth of the Microfinance Sector in India?
- Strengthening Credit Assessment: Establish a standardized household income evaluation model and enhance real-time liability tracking by increasing credit bureau data uploads from fortnightly to weekly.
- Enhancing Borrower Identification: Mandate Aadhaar-based KYC for MFIs to prevent credit duplication and ensure accurate liability assessment.
- Expand credit bureau participation to include all institutional lenders (both regulated and unregulated) for greater transparency.
- Adopt Need-based Lending Models: MFIs should choose lending models based on borrower needs rather than relying only on SHG or JLG.
- MFIs should expand beyond credit to include savings, insurance, and micro-investments, ensuring broader financial inclusion and reduced credit dependency.
- Gender-Inclusive Financing: Promote gender-inclusive financial policies by improving women's access to banking and credit.
- Robust Impact Assessment: Conduct comprehensive and unbiased evaluations of microfinance interventions to accurately measure their effectiveness in poverty alleviation and ensure data-driven policy improvements.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What are the key challenges for microfinance institutions in India, and how can they be mitigated? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Microfinance is the provision of financial services to people of low-income groups. This includes both the consumers and the self-employed. The service/ services rendered under microfinance is/are (2011)
- Credit facilities
- Savings facilities
- Insurance facilities
- Fund Transfer facilities
Select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q. Can the vicious cycle of gender inequality, poverty and malnutrition be broken through microfinancing of women SHGs? Explain with examples. (2021)
10th Anniversary of Soil Health Card Scheme
For Prelims: Soil Health Card (SHC) Scheme, Rabi, Kharif, Organic Carbon (OC), Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY), Green Revolution, Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs), Gram Panchayats.
For Mains: Role of soil health card Scheme in maintaining soil health and increasing agricultural productivity
Why in News?
The year 2025 marks the 10th anniversary of the Soil Health Card (SHC) scheme that was launched on 19th February 2015 at Suratgarh, Rajasthan.
- It helps in improving soil health and tackling soil degradation.
What is a Soil Health Card Scheme?
- About: It is a centrally sponsored scheme to assist state governments in issuing Soil Health Cards (SHCs) to all farmers across India.
- Objective: It provides farmers with information on the nutrient status of their soil along with recommendations for the appropriate dosage of nutrients to improve soil health and fertility.
- Soil samples are collected twice a year, post-harvest of Rabi and Kharif crops or when no standing crop is in the field.
- Contents of SHC: The SHC provides soil status for 12 parameters, including:
- Macronutrients: Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), Potassium (K), Sulphur (S).
- Micronutrients: Zinc (Zn), Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu), Manganese (Mn), Boron (Bo).
- Other soil properties: pH (Acidity or Basicity), Electrical Conductivity (EC), and Organic Carbon (OC).
- Initiatives Under SHC:
- Village Level Soil Testing Labs (VLSTLs): VLSTLs are small, decentralized soil testing labs at local level. As of February 2025, 665 VLSTLs have been set up across 17 states.
- School Soil Health Programme: It aims to educate students on soil health and sustainability through sample collection, testing, and SHC generation.
- As of 2024, the program expanded to 1,020 schools, establishing 1,000 soil testing labs.
- Integration with RKVY: Since 2022-23, the Soil Health Card Scheme has been merged into Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY) as a component under ‘Soil Health & Fertility’.
- RKVY (2007) is an umbrella scheme for ensuring holistic development of agriculture and allied sectors.
- Technological Advancements:
- SHC Portal: For uniform generation of SHCs in all major Indian languages and five dialects.
- SHC Mobile App: For easy access to Soil Health Cards and streamline sample collection.
- GIS Integration: Automatic geo-mapping of soil samples using latitude and longitude so that all the test results are captured and seen on a map.
- Benefits of SHC:
- Improved Yield: The highest increase in yield was recorded for Bengal gram (44%) in Karnataka, followed by wheat (43%) in Karnataka, maize (30%) in Madhya Pradesh, and red gram (22%) in Maharashtra.
- Reduction in Fertilisers Use: Significant reduction in fertilizer use e.g.,nitrogen (7%), phosphorus (41%), potassium (27%) has been observed in case of wheat.
- Reduction in Pest: Pest and disease incidence reduced by 46%.
- Other Benefits: It included improved soil texture (12%), enhanced crop growth (38%), and better grain filling (35%).
|
Read more: Major Soil Types in India |
What is the Current Status of Soil Health in India?
- Unsustainable Agricultural Practices: Intensive farming, with excessive chemicals and monocropping, has caused nutrient depletion and soil acidification.
- E.g., lowered organic carbon levels in Punjab and Haryana due to the Green Revolution.
- Water Mismanagement: Over-extraction and poor irrigation, like flood irrigation, cause soil salinization and waterlogging.
- By 2050, 50% of arable land may be salt-affected.
- Overgrazing: Unregulated livestock grazing has led to vegetation loss, making soil vulnerable to erosion, particularly in arid regions like Rajasthan and Gujarat.
- Shifting Cultivation: The practice of slash-and-burn agriculture causes severe soil degradation by destroying organic matter.
- Invasive Species: The spread of invasive plant species like Lantana camara depletes soil nutrients and disrupts native biodiversity.
Way Forward
- Farmer Education: Only 57% of the farmers whose soils were tested were aware of the SHC scheme.
- Training, demos, and workshops by state agricultural universities (SAUs), and krishi vigyan kendras (KVKs) are needed for awareness.
- Enhancing Soil Testing Infrastructure: There is a need to establish at least one Soil Testing Laboratory (STL) per taluka to improve accessibility and efficiency.
- Timely Distribution of SHCs: The government must ensure that SHCs are distributed promptly, preferably in hard copy before sowing.
- Reduced time lag between soil data collection and distribution of SHC will help farmers apply recommended fertilizer doses in a timely manner.
- Installation of Israel’s Plantarray technology can be introduced that can provide real-time soil data using sensors and boosting information about soil profile.
- Incentives: Incentives and awards for farmers, Gram Panchayats, and officers promoting soil testing can boost participation.
- Recognition for green manure, vermicomposting, and organic farming will enhance soil fertility.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What is the Soil Health Card (SHC) Scheme? Discuss its objectives and significance in sustainable agriculture. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2017)
The nation-wide ‘Soil Health Card Scheme’ aims at
- expanding the cultivable area under irrigation.
- enabling the banks to assess the quantum of loans to be granted to farmers on the basis of soil quality.
- checking the overuse of fertilizers in farmlands.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Sikkim is the first ‘Organic State’ in India. What are the ecological and economical benefits of Organic State? (2018)
China’s EAST Reactor and Nuclear Fusion
For Prelims: Tokamak, Nuclear fusion, Difference between Nuclear Fusion & Nuclear Fission.
For Mains: Advantages of Nuclear Fusion, Challenges in Harnessing Nuclear Energy
Why in News?
China’s Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) nuclear fusion reactor set a new milestone in nuclear fusion by sustaining plasma at 100 million°C for 1,066 seconds.
- This achievement advances the pursuit of clean and sustainable fusion energy for future energy security.
Tokamak: A tokamak is an experimental device designed to generate energy through nuclear fusion.
- Inside the tokamak, the heat produced from the fusion of atoms is absorbed by the vessel’s walls.
- Similar to conventional power plants, this heat is then used to produce steam, which drives turbines and generators to generate electricity.
What is Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST)?
- About:
- EAST is an advanced nuclear fusion research facility located at the Institute of Plasma Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (ASIPP) in Hefei, China.
- It became operational in 2006.
- Purpose:
- It aims to replicate the nuclear fusion process that powers the Sun, contributing to the development of sustainable energy (without any harmful radioactive waste).
- It is a part of the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) initiative, which will be the world's largest fusion reactor when operational by 2035.
- The ITER, established in 1985, is a collaboration of 35 nations located in France. It aims to build the world’s largest tokamak to demonstrate the feasibility of fusion as a large-scale, carbon-free energy source.
- Its members include China, the European Union, India, Japan, Korea, Russia and the US.
- Working Mechanism:
- EAST is based on the nuclear fusion process, where deuterium and tritium nuclei (isotopes of hydrogen) fuse to form a helium nucleus, releasing a large amount of energy.
- Hydrogen fuel is heated to over 150 million°C to form a hot plasma (ionized gas).
- A strong magnetic field confines the plasma, preventing heat loss and enabling sustained fusion reactions.
- Achievements & Significance:
- EAST has achieved significant milestones such as sustaining plasma at 50 million°C for over 60 seconds (2016) and 100 seconds (2017), achieving steady-state high-confinement plasma for 403 seconds (2023).
- Despite these, EAST has yet to achieve ignition (self-sustaining fusion) or produce electricity.
- It serves as a testbed for ITER, a multinational project, including India and the EU, aimed at developing a tokamak capable of achieving net energy gain.
What are Nuclear Reactions?
- About: A nuclear reaction is an interaction between two nuclear particles or two nuclei that results in the formation of new nuclei different from the original ones.
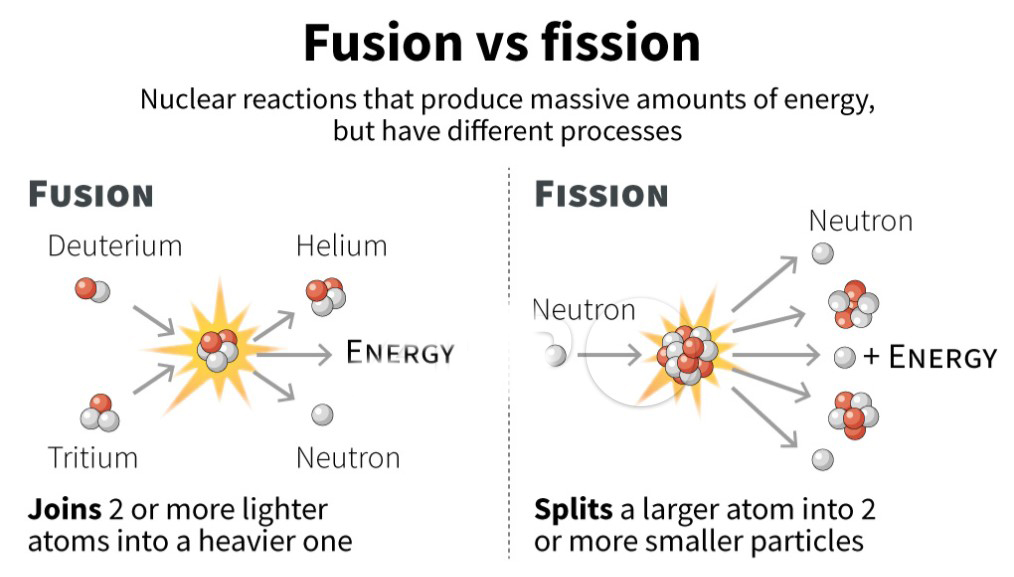
- Nuclear reactions can be classified into two main types: nuclear fission and nuclear fusion.
- Nuclear Fission: It is a reaction that occurs when an atom's nucleus splits into smaller nuclei, releasing energy.
- It can occur naturally (radioactive decay) or be induced in a lab by bombarding the nucleus with neutrons or other particles.
- The combined mass of the resulting fragments is less than the original nucleus, with the lost mass converted into energy.
- All commercial nuclear reactors operate on nuclear fission.
- Nuclear Fusion: It is the process where two light atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier one, releasing massive energy.
- This reaction occurs in plasma state (high-temperature & charged state of matter).
- The Sun and other stars are powered by fusion, requiring temperatures of around 10 million°C to overcome electrical repulsion between nuclei.
- The hydrogen bomb operates on thermonuclear fusion, with a fission bomb (uranium/plutonium-based) providing the initial energy to trigger the reaction.
What are the Challenges in Achieving Nuclear Fusion Reaction?
- Extreme Temperature Requirements: Fusion requires temperatures exceeding those found at the Sun’s core (over 100 million degrees Celsius) to sustain fusion reaction.
- Magnetic Confinement: Maintaining the high-energy plasma in a stable state requires strong magnetic fields, as used in tokamak reactors, to prevent energy loss and sustain reactions.
- Tritium Scarcity: While deuterium is readily available in seawater, tritium is scarce and primarily obtained from specific nuclear fission reactions, raising concerns about long-term fuel supply.
- Current sources of tritium include heavy-water reactors in Canada, India, and South Korea, but ITER’s demands could exhaust global reserves.
- Ignition Milestone: A self-sustaining fusion reaction, where energy output exceeds energy input, remains a major goal yet to be achieved.
- Sustained Reactions: Currently, maintaining stable plasma conditions for prolonged periods remains a major challenge.
Alternative Approaches to Fusion Energy: Apart from tokamaks, researchers are exploring other fusion methods.
- Stellarators: It offers a complex yet promising magnetic confinement method that eliminates the need for a poloidal field (a kind of magnetic field) in tokamak, though they are harder to build.
- Laser Inertial Fusion: It involves the use of high-power laser beams to compress a deuterium-tritium pellet, triggering fusion. The energy released can generate steam to drive turbines, producing electricity.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the role of nuclear energy in achieving global decarbonization goals. What are the key advantages and challenges associated with nuclear energy as a clean energy source? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. The function of heavy water in a nuclear reactor is to (2011)
(a) Slow down the speed of neutrons
(b) Increase the speed of neutrons
(c) Cool down the reactor
(d) Stop the nuclear reaction
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. With growing energy needs should India keep on expanding its nuclear energy programme? Discuss the facts and fears associated with nuclear energy. (2018)
Pliosaur Skull
A massive pliosaur skull (lived 145 million years ago) has been discovered embedded in the Jurassic Coast cliffs in Dorset, England.
- The skull was discovered on a cliff near Kimmeridge Bay along the Jurassic Coast, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- The Jurassic Coast, on England’s southern coast, is one of the world's most renowned fossil hotspots.
- The skull has a prominent cranial crest, an elongated jawline, and a bite force stronger than that of a Tyrannosaurus rex.
- Tyrannosaurus. rex was a large carnivorous dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period (68–66 million years ago).
- Pliosaurs were top predators of the Jurassic oceans and among the deadliest marine reptiles in history.
- Jurassic oceans refer to the vast marine environments that existed during the Jurassic period (199.6 million to 145.5 million years ago).
- Possible sensory pits and a parietal eye suggest advanced hunting adaptations, similar to modern crocodiles.
Read More: Dinosaurs and UNESCO Global Geoparks Tag
Reappearance of South American Tapir
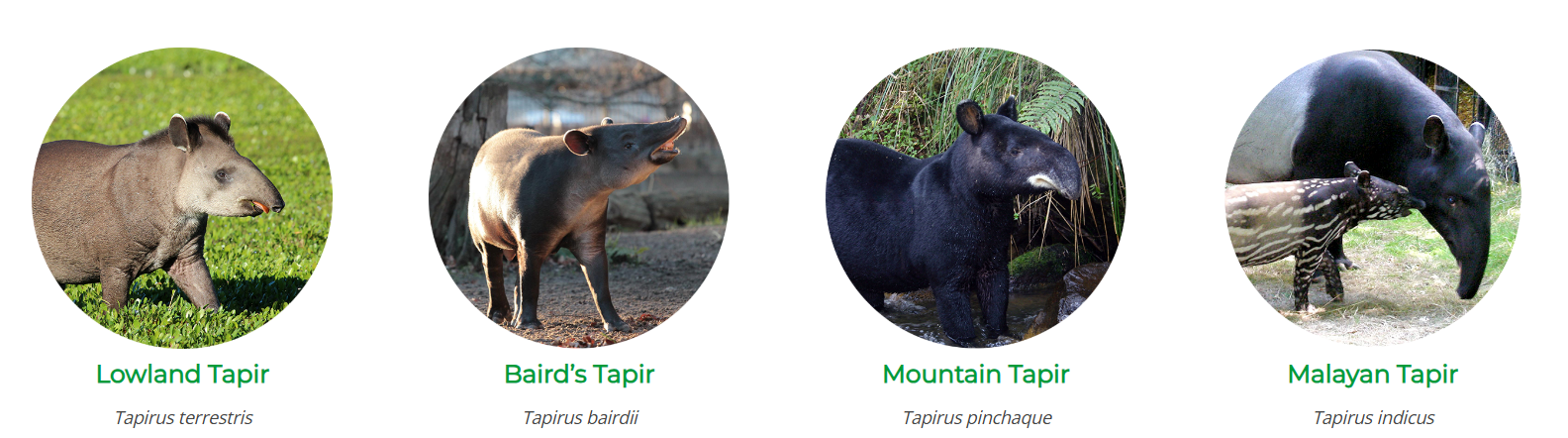
The South American tapir (Lowland tapirs) has been spotted in the Cunhambebe State Park (Brazil’s Costa Verde region) for the first time in 100 years.
- The last confirmed sighting was in 1914 in the Serra dos Orgaos National Park in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
- About Tapir: It is the largest land mammal in South America and has short legs and a rounded body, with a kind of flexible trunk.
- They are herbivores.
- Known as a "forest gardener," the tapir aids seed dispersal, and creates natural trails that allow sunlight to reach the forest floor, enhancing biodiversity.
- IUCN Status: Endangered.
- South American tapirs are one of four species of tapir alongside the Baird’s tapir, mountain tapir and Malayan tapir found in the forests of Central and South America as well as Southeast Asia.
Aravali Safari Park Project
Haryana’s proposed Aravali Safari Park, featuring wildlife enclosures, hotels, and restaurants, faces debate over its impact on ecology, groundwater, and wildlife conservation.
- About Aravali Safari Park Project: It is envisioned as the world’s largest safari park (approx 10,000 acres) and aims to support eco-tourism and compensatory afforestation.
- Inspired by UAE’s Sharjah Park, it is planned for compensatory afforestation to mitigate the loss of 26,000 acres of tropical forests in Great Nicobar.
- It will only be developed in areas where forest density is less than 40%.
- Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980 was amended in 2023 to bring it under the 'forest' activity, and allowing zoos to be built in forest areas.
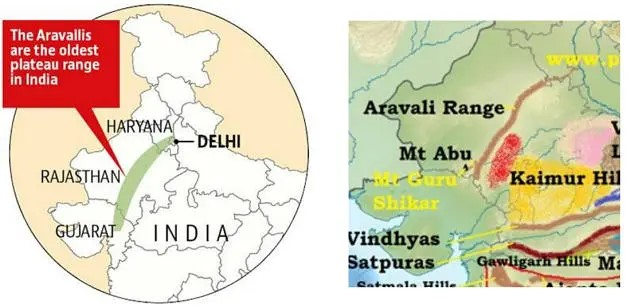
- About Aravalis: It is the oldest fold mountain range in the world and runs diagonally (northeast to southwest) across Gujarat, Rajasthan, Delhi, and Haryana for about 690 km.
- It plays a crucial role in preventing desertification eastwards and recharging groundwater.
- The hidden limb of the Aravallis, extending from Delhi to Haridwar, separates the drainage of the Ganga and Indus rivers.
- Its highest peak is Guru Shikhar on Mount Abu (Rajasthan) at 1,722 metres.
Read More: Critical Threats Facing the Aravallis
DeepSeek AI
Chinese AI startup DeepSeek has launched generative AI models (known as DeepSeek) that rival global leaders like OpenAI, Google, and Meta while offering competitive performance at a significantly lower cost.
DeepSeek:
- About: DeepSeek is a free AI-powered chatbot similar to ChatGPT, providing text-based assistance via web, mobile, and API.
- Deepseek (AI firm) was founded by Liang Wenfeng in May 2023 that specialises in open-source Large Language Models (LLMs).
- Recent Advanced Models: DeepSeek-V3 excels in coding, translation, and writing, while DeepSeek-R1 outperforms OpenAI’s o1 in reasoning, math, and logic.
- Different With Other AI Models:
- Open-Source Advantage: Unlike proprietary models (OpenAI, Google), DeepSeek allows cost-effective AI adoption without licensing fees.
- Advanced Architecture: Uses Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) for specialized tasks and Multi-Head Latent Attention (MLA) for efficiency, reducing training and deployment costs.
- Reinforcement Learning: Enhances reasoning through trial-and-error learning, enabling efficient distillation of large models.
- Real-Time Computation: DeepSeek-R1 displays reasoning in real time, outperforming OpenAI’s o1 in math, coding, and general knowledge.
Read more: Artificial Intelligence (AI)
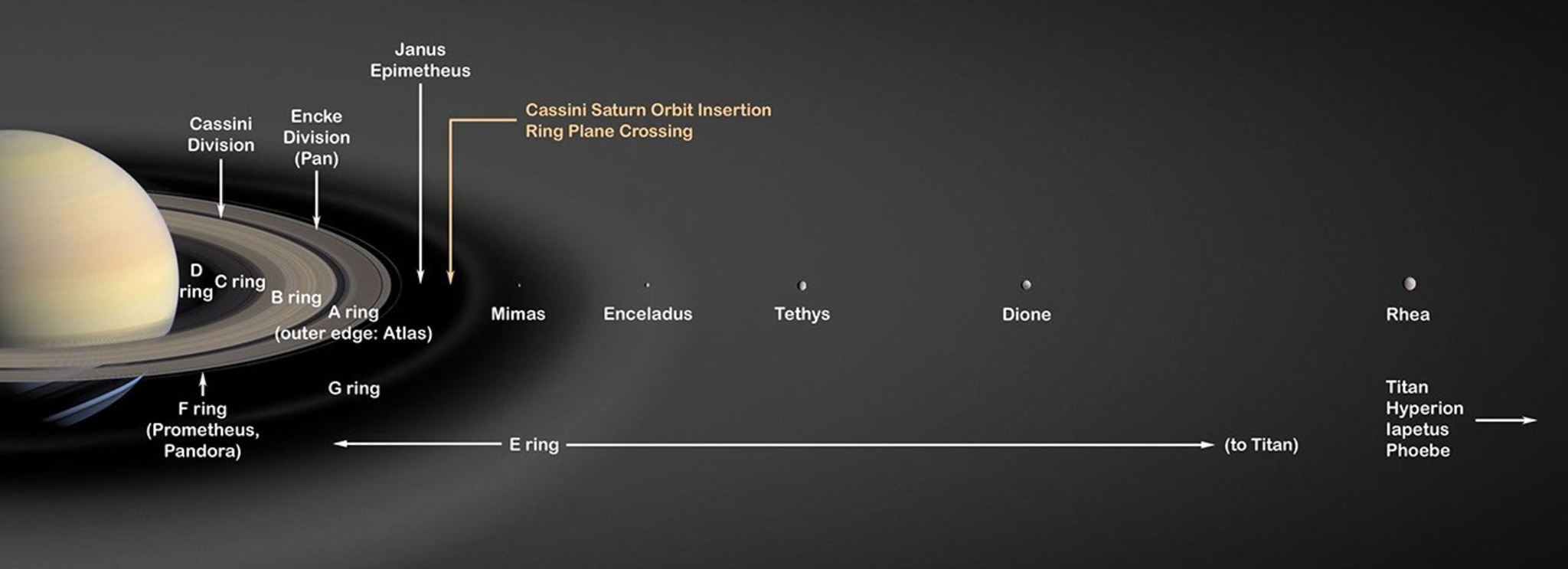
Saturn's Rings
A study challenges the belief that Saturn’s rings are 100 million years old, suggesting they could be as old as the Solar System itself.
- Earlier assumptions based on Cassini spacecraft data suggested Saturn’s rings were young due to their cleanliness, surprising scientists who expected dark dust from space debris.
- But the study finds dust evaporation keeps them clean, proving they may be ancient.
- Cassini: Launched by National Aeronautics and Space Administration along with the European Space Agency's Huygens probe to study Saturn and its moons.
- Saturn: It is the second-largest planet after Jupiter, and is composed of hydrogen and helium. Located at 9.5 Astronomical Unit (AU) (AU is the distance from the Sun to Earth) from the Sun.
- Saturn has 146 moons and is a gas giant of hydrogen and helium.
- Saturn’s Rings: It consists of seven main rings, named in the order of their discovery (D, C, B, A, F, G, E), becoming fainter as they move outward, primarily made of icy snowballs.
- The main rings are A, B, and C, with the A ring easily visible through Earth-based telescopes. The Cassini Division separates the B and A rings.
- F Ring located outside the A ring, G and E Rings are much fainter, with the E ring being the largest ring.
Statehood Day of Mizoram and Arunachal Pradesh
President Droupadi Murmu greeted Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram on Statehood Day (20th February).
- Mizoram: It was originally known as the Lushai Hills district of Assam and was renamed Mizo Hills in 1954. The Mautam famine of 1959 led to the rise of the Mizo National Front (MNF), which sought to establish a sovereign nation for the Mizo people.
- This movement culminated in an armed uprising in 1966, particularly after Nagaland gained statehood in 1963.
- Mizoram became a Union Territory in 1972 after an accord with MNF moderates and gained statehood on 20th February 1987 following the Mizoram Peace Accord (1986) with the Central government.
- Arunachal Pradesh: Formerly the North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA), Arunachal Pradesh became a Union Territory in 1972 and gained statehood on 20th February 1987, under the Arunachal Pradesh Act, 1986. Its capital, Itanagar, is named after the 14th-century Ita Fort.