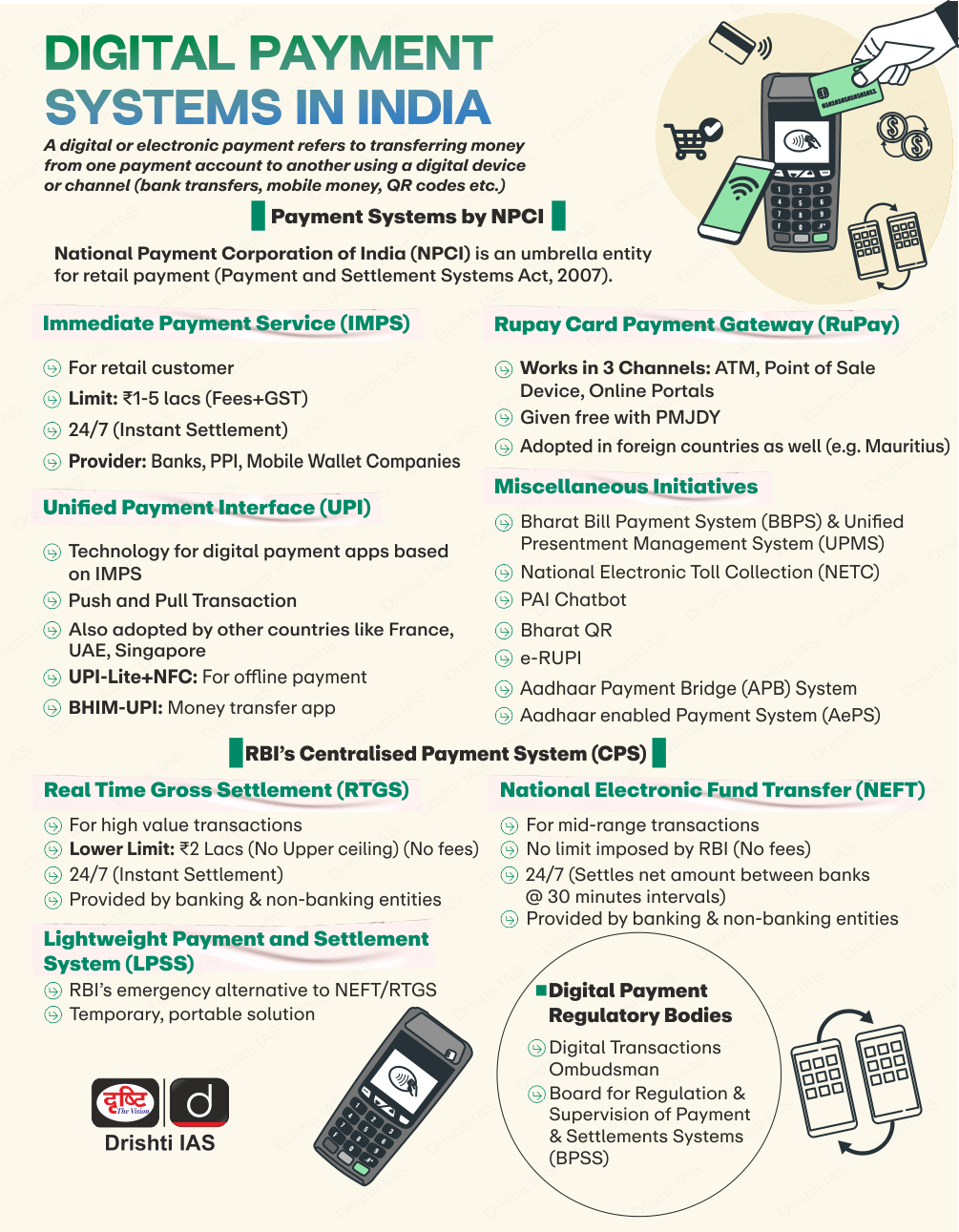
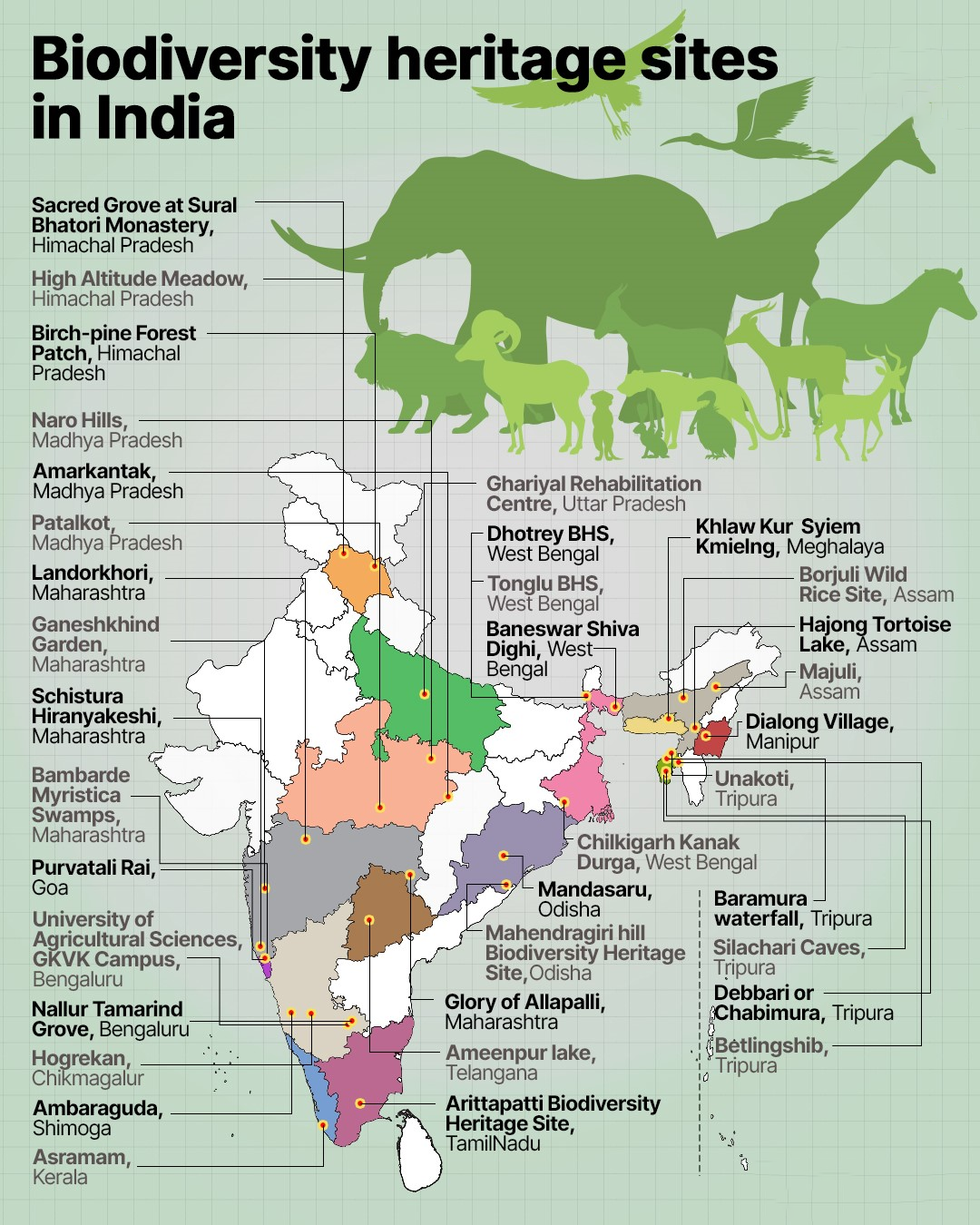
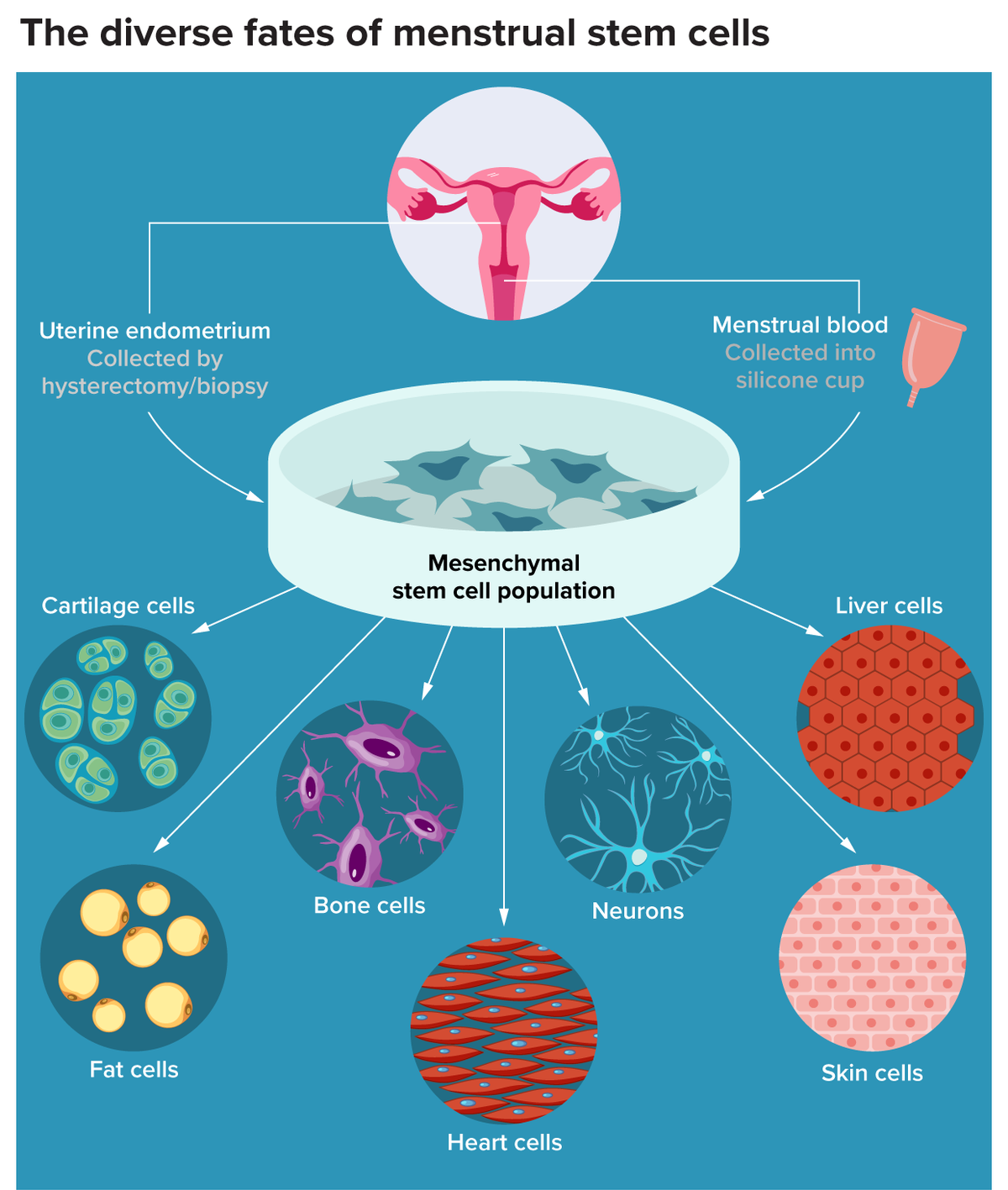
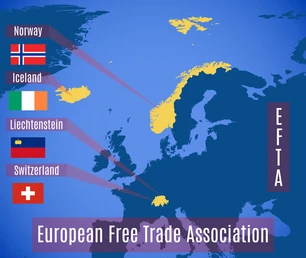
Gupteswar Forest as Biodiversity Heritage Site
For Prelims: Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS), ‘Biological Diversity Act, 2002
For Mains: Biodiversity-Heritage Site (BHS), Environmental pollution and degradation.
Why in News?
The pristine Gupteswar Forest, adjacent to Gupteswar Shiva temple in Odisha’s Koraput district has been declared as the 4th Biodiversity Heritage Site (BHS) of the state.
What are the Key Points Related to Gupteshwar Forest?
- Area and Importance:
- The forest covers 350 hectares of demarcated area and holds immense cultural significance with its sacred groves, traditionally revered by the local community.
- Flora and Fauna Diversity:
- It harbours a remarkable diversity of flora and fauna. The forest is home to at least 608 faunal species, including 28 species of mammals.
- Significant Species:
- Notable faunal species documented in the forest include the mugger crocodile, kanger valley rock gecko, sacred Grove Bush Frog, and various avifauna such as black baza, Jerdon’s baza, Malaber trogon, common hill myna, white-bellied woodpecker, and banded bay cuckoo.
- The limestone caves within the forest are home to eight species of bats, two of which are under the near-threatened category.
- Hipposideros galeritus and Rhinolophus rouxii are under the near-threatened category of the IUCN.
- Floral Diversity:
- The forest also boasts a rich floral diversity. It includes threatened medicinal plants like the Indian trumpet tree and Indian snakeroot.
What is a Biodiversity Heritage Site?
- About:
- Biodiversity Heritage sites (BHS) are well-defined areas that are unique, ecologically fragile ecosystems with a high diversity of wild and domesticated species, the presence of rare and threatened species, and keystone species.
- Legal Provision:
- As per provision under Section 37(1) of ‘The Biological Diversity Act, 2002’ State Governments are empowered to notify in the official gazette, in consultation with ‘local bodies’, areas of biodiversity importance as Biodiversity Heritage Sites.
- Restrictions:
- Creation of BHS may not put any restriction on the prevailing practices and usages of the local communities, other than those voluntarily decided by them. The purpose is to enhance the quality of life of the local communities through conservation measures.
- First BHS of India:
- Nallur Tamarind Grove in Bengaluru, Karnataka was the first Biodiversity Heritage Site of India, declared in 2007.
- According to the National Biodiversity Authority, India has a total of 45 Biodiversity Heritage Sites as of February 2024.
- Last Five Additions to BHS:
- Haldir Char Island West Bengal (May 2023)
- Birampur-Baguran Jalpai West Bengal (May 2023)
- Tungkyong Dho Sikkim (June 2023)
- Gandhamardan Hill Odisha (March 2023)
- Gupteswar Forest Odisha (Feb 2024)
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Two important rivers – one with its source in Jharkhand (and known by a different name in Odisha), and another, with its source in Odisha – merge at a place only a short distance from the coast of Bay of Bengal before flowing into the sea. This is an important site of wildlife and biodiversity and a protected area. Which one of the following could be this? (2011)
(a) Bhitarkanika
(b) Chandipur-on-sea
(c) Gopalpur-on-sea
(d) Simlipal
Ans: (a)
Q2. With reference to India’s biodiversity, Ceylon frogmouth, Coppersmith barbet, Gray-chinned minivet and White-throated redstart are (2020)
(a) Birds
(b) Primates
(c) Reptiles
(d) Amphibians
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. How does biodiversity vary in India? How is the Biological Diversity Act, 2002 helpful in the conservation of flora and fauna? (2018)
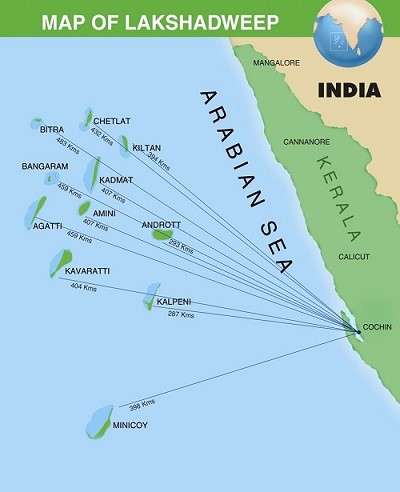
Potential of Lakshadweep
For Prelims: Lakshadweep, Arabian Sea, Coral, Blue Flag Certification, Interim Budget 2024-25.
For Mains: Potential of Lakshadweep, Government Policies & Interventions.
Why in News?
Lakshadweep, India’s smallest Union Territory (UT), due to its proximity to international shipping routes, has the potential to become a logistics hub and a remarkable tourist destination of India.
What are the Tourism and Logistics Potential of Lakshadweep?
- Tourism:
- Lakshadweep's pristine beaches, Coral Reefs, and clear waters present a remarkable tourist destination.
- With proper infrastructure development and sustainable tourism practices, Lakshadweep could become a premier tourist hotspot.
- Trade and Logistics:
- Situated near international shipping routes, Lakshadweep holds the potential to become a strategic logistics hub. Its proximity to coastal Karnataka, particularly Mangaluru (a Major Port), offers opportunities for trade partnerships and cargo handling.
- Many Islands of Lakshadweep are closer to Mangaluru. Many Laksheadweep residents rely on supplies from Mangaluru for their daily living. This business link is centuries-old.
- With the proposed development of port connectivity and infrastructure, Lakshadweep could facilitate smoother trade operations, benefiting both local businesses and the broader regional economy.
- Situated near international shipping routes, Lakshadweep holds the potential to become a strategic logistics hub. Its proximity to coastal Karnataka, particularly Mangaluru (a Major Port), offers opportunities for trade partnerships and cargo handling.
- Regional Growth:
- The development initiatives for Lakshadweep, as outlined in the Interim Budget 2024-25 proposal, not only benefit the islands but also contribute to regional growth, particularly for areas like Mangaluru.
- The Union Finance Minister while presenting the Budget stated that projects for port connectivity, tourism infrastructure, and amenities will be taken on Indian islands including Lakshadweep to address zeal for domestic tourism.
- Enhanced connectivity, coupled with the establishment of cruise routes, could boost tourism and economic activities in both Lakshadweep and its neighbouring regions.
- The development initiatives for Lakshadweep, as outlined in the Interim Budget 2024-25 proposal, not only benefit the islands but also contribute to regional growth, particularly for areas like Mangaluru.
- Ecological Significance:
- Lakshadweep's designation as a restricted area underscores its ecological significance. Suggestions to anchor cruise vessels at sea instead of building large infrastructure on the islands demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices.
What are the Key Facts About Lakshadweep?
- About:
- India’s smallest Union Territory, Lakshadweep is an archipelago consisting of 36 islands with an area of 32 sq km.
- It is a uni-district Union Territory and comprises 12 atolls, three reefs, five submerged banks, and ten inhabited islands.
- All Islands are 220 to 440 km away from the coastal city of Kochi in Kerala, in the emerald Arabian Sea.
- It is directly under the control of the Centre through an administrator.
- There are three main groups of islands:
- Organic Agricultural Area: The entire Lakshadweep group of islands has been declared as an organic agricultural area under the Participatory Guarantee System (PGS) of India.
- Blue Flag Certification: The Blue Flag Certification has been accorded to two new beaches of Lakshadweep- Minicoy Thundi Beach and Kadmat Beach.
What are the Concerns Related to Development in Lakshadweep?
- Environmental Impact:
- The delicate ecosystem of the islands, including coral reefs and marine life, is vulnerable to damage from construction, pollution, and increased human activity.
- Sustainable development practices and stringent environmental regulations are necessary to mitigate these risks.
- Socio-cultural Impact:
- The traditional way of life and cultural heritage of the indigenous communities in Lakshadweep could be at risk with rapid development and increased tourism.
- Infrastructure Development:
- The lack of adequate infrastructure, including transportation, accommodation, and healthcare facilities, poses a significant challenge to tourism and trade in Lakshadweep.
- Developing modern infrastructure while preserving the islands' natural beauty and unique character requires careful planning and investment.
- Security Concerns:
- Lakshadweep's proximity to international shipping routes and its designation as a restricted area raise security concerns. Balancing security needs with the promotion of tourism and trade requires coordinated efforts between government agencies and stakeholders.
- Community Engagement:
- Engaging local communities in the planning and implementation of development projects is crucial for their success and sustainability.
- Ensuring that the benefits of development are equitably distributed among residents and that their concerns are addressed is essential for fostering social cohesion and support for growth initiatives.
Conclusion
- Addressing these concerns and challenges will require a concerted effort from government agencies, private sector stakeholders, civil society organizations, and local communities.
- By adopting a holistic and inclusive approach to development, Lakshadweep can overcome these challenges and realise its full potential as a sustainable and thriving island destination.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following pairs of islands is separated from each other by the ‘Ten Degree Channel’? (2014)
(a) Andaman and Nicobar
(b) Nicobar and Sumatra
(c) Maldives and Lakshadweep
(d) Sumatra and Java
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q. What do you understand by ‘The String of Pearls’? How does it impact India? Briefly outline the steps taken by India to counter this. (2013)
Q. Discuss the political developments in the Maldives in the last two years. Should they be of any cause for concern to India? (2013)
The iOncology-AI Project
For Prelims: Artificial Intelligence, Centre for Development of Advanced Computing, supercomputer, Genomic Data, Genomic sequencing, National Cancer Grid, National Cancer Awareness Day
For Mains: Application of AI to Medical Science, Scientific Innovations
Why in News?
At the forefront of medical innovation, researchers at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) in Delhi have developed an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered model named iOncology-AI Project, integrated with a supercomputer, to aid oncologists in making informed decisions regarding cancer treatment.
What are the Key Highlights of the iOncology-AI Project?
- About:
- The iOncology-AI project emerges from a collaborative effort between the AIIMS in Delhi and Pune’s Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC), and the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology. This partnership brings together expertise in medical research and computational science to revolutionize cancer care.
- It aims to leverage AI to enhance the precision and efficacy of cancer treatment. By analysing vast datasets encompassing genetic profiles, clinical histories, and treatment outcomes, the project seeks to unravel the complex interplay between genetics and cancer therapy.
- Working Procedure:
- The platform, developed with C-DAC, stores and analyses various cancer-related data, including blood tests, lab reports, scans, and patient histories.
- Utilising advanced algorithms, the AI-enabled platform assists doctors in making treatment decisions based on comprehensive genomic data analysis, helping to tailor treatment plans to individual patients.
- By studying the clinical data and genomic makeup of thousands of cancer patients, the platform can provide personalised treatment recommendations, improving therapeutic outcomes.
- Particularly beneficial in resource-constrained settings, the tool aids doctors in making targeted treatment decisions and optimising healthcare delivery.
- While not replacing doctors, the platform serves as a valuable guide by automatically flagging abnormalities in scans and reports, enhancing clinical decision-making.
- Focus on Breast and Ovarian Cancers:
- Given the prevalence of breast and ovarian cancers among women in India, the initial application of iOncology-AI is focused on early detection of these cancers.
- Impacts:
- The iOncology-AI platform can improve cancer patient outcomes and quality of life through early detection and personalised treatment of breast and ovarian cancers.
- It also reduces the burden and cost of cancer care by enhancing healthcare professionals' efficiency and productivity and optimising resource use. Additionally, it contributes to cancer research and innovation by providing valuable insights and data for further analysis and development.
Genomic Data
- Genomic data is information about the structure and function of an organism's genome.
- It is a powerful tool for medical researchers and doctors. It helps them understand how variations in DNA affect our health.
- Through genomic sequencing, they decipher a patient's genetic makeup and spot alterations in our genes. These changes are key to understanding how diseases such as cancer develop.
Global Cancer Scenario
- Cancer is a complex group of diseases characterised by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body.
- These cells, known as cancer cells, can invade and destroy healthy tissues and organs.
- In a healthy body, cells grow, divide, and die in a regulated manner, but in the case of cancer, genetic mutations disrupt this normal cell cycle, causing uncontrollable growth. This can lead to the formation of a tumour.
- The Global Cancer Observatory (GLOBOCAN) estimates for 2020 reported 19.3 million incident cancer cases worldwide, with India ranking third after China and the United States.
- A Lancet study predicts a 57.5% increase in cancer cases in India by 2040, reaching 2.08 million. In 2022 alone, over 8 lakh deaths in India were caused by cancer, primarily due to late detection, resulting in only a 20% survival rate.
What are the Government Initiatives Related to Cancer Treatment?
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke
- National Cancer Grid
- National Cancer Awareness Day
- HPV Vaccine
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q 1. Consider the following statements: (2010)
- The Taxus tree is naturally found in the Himalayas.
- The Taxus tree is listed in the Red Data Book.
- A drug called “taxol” is obtained from Taxus trees and is effective against Parkinson’s disease.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q.1 What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of the society? (2021)
Q.2 What do you understand by nanotechnology and how is it helping in health sector? (2020)
CMS COP14
For Prelims: Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals, Conservation of Migratory Species, Bonn Convention.
For Mains: CMS COP14, Convention on migratory species and Efforts made by India.
Why in News?
The Fourteenth Meeting of the Conference of the Parties (CoP) to the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS 14) has been concluded in Samarkand, Uzbekistan.
What are the Key Highlights of CMS COP 14?
- Adoption of Listing Proposals:
- Parties agreed to adopt listing proposals for 14 migratory species, including the Eurasian lynx, Peruvian pelican, Pallas’s cat, guanaco, Lahille’s bottlenose dolphin, harbour porpoise, Magellanic plover, bearded vulture, Blackchin guitarfish, Bull ray, Lusitanian cownose ray, Gilded catfish, and Laulao catfish.
- These listings aim to enhance protection and conservation efforts for these species.
- Cooperation and Conservation Efforts:
- The proposals emphasised the importance of cooperation between range states to address threats to migratory species, conduct research, and implement conservation activities.
- Range states refer to countries or territories that are within the geographical range where a particular species occurs naturally. These countries or territories are directly involved in the management, conservation, and protection of the species and its habitat.
- Efforts were focused on maintaining existing populations, improving connectivity, safeguarding habitats, and restoring populations.
- The proposals emphasised the importance of cooperation between range states to address threats to migratory species, conduct research, and implement conservation activities.
- Focus on Threats:
- Various threats to migratory species were highlighted, including habitat degradation, fragmentation, illegal trade, bycatch, contaminants, and human activities such as fencing, oil and gas development, mining, and underwater noise.
- The inclusion of these species in the CMS appendices aims to address these threats and promote their conservation.
- International Collaboration:
- Range states collaborated to propose listing amendments and adoption of conservation measures.
- Countries like North Macedonia, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Chile, Argentina, Peru, Brazil, Uruguay, Ecuador, Panama, and others supported listing proposals and urged for joint efforts to protect migratory species and their habitats.
- Recognition of Endangered Status:
- Several species, such as the Lahille’s bottlenose dolphin, Peruvian pelican, and Magellanic plover, were recognized as 'Vulnerable,' 'Endangered,' or 'Critically Endangered' in IUCN Red List, due to population decline and various threats.
- Listing these species in CMS appendices aims to improve their conservation status and provide support for habitat protection.
- Regional and Global Conservation Initiatives:
- The adoption of proposals reflected efforts to address conservation issues at regional and global levels.
- Measures were recommended to protect specific populations, such as the Baltic Proper population of the harbour porpoise and the Mediterranean Sea populations of various species, while also considering broader conservation strategies.
What is a Migratory Species?
- A species or lower taxon of wild animals of which the entire population or any geographically separate part of the population cyclically and predictably cross one or more national jurisdictional boundaries.
- The word ‘cyclically’ relates to a cycle of any nature, such as astronomical (circadian, annual, etc.), life or climatic, and of any frequency.
- The word ‘predictably’ implies that a phenomenon can be anticipated to recur in a given set of circumstances, though not necessarily regularly in time.
What is CMS?
- About:
- It is an intergovernmental treaty under the UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme)- popularly known as Bonn Convention.
- It was signed in 1979 and in force since 1983.
- As of 1st March 2022, the CMS has 133 Parties.
- India has also been a party to CMS since 1983.
- Aim:
- It aims to conserve terrestrial, marine and avian migratory species throughout their range.
- It lays the legal foundation to conduct conservation measures on a global scale.
- The legal instruments under CMS may range from legally binding Agreements to less formal MoU.
- Two appendices under CMS:
- Appendix I lists ‘Threatened Migratory Species’.
- Appendix II lists ‘Migratory Species requiring international cooperation’.
- India and the CMS:
- India has signed a non-legally binding Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with CMS on conservation and management of Siberian Cranes (1998), Marine Turtles (2007), Dugongs (2008), and Raptors (2016).
- With 2.4% of the world’s land area, India contributes to around 8% of the known global biodiversity.
- India also provides temporary shelter to several migratory species including Amur Falcons, Bar-headed Geese, Black-necked Cranes, Marine Turtles, Dugongs, Humpback Whales, etc.
What are Initiatives Taken by India for Migratory Species?
- National Action Plan for the Conservation of Migratory Birds (2018-2023): India has launched the National Action Plan for the conservation of migratory species along the Central Asian Flyway.
- To reduce pressure on critical habitats and migratory routes by addressing the various challenges migratory birds face.
- To stop the decline of migratory birds and reverse the scenario by 2027.
- To avoid threats to habitats and migratory routes and ensure their sustainability for future generations.
- To support transboundary cooperation among countries along the Central Asian Flyway to conserve migratory birds and their habitats.
- To improve the database on migratory birds and their habitats to enhance our understanding of their conservation needs.
- India also Announced:
- Conservation of marine turtles- by launching its Marine Turtle Policy and Marine Stranding Management Policy, by 2020,
- Reduction of pollution from micro-plastic and single-use plastic,
- Transboundary protected areas for conservation of species like Tigers, Asian elephants, Snow Leopard, the Asiatic Lion, the one-horned rhinoceros, and the Great Indian Bustard, and
- Sustainable infrastructure development like Linear Infrastructure Policy Guidelines to tailor development in ecologically fragile areas.
- Project Snow Leopard (PSL): PSL was launched in 2009 to promote an inclusive and participatory approach to conserve snow leopards and their habitat.
- Dugong Conservation Reserve: India has established its first Dugong conservation reserve in Tamil Nadu.
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972:
- Rare and endangered species of birds including migratory birds are included in Schedule-I of the Act thereby according to them highest degree of protection.
- Important habitats of birds, including migratory birds have been notified as protected Areas under the Act for better conservation and protection of birds and their habitats.
- Other Initiatives:
- Focused protection measures involving the local communities have been taken up in the State of Nagaland for protection of Amur Falcons that migrate to Northeast India on their route to Southern Africa.
- India has taken several steps to conserve vultures like imposing ban on veterinary use of diclofenac, establishment of Vulture breeding centres etc.
- Wildlife Crime Control Bureau has been established for control of illegal trade in wildlife and its parts and products.
Read More: Convention on Migratory Species
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. The most important strategy for the conservation of biodiversity together with traditional human life is the establishment of (2014)
(a) biosphere reserves
(b) botanical gardens
(c) national parks
(d) wildlife sanctuaries
Ans: (a)
Q. With reference to the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) and the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), which of the following statements is/are correct? (2015)
- IUCN is an organ of the United Nations and CITES is an international agreement between governments.
- IUCN runs thousands of field projects around the world to better manage natural environments.
- CITES is legally binding on the States that have joined it, but this Convention does not take the place of national laws.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Stem Cells in Menstrual Blood
For Prelims: Stem cell, Menstrual Blood Stem Cells, Insulin, In Vitro fertilization
For Mains: Importance of research and study on Menstrual Blood, Issues Related to Women Health, Biotechnology
Why in News?
Recently, researchers have unveiled the regenerative potential of stem cells in menstrual blood, stemming from studies conducted roughly two decades ago.
- This discovery has opened new avenues for understanding the complex interplay between the female reproductive system and regenerative processes.
What are Menstrual Blood Stem Cells?
- About:
- Menstrual blood-derived stem cells (MenSCs), known as endometrial stromal mesenchymal stem cells, possess multipotent properties, meaning they can differentiate into various tissue types such as fat cells, bone cells, and smooth muscle cells.
- MenSCs are an ethical source of adult stem cells that can be collected painlessly from women.
- MenSCs can be collected through a menstrual cup, providing a less invasive alternative to surgical biopsies.
- MenSCs can be obtained from women's menstrual blood derived from the endometrium (lines the inside of the uterus).
- Role in Women's Health:
- Regenerative Potential:
- MenSCs exhibit multipotent characteristics. This means they can differentiate into various cell types, including neurons, cartilage, fat, bone, heart, liver, and skin cells.
- Treating Endometriosis:
- MenSCs offer potential avenues for treating gynaecological disorders such as endometriosis and infertility.
- Endometriosis is a disease in which tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus. It can cause severe pain in the pelvis and make it harder to get pregnant.
- Endometriosis can start at a person's first menstrual period and last until menopause (end of menstrual cycles).
- Common symptoms of endometriosis include pelvic pain, especially during menstruation, painful intercourse, infertility, heavy menstrual bleeding, and gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhoea or constipation.
- The cause and ways to prevent endometriosis are unknown. There is no cure, but its symptoms can be treated with medicines or, in some cases, surgery.
- The contributing factor to endometriosis is the backflow of menstrual blood into a woman's fallopian tubes.
- This backward flow carries blood into the pelvic cavity, a funnel-shaped space between the bones of the pelvis.
- Endometrial stem cells deposited in these areas may prompt the growth of endometrial-like tissue outside the uterus, resulting in painful lesions, scarring, and often infertility.
- Endometriosis is a disease in which tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows outside the uterus. It can cause severe pain in the pelvis and make it harder to get pregnant.
- MenSCs offer potential avenues for treating gynaecological disorders such as endometriosis and infertility.
- Regenerative Potential:
- Broader Therapeutic Applications:
- Menstrual stem cells have potential therapeutic applications beyond gynaecological diseases.
- Injecting menstrual stem cells into diabetic mice stimulated the regeneration of insulin-producing cells and improved blood sugar levels.
- Treating injuries with stem cells or their secretions helped heal wounds in mice.
- Menstrual stem cells can be transplanted into humans without adverse side effects.
- Challenges:
- Despite the convenience of collecting menstrual stem cells, research in this area represents a tiny fraction of overall stem cell research.
- As of 2020, menstrual stem cell research accounted for only 0.25% of all mesenchymal cell research, while bone marrow stem cells represented 47.7%.
- Ensuring consistent and scalable production of MenSCs for clinical applications remains a challenge.
- Cultural taboos and limited investment in women’s health research pose significant challenges in securing funding for menstrual stem cell studies.
- Addressing gender bias in research funding is crucial to elevate menstrual stem cell research as a promising frontier in regenerative medicine, beyond its association with menstruation.
- Despite the convenience of collecting menstrual stem cells, research in this area represents a tiny fraction of overall stem cell research.
Endometriosis and Fusobacterium bacteria:
- There is a significant association between Fusobacterium bacteria and endometriosis.
- Fusobacterium was found in 64% of endometriosis patients compared to only 7% in healthy individuals. Studies suggest that Fusobacterium exacerbates endometrial lesions.
- A 2022 research paper found that people with endometriosis had an imbalance of microbe populations in the gut, known as gut dysbiosis.
- This altered microbiota could contribute to the progression of endometriosis.
What are Stem Cells?
- About:
- Stem cells are special human cells with the ability to develop into various cell types, such as muscle cells or brain cells.
- They have the potential to repair damaged tissues, offering hope for treating serious illnesses like paralysis and Alzheimer's disease.
- Types of Stem Cells:
- Stem cells are usually categorized as multipotent (able to give rise to multiple cells within a lineage), pluripotent (able to give rise to all cell types in an adult) and totipotent (able to give rise to all embryonic and adult lineages).
- Stem Cells in Medicine:
- Hematopoietic stem cells, found in bone marrow, are currently used to treat diseases like cancer and anaemia by producing new blood cells.
- Potential future applications include treating chronic heart disease, type 1 diabetes, spinal cord injuries, and Alzheimer's disease.
- Pluripotent stem cells offer opportunities for testing new medicines and creating new tissues.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q.1 Consider the following statements: (2020)
- Genetic changes can be introduced in the cells that produce eggs or sperms of a prospective parent.
- A person’s genome can be edited before birth at the early embryonic stage.
- Human induced pluripotent stem cells can be injected into the embryo of a pig.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q1. With reference to ‘stem cells’, frequently in the news, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2012)
- Stem cells can be derived from mammals only
- Stem cells can be used for screening new drugs
- Stem cells can be used for medical therapies
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q.1 Stem cell therapy is gaining popularity in India to treat a wide variety of medical conditions including Leukaemia, Thalassemia, damaged cornea and several burns. Describe briefly what stem cell therapy is and what advantages it has over other treatments? (2017)
Q.2 What are the continued challenges for women in India against time and space? (2019)
Data Exclusivity in Trade Talks with EFTA
Why in News?
India has recently taken a firm stance against the inclusion of 'data exclusivity' clauses in its ongoing discussions with the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) for a free trade agreement.
What is Data Exclusivity under the Trade Agreement?
- About: Data exclusivity pertains to a clause in this draft agreement that puts a minimum 6-year embargo (a legal prohibition on commerce) on clinical trial data generated during the testing and development of a drug.
- Thus, manufacturers seeking to produce generic versions of drugs would either need to generate such data on their own, which is an expensive proposition, or wait out for the above specified period before selling their versions in India.
- Impact on India's Generic Drug Industry: India's generic drug industry has been pivotal in providing affordable alternatives to expensive medications globally.
- However, the imposition of data exclusivity could severely hamper this industry's growth and accessibility of affordable medicines.
- Historical Context and Rejection: Demand for data exclusivity has consistently emerged since 2008 from both the European Union (EU) and the EFTA during trade negotiations with India.
- Despite this, India has consistently refused these requests.
What is the European Free Trade Association?
- About: The EFTA is the intergovernmental organisation of Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland (all four are not a part of the EU).
- It was founded by the Stockholm Convention in 1960.
- It aims to promote free trade and economic integration to the benefit of its four Member States and their trading partners around the globe.
- India and EFTA: The total value of commercial trade between the EFTA members and India exceeded USD 6.1 billion in 2022.
- The biggest exports to India were pharmaceutical items (11.4%) and machinery (17.5%), while organic chemicals (27.5%) made up the majority of EFTA imports.
What is a Free Trade Agreement?
- About: A free trade agreement (FTA) is a pact between two or more nations to reduce barriers to imports and exports among them.
- Under this agreement, goods and services can be bought and sold across international borders with little or no government tariffs, quotas, or prohibitions to inhibit their exchange.
- It is the opposite of trade protectionism or economic isolationism.
- Historical Context: It was first popularised in 1817 by economist David Ricardo in his book, "On the Principles of Political Economy and Taxation."
- He argued that free trade expands diversity and lowers the prices of goods available in a nation while better exploiting its homegrown resources, knowledge, and specialised skills.
- FTA’s of India: So far, India has signed 13 Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) with its trading partners including the Agreement on the South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA), India-Singapore Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA), India-Japan CEPA, and India-Australia Economic Cooperation and Trade Agreement (ECTA).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(b) 3, 4, 5 and 6
(c) 1, 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2, 3, 4 and 6
Ans: (c)
Q. A “closed economy” is an economy in which (2011)
(a) the money supply is fully controlled
(b) deficit financing takes place
(c) only exports take place
(d) neither exports or imports take place
Ans: (d)
TN-SHORE
Why in News?
The Tamil Nadu government has announced a new scheme called TN-SHORE, to revive the coastal resources and protect the endangered species in the 2024-2025 State Budget.
- TN-SHORE, aims to enhance coastal biodiversity, and coastal protection, improve livelihoods of coastal communities, and control pollution in coastal areas.
- Additionally, the Tamil Nadu government also highlighted the Tamil Nadu Endangered Species Conservation Fund aimed at Endangered Species Conservation and the pursuit of Blue Flag certification for 8 beaches.
What are the Key Highlights of TN-SHORE?
- About:
- TN-SHORE (Neithal Meetchi Iyakkam) is announced to restore coastal resources across 14 districts, spanning 1,076 km, at an estimated cost of Rs 1,675 crore.
- The scheme aims to enhance coastal biodiversity, and coastal protection, improve livelihoods of coastal communities, and control pollution in coastal areas.
- TN-SHORE and Blue Economy:
- The Blue Economy refers to the sustainable use of ocean resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods, and jobs while preserving the health of the ocean ecosystem.
- The scheme will capitalise on the potential of the Blue Economy by focusing on the restoration of mangroves, coral reefs, and salt marshes, which are vital for the marine environment and the coastal economy.
- The scheme will also help in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), especially SDG 14 (Life Below Water).
- Benefits the Coastal Communities:
- The scheme will involve the participation of the local communities, especially the youth, in the conservation and management of the coastal resources.
- The scheme will provide alternative livelihood opportunities for the coastal communities, such as ecotourism, waste management, and circular economy solutions.
- The scheme will also contribute to the preservation of the cultural and natural heritage of the coastal areas.
Tamil Nadu (TN) Government's Conservation and Certification Initiatives
- Endangered Species Conservation:
- The TN government emphasised initiatives to protect endangered species through the establishment of the Tamil Nadu Endangered Species Conservation Fund.
- Various stakeholders, including government entities, corporate social responsibility initiatives, and national and international funds, will contribute to this fund to protect endangered and critically endangered species.
- Blue Flag Certification for Beaches:
- The government is actively pursuing Blue Flag certification (BFC) for eight beaches in Tamil Nadu, including the iconic Marina Beach in Chennai.
- BFC is an eco-label given to beaches, marinas, and sustainable tourism boats that meet certain criteria. The criteria include environmental, educational, safety, and accessibility concerns.
- It is accorded by the international jury composed of eminent members - United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), United Nations World Tourism Organisation (UNWTO), Denmark-based NGO Foundation for Environmental Education (FEE) and International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- The government is actively pursuing Blue Flag certification (BFC) for eight beaches in Tamil Nadu, including the iconic Marina Beach in Chennai.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. What is blue carbon?
(a) Carbon captured by oceans and coastal ecosystems
(b) Carton sequestered in forest biomass and agricultural soils
(c) Carbon contained in petroleum and natural gas
(d) Carbon present in atmosphere
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Defining blue revolution, explain the problems and strategies for pisciculture development in India. (2018)
National Conference on Jal Jeevan Mission and Swachh Bharat Mission- Grameen
The Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation recently organised a National Conference on Jal Jeevan Mission and Swachh Bharat Mission -Grameen (G) in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh.
- It aimed to reach at ‘A Unified Approach Towards Sustainable Solutions in Rural WASH Sector".
- State presentations offered insights into initiatives and progress from different regions, promoting discussions on replicability and sustainability.
- Notable state experiences included Kerala's Plastic Waste Management (PWM) initiative, Tamil Nadu's use of plastics in road construction and Bihar's Toilet Clinic.
- Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene (WASH) interventions are designed to provide life-saving, long-term and sustainable access to safe water and sanitation, whilst promoting good hygiene practices that reduce the risk of water-related disease transmission.
Read more: Global Burden of Unsafe Drinking Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene
IEPFA Partners with DBS for Financial Awareness
In a significant move towards enhancing investor awareness and protection, a memorandum of understanding (MoU) was signed between the Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA) and the Development Bank of Singapore Ltd (DBS) in New Delhi.
- The IEPFA was set up on 7th September 2016, under the aegis of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Government of India, for administering the Investor Education Protection Fund (IEPF) for making refunds of shares, unclaimed dividends, and matured deposits/debentures, among other things, to investors.
- IEPF promotes awareness and protects the interests of investors.
- The IEPFA has conducted several Investor Awareness Programmes aimed at increasing financial literacy and empowering investors to protect themselves from financial fraud.
- DBS is a leading financial services group in Asia with a presence in 19 markets. DBS Bank India Limited is the first major foreign bank to function as a wholly-owned, locally incorporated subsidiary in India.
- It offers banking services for enterprises and individuals across all scales.
Odysseus Spacecraft
Intuitive Mission’s Odysseus spacecraft, a private Nova-C lunar lander, is on its way to the Moon after launching on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
- Odysseus is the second private attempt after the Peregrine lander's failure.
- The Falcon 9 is a two-stage rocket designed and manufactured by SpaceX to transport people and payloads into Earth's orbit.
- The spacecraft carries six payloads for NASA under the CLPS initiative, testing new technologies and scientific instruments.
- Key technologies being tested include a LIDAR-based sensor and an electrostatic dust-removal system for spacesuits.
- The spacecraft is set to land on the Moon on 22nd February 2024.
- The mission aims to become the first American spacecraft to land on the Moon in over 50 years. The last time an American spacecraft landed on the Moon was in 1972, with Apollo 17.
- The mission is part of NASA's Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative and Artemis campaign.
Read more: Challenges in Lunar Landing Missions, Space Missions in 2024
Doctor on Wheels
Recently, the Union Minister of Science & Technology stated that "Aarogya-Doctor on Wheels" has provided medical assistance to around 13,000 patients in remote areas of the Udhampur-Kathua-Doda Lok Sabha constituency.
- The Doctor on Wheels initiative utilises AI technology and remote consultations from specialist doctors, delivering prompt and comprehensive medical care within 45 minutes.
- With a focus on inclusivity and cost-effectiveness, it addresses healthcare disparities, bridging the urban-rural divide.
Read more: Shorter Medical Course to Address Rural Doctor Shortage, National Telemedicine Service of India: eSanjeevani