Indian Polity
Court Vacations
For Prelims: Court vacations, Vacation Bench, Supreme Court, CJI, Pendency.
For Mains: Vacation Bench and Related Issues.
Why in News?
Recently, the Chief Justice of India (CJI) has said that the Supreme Court will not have a vacation bench when it breaks for its annual winter vacation.
- While this judicial schedule has its origins in colonial practices, it has come under criticism for quite some time now.
What are Court Vacations?
- About:
- The Supreme Court has 193 working days a year for its judicial functioning, while the High Court's function for approximately 210 days, and trial courts for 245 days.
- High Courts have the power to structure their calendars according to the service rules.
- The Supreme Court takes two long vacations each year, the summer and winter breaks, but is technically not fully closed during these periods.
- Vacation Bench:
- A Vacation Bench of the Supreme Court is a special bench constituted by the CJI.
- Litigants can still approach the Supreme Court and, if the court decides that the plea is an “urgent matter”, the Vacation Bench hears the case on its merits.
- Cases such as bail, eviction, etc. often find precedence in listing before vacation benches.
- It is not uncommon for courts to hear important cases during vacation.
- In 2015, a five-judge Bench of the Supreme Court heard the challenge to the constitutional amendment setting up the National Judicial Appointments Commission (NJAC) during the summer vacation.
- In 2017, a Constitution Bench held a six-day hearing in the case challenging the practice of triple talaq during summer vacation.
- Legal Provisions:
- Under Rule 6 of Order II of The Supreme Court rules, 2013, the CJI has nominated the Division Benches for hearing of urgent miscellaneous matters and regular hearing matters during the summer vacation for the period.
- The rule reads that CJI may appoint one or more Judges to hear during summer vacation or winter holidays all matters of an urgent nature which under these rules may be heard by a Judge sitting singly.
- And, whenever necessary, he may likewise appoint a Division Court for the hearing of urgent cases during the vacation which require to be heard by a Bench of Judges.
What are the Issues with Court Vacations?
- Not Convenient for Justice Seekers:
- The long vacation which the courts obtain is not very convenient for justice-seekers.
- Not good Optics in Light of Pendency:
- Extended frequent vacations are not good optics, especially in the light of mounting pendency of cases and the slow pace of judicial proceedings.
- For an ordinary litigant, the vacation means further unavoidable delays in listing cases.
- Incongruous with European Practices:
- The summer break perhaps began because European judges of the Federal Court of India found Indian summers too hot — and took the winter break for Christmas.
Way Forward
- The issue cannot be resolved until a “new system” on the appointment of judges is evolved
- In 2000, the Justice Malimath Committee, set up to recommend reforms in the criminal justice system, suggested that the period of vacation should be reduced by 21 days, keeping in mind the long pendency of cases. It suggested that the Supreme Court work for 206 days, and High Courts for 231 days every year.
- In its 230th report, the Law Commission of India in 2009 called for reform in this system, considering the staggering arrears, vacations in the higher judiciary must be curtailed by at least 10 to 15 days and the court working hours should be extended by at least half an hour.
- In 2014, when the Supreme Court notified its new Rules, it said that the period of summer vacation shall not exceed seven weeks from the earlier 10-week period.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to the Indian judiciary, consider thefollowing statements: (2021)
- Any retired judge of the Supreme Court of India can be called back to sit and act as a Supreme Court judge by the Chief Justice of India with the prior permission of the President of India.
- A High Court in India has the power to review its own judgement as the Supreme Court does.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither I nor 2
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- As per Article 128 of Indian Constitution, the Chief Justice of India may at any time, with the previous consent of the President, request any person to sit and act as a Judge of the Supreme Court with the following qualifications:
- Who has held the office of a Judge of the Supreme Court. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Who has held the office of a Judge of a High Court and is duly qualified for appointment as a Judge of the Supreme Court.
- Being a Court of Record, the High Court can review its own judgments under Article 226 of the Constitution of India. Similarly, under Article 137, the Supreme Court shall have the power to review any judgment pronounced or order made by it. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Therefore, option C is the correct answer.


Indian Polity
Kerala University Laws (Amendment) Bills
For Prelims: Role of Governor in appointment of Governor in State Universitates.
For Mains: Kerala University Laws (amendment) Bills.
Why in News?
Recently, Kerala Assembly passes University Laws (amendment) Bills to amend laws relating to the governance of State universities and remove the Governor as the Chancellor of State universities.
What is the Background?
- The Governor and the State Government of Kerala had been at loggerheads for months now.
- It got worse when the Governor denied assent to the controversial Lok Ayukta (Amendment) and University Laws (Amendment) Bills earlier passed by the State Assembly.
- The worsening relationship between the State Government and governor reached a tipping point with the Supreme Court order invalidating APJ Abdul Kalam Technological University (KTU) Vice-Chancellor’s (VC) appointment on the grounds that it violated University Grants Commission (UGC) regulations.
- Following this, the governor had sought the resignations of 11 other VCs on the ground that the government had appointed them through the same process deemed unlawful by the Supreme Court.
What are the University Laws (Amendment) Bills?
- The proposed legislation will amend the statutes of 14 universities established by legislative Acts in Kerala and remove the Governor as the Chancellor of those universities.
- The Bills will supplant the Governor and give the government power to appoint eminent academicians as Chancellors of various universities, thus ending the Governor’s watchdog role in university administration.
- The Bills also provide provision to limit the term of the appointed chancellor to five years. However, it also says that the serving chancellor can be reappointed for another term.
What stands in Favour and Against the Proposition?
- Favour
- Earlier UGC Guidelines used to be mandatory for Central universities and “partially mandatory and partially directive” for State universities, had been made legally binding for all universities by way of recent rulings by the Supreme Court.
- Such precedence pointed towards a scenario in which the legislative powers of the Assembly on all subjects on the Concurrent List (of the Constitution) could be undermined through a subordinate legislation or an executive order issued by the Centre.
- It is said that the bill was brought in order to avoid legal tangles in future.
- Against:
- If Chancellors were appointed by the Government, they would be indebted to the ruling front, thus leading to the erosion of Universities’ autonomy.
- It may facilitate appointment of people close to the ruling front.
- This will lead to a scenario in which the governor can appoint only those who are close to the government.
What is the Procedure for Appointing a Vice-Chancellor under UGC rules?
- According to the UGC Regulations, 2018, the VC of a university, in general, is appointed by the Visitor/Chancellor, from a panel of three to five names recommended by the duly constituted Search cum Selection Committee.
- A visitor is empowered to call for a set of fresh names in case of dissatisfaction with the given panel.
- In Indian universities, the President of India is the ex-officio Visitor of all the Central Universities and the Governor of the respective states is the Chancellor of all the state universities.
- Necessarily this system is not uniform in all the universities. As far as the procedures adopted by different states are concerned, they vary.
What are the Governor’s and President’s Powers related Universities?
- State Universities:
- While as Governor he functions with the aid and advice of the Council of Ministers, as Chancellor he acts independently of the Council of Ministers and takes his own decisions on all University matters.
- Central Universities:
- Under the Central Universities Act, 2009, and other statutes, the President of India shall be the Visitor of a central university.
- With their role limited to presiding over convocations, Chancellors in central universities are titular heads, who are appointed by the President in his capacity as Visitor.
- The Vice Chancellor too are appointed by the Visitor from panels of names picked by search and selection committees formed by the Union government.
- The Act adds that the President, as Visitor, shall have the right to authorise inspections of academic and non-academic aspects of the universities and also to institute inquiries.
Way Forward
- M. Anandakrishnan Committee, set up by the Kerala State Higher Education Council in 2009, recommended that universities should have complete autonomy in academic and administrative matters.
- It is advisable to create statutory structures that would distance the Governor and Minister for Higher Education from the day-to-day administration of the universities.
- It is also recommended to immediately incorporate UGC Regulations, 2010 in the
- As recommended by the Punchhi Commission on Centre-State Relations, the Governor should not be burdened with positions and powers that are not specified in the Constitution and may cause controversy or public criticism.
- Governments should devise alternative means of protecting university autonomy so that ruling parties do not exercise undue influence on the functioning of universities.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Whether the Supreme Court Judgment (July 2018) can settle the political tussle between the Lt. Governor and elected government of Delhi? Examine. (2018)
Q. Discuss the essential conditions for exercise of the legislative powers by the Governor. Discuss the legality of re-promulgation of ordinances by the Governor without placing them before the Legislature. (2022)


Social Issues
Law on Acid Attacks in India
For Prelims: National Crime Records Bureau, Indian Penal Code (IPC), The Poisons Act, 1919.
For Mains: Acid Attacks in India, Law on Acid Attacks, Law on the Regulation of Acid Sales, Compensation and Care for the Acid-attack Victims.
Why in News?
Recently, a girl was attacked with an acid-like substance in Delhi by three assailants. The incident has brought back to focus the heinous crime of acid attacks and the easy availability of corrosive substances.
Acid Attacks in India: What’s the Scenario?
- According to the data of the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), there were 150 such cases recorded in 2019, 105 in 2020 and 102 in 2021.
- West Bengal and Uttar Pradesh consistently record the highest number of such cases generally accounting for nearly 50% of all cases in the country year on year.
- The charge sheeting rate of acid attacks stood at 83% and the conviction rate at 54% in 2019.
- In 2020, the figures stood at 86% and 72% respectively. In 2021, the figures were recorded to be 89% and 20% respectively.
- In 2015, the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) issued an advisory to all states to ensure speedy justice in cases of acid attacks by expediting prosecution.
What is the Law on Acid Attacks in India?
- Indian Penal Code: Until 2013, acid attacks were not treated as separate crimes. However, following amendments carried out in the Indian Penal Code (IPC), acid attacks were put under a separate section (326A) of the IPC and made punishable with a minimum imprisonment of 10 years which is extendable to life along with a fine.
- Denial of Treatment: The law also has provisions for punishment for denial of treatment to victims or police officers refusing to register an FIR or record any piece of evidence.
- Denial of treatment (by both public and private hospitals) can lead to imprisonment of up to one year and dereliction of duty by a police officer is punishable by imprisonment of up to two years.
What is the Law on the Regulation of Acid Sales?
- The Poisons Act, 1919: In 2013, the Supreme Court took cognizance of acid attacks and passed an order on the regulation of sales of corrosive substances.
- Based on the order, the MHA issued an advisory to all states on how to regulate acid sales and framed the Model Poisons Possession and Sale Rules, 2013 under The Poisons Act, 1919.
- As a result, states were asked to frame their own rules based on model rules, as the matter fell under the purview of states.
- Maintenance of the Data: Over-the-counter sale (without a valid prescription) of acid was not allowed unless the seller maintains a logbook/register recording the sale of acid.
- This logbook was to also contain the details of the person to whom acid is sold, the quantity sold, the address of the person, and also specify the reason for procuring acid.
- Age Restriction & Documentation: The sale is also to be made only upon presentation of a photo ID containing his address issued by the government. The buyer must also prove he/she is above 18 years of age.
- Confiscation of Acid Stocks: Sellers are also required to declare all stocks of acid with the concerned Sub-Divisional Magistrate (SDM) within 15 days and in case of undeclared stock of acid. The SDM can confiscate the stock and suitably impose a fine of up to Rs 50,000 for a breach of any of the directions.
- A Record-Keeping Requirement: As per the rules, educational institutions, research laboratories, hospitals, government departments and the departments of Public Sector Undertakings, which are required to keep and store acid, to maintain a register of usage of acid and file the same with the concerned SDM.
- Accountability: As per the rules, a person shall be made accountable for the possession and safe keeping of acid in their premises. The acid shall be stored under the supervision of this person and there shall be compulsory checking of the students/ personnel leaving the laboratories/place of storage where acid is used.
What is the Compensation and Care for the Acid-attack Victims?
- Compensation: Acid attack victims are paid compensation of at least Rs. 3 lakhs by the concerned State Government/Union Territory as the aftercare and rehabilitation cost.
- Free of Cost Treatment: States are supposed to ensure that treatment provided to acid attack victims in any hospital, public or private, is free of cost. The cost incurred on treatment is not to be included in the Rs 1 lakh compensation given to the victim.
- Reservation of Beds: Acid attack victims need to undergo a series of plastic surgeries and hence 1-2 beds at private hospitals could be reserved for the treatment of acid attack victims.
- Social Integration Programs: States should also extend social integration programs to the victims for which Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs) could be funded to exclusively look after their rehabilitative requirements.
What can be the Way Forward?
- A Promise to Leave No One Behind: Violence against women continues to be an obstacle to achieving equality, development, peace as well as to the fulfillment of women and girls’ human rights.
- All in all, the promise of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) - to leave no one behind - cannot be fulfilled without putting an end to violence against women and girls.
- Holistic Approach: Crime against women cannot be resolved in a court of law alone. A holistic approach & changing the entire ecosystem is what is required.
- Participation: All the stakeholders need to get their act together, including Law makers, police officers, forensic dept, prosecutors, judiciary, medical & health dept, NGOs, rehabilitation centers.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. What are the continued challenges for Women in India against time and space? (2019)


Science & Technology
Whole Genome Sequencing
For Prelims: Whole Genome Sequencing, DNA, Gene, Genome.
For Mains: Whole Genome Sequence and its Significance
Why in News?
Recently, Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) Bhopal have carried out Whole Genome Sequencing of banyan (Ficus benghalensis) and peepal (Ficus religiosa) from leaf tissue samples.
- The work helped in identifying 17 genes in the case of banyan and 19 genes of peepal with multiple signs of adaptive evolution (MSA) that play a pivotal role in long-time survival of these two Ficus species.
What is Whole Genome Sequencing?
- About:
- All organisms have a unique genetic code, or genome, that is composed of nucleotide bases- Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C) and Guanine (G).
- The unique Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) fingerprint, or pattern can be identified by knowing the sequence of the bases in an organism.
- Determining the order of bases is called sequencing.
- Whole genome sequencing is a laboratory procedure that determines the order of bases in the genome of an organism in one process.
- Methodology:
- DNA Shearing:
- Scientists begin by using molecular scissors to cut the DNA, which is composed of millions of bases (A’s, C’s, T’s and G’s), into pieces that are small enough for the sequencing machine to read.
- DNA Bar Coding:
- Scientists add small pieces of DNA tags, or bar codes, to identify which piece of sheared DNA belongs to which bacteria.
- This is similar to how a bar code identifies a product at a grocery store.
- Scientists add small pieces of DNA tags, or bar codes, to identify which piece of sheared DNA belongs to which bacteria.
- DNA Sequencing:
- The bar-coded DNA from multiple bacteria is combined and put in a DNA sequencer.
- The sequencer identifies the A’s, C’s, T’s, and G’s, or bases, that make up each bacterial sequence.
- The sequencer uses the bar code to keep track of which bases belong to which bacteria.
- Data Analysis:
- Scientists use computer analysis tools to compare sequences from multiple bacteria and identify differences.
- The number of differences can tell the scientists how closely related the bacteria are, and how likely it is that they are part of the same outbreak.
- DNA Shearing:
- Advantages:
- Provides a high-resolution, base-by-base view of the genome
- Captures both large and small variants that might be missed with targeted approaches
- Identifies potential causative variants for further follow-up studies of gene expression and regulation mechanisms
- Delivers large volumes of data in a short amount of time to support assembly of novel genomes
- Significance:
- Genomic information has been instrumental in identifying inherited disorders, characterizing the mutations that drive cancer progression, and tracking disease outbreaks.
- It is beneficial for sequencing agriculturally important livestock, plants, or disease-related microbes.
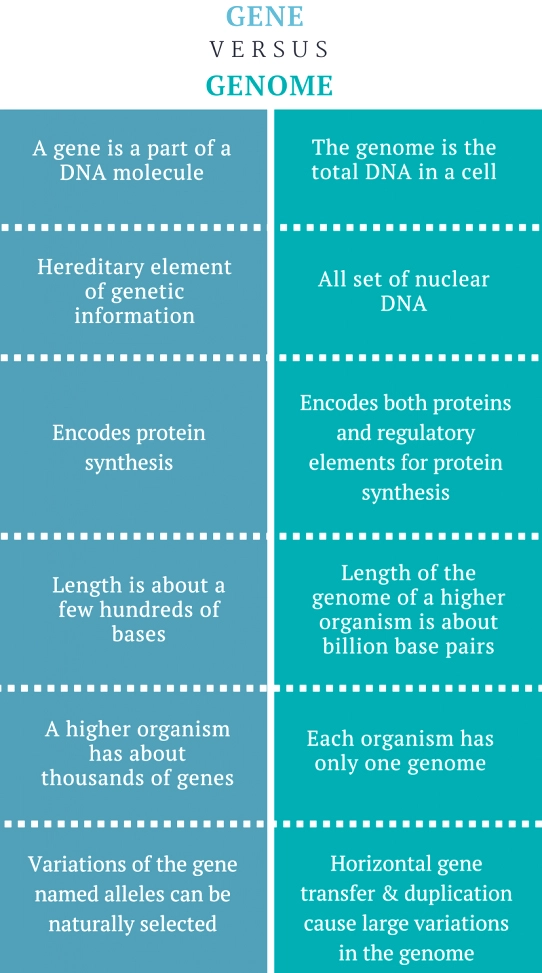
What is Genome?
- A genome refers to all of the genetic material in an organism, and the human genome is mostly the same in all people, but a very small part of the DNA does vary between one individual and another.
- Every organism’s genetic code is contained in its DNA, the building blocks of life.
- The discovery that DNA is structured as a “double helix” by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, started the quest for understanding how genes dictate life, its traits, and what causes diseases.
- Each genome contains all of the information needed to build and maintain that organism.
- In humans, a copy of the entire genome contains more than 3 billion DNA base pairs.
What is the Difference between Genome and Gene?
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q1. With reference to agriculture in India, how can the technique of ‘genome sequencing’, often seen in the news, be used in the immediate future? (2017)
- Genome sequencing can be used to identify genetic markers for disease resistance and drought tolerance in various crop plants.
- This technique helps in reducing the time required to develop new varieties of crop plants.
- It can be used to decipher the host-pathogen relationships in crops.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- Chinese scientists decoded rice genome in 2002. The Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) scientists used the genome sequencing to develop better varieties of rice such as Pusa Basmati-1 and Pusa Basmati-1121, which currently makes up substantially in India’s rice export. Several transgenic varieties have also been developed, including insect resistant cotton, herbicide tolerant soybean, and virus resistant papaya. Hence, 1 is correct.
- In conventional breeding, plant breeders scrutinize their fields and search for individual plants that exhibit desirable traits. These traits arise spontaneously through a process called mutation, but the natural rate of mutation is very slow and unreliable to produce all the plant traits that breeders would like to see. However, in genome sequencing it takes less time, thus it is more preferable. Hence, 2 is correct.
- The host-pathogen interaction is defined as how microbes or viruses sustain themselves within host organisms on a molecular, cellular, organism or population level. The genome sequencing enables the study of the entire DNA sequence of a crop, thus it aids in understanding of pathogens’ survival or breeding zone. Hence, 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q2. Consider the following statements: (2022)
DNA Barcoding can be a tool to:
- assess the age of a plant or animal.
- distinguish among species that look alike.
- identify undesirable animal or plant materials in processed foods.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- The novel technique of identifying biological specimens using short DNA sequences from either nuclear or organelle genomes is called DNA barcoding.
- DNA barcoding has many applications in various fields like preserving natural resources, protecting endangered species, controlling agriculture pests, identifying disease vectors, monitoring water quality, authentication of natural health products and identification of medicinal plants.
- Species identification of endangered wildlife (hence, distinguishes among species that look alike), quarantine pests, and disease vectors (identifying undesirable animals/plants) are just a few areas in which DNA barcoding is enabling researchers, enforcement agents, and consumers to make informed decisions in much shorter time frames.
- Statement 2 and statement 3 are correct, Hence, option (d) is correct (by elimination).
Mains
Q. What are the research and developmental achievements in applied biotechnology? How will these achievements help to uplift the poorer sections of society? (2021)


Important Facts For Prelims
FIFA World Cup Qatar 2022
Why in News?
Recently, Argentina won the FIFA (Fédération internationale de Football Association) World Cup 2022 held in Qatar by defeating France.
What is the FIFA World Cup?
- About:
- The most prestigious tournament in the world - taking place quadrennially.
- First FIFA WC:
- Held in Uruguay in 1930, Won by Uruguay.
- Trophy:
- The trophy cup awarded from 1930 to 1970 was the Jules Rimet Trophy, named for the Frenchman who proposed the tournament.
- A new trophy called the FIFA World Cup was put up for competition in 1970.
- Key Highlights of FIFA WC 2022:
- Awards: FIFA announced a number of awards to recognize the great performance of players throughout the WC including
- Golden Boot (Most number of Goals) - Kylian Mbappe (France)
- Golden Glove - Emiliano Martinez (Argentina)
- Golden Ball (Performer of the Tournament) - Lionel Messi (Argentina)
- Young Player - Enzo Fernandez (Argentina)
- FIFA Fair Play Award - England
- FIFA WC Official Ball:

- Al Rihla (means - ‘the journey’) - a reference to a travelogue written by Ibn Battuta, the 14th-century explorer.
- At the time of First FIFA WC (1930), there was no official ball and both the finalists - Uruguay (T Model ball) and Argentina (Tiento) - brought their own balls.
- Pakistan produces more than 2/3rd of the world's footballs, with Sialkot being the hub of manufacturing.
- Awards: FIFA announced a number of awards to recognize the great performance of players throughout the WC including
- Official Mascot:
- La’eeb was the Official Mascot for FIFA WC 2022.
- ‘La’eeb’ in Arabic translates to ‘super-skilled player’.
- La’eeb was the Official Mascot for FIFA WC 2022.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following statements in respect of the Laureus World Sports Award which was instituted in the year 2000: (2021)
- American golfer Tiger Woods was the first winner of this award.
- The award was received mostly by ‘Formula One’ players so far.
- Roger Federer received this award the maximum number of times compared to others.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q2. Consider the following statements in respect of the 32nd Summer Olympics: (2021)
- The official motto for this Olympics is ‘A New World’.
- Sport Climbing, Surfing, Skateboarding, Karate and Baseball are included in this Olympics.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Q3. Consider the following statements in respect of the ICC World Test Championship: (2021)
- The finalists were decided by the number of matches they won.
- New Zealand was ranked ahead of England because it won more matches than England.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)


Important Facts For Prelims
DISHA Scheme
Why in News?
Recently, the Minister of Law and Justice has informed Lok Sabha that “Designing Innovative Solutions for Holistic Access to Justice” (DISHA) Scheme was launched for a period of five years 2021-2026.
What is DISHA Scheme?
- About:
- It was launched in order to provide a comprehensive, holistic, integrated and systemic solution on access to justice at pan India level.
- It aims to secure “Justice” to the people of India as enunciated in the Preamble and under Articles 39A, 14 and 21 of the Constitution of India.
- It aims to design and consolidate various initiatives to provide citizen- centric delivery of legal services.
- Components: There are three components under DISHA at present,
- Tele-Law: Reaching the Unreached:
- To strengthen pre litigation legal advice and consultation, the Tele-Law Service connects the citizen with the Panel lawyers through the use of video /Teleconferencing facilities available at the Common Service Centres (CSCs) and via Tele-Law Mobile App.
- The Nyaya Bandhu Programme:
- The Nyaya Bandhu (Pro Bono Legal Services) programme aims to provide free legal assistance and counsel to the marginalized sections.
- Nyaya Bandhu Mobile Application, for android and iOS phones, has been developed to connect the registered Pro Bono Advocates with the registered applicants.
- Legal Awareness Programmes:
- To provide for a more robust framework, Legal Service Institutions network at the National, State and District and Taluk level, constituted under the Legal Services Authorities, Act, 1987.
- Information Education and Communication (IEC):
- In order to ensure its widened reach, dedicated Information Education and Communication (IEC) including (Technology) component has been embedded in DISHA.
- Tele-Law: Reaching the Unreached:
What are the Major Steps Taken on Access to Justice?
- National Mission for Justice Delivery and Legal Reforms:
- The Mission has been pursuing a coordinated approach for phased liquidation of arrears and pendency in judicial administration, which, inter-alia, involves better infrastructure for courts, including computerization, an increase in strength of subordinate judiciary, policy and legislative measures.
- Improving Infrastructure for Judicial Officers of District and Subordinate Courts:
- Rs. 9291.79 crores have been released since the inception of the Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) for Development of Infrastructure Facilities.
- The number of court halls has increased from Significantly.
- Leveraging Information and Communication Technology (ICT):
- The Government has been implementing the e-Courts Mission Mode Project throughout the country for information and communication technology enablement of district and subordinate courts.
- The number of computerised district & subordinate courts has increased to 18,735 so far.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. With reference to National Legal Services Authority, consider the following statements: (2013)
- Its objective is to provide free and competent legal services to the weaker sections of the society on the basis of equal opportunity.
- It issues guidelines for the State Legal Services Authorities to implement the legal programmes and schemes throughout the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Q2. In India, Legal Services Authorities provide free legal services to which of the following type of citizens? (2020)
- Person with an annual income of less than `1,00,000
- Transgender with an annual income of less than `2,00,000
- Member of Other Backward Classes (OBC) with an annual income of less than `3,00,000
- All Senior Citizens
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1 and 4 only
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)
Why in News?
India has abstained in the U.N. Economic and Social Council on a draft resolution to oust Iran from its principal global intergovernmental body (Commission on the Status of Women) dedicated to the promotion of gender equality and women empowerment.
What is Commission on the Status of Women (CSW)?
- It is the principal global intergovernmental body exclusively dedicated to the promotion of gender equality and the empowerment of women.
- By the ECOSOC resolution of June 1946, it was established as a functional commission of the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC). The Commission comprises 45 Member States of the United Nations.
What was the Resolution?
- The draft resolution, introduced by the U.S., on the removal of Iran from the membership of the CSW for the remainder of its 2022-2026 term, citing its oppression of women and girls in the country.
- Iran has been rocked by protests since the September 2022 death of 22-year-old Mahsa Amini, who died after being detained by the country's morality police.
- The resolution was adopted by a recorded vote of 29 in favour to 8 against - Bolivia, China, Kazakhstan, Nicaragua, Nigeria, Oman, Russia, Zimbabwe and 16 abstentions, including by Bangladesh, India, Indonesia, Mauritius, Mexico, and Thailand.
What is the UN Economic and Social Council?
- About:
- Established by the UN Charter in 1945, it is the principal body for coordination, policy review, policy dialogue and recommendations on economic, social and environmental issues, as well as implementation of internationally agreed development goals.
- It has 54 members, elected by the UN General Assembly for overlapping three-year terms.
- It is the UN's central platform for reflection, debate and innovative thinking on sustainable development.
- Each year, ECOSOC structures its work around an annual theme of global importance to sustainable development.
- It coordinates the work of the 14 UN specialized agencies, ten functional commissions and five regional commissions, receives reports from nine UN funds and programmes and issues policy recommendations to the UN system and to member states.
- Few Important Bodies under the Purview of ECOSOC:
- International labour Organization (ILO)
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- Bretton Woods Twins (World Bank Group and International Monetary Fund)
- United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF)
- Apart from these there are various Functional and Regional Commissions, Standing Committees, Ad Hoc and Expert Bodies as well.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to the United Nations, consider the following statements: (2009)
- The Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) of UN consists of 24 member States.
- It is elected by a 2/3rd majority of the General Assembly for a 3-year term.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
First Global Water Survey Satellite
Why in News?
Recently, a National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) -led international satellite, Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) was launched from Southern California by SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket.
- The satellite will take the first global survey of Earth’s freshwater systems from space.
What is Surface Water and Ocean Topography?
- About:
- SWOT is an advanced radar satellite that aims to provide scientists with a deeper understanding of the oceans and how climate change impacts them.
- The rocket's payload, the SWOT, incorporates advanced microwave radar technology to collect high-definition measurements of oceans, lakes, reservoirs and rivers over 90% of the globe.
- Significance:
- Using its radar, the satellite will be able to measure the water levels of ocean features ten times more accurately than is currently possible.
- It will also be able to measure over a million lakes and rivers on Earth.
- Through its observations, the satellite will also be able to improve the accuracy of flood forecasts and provide scientists with more precise monitoring of impending droughts, rising sea levels, and life on Earth.
- One major thrust of the mission is to explore how oceans absorb atmospheric heat and carbon dioxide in a process that naturally regulates global temperatures and has helped to minimize climate change.
- Oceans are estimated to have absorbed more than 90% of the excess heat trapped in Earth's atmosphere by human-caused greenhouse gas emissions.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. What is ‘Greased Lightning-10 (GL-10)’, recently in the news? (2016)
(a) Electric plane tested by NASA
(b) Solar-powered two-seater aircraft designed by Japan
(c) Space observatory launched by China
(d) Reusable rocket designed by ISRO
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Greased Lighting–10 (GL–10) is NASA developed battery-powered plane with 10 engines that can take off and land like a helicopter and fly efficiently like an aircraft.
- It is a remotely piloted plane having a 3.05-meter wingspan, eight electric motors on the wings, and two electric motors on the tail and weighs a maximum of 28.1 kilograms at take-off.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.