Indian Economy
India Blockchain Platform
For Prelims: Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Public Digital Infrastructure, Digital India mission, Aadhaar, UPI, Web 3.0, Non-Fungible tokens, decentralized finance (DeFi)
For Mains: Significance and use of Blockchain in India
Why in News?
Recently, India has made several efforts to become a digital society by building a large citizen-scale digital public infrastructure with a significant push from the government.
What is Public Digital Infrastructure?
- About:
- It refers to digital solutions that enable basic functions essential for public and private service delivery, i.e., collaboration, commerce, and governance.
- Indian Initiatives:
- The Government of India and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) have been promoting simplification and transparency to increase the speed of interaction between individuals, markets, and the government.
- With the commencement of the Digital India mission in 2015, the payments, provident fund, passports, driving licenses, crossing tolls, and checking land records all have been transformed with modular applications built on Aadhaar, Unified Payments Interface(UPI), and the India Stack.
- The Government of India and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) have been promoting simplification and transparency to increase the speed of interaction between individuals, markets, and the government.
- Limitations:
- Not Interconnected:
- The existing different digital infrastructures are not interconnected as a design.
- Not Interoperable:
- There is need for a technical integration is required to make them conversant and interoperable.
- Inefficient:
- Today, information travels across multiple systems, and they mostly rely on limited private databases, which makes it more complex, as more network grows it increases the cost and creates inefficiency.
- Not Interconnected:
What are Other Efficient Digital Systems?
- Web 3.0:
- About:
- Web 3.0 is a decentralized internet to be run on blockchain technology, which would be different from the versions in use, Web 1.0 and Web 2.0.
- The internet in Web 1.0 was mostly static web pages where users would go to a website and then read and interact with the static information.
- In Web 2.0 users can create content - primarily, a social media kind of interaction.
- In Web 3.0, users will have ownership stakes in platforms and applications unlike now where tech giants control the platforms.
- Web 3.0 is a decentralized internet to be run on blockchain technology, which would be different from the versions in use, Web 1.0 and Web 2.0.
- Significance:
- The Web 3.0 architecture establishes a new version of the Internet protocol incorporating token-based economics, transparency, and decentralization.
- It is not only the cryptocurrencies but also NFTs or non-fungible tokens, representing physical assets or digital twins.
- A user can access all ecosystem benefits using a distributed token where they can show proof of ownership, tax history, and payment instruments.
- The blockchain records could be visible, compiled, and audited by the regulators in real time.
- About:
- Blockchain:
- About:
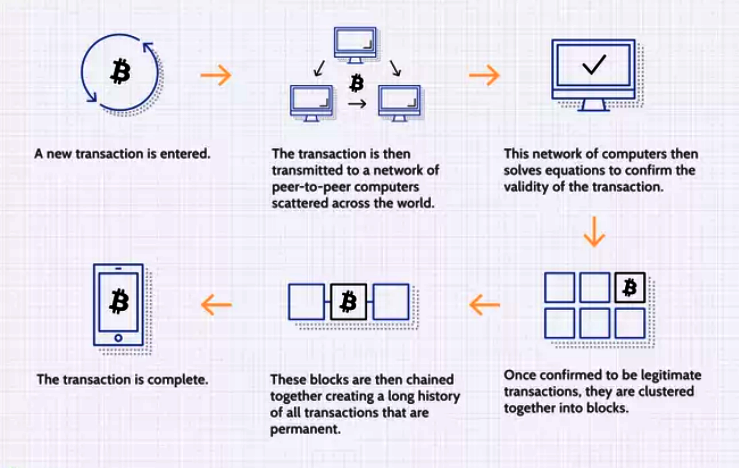
- A blockchain is a distributed database or ledger that is shared among the nodes of a computer network.
- As a database, a blockchain stores information electronically in digital format.
- Blockchains are best known for their crucial role in cryptocurrency systems, such as Bitcoin, for maintaining a secure and decentralized record of transactions.
- The innovation of a blockchain is that it guarantees the fidelity and security of a record of data and generates trust without the need for a trusted third party.
- Global Adoption:
- Estonia, the world’s blockchain capital, is using blockchain infrastructure to verify and process all e-governance services offered to the general public.
- China, launched BSN (Blockchain-based Service Network) to deploy blockchain applications in the cloud at a streamlined rate.
- In Britain, the Centre for Digital Built Britain is running the National Digital Twin program (NDTp) to foster collaboration between owners and developers of digital twins in the built environment.
- The Brazilian government recently launched the Brazilian Blockchain Network to bring participating institutions in governance and the technological system that facilitates blockchain adoption in solutions for the public good.
- Applications:
- They are well-established decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms that rely on blockchain infrastructure.
- These platforms have a multi-country presence and usage and do not come under any particular regulatory ambit.
- DeFi allows users to borrow and lend cryptocurrencies on a short-term basis at algorithmically determined rates.
- DeFi users are rewarded with tokens that confer governance rights, which are analogous to seats on the protocol’s board.
- For example:
- The blockchain provider Solana launched a prototype smartphone with hardware and security that can support decentralized apps for people interested in crypto wallets, Web3, and NFTs.
- About:
How can India Benefit from Blockchain?
- Create Interoperability:
- The Indian digital community, including fintech, academia, think tanks, and institutions, should focus on supporting research in standards, interoperability, and efficient handling of current known issues with the distributed technologies,
- e.g., scalability and performance, consensus mechanisms, and auto-detection of vulnerabilities.
- The Indian digital community, including fintech, academia, think tanks, and institutions, should focus on supporting research in standards, interoperability, and efficient handling of current known issues with the distributed technologies,
- Regulation:
- At the present time, blockchain models are partially permitted or are public like Ethereum which is unregulated and relies on intrinsic standards.
- Creating National Ecosystem on Blockchain:
- The ideal solution to solving most of the known issues of decentralized technologies lies in the middle path, i.e., a national platform operating at L1(layer-1) that interconnects blockchains (both permissioned and public), application providers (decentralized applications — dApps — and existing), token service providers, and infrastructure managers.
- Together they can form a reliable and efficient network for the Indian digital economy.
- The ecosystem can further deploy relevant and purpose-specific applications at L2(Layer-2) for very little cost and effort.
- Further, all chains on this public infrastructure will communicate with each other, thus replicating the communication (and avoiding the need for complex integrations with each other) on the Internet for existing Indian digital infrastructures.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to “Blockchain Technology”, consider the following statements: (2020)
- It is a public ledger that everyone can inspect, but which no single user controls.
- The structure and design of the blockchain is such that all the data in it are about cryptocurrency only.
- Applications that depend on basic features of blockchain can be developed without anybody’s permission.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- A blockchain is a form of public ledger, which is a series (or chain) of blocks on which transaction details are recorded and stored on a public database after suitable authentication and verification by the designated network participants. A public ledger can be viewed but cannot be controlled by any single user. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- The blockchain is not only about the cryptocurrency but it turns out that blockchain is actually a pretty reliable way of storing data about other types of transactions, as well.
- In fact, blockchain technology can be used in property exchanges, bank transactions, healthcare, smart contracts, supply chain, and even in voting for a candidate. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Although cryptocurrency is regulated and needs the approval of the central authorities, blockchain technology is not only about cryptocurrency. It can have various uses, and applications based on basic features of the technology can be developed without anybody’ approval. Hence, statement 3 is correct. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. What is Cryptocurrency? How does it affect global society? Has it been affecting Indian society also? (2021)


Biodiversity & Environment
Air Quality and Health in Cities
For Prelims: State of Global Air, World Health Organisation, WHO’s New Air Quality Guidelines, Particulate Matter.
For Mains: Air Quality and Health in Cities Report, Effects of Air pollution, Environmental Pollution & Degradation.
Why in News?
Recently, a report was released titled Air Quality and Health in Cities, which analysed pollution and global health effects for more than 7,000 cities around the world between 2010 and 2019.
- The study ranked cities on the basis of two major air pollutants found — fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) and Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2).
What is the State of Global Air?
- The State of Global Air (SoGA) is a research and outreach initiative to provide reliable, meaningful information about air quality around the world.
- A collaboration of the US-based Health Effects Institute and the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation’s Global Burden of Disease project, the program gives citizens, journalists, policymakers, and scientists access to high-quality, objective information about air pollution exposure and its health impacts.
What are the Findings?
- PM 2.5 Levels:
- Delhi and Kolkata are ranked first and second in the list of top 10 most polluted cities when PM 2.5 levels were compared.
- PM 2.5 is an atmospheric particulate matter of diameter of fewer than 2.5 micrometres, which is around 3% the diameter of a human hair. It causes respiratory problems and reduces visibility.
- While exposures to PM 2.5 pollution tend to be higher in cities located in low- and middle-income countries, exposure to NO2 is high across cities in high-income as well as low- and middle-income countries.
- Delhi and Kolkata are ranked first and second in the list of top 10 most polluted cities when PM 2.5 levels were compared.
- NO2 Levels:
- No Indian city appeared in the list of top 10 or even top 20 polluted cities when NO2 levels were compared.
- Average NO2 levels for Delhi, Kolkata and Mumbai, according to the report, ranged from 20-30 µg/m3.
- This list saw Shanghai at the top with an average annual exposure of 41 µg/m3.
- NO2 comes mainly from the burning of fuels in older vehicles, power plants, industrial facilities and residential cooking and heating.
- As city residents tend to live closer to busy roads with dense traffic, they are often exposed to higher NO2 pollution than residents of rural areas.
- Other cities with high NO2 population levels included Moscow, Beijing, Paris, Istanbul and Seoul.
- No Indian city appeared in the list of top 10 or even top 20 polluted cities when NO2 levels were compared.
- Death Burden:
- Beijing had the largest disease burden associated with a PM 2.5-related illness, with 124 attributable fatalities per 100,000 persons.
- Five Chinese cities were in the top 20.
- Delhi came in 6th, with 106 deaths per 100,000 and Kolkata at 8th with 99 deaths.
- Beijing had the largest disease burden associated with a PM 2.5-related illness, with 124 attributable fatalities per 100,000 persons.
- Causes:
- Only 117 nations currently have ground-level monitoring systems to track PM 2.5, and only 74 nations are monitoring NO2 levels.
- In 2019, exposure to pollutants in 86% of the more than 7,000 cities exceeded WHO’s standard, therefore, impacting around 2.6 billion people.
What are the WHO’s New Air Quality Guidelines?
- The 2021 guidelines recommend new air quality levels to protect the health of populations, by reducing levels of key air pollutants, some of which also contribute to climate change.
- WHO’s new guidelines recommend air quality levels for 6 pollutants, where evidence has advanced the most on health effects from exposure.
- 6 classical pollutants include particulate matter (PM 2.5 and 10), ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2) and carbon monoxide (CO).
What are the Recommendations?
- Leverage the expanding air quality monitoring toolbox:
- Efforts to expand ground monitoring of air quality can improve the accuracy of estimates of Pollutant levels and understanding of local air quality trends.
- However, in addition to setting up monitors, it is important to invest in resources for calibration and maintenance to ensure the quality of data from these monitors.
- Collect and digitize health records:
- Data on the burden of air pollution on health are vital for assessing the effectiveness of interventions, both in terms of public health benefits and economic impact.
- It is important to collect city-level health data consistently and systematically and make them accessible to researchers. This can help researchers conduct more accurate and local analyses that inform communities and policymakers.
What are Initiatives taken by India for Controlling Air Pollution?
- System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research (SAFAR) Portal
- Air Quality Index
- Graded Response Action Plan
- BS-VI Vehicles,
- Push for Electric Vehicles (EVs),
- Odd-Even Policy as an emergency measure for reducing Vehicular Pollution.
- New Commission for Air Quality Management
- Turbo Happy Seeder (THS) Machine
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In the cities of our country, which among the following atmospheric gases are normally considered in calculating the value of Air Quality Index? (2016)
- Carbon dioxide
- Carbon monoxide
- Nitrogen dioxide
- Sulfur dioxide
- Methane
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- National Air Quality Index (AQI) is a tool for effective communication of air quality status to people in terms which are easy to understand. It transforms complex air quality data of various pollutants into a single number (index value), nomenclature and colour.
- There are six AQI categories, namely Good, Satisfactory, Moderately Polluted, Poor, Very Poor, and Severe.
- It considers eight pollutants namely:
- Carbon Monoxide (CO), hence, 2 is correct.
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2), hence, 3 is correct.
- Sulphur Dioxide (SO2), hence, 4 is correct.
- Ozone (O3),
- PM 2.5,
- PM 10,
- Ammonia (NH3),
- Lead (Pb).
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. Describe the key points of the revised Global Air Quality Guidelines (AQGs) recently released by the World Health Organisation (WHO). How are these different from its last update in 2005? What changes in India’s National Clean Air Programme are required to achieve revised standards? (2021)


Governance
Ban on VLC Media Player
For Prelims: IT Act 2000, IT Rules 2009, Section 69A, Powers of Executive in Banning Content, Cyber Security
For Mains: Provisions of IT Act 2000, Powers of Government in regulating content, Government initiative for cyber security
Why in News?
The website of VideoLAN Client (VLC) Media Player has been banned in India.
- VLC states that according to its statistics, its website has been banned since February 2022 in India.
What do we need to know about the VLC & Its Ban?
- About VLC:
- VLC gained popularity in India in the late 90s when advancements in information technology led to the penetration of personal computers in Indian homes.
- Apart from being free and open source, VLC easily integrates with other platforms and streaming services and supports all file formats without requiring additional codecs.
- Ban on VLC:
- While the VLC website has been banned, the VLC app continues to be available for download on Google and Apple stores.
- Civil society organisations have repeatedly filed Right to Information (RTI) applications with the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) regarding the ban on VLC website.
- However, these applications have been met with similar responses stating that “no information is available” with the Ministry.
- When the website was accessed previously, the message “The website has been blocked as per order of Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology under Information Technology Act, 2000”, was displayed.
- Reasons for Ban:
- China’s Interference:
- Report from cybersecurity firm, Symantec, in April 2022 suggested that Cicada, a hacker group allegedly backed by China, has been using the VLC Media Player to deploy a malicious malware loader.
- Safe Server:
- VLC website has been banned; its app is available for download as the app stores’ servers where the mobile apps are hosted are considered safer than servers where the desktop versions are hosted.
- China’s Interference:
When can the Government Ban Online Content to the Public?
- There are two routes through which content can be blocked online:
- Executive:
- Section 69A of the Information Technology Act, 2000:
- Section 69A allows the government to direct an intermediary to “block for access by the public” any information generated, transmitted, received, stored or hosted in any computer resource if it is necessary or expedient to do so, in the interest of sovereignty and integrity of India, defence of India, security of the state, friendly relations with foreign states or public order or for preventing incitement to the commission of any cognisable offence”.
- Section 69A draws its power from Article 19(2) of the Constitution which allows the government to place reasonable restrictions on the fundamental right to freedom of speech and expression.
- Section 69A of the Information Technology Act, 2000:
- Judiciary:
- Courts in India have the power to direct intermediaries to make content unavailable in India to provide effective remedy to the victim/plaintiff.
- For example, courts may order internet service providers to block websites which provide access to pirated content and violate the plaintiff’s copyright.
- Courts in India have the power to direct intermediaries to make content unavailable in India to provide effective remedy to the victim/plaintiff.
- Executive:
What is the Procedure of Blocking Content Online?
- About:
- Detailed procedure for blocking content is provided by the Information Technology (Procedure and Safeguards for Blocking for Access of Information by Public) Rules, 2009 (IT Rules, 2009) that have been formulated under Section 69A of the Information Technology Act, 2000.
- Only the Central government can exercise the power of directing intermediaries to block access to online content directly, and not the State governments.
- Detailed procedure for blocking content is provided by the Information Technology (Procedure and Safeguards for Blocking for Access of Information by Public) Rules, 2009 (IT Rules, 2009) that have been formulated under Section 69A of the Information Technology Act, 2000.
- Process:
- Central or State agencies appoint a “Nodal Officer” who will forward the blocking order to the “Designated Officer” of the Central government.
- The designated officer, as part of a committee, examines the request of the nodal officer.
- The committee comprises representatives from the Ministries of Law and Justice, Information and Broadcasting, Home Affairs, and the Cert-In.
- The creator/host of the content in question is given a notice to submit clarifications and replies.
- The committee then makes a recommendation on whether the request of the nodal officer should be accepted or not.
- If this recommendation is approved by the MeitY, the designated officer can direct the intermediary to remove content.
What are Government’s Initiatives for Cyber Security?
- Cyber Surakshit Bharat Initiative
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra
- Online cybercrime reporting portal
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC)
- Information Technology Act, 2000
Way Forward
- Transparency:
- Rule 16 of the IT Rules, 2009 provides that strict confidentiality is to be maintained with respect to any requests or actions under the IT Rules, 2009.
- This should be revisited and an element of transparency should be introduced as there is no clarity on why VLC has been blocked.
- Rule 16 of the IT Rules, 2009 provides that strict confidentiality is to be maintained with respect to any requests or actions under the IT Rules, 2009.
- Opportunity to Reply:
- The lack of an opportunity to submit clarifications/replies by the creator/host violates the principles of natural justice.
- Appropriate time should be allowed for the creator/host to present his reply in front of the respective authority.
- The lack of an opportunity to submit clarifications/replies by the creator/host violates the principles of natural justice.
- Review Committee Effectiveness:
- It has been noted that the Review Committee, which is required to meet every two months to review orders, has not disagreed with any of the committee’s decisions.
- It should strive to review the orders of the committee with in-depth analysis and provide the appropriate recommendations.
- It has been noted that the Review Committee, which is required to meet every two months to review orders, has not disagreed with any of the committee’s decisions.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In India, it is legally mandatory for which of the following to report on cyber security incidents? (2017)
- Service providers
- Data centres
- Body corporate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- According to section 70B of the Information Technology Act, 2000 (IT Act), the Union Government by notification should appoint an agency named Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERTIn) to serve as the national agency for incident response.
- The Union Government under section 70B of the IT Act, 2000 established and notified rules of CERT-In in 2014. According to Rule 12(1)(a), it is mandatory for service providers, intermediaries, data centers and corporate bodies to report cyber security incidence to CERT-In within a reasonable time of occurrence of the incident. Hence, 1, 2 and 3 are correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. What are the main socio-economic implications arising out of the development of IT industries in major cities of India? (2021)
Q. Discuss different types of cybercrimes and measures required to be taken to fight the menace. (2020)
Q. Data security has assumed significant importance in the digitized world due to rising cybercrimes. The Justice B.N. Srikrishna Committee Report addresses issues related to data security. What, in your view, are the strengths and weaknesses of the Report relating to protection of personal data in cyber space? (2018)


Indian Economy
Draft Indian Ports Bill, 2022
For Prelims: Major Ports in India, Major Ports vs Minor Ports.
For Mains: Draft Indian Ports Bill, 2022, Indian Ports Act 1908 and the Major Port Trust Act, 1963.
Why in News?
Recently, the government has prepared the Draft Indian Ports Bill, 2022.
- The draft Indian Ports Bill,2022 seeks to repeal and replace the existing Indian Ports Act 1908, which is more than 110 years old, becoming imperative that the Act is revamped to reflect the present-day frameworks.
What does the Bill Propose?
- It seeks to amend the laws relating to ports, for the prevention and containment of pollution at ports, to ensure compliance with the country’s obligation under the maritime treaties and international instruments to which India is a party
- It seeks to empower and establish State Maritime Boards for effective administration, control and management of non-major ports in India
- It aims to provide adjudicatory mechanisms for redressal of port related disputes and to establish a national council for fostering structured growth and development of the port sector.
- It will ensure optimum utilisation of the coastline of India, as may be necessary, and to provide for matters ancillary and incidental thereto, or connected therewith.
What is the Significance of Ports for India?
- India has a 7,500 km long coastline, 14,500 km of potentially navigable waterways and strategic location on key international maritime trade routes.
- About 95% of India’s trade by volume and 65% by value is done through maritime transport facilitated by ports.
How is the Indian Port Ecosystem?
- About:
- Ports sector in India is driven by high growth in external trade.
- The Union Government has allowed Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) of up to 100% under the automatic route for port and harbour construction and maintenance projects.
- Legal Provisions:
- Major Ports are under the Union list of the Indian Constitution and are administered under the Indian Ports Act 1908 and the Major Port Trust Act, 1963.
- Number of Major Ports:
- There are 12 major ports and 200 non-major ports (minor ports) in the country.
- Major ports include Deendayal (erstwhile Kandla), Mumbai, JNPT, Marmugao, New Mangalore, Cochin, Chennai, Kamarajar (earlier Ennore), V O Chidambaranar, Visakhapatnam, Paradip and Kolkata (including Haldia).
- There are 12 major ports and 200 non-major ports (minor ports) in the country.
- Major Ports vs Minor Ports:
- Ports in India are classified as Major and Minor Ports according to the jurisdiction of the Central and State government as defined under the Indian Ports Act, 1908.
- All the 12 Major Ports are governed under the Major Port Trusts act, 1963 and are owned and managed by the Central Government.
- All the Minor Ports are governed under the Indian Port Act, 1908 and are owned and managed by the State Governments.
- Ports in India are classified as Major and Minor Ports according to the jurisdiction of the Central and State government as defined under the Indian Ports Act, 1908.
- Administration of Major Ports:
- Each major port is governed by a Board of Trustees appointed by the Government of India.
- The Trusts operate on the basis of policy directives and orders from the Government of India.
Way Forward
- The ongoing developments and committed investments (public and private) in ports need to be aided by scientific and consultative planning, with a keen focus on ever increasing safety, security and environmental issues.


Governance
Expansion of Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme
For Prelims: Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme, Hospitality Sector, Aatmanirbhar package, Covid-19, NBFC, MSME.
For Mains: Need for Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme in Hospitality and Related Sectors.
Why in News?
Recently, the government approved an enhancement in the Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme (ECLGS) to enterprises in hospitality and related sectors as the pandemic disrupted these sectors.
- The government has increased the amount by Rs 50,000 crore from Rs. 4.5 Lakh crore to Rs. 5 Lakh crore for these sectors which will valid till 31st March, 2023.
What is an Emergency Credit Line Guarantee Scheme?
- About:
- ECLGS was rolled out in 2020 as part of the Centre’s Aatmanirbhar package in response to the Covid-19 crisis.
- The objective was to support small businesses struggling to meet their operational liabilities due to the imposition of a nationwide lockdown.
- A 100% guarantee is provided by the National Credit Guarantee Trustee Company (NCGTC) to Member Lending Institutions (MLIs) - banks, financial institutions and Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs).
- The credit product for which guarantee would be provided under the Scheme shall be named as 'Guaranteed Emergency Credit Line (GECL)'.
- ECLGS 1.0:
- To provide fully guaranteed and collateral free additional credit to MSMEs, business enterprises, MUDRA borrowers and individual loans for business purposes to the extent of 20% of their credit outstanding as on 29th February, 2020.
- MSMEs with up to Rs 25. crore outstanding and Rs. 100 crore turnovers were eligible.
- However, the turnover cap was removed post amendment to ECLGS 2.0 in November 2020.
- ECLGS 2.0:
- The amended version focused on entities in 26 stressed sectors identified by the Kamath Committee along with the healthcare sector with credit outstanding of more than Rs. 50 crore and up to Rs. 500 crores as of 29th February, 2020.
- The scheme also mandated borrower accounts to be less than or equal to 30 days past due as of 29th February, 2020, that is, they should not have been classified as SMA 1, SMA 2, or NPA by any of the lenders as of 29th February 2020.
- SMAs are special mention accounts, which show signs of incipient stress, that lead to the borrower defaulting in servicing the debt.
- While SMA-0 accounts have payments partially or wholly overdue for 1-30 days, SMA-1 and SMA-2 accounts have payments overdue for 31-60 days and 61-90 days respectively.
- SMAs are special mention accounts, which show signs of incipient stress, that lead to the borrower defaulting in servicing the debt.
- The revised scheme also has a five-year repayment window up from four years in ECLGS 1.0.
- ECLGS 3.0:
- It involves extending credit of up to 40% of total credit outstanding across all lending institutions as of 29th February 2020.
- The tenor of loans granted under ECLGS 3.0 would be 6 years, including a moratorium period of 2 years.
- Covers business enterprises in Hospitality, Travel & Tourism, Leisure & Sporting sectors, which had, as on 29th february 2020,
- Total credit outstanding not exceeding Rs. 500 crore and overdue, if any, were for 60 days or less.
- ECLGS 4.0:
- A 100 % guarantee to cover loans up to Rs 2 crore to hospitals, nursing homes, clinics, medical colleges for setting up on-site oxygen generation plants with the interest rate capped at 7.5 %.
What is National Credit Guarantee Trustee Company Ltd?
- NCGTC is a private limited company incorporated under the Companies Act, 1956 in 2014, established by the Department of Financial Services, Ministry of Finance, as a wholly owned company of the Government of India, to act as a common trustee company for multiple credit guarantee funds.
- Credit guarantee programmes are designed to share the lending risk of the lenders and in turn, facilitate access to finance for the prospective borrowers.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana is aimed at (2016)
(a) bringing the small entrepreneurs into formal financial system
(b) providing loans to poor farmers for cultivating particular crops
(c) providing pensions to old and destitute persons
(d) funding the voluntary organizations involved in the promotion of skill development and employment generation
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY) is a scheme launched by the GoI in 2015 for providing loans upto 10 lakh to the non-corporate, non-farm small/micro enterprises.
- These loans are given by Commercial Banks, Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), Small Finance Banks, Cooperative Banks, Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs) and Non Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs).
- Under the aegis of PMMY, MUDRA has created three products, namely ‘Shishu’, ‘Kishore’ and ‘Tarun’ to signify the stage of growth/development and funding needs of the beneficiary micro unit/ entrepreneur and also provide a reference point for the next phase of graduation/growth.
- Shishu: loans upto 50,000,
- Kishor: loans above 50,000 and upto 5 lakh,
- Tarun: loans above 5 lakh and upto 10 lakh.
- The funding support from MUDRA are of four types:
- Micro Credit Scheme (MCS) for loans upto 1 lakh finance through MFIs,
- Refinance Scheme for Commercial Banks/
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)/Scheduled Cooperative Banks,
- Women Enterprise programme,
- Securitization of loan portfolio.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer
Q. With reference to the Non-banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) in India, consider the following statements: (2010)
- They cannot engage in the acquisition of securities issued by the government.
- They cannot accept demand deposits like Savings Account.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- A Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) is a company registered under the Companies Act, 1956 engaged in the business of loans and advances, acquisition of shares/stocks/bonds/debentures/ securities issued by the Government or local authority. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- NBFCs lend and make investments and hence, their activities are akin to that of banks. However, there are a few differences like NBFC do not form part of the payment and settlement system, they cannot accept demand deposits, and they cannot issue cheques drawn on itself. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.


Important Facts For Prelims
Governing Council Meeting of NITI Aayog
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister chaired the seventh meeting of the Governing Council (GC) of NITI Aayog.
What is NITI Aayog?
- The Planning Commission was replaced by a new institution – NITI Aayog on 1st January, 2015 with emphasis on ‘Bottom –Up’ approach to envisage the vision of Maximum Governance, Minimum Government, echoing the spirit of ‘Cooperative Federalism’.
- It has two Hubs,
- Team India Hub acts as an interface between States and Centre.
- Knowledge and Innovation Hub builds the think-tank acumen of NITI Aayog.
What are the Key Highlights?
- Key Agenda:
- Crop diversification and achieving self-sufficiency in pulses, oilseeds and other agri-commodities
- Implementation of National Education Policy (NEP) in school Education,
- Implementation of National Education Policy in higher education, and
- Urban governance.
- PM’s Address:
- Every State played a crucial role according to its strength and contributed to India’s fight against Covid-19, leading India to emerge as an example for the developing nations to look up to as a global leader.
- Each state should focus on promoting its 3Ts, Trade, Tourism, Technology, through every Indian Mission around the world.
What is NITI Aayog’s Governing Council?
- It is the premier body trusted with developing a shared vision of national priorities and strategies with the active involvement of States and Union Territories.
- It is a platform to discuss inter-sectoral, inter-departmental and federal issues.
- It comprises:
- The Prime Minister of India.
- Chief Ministers of all the states and union territories with the legislature.
- Lt Governors of other UTs.
- Ex-Officio Members, Vice Chairman, NITI Aayog, Full-Time Members, NITI Aayog.
- Special Invitees.
What are the Initiatives of NITI Aayog?
- SDG India Index
- Composite Water Management Index
- Atal Innovation Mission
- SATH Project.
- Aspirational District Programme
- School Education Quality Index
- District Hospital Index
- Health Index
- Agriculture Marketing And Farmer Friendly reform Index
- India Innovation Index
- Women Transforming India Awards
- Good Governance Index
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Atal Innovation Mission is set up under the (2019)
(a) Department of Science and Technology
(b) Ministry of Labour and Employment
(c) NITI Aayog
(d) Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- The Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) is a flagship initiative set up by the NITI Aayog to promote innovation and entrepreneurship based on a detailed study and deliberations on innovation and entrepreneurial needs of the country.
- AIM is envisaged as an umbrella innovation organization that would play an instrumental role in alignment of innovation policies between Central, State and sectoral innovation schemes incentivizing the establishment and promotion of an ecosystem of innovation and entrepreneurship at various levels – higher secondary schools, science, engineering and higher academic institutions, SME/MSME industry, corporate and NGO levels.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q. The Government of India has established NITI Aayog to replace the (2015)
(a) Human Rights Commission
(b) Finance Commission
(c) Law Commission
(d) Planning Commission
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. How are the principles followed by the NITI Aayog different from those followed by erstwhile Planning Commission in India? (2018)


Important Facts For Prelims
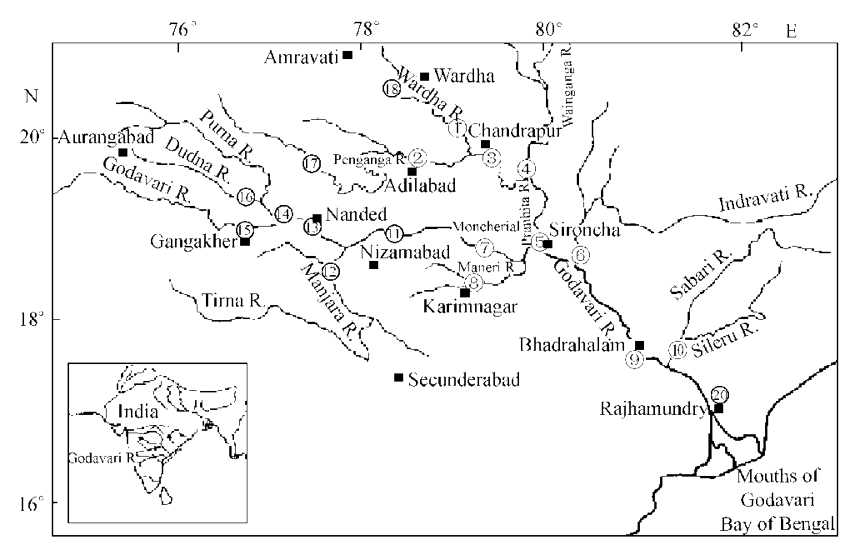
Godavari River
Why in News?
Recently, Officials issued the second warning with the flood level crossing 50 feet in Godavari River at Bhadrachalam, Telangana, and the flow in the river crossing the 13-lakh cusecs mark.
Why is the River Overflowing?
- Due to heavy rains in the catchment areas in Upper Godavari Basin.
- Discharge of water from Medigadda Barrage, receding with inflow coming down into all reservoirs.
- Discharge of water from projects in the Krishna Basin, Almatti, Narayanpur, and Tungabhadra in Karnataka, which get most of the inflows into projects in Telangana and Andhra Pradesh.
- Further, Srisaialam reservoir (Hydro-electric Power plant) was getting over 3.60 lakh cusecs flood and discharge was over 3.17 lakh cusecs.
What are the Key Points of Godavari River?
- About:
- The Godavari is the largest Peninsular River system. It is also called the Dakshin Ganga.
- The basin is bounded on the north by the Satmala hills, on the south by the Ajanta range and the Mahadeo hills, on the east by the Eastern Ghats and on the west by the Western Ghats.
- Source:
- Godavari River rises from Trimbakeshwar near Nasik in Maharashtra and flows for a length of about 1465 km before outfalling into the Bay of Bengal.
- Drainage Basin:
- The Godavari basin extends over states of Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Odisha in addition to smaller parts in Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka and Union territory of Puducherry.
- Tributaries:
- Pravara, Purna, Manjra, Penganga, Wardha, Wainganga, Pranhita (combined flow of Wainganga, Penganga, Wardha), Indravati, Maner and the Sabri.
- The Pravara, Manjira and Maner are right bank tributaries.
- The Purna, Pranhita, Indravathi and Sabari are important left bank tributaries
- Pravara, Purna, Manjra, Penganga, Wardha, Wainganga, Pranhita (combined flow of Wainganga, Penganga, Wardha), Indravati, Maner and the Sabri.
- Cultural Significance:
- Kumbh Mela also takes place on the banks of the Godavari River in Nashik.
- Other locations for Kumbh are the Shipra River in Ujjain, the Ganges in Haridwar, and the confluence of the Ganges, Yamuna, and the mythical Saraswati River in Prayag.
- Kumbh Mela also takes place on the banks of the Godavari River in Nashik.
- Urban Centers:
- Nagpur, Aurangabad, Nashik, Rajhmundry.
- Industries:
- Nashik and Aurangabad have a large number of industries, especially automobiles.
- The industries in the basin are mostly based on agricultural produce such as rice milling, cotton spinning and weaving, sugar and oil extraction.
- Cement and some small engineering industries also exist in the basin.
- Important Projects on Godavari:
- Polavaram Irrigation Project
- Kaleshwaram.
- Sadarmatt Anicut
- Inchampalli project
- Sriram Sagar Project (SRSP)
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following rivers: (2015)
- Vamsadhara
- lndravati
- Pranahita
- Pennar
Which of the above are tributaries of Godavari?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 2 and 3 only
Ans: (d)


Important Facts For Prelims
India & China in Russian War Games
Why in News?
Indian and Chinese troops will take part in military exercises in Russia at the end of August 2022, the first such major war games (military drills) to be hosted by Russia since its invasion of Ukraine in February 2022.
- While there was no comment from the Ministry of External Affairs of India, the Chinese Defence Ministry said the exercise is ‘unrelated’ to the regional conditions.
What do we need to know about the Military Drill?
- Led by host Russia, the drill will include troops from India, Belarus, Mongolia, Tajikistan and other countries besides China.
- The drill, which will be held between 30th August 2022 to 5th September 2022 at various military facilities in Russia.
- It is likely to be closely tracked globally given the ongoing Russian invasion of Ukraine.
- The drills will bring together the airborne forces, long-range and military transport aircraft and also military contingents of other countries.
What are India’s Exercises with China & Russia?
- China:
- Exercise Hand-in-Hand:
- The aim of the exercise is to practice joint planning and conduct of counter terrorist operations in semi urban terrain.
- Exercise Hand-in-Hand:
- Russia:
- Exercise Indra:
- The exercise will entail the conduct of counter terror operations under the United Nations mandate by a joint force against international terror groups.
- The INDRA series of exercises began in 2003 and was conducted as a bilateral naval exercise alternately between the two countries.
- However, the first joint Tri-Services Exercise was conducted in 2017.
- Exercise TSENTR:
- Exercise TSENTR 2019 is part of the annual series of large-scale exercises that form part of the Russian Armed Forces' annual training cycle.
- The series rotates through the four main Russian operational strategic commands i.e Vostok (East), Zapad (West), TSENTR (Centre) and Kavkas (South).
- Exercise Indra: