25th Anniversary of the India France Strategic Partnership
For Prelims: Rafale jets, P75 program, Earth observation satellite, Supercomputing, Blue Economy, Exercise Shakti, Exercise Varuna, Exercise Garuda, United Nations Security Council, International Solar Alliance, Paris Agreement.
For Mains: Major Areas of Cooperation between India and France
Why in News?
The Indian Prime Minister joined French President as the Guest of Honour at the Bastille Day Parade, where an Indian tri-services marching contingent participated. Rafale jets from the Indian Air Force were also part of the flypast.
- Also, joint statement titled "25th Anniversary of the Strategic Partnership between France and India: towards a Century of Indo-French Relations" sets the course for bilateral relations until 2047, marking significant milestones for both nations.
- The roadmap for the relationship is built upon three pillars: partnership for security and sovereignty, partnership for the planet, and partnership for the people.
What are the Major Highlights of the Visit?
- Pillar 1: Partnership for Security and Sovereignty:
- Defence: Continuation of cooperation on fighter jets and submarines, following the timely delivery of the 36 Rafale jets for the IAF and the success of the P75 program (six Scorpene submarines).
- Space: Enhancement of scientific and commercial partnership through agreements between France's CNES and India's ISRO.
- This includes the joint Earth observation satellite TRISHNA, maritime surveillance satellites in the Indian Ocean, and the protection of Indo-French satellites in orbit.
- Civil Nuclear Energy: Progress on the 6- European Pressurized Reactors power plant project in Jaitapur, Maharashtra and the launch of a cooperation program on small modular reactors and advanced modular reactors.
- Indo-Pacific: Adoption of a roadmap for joint actions in the Indo-Pacific, covering all aspects of the comprehensive strategy for the region.
- Discussion on finalizing an Indo-French development fund for third countries, enabling joint financing of sustainable development projects in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Counter-Terrorism: Strengthening cooperation between France's GIGN and India's National Security Guard.
- Critical Technology: Strengthening cooperation on cutting-edge digital technology, including supercomputing, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and quantum computing.
- Announcement of an agreement between Atos and the Ministry of Earth Sciences of India for the supply of supercomputers.
- Civil Aviation: Signing of technical and safety agreements in the field of civil aviation to support the expansion of routes between France and India and the growth of the Indian civil aviation market.
- Pillar 2: Partnership for the Planet and Global Issues:
- Plastic Pollution: Commitment by France and India to adopt an international treaty to put an end to plastic pollution throughout the entire life cycle of plastic products.
- Health: Signing of a Letter of Intent on health and medicine to structure cooperation in hospitals, medical research, digital technology, biotechnology, public health, and combating micro-bacterial resistance.
- Blue Economy: Launch of a partnership between France's IFREMER and India's National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT) on ocean research under the Blue Economy and Ocean Governance roadmap.
- Financing the Energy Transition: Announcement of financing from the French Development Agency for India's sustainable cities program "CITIIS 2.0" and financing from Proparco for the South Asia Growth Fund (SAGF III).
- Decarbonized Hydrogen: Manufacturing electrolyzers in India, in line with the Indo-French roadmap for decarbonized hydrogen.
- Pillar 3: Partnership for People:
- Student Mobility: Target of welcoming 30,000 Indian students in France by 2030.
- Issuance of 5-year short-stay Schengen visas for Indian students with a Master's degree from a French university.
- Diplomatic and Consular Network: Opening of a Consulate General of India in Marseille, France and a Bureau de France in Hyderabad, India.
- Culture: France's selection as India's partner for establishing a major new National Museum in New Delhi.
- Agreement between France Médias Monde and Prasar Bharati for the exchange of audio-visual content and co-production of programs.
- Research: Increase in funding for the Indo-French Centre for the Promotion of Advanced Research to support new projects.
- Student Mobility: Target of welcoming 30,000 Indian students in France by 2030.
- Other Highlights:
- France gifted India a framed facsimile of a 1916 photograph depicting a Parisian presenting flowers to a Sikh officer.
- France also presented a replica of the Charlemagne chessmen and a series of novels by Marcel Proust.
- Indian Prime Minister was honored with the Grand Cross of the Legion of Honour, France's highest civilian and military honor, during his visit.
- Also, the final joint statement, did not have any reference to the pact on buying three Scorpene submarines and joint development of a combat aircraft engine.
What are the Major Areas of Cooperation between India and France?
- Background:
- France was one of the first countries with which India signed a “strategic partnership” after the end of the Cold War, in January 1998.
- France was also one of the very few countries to support India’s decision to test nuclear weapons in 1998.
- Defence Cooperation: France has emerged as a key defence partner for India, becoming the second largest defence supplier in 2017- 2021.
- Joint Exercises: Exercise Shakti (Army), Exercise Varuna (Navy), Exercise Garuda (Air Force)
- Economic Cooperation: Bilateral trade between two countries reached a new peak at USD 13.4 billion in 2022-23, with exports from India crossing USD 7 billion.
- France is the 11th largest foreign investor in India, with a cumulative investment of USD 10.49 billion from April 2000 to December 2022.
- Cooperation at International Forum: France supports India’s bid for permanent membership of the United Nations Security Council as well as its entry into the Nuclear Suppliers Group.
- Climate Cooperation: Both countries are concerned about climate change, where India has supported France in the Paris Agreement expressing its strong commitment to mitigating the effects of climate change.
- Both countries, as part of their joint efforts on climate change, launched the International Solar Alliance in 2015.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
- The International Solar Alliance was launched at the United Nations Climate Change Conference in 2015.
- The Alliance includes all the member countries of the United Nations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
National Multidimensional Poverty Index
For Prelims: National Multidimensional Poverty Index, NITI Aayog, National Family Health Survey, Poverty, Sustainable Development Goals.
For Mains: National Multidimensional Poverty Index.
Why in News?
Recently, NITI Aayog has released the Report “National Multidimensional Poverty Index: A Progress Review 2023”, claiming that a significant number of people have come out of multidimensional poverty in India.
What is the National Multidimensional Poverty Index?
- The report has been prepared based on the latest National Family Health Survey-5 ( 2019-21 ) and is the 2nd edition of the National Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI).
- The first edition of MPI was released in 2021.
- The MPI seeks to measure Poverty across its multiple dimensions and in effect complements existing poverty statistics based on per capita consumption expenditure.
- It has three equally weighted dimensions – Health, Education, and Standard of living.
- These three dimensions are represented by 12 indicators such as nutrition, child and adolescent mortality, maternal health, years of schooling, school attendance, cooking fuel, sanitation, drinking water, electricity, housing, assets, and bank accounts.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Reduction in Multidimensional Poverty:
- Between 2015-16 and 2019-21, India witnessed a significant decline in the number of multidimensionally poor individuals.
- Around 13.5 crore people moved out of multidimensional poverty during this period.
- Decline in Poverty Percentage:
- India's population living in multidimensional poverty decreased from 24.85% in 2015-16 to 14.96% in 2019-21, reflecting a decline of 9.89 % points.
- Rural-Urban Divide:
- The rural areas of India experienced the fastest decline in poverty, with the poverty rate dropping from 32.59% to 19.28% between 2015-16 and 2019-21.
- In urban areas, the poverty rate reduced from 8.65% to 5.27% during the same period.
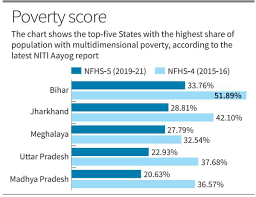
- State-Level Progress:
- In terms of number of MPI poor, Uttar Pradesh saw the largest decline in the number of poor individuals, with 3.43 crore (34.3 million) people escaping multidimensional poverty.
- The states of Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan also witnessed significant progress in reducing multidimensional poverty.
- Bihar saw the fastest reduction in MPI value in absolute terms with the proportion of multidimensional poor reducing from 51.89% to 33.76% in 2019-21 followed by Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh.
- SDG Target:
- The MPI value for India has nearly halved from 0.117 to 0.066 between 2015-16 and 2019-21.
- The intensity of poverty has reduced from 47% to 44%, indicating that India is on track to achieve SDG (Sustainable Development Goals) Target 1.2 (reducing multidimensional poverty by at least half) ahead of the stipulated timeline of 2030.
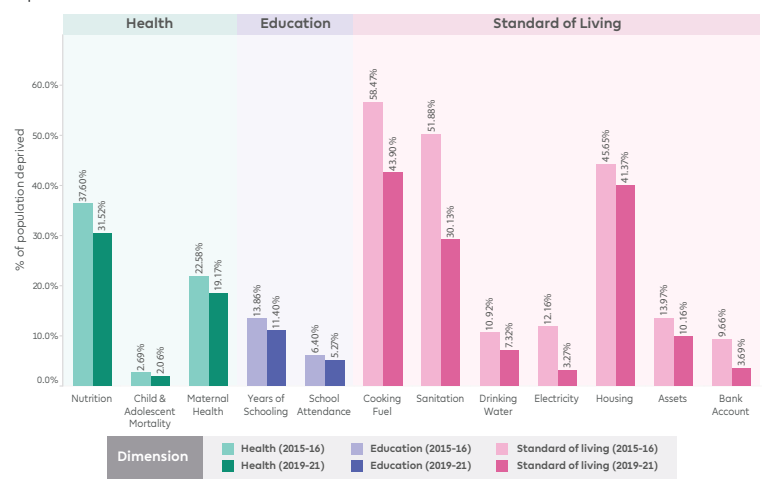
- Improvement in Indicators:
- All 12 indicators used to measure multidimensional poverty showed marked improvements.
- The impact of Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) and Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) is evident in the swift 21.8% points improvement in sanitation deprivations.
- The Poshan Abhiyan and Anaemia Mukt Bharat have contributed to reduced deprivations in health.
- The provision of subsidized cooking fuel through the Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) has positively transformed lives, with a 14.6% improvement in cooking fuel deprivations.
What are the Government Initiatives for Reducing deprivations and Improving the Well-Being of Citizens?
- National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM)
- The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act 2005 (MNREGA)
- Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G)
- Public Distribution System (PDS)
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY)
- Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana (Saubhagya)
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY)
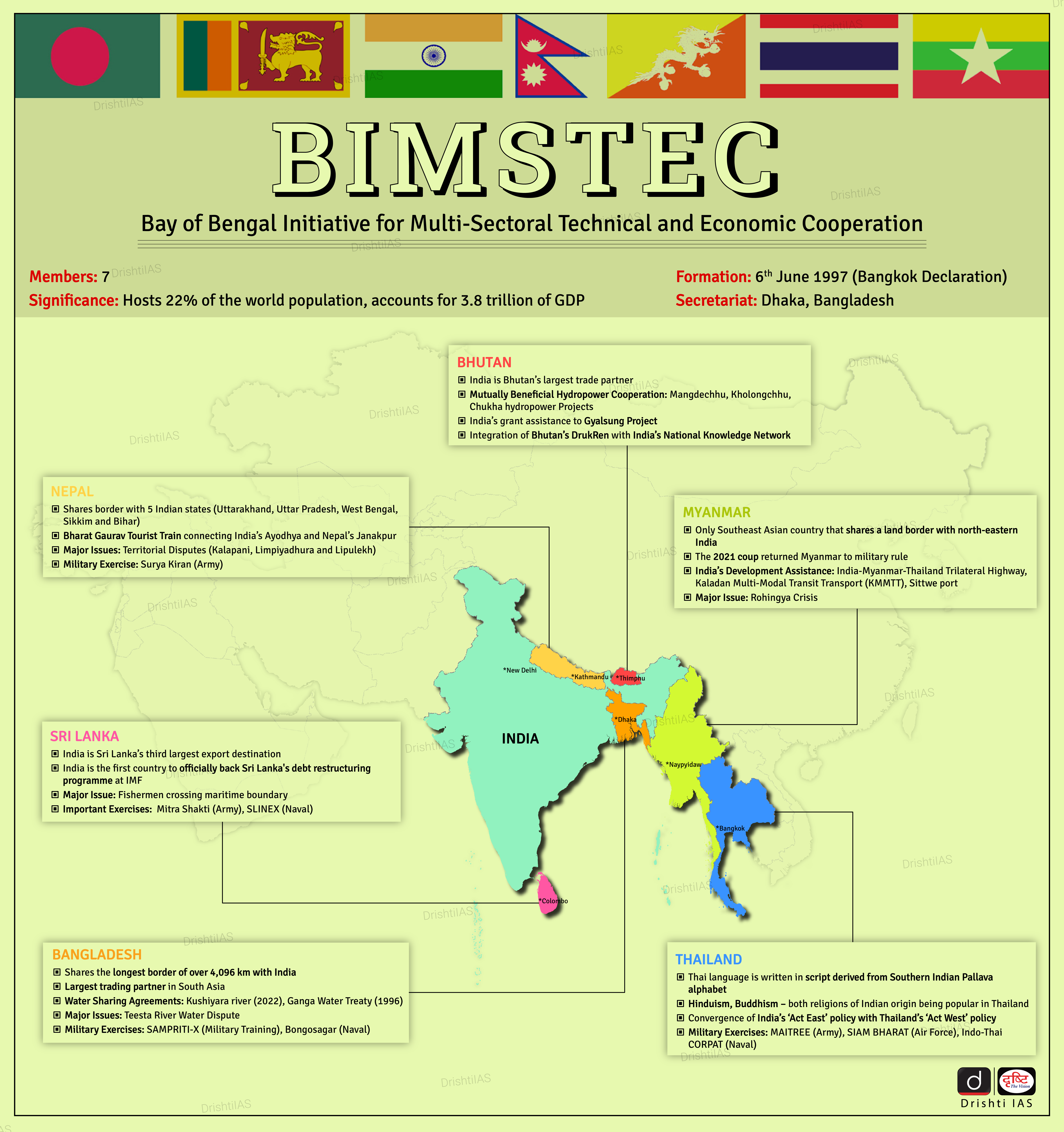
BIMSTEC
For Prelims: Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation, Indo-Pacific Region, Indian Ocean, South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation.
For Mains: Significance of BIMSTEC for Regional Cooperation.
Why in News?
Recently, the first-ever Foreign Ministers’ meeting of the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) began in Bangkok, Thailand.
- Areas of coordination challenges were discussed, including food, health and energy security.
What is BIMSTEC?
- About:
- The BIMSTEC is a regional organisation comprising seven Member States: five deriving from South Asia, including Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Sri Lanka and two from Southeast Asia, including Myanmar and Thailand.
- This sub-regional organisation came into being on 6th June 1997 through the Bangkok Declaration.
- The BIMSTEC Secretariat is in Dhaka, Bangladesh.
- Institutional Mechanisms:
- BIMSTEC Summit
- Ministerial Meeting
- Senior Officials’ Meeting
- BIMSTEC Working Group
- Business Forum & Economic Forum
- Cooperation:
- Cooperation within the BIMSTEC had initially focused on six sectors in 1997 (trade, technology, energy, transport, tourism, and fisheries) and expanded in 2008 to other areas.
- In 2021, a reorganization led to each of the Member States leading certain sectors.
- India focuses on security, along with counterterrorism and transnational crime, disaster management and energy.
What is the Significance of BIMSTEC?
- Significant Global Weightage:
- Around 22% of the world’s population live in the seven countries around the Bay of Bengal, with a combined GDP close to USD 2.7 trillion.
- All seven countries have sustained average annual rates of growth between 3.4% and 7.5% from 2012 to 2016.
- A fourth of the world’s traded goods across the bay every year.
- Regional Strategic Incentives:
- The BIMSTEC countries have strategic incentives in the growth of BIMSTEC.
- For instance, Bangladesh sees BIMSTEC as a platform to elevate its status beyond being a small state on the Bay of Bengal.
- Sri Lanka views it as an opportunity to connect with Southeast Asia and become a hub for the wider Indo-Pacific Region.
- Nepal and Bhutan aim to connect with the Bay of Bengal region to overcome their landlocked geographic positions.
- Myanmar and Thailand see deeper connections with India and BIMSTEC as a means to access India's rising consumer market, balance China's influence in the region, and develop alternatives to China's inroads into Southeast Asia.
- It allows for economic integration, regional security cooperation, and leveraging shared values and histories for peace and development.
- Importance for India:
- BIMSTEC not only connects South and Southeast Asia but also encompasses the ecologies of the Great Himalayas and the Bay of Bengal.
- India sees BIMSTEC as a natural platform to prioritize its foreign policy objectives of "Neighborhood First" and "Act East."
- The significance of BIMSTEC was highlighted when some of its member countries supported India's call for a boycott of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) summit in Islamabad, leading to its postponement.
- India claimed victory in isolating Pakistan through this move.
- Crucial Against Assertive China:
- The Bay of Bengal is crucial for an increasingly assertive China in maintaining its access route to the Indian Ocean.
- As China has undertaken a massive drive to finance and build infrastructure in South and Southeast Asia through the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) in almost all BIMSTEC countries, except Bhutan and India, BIMSTEC is a new battleground in the India-China battle for dominance.
- BIMSTEC can allow India to push a constructive agenda to counter Chinese investments, and instead follow best practices for connectivity projects based on recognised international norms.
- The Chinese projects are widely seen as violating these norms.
- The Bay of Bengal is crucial for an increasingly assertive China in maintaining its access route to the Indian Ocean.
- Preserve Peace and Freedom of Navigation:
- The Bay of Bengal can be showcased as open and peaceful, contrasting it with China’s behavior in the South China Sea.
- It can develop codes of conduct that preserve freedom of navigation and apply existing law of the seas regionally.
- Moreover, BIMSTEC can stem the region’s creeping militarisation by instituting, for instance, a Bay of Bengal Zone of Peace that seeks to limit any bellicose behavior of extraregional power.
How BIMSTEC is Different from SAARC?
| SAARC | BIMSTEC |
|
1. A regional organisation looking into South Asia 2. Established in 1985 during the cold war era. 3. Member countries suffer for mistrust and suspicion. 4. Suffers from regional politics. 5. Asymmetric power balance. 6. Intra-regional trade only 5 percent. |
1. Interregional organisation connecting South Asia and South East Asia. 2. Established in 1997 in the post-Cold War. 3. Members maintain reasonably friendly relations. 4. Core objective is the improvement of economic cooperation among countries. 5. Balancing of power with the presence of Thailand and India on the bloc. 6. Intra-regional trade has increased around 6 precent in a decade. |
Way Forward
- BIMSTEC member countries should focus on deepening cooperation in various sectors such as trade, technology, energy, transport, tourism, fisheries, security, counterterrorism, disaster management, and energy.
- The organization should work towards implementing existing agreements and exploring new avenues for collaboration.
- BIMSTEC should work towards enhancing trade facilitation, reducing barriers, and promoting economic integration among member countries.
- The organization should explore opportunities for a free trade agreement (FTA) to boost regional trade and investment.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Do you think that BIMSTEC is a parallel organisation like the SAARC? What are the similarities and dissimilarities between the two? How are Indian foreign policy objectives realized by forming this new organisation? (2022)
UNAIDS Report: Progress & Challenges in HIV/AIDS Fight
For Prelims: World AIDS Day, AIDS, HIV
For Mains: Status of AIDS Globally and Nationally, AIDS, HIV, Related Initiatives
Why in News?
A recent report titled "The Path That Ends AIDS" by the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) sheds light on the progress made in combating reveals the ongoing challenges and progress in the global fight against Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
- The report emphasizes the need for continued efforts to ensure access to treatment, address inequalities, combat stigma and discrimination, and secure adequate funding.
What are the Key Highlights of the UNAIDS Report?
- AIDS-Related Deaths and Access to Treatment:
- AIDS claimed a life every minute in 2022.
- Approximately 9.2 million people living with HIV worldwide lacked access to treatment in 2022.
- Out of the 2.1 million people receiving treatment, many were not virally suppressed.
- Treatment Progress and Global Targets:
- 29.8 million out of 39 million people living with HIV globally are receiving life-saving treatment.
- Between 2020 and 2022, 1.6 million additional people received HIV treatment each year.
- The global target of 35 million people receiving HIV treatment by 2025 is within reach if the progress is sustained.
- Slow Treatment Progress in Certain Regions:
- Eastern Europe, Central Asia, the Middle East, and North Africa exhibited slower treatment progress.
- Only around half of the over two million people living with HIV in these regions received antiretroviral therapy in 2022.
- Gender Discrimination and Treatment Rates:
- Men living with HIV in sub-Saharan Africa, the Caribbean, Eastern Europe, and Central Asia are less likely to receive treatment compared to women.
- Gender discrimination needs to be addressed to ensure equal access to treatment.
- Impact on Children:
- AIDS-related deaths among children reduced by 64% from 2010 to 2022.
- However, approximately 84,000 children lost their lives to HIV in 2022.
- Around 43% of the 1.5 million children living with HIV did not receive treatment in 2022.
- AIDS-related deaths among children reduced by 64% from 2010 to 2022.
- Challenges in HIV Prevention:
- Women and girls accounted for 63% of all new HIV infections in sub-Saharan Africa.
- Only about 42% of districts with high HIV incidence in the region have dedicated prevention programs.
- Enhanced prevention efforts are needed to address this gap.
- Funding Gaps:
- HIV incidence has declined in regions with increased prevention funding.
- Eastern Europe, Central Asia, the Middle East, and North Africa face challenges in their HIV epidemics due to a lack of funding.
- In 2022, only USD 20.8 billion was available for HIV programs in low- and middle-income countries, falling short of the USD 29.3 billion required by 2025.
- Fluctuating Funding Levels:
- In the early 2010s, funding substantially increased, but it has since fallen back to 2013 levels.
- In 2022, there was a 2.6% drop in funding compared to the previous year, with only USD 20.8 billion available for HIV programs in low- and middle-income countries.
- The funding gap remains significant, as the required amount by 2025 is USD 29.3 billion.
Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS:
- It is leading the global effort to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals. It was started in 1996.
- UNAIDS has a vision of zero new HIV infections, zero discrimination and zero AIDS-related deaths, and a principle of leaving no one behind.
- The UN Political declaration on ending AIDS was adopted in 2016 which seeks to end AIDS as a public health threat by 2030.
What is AIDS Disease?
- About:
- AIDS is a chronic, potentially life-threatening health condition caused by HIV that interferes with the body's ability to fight infections.
- HIV attacks CD4, a type of White Blood Cell (T cells) in the body’s immune system.
- T cells are those cells that move around the body detecting anomalies and infections in cells.
- After entering the body, HIV multiplies itself and destroys CD4 cells, thus severely damaging the human immune system. Once this virus enters the body, it can never be removed.
- The CD4 count of a person infected with HIV reduces significantly. In a healthy body, CD4 count is between 500- 1600, but in an infected body, it can go as low as 200.
- Transmission:
- HIV spreads through contact with certain body fluids (blood, semen, etc.) from an infected person.
- Transmission routes include unprotected sex, sharing contaminated needles, and mother-to-child during childbirth or breastfeeding.
- Symptoms:
- Initial symptoms include fatigue, fever, and sores.
- Progression to AIDS may lead to severe symptoms like pneumonia and certain cancers.
- Prevention:
- Precautions can be taken to prevent mother-to-child transmission.
- Early diagnosis and treatment should be sought.
- Pre-marital testing can be considered, including an HIV test, for overall safety.
- Protective techniques should be used to ensure safety from Sexually Transmitted Diseases.
What are India’s Initiatives to Curb AIDS Disease?
- HIV and AIDS (Prevention and Control) Act, 2017:
- According to this act, the central and state governments shall take measures to prevent the spread of HIV or AIDS.
- Access to ART:
- India has made Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) affordable and accessible to over 90 per cent of people living with HIV in the world.
- Memorandum of Understanding (MoU):
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare signed a MoU with the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment in 2019 for enhanced HIV/AIDS outreach and to reduce the incidence of social stigma and discrimination against victims of drug abuse and Children and People Living with HIV/AIDS.
- Project Sunrise :
- Launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare in 2016, to tackle the rising HIV prevalence in north-eastern states in India, especially among people injecting drugs.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which of the following diseases can be transmitted from one person to another through tattooing? (2013)
- Chikungunya
- Hepatitis B
- HIV-AIDS
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
India's Only Ape Species: The Hoolock Gibbon
Why in News?
The conservation status of India's sole ape species, the hoolock gibbon, has become a pressing global concern.
- The Global Gibbon Network (GGN) recently convened its inaugural meeting in Haikou, China's Hainan province, shedding light on the critical situation faced by these primates.
Note: Global Gibbon Network was initiated at the International Gibbon Day 2020 event, representatives from 20 gibbon conservation organizations came together for the first time to discuss gibbon conservation.
What are the Key Facts about Hoolock Gibbon?
- About:
- Gibbons, known as the smallest and fastest of all apes, inhabit tropical and subtropical forests in Southeast Asia.
- They have high intelligence, distinct personalities, and strong family bonds similar to other apes.
- They represent one of the 20 gibbon species found worldwide.
- Gibbons, known as the smallest and fastest of all apes, inhabit tropical and subtropical forests in Southeast Asia.
- Population and Habitat:
- The current population of hoolock gibbons is estimated to be around 12,000 individuals.
- They are found in forested areas of Northeast India, Bangladesh, Myanmar and Southern China.
- Gibbon Species in India:
- Two distinct hoolock gibbon species are found in India's northeastern region: the eastern hoolock gibbon (Hoolock leuconedys) and the western hoolock gibbon (Hoolock hoolock).
- A recent study by the Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB) in Hyderabad analyzed the genetics of these gibbons.
- The study revealed that there is actually only one species of gibbon in India, debunking the previous belief of separate eastern and western species based on coat color.
- The genetic analysis showed that the populations previously thought to be eastern and western hoolock gibbons diverged approximately 1.48 million years ago.
- The study also estimated that gibbons diverged from a common ancestor around 8.38 million years ago.
- Threats:
- All 20 gibbon species, including hoolock gibbons, are at a high risk of extinction due to conservation challenges.
- Gibbon populations and their habitats have significantly declined over the past century, leaving small populations restricted to tropical rainforests.
- In India, the primary threat to hoolock gibbons is the loss of their natural habitat caused by deforestation for infrastructure projects.
- Conservation Status:
- International Union for Conservation of Nature's Red List:
- Western Hoolock Gibbon: Endangered
- Eastern Hoolock Gibbon: Vulnerable.
- Also, both the species are listed on Schedule 1 of the Indian (Wildlife) Protection Act 1972.
- International Union for Conservation of Nature's Red List:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2010)
| Protected area | Well-known for | |
| 1. | Bhiterkanika, Orissa | Salt Water Crocodile |
| 2. | Desert National Park, Rajasthan | Great Indian Bustard |
| 3. | Eravikulam, Kerala | Hoolock Gibbon |
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic Fever
Why in News?
As Europe experiences heatwaves and wildfires, concerns are mounting about the spread of viruses typically associated with warmer climates. Alert has been sounded about the Crimean-Congo Haemorrhagic fever (CCHF) an infection spread by ticks.
What is CCHF?
- About:
- CCHF is a viral haemorrhagic fever transmitted by ticks and contact with viremic animal tissues.
- It poses a threat to public health due to its potential for epidemics, high case fatality ratio (10-40%), according to the World Health Organization (WHO). and difficulty in prevention and treatment.
- CCHF Symptoms and Cure:
- Symptoms include fever, muscle ache, dizziness, headache, abdominal pain, and mood swings.
- There is no vaccine available, and treatment primarily focuses on symptom management.
- The antiviral drug ribavirin has shown potential benefits in treating CCHF infections.
- Transmission:
- CCHF virus is primarily transmitted through tick bites or contact with infected animal blood or tissues during and after slaughter.
- Human-to-human transmission can occur through close contact with infected individuals or improper sterilization of medical equipment.
- Prevention and Control of CCHF:
- Controlling CCHF in animals and ticks is difficult due to unnoticed tick-animal-tick cycle and widespread tick vectors.
- Measures can be taken to ensure that animals remain tick-free for 14 days in a quarantine station before slaughter.
- There are no vaccines available for use in animals.
- The only way to reduce infection in people is by raising awareness of the risk factors and educating people about the measures they can take to reduce exposure to the virus.
- Wear protective clothing (long sleeves, long trousers) and light-colored clothing to allow easy detection of ticks on clothes.
- Avoid close physical contact with CCHF-infected people.
- Wear gloves and protective equipment when taking care of ill people.
- Spread of CCHF:
- Initially endemic to Africa, the Balkan countries, the Middle East, and parts of Asia, CCHF has been spreading northward and westward in Europe.
- Reported cases have emerged in Spain, Russia, Turkey, and the UK.
- Climate Change and Disease Spread:
- Climate change plays a role in the expansion of pathogens into new territories.
- Warmer temperatures and altered habitats allow ticks and other insects to thrive in previously unsuitable regions.
- Changes in water habitats and animal migration patterns contribute to disease spread.
UPU to Assess UPI for Cross-Border Remittances
Why in News?
The Universal Postal Union (UPU) has announced plans to evaluate the integration of the Unified Payment Interface (UPI) with cross-border remittances using the global postal network.
- This evaluation aims to explore the potential of UPI in facilitating secure and efficient international money transfers.
What are the Benefits of Integrating UPI with UPU?
- UPI offers a secure, convenient, and real-time payment experience, making it a promising platform for cross-border remittances.
- Leveraging the global postal network, which has extensive reach and infrastructure, can further expand the reach of UPI-enabled remittances.
- The integration of UPI with postal channels can provide a reliable and accessible remittance solution for individuals, particularly in remote areas where traditional banking services may be limited.
- This initiative aligns with UPU's goal of promoting efficient and inclusive postal services globally.
What is Universal Postal Union (UPU)?
- About:
- The UPU is a United Nations specialized agency and the postal sector's primary forum for international cooperation.
- UPU is the second oldest international organization.
- Establishment and Structure:
- The UPU was established in 1874 through the Treaty of Bern.
- UPU's headquarters are located in Bern, Switzerland.
- The organization consists of four bodies: Congress, the Council of Administration (CA), the Postal Operations Council (POC), and the International Bureau (IB).
- It also oversees the Telematics and Express Mail Service (EMS) cooperatives.
- Membership:
- Any member country of the United Nations can become a member of the UPU.
- Non-member countries of the United Nations can join the UPU if approved by at least two-thirds of the member countries.
- The UPU has now 192 member countries.
- India joined the UPU in 1876.
- Role and Functions:
- UPU coordinates postal policies among member nations and the global postal system.
- The union sets rules for international mail exchanges and makes recommendations to stimulate growth in mail, parcel, and financial services volumes.
- It aims to improve the quality of service for customers and promote efficiency in international postal operations.
What is UPI?
- UPI is India’s mobile-based fast payment system, which facilitates customers to make round-the-clock payments instantly, using a Virtual Payment Address (VPA) created by the customer.
- VPA is a unique identifier assigned to an individual to facilitate the transfer of funds through a digital payments system.
- It is a user-created identifier that can be used instead of providing sensitive bank account details while making payments.
- It eliminates the risk of sharing bank account details by the remitter. UPI supports both Person-to-Person (P2P) and Person-to-Merchant (P2M) payments, and it also enables a user to send or receive money.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. With reference to digital payments, consider the following statements: (2018)
- BHIM app allows the user to transfer money to anyone with a UPI-enabled bank account.
- While a chip-pin debit card has four factors of authentication, BHIM app has only two factors of authentication.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Q2. Which of the following is a most likely consequence of implementing the ‘Unified Payments Interface (UPI)’? (2017)
(a) Mobile wallets will not be necessary for online payments.
(b) Digital currency will totally replace the physical currency in about two decades.
(c) FDI inflows will drastically increase.
(d) Direct transfer of subsidies to poor people will become very effective.
Ans: (a)
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
India-Russia Vande Bharat Deal
Recently, the India-Russia Vande Bharat joint venture (JV) deal was revived as Rail Vikas Nigam Limited (RVNL) subsidiary, Kinet Railway Solutions Limited, signed a share purchase agreement with Russian company Metrowagonmash and Locomotive Electronic Systems. This JV aims to manufacture 120 Vande Bharat train sets. The consortium aims to develop two prototype trains by June 2025, followed by annual production of 12 to 18 trains. Maintenance services will be provided for 35 years, with a total investment of USD 1.8 billion for train supply and USD 2.5 billion for maintenance.
Read more: Vande Bharat Trains, Vande Bharat Express 2.0
Commission on Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture
Recently, delegates worldwide gathered in Rome, Italy the Food and Agriculture Organization’s (FAO) headquarters, for the 19th session of the Commission on Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (CGRFA). The five-day session will focus on three key topics: a review of work on biodiversity, nutrition, and human health; access and benefit-sharing for food and agriculture; and digital sequence information for food and agriculture.
The CGRFA is a specialized agency of FAO of the United Nations. It is the main intergovernmental body that deals with all matters related to biodiversity for food and agriculture and aims to conserve and use it sustainably for food security, human well-being, and development worldwide.
Read more: Food and Agriculture Organization’s (FAO)
Mission Organic Value Chain Development for Northeastern Region
Recently Mission Organic Value Chain Development for Northeastern Region was reviewed with focus on how to liquidate the committed liability of Phase III and roadmap for implementation of Phase IV of the scheme starting 2023-24.
Realizing the potential of organic farming in the North-Eastern Region of the country Ministry of Agriculture and Farmer Welfare has launched “Mission Organic Value Chain Development for North-Eastern Region” for implementation in the states of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim and Tripura, during the 12th plan period. It is a Central Sector Scheme which aims at development of certified organic production in a value chain mode to link growers with consumers and to support the development of entire value chain starting from inputs, seeds, certification, to the creation of facilities for collection, aggregation, processing marketing and brand building initiative.
Read more: Organic Farming in India