Governance
Export Preparedness Index 2022
For Prelims: Export Preparedness Index, NITI Aayog, Export Promotion, Research and Development, Global Trade Context.
For Mains: Export Preparedness Index.
Why in News?
Recently, NITI Aayog has released the 3rd edition of Export Preparedness Index (EPI) for States/UTs of India for the year 2022.
- The report discusses India’s export performance amid the prevailing global trade context in FY22, followed by an overview of the country’s sector-specific export performance.
What is the Export Preparedness Index?
- About:
- EPI is a comprehensive tool which measures the export preparedness of the States and UTs in India.
- Exports are vital for simulating economic growth and development in a country, which necessitates understanding the factors which influence export performance.
- The index undertakes a comprehensive analysis of States and UTs across export-related parameters in order to identify their strengths and weaknesses.
- Pillars:
- Policy: A comprehensive trade policy providing a strategic direction for exports and imports.
- Business Ecosystem: An efficient business ecosystem helping states attract investments and create an enabling infrastructure for individuals to initiate start-ups.
- Export Ecosystem: Assess the business environment, which is specific to exports.
- Export Performance: This is the only output-based parameter and examines the reach of export footprints of States and UTs.
- Sub Pillars:
- The index also took into consideration 10 sub-pillars: Export Promotion Policy; Institutional Framework; Business Environment; Infrastructure; Transport Connectivity; Export Infrastructure; Trade Support; R&D Infrastructure; Export Diversification; and Growth Orientation.
- Features: The EPI is a data-driven effort to identify the core areas crucial for export promotion at the sub-national level (states and union territories).
- It explores and highlights India’s export potential by examining the different contributions made by each state and union territories.
What are the Key Highlights of the EPI 2022?
- Performance of States:
- Top Performers:
- Tamil Nadu has topped in EPI 2022, followed by Maharashtra and Karnataka.
- Gujarat, which held the top position in EPI 2021 (released in 2022) has been pushed to the fourth slot in EPI 2022.
- Tamil Nadu's performance in terms of export performance indicators, including the value of exports, export concentration, and global market footprint, contributed to its top ranking.
- It has been a consistent leader in sectors such as automotive, leather, textiles, and electronic goods.
- Tamil Nadu has topped in EPI 2022, followed by Maharashtra and Karnataka.
- Hilly/Himalayan States:
- Uttarakhand secured the top position among hilly/Himalayan states in the EPI 2022. It is followed by Himachal Pradesh, Manipur, Tripura, Sikkim, Nagaland, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, and Mizoram.
- Landlocked Regions:
- Haryana topped the chart among the landlocked regions, indicating its preparedness for exports.
- It was followed by Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Madhya Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
- Union Territories/Small States:
- Among union territories and small states, Goa ranked first in the EPI 2022.
- Jammu and Kashmir, Delhi, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, and Ladakh secured the second, third, fourth, and fifth positions, respectively.
- Among union territories and small states, Goa ranked first in the EPI 2022.
- Top Performers:
- Global Economy:
- Global trade in 2021 showed signs of recovery from the Covid-19. Factors like increased demand for goods, fiscal policies, vaccine distribution, and easing of restrictions contributed to a 27% increase in merchandise trade and a 16% increase in services trade compared to the previous year.
- The Russo-Ukrainian war in February 2022 slowed down the recovery, impacting sectors like grain, oil, and natural gas.
- Trade in goods saw significant growth, and services trade recovered to pre-pandemic levels by Q4 2021.
- India’s Export Trends:
- Despite global slowdown, India’s exports in 2021-22 crossed an unprecedented USD 675 Billion, with trade in goods accounting for USD 420 billion.
- The value of merchandise exports crossed USD 400 billion in FY2022, an ambitious goal set by the government, reaching up to USD 422 billion by March 2022.
- The cause of this performance was manifold. Globally, the increase in prices of commodities and rise in demand from developed countries helped increase India’s merchandise exports.
What are the Key Learnings of the Exports Preparedness Index (EPI)?
- Coastal states have fared the best across all indicators with six out of the top states in the index coming from the coastal region of the country.
- States like Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Gujarat (all of them performing the best in at least one pillar).
- In terms of strengths, the policy ecosystem is a positive story with multiple states adopting the necessary policy measures to drive exports in their states.
- At the district-level, 73 % of districts in the country have an export action plan and over 99 % are covered under the ‘One District One Product’ scheme.
- States have lagged in terms of transport connectivity. The absence of air connectivity hampers the movement of goods across regions, especially in states which are landlocked or geographically disadvantaged.
- The lower performance of the country in terms of Research and Development (R&D) indicates the lack of attention given to the role of innovation in exports.
- The state government has to both continue and extend its support to the industries which are struggling.
- 26 states in the country have registered a decrease in the gross value addition of their manufacturing sector.
- 10 states have registered a decrease in the inflow of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI).
- The lack of capacity-building workshops for exporters hampers their ability to penetrate the global markets as 25 of 36 states have organized less than 10 workshops across a year.
- For the effectiveness of existing government schemes to support states, timely approval of projects is a must.
What are the Recommendations of the EPI?
- Adoption of Good Practices: States should be encouraged to adopt good practices from their peers if they suit their needs. Learning from successful states can help lagging states improve their export performance.
- Investment in Research and Development (R&D): States should invest in R&D to drive product innovation, market-specific product creation, improvement in product quality, cost reduction, and efficiency improvement.
- Establishing dedicated research institutes with regular funding can help states improve their exports.
- Leveraging Geographical Indication (GI) Products: States should capitalize on their unique GI products to establish a presence in the global market. Promoting and improving the manufacturing and quality of GI products can boost exports.
- For example, Kancheepuram Silk products can only be exported by Tamil Nadu and have no competition across the country.
- Diversification of Export Markets: Identifying and promoting high-growth sectors, such as information technology, pharmaceuticals, automotive, textiles, and renewable energy, can enhance India's export potential.
Governance
World Youth Skills Day: Namda Art, AI for India 2.0
For Prelims: World Youth Skills Day, Namda Art, AI for India 2.0, Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana
For Mains: Impacts of Skill Development in India.
Why in News?
Recently, on the occasion of World Youth Skills Day (15th July), the Skill India project achieved a remarkable feat by successfully reviving the dying Namda Art of Jammu and Kashmir, by flagging off the first batch of Namda Art products for export to the UK.
- On the same occasion, the Union Minister of Education and Skill Development and Entrepreneurship, launched AI for India 2.0.
What is World Youth Skills Day?
- About:
- Every year, the 15th of July is observed as World Youth Skills Day.
- The day highlights the critical role of skills development in preparing young people for the labor market and fostering their active participation in society.
- Celebrates the strategic importance of equipping young people with skills for employment, decent work, and entrepreneurship.
- Background:
- Designated by the United Nations General Assembly in 2014.
- World Youth Skills Day 2023 Theme:
- Skilling Teachers, Trainers, and Youth for a Transformative Future.
What is Namda Art?
- Origin and Introduction:
- Namda Art began in the 16th century when Mughal Emperor Akbar desired protective coverings for his horses.
- It was introduced to Kashmir by Sufi saint Shah-e-Hamdan.
- Creation and Materials:
- Namda is a type of traditional Kashmiri felted carpet made using sheep wool.
- The wool is compressed and matted together; a process known as felting, giving it a distinct texture.
- Manufacturing Process:
- Namda carpets are typically created by layering multiple wool layers on top of each other.
- Each layer is sprinkled with water and pressed using a tool called a 'pinjra' (woven willow wicker).
- The layers are compressed to create a solid and durable carpet.
- Decline and Revival:
- Due to low availability of raw material, lack of skilled manpower and marketing techniques, the export of this craft has declined almost 100% between 1998 and 2008.
- Hence, the Skill India project under the Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) has designed a short-term training curriculum to preserve this endangered craft.
- The training provided under this initiative has empowered local artisans and helped preserve this traditional craft for future generations.
- Kashmir has also been seeking GI registration for various products, including Kashmir Namda and Gabba (two types of Valley-specific woollen rugs) (besides Wagguv (mat made of reed and paddy straw), Shikara and Kashmir Willow bat).
- Due to low availability of raw material, lack of skilled manpower and marketing techniques, the export of this craft has declined almost 100% between 1998 and 2008.
What is Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana?
- About:
- It is a flagship scheme under the Skill India Mission launched in 2015.
- It aims to train over 40 crore people in India by 2022, providing vocational training and certification for better livelihoods and societal respect.
- PMKVY 1.0:
- Launch: Introduced on July 15, 2015, on World Youth Skills Day.
- Objective: Encouraging skill development by offering free short-term training and monetary rewards for skill certification.
- PMKVY 2.0 (2016-20):
- Coverage: Scaled up for greater alignment with missions like Make in India, Digital India, Swachh Bharat, etc.
- Funding and Targets: NSDC:State Governments = 75:25.
- Outcome: Over 1.2 Crore youth trained/oriented under PMKVY 1.0 and 2.0.
- PMKVY 3.0 (2020-22):
- Coverage: Launched in 717 districts across 28 States and 8 UTs.
- Implementation: Decentralized structure with increased involvement and support from States/UTs and Districts.
- Features:
- Focus on new-age and Industry 4.0 job roles
- Emphasis on vocational education and early skill development
- Bottom-up approach to identify local job opportunities
- PMKVY 4.0 (2023-26):
- Coverage:
- Latest phase of the scheme announced in Union Budget 2023-24.
- It will emphasize On-job training, industry partnership, and alignment of courses with the needs of the industry.
- Implementation:
- To be implemented by NSDC, will involve state govts, industry associations, and other stakeholders.
- To be monitored by an empowered committee under the Minister of State for Skill Development and Entrepreneurship.
- Features:
- Offers skill training and certification in various fields ranging from AI, blockchain, mobile repairing, vehicle maintenance, and management, etc.
- Align the training course of National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF).
- Provide soft skills, entrepreneurship, financial and digital literacy training to the candidates.
- Coverage:
- Other Initiatives for Skill Development:
- SANKALP.
- STRIVE Project.
- TEJAS Initiative for Skilling
- Mandatory CSR Expenditure in Skilling: Since the implementation of mandatory CSR spending under the Companies Act, of 2013, corporations in India have invested over Rs. 100,000 crores in diverse social projects.
What is AI for India 2.0?
- About:
- AI for India 2.0 is a free online training program focused on Artificial Intelligence.. The program is a continuation of AI for India 1.0, which was launched on February 24, 2021. AI for India 1.0 was a one-day online event that provided a complimentary course on Python programming language, a widely used language in AI development.
- It is a Joint Collaboration between Skill India and GUVI, an IIT Madras incubated startup.
- Completion of the program results in recognition and certification of acquired AI skills.
- Aim:
- Aims to future-proof India's youth by offering AI skill training.
- Equipping Indian youth with frontier AI skills.
- Enhancing employability and fostering skill development.
- Accreditation:
- Accredited by NCVET (National Council for Vocational Education and Training) and IIT Madras.
- Salient Features:
- Accessibility:
- Envisions easy accessibility of AI learning across the nation.
- Empowering youth with cutting-edge technologies.
- Language Inclusivity:
- Focuses on providing AI skill training in Indian languages.
- Addresses the language barrier in technology education.
- Technological Advancements:
- Contributes to India's position as a technology-savvy country.
- Expanding training in cutting-edge technologies.
- Accessibility:
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, consider the following statements: (2018)
- It is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- It, among other things, will also impart training in soft skills, entrepreneurship, and financial and digital literacy.
- It aims to align the competencies of the unregulated workforce of the country to the National Skill Qualification Framework.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) is a flagship scheme for skill training of youth implemented by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship through the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC). Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The individuals with prior learning experience or skills shall be assessed and certified under the Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL) component of the Scheme. RPL aims to align the competencies of the unregulated workforce of the country to the NSQF.
- Skill training would be based on the National Skill Qualification Framework (NSQF) and industry-led standards. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- Apart from providing training according to the NSQF, training centres shall also impart training in soft skills, entrepreneurship, and financial and digital literacy. Hence, statement 2 is correct. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. “Demographic Dividend in India will remain only theoretical unless our manpower becomes more educated, aware, skilled and creative.” What measures have been taken by the government to enhance the capacity of our population to be more productive and employable? (2016)
International Relations
India-UAE Local Currency Settlement System
For Prelims: Local Currency Settlement System, India-UAE, Indian Rupee, Unified Payment Interface, UAE’s Instant Payment Platform, India-UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement.
For Mains: Local Currency Settlement System between India-UAE.
Why in News?
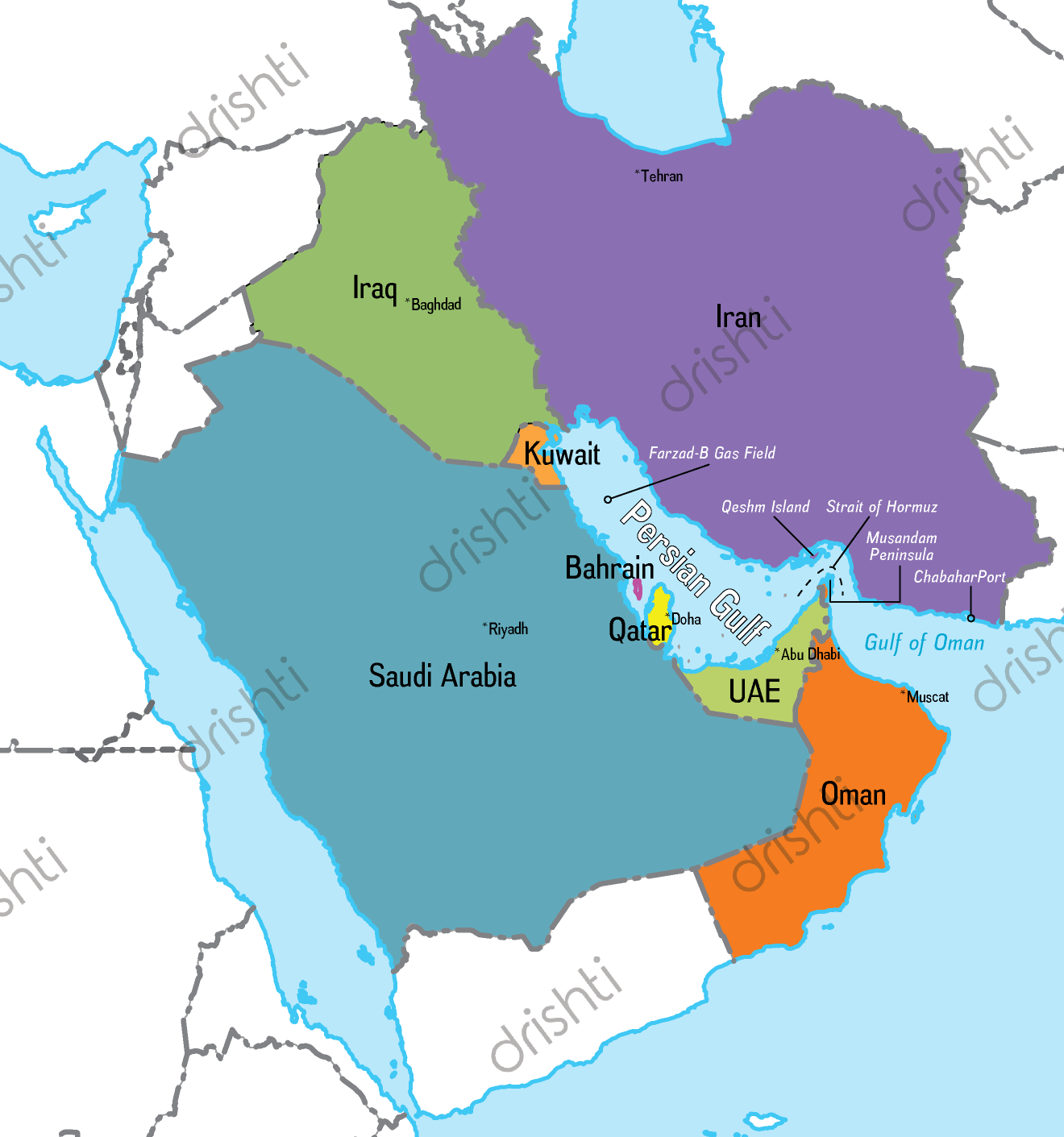
India and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) have signed a pact to establish Local Currency Settlement System (LCSS) to promote the use of the Indian rupee (INR) and UAE Dirham (AED) for cross-border transactions.
- The deal was signed during the Prime Minister’s recent visit to Abu Dhabi, UAE.
Note: The RBI (Reserve Bank of India) in 2022 announced a framework for settling Global Trade in Rupees, primarily targeting trade with Russia. But this is yet to take off in a substantive manner.
What are the Key Agreements?
- LCSS:
- It covers all current account transactions and permitted capital account transactions.
- The LCSS will enable exporters and importers to pay in their respective domestic currencies and enable the development of an INR-AED forex market.
- It will reduce transaction costs and settlement time, including for remittances by Indians in the UAE.
- India could use this mechanism to pay for imports of oil and other commodities from the UAE, its 4th largest energy supplier (in FY 22-23).
- UPI-IPP:
- The central banks of both countries have signed to cooperate on linking India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI) with the UAE’s Instant Payment Platform (IPP) and RuPay switch and UAESWITCH.
- The UPI-IPP link will enable users in both countries to make fast, safe and cost-effective cross-border transfers.
- The linking of card switches will facilitate the mutual acceptance of domestic cards and the processing of card transactions.
- The MoUs were signed by the respective Governors of the RBI and the Central Bank of UAE.
- They will also explore the linking of India’s Structured Financial Messaging System (SFMS) with the payments messaging system of the UAE.
- The central banks of both countries have signed to cooperate on linking India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI) with the UAE’s Instant Payment Platform (IPP) and RuPay switch and UAESWITCH.
- IIT Delhi campus to be set up in Abu Dhabi:
- An MoU was signed for establishment of IIT Delhi campus in Abu Dhabi.
- The new MoU is an addition in the ‘IITs go Global’ campaign.
- This will be the second international IIT campus after IIT Madras Zanzibar, Tanzania.
- The degrees will be offered starting 2024 with courses covering several areas such as Energy and Sustainability, AI, Computer Science and Engineering, Healthcare, Mathematics and Computing and other disciplines of engineering, sciences and humanities.
- An MoU was signed for establishment of IIT Delhi campus in Abu Dhabi.
What is the Significance of Rupee Based Cross Border Transaction?
- India is looking to work out a way to mitigate exchange rate risks in the rupee-based trade to limit losses for Indian exporters.
- The rupee-based transaction is part of a concerted policy effort by India to Internationalize the Rupee to bring down the dollar demand.
- Apart from Russia, countries in Africa, the Gulf region, Sri Lanka and Bangladesh had also expressed interest in trading in rupee terms.
- The RBI’s plan to settle international trade in the local currency will let importers make payments in the rupee, which will be credited to the special account of the correspondent bank of the partner country, while exporters will be paid from the balances in the designated special account.
How has been India- UAE Bilateral Relations?
- Diplomatic Ties:
- India and the UAE established diplomatic relations in 1972.
- The greater push has been achieved in bilateral relations when the visit of India’s Prime Minister to the UAE in August 2015 marked the beginning of a new strategic partnership between the two countries.
- Further, during the visit of the Crown Prince of Abu Dhabi to India in January 2017 as the chief guest at India’s Republic Day celebrations, it was agreed that bilateral relations were to be upgraded to a comprehensive strategic partnership.
- This gave momentum to launching negotiations for an India-UAE comprehensive economic partnership agreement.
- Bilateral Trade:
- Bilateral trade between India and the UAE was worth ~USD 85 billion in 2022-23 making the UAE India’s 3rd-largest trading partner for 2022-23 and India’s 2nd-largest export destination.
- India is the 3rd largest oil importer in the world and the UAE was its 4th biggest supplier of crude in 2022.
- In 2022, India became the first country with which the UAE signed a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement.
- The UAE, which imports most of its food requirements, has pledged USD 2 billion to develop a series of food parks in India.
- Many Indian companies have set up manufacturing units either as joint ventures or in Special Economic Zones for cement, building materials, textiles, engineering products, consumer electronics, etc. in the UAE.
- Many Indian companies have also invested in the tourism, hospitality, catering, health, retail, and education sectors.
- Bilateral trade between India and the UAE was worth ~USD 85 billion in 2022-23 making the UAE India’s 3rd-largest trading partner for 2022-23 and India’s 2nd-largest export destination.
- Defense Exercises:
- Bilateral:
- In-UAE BILAT (bilateral naval exercise)
- Desert Eagle-II (bilateral air force exercise).
- Exercise Desert Flag-VI: UAE
- Multilateral:
- Pitch Black: Biennial, multilateral air combat training exercise of Australia.
- Red Flag: Multilateral air exercise of the USA.
- Bilateral:
Way Forward
- The India-UAE LCSS can potentially serve as a precursor for other bilateral currency accords - an important first step for the internationalization of the rupee.
- The idea is laudable; however, its actual success will hinge on the extent of adoption by businesses in both nations.
- Continued collaboration in areas such as technology, renewable energy, infrastructure development, tourism, and healthcare can further strengthen the bilateral relationship between India and the UAE.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. The question of India’s Energy Security constitutes the most important part of India’s economic progress. Analyse India’s energy policy cooperation with West Asian countries. (2017)
Important Facts For Prelims
Treatment for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Why in News?
A collaborative effort between doctors from Tamil Nadu, India, and scientists from Japan has resulted in the development of a disease-modifying treatment for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD).
What is the Disease Modifying Treatment for DMD and Major Findings?
- This treatment utilizes a food additive called beta-glucan, derived from the N-163 strain of the yeast Aureobasidium pullulans.
- The six-month-long clinical study involved 27 children with DMD, of which 18 were in the treatment group and 9 in the control group.
- In addition to regular treatment, all participants (age >3) received the beta-glucan as a food supplement.
- The study yielded the following notable findings:
- Reduction in Muscle Weakness and Damage: Evidence indicated a reduction in muscle weakness and damage among the treatment group.
- It also led to improved Muscle Strength.
- Safety and Lack of Adverse Reactions: No adverse reactions were observed in the participants, and the treatment showed no side effects on the liver and kidneys.
- Reduction in Muscle Weakness and Damage: Evidence indicated a reduction in muscle weakness and damage among the treatment group.
Note: Beta-glucan is a polysaccharide (a complex sugar) that has anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory and antioxidant properties.
What is Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy?
- About:
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is a rare genetic disease characterized by the inability of muscles to produce dystrophin, an enzyme that aids in muscle wear and tear as well as its regeneration.
- It affects only male children.
- The absence of dystrophin leads to muscle damage, resulting in muscle weakness and ultimately wheelchair-bound conditions in early teens and consequent premature deaths.
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is a rare genetic disease characterized by the inability of muscles to produce dystrophin, an enzyme that aids in muscle wear and tear as well as its regeneration.
- Common Symptoms:
- Progressive muscle weakness and atrophy (loss of muscle bulk) that begins in the legs and pelvis and later affects the arms, neck and other areas of the body.
- Difficulty walking, running, jumping, climbing stairs and getting up from a lying or sitting position.
- Frequent falls, waddling gait (abnormal walking pattern) and toe walking.
- Prevalence:
- According to a 2020 study on the global epidemiology of DMD, the pooled global DMD prevalence was 7.1 cases per 100,000 males and 2.8 cases per 100,000 in the general population.
- Also, it has approximately 5,000 patients in Japan and 80,000 in India.
- Current Treatments:
- Currently, there is no known cure for DMD. Treatment aims to control symptoms to improve quality of life.
- Available treatments for DMD include gene therapy, exon-skipping, and disease-modifying agents such as anti-inflammatory medications and steroids.
Important Facts For Prelims
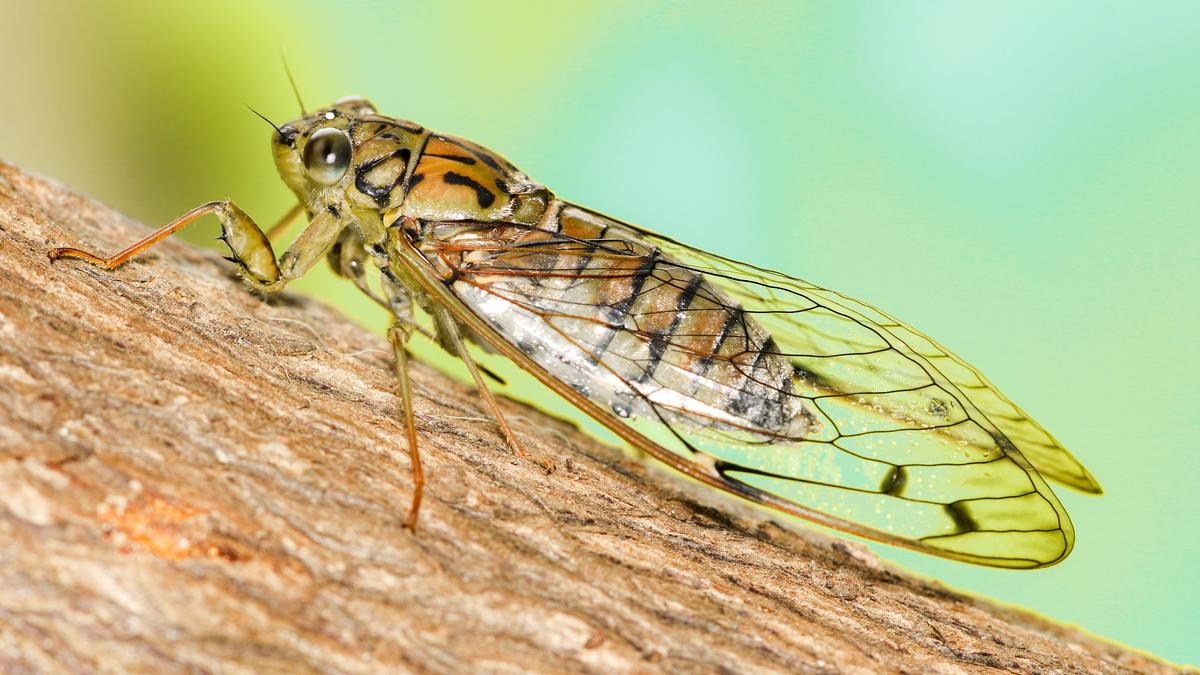
South Indian Cicada Species Gets a New Identity
Why in News?
Recent taxonomic research has unveiled a significant discovery regarding a cicada species commonly found in South India.
- Previously mistaken for the Malaysian species Purana tigrina, this cicada has now been identified as a distinct species named Purana cheeveeda.
- The study also highlights the potential implications of the cicada's distribution for ecological assessments.
What are the Major Findings of the Research?
- P. cheeveeda's distribution extends across tropical evergreen forests from Goa to Kanyakumari in South India.
- This discovery supports a high degree of endemism among cicadas.
- The declining presence of cicadas in homesteads may indicate the deterioration of soil quality and vegetation.
What are Cicadas?
- About:
- Cicadas are insects that belong to the order Hemiptera and the superfamily Cicadoidea.
- Hemipteran insects, also called true bugs, have mouthparts used for piercing and sucking and have two pairs of wings.
- They have large eyes, transparent wings and loud calls that are produced by special organs called tymbals.
- Cicadas are insects that belong to the order Hemiptera and the superfamily Cicadoidea.
- Dietary Pattern and Life Cycle:
- Cicadas are mostly herbivorous and feed on plant sap using their piercing and sucking mouthparts.
- They have complex life cycles that involve long periods of underground development and short periods of adult emergence.
- Habitat:
- Most cicadas are canopy dwellers and are found in natural forests with large trees; found in every continent except Antarctica.
- The generic diversity of cicadas in India and Bangladesh ranks the highest in the world, followed by China.
- Significance:
- Cicadas are important for biodiversity because they provide food for many predators, pollinate flowers, aerate the soil, recycle nutrients and indicate environmental health.
- Major Threat:
- Human development activities reduce the number of trees that cicadas depend on for feeding and reproduction.
- Climate change may disrupt the timing and synchronization of cicada emergence.
- Pesticides, herbicides and fungicides contaminate the soil and water and affect the health and survival of cicadas and their host plants.
Important Facts For Prelims
International SMS Tariffs
Why in News?
Tech firms and telecom operators are facing off over steep SMS tariffs, causing one-time passcodes and messages to consumers from abroad to cost several times more than what they cost domestically.
- The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) has issued a consultation paper to seek views on whether there is a need to change the definition of ‘international traffic’, a key term that determines what an international SMS is, and by extension, what it should cost.
What is International Traffic?
- According to the consultation paper by TRAI, ‘international traffic’ is the international long-distance load or data transmitted over a telecommunication network that originates in one country and is destined for another country.
- For example, a voice call or an SMS from India to Bangladesh would be considered as international traffic.
- It includes various types of communication, such as voice calls, SMS messages, and data transfer, that cross national boundaries.
- An international SMS is a text message that originates in a foreign country and terminates in India, or vice versa.
- International traffic is distinct from domestic traffic, which involves communication within a single country.
- It influences pricing structures and policies related to international communication services, such as call rates, SMS tariffs, and data roaming charges.
- The existing Unified Licensing Agreement in India focuses primarily on regulating domestic traffic, leaving international traffic, without clearly defined regulations and pricing structures.
- Telecommunication Traffic in India:
- Telecommunication in India is divided into 22 circles, which are geographical regions or zones designated for efficient administration and regulation of telecommunication services. These circles ensure effective coverage and management of telecommunication operations across the country.
- Domestic Traffic:
- Intra-Circle Traffic: Communication within the boundaries of the same Telecom Circle/Metro Area.
- Inter-Circle Traffic: Long-distance communication originating in one Telecom Circle/Metro Area and terminating in another.
- International Traffic:
- Communication between India and foreign countries.
- Termination Charges:
- Domestic SMS: Regulated termination charges.
- International SMS: Telecom operators have the freedom to set termination charges, making it highly profitable.
What is the Issue of Redefinition of International Traffic?
| Telecom Operators' Stance | Tech Firms' Perspective |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Telecom Regulatory Authority of India
- TRAI, established under the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India Act, 1997, regulates telecom services and tariff fixation/revision.
- It ensures a fair and transparent policy environment, fostering a level playing field and promoting fair competition.
- The establishment of Telecom Disputes Settlement and Appellate Tribunal (TDSAT), as an amendment to the TRAI Act, transfers adjudicatory and dispute functions from TRAI. TDSAT resolves disputes between licensors, licensees, service providers, and consumers, and handles appeals against TRAI's directions, decisions, or orders.
Important Facts For Prelims
Advancements in Smart Windows
Why in News?
Researchers at the Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Science in Bengaluru have introduced a new dimension to smart window technology by combining hierarchical double network polymers with liquid crystals.
What is a Hierarchical Double Network of Polymers?
- Hierarchical Double Networks of Polymers are a type of interpenetrating polymer networks (IPNs).
- IPNs are soft matter systems that combine different polymer networks to optimize various properties.
- IPNs have potential applications in fields like smart windows, and sensors.
- Hierarchical Double Networks combine rigid and soft networks to achieve desired thermal, electrical, and optical properties.
- They can be tailored to specific requirements, such as mechanical, optical, and electrical properties.
- Polymer:
- Polymers are large molecules composed of smaller molecules called monomers, which are linked together in a chain-like structure.
- Examples of polymers include common materials like plastic and rubber.
What are the Advancements in Smart Windows?
- Enhanced Control with Double Networks:
- These double networks combine different materials and allow for precise manipulation of their properties.
- Integration of multiple functionalities into a single window system.
- Combining Light and Temperature:
- The research team has utilized both light and temperature control to create double networks. Light is used to form a self-assembled polymer network, while temperature triggers the formation of a second network that traps the first one. This unique combination of stimuli provides advanced control over the window's properties.
- Trapping Liquid Crystals:
- The double network structure effectively traps liquid crystals, which are responsible for regulating light transmission. This enables the smart windows to switch between transparency and opacity, providing privacy and energy-saving features.
- Benefits:
- Energy Efficiency: They consume very little energy, making them environmentally friendly and cost-effective.
- Privacy Control: The windows can change from transparent to opaque, giving users control over their privacy.
- Smart windows capable of switching between high and low haze states.
- High Resolution: The use of modern techniques allows for precise control over the level of opacity, providing excellent resolution.
Important Facts For Prelims
New Diarrhoea Causing Parasite: Entamoeba moshkovskii
Why in News?
The recent three-year surveillance study by the National Institute of Cholera and Enteric Diseases (ICMR-NICED) reveals the emergence of Entamoeba moshkovskii (E. Moshkovskii) as a leading pathogen causing diarrhoea outbreaks in the Kolkata region.
- The previously non-pathogenic amoeba, Entamoeba moshkovskii, has now become the primary cause of amoebic infections, surpassing the once dominant pathogen, E. histolytica.
What are the Key Findings of the Study?
- Prevalence of Entamoeba moshkovskii:
- The study found that over 3% of patients with diarrhoea were infected with E. moshkovskii, making it the leading cause of amoebic infections in humans in Kolkata.
- The decline of E. histolytica:
- Infections caused by E. histolytica, the previous predominant amoeba pathogen, were decreasing, while E. moshkovskii was taking its place.
- Unique Seasonal Pattern:
- Unlike E. histolytica, which usually peaked during the wet season and decreased during the dry season, E. moshkovskii infections in Kolkata exhibited two distinct infection peaks coinciding with the summer and post-fall seasons.
- Age Predominance:
- E. moshkovskii infections were most prevalent in children aged 5-12 years.
- Pathogenic Potential:
- The study indicated that E. moshkovskii may act as a "potential" pathogen, causing diarrhoea and gastrointestinal disorders, rather than solely being a commensal of the human gut.
- Molecular Identification:
- Due to the morphological similarities between E. histolytica and E. moshkovskii, PCR-based molecular identification was used to differentiate between the two.
- E. moshkovskii was identified in over 50% of diarrhoea cases caused by amoebic parasites.
- Due to the morphological similarities between E. histolytica and E. moshkovskii, PCR-based molecular identification was used to differentiate between the two.
What is Entamoeba moshkovskii?
- About:
- It belongs to the same genus as E. histolytica but has distinct genetic and biochemical traits.
- Originally isolated from sewage in Moscow in 1941.
- Found in soil, water, and animals.
- Symptoms:
- Causes problems like diarrhea, tummy pain, fever, and dehydration.
- It can damage the intestines, leading to ulcers, bleeding, or even serious issues like infections in the liver.
- Transmission:
- People can get infected by eating contaminated food or drinking contaminated water.
- Direct contact with poop can also spread the infection.
- Diagnosis Challenges:
- Looks like Entamoeba histolytica under a microscope, so it's hard to tell them apart.
- Special tests like PCR or DNA sequencing are needed for accurate identification.
- Treatment:
- Treating infections caused by Entamoeba moshkovskii can be tricky.
- The usual drugs used for amoebic infections may not work well.
- More research is needed to find the best treatment options.
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Gambusia Fish Release for Mosquito Control in Andhra Pradesh
The Andhra Pradesh government's recent release of approximately 10 million Gambusia fish, also known as mosquitofish, into the state's water bodies to combat mosquito-borne diseases has sparked concerns about potential harm to native species and ecosystem balance. The Gambusia fish, native to the southeastern United States, can consume 100 to 300 mosquito larvae per day.
While the fish is widely used as a biological agent to control mosquito larvae, its introduction as an invasive alien species raises questions about its effectiveness and unintended consequences.
International Union for Conservation of Nature declare Gambusia one of the 100 worst invasive alien species in the world. Multiple countries, including India have also listed Gambusia as invasive species.
However, the fish continues to be a prominent part of the country’s malaria control program and the fish continue to be released into freshwater bodies across the country, like Andhra Pradesh, Chandigarh and Uttar Pradesh.
Read more: International Union for Conservation of Nature, Invasive alien species
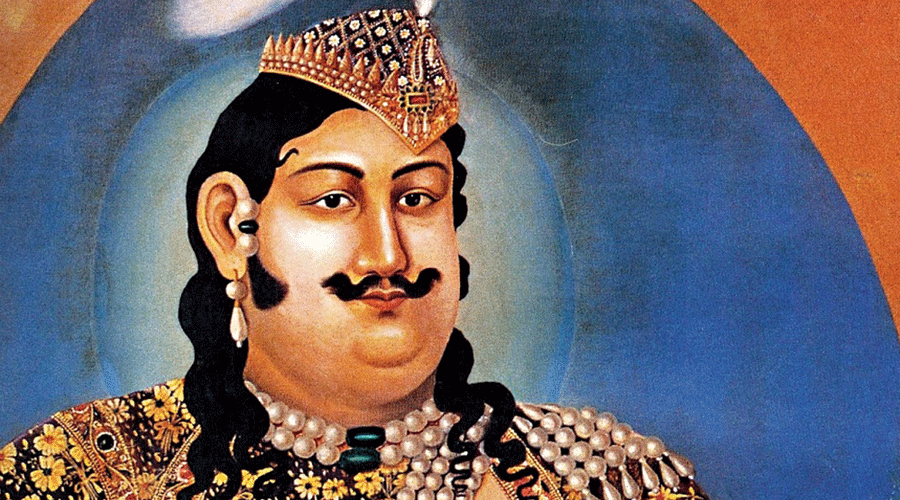
Tribute to Nawab Wajid Ali Shah, the Last King of Awadh
Kolkata is all set to celebrate the bicentenary year of Nawab Wajid Ali Shah, the last king of Awadh who was deposed by the British and exiled to Metiabruz, a suburb of Kolkata, where he spent his final years.
Nawab Wajid Ali Shah was a fine connoisseur of art, music, dance, poetry and cuisine, and he supported many artists and performers in his court. Although Wajid Ali Shah's pen-name was "Qaisar", he used pseudonym "Akhtarpiya" for his numerous compositions.
CRCS-Sahara Refund Portal
The Ministry of Cooperation inaugurated the 'CRCS-Sahara Refund Portal' in New Delhi, marking a significant step towards addressing the grievances of depositors of the Sahara Group of Cooperative Societies. This dedicated portal aims to streamline the disbursement process of Rs. 5000 Crores, transferred from the "Sahara-SEBI Refund Account" to the Central Registrar of Cooperative Societies (CRCS), as directed by the Supreme Court. Genuine depositors can now conveniently submit their claims through this online platform.
Cooperatives are governed by state jurisdictions, those operating across multiple states are registered under the Multi-State Co-operative Societies Act (MSCS) of 2002, with administrative and financial control under the central registrar.
Read more: Cooperative Societies
Russia's Halting of Black Sea Grain Initiative Impacts Global Food Security
The recent halt in the Black Sea Grain Initiative by Russia has raised concerns over global food security. This breakthrough accord, brokered by the United Nations and Turkey in July 2022, allowed Ukraine to ship grain to countries in Africa, the Middle East, and Asia. However, Russia's decision to suspend the deal has disrupted the flow of essential food supplies, particularly in regions where hunger is a growing threat and high food prices have already pushed more people into poverty.
Read more: Black Sea Grain Initiative