UN Specialised Agencies: ILO, WHO and ITU (Part–3)
UN Specialised Agencies (Part–1) and (Part–2) and (Part 4) and (Part 5)
Inter-Services Organizations Bill, 2023
For Prelims: IAF, Navy, Army, Joint command in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
For Mains: Inter-Services Organizations Bill, 2023.
Why in News?
Recently, the Inter-Services Organisations (Command, Control and Discipline) Bill, 2023, was introduced in Lok Sabha to empower designated military commanders to take charge of soldiers and enforce discipline, regardless of the service they belong to.
- The bill came ahead of the impending move to establish integrated or joint commands, where all the manpower and assets will be under the operational control of a single three-star general of the Indian Army, Navy and IAF (Indian Air Force).
What are the Key Provisions of the Bill?
- The system is likely to include five joint services commands - western, eastern, northern, maritime, and air defense.
- The central government may constitute an Inter-services Organisation, which may include a Joint Services Command.
- It will empower the Commander-in-Chief/the Officer-in Command of Inter-Services Organisations to maintain discipline and ensure proper discharge of duties of all the personnel from the army, navy and IAF serving under his command.
- The Commander-in-Chief or the Officer-in-Command of an Inter-services Organisation shall be the head of such Inter-services Organisation.
What is the Current Set up of Indian Armed forces?
- At present, soldiers from their respective services are governed by different Acts of Parliament.
- They are the Navy Act of 1957, the Air Force Act of 1950, and the Army Act of 1950.
- In a current joint services setup, an army soldier commanded by a navy officer would have to be sent back to his parent unit for any disciplinary proceedings. The navy officer does not have administrative powers over the said soldier.
- The Indian armed forces currently have 17 commands. There are 7 commands each of the Army and the Air Force. The Navy has 3 commands.
- Each command is headed by a 4-star rank military officer.
- There is one joint command in Andaman and Nicobar Islands which is the first Tri-Service theatre command of the Indian Armed Forces, based at Port Blair in Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India.
- The other tri-service command, the Strategic Forces Command (SFC), looks after the delivery and operational control of the country’s nuclear assets.
- There are also some tri-service organisations like the Defence Intelligence Agency, Defence Cyber Agency, Defence Space Agency, etc.
How does China Operate its Armed Forces?
- In 2016, China re-organised its 2.3-million People’s Liberation Army into five theatre commands to boost offensive capabilities.
- Its Western Theatre Command handles the entire 3,488-km Line of Actual Control from eastern Ladakh to Arunachal Pradesh.
- India has four Armies and three IAF commands for the northern borders with China.
What is the Significance of the Move?
- The bill will pave way for various tangible benefits such as expeditious disposal of cases, saving time and public money by avoiding multiple proceedings and greater integration and joint Manship amongst Armed Forces personnel.
Basic Animal Husbandry Statistics 2022
For Prelims: Animal Husbandry, Livestock, Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund.
For Mains: Basic Animal Husbandry Statistics 2022, Status of India’s Livestock Sector.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying has released the ‘Basic Animal Husbandry Statistics 2022, showing an increase in the milk, eggs and meat productions in India.
- The contribution of livestock in the agriculture sector has been showing steady improvement that signifies its growing importance for the country’s economy.
What are the Key Highlights?
- Milk Production:
- Total milk production in India was 221.06 million tonnes in 2021-2022, keeping It the largest milk producing country in the world.
- Production had increased by 5.29% over the previous year.
- The Indigenous cattle contribute 10.35% of the total milk production in the country whereas non-descript cattle contribute 9.82% and non-descript buffaloes contribute 13.49% of the total milk production in the country.
- Top five major milk producing States are Rajasthan (15.05%), Uttar Pradesh (14.93%), Madhya Pradesh (8.06%), Gujarat (7.56%) and Andhra Pradesh (6.97%).
- Egg Production:
- The total egg production was 129.60 billion numbers, and it is an increase by 6.19% than the previous year.
- Top five egg producing States are Andhra Pradesh (20.41%), Tamil Nadu (16.08%), Telangana (12.86%), West Bengal (8.84%) and Karnataka (6.38%) and these States together contribute 64.56% of total egg production in the country.
- Meat Production:
- The total meat production in the country was 9.29 million tonnes, increasing by 5.62% as compared to the previous year.
- The meat production from poultry is contributing about 51.44% of the total production.
- The top five meat producing States are Maharashtra (12.25%), Uttar Pradesh (12.14%), West Bengal (11.63%), Andhra Pradesh (11.04%) and Telangana (10.82%). They together contribute 57.86% of total meat production in the country.
- Wool:
- The total wool production in the country during 2021-22 was 33.13 thousand tonnes which had declined by 10.30% as compared to previous year.
- The top five major wool producing States are Rajasthan (45.91%), Jammu and Kashmir (23.19%), Gujarat (6.12%), Maharashtra (4.78%) and Himachal Pradesh (4.33%).
What is Animal Husbandry?
- About:
- Animal husbandry refers to livestock raising and selective breeding. It is the management and care of animals in which the genetic qualities and behavior of animals are further developed for profit.
- India is the highest livestock owner of the world.
- As per the 20th Livestock Census, the total Livestock population is 535.78 million in the country showing an increase of 4.6% over Livestock Census-2012.
- Animal rearing has multidimensional potential.
- For instance, Operation Flood, launched in 1970, helped dairy farmers direct their own development, increased milk production ("a flood of milk"), augmented rural incomes and ensured reasonable prices for consumers.
- Significance:
- Economic Development: Animal husbandry is a significant contributor to the economy of many countries. It generates employment opportunities, income, and foreign exchange through the export of animal-based products.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Animal husbandry plays a crucial role in sustainable agriculture by providing manure for soil fertility, controlling pests and weeds, and reducing the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
- Genetic Improvement: Animal husbandry also contributes to genetic improvement of livestock through selective breeding and genetic engineering, leading to higher productivity, improved disease resistance, and better quality of animal-based products.
- Related Initiatives:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 Which of the following is the chief characteristic of ‘mixed farming’? (2012)
(a) Cultivation of both cash crops and food crops
(b) Cultivation of two or more crops in the same field
(c) Rearing of animals and cultivation of crops together
(d) None of the above
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Livestock rearing has a big potential for providing non-farm employment and income in rural areas. Discuss suggesting suitable measures to promote this sector in India. (2015)
Inter-State Variations in Central Tax Distribution
For Prelims: 15th Finance Commission, Central Tax Distribution, Horizontal equity, Article 280 of the Constitution.
For Mains: Taxes Distribution Among States, Recommendations of 15th Finance Commission.
Why in News?
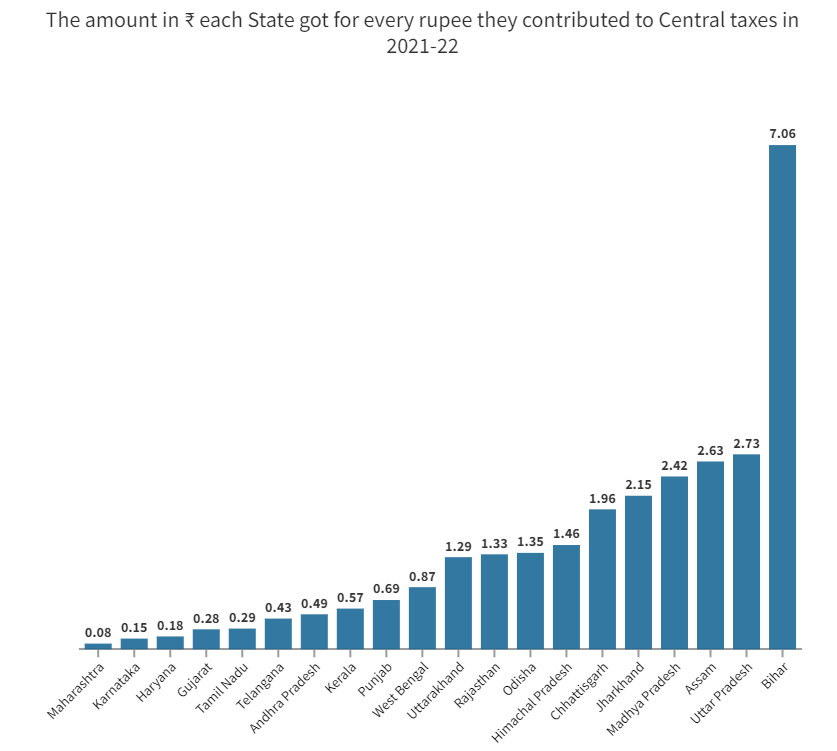
Critics argue that the 15th Finance Commission formula is skewed in favour of some states, resulting in wide inter-state variations.
- Tamil Nadu gets back only 29 paise for every one rupee it gives to the Centre, while Uttar Pradesh gets ₹2.73 and Bihar gets back ₹7.06.
How Taxes are Distributed Among States?
- About:
- The Centre collects taxes from states and distributes it among them based on the Finance Commission's (XVFC) formula.
- XVFC Formula:
- The XVFC formula is based on each state's needs (population, area and forest and ecology), equity (per capita income difference), and performance (own tax revenue and lower fertility rate).
- Weightage:
- Needs are given 40% weightage, equity 45%, and performance 15%.
- The XVFC introduced the fertility rate component to reward states that have reduced fertility levels, but this has a lower weightage than equity and needs.
- Arguments:
- Critics argue that this formula favours some northern states, as the population is given higher weightage.
- The southern states' share has consistently declined in successive Finance Commissions.
- Some argue that transfers enable a state to provide comparable levels of services and ensure horizontal equity.
- However, others contend that the formula should not adversely impact a state's efficiency and progress.
- Critics argue that this formula favours some northern states, as the population is given higher weightage.
What is the 15th Finance Commission?
- About:
- The Finance Commission (FC) is a constitutional body that determines the method and formula for distributing the tax proceeds between the Centre and states, and among the states as per the constitutional arrangement and present requirements.
- Constitutionality:
- Under Article 280 of the Constitution, the President of India is required to constitute a Finance Commission at an interval of five years or earlier.
- 15th Finance Commission
- The 15th Finance Commission was constituted by the President of India in November 2017, under the chairmanship of NK Singh.
- Its recommendations will cover a period of five years from the year 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- The government accepted the 15th Finance Commission’s recommendation to maintain the States’ share in the divisible pool of taxes to 41% for the five-year period starting 2021-22.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. How have the recommendations of the 14th Finance Commission of India enabled the States to improve their fiscal position? (2021)
PM MITRA Scheme and Textile Sector
For Prelims: PM MITRA Scheme, Textile Sector, PPP, FDI, GDP, Agriculture, IIP, SAFTA.
For Mains: Textile Sector of India, Potential and Challenges.
Why in News?
The Centre has selected sites in Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh to set up new textile parks under the PM Mega Integrated Textile Regions and Apparel (PM MITRA) scheme.
- The parks will be set up by 2026-27. The total outlay for the project is Rs 4,445 crore, though the initial allocation in the 2023-24 Budget is only Rs 200 crore.
What is the PM MITRA Scheme?
- About:
- PM MITRA Park will be developed by a Special Purpose Vehicle which will be owned by the Central and State Government and in a Public Private Partnership (PPP) Mode.
- Each MITRA Park will have an incubation centre, common processing house and a common effluent treatment plant and other textile related facilities such as design centres and testing centres.
- Implementation:
- Special Purpose Vehicle: An SPV owned by the Centre and State Government will be set up for each park which will oversee the implementation of the project.
- Development Capital Support: The Ministry of Textiles will provide financial support in the form of Development Capital Support upto Rs 500 crore per park to the park SPV.
- Competitive Incentive Support (CIS): A CIS upto Rs 300 crore per park to the units in PM MITRA Park shall also be provided to incentivise speedy implementation.
- Convergence with other Schemes: Convergence with other Government of India schemes shall also be facilitated in order to ensure additional incentives to the Master Developer and investor units.
What is the Significance of the Scheme?
- Reduce Logistics Cost:
- It will reduce logistics costs and strengthen the value chain of the Textile Sector to make it globally competitive.
- High logistics costs are considered a key hurdle to India’s goal of boosting textile exports.
- Employment:
- An investment of Rs 70,000 crore into these parks can generate employment for about 20 lakh people.
- Attract FDI:
- The parks are crucial to attract Foreign Direct Investment (FDI).
- From April 2000 to September 2020, India’s textile sector received Rs 20,468.62 crore of FDI, which is just 0.69% of the total FDI inflows during the period.
- Competitiveness:
- This cluster-based approach will reduce the increased wastage and logistical costs of the sector, and thus will improve the competitiveness of the country's textile sector.
What is the Scenario of the Textile Sector of India?
- Status:
- The textile sector is one of the critical sectors of the Indian economy, accounting for more than 2% of the total GDP (Gross Domestic Product) and more than 12 % of the manufacturing sector GDP.
- The textile sector has a diverse value chain spread across fibre to readymade garments.
- Potential:
- The sector is the 2nd largest provider of employment in India, after agriculture.
- It provides employment to an estimated 45 million people directly and to another 60 million indirectly through allied activities.
- India is the 6th largest exporter of textile and apparel in the world, with 4% share of the global trade in textiles and apparel.
- India’s textile and apparel exports (including handicrafts) stood at USD 44.4 billion in FY22, a 41% increase YoY.
- India’s textiles industry has around 4.5 crore employed workers including 35.22 lakh handloom workers across the country.
- The sector is the 2nd largest provider of employment in India, after agriculture.
- Challenges:
- Decline in Production:
- The production of textiles as measured by the Index of Industrial Production (IIP) for textile has seen a consistent decline since March 2022.
- The index value, which was 118.5 in March 2022, has fallen to 102.3 in October 2022.
- Surge in Imports:
- In the period from April to November 2022, imports of textiles were valued at Rs 433 billion, same as last year they were valued at Rs. 313 billion.
- India allowed duty-free import of readymade garments from Bangladesh under the South Asian Free Trade Agreement (SAFTA) in 2006, resulting in an increase in imports of apparels made with Chinese fabrics and yarns.
- Exports Suffer:
- India suffers from the disadvantage of duties being imposed by the importing countries.
- Countries like Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and African countries get duty-free access and make India’s textiles comparatively less competitive in the international landscape.
- Inverted Duty Structure:
- The Man-Made Fibre (MMF) value chain in the textile industry currently faces an Inverted Duty Structure, that is the tax on output, or the final product is lower than taxes on inputs, creating an inverse accumulation of input tax credit.
- This is usually refunded by the government, creating a revenue outflow for the government, but also blocks crucial working capital flow for businesses in the meantime.
- Decline in Production:
What are the Initiatives Related to the Textile Sector?
Way Forward
- The DGTR (Directorate General of Trade Remedies) has recommended the levying of Anti-Dumping Duty (ADD) on VSF imported from Indonesia. The investigations showed that imports from Indonesia have increased after the lifting of the anti-dumping duty.
- India can make the sector organised by setting up mega apparel parks and common infrastructure for the textile industry. The focus should be on the modernisation of obsolete machinery and technology.
- India needs a comprehensive blueprint for the textile sector. Once that is drawn up, the country needs to move into mission mode to achieve it.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The value of Indo-Sri Lanka trade has consistently increased in the last decade.
- “Textile and textile articles” constitute an important item of trade between India and Bangladesh.
- In the last five years, Nepal has been the largest trading partner of India in South Asia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Analyse the factors for highly decentralized cotton textile industry in India. (2013)
Starberry-Sense
Why in News?
Researchers at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have developed a low-cost star sensor for astronomy and small CubeSat class satellite missions.
- The star sensor named Starberry-Sense can help small CubeSat class satellite missions find their orientation in space.
- The Department of Science and Technology (DST) said that the Starberry-Sense is ready for launch on the PS4-Orbital Platform by ISRO and can be used for CubeSats and other small satellite missions in the future.
What is Star Sensor?
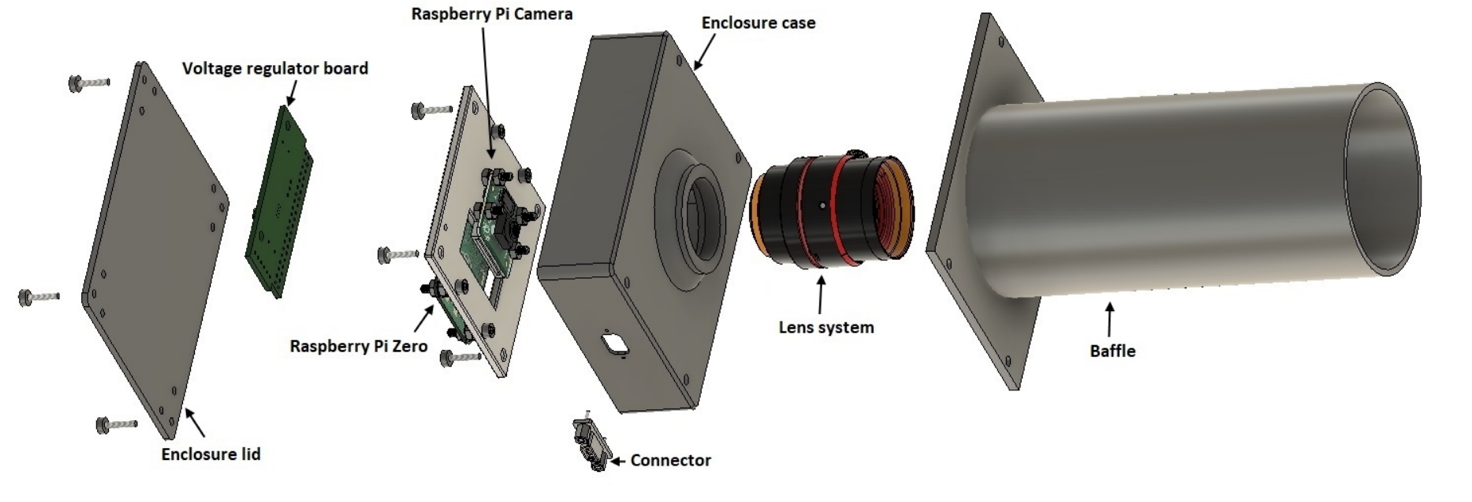
- Star sensor is one of the precise attitude determination sensors. It is an electro-optical system that takes an image from a set of stars and by comparing it with the star catalogue determines angle deviation of the satellite and modifies its attitude. Star sensor is composed of baffle, optical system, detector, and electronic and image processing system.
Why Starberry-Sense is Better than Other Star Sensor?
- This star sensor is less expensive than those on the market by less than 10% based on the commercial/off-the-shelf components which are readily available.
- The system is developed is developed by using Raspberry Pi Zero with is available at low cost.
- The Raspberry Pi Zero is a compact size (smaller than a credit card) computer with low power consumption, and ability to run custom software make it a suitable platform for a star sensor application.
What is Indian Institute of Astrophysics?
- The IIA is a premier research institute in India dedicated to the study of astronomy, astrophysics, and related fields. Wholly financed by the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India.
- It has several observational facilities, including the Vainu Bappu Observatory in Kavalur, Tamil Nadu, the Gauribidanur Radio Observatory in Karnataka, and the Hanle Observatory in Ladakh, Jammu, and Kashmir.
Zojila Pass and Razdan Pass Reopen After Short Winter Closure
Why in News?
The Border Roads Organisation (BRO) has announced that the strategic Zoji La Pass, located at an altitude of 11,650 feet in the Greater Himalayan Range, has been reopened after a winter closure.
- Similarly, the Razdan Pass, which connects the Gurez sector to the Kashmir Valley, has also been reopened after a brief winter closure.
- Snow clearance operations were undertaken by Project Beacon and Vijayak from both sides of the pass.
What is the Significance of Zoji La Pass?
- Zoji La is a high mountain pass located in the Kargil district of Ladakh.
- The pass links Leh and Srinagar and provides an important link between Union Territories of Ladakh and Kashmir.
- Zoji La pass remains closed during winters due to heavy snowfall, cutting off Ladakh region from Kashmir.
- In 2018, the Zoji La tunnel project was launched. The tunnel is Asia's longest and strategic bi-directional tunnel, which will provide all-weather connectivity between Srinagar, Kargil and Leh.
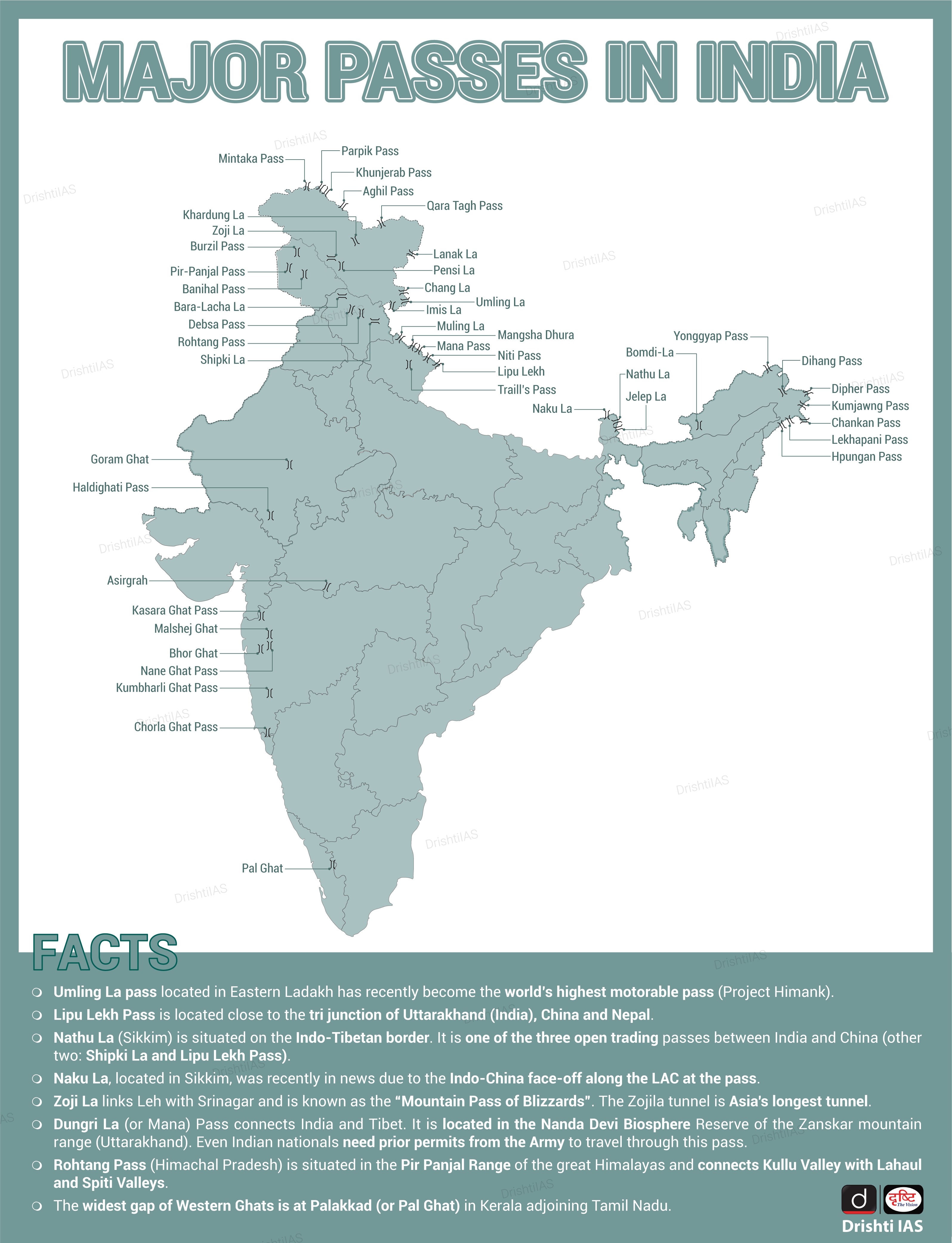
What are the Other Important Passes in India?
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Siachen Glacier is situated to the (2020)
(a) East of Aksai Chin
(b) East of Leh
(c) North of Gilgit
(d) North of Nubra Valley
Ans: (d)
Active Volcanoes on Venus
Why in News?
Recently, NASA Magellan spacecraft captured images of Venus’ surface from different orbits. A few locations, including those suspected to have volcanic activity, were observed two or three times over two years
What are the Observations Made?
- A study looking into decades-old radar images gave new evidence of having active volcanoes on Venus.
- A 2.2 square kilometre volcanic vent on Venus changed shape in eight months, indicating volcanic activity.
- A volcanic vent is a spot through which molten rock erupts.
- It showed signs of drained lava, the radar images indicated that the same vent had doubled in size and the lava lake seemed to have reached the rim. The vent is associated with Maat Mons.
- Maat Mons is the planet’s second-highest volcano. It sits in the Atla Regio, a vast highland region near Venus’ equator. These changes were likely due to lava flow escaping the vent, hinting at a possible volcanic activity.
What was Magellan Mission?
- NASA's Magellan mission to Venus was one of the most successful deep space missions.
- It was the first spacecraft to image the entire surface of Venus and made several discoveries about the planet it was launched on May 4, 1989.
- On October 13, 1994, communication with Magellan was lost when it was instructed to descend into the atmosphere of Venus.
What are the Upcoming Expeditions to Venus?
- The Indian Space Research Organisation is also working on Shukrayaan-1 to study Venus. The orbiter will likely study the planet’s geological and volcanic activity, emissions on the ground, wind speed, cloud cover, and other planetary characteristics from an elliptical orbit
- The new study will help to identify target areas for future missions such as Europe's Envision that is scheduled to launch in 2032.
- Two missions are being planned to Venus that are NASA’s VERITAS and DAVINCI are expected to observe venus in the 2030s.
What is Venus?
- About:
- It is the second closest planet to the sun and the sixth-largest planet in the solar system. It is also known as earth's twin.
- It is the hottest planet in the solar system and its extreme temperatures (450o C) and acidic clouds make it an unlikely place for life.
- Along with Uranus it spins backwards with respect to other planets i.e. Its sun rises in the west and sets in the east.
- Along with Mercury it has no moons and no rings.
- Previous Missions Sent on Venus:
| Previous Missions Sent on Venus | |||
| US | Russia | Japan | Europe |
|
|
|
|
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Which of the following pairs is/are correctly matched? (2014)
Spacecraft Purpose
- Cassini-Huygens: Orbiting the Venus and transmitting data to the Earth
- Messenger: Mapping and investigating the Mercury
- Voyager 1 and 2: Exploring the outer solar system
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Cassini-Huygens was sent to study Saturn and its moons. It was a joint collaboration between NASA and European Space Agency. It was launched in 1997 and entered Saturn’s orbit in 2004. The mission ended in 2017. Hence, pair 1 is not correctly matched.
- Messenger, a spacecraft by NASA was sent to map and investigate Mercury. It was launched in 2004 and entered Mercury’s orbit in 2011. The mission ended in 2015. Hence, pair 2 is correctly matched.
- Voyager 1 and 2 were launched by NASA in 1977 to explore the outer solar system. Both the spacecrafts are still operational. Hence, pair 3 is correctly matched.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Horseshoe Crabs Disappearing off Odisha Coast
Horseshoe crabs, medicinally priceless and one of oldest living creatures on the earth, appear to be disappearing from their familiar spawning grounds due to destructive fishing practices along Chandipur and Balaramgadi coast in Odisha’s Balasore district.
India has two species of Horseshoe crabs- the coastal horseshoe crab (Tachypleus gigas),the mangrove horseshoe crab (Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda) and major concentration of the animal is found in Odisha. Both these species are not listed on IUCN red list yet but are part of Schedule 4 of Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
The blood of Horseshoe crab is very important for preparation of rapid diagnostic reagent. All injectable and medicines are tested with the help of Horseshoe crabs. A molecule has been developed from reagent of Horseshoe crab that would help treat pre-eclampsia ,a disease affecting pregnant women.
Palaeontological studies say the age of Horseshoe crabs is 450 million years. The creature has lived on earth without undergoing any morphological change due to its strong immune system.
India moots Action Plan to Mark 2023 as Year of Tourism Development at SCO Meet
India mooted an action plan to mark 2023 as the year of tourism development in the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) region at the tourism ministers’ conference.
A joint action plan for implementing the agreement between the Member States on cooperation in the tourism sector was approved. It comprises promotion of the SCO tourism brand, promotion of the cultural heritage of member states; sharing of information and digital technologies in tourism; and promotion of mutual cooperation in medical and health tourism. Kashi has been declared as the first tourism and cultural capital of SCO. The meeting also adopted the Action Plan for ‘Year of Tourism Development in the SCO Space in 2023’.
SCO is a permanent intergovernmental international, Eurasian, political, economic and military organization aiming to maintain peace, security and stability in the region.It’s members include Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, India, Pakistan and Iran.
President’s Colour to INS Dronacharya
The President of India presented the President’s Colour to INS Dronacharya. It is the highest award bestowed on a military unit in India in recognition of its exceptional services to the nation. It is also known as ′Nishaan′ which is an emblem that is worn by all unit officers on the left-hand sleeve of their uniform.
Out of the three defence forces, the Indian Navy was the first Indian Armed Force to be awarded the President Colour by Dr. Rajendra Prasad in 1951.
In India, as well as many Commonwealth nations, the tradition of Colours has been drawn from the British Army. Traditionally, there have been four kinds of symbols associated with Colours —Standards, Guidons, Colours and Banners.
The Indian Navy’s INS Dronacharya is a prestigious gun nery school located in Kochi, Kerala. is responsible for training officers and ratings in various fields such as small-arms, naval missiles, artillery, radar, and defensive countermeasures.
Research, Education and Training Outreach (REACHOUT) Scheme
An umbrella scheme Research, Education and Training Outreach (REACHOUT) is being implemented by the Ministry of Earth Sciences for capacity building. It consists of the following sub-schemes:
- R&D in Earth System Science (RDESS)
- International Training Centre for Operational Oceanography (ITCOocean)
- Program for Development of Skilled manpower in Earth System Sciences (DESK)
The scheme is being implemented for entire country and not State/UT-wise. The main objectives of the above sub-schemes are:
- Supporting various R &D activities in the thrust areas of different components of Earth System Sciences that are theme and need based and that would help in attaining the National goals set up for MoES.
- Develop useful collaborations with international organizations for mutual transfer of advanced knowledge in science and technology in Earth Sciences and to provide services to developing countries.
- Develop skilled and trained manpower in Earth Sciences with the support of academic institutions in the country and abroad.

.png)