Maps
South China Sea
Key Points
- Physical Geography:
- An arm of the western Pacific Ocean that borders the Southeast Asian mainland.
- Bordered by Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines Singapore, Taiwan, Thailand and Vietnam.
- It is connected by the Taiwan Strait with the East China Sea and by the Luzon Strait with the Philippine Sea (both marginal seas of the Pacific Ocean).
- Comprise three archipelagoes, namely, the Spratly Islands, Paracel Islands, Pratas Islands and Macclesfield’s Bank and Scarborough Shoal.
- Dispute:
- China’s Nine Dash Line: Defines area claimed by China - by far the largest portion of the Sea.
- Scarborough Shoal: Claimed both by the Philippines and China (known as Huangyan Island in China).
- Spratlys: Occupied by claimants, which consist of Taiwan, Vietnam, the Philippines, China and Malaysia.
- Paracel Islands: Subject of overlapping claims by China, Vietnam and Taiwan.
- Island Chain Strategy: A geographical security concept crafted by the United States in the 1940s to deter China and the Soviet Union’s maritime ambitions.
- Recent Related Events:


Infographics
Indian History
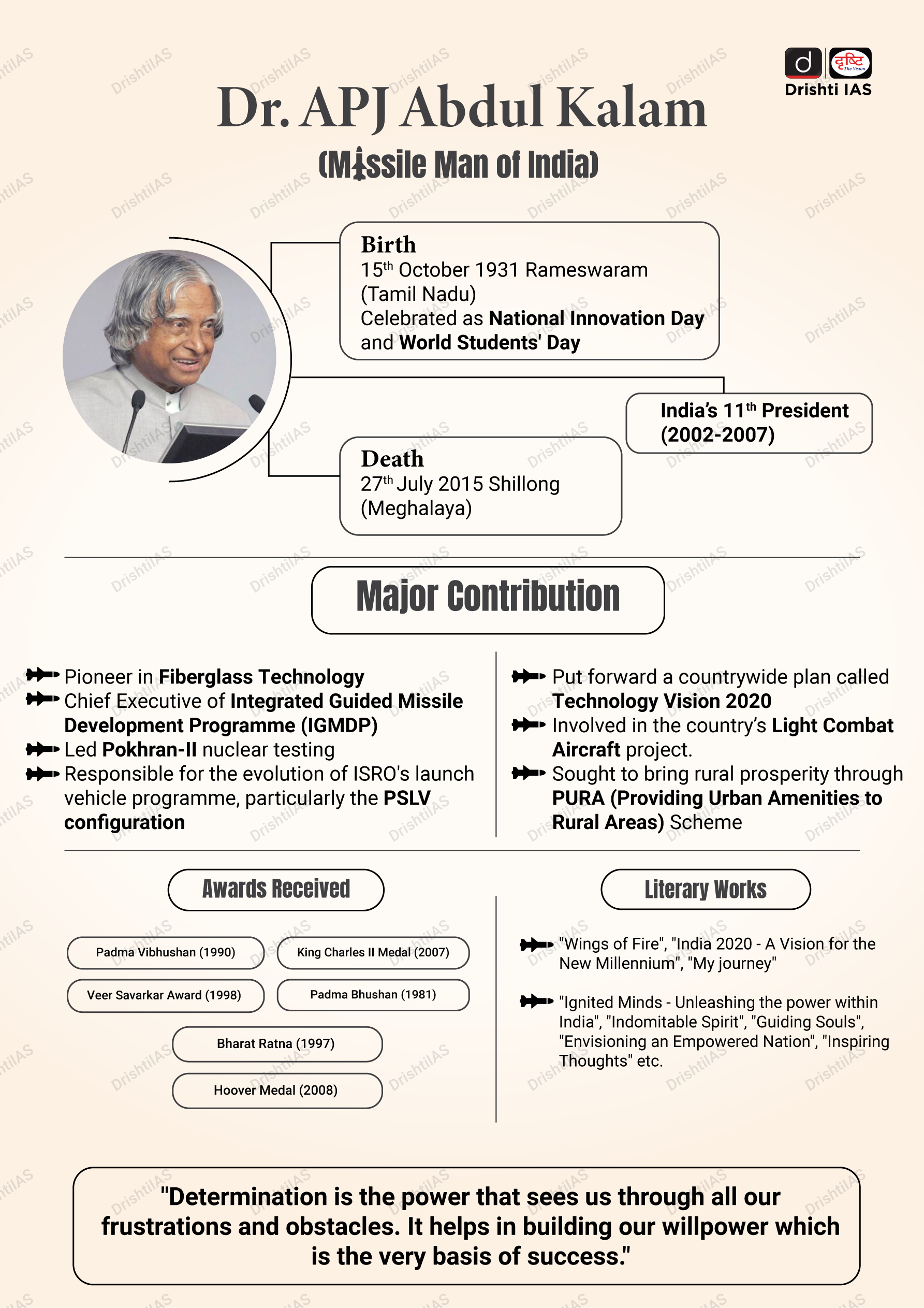
Dr A. P. J. Abdul Kalam
For Prelims: Dr A. P. J. Abdul Kalam, PURA (Providing Urban Amenities to Rural Areas)
For Mains: Dr A. P. J. Abdul Kalam, Important Personalities
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister paid tribute to the former President APJ Abdul Kalam on his 90th birth anniversary.
Who was Dr A. P. J. Abdul Kalam?
- About:
- Born on 15th October 1931 at Rameswaram in Tamil Nadu.
- His birth anniversary is celebrated as the National Innovation Day and World Students' Day.
- He graduated in Science from St Joseph's College, Trichy in 1954 and specialized in Aeronautical Engineering from Madras Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1957.
- He is one of the most distinguished scientists of India with the unique honour of receiving honorary doctorates from 48 Universities and institutions from India and abroad.
- He was sworn in as India’s 11th President in 2002 and completed the full term in 2007.
- He planned programmes to produce a number of successful missiles, which helped earn him the nickname “Missile Man of India”.
- Born on 15th October 1931 at Rameswaram in Tamil Nadu.
- Awards Received:
- He was awarded the coveted civilian awards - Padma Bhushan (1981) and Padma Vibhushan (1990) and the highest civilian award Bharat Ratna (1997).
- Literary Works:
- "Wings of Fire", "India 2020 - A Vision for the New Millennium", "My journey" and "Ignited Minds - Unleashing the power within India", "Indomitable Spirit", "Guiding Souls", "Envisioning an Empowered Nation", "Inspiring Thoughts" etc.
- Death:
- 27th July 2015 at Shillong, Meghalaya.
What has been the Contribution of Dr A. P. J. Abdul Kalam?
- His Contribution:
- Pioneer in Fiberglass Technology:
- He was a pioneer in fiberglass technology and led a young team to initiate this effort in ISRO from design, development leading to the production of composites rocket motor cases.
- Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV-3):
- He made a significant contribution as Project Director to develop India's first indigenous Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV-3) which successfully injected the Rohini satellite into Near-Earth Orbit in July 1980 and made India an exclusive member of Space Club.
- He was responsible for the evolution of ISRO's launch vehicle programme, particularly the PSLV configuration.
- Indigenous Guided Missiles:
- After working for two decades in ISRO and mastering launch vehicle technologies, he took up the responsibility of developing Indigenous Guided Missiles at the DRDO.
- He was the Chief Executive of Integrated Guided Missile Development Programme (IGMDP).
- He led to the weaponization of strategic missile systems and the Pokhran-II nuclear tests in collaboration with the Department of Atomic Energy, which made India a nuclear weapon State.
- After working for two decades in ISRO and mastering launch vehicle technologies, he took up the responsibility of developing Indigenous Guided Missiles at the DRDO.
- Technology Vision 2020:
- In 1998, he put forward a countrywide plan called Technology Vision 2020, which he described as a road map for transforming India from a less-developed to a developed society in 20 years.
- The plan called for, among other measures, increasing agricultural productivity, emphasising technology as a vehicle for economic growth, and widening access to health care and education.
- In 1998, he put forward a countrywide plan called Technology Vision 2020, which he described as a road map for transforming India from a less-developed to a developed society in 20 years.
- Medical and Healthcare:
- APJ Abdul Kalam in collaboratation with cardiologist B. Soma Raju designed a cost-effective coronary stent known as ‘Kalam-Raju-Stent’ for coronary heart disease which made healthcare accessible to all.
- The device led to reduction of prices of imported coronary stents in India by more than 50%.
- Light Combat Aircraft project:
- He was deeply involved in the country’s Light Combat Aircraft project.
- He had been associated with avionics. He also became the first Indian Head of State to fly a fighter plane. His first aeronautical project led him to designing India’s first indigenous hovercraft ‘Nandi”.
- A hovercraft is a vehicle that can travel over land, water, mud and ice by lifting itself off the ground with large blowers that create an air cushion beneath the craft.
- Others:
- He was passionate about bringing rural prosperity through PURA (Providing Urban Amenities to Rural Areas), in which science and technology has to play a key role.
- Based on his diverse experience he propagated the concept of World Knowledge Platform through which the core competencies of organizations and nations can be synergized to innovate and create solutions and products for the challenges of the 21st century.
- Pioneer in Fiberglass Technology:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. “Where there is righteousness in the heart, there is beauty in the character. When there is beauty in the character, there is harmony in the home. When there is harmony in the home, there is order in the nation. When there is order in the nation, there is peace in the world.” – A.P.J. Abdul Kalam (2019)
Q. "If a country is to be corruption free and become a nation of beautiful minds, I strongly feel that there are three key societal members who can make a difference. They are father, mother and teacher." – A.P.J. Abdul Kalam (2022)


Social Justice
Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA)
For Prelims: Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), Minimum Wages Act, 1948
For Mains: Poverty, Government Policies & Interventions, Issues Relating to Development, MGNREGA and related Issues
Why in News?
Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) helped compensating 20-80% of the income loss incurred because of the Covid-19 induced lockdown, as per a study conducted by Azim Premji University across four states (Bihar, Karnataka, Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh).
- However, 39% of the surveyed households didn’t get a single day of work in the Covid-19 year due to lack of adequate works being sanctioned/opened.
What is MGNREGA?
- About: MGNREGA is one of the largest work guarantee programmes in the world launched in 2005 by the Ministry of Rural development.
- The primary objective of the scheme is to guarantee 100 days of employment in every financial year to adult members of any rural household willing to do public work-related unskilled manual work.
- As of 2022-23, there are 15.4 crore active workers under the MGNREGA.
- Legal Right to Work: Unlike earlier employment guarantee schemes, the act aims at addressing the causes of chronic poverty through a rights-based framework.
- At least one-third of beneficiaries have to be women.
- Wages must be paid according to the statutory minimum wages specified for agricultural labourers in the state under the Minimum Wages Act, 1948.
- Demand-Driven Scheme: The most important part of MGNREGA’s design is its legally-backed guarantee for any rural adult to get work within 15 days of demanding it, failing which an ‘unemployment allowance’ must be given.
- This demand-driven scheme enables the self-selection of workers.
- Decentralised planning: There is an emphasis on strengthening the process of decentralisation by giving a significant role in Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) in planning and implementing these works.
- The act mandates Gram sabhas to recommend the works that are to be undertaken and at least 50% of the works must be executed by them.
What are the Issues Associated with Implementation of Scheme?
- Delay and Insufficiency in Funds Dispersal: Most states have failed to disburse wages within 15 days as mandated by MGNREGA. In addition, workers are not compensated for a delay in payment of wages.
- This has turned the scheme into a supply-based programme and subsequently, workers had begun to lose interest in working under it.
- There is ample evidence by now, including an admission by the Ministry of Finance, that delays in wage payments are a consequence of insufficient funds.
- Caste Based Segregation: There were significant variations in delays by caste. While 46% of payments to SC (Scheduled Caste) workers and 37% for ST (Scheduled Tribes) workers were completed in the mandated seven-day period, it was a dismal 26% for non-SC/ST workers.
- The negative impact of caste-based segregation was felt acutely in poorer States such as Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal.
- Ineffective Role of PRI: With very little autonomy, gram panchayats are not able to implement this act in an effective and efficient manner.
- Large Number of Incomplete works: There has been a delay in the completion of works under MGNREGA and inspection of projects has been irregular. Also, there is an issue of quality of work and asset creation under MGNREGA.
- Fabrication of Job cards: There are several issues related to the existence of fake job cards, the inclusion of fictitious names, missing entries and delays in making entries in job cards.
Way Forward
- There is a need for better coordination between various government departments and the mechanism to allot and measure the work.
- Some discrepancies in the payouts need to be addressed, too. Women in the sector, on an average, earn 22.24% less than their male counterparts.
- State governments must ensure that public work gets started in every village. Workers turning up at the worksite should be provided work immediately, without much delay.
- Local bodies must proactively reach out to returned and quarantined migrant workers and help those in need to get job cards.
- Gram panchayats need to be provided with adequate resources, powers, and responsibilities to sanction works, provide work on demand, and authorise wage payments to ensure there are no delays in payments.
- MGNREGA should be converged with other schemes of the government. For example, Green India initiative, Swachh Bharat Abhiyan etc.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Among the following who are eligible to benefit from the “Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act”? (2011)
(a) Adult members of only the scheduled caste and scheduled tribe households
(b) Adult members of below poverty line (BPL) households
(c) Adult members of households of all backward communities
(d) Adult members of any household
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee (MGNREGA), which is the largest work guarantee programme in the world, was enacted in 2005 with the primary objective of guaranteeing 100 days of wage employment per year to every household whose adult members volunteer to do unskilled manual work.
- It aims at addressing the causes of chronic poverty through the ‘works’ (projects) that are undertaken, and thus ensuring sustainable development. There is also an emphasis on strengthening the process of decentralisation by giving a significant role to Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) in planning and implementing these works.
- Therefore, option D is the correct answer.


Science & Technology
Mangalyaan Mission Over
For Prelims: ISRO, NASA, MOM, Roscosmos, MOM-2, Gaganyaan, Chandrayaan-3 and Aditya – L1
For Mains: Reasons for the End of Mangalyan Mission
Why in News?
The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) confirmed that the Mars Orbiter craft has lost communication and is non-recoverable and the Mangalyaan mission has attained end-of-life.
- Despite being designed for a life-span of six months as a technology demonstrator, the Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) has lived for about eight years in the Martian orbit.
What caused the End of MOM?
- Because of propellant (fuel) exhaustion the desired altitude pointing could not be achieved for sustained power generation and it lost communication from the ground station.
- Recently there were back-to-back eclipses including one that lasted seven-and-half hours because that satellite has consumed all the propellant on board.
- As the satellite battery is designed to handle eclipse duration of only about one hour and 40 minutes, a longer eclipse would drain the battery beyond the safe limit.
What is MOM?
- About:
- The Rs 450 crore Mars Orbiter Mission was launched onboard PSLV-C25 on 5th November, 2013, and the MOM spacecraft was successfully inserted into the Martian orbit in September, 2014 in its first attempt.
- Mangalyaan was India's first interplanetary mission.
- The mission made India the first Asian country, and the fourth in the world after Roscosmos, NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration), and the European Space Agency, to get to the planet.
- China referred to India's successful Mangalyaan as the "Pride of Asia".
- Description:
- It carried 850 kg of fuel and 5 science payloads including a Mars Color Camera (MCC) which it was using to study the Martian surface and atmosphere since entering orbit successfully.
- The highly elliptical orbit geometry of MOM enabled MCC to take snapshots of the 'Full disc' of Mars at its farthest point and finer details from the closest point.
- The MCC has produced more than 1000 images and published a Mars Atlas.
- Other instruments are: Thermal Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (TIS), Methane Sensor for Mars (MSM), Mars Exospheric Neutral Composition Analyser (MENCA) and Lyman Alpha Photometer (LAP).
- It carried 850 kg of fuel and 5 science payloads including a Mars Color Camera (MCC) which it was using to study the Martian surface and atmosphere since entering orbit successfully.
- Objectives:
- It was aimed at studying the Martian atmosphere.
- To explore Martian surface features, mineralogy, morphology and atmosphere using indigenous scientific instruments.
- A crucial objective of MOM was to develop technologies required in planning, designing, management and operations of an interplanetary mission.
What is the Future Indian Mars Mission?
- ISRO came out with an 'Announcement of Opportunity' (AO) for future Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM-2) in 2016 but 'Gaganyaan', 'Chandrayaan-3' and 'Aditya - L1' projects are in the current priority list.
- Mangalyaan-2 will only be an orbiter mission.
What are the Various Mars Missions?
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO
- is also called the Mars Orbiter Mission
- made India the second country to have a spacecraft orbit the Mars after USA
- made India the only country to be successful in making its spacecraft orbit the Mars in its very first attempt
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology has helped India in its socio-economic development? (2016)


Indian Economy
75 New Digital Banking Units in India
For Prelims: Digital Banks, Financial Inclusion
For Mains: Digital Banking Units, Benefits & Services of Digital Banking Units
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister of India has dedicated 75 Digital Banking Units (DBU) across 75 districts to the nation.
- As part of the Union budget speech for 2022-23, the Finance Minister announced setting up the 75 DBUs in 75 districts to commemorate our country's 75 years of independence.
What are Digital Banking Units?
- About:
- A Digital Banking Unit is a specialised fixed point business unit or hub, set up by scheduled commercial banks, housing certain minimum digital infrastructure for delivering digital banking products and services as well as servicing existing financial products and services digitally in self-service mode at any time.
- The DBUs are being set up with the objective to ensure the benefits of digital banking reach every nook and corner of the country and will cover all the States and Union territories.
- Benefits:
- The DBUs will enable those who do not have Information and Communications Technology (ICT) infrastructure to access banking services digitally.
- They will also assist those who are not tech savvy to adopt digital banking.
- DBU Services:
- Services being offered through DBU include banking facilities like opening of savings account, balance-check, print passbook, transfer of funds, investment in fixed deposits, loan applications, stop-payment instructions for cheques issued, application for credit / debit cards, view statement of account, pay taxes, pay bills, make nominations, etc.
- The DBUs will also facilitate onboarding to Government credit link schemes through the Jan Samarth portal and end-to-end digital processing of small ticket MSME/retail loans.
- Difference between DBU & Traditional Banks:
- DBU will provide banking services including cash deposit & withdrawal 24 x 7.
- Services of DBU shall be provided digitally.
- People not having connectivity or computing devices can do banking transactions from DBU in a paperless mode.
- Bank staff will be available to help and guide users for banking transactions in assisted mode.
- DBU will help in providing digital financial literacy and create awareness for adopting digital banking.
- Difference between the Digital Banks and DBUs:
- Balance Sheet/Legal Personality:
- DBUs do not have legal personality and are not licensed under Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
- Legally, they are equivalent to “banking outlets” i.e., branches.
- Digital Banks will have a balance sheet and legal personality & are proposed to be duly licensed banks under Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
- DBUs do not have legal personality and are not licensed under Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
- Level of Innovation/Competition:
- DBUs improve existing channel architecture by offering regulatory recognition to digital channels. However, they are silent on competition.
- The DBU guidelines expressly state that only existing commercial banks may establish DBUs.
- In contrast, a licensing and regulatory framework for Digital banks as proposed here, is more enabling along competition/innovation dimensions.
- Balance Sheet/Legal Personality:
What are other Initiatives for Financial Inclusion?
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Accounts
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
- Direct Bank Transfer
- Fintech
- India Stack
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) is necessary for bringing unbanked to the institutional finance fold. Do you agree with this for financial inclusion of the poorer section of the Indian society? Give arguments to justify your opinion. (2013)


Governance
6th East Asia Summit Education Minister’s Meeting
For Prelims: National Education Policy 2020, PM SHRI scheme, PM- eVidya, East Asia Summit
For Mains: Education and related issues in India, Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
Recently, India participated in the 6th East Asia Summit Education Minister’s Meeting held in Hanoi, Vietnam.
What is the East Asia Summit?
- About:
- Established in 2005, it is a forum of 18 regional leaders for strategic dialogue and cooperation on the key political, security, and economic challenges facing the Indo-Pacific region.
- The concept of an East Asia Grouping was first promoted in 1991 by the then Malaysian Prime Minister, Mahathir bin Mohamad.
- There are six priority areas of regional cooperation within the framework of the EAS.
- These are – Environment and Energy, Education, Finance, Global Health Issues and Pandemic Diseases, Natural Disaster Management, and ASEAN Connectivity.
- Membership:
- It comprises the ten member states of the ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) which are Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam, along with 8 other countries namely Australia, China, Japan, India, New Zealand, the Republic of Korea, Russia and the USA.
- It is an ASEAN-centred forum so it can only be chaired by an ASEAN member.
- Brunei Darussalam is the chair for 2021.
- It is an ASEAN-centred forum so it can only be chaired by an ASEAN member.
- It comprises the ten member states of the ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) which are Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam, along with 8 other countries namely Australia, China, Japan, India, New Zealand, the Republic of Korea, Russia and the USA.
- EAS Meetings and Processes:
- The EAS calendar culminates in the annual Leaders' Summit, which is usually held alongside ASEAN Leaders' meetings in the fourth quarter of every year.
- Meetings of EAS Foreign Ministers and Economic Ministers are also held annually.
- India and EAS:
- India is one of the founding members of the East Asia Summit.
- At the East Asia Summit in Bangkok in November 2019, India had unveiled India’s Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI), which is aimed at forging partnerships to create a secure and stable maritime domain.
What are the Issues Related to the Education Sector in India?
- Inadequate Infrastructure in Schools: According to the Unified District Information System for Education (UDISE) for 2019-20, only 12% of schools have internet facilities and 30% have computers.
- High Dropout Rate: The dropout rate is very high in primary and secondary levels. Most of the students in 6-14 age groups leave the school before completing their education. It leads to wastage of financial and human resources.
- Problem of Brain Drain: Due to cutthroat competition for getting admission in top institutes like IITs and IIMs, a challenging academic environment is created for a large number of students in India, so they prefer going abroad, that makes our country deprived of good talent.
- Mass Illiteracy: In spite of constitutional directives and efforts aimed at enhancing education, around 25% of Indians still remain illiterate, which also leaves them socially and digitally excluded.
- Lack of Technical and Vocational Education: Development of technical and vocational education is quite unsatisfactory, due to which the number of educated unemployed persons is increasing day by day.
- Gender-Inequality: Despite the government's effort to ensure equality of opportunity for education for both men and women in our society, the literacy rate of women in India, especially in rural areas, still remains very poor.
What are the Education Initiatives taken by India?
- National Education Policy 2020:
- NEP 2020 encourages a holistic, flexible & multidisciplinary approach to education and it is based on foundational pillars of access, equality, quality, affordability & accountability & is aligned with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) 2030.
- PM SHRI scheme:
- Under the scheme, more than 14,500 schools will be developed across India with all components of NEP 2020 as exemplar schools.
- These schools will offer mentorship to other schools in their vicinity.
- PM- eVidya:
- The Central government had launched the PM e-Vidya programme in 2020 to boost online learning.
- It unifies all efforts related to digital/online/on-air education to enable multi-mode access for imparting education by using technology to minimise learning losses.
- e-Learning Platforms: Government had also launched various e-learning platforms like DIKSHA, SWAYAM MOOCS platform, Virtual Labs, e-PG Pathshala and National Digital Library.
Way Forward
- There is a need for inclusion of problem-solving and decision-making related subjects in the school curriculum to offer a hands-on learning experience to students and prepare them to face the outside world when they enter into the workforce.
- India's educational setup needs to be enhanced by integrating vocational learning with mainstream education and providing right mentorship at school (especially in government schools) to ensure that students are guided in the right direction from the start and are aware of career opportunities.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. National Education Policy 2020 is in conformity with the Sustainable Development Goal-4 (2030). It intends to restructure and reorient education system in India. Critically examine the statement. (2020)


International Relations
The Interpol General Assembly Meeting in Delhi
For Prelims: International Criminal Police Organisation (Interpol), CBI, Notices of Intepol.
For Mains: India’s cooperation with Interpol, Issues in the Interpol, Working of CBI.
Why in News?
The General Assembly of the International Criminal Police Organisation (Interpol) is meeting in Delhi for four days from October 18, 2022.
- This is the second time since 1997 the 195 member-strong body is holding such a large conference in India.
What is the Interpol?
- It was set up in 1923, as a secure information-sharing platform that facilitates criminal investigation of police forces across the globe through collection and dissemination of information received from various police forces.
- It is headquartered in Lyon, France.
- It keeps track of the movements of criminals and those under the police radar in various regions and tips off police forces which had either sought the Interpol’s assistance or which in its opinion will benefit from the particulars available with it.
- It aims to promote the widest-possible mutual assistance between criminal police forces.
How is the Interpol Organised?
- The head of Interpol is the President who is elected by the General Assembly. He comes from one of the member-nations and holds office for four years.
- The day-to-day activities are overseen by a full-time Secretary General elected by the General Assembly, who holds office for five years.
- The General Assembly lays down the policy for execution by its Secretariat which has several specialised directorates for cybercrime, terrorism, drug trafficking, financial crime, environmental crime, human trafficking, etc. Every member-country is the Interpol’s face in that country.
- All contact of a country’s law enforcement agency with Interpol is through the highest investigating body of the land.
- The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) assumes this role in India with one of its senior officers heading its exclusive Interwing (the National Central Bureaus) for collation of information and liaison with the world body.
What are Interpol Notices?
- About: Its notices are international requests for cooperation or alerts allowing police in member countries to share critical crime-related information.
- Notices are issued by the General Secretariat at the request of a member country’s INTERPOL National Central Bureau and are made available for all our member countries to consult in our Notices database.
- Different Notices:
- Notices can also be used by the United Nations, International Criminal Tribunals and the International Criminal Court to seek persons wanted for committing crimes within their jurisdiction, notably genocide, war crimes, and crimes against humanity.
What are Interpol’s Future Challenges?
- The rising spectre of transnational, cyber and organised crime requires a globally coordinated law enforcement response.
- Interpol has a legacy of trust and reliability. It needs to acquire powers of sanction against a country which refuses to cooperate in implementing a red notice. It is however highly unlikely that member-nations will ever agree to dilute their sovereignty and invest the Interpol with such authority.


Important Facts For Prelims
Election Symbols
Why in News?
The Election Commission allotted the “two swords and shield” symbol to the Maharashtra Chief Minister Eknath Shinde-led faction of the Shiv Sena for the upcoming byelection.
- The Election Symbols (Reservation and Allotment) Order, 1968 empowers the Election Commission to recognise political parties and allot symbols.
What are the Key Points Related to Election Symbols?
- About:
- An electoral or election symbol is a standardized symbol allocated to a political party.
- They are used by the parties during their campaigning and are shown on Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs), where the voter chooses the symbol and votes for the associated party.
- They were introduced to facilitate voting by illiterate people, who can’t read the name of the party while casting their votes.
- In the 1960s, it was proposed that the regulation, reservation, and allotment of electoral symbols should be done through a law of Parliament, i.e., Symbol Order.
- In a response to this proposal, the ECI stated that the recognition of political parties is supervised by the provisions of Election Symbols (Reservation and Allotment) Order, 1968 and so will the allotment of symbols.
- The Election Commission registers political parties for the purpose of elections and grants them recognition as national or state parties on the basis of their poll performance. The other parties are simply declared as registered-unrecognised parties.
- The recognition determines their right to certain privileges like allocation of the party symbols, provision of time for political broadcasts on television and radio stations and access to electoral rolls.
- Every national party and every state party is allotted a symbol exclusively reserved for its use throughout the country and the states respectively.
- Election Symbols (Reservation and Allotment) Order, 1968:
- Under Paragraph 15 of the Order, EC can decide disputes among rival groups or sections of a recognised political party staking claim to its name and symbol.
- The EC is the only authority to decide issues on a dispute or a merger under the order. The Supreme Court (SC) upheld its validity in Sadiq Ali and another vs. ECI in 1971.
- It applies to disputes in recognised national and state parties.
- For splits in registered but unrecognised parties, the EC usually advises the warring factions to resolve their differences internally or to approach the court.
- In almost all disputes decided by the EC so far, a clear majority of party delegates/office bearers, MPs and MLAs have supported one of the factions.
- Before 1968, the EC issued notifications and executive orders under the Conduct of Election Rules, 1961.
- The splinter group of the party - other than the group that got the party symbol - had to register itself as a separate party.
- They could lay claim to national or state party status only on the basis of its performance in state or central elections after registration.
- Under Paragraph 15 of the Order, EC can decide disputes among rival groups or sections of a recognised political party staking claim to its name and symbol.


Important Facts For Prelims
World Food Day
Why in News?
World Food Day is celebrated to commemorate the establishment of the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) on 16th October 1945.
- FAO is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger.
What are the Key Highlights of World Food Day 2022?
- About:
- It is observed annually to address the problem of global hunger.
- It emphasises Sustainable Development Goal 2 (SDG 2) i.e., Zero Hunger.
- Theme: Leave No One Behind.
- Significance:
- As a global community, we each have a role to play in bringing forward those left behind by making our agrifood systems more inclusive and sustainable.
- Promote worldwide awareness and action for those who suffer from hunger and for the need to ensure healthy diets for all.
- Many awareness initiatives are also held to educate people about malnutrition and obesity, both of which cause major health consequences.
What is the Status of Global Hunger according to Various Reports?
- The Hunger Hotspots Outlook (2022-23), a report by the FAO and World Food Programme (WFP) — forebodes escalating hunger, as over 205 million people across 45 countries will need emergency food assistance to survive.
- The Global Report on Food Crises 2022 released in May by the Global Network against Food Crises underscored that about 180 million people across 40 countries will face inescapable food insecurity.
- Global Hunger Report, 2022: Globally, the progress against hunger has largely stagnated in recent years, with a global score of 18.2 in 2022 as compared to 19.1 in 2014, there is only a slight improvement,
- Barring war-torn Afghanistan, India has performed worse than all the countries in the South Asian region in the the Global Hunger Index 2022.
- It has ranked 107 out of 121 countries.
- Barring war-torn Afghanistan, India has performed worse than all the countries in the South Asian region in the the Global Hunger Index 2022.
What are the Related Indian Initiatives?
- Eat Right India and Fit India Movement along with Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, Jal Jeevan Mission and other efforts will improve the health of Indians and heal the environment.
- Introduction of 17 new biofortified varieties of crops to overcome the shortcomings of the common variety of crops which lacks important micronutrients.
- Example: MACS 4028 Wheat, Madhuban Gajar, etc.
- Increased ambit and effective implementation of the Food Security Act, 2013.
- Amendments to the APMC (agricultural produce market committee) Acts to make them more competitive.
- Steps to ensure that farmers get one and a half times the cost as Minimum Support Price (MSP), which along with the government procurement, is an important part of ensuring the country's food security.
- Development of a large network of Farmer Producer Organisations (FPOs).
- Amendments in the Essential Commodities Act, 1955 to deal with the issue of grain wastage in India.
- The government is making efforts to make India Trans Fat free by 2022, a year ahead of the World Health Organisation (WHO) target, in synergy with the vision of New India @75 (75 years of India’s independence).
- Trans Fat is a food toxin present in Partially Hydrogenated Vegetable Oils (PHVOs) (e.g., vanaspati, shortening, margarine, etc.), baked and fried foods.
- FAO supported India's proposal to declare 2023 as the International Year of Millets.
- For improving food access, especially for vulnerable populations, the Government of India drives programmes such as the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY).
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which of the following are the objectives of ‘National Nutrition Mission’? (2017)
- To create awareness relating to malnutrition among pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- To reduce the incidence of anaemia among young children, adolescent girls and women.
- To promote the consumption of millets, coarse cereals and unpolished rice.
- To promote the consumption of poultry eggs.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 3 and 4 only
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- National Nutrition Mission (POSHAN Abhiyaan) is a flagship programme of the Ministry of Women and Child Development, GoI, which ensures convergence with various programmes like Anganwadi services, National Health Mission, Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana, Swachh-Bharat Mission, etc.
- The goals of National Nutrition Mission (NNM) are to achieve improvement in nutritional status of children from 0-6 years, adolescent girls, pregnant women and lactating mothers in a time bound manner during the next three years beginning 2017- 18. Hence, 1 is correct.
- NNM targets to reduce stunting, under-nutrition, anaemia (among young children, women and adolescent girls) and reduce low birth weight of babies. Hence, 2 is correct.
- There is no such provision relating to consumption of millets, unpolished rice, coarse cereals and eggs under NNM. Hence, 3 and 4 are not correct. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer


Important Facts For Prelims
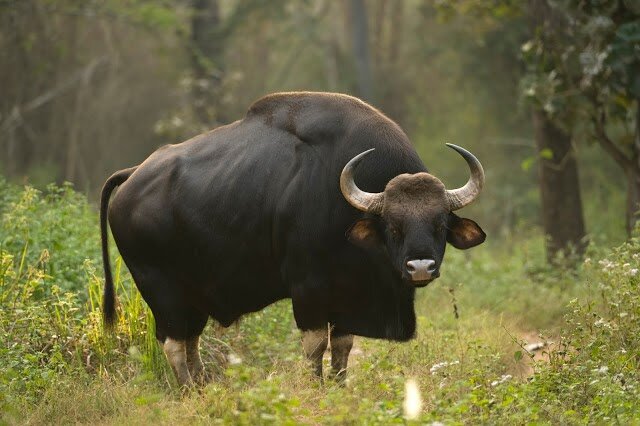
Indian Bison (Gaur)
Why in News?
Recently, Sri Lanka asked India to translocate 6 Indian Bisons to reintroduce them in the island from where they became extinct by the end of 17th century.
- If the project is cleared, it would be the first such agreement between India and Sri Lanka.
What are the Important Facts about Indian Bison?
- About:
- The Indian Bison or Gaur (Bos gaurus) is the tallest species of wild cattle found in India and largest extant bovine.
- There are about 13,000 to 30,000 gaurs in the world with approximately 85% of the population present in India.
- The first-ever population estimation exercise of the Indian gaur carried out in the Nilgiris Forest Division in February 2020 estimated around 2,000 Indian gaurs to be inhabiting the division.
- Geography:
- It is native to South and Southeast Asia.
- In India, they are very much prevalent in the Western Ghats.
- They are primarily found in Nagarhole National Park , Bandipur National Park, Masinagudi National Park and Biligirirangana Hills (BR Hills).
- It is also found in Burma and Thailand.
- Habitat:
- They prefer evergreen forests and moist deciduous forests.
- However, they can survive in dry deciduous forests also.
- They are not found in the Himalayas with an altitude greater than 6,000 ft.
- They generally stick to the foothills only.
- They prefer evergreen forests and moist deciduous forests.
- Food Habits:
- The Indian Bison is a grazing animal and generally feeds in the early morning and in the late evenings.
- Conservation Status:
- Vulnerable in IUCN Red List.
- Included in the Schedule I of the Wild Life Protection Act, 1972.
- Threats:
- Food Scarcity: Due to the destruction in the grasslands, planting of commercially important trees, invasive plant species and indiscriminate grazing of domestic animals
- Poaching: For their commercial value as well as due to the high demand of gaur meat.
- Habitat Loss: Due to deforestation and commercial plantations.
- Human-Animal Conflict: Due to living in proximity with human habitations.



.png)