Governance
Central Bureau of Investigation
For Prelims: Delhi Special Police Establishment (DSPE) Act, Santhanam Committee on Prevention of Corruption, Prevention of Corruption Act
For Mains: Issues Related to CBI and Recommendations
Why in News?
Recently, the Tamil Nadu government has announced that it has withdrawn the general consent given to the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI), under Section 6 of the Delhi Special Police Establishment (DSPE) Act, 1946.
- Mizoram, West Bengal, Chhattisgarh, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Kerala, Jharkhand, Punjab and Meghalaya had withdrawn their general consent given to CBI as of March. 2023.
What is the Central Bureau of Investigation?
- The CBI was established by a resolution of the Ministry of Home Affairs and later transferred to the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions, currently functioning as an attached office.
- Its establishment was recommended by the Santhanam Committee on Prevention of Corruption.
- The CBI operates under the DSPE Act, 1946. It is neither a constitutional nor a statutory body.
- It investigates cases related to bribery, governmental corruption, breaches of central laws, multi-state organized crime, and multi-agency or international cases.
How does the CBI function in India?
- Provision of Prior Permission:
- The CBI is required to obtain the prior approval of the Central Government before conducting any inquiry or investigation into an offence committed by officers of the rank of joint secretary and above in the Central Government and its authorities.
- However, in 2014, the Supreme Court held it invalid and held that Section 6A of the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act, which granted protection to joint secretary and above officers from facing even a preliminary inquiry by the CBI in corruption cases, was violative of Article 14.
- General Consent Principle for CBI:
- The consent of the state government to CBI can be either case-specific or “general”.
- General consent is normally given by states to help the CBI in the seamless investigation of cases of corruption against central government employees in their states.
- This is essentially consent by default, which means CBI may begin investigations taking consent as having been already given.
- In the absence of general consent, CBI would have to apply to the state government for its consent in every individual case, and before taking even small actions.
What are the Challenges Before CBI?
- Lack of Autonomy:
- One of the major challenges is political interference in its functioning.
- Resource Constraint:
- The CBI also faces a lack of infrastructure, sufficient manpower, and modern equipment.
- There have also been concerns about questionable methods of procuring evidence and officers failing to abide by the rule book.
- Legal Limitations:
- The agency currently operates under outdated legislation that does not adequately address contemporary challenges.
- It has resulted in several issues, including ambiguity in its jurisdiction, lack of transparency, and inadequate accountability mechanisms.
- Procedural Delays:
- Legal procedures and lengthy court processes can pose challenges for the CBI.
- Obtaining search warrants, recording statements, and presenting evidence in court can be time-consuming, leading to delays in completing investigations and securing convictions.
Why is There Need for Institutional Reforms in the CBI?
- Independence and Autonomy:
- Establishing the CBI as an independent investigative agency separate from the administrative control of the Central Government.
- Ensuring functional autonomy to carry out investigations without undue interference from political or bureaucratic influences.
- Strengthening legal provisions to safeguard the autonomy and impartiality of the CBI.
- Jurisdiction and Coordination:
- Clarifying its jurisdictional boundaries to avoid conflicts with state police forces and ensuring smooth coordination and strengthening collaboration and information sharing with state agencies to streamline investigations.
- Legal Framework:
- Reviewing and updating existing laws to enhance its investigative powers, providing statutory backing to investigative techniques, and streamlining legal procedures to expedite investigations and trials.
- Technological Upgradation:
- Investing in advanced technology and infrastructure to equip the CBI with modern tools for digital forensics, data analysis, and crime mapping.
What are Some Supreme Court Observations on CBI?
- Coalgate Case:
- In 2013, a Bench headed by Justice R M Lodha described the CBI as “a caged parrot speaking in its master’s voice”
- CBI VS CBI Case:
- The SC in CBI VS CBI case held that the power to remove/send on leave the director of CBI, vested in the selection committee, not with the central govt.
- SC says this verdict when CBI Director challenge the decision of central govt to send him on leave without his will.
Way Forward
- Statutory Backing:
- Several committees have proposed conferring statutory status to the CBI to ensure its smooth functioning and operational autonomy. The suggested measures include granting the authority to initiate investigations, file chargesheets, and prosecute cases without any undue external influence.
- Whistleblower Protection:
- Provisions should be included in the law to protect whistleblowers within the CBI, ensuring transparency, exposing corruption, and safeguarding individuals who report misconduct from retaliation through confidential reporting mechanism.
- Capacity Building:
- The new law should promote regular training and professional development programs for CBI personnel to enhance their skills, knowledge, and understanding, enabling them to effectively handle complex cases.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. The jurisdiction of the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) regarding lodging an FIR and conducting a probe within a particular state is being questioned by various States. However, the power of the States to withhold consent to the CBI is not absolute. Explain with special reference to the federal character of India. (2021)
Agriculture
Ceiling on Stocks of Wheat and Pulses
For Prelims: Food Security, Essential Commodities Act (ECA), 1955, IMD, Inflation, PDS.OMSS.
For Mains: Ceiling on Stocks of Wheat and Pulses.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution has imposed limits on Stock of Wheat that can be held by traders, wholesalers, retailers, big chain retailers and processors to manage the overall food security and to prevent hoarding and unscrupulous speculation.
- The Ministry has also imposed stock limits on Tur and Urad by invoking the Essential Commodities Act (ECA), 1955 due to same reasons.
Why are the Stock Limits being Imposed?
- Concerns over Wheat Production:
- Unseasonal rains, hailstorms, and higher temperatures in Feb 2023 raised concerns about the overall wheat output.
- Lower production leads to higher prices, which may surpass the government's purchase prices and affect supply stability.
- There are indications of a potential 20% decrease in wheat procurement compared to initial estimate.
- Approximately 5.23 lakh hectares of wheat crop were estimated to be damaged in MP, Rajasthan and UP due to hailstorms.
- The India Meteorological Department had warned of adverse effects on wheat crops due to higher temperatures during the reproductive growth period.
- Unseasonal rains, hailstorms, and higher temperatures in Feb 2023 raised concerns about the overall wheat output.
- Invoking ECA 1955 for Tur and Urad:
- Tur prices have risen since mid-July 2022 amid slow progress in Kharif sowing as compared to 2021 due to excess rainfalls and water logging conditions in some parts of major Tur growing states of Karnataka, Maharashtra and MP.
- To control any unwarranted price rise, the government is taking pre-emptive steps to ensure overall availability and controlled prices of pulses in the domestic as well as overseas markets.
What are the Government Orders regarding Wheat Stock Limits?
- Imposition of Stock Limits to Stabilize Prices:
- The permissible stock limits are set at 3,000 metric tonnes for traders/wholesalers, 10 metric tonnes at each outlet for retailers, and 3,000 metric tonnes at all depots (combined) for big chain retailers.
- Processors are allowed to stock up to 75% of their annual installed capacity.
- Entities are required to declare their stock positions regularly on the Department of Food and Public Distribution's portal.
- In case of stocks being held are higher than the limit, the time limit is 30 days from the day of issuing notification to bring the same under the prescribed limits.
- Offloading Wheat through OMSS:
- The government has decided to sell 15 lakh tonnes of wheat from the central pool through the Open Market Sale Scheme (OMSS).
- Wheat will be sold via e-auction to flour mills, private traders, bulk buyers, and manufacturers of wheat products.
- The sale will be conducted in lot sizes of 10 to 100 metric tonnes, with the possibility of releasing more batches based on prices and demand.
- A similar plan is being considered for offloading rice to moderate its prices.
What does the Government Seek from these Orders?
- Stabilize Prices:
- The primary aim is to stabilize wheat prices in the market. By imposing stock limits on various entities involved in the wheat supply chain, the government aims to prevent hoarding and speculation, ensuring a steady supply of wheat and avoiding price volatility.
- Ensure Affordability:
- By stabilizing prices, the government intends to make wheat more affordable for consumers.
- Controlling retail prices through the offloading of wheat from the central pool via the OMSS ensures that wheat remains accessible to the public at reasonable rates.
- Prevent Supply Shortages and Maintain Food Security:
- By monitoring and managing the stock limits, the government aims to ensure an adequate supply of wheat to meet the demand and avoid any scarcity in the market and make wheat available to vulnerable sections of society via Public Distribution System.
What is the Essential Commodities Act 1955?
- Background:
- The ECA Act 1955 was legislated at a time when the country was facing a scarcity of foodstuffs due to persistent low levels of foodgrains production.
- The country was dependent on imports and assistance (such as wheat import from the US under PL-480) to feed the population.
- India signed a long-term Public Law (PL) 480 agreement to get food aid under Government agricultural trade development assistance, with the US in 1954.
- To prevent hoarding and black marketing of foodstuffs, the Essential Commodities Act was enacted in 1955.
- Objective:
- The ECA 1955 is used to curb inflation by allowing the Centre to enable control by state governments of trade in a wide variety of commodities.
- Essential Commodity:
- There is no specific definition of essential commodities in ECA 1955. Section 2(A) of the Act states that an “essential commodity” means a commodity specified in the Schedule of the Act.
- Centre's Role:
- The Act gives powers to the central government to add or remove a commodity in the Schedule.
- The Centre, if it is satisfied that it is necessary to do so in the public interest, can notify an item as essential, in consultation with state governments.
- Impact:
- By declaring a commodity as essential, the government can control the production, supply, and distribution of that commodity, and impose a stock limit.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following crops: (2013)
- Cotton
- Groundnut
- Rice
- Wheat
Which of these are Kharif crops?
(a) 1 and 4
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains:
Q. What are the major reasons for declining rice and wheat yield in the cropping system? How is crop diversification helpful to stabilize the yield of the crops in the system? (2017)
Indian Economy
CBIC Releases National Time Release Study (NTRS) 2023 Report
For Prelims: National Time Release Study (NTRS), World Customs Organization (WCO), Cargo Release Time
For Mains: TFA in India and its impact on cross-border trade. Ease of doing business in India.
Why in News?
Recently, the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) has released the National Time Release Study (NTRS) 2023 report, which measures the cargo release time at various ports in India.
- The report aims to assess the progress made towards the National Trade Facilitation Action Plan (NTFAP) targets, identify the impact of various trade facilitation initiatives, and identify the challenges to more expeditious reduction in release time.
- The study was conducted based on a sample period of January 1-7, 2023, comparing the performance with the corresponding periods of 2021 and 2022.
- The ports included in the study represent seaports, air cargo complexes (ACCs), inland container depots (ICDs), and integrated check posts (ICPs). These account for approximately 80% of bills of entry and 70% of shipping bills filed in the country.
What is the Cargo Release Time?
- Cargo release time is defined as the time taken from the arrival of the cargo at the Customs station to its out-of-charge for domestic clearance in case of imports and arrival of the cargo at the Customs station to the eventual departure of the carrier in case of exports.
- Cargo release time is a key indicator of trade efficiency and ease of doing business, as it reflects the effectiveness of customs procedures and other regulatory processes involved in cross-border trade.
- Cargo release time is measured using Time Release Study (TRS), a performance measurement tool recommended by the World Customs Organization (WCO).
What are the Key Highlights of NTRS 2023?
- Import Release Time Improvements:
- The average import release time has shown improvements compared to previous years.
- There was a 20% reduction in release time for ICDs, an 11% reduction for ACCs, and a 9% reduction for seaports in 2023 over 2022.
- In absolute terms, the import release time for seaports is 85 hours and 42 minutes, for ICDs is 71 hours and 46 minutes, for ACCs is 44 hours and 16 minutes, and for ICPs is 31 hours and 47 minutes.
- The lower measure of standard deviation indicates a greater certainty of expeditious release of imported cargo.
- Reaffirmation of 'Path to Promptness':
- The findings of NTRS 2023 reaffirm the importance of the three-fold 'Path to Promptness' strategy.
- This strategy includes advance filing of import documents for pre-arrival processing, risk-based facilitation of cargo, and the benefits of the trusted client program - Authorised Economic Operators.
- Cargoes that combine all three features under the 'Path to Promptness' achieve the National Trade Facilitation Action Plan (NTFAP) release time target across all port categories.
- Focus on Export Release Time:
- NTRS 2023 has placed a greater focus on measuring the release time for exports.
- The study recognizes the distinction between regulatory clearance (customs release) and physical clearance.
- Regulatory clearance is completed with the grant of Let Export Order (LEO), while physical clearance occurs upon the completion of logistics processes and the departure of th e carrier with the goods.
What are the Sources of Information for NTRS 2023?
- NTRS 2023 is based on data collected from various sources, such as ICEGATE portal, port authorities, customs brokers and participating government agencies (PGAs).
- NTRS 2023 also incorporates feedback from various stakeholders, such as exporters, importers, trade associations and chambers of commerce.
- NTRS 2023 is aligned with the WCO TRS methodology and follows international best practices.
What are the Benefits of NTRS 2023?
- NTRS 2023 provides a comprehensive and objective assessment of the cargo release time performance at various ports in India.
- NTRS 2023 helps to identify the areas of improvement and benchmarking against global standards.
- NTRS 2023 supports evidence-based policy making and implementation of trade facilitation measures that enhance trade efficiency and competitiveness.
- NTRS 2023 contributes to achieving the NTFAP targets and fulfilling India's commitments under the WTO Trade Facilitation Agreement.
National Trade Facilitation Action Plan (NTFAP)
- NTFAP aims to implement the provisions of the WTO's Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA) in India.
- TFA focuses on simplifying customs procedures and norms for cross-border trade.
- NTFAP was prepared by the National Committee on Trade Facilitation (NCTF) chaired by the Cabinet Secretary.
- It includes over 90 specific activities with timelines for implementation, aligned with India's policy objectives.
- NTFAP covers areas like advance import document filing, risk-based cargo facilitation, trusted client program, infrastructure upgrades, legislative issues, outreach programs, and agency coordination.
- NTFAP reduces trade costs, enhances efficiency, supports evidence-based policy making, and fulfills India's TFA commitments.
What are the Initiatives Related to Logistics?
- National Logistics Policy (NLP)
- Multimodal Transportation of Goods Act, 1993.
- PM Gati Shakti Scheme
- Multi Modal Logistics Parks
- LEADS Report
- Dedicated Freight Corridor
- Sagarmala Projects
- Bharatmala Project
Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs
- It is a part of the Department of Revenue under the Ministry of Finance.
- The Central Board of Excise and Customs (CBEC) was renamed as the CBIC in 2018 after the roll out of the GST.
- It deals with the tasks of formulation of policy concerning levy and collection of customs, central excise duties, Central GST (CGST) and Integrated GST (IGST).
- GST Law comprising (i) Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 (ii) State Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 (iii) Union Territory Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, (iv) Integrated Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 (v) Goods and Services Tax (Compensation to States) Act, 2017.
International Relations
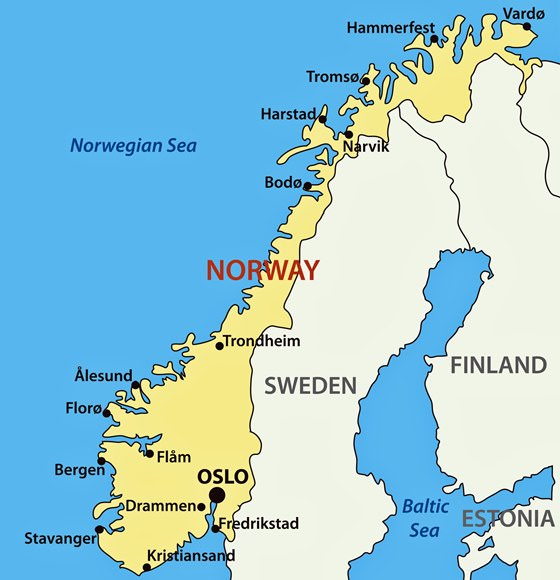
Oslo Forum and Afghan Peace Talks
Prelims: Oslo Forum, Central Asian Republics (CARs), Operation Devi Shakti, SAARC
Mains: India-Afghanistan relations: Significance and Way Forward.
Why in News?
Recently, for the first time, India participated in Norway’s Oslo forum organized for peace talks on Afghanistan.
- Oslo Forum is the leading series of retreats for international mediators and peacemakers.
- Earlier India had participated in the Moscow Format dialogue (2022) and in Doha dialogue (2020) for the peace talks.
What is OSLO Forum?
- The Oslo Forum (started in 2003) is a series of retreats for international conflict mediators, high-level decision-makers, and other peace process actors.
- It provides a discreet and informal space to reflect on current mediation practice, collaborate across institutional and conceptual divides and advance negotiations.
- The Forum is co-hosted by the Royal Norwegian Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the Centre for Humanitarian Dialogue (HD).
- The Centre for Humanitarian Dialogue (HD) is a private diplomacy organization that specializes in mediation and dialogue processes to prevent and resolve armed conflicts.
- HD was Established in 1999, based in Geneva, Switzerland, and operates globally.
- All discussions take place under the Chatham House Rule. Participation is by invitation only.
- Chatham House (UK) is an independent policy institute and a forum for debate and dialogue.
- When a meeting, or part thereof, is held under the Chatham House Rule, participants are free to use the information received, but neither the identity nor the affiliation of the speaker(s), nor that of any other participant, may be revealed.
What is the Present approach of India towards Afghanistan?
- India has not recognized the Taliban regime but has engaged with it on humanitarian and security issues.
- India’s main objectives in Afghanistan are to protect its security interests, to prevent any terrorist threats from Afghan soil.
- India has cemented its position as a major developmental partner of Afghanistan and has also earned the goodwill of Afghans.
- It does not project a narrowly defined strategic ambition with its investment in Afghanistan; rather, it seeks to take part in effectively creating a conducive environment for growth for the Afghans.
- India has also participated in regional and international forums to discuss the situation in Afghanistan and to coordinate efforts for peace and stability.
What is the significance of Afghanistan for India?
- Gateway to the Central Asia: Afghanistan is a gateway to the Central Asian Republics (CARs), which are rich in natural resources and potential markets for Indian goods and services.
- Counterbalance to Pakistan and China: A stable and friendly Afghanistan can help India contain the threats of terrorism, extremism and radicalism emanating from Pakistan.
- Partner in India’s Soft Power assistance: India has invested over $3 billion in various projects in Afghanistan, such as roads, dams, schools, hospitals, parliament building, etc.
- India also provides scholarships, training, cultural exchanges and humanitarian aid to Afghanistan.
- Cultural & Historical ties: The two countries share a common heritage of Buddhism, Hinduism, Sufism and the Mughal empire. Many Afghan leaders, including former President Hamid Karzai, have studied in India.
How has the Taliban takeover affected India's interests?
- Security Risks:
- The Taliban is seen as a proxy for Pakistan and a supporter of anti-India terrorist groups like Jaish-e-Muhammad and Lashkar-e-Taiba.
- The Taliban is also close to China, which is India’s strategic rival in the region.
- Influence and Leverage:
- India had no direct engagement with the Taliban and had invested heavily in the previous government and its institutions.
- India also lost its access to the Central Asian Republics through Afghanistan, which was a key part of its connectivity and energy projects.
- Trade and Development:
- The Taliban has stopped the movement of cargo through Pakistan and created uncertainty over the future of India’s aid and projects in Afghanistan.
- India had contributed over $3 billion in various sectors such as infrastructure, health, education, agriculture, etc. in Afghanistan.
- Humanitarian Crisis:
- Thousands of Afghans who have worked with India or have family ties with India are seeking refuge and protection from the Taliban’s repression.
- India has launched an evacuation mission called Operation Devi Shakti to bring back its citizens and Afghan partners from Kabul.
How should India handle the situation?
- Maintain a Balanced Approach: India should adopt a balanced approach in its dealings with Afghanistan, avoiding excessive alignment or confrontation. While expressing concerns about human rights, terrorism, and the treatment of minorities,
- India can also explore areas of common interest such as trade, cultural exchange, and regional connectivity.
- Support Afghan Reconciliation: India can actively support efforts for an inclusive and representative government in Afghanistan. This involves advocating for an inclusive political process that accommodates the interests of all ethnic and religious groups in the country.
- Engage with Regional Players: India should engage with regional players, particularly neighbouring countries, to coordinate their efforts and ensure a collective approach to stability in Afghanistan.
- This can involve collaborating with countries such as Iran, Russia, and Central Asian nations to address common concerns and promote stability in the region.
- Focus on Development Assistance: India has been a significant contributor to Afghanistan's development, providing infrastructure projects, education, and humanitarian aid.
- Despite the Taliban takeover, India could continue supporting development initiatives that benefit the Afghan people directly, such as infrastructure development, healthcare, education, and capacity building.
- Strengthen International Partnerships: India should work closely with international partners, including the United States, European Union, United Nations, and regional organizations like the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC), to collectively address the evolving situation in Afghanistan. Collaborative efforts can help shape a more stable and secure environment in the country.
What are Some previous efforts made by India in engaging with Taliban?
- In 2017, the launch of Moscow dialogue brought together representatives from Afghanistan, China, India and others. The goal of the dialogue is to facilitate the reconciliation process in Afghanistan and to promote regional cooperation on security and economic issues.
- The Moscow Dialogue has been held several times since its inception. The most recent meeting was held in February 2023.
- In 2020, India participated in the intra-Afghan peace talks taking place in Doha via video link. This was seen as a significant step forward in India's engagement with the Taliban.
- In August 2021, two weeks after the Taliban took control of Kabul, India held its first publicly acknowledged meeting with Taliban representatives in Doha. The meeting was described as "exploratory" and focused on humanitarian issues.
- In June 2022, a team of Indian officials visited Kabul to discuss bilateral ties and humanitarian aid with the Taliban. This was the first such visit by Indian officials since the Taliban took power.
Social Justice
One Nation One Anganwadi Program
For Prelims: Anganwadi Program, Ministry of Women and Child Development (MoWCD), Government e-Market (GeM), POSHAN Abhiyaan (Prime Minister's Overarching Scheme for Holistic Nutrition), PM POshan SHAkti Nirman (PM-POSHAN), National Food Security Act, 2013 (NFSA), Mid-Day Meal, Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0, NRHM.
For Mains: Effect of one nation one Anganwadi program in tackling issue of nutrition in India, need of localized and diversified solution to the issue of hidden hunger.
Why in News?
More than 57,000 migrant workers have registered for the special one nation one Anganwadi program on Poshan Tracker App.
- Poshan app will allow migrant workers to access nurseries at their respective locations by using the Poshan Tracker App on mobile phones.
What is Poshan Tracker App?
- The Ministry of Women and Child Development (MoWCD) has launched an application called Poshan Tracker.
- The Poshan Tracker management application provides a 360-degree view of the activities of the Anganwadi Centre.
- The app facilitates efficient service delivery by digitizing and automating the tasks performed by Anganwadi Workers.
- To support their work, smartphones procured through Government e-Market (GeM) have been provided to the workers.
- Additionally, a designated individual has been appointed in each state to offer technical support and resolve any issues related to downloading and using the new Poshan Tracker application.
- Migrant workers who have registered in their original state can visit the nearest Anganwadi in their current place of residence to access the schemes and services provided through the app.
What are the Achievements of the App?
- Since the launch of the Poshan Abhiyan in 2018, a total of 10 crore 6 lakh beneficiaries have been registered on App.
- There has been a significant decline over the years in the numbers of girls dropping out in the age group of 11-14 years.
- In the Northeast and in aspirational districts, as many as 22.40 lakh adolescent girls have been identified, who will be covered under this new scheme which now falls under the ambit of the Poshan 2.0.
- An age-appropriate take-home ration is being designed for children up to six years of age.
What is Poshan Abhiyan?
- About:
- POSHAN Abhiyaan (Prime Minister's Overarching Scheme for Holistic Nutrition) was launched the Prime Minister on 8th March 2018 in Jhunjhunu district of Rajasthan.
- Objectives:
- Prevent and reduce Stunting in children (0- 6 years)
- Prevent and reduce under-nutrition (underweight prevalence) in children (0-6 years)
- Reduce the prevalence of anemia among young Children (6-59 months)
- Reduce the prevalence of anemia among Women and Adolescent Girls in the age group of 15-49 years
- Reduce Low Birth Weight (LBW).
What is Anganwadi?
- Anganwadi Services (Now renamed as Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0) is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme implemented by States/UTs.
- It provides a package of six services, namely, (i) Supplementary Nutrition; (ii) Pre-school Non-formal Education; (iii) Nutrition & Health Education; (iv) Immunization; (v) Health Check-up; and (vi) Referral Services.
- It provides services to all eligible beneficiaries, namely, children in the age group of 0-6 years, pregnant women and lactating mothers through the platform of Anganwadi Centres across the country.
- Three of the services viz. Immunization, Health Check-up and Referral Services are related to health and are provided through NRHM & Public Health Infrastructure.
What are the other related Initiatives?
- Anemia Mukt Bharat Abhiyan
- The National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY)
- PM POshan SHAkti Nirman (PM-POSHAN).
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following are the objectives of ‘National Nutrition Mission’? (2017)
- To create awareness relating to malnutrition among pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- To reduce the incidence of anaemia among young children, adolescent girls and women.
- To promote the consumption of millets, coarse cereals and unpolished rice.
- To promote the consumption of poultry eggs.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 3 and 4 only
Ans: (a)
Important Facts For Prelims
VAIBHAV Scheme
Why in News?
The Government of India has introduced a new fellowship programme called Vaishvik Bhartiya Vaigyanik (VAIBHAV) to facilitate collaboration between the Indian diaspora in Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics and Medicine (STEMM) and Indian academic and research institutions.
- VAIBHAV Summit was also organised as an event dedicated to connecting the Indian STEMM diaspora with Indian institutions.
What is the VAIBHAV Fellowship Scheme?
- About:
- The VAIBHAV Fellowship aims at improving the research ecosystem of India’s Higher Educational and Scientific Institutions by facilitating academic and research collaborations between Indian Institutions and the best institutions in the world through mobility of faculty/researchers from overseas institutions to India.
- It is implemented by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Ministry of Science and Technology.
- Key Features of the VAIBHAV Fellowship Programme:
- Knowledge Verticals: The programme will focus on 18 identified knowledge verticals, including quantum technology, health, pharmaceuticals, electronics, agriculture, energy, computer sciences, and material sciences, among others.
- Eligibility: The fellowship is open to outstanding scientists and technologists of Indian origin (Non-resident Indians (NRI)/ Persons of Indian Origin (PIO)/Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) who are actively engaged in research activities in their respective countries.
- Collaboration Duration: Selected fellows will have the opportunity to work in collaboration with Indian Higher Educational Institutions (HEIs), universities, and public-funded scientific institutions.
- They may spend up to two months per year, for a maximum of three years, at an Indian institution of their choice.
- Fellowship Grant: VAIBHAV fellows will receive a monthly fellowship grant of INR 4,00,000, which will support their research activities during the collaboration period.
- Travel, Accommodation, and Contingencies: The fellowship will cover international and domestic travel expenses, accommodation, and contingencies, ensuring a conducive research environment for the fellows.
What are the Other Government Initiatives involving Overseas Indian?
- Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD) is celebrated on 9th January every year to mark the contribution of the Overseas Indian community in the development of India.
- Know India Program (KIP) is a flagship initiative of the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) for diaspora engagement which familiarises Indian-origin youth (18-30 years) with their Indian roots and contemporary India.
- VAJRA (Visiting Advanced Joint Research) Faculty Scheme of the Department of S&T enables NRIs and overseas scientific communities to participate and contribute to research and development in India.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. ‘Indian diaspora has a decisive role to play in the politics and economy of America and European Countries’. Comment with examples. (2020)
Important Facts For Prelims
India Approves Acquisition of MQ-9B Armed Drones from the US
Why in News?
Recently, India's Ministry of Defence has granted approval for the procurement of 31 MQ-9B armed drones from the United States. The deal, worth a little over $3 billion, is expected to be announced during Prime Minister Narendra Modi's state visit to Washington.
- The acquisition of these advanced drones aims to enhance India's surveillance capabilities and strengthen its armed forces.
What are MQ-9B Armed Drones?
- About:
- The MQ-9B drone is a variant of the MQ-9 "Reaper" which was used to launch a modified version of the Hellfire missile that eliminated al-Qaeda leader Ayman al-Zawahiri in Kabul.
- The MQ-9B has two variants SkyGuardian and its sibling SeaGuardian. The Indian Navy has been operating the MQ-9B Sea Guardian since 2020.
- The drone can operate at over 40,000 feet, giving the Indian military surveillance capacity in the high-altitude Himalayan border areas.
- The Predator also has the maximum endurance of 40 hours, making it useful for long-hour surveillance.
- MQ-9B drones are equipped with advanced features such as automatic take-off and landing, detect and avoid system, anti-spoofing GPS, and encrypted communication links.
- Need For India:
- India needs MQ-9B armed drones to enhance its surveillance and strike capabilities across its land and maritime borders, especially in the context of the ongoing standoff with China in Ladakh and the rising tensions with Pakistan.
- India also needs MQ-9B armed drones to counter the growing presence of Chinese submarines and warships in the Indian Ocean Region, and to protect its vital sea lanes of communication and trade.
- India also needs MQ-9B armed drones to support its counter-terrorism and counter-insurgency operations in Kashmir and other regions.
- Benefits of Acquiring MQ-9B Armed Drones to India:
- Acquiring MQ-9B armed drones will provide India with a strategic edge over its adversaries, as it will be able to conduct long-range surveillance and precision strikes without risking its manned aircraft or pilots.
- Acquiring MQ-9B armed drones will also boost India's defence cooperation with the US, which has emerged as a key partner for India in the Indo-Pacific region.
- The deal will also strengthen India's role in the Quad grouping of democracies along with the US, Japan and Australia.
- Acquiring MQ-9B armed drones will also create opportunities for India's defence industry, as it will involve technology transfer and joint production under the Make in India initiative.
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
International Energy Agency
International Energy Agency (IEA) to review all its full membership conditions for India’s inclusion.
To become a member of the IEA, a candidate country must be a member country of the OECD and demonstrate several requirements. These include having crude oil and/or product reserves equivalent to 90 days of the previous year’s net imports, to which the government has immediate access and could be used to address disruptions to global oil supply; a demand restraint program to reduce national oil consumption by up to 10%; legislation and organization to operate the Coordinated Emergency Response Measures (CERM) on a national basis; legislation and measures to ensure that all oil companies under its jurisdiction report information upon request; and measures in place to ensure the capability of contributing its share of an IEA collective action. India is not a member of IEA.
IEA is an autonomous intergovernmental organization established in 1974 in Paris, France. It focuses on energy policies, including economic development, energy security, and environmental protection. The IEA is made up of 31 member countries.
Read more: IEA Invites India to be a Full-Time Member
Mayon Volcano
Recently, the Mayon volcano began expelling lava on June 11, 2023, night, forcing nearly 18,000 people to flee to emergency shelters. Mayon Volcano is an active volcano located in the southeastern part of Luzon, Philippines, dominating the city of Legaspi. It is known for its picturesque conical shape and is the most active of 24 known volcanoes in the Philippines. Mayon has erupted over 30 times since 1616, with its most destructive eruption occurring in 1814, burying entire villages and leaving more than 1,000 people dead. The volcano is popular with climbers and campers and is the center of Mayon Volcano National Park.
Read more: Semeru Volcano of Indonesia
Government Reduces Import Duty on Refined Edible Oils
The Indian government has taken a significant step to address the availability and pricing concerns of edible oils by reducing the import duty on refined soybean and sunflower oils. The import duty has been lowered from 17.5% to 12.5% , with immediate effect.
While India typically imports crude soybean and sunflower oils, the decision to reduce duties on their refined counterparts aims to boost domestic availability and stabilize prices. Despite this reduction, the effective duty on refined edible oils, including social welfare cess, remains at 13.7%, while major crude edible oils have an effective duty of 5.5 %.
India currently relies on imports to fulfil around 60% of its edible oil demand, highlighting the significance of addressing the supply-demand gap to maintain stability in the domestic market.
Read more: Edible Oil Sector in India
Kari Ishad Mango Receives GI Tag
Kari Ishad mango from Ankola taluk of Uttara Kannada Karnataka has received the Geographical Indication (GI) tag from the Geographical Indications Registry under the Union Government. The GI certificate issued to Matha Totagars Farmer Producer Company Limited.
Recognized for its exceptional attributes, including a distinctive aroma, delightful taste, generous pulp content, and desirable shape and size, the Kari Ishad mango is celebrated as one of the finest mango varieties.
Read more: Geographical Indication Tag