Climate Change and Food Security
For Prelims: Climate Change and Food Security, Western Disturbance, El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO), Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD).
For Mains: Impact of Climate Change and Food Security.
Why in News?
In 2023, India experienced a series of disruptive weather and climate phenomena, highlighting the intricacies of its precipitation system, impacting the Food Security.
How have been the Weather and Climate Phenomena?
- Western Disturbance:
- The Western Disturbance traditionally brings vital moisture from European seas to the western Himalayas and parts of northern India in the winter and spring.
- In 2023, the Western disturbance persisted late into the summer, complicating the transition to the Southwest Monsoon season. This unusual behavior raised concerns about its effects on precipitation patterns.
- Climate-linked warming is likely to weaken winter precipitation from the Western disturbance and shift it to more intense rain events.
- El Niño and IOD:
- An El Niño phase of the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) was intensifying, which can adversely affect the southwest monsoon.
- While not all El Niño events negatively impact the monsoon due to its complexity, the dynamics between El Niño and the monsoon are evolving.
- The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) can balance the adverse impact of the El Nino on the South West Monsoon.
- Dynamic regression models indicate that 65% of the inter-annual variability in the southwest monsoon is attributed to the combined effects of ENSO and the IOD.
- Some Studies have found that 43% of heavy rainfall events in the Northeast Monsoon coincided with an El Niño.
- An El Niño phase of the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) was intensifying, which can adversely affect the southwest monsoon.
How Can Such Climate Phenomena Impact Agriculture and Water Resources?
- El Niño's Effects on Green Water:
- Agriculture relies on two types of water - green water from rain-fed soil moisture and blue water from rivers, lakes, reservoirs, and groundwater for irrigation. Both are vital for food security.
- Climate phenomena like El Niño can disrupt rainfed agriculture, affecting sowing, plant growth, and soil moisture.
- Despite investments in irrigation infrastructure, around half of India's cultivated area depends on green water, underscoring the significance of rainfed agriculture for food security.
- Contributions of green water from the monsoon and the Western disturbance play significant roles in preserving blue water stock and groundwater to determine the fate of the Rabi Crops sown in winter and the overall water security.
- El Niño's Effects on Crop Vulnerability:
- Even in irrigated areas, crops like rice paddy, soybean, tur dal, groundnut, and maize rely on green water, making them vulnerable to climate variability. For instance, soybean production saw a 28% decline during the 2015-2016 El Niño year.
How are the Emerging Climate Hotspots in India Impacted by Declining Monsoon Precipitation?
- Water Stress in Central India:
- Certain regions in Central India are emerging as climate change hotspots with critical implications for water, food, and ecological security.
- Persistent water stress and urban centers facing water shortages pose challenges.
- Declining Monsoon Precipitation:
- Monsoon precipitation has been declining since the 1950s, potentially due to reduced land-sea thermal gradients due to the warming of the seas.
- However, increasing intensity of rain events and heat stress are observed, adding complexity.
- Model Uncertainties:
- Global climate models struggle to simulate observed precipitation trends, creating uncertainties in future projections. Climate scientists are working to improve these models.
What can be the Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies?
- Shift to Less Water-Intensive Crops:
- Reducing dependence on water-intensive crops in favor of less water-intensive crops like millets can enhance food system resilience to phenomena like El Niño.
- Shifting crops may save 30% of blue water, but policies are needed to prevent new demands for the saved water.
- Alternative Crop Strategies:
- Encouraging farmers to adopt shorter-growing-cycle crops and diversify agricultural practices.
- Improved Forecasting:
- Utilizing forecasts of climate phenomena like El Niño for informed decision-making.
- Water Storage Management:
- Effective management of dams and reservoirs is crucial to reduce flood risks and ecological damage.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. La Nina is suspected to have caused recent floods in Australia. How is La Nina different from El Nino? (2011)
- La Nina is characterised by an usually cold ocean temperature in equatorial Indian Ocean whereas El Nino is characterised by unusually warm ocean temperature in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- El Nino has adverse effect on south-west monsoon of India but La Nina has no effect on monsoon climate.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: D
Q. The scientific view is that the increase in global temperature should not exceed 2°C above preindustrial level. If the global temperature increases beyond 3°C above the pre-industrial level, what can be its possible impact/impacts on the world? (2014)
- Terrestrial biosphere tends toward a net carbon source.
- Widespread coral mortality will occur.
- All the global wetlands will permanently disappear.
- Cultivation of cereals will not be possible anywhere in the world.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Q. Which of the following pairs of crops are considered to be water intensive?
A) Wheat and rice
B) Wheat and sugarcane
C) Sugarcane and rice
D) Wheat and gram
Ans: C)
Mains:
Q. ‘Climate change’ is a global problem. How India will be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India will be affected by climate change? (2017)
NavIC Integration in Smartphones
For Prelims: NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation), Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Production-Linked Incentive (PLI), International Maritime Organization, GPS (Global Positioning System).
For Mains: NavIC Integration in Smartphones and its Significance for India.
Why in News?
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, Government of India, is planning on making it mandatory for all devices to support the homegrown Navigation System NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation).
- This comes at a time when the newly launched Apple iPhone 15 has integrated the navigation system developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) into its hardware.
- India's NavIC is not intended to replace other global navigation systems but rather complement them.
What are the Government's Plans for NavIc Integration on Smartphones?
- The Union government is considering mandating NavIC integration in all smartphones sold in India by 2025, particularly targeting 5G phones.
- Manufacturers could receive additional incentives through Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes for using chips that support NavIC technology, fostering domestic chip design and production.
What are the Roadmap and Future Prospects for NavIC Adoption?
- To bolster NavIC's adoption, ISRO had launched second-generation Navigation satellites in May 2023 that will enhance interoperability with other satellite-based navigation systems and expand usage.
- The second-generation satellites will send signals in a third frequency, L1, besides the L5 and S frequency signals that the existing satellites provide.
- The L1 frequency is among the most commonly used in the Global Positioning System (GPS) and will increase the use of the regional navigation system in wearable devices and personal trackers that use low-power, single-frequency chips.
- This strategic move aligns with India's aspirations to establish technological sovereignty and emerge as a dominant space-faring nation.
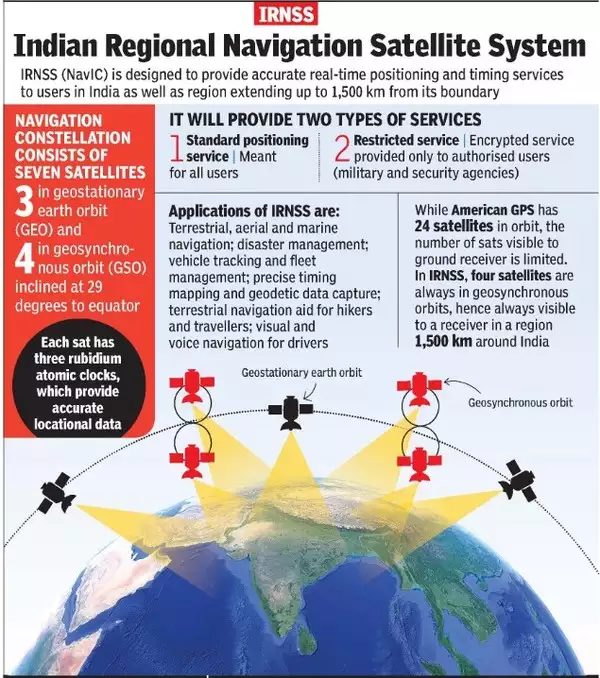
What is Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC)?
- About:
- India's NavIC is an independent navigation satellite system developed by ISRO becoming operational in 2018.
- It is providing accurate real-time positioning and timing services over
- India and a region extending approximately 1500 km around the Indian Mainland.
- It is designed with a constellation of 7 satellites and a network of ground stations operating 24×7.
- There are a total of eight satellites however only seven remain active.
- Three satellites in geostationary orbit and four satellites in geosynchronous orbit.
- Recognition:
- It was recognised by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) as a part of the World-Wide Radio Navigation System (WWRNS) for operation in the Indian Ocean Region in 2020.
- Potential Uses:
- Terrestrial, aerial and marine navigation;
- Disaster management;
- Vehicle tracking and fleet management (especially for mining and transportation sector);
- Integration with mobile phones;
- Precise timing (as for ATMs and power grids);
- Mapping and geodetic data capture.
What is the Significance of Integrating NavIC in Smartphones for India?
- Strategic Technological Autonomy:
- NavIC reduces dependence on foreign global navigation systems like GPS (Global Positioning System), showcasing India's ability to develop and deploy critical technology independently.
- Ensures that the nation can control and secure its vital navigation infrastructure, which is crucial for national security and defense applications.
- Enhanced Accuracy and Reliability:
- NavIC provides highly accurate and reliable positioning and timing information, especially in the Indian subcontinent and the surrounding region.
- Better accuracy is essential for a range of applications, from Disaster Management and agriculture to urban planning and transportation, improving overall efficiency and decision-making.
- Tailored Solutions for Indian Terrain:
- NavIC is designed to offer superior performance in the specific geographical and topographical conditions of India, where conventional global navigation systems may have limitations.
- Tailoring the navigation system to suit India's diverse landscape ensures a more precise and efficient location-based service.
- Broadening Use Cases and Innovation:
- NavIC's integration opens up opportunities for a plethora of location-based services, navigation apps, and other innovative solutions that can be tailored to specific local needs and preferences.
- This spurs entrepreneurship and supports a thriving app development ecosystem, encouraging creativity and innovation in technology.
What are the other Navigation Systems operational in the world?
- Four Global Systems:
- GPS from the U.S.
- GLONASS from Russia.
- Galileo from European Union
- BeiDou from China.
- Two Regional Systems:
- NavIC from India
- QZSS from Japan.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q.1 Which one of the following countries has its own Satellite Navigation System? (2023)
a. Australia
b. Canada
c. Israel
d. Japan
Ans: d
Q.2 With reference to the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), consider the following statements: (2018)
- IRNSS has three satellites in geostationary and four satellites in geosynchronous orbits.
- IRNSS covers entire India and about 5500 sq. Km beyond its borders.
- India will have its own satellite navigation system with full global coverage by the middle of 2019.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) None
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q.1 Why is Indian Regional Navigational Satellite System (IRNSS) needed? How does it help in navigation? (2018)
Reciprocity and Non Reciprocity
For Prelims: Non-Reciprocity Methods, Reciprocity Phenomenon, Radar Systems, Magnetic resonance imaging.
For Mains: Non-Reciprocity Methods for tackling the challenges related to Reciprocity.
Why in News?
Scientists have developed devices which break the Principles of Reciprocity tackling the challenges that arise out of the Reciprocity Phenomenon.
What is Reciprocity?
- About:
- Reciprocity means that if a signal is sent from one point to another, it is sent back from the second point to the first.
- For Example: It's like when you shine a flashlight at a friend, they can shine it back at you because the light can go both ways through the air.
- However, there are situations where reciprocity doesn't work as expected.
- For example, in some movies, a person being questioned can't see the police officers through a window, but the officers can see them.
- Also, in the dark, one can see someone under a streetlight, but they can't see that person.
- Reciprocity means that if a signal is sent from one point to another, it is sent back from the second point to the first.
Note: Non-reciprocity: The physics of letting waves go one way but not the other.
- Applications:
- Antenna Testing: Reciprocity simplifies antenna testing. Instead of using multiple signal sources in various directions, one can send one signal into the antenna and observe how it transmits it back.
- This helps determine the antenna's ability to receive signals from different directions, known as its far-field pattern.
- Radar Systems: Engineers use reciprocity to test and operate radar systems. By studying how radar antennas send and receive signals, they can improve the system's performance and accuracy.
- Radar is an electromagnetic sensor used for detecting, locating, tracking, and recognizing objects of various kinds at considerable distances.
- Sonar Systems: In sonar technology, which is used for underwater detection and navigation, reciprocity aids in testing and optimizing the performance of sonar devices.
- Seismic Surveys: Reciprocity simplifies the testing and operation of seismic survey equipment used in geology and oil exploration to study subsurface structures.
- Medical Imaging (MRI): MRI scanners utilize reciprocity principles to send and receive signals for creating detailed medical images of the human body.
- Antenna Testing: Reciprocity simplifies antenna testing. Instead of using multiple signal sources in various directions, one can send one signal into the antenna and observe how it transmits it back.
What are the Challenges of Reciprocity?
- Spying and Information Security:
- Reciprocity means that while one can receive signals from the target, his own equipment may unintentionally transmit signals, potentially exposing his location or intentions.
- Back Reflections:
- When designing high-power lasers for signal transmission, imperfections in the transmission line can lead to harmful backreflections. Reciprocity dictates that these backreflections could re-enter the laser, potentially causing damage or interference.
- In communication systems, strong back-reflections can occur due to reciprocity, leading to interference and signal degradation.
- Managing these back-reflections is essential for maintaining the quality and reliability of communication networks.
- Signal Amplification for Quantum Computing:
- Quantum computers use extremely sensitive qubits that need to be maintained at very low temperatures.
- To sense their quantum states, the signals must be amplified significantly.
- However, reciprocity can introduce challenges in achieving efficient and controlled signal amplification without introducing noise or unwanted interactions.
- Miniaturization:
- As technology moves toward miniaturization at nanometer and micrometer scales, ensuring signal efficiency and control becomes increasingly challenging. In self-driving cars, where monitoring various signals is crucial for safety, managing the complexities of reciprocal signal interactions presents a significant challenge.
What are the Methods Devised to Overcome Challenges Related to Reciprocity?
- Magnet-Based Non-Reciprocity:
- Scientists have developed magnet-based Non-Reciprocal Devices, consisting of components like wave plates and Faraday rotators.
- The Faraday rotator, using a magnetic material, allows waves to pass in one direction but blocks them in the reverse direction, breaking the principle of reciprocity.
- Scientists have developed magnet-based Non-Reciprocal Devices, consisting of components like wave plates and Faraday rotators.
- Modulation:
- Modulation involves continuously changing some parameter of the medium, either in time or in space.
- By altering the properties of the medium, scientists can control wave transmission and address challenges related to signal routing, communication, and interference.
- This method provides flexibility in managing signals under different conditions.
- Nonlinearity:
- Nonlinearity involves making the properties of the medium depend on the strength of the incoming signal, which, in turn, depends on the signal's propagation direction.
- This approach allows scientists to control signal transmission by manipulating the nonlinear response of the medium. It offers a way to achieve non-reciprocity and control signal interactions.
National Judicial Data Grid
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court has integrated its case data on the National Judicial Data Grid (NJDC).
- The integration with NJDG as part of an 'Open Data Policy (ODP)' to provide transparent case information to the public.
- ODP is increasingly a set of policies - that promotes transparency, accountability, and value creation by making government data available to all.
What is the National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG)?
- About:
- The NJDG portal is a national repository of data relating to cases instituted, pending, and disposed of by the courts across the country.
- It is a database of orders, judgments and case details of 18,735 District and subordinate Courts and High Courts created as an online platform under the e-Courts Project.
- Its key feature is that the data is updated in real-time and has granular data up to the Taluka level.
- It was built as part of Phase II of the e-Courts project, which is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
- Currently, litigants can access case status information of 23.81 crore cases and more than 23.02 crore orders/judgments.
- Developed By:
- The platform has been developed by the National Informatics Centre (NIC) in close coordination with the in-house software development team of the Computer Cell, Registry of the Supreme Court (SC) with an interactive interface and analytics dashboard.
- Significance:
- NJDG works as a monitoring tool to identify, manage & reduce pendency of cases.
- It helps identify specific bottlenecks in judicial processes. For example, if the number of land disputes in a particular state shoots up, it helps policymakers look into whether the law needs to be strengthened.
- It also helps generate inputs related to particular areas of law. For example, to track cases related to land disputes, Land Records data of 26 States have been linked with NJDG.
What is the Current Pandency Status of Cases?
- For the year 2023, the total pendency of registered cases in SC is 64,854.
- In SC, there are 5,412 cases filed and 5033 cases disposed in August 2023.
- There are 583 three-judge Bench matters, 288 five-judge Bench cases, 21 seven-judge Bench cases, and 135 nine-judge Bench cases, all of which are civil, pending in the Supreme Court.
What are the Other Initiatives under E-court Projects?
For Legal Insights, click here
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In India, Judicial Review implies (2017)
(a) the power of the Judiciary to pronounce upon the constitutionality of laws and executive orders.
(b) the power of the Judiciary to question the wisdom of the laws enacted by the Legislatures.
(c) the power of the Judiciary to review all the legislative enactments before they are assented to by the President.
(d) the power of the Judiciary to review its own judgements given earlier in similar or different cases.
Ans: (a)
Hangzhou 2022 Asian Games
Why in News?
In a year that witnessed India's national football team achieving remarkable success in the SAFF Cup 2023, the sport finds itself caught in a contentious club versus country-debate.
- The dispute between Indian Super League (ISL) clubs and the All India Football Federation (AIFF) has escalated regarding player availability, and a cloud of uncertainty looms over the composition of the upcoming Asian Games squad.
- The 19th Asian Games will take place in Hangzhou, China, from 23rd September 2023 to 8th October 2023, which was originally scheduled to be held in 2022 and was postponed due to the Covid-19 pandemic.
What are the Asian Games?
- About:
- The Asian Games is the biggest sports competition in Asia, held once every four years. They are organized by the Olympic Council of Asia (OCA).
- The symbol for the Asian Games is the rising sun with interlocking rings.
- It is recognised by the International Olympic Committee.
- The Asian Games is the biggest sports competition in Asia, held once every four years. They are organized by the Olympic Council of Asia (OCA).
- Background and Inauguration:
- After the Second World War, many Asian countries gained independence and Guru Dutt Sondhi, a member of the Indian International Olympic Committee, proposed the idea of Asian Games as a sporting event, where all Asian nations can be represented.
- The first-ever Asian Games were held in New Delhi in 1951.
- After the Second World War, many Asian countries gained independence and Guru Dutt Sondhi, a member of the Indian International Olympic Committee, proposed the idea of Asian Games as a sporting event, where all Asian nations can be represented.
- Regulation:
- Asian Games were regulated by the Asian Games Federation from 1951 to 1978. Since 1982, Olympic Council of Asia regulates the Asian Games.
- India as a Host:
- India is a founder member of Asian Games and also the host of the first Asian Games.
- The 9th edition of the Asian Games was also held in New Delhi in November and December 1982.
- Appu, the Indian elephant, was the first mascot to be used for the Asian Games.
- 19th Asian Games Hangzhou, China:
- A total of 40 sports and 61 disciplines will take center stage across 54 competition venues in Hangzhou and five co-host cities.
- Competitions in archery, artistic swimming, boxing, breaking, hockey, modern pentathlon, sailing, tennis, and water polo will also serve as Olympic qualifiers, with Paris 2024 quota spots available in those nine sports.
- The mascots of the 19th Asian Games are a group of robots named: Chenchen, Congcong, Lianlaian.
- The torch of the 19th Asian Games is named "Eternal Flame". The design was inspired by the Liangzhu Culture of ancient Chinese Civilisation
- Esports and Breaking (Breakdance) are scheduled to make their inaugural appearances as recognized and official sporting events.
What are Esports and Breaking?
- Esports (Electronic Sports) is a competitive sport where gamers use their physical and mental abilities to compete in various games in a virtual, electronic environment.
- Example: League of Legends, Overwatch, Fortnite, DOTA 2.
- Breaking: Breaking is a style of street dancing that incorporates coordination, acrobatic and intricate body movements, style, and aesthetics.
- It evolved from the hip hop movement during the early 1970s and is the most widely known of all hip hop dance styles.
Note: The 20th Asian Games are to be held in Nagoya, Japan in 2026.
What is AIFF?
- AIFF is the governing body for the football associations in India.
- It was formed on 23th June 1937 after representatives from six regional football associations met at the Army Headquarters in Shimla, India.
- In 1948, one year after independence the AIFF gained affiliation with FIFA.
- AIFF runs both the national teams as well as the various league and club level competitions throughout the country.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following statements in respect of the 32nd Summer Olympics: (2021)
- The official motto for this Olympics is ‘A New World’.
- Sport Climbing, Surfing, Skateboarding, Karate and Baseball are included in this Olympics.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Q. Consider the following statements in respect of the Laureus World Sports Award which was instituted in the year 2000: (2021)
- American golfer Tiger Woods was the first winner of this award.
- The award was received mostly by ‘Formula One’ players so far.
- Roger Federer received this award maximum number of times compared to others.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar
Why in News?
The Ministry of Women & Child Development, Government of India, organises Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar every year to celebrate the energy, determination, ability, zeal and enthusiasm of our children.
What is Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar?
- Two Categories: The Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar is given under two categories:
- Bal Shakti Puraskar, and
- Bal Kalyan Puraskar.
- Bal Shakti Puraskar:
- Recognition:
- It is given by the Government of India every year to recognize exceptional achievements of children in various fields i.e., innovation, scholastic achievements, social service, arts & culture, sports and bravery.
- Eligibility:
- A child who is an Indian Citizen and residing in India and is between 5-18 years of age.
- Award:
- A medal, a cash prize of Rs. 1,00,000, book vouchers worth Rs.10,000, a certificate and citation.
- Background:
- It was instituted in 1996 as the National Child Award for Exceptional Achievement, renamed from 2018 as Bal Shakti Puraskar.
- Recognition:
- Bal Kalyan Puraskar:
- Recognition:
- It is given as recognition to Individuals and Institutions, who have made an outstanding contribution towards service for children in the field of child development, child protection and child welfare.
- Eligibility:
- An individual who is an Indian Citizen and residing in India and should have attained the age of 18 years or above (as on 31st August of respective year). She/he should have worked for the cause of children for not less than 7 years.
- The institution should not be entirely funded by the government and should have been in the field of child welfare for 10 years and performing consistently in the field.
- Award:
- Three awards are given in each of the two categories - Individual and Institution - along with cash prizes (Rs. 1,00, 000 and Rs. 5,00, 000 respectively).
- Background:
- It was instituted in 1979 as the National Child Welfare Awards, renamed from 2018 as Bal Kalyan Puraskar.
- Recognition:
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Ponzi Scheme
- An actor faces scrutiny over his alleged involvement in a Rs.1,000 crore Ponzi scheme with 2 lakh investors.
- A Ponzi scheme is a type of investment fraud that promises high returns with little or no risk to investors.
- These are investment operations that pay returns to old investors from the money garnered from new investors.
- It is named after Charles Ponzi, an Italian businessman who ran such a scheme in the 1920s.
- Ponzi schemes do not fall under the regulatory purview of Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- In India, Ponzi schemes are banned under the Banning of Unregulated Deposit Schemes Act, 2019 and Prize Chit and Money Circulation Schemes (Banning) Act, 1978 .
RBI Directs Banks to Return Documents Within 30 Days of Loan Repayment
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has issued new directives to Regulated Entities (banks and non-banking financial companies) regarding the return of original property documents after the full repayment or settlement of loans.
- These norms will apply to all cases in which the return of original documents becomes due on or after 1st December 2023.
- In cases where borrowers are no longer alive, lenders must establish a clear procedure for returning the original property documents to the legal heirs.
- Applicable to personal loans, including consumer credit, education loans, housing loans, and financial asset loans.
- If original property documents are lost or damaged, the lender will help the borrower get duplicate or certified copies, covering the costs and compensating at Rs 5,000 per day for delays exceeding 30 days.
- The aim is to standardise document release practices and promote responsible lending conduct.
Ian Wilmut, Creator of Dolly the Sheep, Passes Away at 79
Ian Wilmut, the renowned cloning pioneer responsible for the groundbreaking creation of Dolly the Sheep in 1996, has recently passed away at the age of 79.
- In 1996, the birth of Dolly, a cloned sheep at the Roslin Institute in Scotland, rocked the world, sparking both excitement and fear about the possibilities of cloning technology.
- This achievement marked the first time mature adult cells were induced to mimic newly fertilized embryo cells, resulting in the birth of a genetically identical animal, later named Dolly.
- Wilmut's legacy extends beyond Dolly, as his work paved the way for advancements in regenerative medicine.
President of India Inaugurates NeVA
Recently, the President of India inaugurated the 'National e-Vidhan Application' (NeVA) and addressed the Gujarat Legislative Assembly in Gandhinagar.
- The President highlighted the significance of the E-Assembly, which transforms the legislative house into a digital entity, promoting speed and transparency.
- NeVA is one of the 44 Mission Mode Projects (MMPs) under the “Digital India Programme” which aims to make the functioning of all the State Legislatures paperless by transforming them into ‘Digital House’.
Read more: Digital India Programme