Infographics
Social Justice
UNDP's 2023 Gender Social Norms Index
For Prelims: United Nations Development Programme, UNDP's Gender Social Norms Index, Women Representation in Parliament, Human Development Index, Sukanya Samriddhi Yojna, Beti Bachao Beti Padhao Scheme, Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana, Pradhan Mantri Mahila Shakti Kendra Scheme
For Mains: Major Challenges Related to Gender Equality in India.
Why in News?
Biased gender social norms continue to impede progress towards achieving gender equality and violate human rights, according to the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- Despite global efforts and campaigns advocating for women's rights, a significant percentage of people still hold biased beliefs against women.
- The UNDP's 2023 Gender Social Norms Index (GSNI) provides insights into the persistence of these biases and their impact on various aspects of women's lives.
What are the Key Findings of the Index?
- About:
- UNDP tracked people’s attitudes towards women in four dimensions: political, educational, economic and physical integrity. UNDP reports that nearly 90% of people still hold at least one bias against women.
- Findings:
- Political Participation and Representation: Biases in gender social norms contribute to a lack of equality in political participation. Approximately half of the world's population believes men make better political leaders, while two in five believe men make better business executives.
- Countries with greater bias exhibit lower representation of women in parliament.
- On average, the share of heads of state or government who are women has remained around 10% worldwide since 1995, and women hold just over a quarter of parliament seats globally.
- Women are grossly underrepresented in leadership in conflict-affected countries, mainly at the negotiation tables in the recent conflicts in Ukraine (0%), Yemen (4%), and Afghanistan (10%).
- Indigenous women, migrant women, and women with disabilities face even more significant challenges in attaining political representation.
- Countries with greater bias exhibit lower representation of women in parliament.
- Political Participation and Representation: Biases in gender social norms contribute to a lack of equality in political participation. Approximately half of the world's population believes men make better political leaders, while two in five believe men make better business executives.
- Economic Empowerment: Despite progress in education, gender gaps in economic empowerment persist.
- The increase in women's education has not translated into better economic outcomes.
- In 59 countries where adult women are more educated than men, the average income gap is 39%.
- Domestic Chores and Care Work: Countries with higher bias in gender social norms witness a significant disparity in domestic chores and care work.
- Women spend nearly six times more time on these tasks than men, limiting their opportunities for personal and professional growth.
- Also, Alarmingly, 25% of people believe it is justified for a man to beat his wife, revealing deep-rooted biases.
- Hopeful Signs and Breakthroughs: While overall progress has been limited, an increase in the share of people with no bias in any indicator is observed in 27 out of 38 surveyed countries.
- The largest improvements were seen in Germany, Uruguay, New Zealand, Singapore, and Japan, with progress greater among men than women.
- Breakthroughs in gender social norms have been achieved through policies, regulations, and scientific advancements.
- The Urgent Need for Change: Biased gender social norms not only impede women's rights but also hinder societal development and well-being.
- The lack of progress in gender social norms coincides with a decline in the Human Development Index (HDI).
- Achieving freedom and agency for women benefits society as a whole.
What are the Major Challenges Related to Gender Equality in India?
- Cultural and Societal Norms: India has deep-rooted cultural and societal norms that perpetuate gender bias. Traditional beliefs regarding gender roles and expectations limit women's freedom and opportunities.
- For instance, the preference for male children, leading to a significant gender imbalance and instances of female infanticide.
- Violence against Women: Incidents of violence against women, such as domestic violence, sexual harassment, and rape, continue to be prevalent in India.
- Although laws have been enacted and awareness campaigns launched, these incidents persist, demonstrating the challenge of changing deep-seated attitudes and behaviours.
- Recent cases, such as the Hathras gang rape case in 2020, highlighted the gaps in the system and sparked outrage regarding the handling of such cases.
- Economic Disparities: Economic disparities between men and women contribute to gender bias. Women in India often face unequal pay, limited job opportunities, and lack of representation in decision-making roles.
- The gender wage gap remains a persistent issue, with women earning less than men for similar work.
- Limited Access to Education and Healthcare: Gender bias is perpetuated by limited access to education and healthcare for women in certain parts of India.
- Despite progress in increasing female literacy rates, particularly in urban areas, rural areas still face significant challenges.
- Moreover, inadequate access to healthcare, including reproductive health services, poses additional obstacles for women's well-being and development.
- Differentiation in the Socialisation Process: In many parts of India, especially in rural regions, there are still different socialisation norms for men and women.
- Women are expected to be soft-spoken, calm, and quiet. They should walk, talk, sit and behave in a certain manner. Whereas men ought to be confident, loud, and could display any behaviour as per their wish.
What are the Recent Government Schemes Related to Women Empowerment?
Way Forward
- Better Education Opportunities: Giving education to women means giving education to the whole family. Education plays an important role in building self-confidence among women.
- Also, India’s education policy should target young men and boys to positively change their attitudes towards girls and women.
- Also, there is a need to incorporate gender equality and sensitivity into the school curriculum from an early age, emphasising respect, empathy, and equal opportunities for all.
- Economic Independence: There is a need to encourage entrepreneurship and provide financial support, training, and mentorship to women to establish their businesses, and promote equal pay and flexible work arrangements.
- There is also a need to implement skill development programs to enhance women's employability and promote their participation in traditionally male-dominated sectors.
- Awareness About Safety Measures: A multi-sectoral strategy to raise awareness among women about the current government initiatives and mechanisms should be devised to ensure the safety of women throughout the country.
- Panic Button, Nirbhaya Police Squad are some good steps in the direction of women’s safety.
- From Women Development to Women Led Development: Women should be reimagined as architects of India’s progress and development, rather than being passive recipients of the fruits of development.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Two of the schemes launched by the Government of India for Women’s development are Swadhar and Swayam Siddha. As regards the difference between them, consider the following statements: (2010)
- Swayam Siddha is meant for those in difficult circumstances such as women survivors of natural disasters or terrorism, women prisoners released from jails, mentally challenged women etc., whereas Swadhar is meant for holistic empowerment of women through Self Help Groups.
- Swayam Siddha is implemented through Local Self Government bodies or reputed Voluntary Organizations whereas Swadhar is implemented through the ICDS units set up in the states.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q.1 “Empowering women is the key to control population growth”. Discuss. (2019)
Q.2 Discuss the positive and negative effects of globalization on women in India? (2015)
Q.3 Male membership needs to be encouraged in order to make women’s organization free from gender bias. Comment. (2013)


Governance
The Hiroshima AI Process for Global AI Governance
For Prelims: The Hiroshima AI Process, Global AI Governance, Generative AI, G-7, OECD, GPAI, IPR.
For Mains: The Hiroshima AI Process for Global AI Governance.
Why in News?
Recently, the annual G7 Summit held in Hiroshima, Japan, initiated the Hiroshima AI Process (HAP), which is likely to conclude by December 2023, signaling a significant step towards regulating Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- The G7 Leaders' Communiqué recognized the importance of inclusive AI governance and set forth a vision of trustworthy AI aligned with shared democratic values.
What is the Hiroshima AI Process?
- About:
- The HAP aims to facilitate international discussions on inclusive AI governance and interoperability to achieve a common vision and goal of trustworthy AI.
- It recognizes the growing prominence of Generative AI (GAI) across countries and sectors and emphasizes the need to address the opportunities and challenges associated with it.
- Working:
- The HAP will operate in cooperation with international organizations such as the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the Global Partnership on AI (GPAI).
- Objectives:
- The HAP aims to govern AI in a way that upholds Democratic values, ensures fairness and accountability, promotes transparency, and prioritizes the safety of AI technologies.
- It seeks to establish procedures that encourage openness, inclusivity, and fairness in AI-related discussions and decision-making processes.
What are the Potential Challenges and Outcomes?
- The HAP faces challenges due to differing approaches among G7 countries in regulating AI risks. However, it aims to facilitate a common understanding on important regulatory issues while preventing complete discord.
- By involving multiple stakeholders, the HAP strives to find a balanced approach to AI governance that considers diverse perspectives and maintains harmony among G7 countries.
- For now, there are three ways in which the HAP can play out,
- It may enable the G7 countries to move towards a divergent regulation based on shared norms, principles and guiding values.
- It becomes overwhelmed by divergent views among the G7 countries and fails to deliver any meaningful solution.
- It delivers a mixed outcome with some convergence on finding solutions to some issues but is unable to find common ground on many others.
How can the HAP Resolve the issue of IPR in relation to GAI?
- Currently, there is ambiguity regarding the relationship between AI and IPR (Intellectual Property Rights), leading to conflicting interpretations and legal decisions in different jurisdictions.
- The HAP can contribute by establishing clear rules and principles regarding AI and IPR, helping the G7 countries reach a consensus on this matter.
- One specific area that can be addressed is the application of the "Fair Use" doctrine, which permits certain activities such as teaching, research, and criticism without seeking permission from the copyright owner.
- However, whether using copyrighted material in machine learning qualifies as fair use is a subject of debate.
- By developing a common guideline for G7 countries, the HAP can provide clarity on the permissible use of copyrighted materials in machine learning datasets as fair use, with certain conditions. Additionally, it can distinguish between the use of copyrighted materials for machine learning specifically and other AI-related uses.
- Such efforts can significantly impact the global discourse and practices surrounding the intersection of AI and intellectual property rights.
How is Global AI currently Governed?
- India:
- NITI Aayog, has issued some guiding documents on AI Issues such as the National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence and the Responsible AI for All report.
- Emphasises social and economic inclusion, innovation, and trustworthiness.
- US:
- The US released a Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights (AIBoR) in 2022, outlining the harms of AI to economic and civil rights and lays down five principles for mitigating these harms.
- The Blueprint, instead of a horizontal approach like the EU, endorses a sectorally specific approach to AI governance, with policy interventions for individual sectors such as health, labour, and education, leaving it to sectoral federal agencies to come out with their plans.
- China:
- In 2022, China came out with some of the world’s first nationally binding regulations targeting specific types of algorithms and AI.
- It enacted a law to regulate recommendation algorithms with a focus on how they disseminate information.
- EU:
- In May 2023, the European Parliament reached a Preliminary Agreement on a new draft of the Artificial Intelligence Act, which aims to regulate systems like OpenAI's ChatGPT.
- The legislation was drafted in 2021 with the aim of bringing transparency, trust, and accountability to Al and creating a framework to mitigate risks to the safety, health, Fundamental Rights, and democratic values of the EU.
- In May 2023, the European Parliament reached a Preliminary Agreement on a new draft of the Artificial Intelligence Act, which aims to regulate systems like OpenAI's ChatGPT.
Way Forward
- Non-G7 countries also have the opportunity to launch similar processes to influence global AI governance. This shows that AI governance has become a global issue, with more complexity and debates expected in the future.
- In this context, the Indian government should take proactive steps by creating an open-source AI risk profile, setting up controlled research environments for testing high-risk AI models, promoting explainable AI, defining intervention scenarios, and maintaining vigilance.
- It is important to establish a simple regulatory framework that defines AI capabilities and identifies areas prone to misuse. Prioritizing data privacy, integrity, and security while ensuring data access for businesses is crucial.
- Enforcing mandatory explainability in AI systems will enhance transparency and help businesses understand the reasoning behind decisions.
- Policymakers should strive to strike a balance between the scope of regulation and the language used, seeking input from various stakeholders, including industry experts and businesses. This way forward will contribute to effective AI regulations that address concerns and promote responsible AI deployment.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)


Social Justice
National Commission for Scheduled Castes
For Prelims: National Commission for Scheduled Castes,Article 338 of the Constitution, 89th Amendment Act, 2003, 89th Amendment Act, 2003.
For Mains: Functions of NCSC.
Why in News?
The National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC) has recently issued a notice to Zomato, regarding an advertisement that was deemed "inhuman" and casteist.
What is the National Commission for Scheduled Castes?
- About:
- The NCSC is a constitutional body established with a view to provide safeguards against the exploitation of Scheduled Castes and to promote and protect their social, educational, economic and cultural interests.
- History:
- Special Officer:
- Initially, the constitution provided for the appointment of a Special Officer under Article 338. The special officer was designated as the Commissioner for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
- 65th Amendment Act, 1990:
- It amended Article 338 of the Constitution and replaced the one-member system with a multi-member National Commission for Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes(ST).
- 89th Amendment Act, 2003:
- Article 338 was amended, and the erstwhile National Commission for SC and ST was replaced by two separate Commissions from the year 2004 which were:
- National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC) and
- National Commission for Scheduled Tribes (NCST)
- Article 338 was amended, and the erstwhile National Commission for SC and ST was replaced by two separate Commissions from the year 2004 which were:
- Special Officer:
- Composition:
- The NCSC comprises a Chairperson, a Vice-Chairperson, and three additional Members.
- These positions are filled through the President's appointment, indicated by a warrant under his hand and seal.
- Their conditions of service and tenure of office are also determined by the President.
- Functions:
- To investigate and monitor all matters relating to the constitutional and other legal safeguards for the SCs and to evaluate their working;
- To inquire into specific complaints with respect to the deprivation of rights and safeguards of the SCs;
- To participate and advise on the planning process of socioeconomic development of the SCs and to evaluate the progress of their development under the Union or a state;
- To present to the President, annually and at such other times as it may deem fit, reports upon the working of those safeguards;
- To make recommendations as to the measures that should be taken by the Union or a state for the effective implementation of those safeguards and other measures for the protection, welfare and socio-economic development of the SCs
- Till 2018, the commission was also required to discharge similar functions with regard to the other backward classes (OBCs). It was relieved from this responsibility by the 102nd Amendment Act, 2018.
What are the Other Constitutional Provisions for Upliftment of the Schedule Caste?
- Article 15: This article specifically addresses the issue of discrimination based on caste, emphasizing the protection and upliftment of Scheduled Castes (SCs)
- Article 17: This article abolishes untouchability and prohibits its practice in any form. It seeks to eliminate social discrimination and promote the equality and dignity of all individuals.
- Article 46: Promotion of Educational and Economic Interests: This article directs the State to promote the educational and economic interests of Scheduled Castes and other weaker sections of society and protect them from social injustice and all forms of exploitation.
- Article 243D(4): This provision mandates the reservation of seats for SCs in Panchayats (local self-government institutions) in proportion to their population in the area.
- Article 243T(4): This provision ensures the reservation of seats for SCs in Municipalities (urban local bodies) in proportion to their population in the area.
- Article 330 and Article 332 provide for reservation of seats in favour of the Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes in the Lok Sabha and in the legislative assemblies of the States (respectively).
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. In 2001, RGI stated that Dalits who converted to Islam or Christianity are not a single ethnic group as they belong to different caste groups. Therefore, they cannot be included in the list of Scheduled Castes (SC) as per Clause (2) of Article 341, which requires a single ethnic group for inclusion. (2014)
Q. Whether the National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC) can enforce the implementation of constitutional reservation for the Scheduled Castes in the religious minority institutions? Examine. (2018)


Important Facts For Prelims
SIPRI Yearbook 2023
Why in News?
Recently, Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) Yearbook 2023 revealed that China could potentially have as many Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) as U.S. or Russia by the end of the decade.
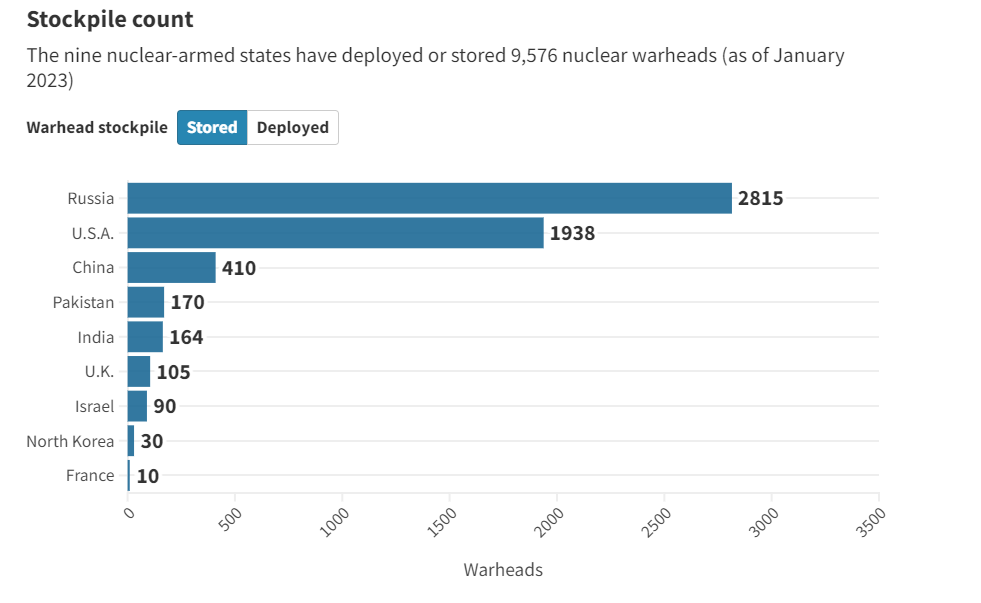
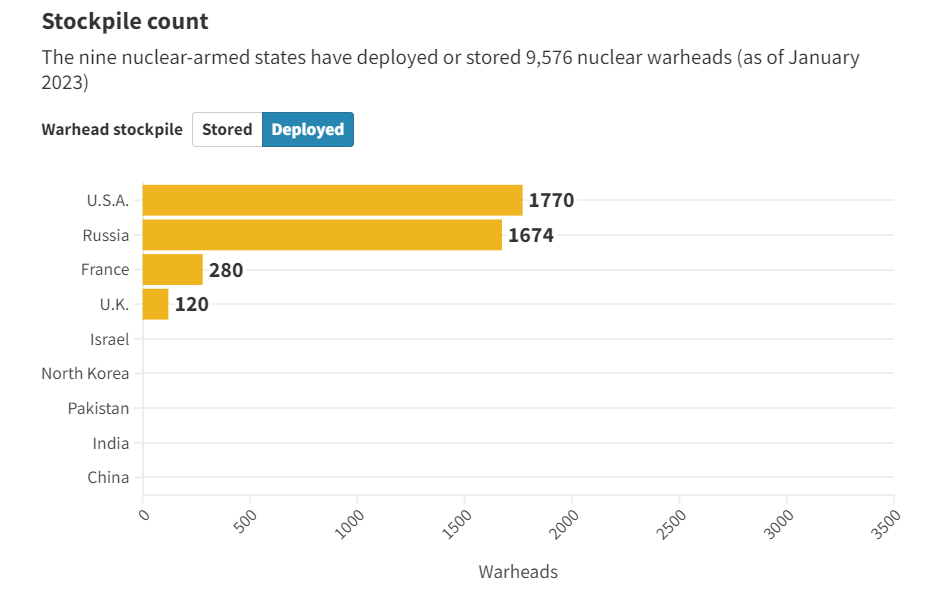
- Russia has the highest number of stored nuclear arsenals followed by US and China while the US has deployed the highest number of nuclear arsenals followed by Russia and France.
What SIPRI Reveal About Nuclear Arsenals?
- Global Nuclear Arsenals:
- Modernization and Expansion:
- The nine nuclear-armed states, including the United States, Russia, and China, continue to modernize and expand their nuclear arsenals, deploying new nuclear-armed or nuclear-capable weapon systems in 2022.
- Other nuclear-armed countries are UK, France, India, Pakistan, the North Korea and Israel
- Total Global Inventory:
- As of January 2023, the total global inventory of warheads is estimated at 12,512, with approximately 9,576 warheads held in military stockpiles for potential use.
- Modernization and Expansion:
- Dominance of Russia and U.S.:
- 90% of all Nuclear Weapons:
- Russia and the United States possess almost 90% of all nuclear weapons, with relatively stable sizes of their respective nuclear arsenals.
- Arms Control Concerns:
- Transparency and dialogue regarding nuclear forces declined between Russia and the United States following Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
- The suspension of the strategic stability dialogue and the Treaty on Measures for the Further Reduction and Limitation of Strategic Offensive Arms (New START) has halted discussions for a follow-on treaty.
- New START Limits Maintained:
- Despite the strained relations, both Russia and the United States remained within the limits set by New START for their deployed strategic nuclear forces as of January 2023, according to SIPRI's assessment.
- 90% of all Nuclear Weapons:
 |
 |
- India's Nuclear Arsenal:
- Growth in Arsenal:
- India's nuclear arsenal also expanded, increasing from 160 warheads in 2022 to 164 warheads in 2023 and that of Pakistan from 165 to 170 in the same period.
- Focus on Longer-Range Weapons:
- India's nuclear deterrent, while primarily focused on Pakistan, is placing growing emphasis on longer-range weapons capable of reaching targets across China.
- Upgrading Ballistic Missiles:
- India is in the process of upgrading its ballistic missiles, with the development of a submarine-launched intermediate-range ballistic missile and the imminent induction of a new generation ballistic missile called 'Agni Prime.'
- Growth in Arsenal:
- China's Nuclear Arsenal:
- Increased Size:
- China's nuclear arsenal grew from 350 warheads in January 2022 to 410 warheads in January 2023, according to the SIPRI.
- Concerns About Expansion:
- The significant expansion of China's nuclear arsenal raises concerns as it contradicts China's stated goal of maintaining minimum nuclear forces for national security.
- Increased Size:
What is SIPRI?
- The SIPRI is an independent international institute dedicated to research into conflict, armaments, arms control and disarmament.
- Established in 1966 at Stockholm, SIPRI provides data, analysis and recommendations, based on open sources, to policymakers, researchers, media and the interested public.


Important Facts For Prelims
First Indigenously Developed Animal-Derived Biomedical Device
Why in News?
Recently, Indian Drugs Controller approved the first indigenously developed animal-derived Class D Biomedical Device, Cholederm, that can rapidly heal skin wounds at low-cost with minimum scarring.
- As per the Medical Devices Rules, 2017, medical devices are classified into four classes based on the risk level: Class A (low risk), Class B (low moderate risk), Class C (moderate high risk); Class D (high risk).
What are the Key Details of the Development?
- About:
- The Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST), an autonomous institution under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), developed the tissue engineering scaffold.
- It is the first institution in India to develop Class D medical devices that meet the requirements of the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO).
- It is an innovative technology for preparing tissue engineering scaffolds from mammalian organs.
- The concept of using animal-derived materials as advanced wound care products is not new.
- However, indigenous technology was so far not available for fabricating quality products that satisfy the requirements of the Drugs Controller General
- Healing Capabilities:
- The tissue engineering scaffold, called Cholederm, demonstrated the ability to heal various types of skin wounds, including burn and diabetic wounds, in rat, rabbit, or dog models faster than existing products in the market, while minimizing scarring.
- It showed that graft-assisted healing was regulated by anti-inflammatory M2 type of macrophages, which helped modulate or mitigate scarring reactions in different tissues.
- Cost Reduction and Market Potential:
- The introduction of Cholederm to the Indian market is expected to reduce treatment costs from Rs 10,000/- to Rs 2,000/-, making it more affordable.
- Additionally, the technology provides a competitive advantage in the international market and creates an income-generating opportunity.
- Future Developments:
- The research team is currently developing injectable gel formulations of the scaffold for easier application in treating cardiac injuries, aiming to revolutionize the management of patients suffering from myocardial infarction.
Note:
- Medical devices are regulated as drugs under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940.
- CDSCO is the national regulating authority for medical devices and pharmaceuticals while NPPA is empowered by the Drugs (Price Control) Order, 2013, to control the prices of drugs and medical devices.
What is CDSCO?
- The CDSCO is the Central Drug Authority for discharging functions assigned to the Central Government under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940.
- The CDSCO under Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India is the National Regulatory Authority (NRA) of India.
- Its headquarter is in New Delhi
- Major Functions:
- Regulatory control over the import of drugs, approval of new drugs and clinical trials.
- Approval of certain licences as Central Licence Approving Authority.
What is the National Pharmaceuticals Pricing Authority (NPPA)?
- NPPA is an organization under Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers which was set up in 1997 to revise the prices of controlled bulk drugs and formulations and to enforce prices and availability of medicines in the country, under the Drugs (Prices Control) Order (DPCO), 1995.
- The prices are now fixed/revised under Drugs (Prices Control) Order (DPCO), 2013.
- It also monitors the prices of decontrolled drugs in order to keep them at reasonable levels.


Important Facts For Prelims
Ram Prasad Bismil
Why in News?
On 11th June 2023, 126th birth anniversary of Ram Prasad Bismil was commemorated. Known for his revolutionary spirit and poetic prowess, Bismil played a significant role in the fight against British colonial rule.
What are the Key Points about Bismil?
- Birth:
- Bismil was born on 11th June 1897, in a village in Uttar Pradesh’s Shahjahanpur district to Murlidhar and Moolmati.
- About:
- Bismil joined the Arya Samaj (founded in 1875 by Dayanand Saraswati) and became a talented writer and poet, using pen names like 'Bismil' meaning 'wounded' or 'restless.'
- The ideals of a revolution first took root in his mind when he read about the death sentence awarded to Bhai Parmanand, an Indian nationalist and Arya Samaj missionary.
- He was 18 then and vented his anguish through his poem ‘Mera Janm’.
- He believed in revolutionary methods of freedom struggle which were in contrast to Gandhian methods.
- Contributions of Ram Prasad Bismil:
- The Mainpuri Conspiracy:
- Bismil grew disillusioned with the moderate wing of the Congress Party and founded a revolutionary organization called ‘Matrivedi’.
- In 1918, Bismil and Dixit got involved in the Mainpuri Conspiracy in which they distributed prohibited literature.
- On 28 January 1918, Bismil distributed two of his writings to people- a pamphlet titled Deshwasiyon ke Naam Sandesh (A Message to Countrymen) and Mainpuri ki Pratigya (Vow of Mainpuri).
- To collect funds for their parties they looted government coffers on three occasions in 1918
- Founding the Hindustan Republican Association:
- In 1920, he formed the Hindustan Republican Association (HRA) with Sachindra Nath Sanyal and Jadugopal Mukherjee.
- The HRA's manifesto, largely penned by Bismil, aimed to establish a federal Republic of United States of India through an armed revolution.
- The Kakori Train Action:
- The Kakori train robbery in 1925 was a major action of the HRA, aimed at acquiring funds for their activities and generating publicity.
- Bismil and his companions Chandrasekhar Azad and Ashfaqulla Khan decided to loot a train in Kakori near Lucknow.
- They were successful in their attempt but were arrested alongside a dozen other HRA members within a month of the attack and tried under the Kakori Conspiracy Case.
- The legal process lasted 18 months. Bismil, Lahiri, Khan and Thakur Roshan Singh were awarded death sentences.
- Poetry and Writing:
- Bismil's prolific writings, including patriotic verses in Hindi and Urdu, inspired Indians to join the freedom struggle.
- His poems reflected concerns for societal issues and principles of equality and human dignity.
- Advocacy for Hindu-Muslim Unity:
- Bismil's close friendship with fellow revolutionary poet Ashfaqullah Khan symbolized communal harmony.
- In his last letter before his hanging, he emphasized the need for Hindus and Muslims to unite for the nation's service.
- The Mainpuri Conspiracy:
- Death:
- He was hanged on 19th December 1927 at Gorakhpur Jail.
- He was cremated on the banks of river Rapti, and the site was rechristened as Raj Ghat later.


Important Facts For Prelims
Disinflation in India
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently stated that India's disinflation process is expected to be gradual and prolonged, with the 4% inflation target likely to be achieved only over the medium term.
What is Disinflation?
- About:
- Disinflation refers to a decrease in the rate of inflation, which means that prices are still rising but at a slower pace than before.
- It is important to note that disinflation is different from deflation, which refers to a sustained decrease in the overall price level.
- A healthy amount of disinflation is necessary since it prevents the economy from overheating.
- Disinflation refers to a decrease in the rate of inflation, which means that prices are still rising but at a slower pace than before.
- Causes:
- Disinflation can be caused by various factors, such as:
- A slowdown in economic growth or demand
- A tight monetary policy or higher interest rates
- A fiscal consolidation or lower government spending
- A stronger exchange rate.
- Disinflation can be caused by various factors, such as:
What is Inflation and Deflation?
- About:
- Inflation refers to the rise in the prices of most goods and services of daily or common use, such as food, clothing, housing, recreation, transport, consumer staples, etc.
- Inflation measures the average price change in a basket of commodities and services over time.
- The opposite and rare fall in the price index of this basket of items is called ‘deflation’.
- Inflation is indicative of the decrease in the purchasing power of a unit of a country’s currency. This is measured in percentage.
- Inflation refers to the rise in the prices of most goods and services of daily or common use, such as food, clothing, housing, recreation, transport, consumer staples, etc.
- Evaluation:
- In India, inflation is primarily measured by WPI (Wholesale Price Index) and CPI (Consumer Price Index), which measure wholesale and retail-level price changes, respectively.
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) uses CPI data to control inflation.
- MPC, led by the RBI governor, is responsible for reducing inflation to 4% over the medium term, while maintaining it between 2% and 6% in the long run.
What Recent Updates has the RBI Provided Regarding Inflation?
- Current Inflation Landscape:
- As of May, 2023 India's annual retail inflation stood at 4.25%, down from 4.7% in April, 2023. However, analysts forecast that inflation will remain persistent in the coming months, posing challenges to achieving the 4% target.
- Inflation Projection for 2023-24:
- RBI stated that the inflation projection for FY 23-24 is estimated at 5.1%, which is lower than previous figures but still above the target. This indicates the need for continued vigilance and policy measures to curb inflationary pressures and ensure macroeconomic stability.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 With reference to Indian economy, demand-pull inflation can be caused/increased by which of the following?
- Expansionary policies
- Fiscal stimulus
- Inflation-indexing of wages
- Higher purchasing power
- Rising interest rates
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (a)
Q.2 Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The weightage of food in Consumer Price Index (CPI) is higher than that in Wholesale Price Index (WPI).
- The WPI does not capture changes in the prices of services, which CPI does.
- Reserve Bank of India has now adopted WPI as its key measure of inflation and to decide on changing the key policy rates.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Wealthy Indians Seek Greener Pastures as Outflow of Ultra-Rich Continues
According to the Henley Private Wealth Migration Report (2023), released by Henley & Partners, India is projected to experience a net outflow of 6,500 High Net-Worth Individuals (HNWIs) in 2023, making it the second-worst performer in terms of losing ultra-rich individuals, trailing behind China.
The report defines HNWIs as those with investable wealth of USD 1 million or more, equivalent to Rs 8.2 crore or more in rupee terms. This trend follows a previous outflow of 7,500 such individuals in 2022. Conversely, Australia, the UAE, Singapore, the USA, and Switzerland are expected to be the top destinations for net inflows of HNWIs in 2023.
India ranked 10th among the wealthiest countries in the world based on HNWI population. It boasts 3,44,600 HNWIs, 1,078 centi-millionaires, and 123 billionaires. In comparison, China has 7,80,000 HNWIs and 285 billionaires, while the US, with a population of just 340 million, has 52,70,000 HNWIs and 770 billionaires.
The W10 grouping, comprising the US, Japan, China, Germany, the UK, Switzerland, Australia, Canada, France, and India, represents the top 10 countries with the highest number of HNWIs.
Read more: Human Migration: Reasons & Impact
Djokovic and Swiatek Claim Historic French Open Victory
Novak Djokovic made history at the French Open,2023 securing his third title at Roland-Garros and solidifying his position as the most successful men's singles tennis player. Despite a slow start, the 36-year-old Serbian overpowered his Norwegian opponent, Casper Ruud, with a straight sets victory of 7-6 (1), 6-3, 6-5.
This win marked Djokovic's 23rd major men's singles crown, surpassing all other players in the history of the sport. He also equaled Serena Williams' record for the most Grand Slam titles won in the Open Era.
Meanwhile, in the women's division, Iga Swiatek, the world number one player, successfully defended her title at Roland Garros. In a thrilling final against Karolina Muchova, Swiatek emerged victorious with a score of 6-2, 5-7, 6-4. This marked Swiatek's third career championship at the French Open and her fourth Grand Slam title overall.
Read more: Roland Garros
Decrease in India’s Remittance
India experienced a significant growth in inward remittances in 2022 at the growth of 24%, reaching USD 111 billion, surpassing the World Bank's estimate of USD100 billion. This accounted for 63% of South Asia's remittance flows, which amounted to USD176 billion. However, remittance flows to India are projected to increase by only 0.2% in 2023 as per the latest Migration and Development Brief released by the World Bank due to a slowdown in OECD economies, particularly impacting employment opportunities and wages for migrants. The diversion of formal remittances to informal channels is also expected. High-skilled Indian migrants in the United States, United Kingdom, and Singapore played a substantial role in India's remittances, benefiting from post-pandemic recovery and wage increases.
Gabon’s First Agri-SEZ Project
The Union Minister of Education and Skill Development and Entrepreneurship officially started Gabon’s first Agri- SEZ (Special Economic Zone) project. The project will be implemented by AOM group with Centurion University as the technical and knowledge partner.
In the first phase of the program, 30 farmers and 20 B.Sc./M.Sc. Agri and B.Tech/M.Tech Engineering students from Gajapati district, which is an Aspirational district of Odisha, India. will be travelling together as agri-technical and technical consultants for the agriculture SEZ in Gabon which is being developed under this project.
Anti-colonial solidarity, diasporic goodwill, and the principle of 'South-South' cooperation, among others, are playing a significant role in strengthening the partnership between India and the African continent.
Read more: Special Economic Zone