Internal Security
SIPRI Yearbook 2022
- 14 Jun 2022
- 5 min read
For Prelims: Highlights of the Report
For Mains: Need for Military Spending and associated Concerns
Why in News?
Recently, the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) launched the findings of SIPRI Yearbook 2022, which assesses the current state of armaments, disarmament and international security.
What is SIPRI?
- The SIPRI is an independent international institute dedicated to research into conflict, armaments, arms control and disarmament.
- Established in 1966 at Stockholm, SIPRI provides data, analysis and recommendations, based on open sources, to policymakers, researchers, media and the interested public.
What are the Key Highlights?
- Nuclear warheads:
- Global Scenario:
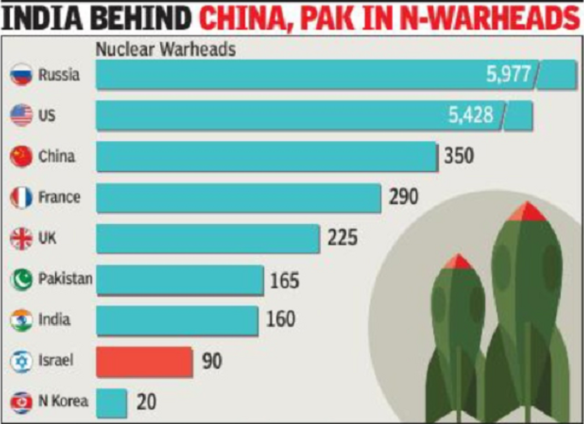
- The nine nuclear-armed states—the United States, Russia, the United Kingdom, France, China, India, Pakistan, Israel and the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea (North Korea)—continue to modernize their nuclear arsenals and although the total number of nuclear weapons declined slightly between January 2021 and January 2022, the number will probably increase in the next decade.
- India
- India had 160 nuclear warheads as of January 2022 and it appears to be expanding its nuclear arsenal.
- Nuclear warheads are the explosive head of a missile or torpedo that uses nuclear energy.
- India’s nuclear stockpile increased from 156 in January 2021 to 160 in January 2022.
- India had 160 nuclear warheads as of January 2022 and it appears to be expanding its nuclear arsenal.
- China
- China had 350 nuclear warheads in January 2021 as well as January 2022.
- India does not share official data on its nuclear arsenal.
- China had 350 nuclear warheads in January 2021 as well as January 2022.
- Russia and the USA together possess over 90% of all nuclear weapons.
- Global Scenario:
- Importers of Major Arms:
- SIPRI identified 164 states as importers of major arms in 2016-20.
- Country Wise:
- The five largest arms importers were Saudi Arabia, India, Egypt, Australia and China, which together accounted for 36% of total arms imports.
- Region wise:
- The region that received the largest volume of major arms supplies in 2016-20 was Asia and Oceania, accounting for 42% of the global total, followed by the Middle East, which received 33%.
- Suppliers of Major Arms:
- The five largest suppliers in 2016-20 - the United States, Russia, France, Germany and China - accounted for 76% of the total volume of exports of major arms.
What are the Several Landmarks in the Nuclear Diplomacy?
- Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW):
- After receiving the required 50 ratifications, the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW) entered into force in January 2021.
- New START:
- US-Russian arms control agreement New START was extended for five years.
- Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA):
- The start of talks on the USA rejoining, and Iran returning to compliance with the Iran nuclear deal, the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA).
- Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons:
- Nuclear-armed permanent members (P5) of the United Nations Security Council reaffirmed their commitment to complying with non-proliferation, disarmament, and arms control agreements and pledges as well as their obligations under the 1968 Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons.
What are the Hindrances in Nuclear Diplomacy?
- All P5 members continue to expand or modernize their nuclear arsenals and appear to be increasing the salience of nuclear weapons in their military strategies.
- Russia has even made open threats about possible nuclear weapon use in the context of the war in Ukraine.
- Bilateral Russia–USA strategic stability talks have stalled because of the war, and none of the other nuclear-armed states are pursuing arms control negotiations.
- Moreover, the P5 members of UNSC have voiced opposition to the TPNW, and the JCPOA negotiations have not yet reached a resolution.