International Relations
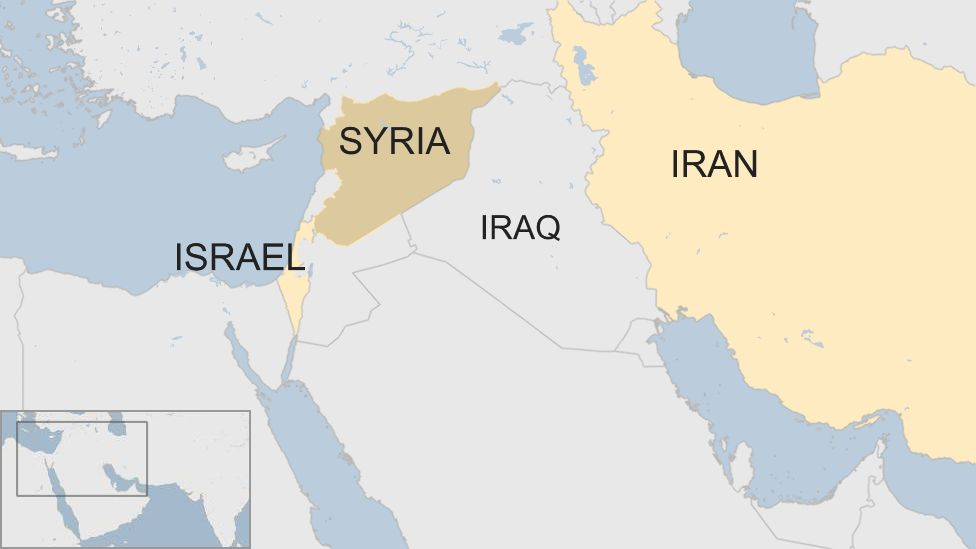
Conflict between Israel and Syria
For Prelims: Conflict between Israel and Syria, Al-Aqsa Mosque, Middle East, Golan Heights Law, UNSC.
For Mains: Impact of the ongoing Syria-Israel conflict on the stability of the Middle East region.
Why in News?
Recently, Israel has fired retaliatory rockets after three rockets had been launched towards Israel from Syria.
What is the Background of Recent Conflict between the Two?
- The situation in Israel and its neighboring countries has been tense for several months now, with an ultra-nationalist government coming to power in Israel, raising concerns among its neighbors.
- The recent raid on the Al-Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem by Israel sparked a wave of rocket attacks from Lebanon, Gaza Strip, and Syria.
- Israel fears that arch-rival Iran is using the long-running war in Syria to station its fighters and weapons close to Israel's borders.
- Israel has been conducting strikes in Syria in recent weeks, targeting both Iranian-linked figures and infrastructure, including the airports of Damascus and Aleppo.
- The situation in the region is complex and volatile, with multiple actors involved and competing interests in the play.
- The ongoing conflicts have resulted in the displacement of millions of people and the loss of countless lives.
- The international community has called for calm and a peaceful resolution to the conflicts, but the situation remains tense and uncertain.
What is the Timeline of the Conflict between Israel and Syria?
- Six-Day War in 1967:
- The conflict between Israel and Syria goes back to the Six-Day War in 1967, in which Israel seized the Golan Heights from Syria, which it has occupied since then.
- The fertile plateau of the Golan Heights overlooks both Israel and Syria, offering a commanding military vantage.
- In 1973, Syrian forces made an unsuccessful bid to recapture the area during the Yom Kippur War. Although a ceasefire agreement was reached in 1974, most of the Golan Heights remains under Israeli control.
- Yom Kippur War, also called the October War was fourth of the Arab-Israeli wars, which was initiated by Egypt and Syria on the Jewish holy day of Yom Kippur.
- The war eventually drew both the US and the erstwhile USSR into indirect confrontation in defense of their respective allies.
- The conflict between Israel and Syria goes back to the Six-Day War in 1967, in which Israel seized the Golan Heights from Syria, which it has occupied since then.
- Israel's Golan Heights Law:
- In 1981, Israel passed the Golan Heights Law, extending its "laws, jurisdiction and administration" to the area and effectively annexing it.
- A United Nations Security Council (UNSC) resolution was passed declaring Israel's imposition of law in the occupied Syrian Golan Heights "null and void and without international legal effect".
- However, it has not changed the situation on the ground, but the frontier has not seen major hostilities for more than 40 years.
- In 2000, Israel and Syria attempted to negotiate a settlement but failed.
- Syrian Civil War:
- Israel and Syria's long-standing conflict escalated after the start of the Syrian civil war in 2011.
- Iran, which denies Israel's right to exist, emerged as a key player in the conflict and has been providing weapons, money, and fighters to support the Syrian President's regime.
- As a result, rockets sometimes land in Israel as "errant fire" during the fighting in Syria.
- Israel and Syria's long-standing conflict escalated after the start of the Syrian civil war in 2011.
- Targeted Strikes in Syria:
- Israel has been accused of carrying out targeted strikes in Syria in recent years, although it does not acknowledge them.
- The recent wave of attacks, however, has raised concerns of an escalation in the conflict, further destabilizing the already volatile region.
What is India's Position in the Conflict?
- India maintains a balanced position in the Syrian Israeli conflict and has urged all parties to exercise restraint and resolve their differences peacefully through negotiations.
- India has consistently supported the sovereignty and territorial integrity of Syria and called for an end to external interference in its internal affairs.
- Implications of Conflict for India:
- The conflict between Syria and Israel could have implications for India, primarily in terms of energy security.
- India is heavily dependent on oil imports from the Middle East, including Syria, and any disruption in the oil supply chain could have a significant impact on the Indian economy.
- The conflict could also have security implications for India, as extremist groups in the region could exploit the situation to further their agenda.
- India has a significant Muslim population, and any escalation of the conflict could lead to sectarian tensions within the country.
- The conflict between Syria and Israel could have implications for India, primarily in terms of energy security.
Way Forward
- From an international perspective, the Syrian conflict is seen as a proxy war between major powers such as the US, Russia, and Iran, each supporting different sides in the conflict. The situation in Syria remains complex and unresolved, with no clear path to peace.
- It requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the root causes of the conflict and takes into account the concerns and interests of all parties involved.
- One possible way forward could be through diplomatic efforts aimed at finding a peaceful and just solution to the conflict.
- This could involve engaging with all the parties involved, including Israel, Syria, Iran, Hezbollah, and other regional and international actors.
- Another approach could be through regional cooperation and dialogue, which could help build trust and confidence among the parties and reduce tensions in the region.
- The recent Abraham Accords signed between Israel and several Arab states could provide a positive example of such cooperation and dialogue.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following pairs: (2018)
| Towns sometimes mentioned in news | Country | |
| 1. | Aleppo | Syria |
| 2. | Kirkuk | Yemen |
| 3. | Mosul | Palestine |
| 4. | Mazar-i-sharif | Afghanistan |
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1 and 4
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Q2. Which one of the following countries of South-West Asia does not open out to the Mediterranean Sea? (2015)
(a) Syria
(b) Jordan
(c) Lebanon
(d) Israel
Ans: (b)
Q3. The area known as ‘Golan Heights’ sometimes appears in the news in the context of the events related to (2015)
(a) Central Asia
(b) Middle East
(c) South-East Asia
(d) Central Africa
Ans: (b)
Q4. Yom Kippur War was fought between which sides/ countries? (2008)
(a) Turkey and Greece
(b) Serbs and Croats
(c) Israel, and Arab countries led by Egypt and Syria
(d) Iran and Iraq
Ans: (c)


Science & Technology
Quantum Technology for Securing Maritime Communications
For Prelims: Indian Navy, Quantum mechanics, Semiconductor, Internet-of-Things, machine learning, Robotics, Artificial intelligence.
For Mains: Quantum Technology, Significance and Challenges.
Why in News?
RRI (Raman Research Institute) has inked a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Indian Navy on Quantum Technologies to develop secure maritime communications.
- RRI is an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
- Under this agreement, RRI’s Quantum Information and Computing (QuIC) lab will lead the research efforts towards developing Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) techniques that the Indian Navy could leverage in the nation's efforts towards securing free space communications.
Note
- Quantum Technology is a field of science and engineering that deals with the study and application of quantum mechanics principles.
- Quantum mechanics is the branch of physics that describes the behavior of matter and energy at the atomic and subatomic level.
- There are Four domains of Quantum Technology:
- Quantum communication
- Quantum simulation
- Quantum computation
- Quantum sensing and metrology
What is Quantum Communication?
- Quantum Communication:
- Quantum communication is a subfield of quantum technology that focuses on the development of secure communication systems that use the principles of quantum mechanics.
- Quantum communication uses a fundamentally different approach to encryption.
- The most common example of quantum communication is QKD, which allows two parties to generate an encryption key that is virtually uncrackable.
- Mechanism of Quantum Communication:
- Encoding Information: Information is encoded onto quantum bits (qubits), which can exist in multiple states simultaneously.
- This property is known as superposition.
- Transmitting Information: The encoded qubits are transmitted over a quantum communication channel, such as a fiber optic cable or a free-space link.
- The qubits are typically transmitted one at a time.
- Receiving Information: The receiving party measures the qubits using a quantum measurement device.
- The measurement process collapses the superposition state of the qubit to a single state, revealing the encoded information.
- Detecting Eavesdropping: One of the key features of quantum communication is that any attempt to eavesdrop on the communication will disturb the quantum state of the qubit, making it immediately detectable.
- This is known as the "no-cloning theorem" and is a fundamental principle of quantum mechanics.
- Establishing a Secret Key: By exchanging a sequence of qubits, the transmitting and receiving parties can establish a secret key that can be used for secure communication.
- This key can be used with conventional encryption algorithms to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of transmitted information.
- Encoding Information: Information is encoded onto quantum bits (qubits), which can exist in multiple states simultaneously.
How Can Quantum Technology be useful In Maritime Communication?
- Secure Communication:
- Quantum encryption can be used to ensure secure communication between ships and shore stations, making it difficult for hackers to intercept or eavesdrop on the communication.
- High-speed Communication:
- Quantum technology can enable faster communication between ships and shore stations by using quantum entanglement to transmit information instantaneously over long distances.
- This could be particularly useful for communication in remote areas where traditional communication methods are limited.
- Quantum technology can enable faster communication between ships and shore stations by using quantum entanglement to transmit information instantaneously over long distances.
- Precision Navigation:
- Quantum sensors can be used to improve navigation accuracy by measuring the Earth's magnetic field with high precision.
- This could help ships navigate through narrow channels, avoid obstacles, and improve overall safety.
- Improved Weather Forecasting:
- Quantum computers can be used to run complex simulations of weather patterns, which can provide accurate and timely information to mariners about impending storms or other dangerous weather conditions.
Way Forward
- Implementing quantum communication technologies, such as QKD at scale is a major challenge as they are still in the early stages of development and implementation.
- Pilot projects can be established to test the technology in real-world settings and refine the implementation process.
- Quantum communication technologies are expensive to develop and deploy. Adequate funding for R&D could lead to more cost-effective solutions.
- Quantum communication technologies are not yet standardized, making it difficult for different systems to communicate with each other.
- Standards and protocols can be developed to enable different quantum communication systems to communicate with each other


Governance
Ranganath Report and Quota for Dalit Converts
For Prelims: Criterion for SC Status, Constitution (Scheduled Castes) Order of 1950, Registrar General of India.
For Mains: Criterion for SC Status and Arguments for and against the Inclusion of Dalit Christians and Muslims.
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court revisited a 2007 report by the Justice Ranganath Mishra Commission for Religious and Linguistic Minorities, which recommended Scheduled Caste (SC) reservation for Dalit converts to Christianity and Islam.
- The Centre had discredited the report, but the apex court believes it contains valuable information that could help determine if excluding Dalit converts from the SC category is unconstitutional according to the Constitution Order of 1950.
Note
- Rejecting the Mishra report, the government had recently constituted a new Commission headed by a former CJI K.G. Balakrishnan, giving it two years to prepare a report on the question of granting SC status to “new persons who have historically belonged to the Scheduled Castes but have converted to religions other than Hinduism, Buddhism and Sikhism”.
- For rejecting the report, the Centre has argued that “Dalits who converted to Christianity or Islam to overcome the burdens of caste cannot claim reservation benefits enjoyed by those who chose to stay back in the Hindu religious system”.
What are the Key Highlights of the Ranganath Report?
- The recommendation of Scheduled Caste reservation for Dalit converts to Christianity and Islam was made in the 2007 report of the Justice Ranganath Mishra Commission for Religious and Linguistic Minorities.
- Dalit Christians and Muslims face discrimination not only from upper-caste members of their own religion but also from the broader Hindu-dominated society.
- The exclusion of Dalit converts to Christianity and Islam from the SC category violates the constitutional guarantee of equality and is against the basic tenets of these religions, which reject caste discrimination.
- The denial of SC status to Dalit converts to Christianity and Islam has led to their socio-economic and educational backwardness and has deprived them of access to reservations in education and employment opportunities (as provided under article 16).
Who is Included in the Constitution Order of 1950?
- When enacted, the Constitution (Scheduled Castes) Order of 1950, initially provided for recognizing only Hindus as SCs, to address the social disability arising out of the practice of untouchability. However, the order also provided that every member of Ramdasi, Kabirpanthi, Mazhabi, or Sikligar caste resident in Punjab or the Patiala and East Punjab, be deemed to be a member of the Scheduled Castes whether he professes the Hindu or Sikh religion.
- The Order was amended in 1956 to include Dalits who had converted to Sikhism (in entirety) and once more in 1990 to include Dalits who had converted to Buddhism.
- Both amendments were aided by the reports of the Kaka Kalelkar Commission in 1955 and the High-Powered Panel (HPP) on Minorities, Scheduled Castes, and Scheduled Tribes in 1983 respectively.
- The 1950 Order (post amendments in 1956 and 1990), mandates that anybody who is not a Hindu, Sikh or Buddhist cannot be granted SC status.
Why are Dalit Christians and Muslims Excluded?
- Avoid Surge in SC Population: The Office of the Registrar General of India (RGI) had cautioned the government that SC status is meant for communities suffering from social disabilities arising out of the practice of untouchability, which it noted was prevalent in Hindu and Sikh communities.
- It also noted that such a move would significantly swell the population of SCs across the country.
- Diverse Ethnic Groups who Converted: In 2001, RGI stated that Dalits who converted to Islam or Christianity are not a single ethnic group as they belong to different caste groups.
- Therefore, they cannot be included in the list of Scheduled Castes (SC) as per Clause (2) of Article 341, which requires a single ethnic group for inclusion.
- Untouchability not Prelavent in Other Religions: The RGI further opined that since the practice of “untouchability” was a feature of the Hindu religion and its branches, allowing the inclusion of Dalit Muslims and Dalit Christians as SCs could result in being “misunderstood internationally” as India trying to “impose its caste system” upon Christians and Muslims.
- The 2001 note also stated that Christians and Muslims of Dalit origin had lost their caste identity by way of their conversion and that in their new religious community, the practice of untouchability is not prevalent.
What is the Registrar General of India?
- The Registrar General of India was founded in 1961 by the Government of India under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- It arranges, conducts, and analyses the results of the demographic surveys of India including the Census of India and Linguistic Survey of India.
- The position of Registrar is usually held by a civil servant holding the rank of Joint Secretary.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. In 2001, RGI stated that Dalits who converted to Islam or Christianity are not a single ethnic group as they belong to different caste groups. Therefore, they cannot be included in the list of Scheduled Castes (SC) as per Clause (2) of Article 341, which requires a single ethnic group for inclusion. (2014)
Q. Whether the National Commission for Scheduled Castes (NCSC) can enforce the implementation of constitutional reservation for the Scheduled Castes in the religious minority institutions? Examine. (2018)
International Relations
Changing Foreign Policy of Saudi Arabia
For Prelims: OPEC+, Neighboring countries of Saudi Arabia
For Mains: Implications of Saudi Arabia's New Foreign Policy, increasing influence of China in west asia
Why in News?
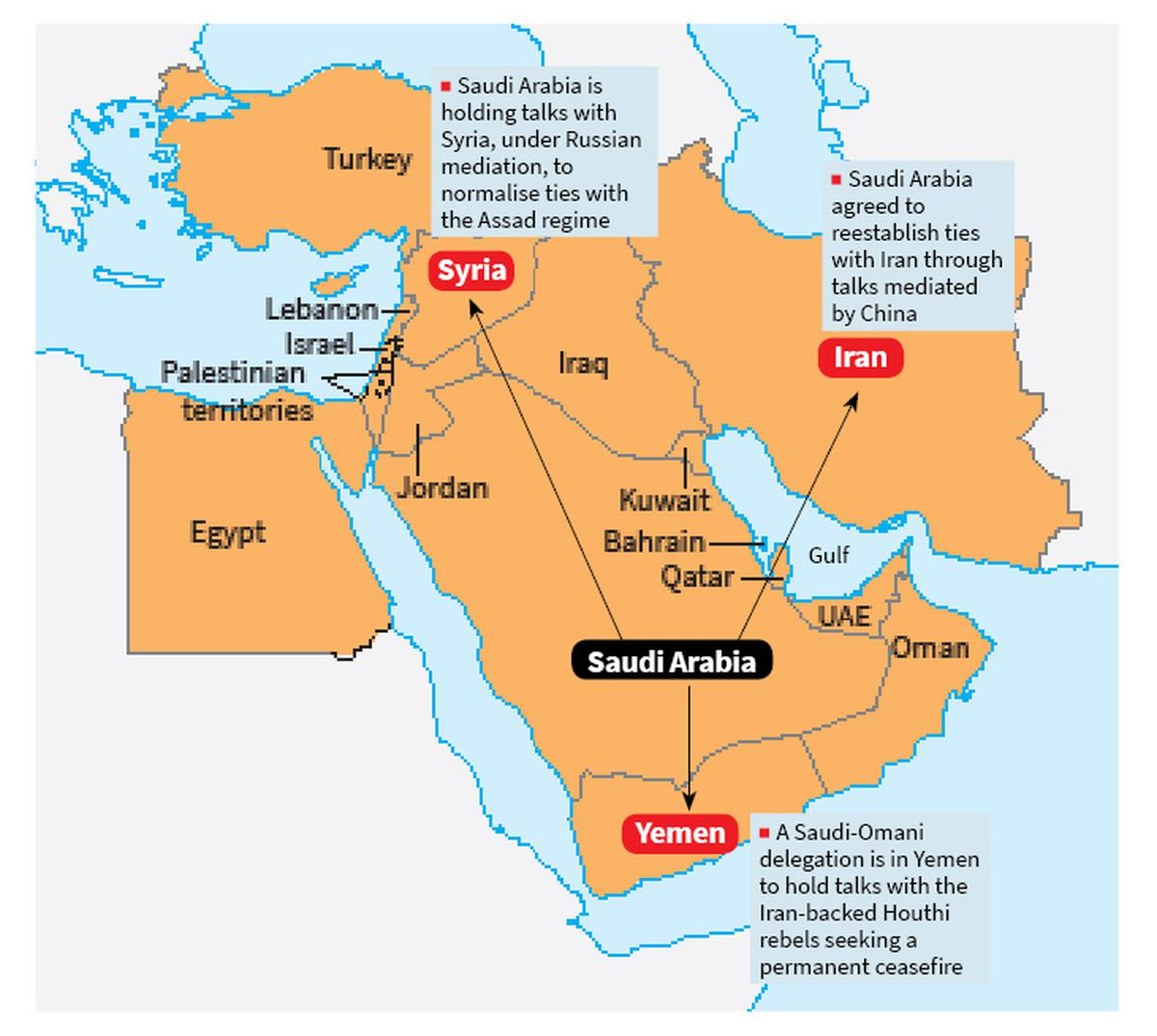
Saudi Arabia is making a significant shift in its foreign policy as it moves away from its aggressive stance towards Iran and seeks to create balance between great powers while also transforming its own economy.
How is Saudi Arabia's Foreign Policy Changing?
- Changing Stance Towards Iran:
- Saudi Arabia's foreign policy had always centered around Iran, resulting in proxy conflicts across the region. It's stance, in the past, has always been aggressive towards Iran.
- However, recently Saudi Arabia announced a deal, after China-mediated talks to normalise diplomatic ties with Iran.
- There has been a shift from strategic rivalry and proxy conflicts to tactical de-escalation and mutual coexistence with Iran.
- Balancing Ties with Global Powers:
- Saudi Arabia has also been trying to balance between the US, its largest arms supplier, Russia, its OPEC-Plus partner, and China, the new superpower in the region.

- Saudi Arabia has also been trying to balance between the US, its largest arms supplier, Russia, its OPEC-Plus partner, and China, the new superpower in the region.
- Reason for Change in Policy:
- Recent regional bets were either unsuccessful or only partially successful.
- Failed regional policies such as for Syria and Yemen, where the Saudi intervention failed to deter the Iran-backed Houthi rebels.
- Also, the Houthis, with their drones and short-range missiles, now pose a serious security threat to Saudi Arabia.
- The US's priority is shifting away from West Asia.
- US's deprioritisation of West Asia, making Saudi Arabia realise that it needs to establish its own autonomy by building loyal alliances with other great powers.
- China, which has good ties with both Iran and Saudi Arabia, offered to mediate between the two, and the Saudi seized the opportunity.
- Recent regional bets were either unsuccessful or only partially successful.
- Implications on US-Saudi Relations:
- Saudi's changing foreign stance, however, does not mean that it is moving away from the US.
- The country remains Saudi Arabia's largest defence supplier and plays a major security role in the region.
- Saudi Arabia is also trying to develop advanced missile and drone capabilities to counter Iran's edge in these areas with help from the US and others.
- It is rather, just trying to use the vacuum created by the U.S. policy changes to autonomize its foreign policy.
- The country remains Saudi Arabia's largest defence supplier and plays a major security role in the region.
- US’ Response: Though the U.S. has publicly welcomed the Saudi-Iran rapprochement, it raised its concerns to the Crown Prince of Saudi about being “blindsided” on the Iran deal.
- The US largely remained as a spectator in China and Russia led mediation talks, especially considering its huge military presence in the region and the fact that the US had been part of almost all major realignments.
- Saudi's changing foreign stance, however, does not mean that it is moving away from the US.
How will Saudi's Changing Policy Affect the Region?
- Saudi Arabia's talks with Syria and the Houthis are part of a bigger picture of Saudi-Iran rapprochement.
- Ending the Yemen war through a settlement with the Houthis would give Saudi a calmer border and allow Iran to retain influence in Saudi's backyard.
- These agreements could bring some stability across the Gulf, but tensions between Israel and Iran could impact this.
- Saudi also needs to maintain autonomy without irking the US, who may not be happy with Syria being re-accommodated into the West Asian mainstream.
What is at Stake for India?
- Saudi Arabia is an important player in the Middle East, and any significant changes in its foreign policy could impact India's relations with other countries in the region.
- It can lead to creation of China-Pakistan-Saudi Arabia.
- India maintains cordial relations with both Iran and Saudi Arabia and plays a role in maintaining peace and stability in the region.
- Normalizing ties between these two countries could help India in its efforts to promote peace and security in the region.
- However, Chinese mediation between Iran and Saudi will create challenges for India as it will contribute to increasing Chinese influence in the region.
- India needs to be vigilant about the increasing Chinese influence in the region and work towards securing its strategic interests in the Middle East.


Governance
Agnipath Scheme and Doctrine of Promissory Estoppel
For Prelims: Supreme Court, Agnipath Scheme, Doctrine of Promissory Estoppel
For Mains: Supreme Court’s Stand on Doctrine of Promissory Estoppel
Why in News?
The Supreme Court has recently dismissed petitions challenging the Delhi HC’s judgement that upheld the Agnipath scheme for recruitment to the armed forces.
- An argument on Doctrine of Promissory Estoppel was floated in the Supreme Court related to petitions of shortlisted candidates in the earlier recruitment process to Army and Air Force which was cancelled when Agnipath scheme was notified.
What is the Doctrine of Promissory Estoppel?
- About:
- Promissory estoppel is a concept developed in contractual laws. It prevents a “promisor” from backing out of an agreement on the grounds that there is no “consideration.”
- The doctrine is invoked in court by a plaintiff (the party moving court in a civil action) against the defendant to ensure the execution of a contract or seek compensation for failure to perform the contract.
- Related Case:
- In the Chhaganlal Keshavalal Mehta v. Patel Narandas Haribhai (1981) case, the Supreme Court listed out a checklist for when the doctrine can be applied.
- Firstly, there must be a clear and unambiguous promise.
- Secondly, the plaintiff must have acted relying reasonably on that promise.
- Thirdly, the plaintiff must have suffered a loss.
- In the Chhaganlal Keshavalal Mehta v. Patel Narandas Haribhai (1981) case, the Supreme Court listed out a checklist for when the doctrine can be applied.
- Current Stance of SC over Agnipath Petition:
- The Supreme Court pointed out that “promissory estoppel is always subject to overarching public interest”.
- It also added that “this is not a contract matter where promissory estoppel in public law was applied, it is a public employment” and that “the question of applying this principle will not arise in this case”.
- The Supreme Court pointed out that “promissory estoppel is always subject to overarching public interest”.
What is the Agnipath Scheme?
- About:
- It allows patriotic and motivated youth to serve in the Armed Forces for a period of four years.
- The youth joining the army will be called Agniveer.
- Under the new scheme, around 45,000 to 50,000 soldiers will be recruited annually.
- However, after four years, only 25% of the batch will be recruited back into their respective services, for a period of 15 years.
- It allows patriotic and motivated youth to serve in the Armed Forces for a period of four years.
- Objectives:
- It is expected to bring down the average age profile of the Indian Armed Forces by about 4 to 5 years.
- The scheme envisions that the average age in the forces is 32 years today, which will go down to 26 in six to seven years.
- It is expected to bring down the average age profile of the Indian Armed Forces by about 4 to 5 years.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- It is only for personnel below officer ranks (those who do not join the forces as commissioned officers).
- Commissioned officers are the army's highest ranked officers. They hold an exclusive rank in the Indian armed forces. They often hold a commission under the president's sovereign power and are officially instructed to protect the country.
- Aspirants between the ages of 17.5 years and 23 years will be eligible to apply.
- It is only for personnel below officer ranks (those who do not join the forces as commissioned officers).
- Benefits for Agniveers:
- Upon the completion of the 4-years of service, a one-time ‘Seva Nidhi’ package of Rs 11.71 lakhs will be paid to the Agniveers that will include their accrued interest thereon.
- They will also get a Rs 48 lakh life insurance cover for the four years.
- In case of death, the payout will be over Rs 1 crore, including pay for the unserved tenure.
- The government will help rehabilitate soldiers who leave the services after four years. They will be provided with skill certificates and bridge courses.
- Upon the completion of the 4-years of service, a one-time ‘Seva Nidhi’ package of Rs 11.71 lakhs will be paid to the Agniveers that will include their accrued interest thereon.


Important Facts For Prelims
Dark Matter
Why in News?
Recently, researchers have created a detailed map of the invisible dark matter that makes up 85% of the universe.
What do the Findings Suggest?
- The new findings align with the standard model of cosmology based on Einstein's theory of gravity.
- The researchers used the Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT) to map dark matter using light from the early universe, known as the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation.
- They used the CMB radiation to map dark matter by observing how it interacts with the gravity of massive objects like galaxy clusters and lumps of dark matter.
- The gravitational field generated by these objects bends and distorts the light that passes through them, which helps in detecting dark matter.
What is Dark Matter?
- About:
- Dark matter is a hypothetical form of matter that is believed to exist in the universe but is invisible and does not interact with light.
- Importance of Dark Matter:
- Dark matter is essential to explaining the observed structure of the universe.
- It helps to account for the distribution of matter in galaxies and the cosmic web. Understanding dark matter is important for developing a complete understanding of the universe and its evolution.
- Dark Energy:
- It is a type of energy that is thought to be responsible for the accelerating expansion of the universe.
- It is a form of energy that fills the entire universe and exerts a negative pressure, pushing galaxies and other matter away from each other.
- Dark energy is estimated to make up about 68% of the total energy content of the universe.
- It is a type of energy that is thought to be responsible for the accelerating expansion of the universe.
- Evidence Related to Dark Matter:
- There is strong indirect evidence, as reflected in various levels like distance scales:
- For example, as we move from the centre of the galaxy to its periphery, there is a significant disparity between the observed plot of star speeds and their estimated figure.
- This implies that the galaxy has a significant amount of dark matter.
- Other Distance Scale Evidence:
- There are Bullet clusters of galaxies that are formed through the merging of two galaxies, as per scientists their merger could only be explained through the presence of some dark matter.
- There is strong indirect evidence, as reflected in various levels like distance scales:
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In the context of modern scientific research, consider the following statements about ‘IceCube’, a particle detector located at South Pole, which was recently in the news: (2015)
- It is the world’s largest neutrino detector, encompassing a cubic kilometre of ice.
- It is a powerful telescope to search for dark matter.
- It is buried deep in the ice.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)


Important Facts For Prelims
Solar Energy Corporation of India Limited
Why in News?
Recently, the Solar Energy Corporation of India Limited (SECI) has been recognized as a Miniratna Category-I Central Public Sector Enterprise (CPSE) by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Govt. of India.
What is Solar Energy Corporation of India Limited?
- About:
- SECI was incorporated in 2011 and serves as the primary implementing agency of the MNRE for Renewable Energy schemes/projects towards fulfilling India's international commitments.
- Achievement:
- SECI has already awarded Renewable Energy (RE) project capacities of over 56 GW and is also involved in setting up of projects through its own investments and for other public sector entities as Project Management Consultant (PMC).
- SECI has also achieved the highest credit rating of AAA by ICRA.
- SECI has already awarded Renewable Energy (RE) project capacities of over 56 GW and is also involved in setting up of projects through its own investments and for other public sector entities as Project Management Consultant (PMC).
- Contribution to Solar Sector:
- SECI has also played a key role in the development of innovative solar power technologies, such as floating solar power plants and solar-wind hybrid systems.
- It has been involved in the auction of large-scale solar projects, which has attracted significant investments from domestic and international players.
- In addition, SECI has implemented various initiatives to promote the use of solar energy in rural and remote areas of the country, such as off-grid solar power projects and solar pumps for irrigation.
- These initiatives have helped to improve the quality of life of people living in these areas by providing access to clean energy.
- SECI has also played a key role in the development of innovative solar power technologies, such as floating solar power plants and solar-wind hybrid systems.
What are the Criteria for Miniratna Status for CPSEs?
- Miniratna Category-I Status: The CPSEs which have made profit in the last three years continuously, pre-tax profit is Rs.30 crores or more in at least one of the three years and have a positive net worth are eligible to be considered for grant of Miniratna-I status.
- Miniratna Category-II Status: The CPSEs which have made profit for the last three years continuously and have a positive net worth are eligible to be considered for grant of Miniratna-II status.
- Miniratna CPSEs should have not defaulted in the repayment of loans/interest payment on any loans due to the Government.
- Miniratna CPSEs shall not depend upon budgetary support or Government guarantees.


Important Facts For Prelims
International Aviation Safety Assessment
Why in News?
The aviation safety regulator of the U.S. - the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), has retained the “Category 1” status for India’s aviation safety oversight following a review.
What is the International Aviation Safety Assessment?
- About:
- The FAA conducted the International Aviation Safety Assessment (IASA) program over a one-year period, which included physical audits and a further review in 2022.
- The program focuses on three broad areas:
- Personnel licensing
- Operation of aircraft
- Airworthiness of aircraft
- This assessment determines whether a country’s aviation safety oversight standards comply with the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) safety standards.
- Findings about India:
- The FAA has informed the DGCA (Directorate General of Civil Aviation) that India meets the international standards for aviation safety oversight of the Chicago Convention and its Annexes and continues to retain FAA IASA Category 1 status which was last assessed in July 2018.
- The countries listed under ‘Category-1’ meet the ICAO standards for safety oversight of civil aviation.
- The FAA has informed the DGCA (Directorate General of Civil Aviation) that India meets the international standards for aviation safety oversight of the Chicago Convention and its Annexes and continues to retain FAA IASA Category 1 status which was last assessed in July 2018.
- Significance of Findings for India:
- It reaffirms India's reputation as a safe and reliable aviation market.
- It allows Indian airlines to continue to operate flights to the U.S. and enter into codeshare partnerships with U.S. carriers, which can help to increase trade and investment.
- It demonstrates India's commitment to complying with safety standards established by the UN aviation watchdog, ICAO.
What is the International Civil Aviation Organisation?
- ICAO is a United Nations (UN) specialized agency, established in 1944, which laid the foundation for the standards and procedures for peaceful global air navigation.
- The Convention on International Civil Aviation was signed on 7th December 1944 in Chicago (hence called Chicago Convention 1944).
- It established the core principles permitting international transport by air, and also led to the creation of the ICAO.
- It covers a wide range of issues, including the rights of aircraft in international airspace, the registration of aircraft, safety standards, air traffic control, and environmental protection.
- One of the objectives of ICAO is to foster the planning and development of international air transport so as to ensure the safe and orderly growth of international civil aviation throughout the world.
- India is among its 193 members.
- It is headquartered in Montreal, Canada.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
GI Tag for Cumbum Grapes
Tamil Nadu’s famous Cumbum Panneer Thratchai, also known as Cumbum grapes recently earned the Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
The Cumbum Valley located at the Western Ghats in Tamil Nadu is known as the ‘Grapes City of South India’ and cultivates the Panneer Thratchai. This variety, also known as Muscat Hamburg, is popular for its quick growth and early maturity, ensuring that the crop is available in the market almost throughout the year.
The Panneer grapes were first introduced in Tamil Nadu by a French priest in 1832 and are rich in vitamins, tartaric acid and antioxidants and reduce the risk of some chronic diseases. They are also known for a superior taste apart from the purplish brown-colour.
A GI is a sign used on products that have a specific geographical origin and possess qualities or a reputation that are due to that origin. The Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 seeks to provide for the registration and better protection of geographical indications relating to goods in India. It is governed and directed by the WTO Agreement on TRIPS.
Read More: GI Tag
Quality Control Orders
Recently, the Ministry of Textiles announced two Quality Control Orders (QCOs) for 31 items, comprising geo-textiles and protective textiles, following the due process of notification of technical regulations. As per the Ministry, these orders mark the first technical regulation from India for the technical textiles industry.
Geo-textiles are used for infrastructure projects and environmental applications while protective textiles are used to protect human life from hazardous and adverse working conditions.
QCOs will ensure the standard and quality of Technical Textiles and encourage the growth of this industry in India in producing quality products at competitive pricing.
The QCOs will come into force 180 days after the date of its publication in the Official Gazette. The conformity assessment requirements specified in these QCOs are equally applicable to domestic manufacturers as well as foreign manufacturers who intend to export their products to India.
Read More: National Technical Textiles Mission (NTTM), India’s Textile Sector
Graphene and Magnetoresistance
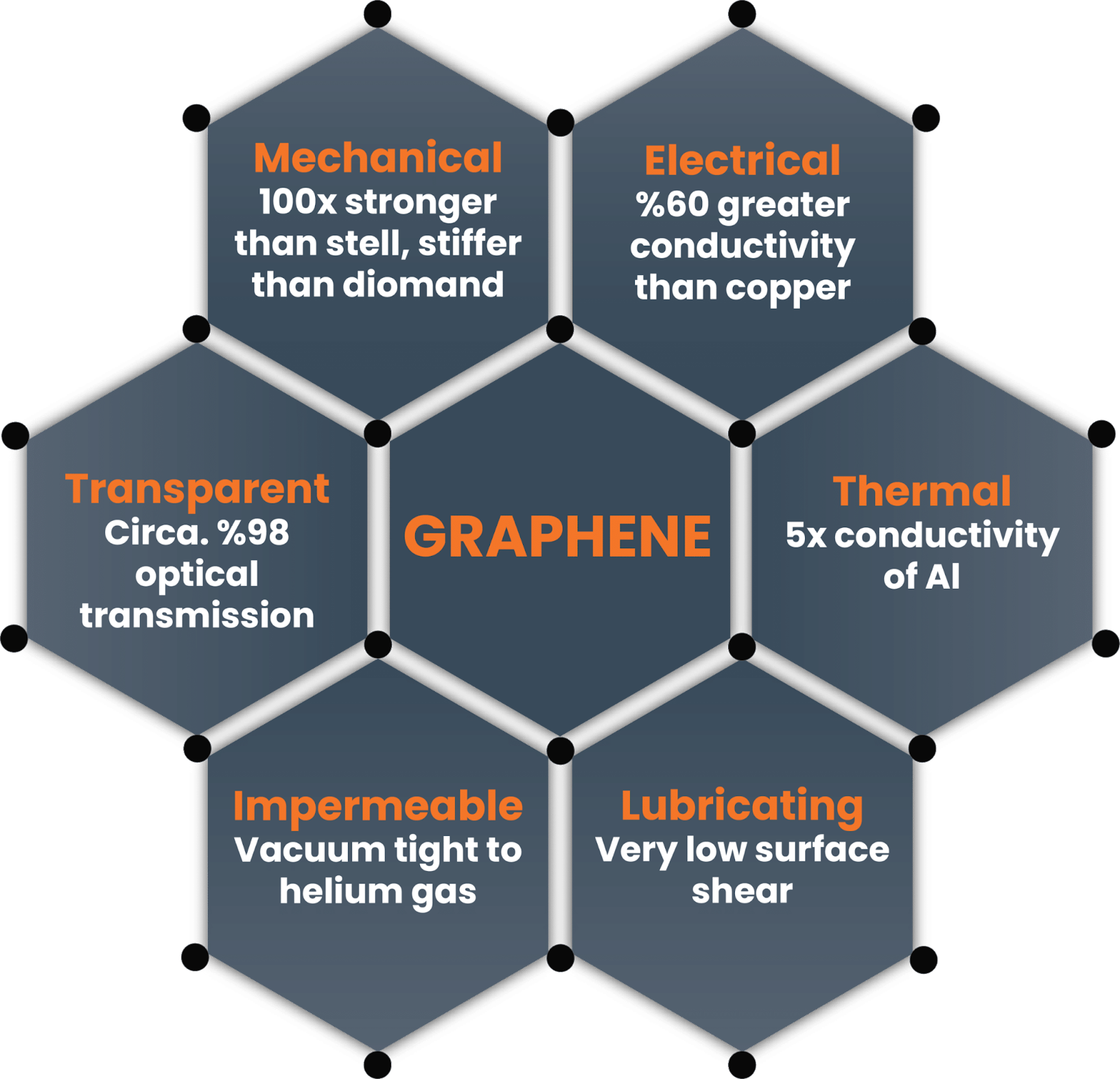
Another property of graphene has been discovered by UK researchers. At room temperature, it exhibits an anomalous giant magnetoresistance (GMR).
The GMR phenomenon occurs when adjacent magnetic fields influence the electrical resistance of a conductor. It is used in hard disk drives and magnetoresistive RAM in computers, biosensors, automotive sensors, microelectromechanical systems, and medical imagers. GMR-based devices are particularly used to sense magnetic fields.
The new study has found that Graphene-based devices do not require very low temperatures in order to sense these fields, in contrast to their conventional ferromagnetic counterparts.
Graphene is a one-atom-thick layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. It is the building-block of Graphite. It is the thinnest, most electrically and thermally conductive material in the world, while also being flexible, transparent and incredibly strong. Graphene is also known as a wonder material due to its vast potential in the energy and medical world.
Read More: India’s First Graphene Innovation Centre
Indelible Ink
As Karnataka prepares for Assembly elections, Mysore Paints & Varnish Ltd. in Mysuru is again in news as the latter is the only company authorised to produce the indelible ink used in general elections in India.
The Maharaja of Mysore Nalwadi Krishnaraja Wodeyar established the factory in 1937 to provide employment for people and for utilisation of natural resources from the forests nearby. In 1962, it was selected to manufacture indelible ink, which was first used in the country’s third general election. From then till now, the company has supplied the ink for every election across India. It has also exported ink to other countries. The unit was converted into a public limited company in 1947, as one of the important public sector companies of Karnataka.
Indelible ink, which is also known as the 'voter's ink' ensures that no eligible voter votes twice in an election and hence plays a key role in avoiding fraudulent and multiple voting.
Read More: Free and Fair Elections