International Relations
India & Gulf Countries
- 07 Jun 2022
- 11 min read
For Prelims: Types of Trade Agreements, India & Gulf Countries
For Mains: India and its Neighbourhood, Bilateral Groupings & Agreements, Significance of Indian-Gulf Relations
Why in News?
Recently, Indian Vice President visited Qatar, which is one of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Countries (Bahrain, Kuwait, Qatar, Oman, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE), where he highlighted the strength of India-Qatar ties and called for building an enabling environment and forging more collaborations for mutual benefit.
What are the Key Highlights of the Vice President’s Visit to Qatar?
- India-Qatar Start Up bridge:
- The Vice President launched the “India-Qatar Start Up bridge” that aims to link the start-up ecosystems of the two countries.
- India has emerged as the 3rd largest ecosystem for startups globally, with over 70,000 registered Startups.
- India is home to 100 unicorns with a total valuation of over USD 300 billion.
- The Vice President launched the “India-Qatar Start Up bridge” that aims to link the start-up ecosystems of the two countries.
- Environment and Climate Change:
- India has been making sustained efforts for the protection of environment and combating climate change.
- He recalled India’s leadership in establishing the International Solar Alliance (ISA) and increasing the thrust on renewable energy.
- He invited Qatar, as India’s trusted partner in its energy security, to be a partner in this journey for sustainability and join the ISA.
- Joint Business Council Between Business Chambers:
- He expressed happiness that a Joint Business Council between Business Chambers of India and Qatar has been established and that a Joint Task Force on Investments would take its work forward.
- He also complimented Invest India and Qatar Investment Promotion Agency for entering into a partnership of guiding and assisting businesses on both sides to tap new and emerging opportunities.
- Collaborations at Multilateral Forums:
- He called for more collaboration between India and Qatar at multilateral forums like the Inter Parliamentary Union (IPU), Asian Parliamentary Assembly, and others.
Why is the Gulf Region Crucial for India?
- India has enjoyed centuries of good relations with countries like Iran, while smaller gas-rich nation Qatar is one of India’s closest allies in the region.
- India shares good relations with most of the countries in the Gulf.
- The two most important reasons for the relationship are oil and gas, and trade.
- Two additional reasons are the huge number of Indians who work in the Gulf countries, and the remittance they send back home.
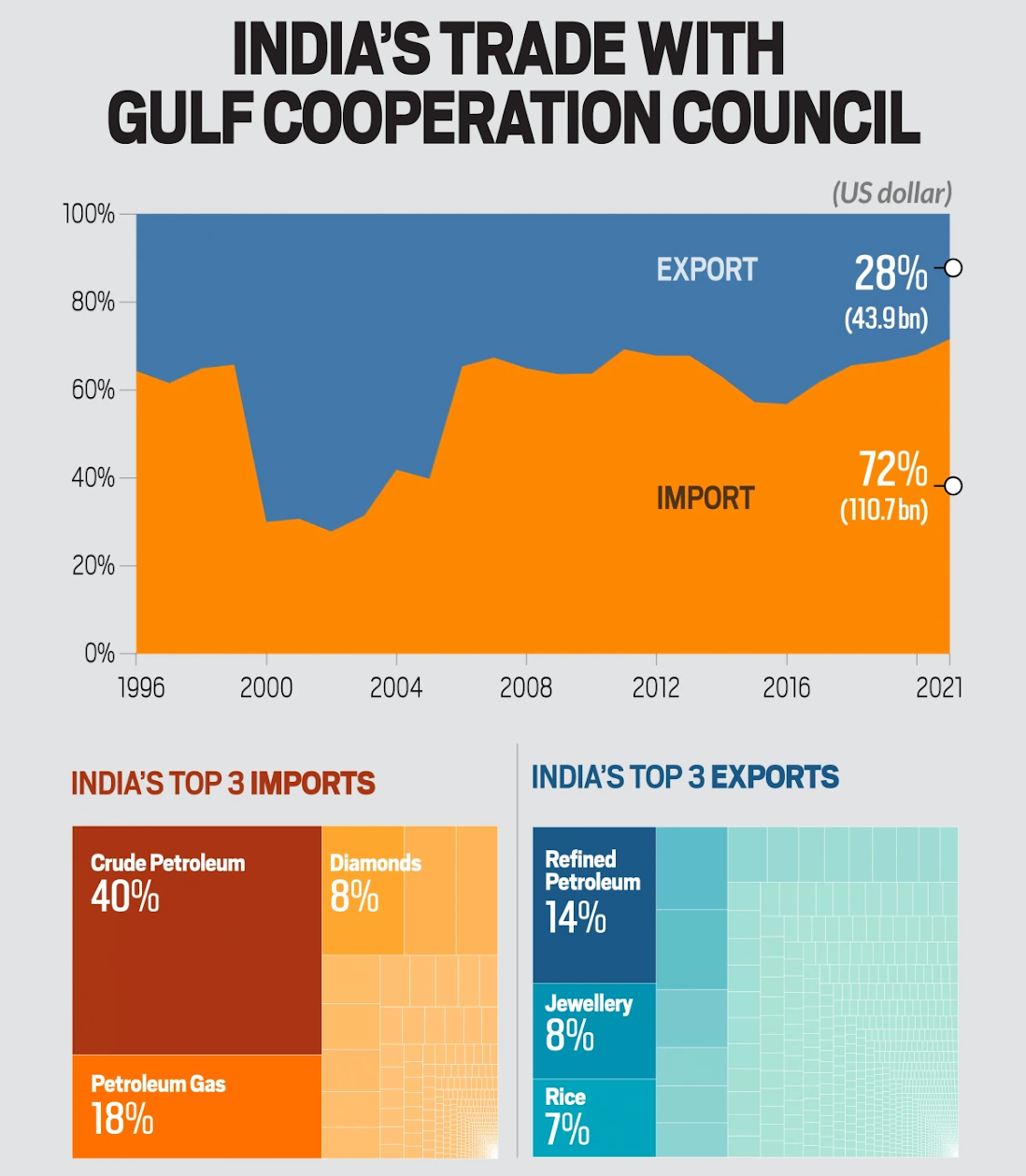
How much trade does India do with countries in this region?
- UAE:
- The UAE was India’s third largest trading partner in 2021-2022, and second largest for both exports (USD 28 billion) and imports (USD 45 billion) when these are counted individually.
- In terms of total trade volume, the UAE (USD 72.9 billion) was behind the United States (USD 1.19 trillion) and China (USD 1.15 trillion).
- The UAE accounted for 6.6% of India’s total exports and 7.3% of imports in the last financial year, up 68.4% since the previous year when international trade was impacted by the pandemic.
- Saudi Arabia:
- At a total volume of USD 42.9 billion in 2021-22, Saudi Arabia was India’s fourth largest trading partner.
- While exports were low at USD 8.76 billion (2.07% of India’s total exports), imports from Saudi Arabia were the fourth largest at USD 34.1 billion (7%), up 50% from the previous year. Most of it was crude oil.
- Iraq:
- It was India’s fifth largest trading partner in 2021-22 at USD 34.3 billion.
- Qatar:
- The total trade was USD 15 billion, accounting for just 1.4% of India’s total trade, but the country is India’s most important supplier of natural gas.
- Qatar accounts for 41% of India’s total natural gas imports.
- The UAE accounts for another 11%.
- Oman:
- For Oman, India was the 3rd largest (after UAE and China) source for its imports and 3rd largest market (after UAE and Saudi Arabia) for its non-oil exports in 2019.
- Major Indian financial institutions have a presence in Oman. Indian companies have invested in Oman in sectors like iron and steel, cement, fertilisers, textile etc.
How much oil does India import?
- The 239 million tonnes of oil petroleum imports were worth USD 77 billion and accounted for nearly one-fifth of the country’s total imports in 2021.
- The share of Persian Gulf countries in India’s crude imports has remained at around 60% over the last 15 years.
- In 2021-2022, the largest exporter of oil to India was Iraq, whose share has gone up from 9% in 2009-2010 to 22%.
- Saudi Arabia has accounted for 17-18% of India’s oil imports for over a decade. Kuwait and UAE remain major oil exporters to India. Iran used to be the second largest oil exporter to India in 2009-2010, its share went down to less than 1% in 2020-21, due to US sanctions.
What is the Scenario of Indians in the Gulf and the Remittances?
- More than 13.46 million Indian citizens work abroad. If Persons of Indian Origin (those who have taken up citizenship of other countries, and their descendants) are added, this number goes up to over 32 million.
- Counting only the 13.4 million non-resident Indians (NRIs), the Gulf has the largest numbers.
- The UAE (3.42 million), Saudi Arabia (2.6 million) and Kuwait (1.03 million) together account for over half of all NRIs.
- In terms of remittances from abroad, India was the largest recipient in 2020 at USD 83.15 billion, according to World Bank data.
- This was nearly twice the remittances to the next highest recipient, Mexico, at USD 42.9 billion.
- The largest contributor is the huge Indian diaspora in the Gulf.
- The UAE accounted for 26.9%, Saudi Arabia for 11.6%, Qatar for 6.4%, Kuwait for 5.5% and Oman for 3%. Beyond the GCC, remittances from the US accounted for 22.9%, second only to the UAE.
What are Recent Developments?
- Recently, India and Oman signed a Programme of Cooperation (POC) in the fields of Science and Technology for the period 2022 – 2025.
- The POC for Cooperation in the fields of Science and Technology was signed in pursuance of the Agreement for Cooperation in Science and Technology(S&T) concluded on 5th October, 1996 between Oman and India.
- In September 2021, India and the UAE formally launched negotiations on the India-UAE Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA).
- In 2021, the Indian External Affairs Minister met the Foreign Minister of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, where both countries discussed bilateral cooperation in multilateral forums such as the United Nations, G-20 and Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC).
- In 2021, India and Bahrain agreed to strengthen their historic ties, including in areas of defence and maritime security.
- In 2020, the legal and legislative committee of Kuwait’s National Assembly approved the draft expat (expatriate) quota bill.
- According to the bill, Indians should not exceed 15% of the population and if it is enacted into law, over 8 lakh Indians could be forced out of Kuwait.
Way Forward
- There is a need to focus on the new and long-term possibilities for economic cooperation with the Gulf countries, which is looking at a future beyond oil.
- The Gulf states have embarked on massive economic diversification and are investing in a variety of new projects including renewable energy, higher education, technological innovation, smart cities, and space commerce.
- With the rise of Khaleeji capitalism, the Gulf countries today deliver economic and security assistance to friendly states, build ports and infrastructure, acquire military bases and broker peace between warring parties and states.
- The UAE currently chairs the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) and has been eager to work with India in developing joint infrastructure projects.
- India needs to bring scale and depth to its regional initiatives on connectivity and security in the Indian Ocean.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Q. Which of the following is not a member of ‘Gulf Cooperation Council’? (2016)
(a) Iran
(c) Oman
(b) Saudi Arabia
(d) Kuwait
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) is an alliance of 6 countries in the Arabian Peninsula – Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. Iran is not a member of the GCC.
- It was established in 1981 to promote economic, security, cultural and social cooperation between the members and holds a summit every year to discuss cooperation and regional affairs.
- Hence, option (a) is the correct answer.