Indian and Chinese Troops Clash in Arunachal Pradesh
For Prelims: Location of Tawang Sector, Arunachal Pradesh
For Mains: Issues in India - China relations and the Solution
Why in News?
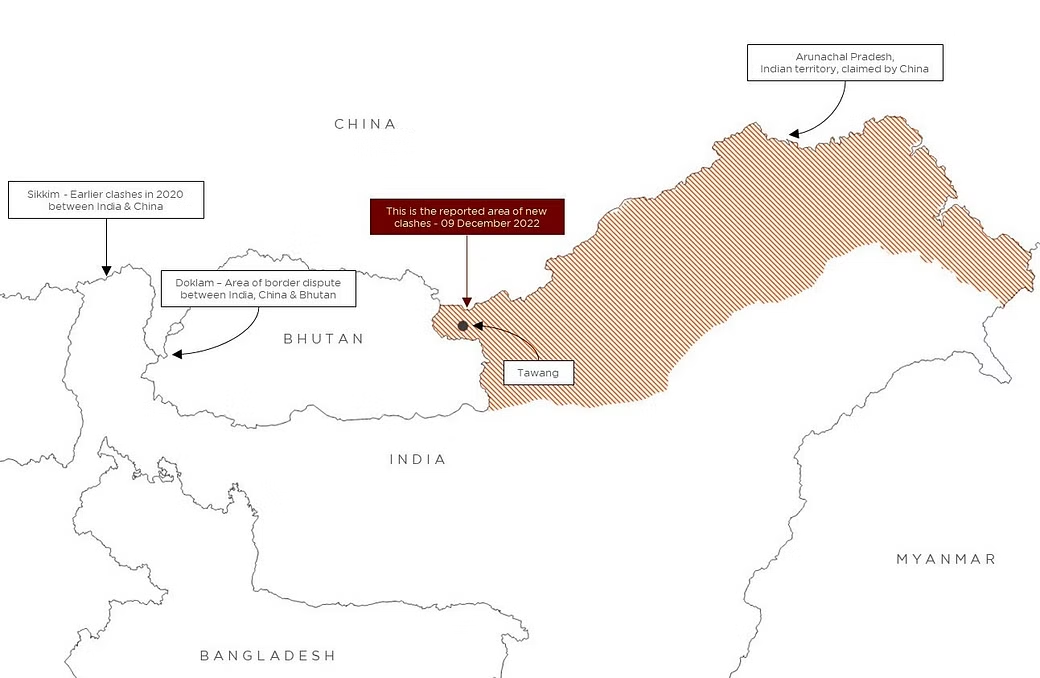
Recently, India and China troops clashed along the Yangste river in Tawang sector in Arunachal Pradesh.
- This was the first such incident involving the Indian soldiers and Chinese PLA troops since the Galwan Valley incident in 2020.
- Both sides patrol areas up to their claim lines and this has been a trend since 2006.
What is the Background?
- According to the India Army, there are certain areas along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) in the Tawang Sector that are areas of differing perception.
- The LAC is divided into western (Ladakh), middle (Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand), Sikkim, and eastern (Arunachal Pradesh) sectors.
- The incident came days after China expressed objection to Operation Yudhabhyas, an India-US joint military exercise at Auli in the Uttarakhand hills, claiming it was a violation of 1993 and 1996 border agreements.
What is the Importance of Arunachal Pradesh from an Indian/Chinese Perspective?
- Strategic Significance:
- Arunachal Pradesh, known as the Northeast Frontier Agency (NEFA) until 1972, is the largest state in the northeast and shares international borders with Tibet to the north and northwest, Bhutan towards the west and Myanmar to the east.
- The state is like a protective shield to the northeast.
- However, China claims Arunachal Pradesh as a part of southern Tibet.
- And while China may lay claim to the entire state, its main interest lies in the district of Tawang, which is in the north-western region of Arunachal and borders Bhutan and Tibet.
- Bhutan Factor:
- Taking control of Arunachal would mean that Bhutan would have Chinese neighbours on both its western and eastern borders if Beijing gained control.
- On the western side of Bhutan, China has already begun building motorable roads linking strategic points.
- Taking control of Arunachal would mean that Bhutan would have Chinese neighbours on both its western and eastern borders if Beijing gained control.
- Waterpower:
- Since, China has control over India's water supply to the northeastern region. It has constructed several dams and can use water as a geo-strategic weapon against India by causing flooding or drought in the region.
- The Tsangpo river, which originates in Tibet, flows into India and is called Siang in Arunachal Pradesh before it becomes the Brahmaputra.
- In 2000, a dam breach in Tibet caused floods that wreaked havoc in northeast India claiming 30 lives and leaving more than 100 missing.
Why is China Interested in the Tawang Sector?
- Strategic Importance:
- China's interest in Tawang could be for tactical reasons as it provides a strategic entry into India's northeastern region.
- Tawang is a critical point in the corridor between Tibet and Brahmaputra Valley.
- China's interest in Tawang could be for tactical reasons as it provides a strategic entry into India's northeastern region.
- Tawang Monastery:
- Tawang, which also borders Bhutan, hosts the Galden Namgey Lhatse, the world's second-largest monastery of Tibetan Buddhism, the largest being the Potala Palace in Lhasa.
- The monastery was founded by Merag Lodroe Gyamtso in the year 1680-81 to honour the wishes of the fifth Dalai Lama.
- China claims that the monastery is evidence that the district once belonged to Tibet. They cite historical ties between the Tawang monastery and the Lhasa monastery in Tibet to support their claim over Arunachal.
- Tawang, which also borders Bhutan, hosts the Galden Namgey Lhatse, the world's second-largest monastery of Tibetan Buddhism, the largest being the Potala Palace in Lhasa.
- Cultural Connections and China’s Anxieties:
- Tawang is an important center of Tibetan Buddhism and there are some tribes in the upper Arunachal region which have cultural connections to the people of Tibet.
- The Monpa tribal population practices Tibetan Buddhism and are also found in some areas of Tibet.
- According to some experts, China fears that the presence of these ethnic groups in Arunachal could at some stage give rise to a pro-democracy Tibetan movement against Beijing.
- Tawang is an important center of Tibetan Buddhism and there are some tribes in the upper Arunachal region which have cultural connections to the people of Tibet.
- Political Significance:
- When the Dalai Lama escaped Tibet in 1959 amid China crackdown, he entered India through Tawang and stayed in the Tawang monastery for some time.
Way Forward
- India needs to be vigilant enough for any new development in China near its border to protect its interests efficiently.
- Further, it needs to build robust Infrastructure in difficult border areas in its territory to ensure movement of personnel and other logistical supplies in an efficient manner.
- Border troops should continue their dialogue, quickly disengage, maintain proper distance and ease tensions.
- The two sides should abide by all the existing agreements and protocols on China-India boundary affairs and avoid any action that could escalate matters.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. “The USA is facing an existential threat in the form of China, that is much more challenging than the erstwhile Soviet Union.” Explain. (2021)
Q. “China is using its economic relations and positive trade surplus as tools to develop potential military power status in Asia”. In the light of this statement, discuss its impact on India as her neighbour. (2017)
National Energy Conservation Day 2022
For Prelims: Bureau of Energy Efficiency, Energy Conservation Day, global warming, climate change
For Mains: Scenario of the Power Sector of India and related Initiatives
Why in News?
National Energy Conservation Day is celebrated every year on 14th December 2022.
What do we celebrate Energy Conservation Day?
- Background:
- The Ministry of Power, Government of India, launched the National Energy Conservation Awards in 1991 to recognise the contribution of industries and establishments in reducing energy consumption while maintaining their production through awards.
- The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) spearheads the celebrations every year.
- The first time the awards were given away was on 14th December, 1991.
- Since then, the day has been declared as National Energy Conservation Day. These awards are given away by eminent dignitaries at a function organised every year on the same day.
- The Ministry of Power, Government of India, launched the National Energy Conservation Awards in 1991 to recognise the contribution of industries and establishments in reducing energy consumption while maintaining their production through awards.
- Objective:
- The day focuses on making people aware of global warming and climate change and promotes efforts towards saving energy resources. It also highlights the achievements of the country in the fields of energy efficiency and conservation.
- Main attractions of India’s Celebration:
- National Energy Efficiency Innovation Awards (NEEIA) 2022:
- To recognize outstanding work and innovative minds of India in the area of Energy Efficiency, NEEIA awards were started in the year 2021.
- The awards are evaluated based on Replicability, Affordability, Reliability, Impact on Energy Savings and Impact on Environment & Sustainability.
- Launch of ‘EV-Yatra portal’ and Mobile App:
- The Bureau of Energy Efficiency has developed a mobile application titled “EV Yatra” that has been designed and developed to facilitate in-vehicle navigation to the nearest public EV charger and a web-portal to enable Charging Point Operators (CPOs) to register their charging details securely into the National Online Database.
- National Energy Efficiency Innovation Awards (NEEIA) 2022:
What is Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE)?
- The BEE is a statutory body established through the Energy Conservation Act, 2001 under the Union Ministry of Power.
- It assists in developing policies and strategies with the primary objective of reducing the energy intensity of the Indian economy.
- BEE coordinates with designated consumers, designated agencies, and other organizations to identify and utilize the existing resources and infrastructure, in performing its functions.
What is Energy Conservation?
- It refers to the efforts made to ensure that energy is used efficiently by either using less energy for a particular constant purpose – like switching off lights and fans when not being used – or reducing the use of a particular service that uses energy – like driving less and using public transport instead.
- Energy conservation is a conscious, individual effort, and at a macro level, it leads to energy efficiency.
- The end goal of energy conservation is to reach sustainable energy.
- It is different from the term ‘energy efficiency’, which is using technology that requires less energy to perform the same function.
What is the Scenario of the Power Sector of India?
- Overall Capacity: India is the third-largest producer and consumer of electricity worldwide, with an installed power capacity of 408.71 GW as of October 2022.
- Thermal, nuclear, and renewable energy systems are the major sources for generating India’s electricity.
- Renewable Energy Sector: The renewable energy sector in India is the fourth most attractive renewable energy market globally.
- In terms of wind energy installation capacity, India was ranked fourth, while it was placed fifth in solar energy installation capacity.
- India has achieved 165.94GW of renewable energy capacity till October, 2022 as against the target of 175GW by 2022.
- In line with the Prime Minister's announcement at COP26, the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy is working towards achieving 500 GW of installed electricity capacity from non-fossil sources by 2030.
- In terms of wind energy installation capacity, India was ranked fourth, while it was placed fifth in solar energy installation capacity.
What are the Initiatives related to Energy Conservation?
- National:
- Perform Achieve and Trade Scheme (PAT): It is a market-based mechanism to enhance the cost-effectiveness in improving Energy Efficiency in Energy Intensive industries through certification of energy saving which can be traded.
- Standards and Labeling: The scheme was launched in 2006 and is currently invoked for equipment/appliances.
- Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC): It was developed for new commercial buildings in 2007.
- Demand Side Management: It is the selection, planning, and implementation of measures intended to have an influence on the demand or customer-side of the electric meter.
- Global Efforts:
- International Energy Agency (IEA): It works with countries around the world to shape energy policies for a secure and sustainable future.
- India is not a member country but an association country. However IEA has invited India to be a full time member.
- Sustainable Energy for All (SEforALL):
- It is an international organization that works in partnership with the United Nations and leaders in government, the private sector, financial institutions and civil society to drive faster action towards the achievement of Sustainable Development Goal 7 (SDG7) – access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all by 2030 – in line with the Paris Agreement on climate.
- Paris Agreement:
- It is a legally binding international treaty on climate change. Its goal is to limit global warming to well below 2, preferably to 1.5 degrees Celsius, compared to pre-industrial levels.
- Mission Innovation (MI):
- It is a global initiative of 24 countries and the European Commission (on behalf of the European Union) to accelerate clean energy innovation.
- India is one of the member countries.
- International Energy Agency (IEA): It works with countries around the world to shape energy policies for a secure and sustainable future.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. On which of the following can you find the Bureau of Energy Efficiency Star Label? (2016)
- Ceiling fans
- Electric geysers
- Tubular fluorescent lamps
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Describe the major outcomes of the 26th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). What are the commitments made by India in this conference? (2021)
Family Pehchan Patra for J&K Residents
For Prelims: Aadhar, Targeted PDS, NFSA
For Mains: Family Databases for welfare schemes - efficiency, significance and challenges.
Why in News?
The Government of India has recently decided to introduce a Family Pehchan Patra (FPP) for residents of the Union Territory of Jammu & Kashmir.
What is the Proposed Family Pehchan Patra?
- About:
- The FPP will be an identity card with a unique 8-digit alphanumeric number (like in a PAN Card) to identify each family and its members through the head of the family.
- It will be a single identifier for every family and individual in the UT unlike the Aadhar card which contains information about an individual only.
- Details and Linking:
- The card will contain details of all members of the family, including their names, ages, qualifications, employment status, etc. and will be linked with the Aadhaar and bank account number of the head of the family.
- Significance:
- Better Delivery of Welfare Schemes: The FPP aims to create an authentic, verified, and reliable database of families in J&K to ensure speedy and transparent doorstep delivery of welfare schemes to eligible beneficiaries.
- Smoother Direct Benefit Transfers: Such a system would facilitate direct transfer of benefits to their bank accounts with minimum human interference.
- Eliminating Duplicacy: The database will also help in identifying and weeding out duplicate ration cards and Aadhaar and will help the government identify families that have a number of educated youth, but without jobs.
- Automatic Updation of Data: The information in the database (births, deaths, and marriages) will be continuously and automatically updated and people will no longer have to visit local officials for such purposes.
- It will also help the government plan policy based on authentic, updated population data.
- Non-Consent regarding FPP:
- As per the Government, the database will be created only with the consent of the family. However, the families that do not consent to having a family card will likely face practical difficulties in availing benefits of the welfare schemes.
- Subsidised rations through the Targeted Public Distribution System (PDS) under the National Food Security Act, free medical treatment, old age/ widow/family pensions, help to victims of militancy, scholarships, etc. will all be linked with the family ID card.
- Arguments against FPP:
- The opposition parties have criticised the idea of a FPP describing it as a ‘surveillance tool’ to keep a watch on Kashmiris.
- They claim the “unique family IDs” as a symbol of widening trust deficit on the people of J&K.
- The proposed unique IDs were criticised as a waste of time and resources and were not needed as a similar system - Aadhar - already exists.
- There are also concerns regarding the ability of the government in protecting the personal data of the residents in the wake of recent cyber and ransomware attacks by Chinese entities.
- The opposition parties have criticised the idea of a FPP describing it as a ‘surveillance tool’ to keep a watch on Kashmiris.
Which Other States have Similar Family Databases?
- Several other states have proposed or created similar databases; Haryana was the first state to introduce the concept of the family pehchan patra.
- Punjab introduced such a system in 2021 for direct transfer of benefits to families who are eligible for various social service schemes of the government.
- More recently, in November 2022, the Uttar Pradesh government decided to launch a UP Parivar Kalyan Card for similar purposes.
- The state of Rajasthan has also introduced “Jan Aadhaar Yojana” which aims to be the single identifier of a family (and an individual) and the sole vehicle in the state on which delivery of all kinds of cash as well non-cash benefits takes place.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the provisions made under the National Food Security Act, 2013, consider the following statements: (2018)
- The families coming under the category of ‘below poverty line (BPL)’ only are eligible to receive subsidised food grains.
- The eldest woman in a household, of age 18 years or above, shall be the head of the household for the purpose of issuance of a ration card.
- Pregnant women and lactating mothers are entitled to a ‘take-home ration’ of 1600 calories per day during pregnancy and for six months thereafter.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. What are the reformative steps taken by the Government to make the food grain distribution system more effective? (2019)
Q. Performance of welfare schemes that are implemented for vulnerable sections is not so effective due to absence of their awareness and active involvement at all stages of policy process. Discuss. (2019)
Q. What are the major challenges of Public Distribution System (PDS) in India? How can it be made effective and transparent? (2022)
Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Mela
For Prelims: National Skill Development Mission, PMKVY, Initiatives related to Skill development.
For Mains: Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Mela, Skill India Mission.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) has held Pradhan Mantri National Apprenticeship Mela (PMNAM) under Skill India Mission.
- The event witnessed the participation of various companies from different sectors and had the chance to meet potential apprentices on a single platform and choose applicants on the spot and provide them with an opportunity to be a part of their organization.
What are the Key Points of PMNAM?
- Under NSDM, apprenticeship melas are hosted every month, wherein selected individuals receive a monthly stipend in accordance with government criteria for gaining new skills.
- PMNAM is being used as a platform to increase the participation of establishments and students. It is also providing awareness to the youth on various opportunities existing across the participating companies.
- The major purpose of this programme is to encourage companies to hire more apprentices, while also assisting employers in discovering the right talent and developing their potential via training and practical experience.
- It aims to raise apprenticeship opportunities in India to 10 lakhs by the end of 2022, and to 60 lakhs by 2026.
- The government is striving to train 1 million youth per annum through apprenticeship training and to fulfil this mission.
What is Skill India Mission?
- Skill India Mission was launched on 15th July, 2015 by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship.
- The initiatives include National Skill Development Mission, National Policy for Skill Development and Entrepreneurship, Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) scheme and the Skill Loan scheme.
- PMKVY incentivises skill training by providing financial rewards to candidates who successfully complete approved skill training programmes.
- Under the Skill Loan scheme, loans ranging from RS 5,000-1.5 lakh is made available to youths seeking to attend skill development programmes.
- It was launched in order to provide a strong institutional framework to implement and scale up skill development efforts across the country.
What are the Various Initiatives taken for Skill Development?
- SANKALP and STRIVE: The SANKALP programme which focuses on the district-level skilling ecosystem and the STRIVE project which aims to improve the performance of ITIs (Industrial Training Institute) are other significant skilling interventions.
- Initiatives from Several Ministries: Nearly 40 skill development programmes are implemented by 20 central ministries/departments. The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship contributes about 55% of the skilling achieved.
- Initiatives by all ministries have resulted in nearly four crore people being trained through various traditional skills programmes since 2015.
- Mandatory CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility)Expenditure in Skilling: Since the implementation of mandatory CSR spending under the Companies Act, 2013, corporations in India have invested over ₹100,000 crores in diverse social projects.
- Of these, about ₹6,877 crores were spent on skilling and livelihood enhancement projects. Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Karnataka, and Gujarat were the top five recipient States.
- TEJAS Initiative for Skilling: TEJAS (Training for Emirates Jobs and Skills), a Skill India International Project to train overseas Indias was launched at the Dubai Expo, 2020.
- The project aims at skilling, certification and overseas employment of Indians and creating pathways to enable the Indian workforce to get equipped for skill and market requirements in the UAE.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, consider the following statements: (2018)
- It is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- It, among other things, will also impart training in soft skills, entrepreneurship, financial and digital literacy.
- It aims to align the competencies of the unregulated workforce of the country to the National Skill Qualification Framework.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. “Demographic Dividend in India will remain only theoretical unless our manpower becomes more educated, aware, skilled and creative.” What measures have been taken by the government to enhance the capacity of our population to be more productive and employable? (2016)
Section 10A of the Divorce Act, 1869
For Prelims: Fundamental Rights, Secularism, Universal Declaration of Human Rights,
For Mains: Significance of Uniform Marriage Code, Right to Judicial Remedy.
Why In News?
Recently, the Kerala High Court stated that the stipulation of the period of one year or more for filing a divorce petition by mutual consent under Section 10 A of the Divorce Act, 1869 violates fundamental rights and is unconstitutional.
- The court suggested to the Union government that there should be a uniform marriage code in India to promote the common welfare and good of spouses in matrimonial disputes.
Why did the Court Strike Down Section 10A of the Indian Divorce Act, 1869?
- The Section 10A is discriminatory because of the reason that different communities in equal circumstances are given different treatment.
- The legislature cannot take away liberty without adequately safeguarding the interest of the individuals whose interests to seek remedy are affected even if such legislation intends to achieve laudable objectives.
- The right to a judicial remedy curtailed by statutory provisions, which is a violative of a fundamental right.
- The right to life encompasses judicial remedy as well.
What is the Source of Section 10A of the Indian Divorce Act,1869?
- The one-year period is stipulated in Section 28(1) of the Special Marriage Act, Section 13B (1) of the Hindu Marriage Act and Section 32B (1) of the Parsi Marriage and Divorce Act.
- Earlier the Section 10A of the Indian Divorce Act mandated a 2-years waiting period for the application of divorce.
- The Kerala High Court itself, in Saumya Ann Thomas v. The Union of India & Ors. (2010) held that the stipulation of a period of two years as the minimum mandatory period under Section 10A was arbitrary and oppressive and the period of two years has to be read as one year.
- Article 8 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights declares that everyone has the right to an effective remedy by the competent national Tribunals for acts violating fundamental rights granted by the constitution or by law.
What is the Universal Declaration of Human Rights?
- The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is a milestone in the history of human rights.
- The Declaration was proclaimed by the United Nations General Assembly in Paris, December 1948 on Human Right Day.
- Every year Human Rights Day is celebrated on 10th December all around the world.
- It sets out, for the first time, fundamental human rights to be universally protected.
- Everyone is entitled to all the rights and freedoms set forth in this Declaration, without distinction of any kind, such as race, colour, sex, language, religion, political or other opinion, national or social origin, property, birth or other status.
- All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.
Conclusion
- The basic motive behind the mandated one-year period to apply for the divorce is basically intended to provide the proper time to the couples to understand each other and different family culture. It is not necessary that in every matrimonial case this approach works with the same outcome so there should be some other remedial measures to get rid of toxic marital relationships.
- The Kerala High Court is basically trying to conserve the right to dignified life of the couples who are facing severe hardship in their married life.
India Internet Governance Forum 2022
For Prelims: India Internet Governance Forum 2022
For Mains: Internet Governance, Fundamental Rights, Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
Recently, the Minister of State for Electronics & Information Technology and Skill Development & Entrepreneurship addressed the India Internet Governance Forum (IIGF) 2022.
- Theme for 2022: ‘Leveraging Techade for Empowering Bharat’.
- The event's goal is to discuss the roadmap to digitization and to reaffirm India's place on the global stage by emphasising its role and importance in international policy development on internet governance.
What is IIGF?
- It is an initiative associated with the UN Internet Governance Forum (UN-IGF).
-
UN-IGF is a multi-stakeholder platform bringing together representatives from various groups, considering all to be at par to discuss public policy issues related to the Internet.
-
The IGF is an outcome of the Tunis Agenda of the World Summit on the Information Society that took place in 2005.
-
Since its first meeting, in 2006, the IGF has been convened annually by the United Nations Secretary-General, in accordance with the mandate set out in the Tunis Agenda for the Information Society.
-
What is the State of India’s Internet Connectivity?
- India is the largest Connected Nation:
- India is the largest ‘connected’ nation in the world with 800 million Indian users.
- 5G and the largest rural broadband connectivity network project at BharatNet will have 1.2 billion Indian users constituting the single largest presence of the global internet.
- India also has improved accessibility to the internet to countries in the Global South which have not been able to step up and create the same sort of pace of digitization of the economy as internetization of their economies.
- Benefits of Internet:
- These benefits include increased productivity, financial independence, and greater access to information.
What is Internet Governance?
- About:
- Internet Governance, broadly defined, is the development and application by Governments, the private sector and civil society, in their respective roles, of shared principles, norms, rules, decision-making procedures, and programs that shape the evolution and use of the Internet.
- It covers activities such as development and coordination of technical standards, operation of critical infrastructure and public policy issues.
- Internet Governance involves Internet Protocol Addressing (IP Addressing), Domain Name System (DNS), Routing, Technical Innovations, Standardization, Security, Public Policy, Privacy, Legal Issues, Cyber Norms, Intellectual Property and taxation.
- Layers of internet Governance:
- Physical Infrastructure layer
- Code or Logical layer
- Content layer
- Security
- India’s Approach:
- India supports a multi-stakeholder approach in matters on Internet Governance.
- On matters relating to national security, the Government will continue to have supreme right and control.
- India’s strength in the sector is its industry and human resource which can be leveraged in a multi-stakeholder approach.
- Challenges:
- Continuously evolving nature of the internet, concentration of digital power in a few companies and countries, decision making skewed to the supply side rather than to the demand side etc.
Near-Earth Asteroid Ryugu
Why in News?
A sample of a space rock called Ryugu that was carried to Earth in 2020 by the Japanese space agency’s asteroid sample-return mission, Hayabusa 2 may hold the answers to the origin of the Earth.
- It is the first time several grams of asteroid samples have been brought back to Earth.
What is Asteroid Ryugu?
- Asteroid Ryugu is a diamond-shaped space rock. The asteroid's name means "dragon palace" in Japanese and refers to a magical underwater castle in a Japanese folktale.
- Ryugu was discovered in 1999 by the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research (LINEAR) project, a collaborative, U.S.-based project to catalogue and track space rocks.
- The asteroid is about 2,952 feet (900 meters) in diameter.
- Ryugu is orbiting the sun between Earth and Mars and occasionally crosses Earth's orbit, which means the space rock is classified as "potentially hazardous," though the body poses no imminent danger to our world.
What are the Key Highlights?
- Findings:
- Roughly 5 % of materials that assembled to form Earth more than 4.5 billion years ago could have come from space rocks similar to near-Earth asteroid Ryugu.
- These asteroid samples represent the first solids to be formed in the solar system. This means they could be the building blocks of Earth.
- Ryugu has copper and zinc isotope ratios similar to a very rare group of meteorites that are likely the most primitive (ones with the closest composition to the Sun).
- They are primitive because they likely formed in the outer solar system, where volatile elements are preserved.
- In contrast, materials created closer to the Sun may have lost a part of their volatile inventory due to evaporation.
- Significance:
- These samples could help evaluate the role of Ryugu-like objects in depositing volatile elements to terrestrial planets.
- Volatile elements such as hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen are thought to have played a key role in forging complex organic molecules — ingredients essential to build habitable worlds like Earth.
- It can also help to evaluate whether Ryugu-type materials also contributed to the origin of Mars.
- These samples could help evaluate the role of Ryugu-like objects in depositing volatile elements to terrestrial planets.
What are Asteroids?
- About
- Asteroids are also known as minor planets.
- They are rocky remnants left over from the early formation of our solar system about 4.6 billion years ago.
- Most asteroids are irregularly shaped, though a few are nearly spherical.
- Many asteroids are known to have a small companion moon (some have two moons).
- There are also binary (double) asteroids, in which two rocky bodies of roughly equal size orbit each other, as well as triple asteroid systems.
- Classification of Asteroids:
- Main Asteroid Belt: The majority of known asteroids orbit within the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
- Trojans: These asteroids share an orbit with a larger planet, but do not collide with it because they gather around two special places in the orbit (called the L4 and L5 Lagrangian points). There, the gravitational pull from the sun and the planet are balanced.
- Lagrange Points are positions in space where the gravitational forces of a two-body system like the Sun and the Earth produce enhanced regions of attraction and repulsion. These can be used by spacecraft to reduce fuel consumption needed to remain in position.
- Near-Earth Asteroids: These objects have orbits that pass close by that of Earth. Asteroids that actually cross Earth's orbital path are known as Earth-crossers.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. What is the difference between asteroids and comets? (2011)
- Asteroids are small rocky planetoids, while comets are formed of frozen gases held together by rocky and metallic material.
- Asteroids are found mostly between the orbits of Jupiter and Mars, while comets are found mostly between Venus and Mercury.
- Comets show a perceptible glowing tail, while asteroids do not.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
World Monkey Day
Why in News?
World Monkey Day is celebrated worldwide on 14th December, every year.
What is World Monkey Day?
- Monkey Day has been created to celebrate monkeys and other non-human primates.
- A primate is any mammal of the group that includes lemurs, lorises, tarsiers, monkeys, apes, and humans.
- It is a great day when it comes to raising awareness about different types of monkeys and primates around the world, as well as the issues they face and how we can help them.
What are the Key Facts about Monkey?
- About:
- Monkeys, also known as simians, live all over the world.
- More than 250 species of monkeys populate Africa, Central America, South America, and Asia.
- Monkeys are divided into two categories– Old World monkeys and New World monkeys.
- Old World monkeys are native to Africa and Asia while New World monkeys are indigenous to the Americas, but their homes are not the only ways in which they are different.
- Physical Characteristics:
- They range in size from mere ounces like the pygmy marmoset to the mandrill at a heavier 80 pounds.
- Monkeys tend to walk on all four limbs.
- As a member of the primate family, they are considered a lesser ape.
- Most monkeys have a tail, though not all do.
- Usually, New World monkeys possess prehensile tails, meaning they can use their tails to grasp or hold on to objects.
- On the other hand, Old World monkeys all have tails, but they lack the ability to grasp objects.
- IUCN Status:
- According to International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), approximately 70% of Asian species are Endangered, as are about 50% of African species and 40% of neo-tropical species. Some of them are:
- Western Chimpanzee: Critically Endangered.
- Roloway Monkey: Critically Endangered.
- Lion-tailed Macaque: Endangered.
- Diana Monkey: Endangered.
- Long-tailed Macaque: Endangered.
- Gee’s Golden Langur: Endangered.
- According to International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), approximately 70% of Asian species are Endangered, as are about 50% of African species and 40% of neo-tropical species. Some of them are:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Which one of the following groups of animals belongs to the category of endangered species? (2012)
(a) Great Indian Bustard, Musk Deer, Red Panda and Asiatic Wild Ass
(b) Kashmir Stag, Cheetal, Blue Bull and Great Indian Bustard
(c) Snow Leopard, Swamp Deer, Rhesus Monkey and Saras (Crane)
(d) Lion-tailed Macaque, Blue Bull, Hanuman Langur and Cheetal
Ans: (a)