Infographics
Economy
India’s Farm Exports
Prelims: APEDA, Rice and Sugar, Agri Export Policy, TIES.
Mains: India’s Farm Exports and Imports.
Why in News?
The agriculture sector in India has experienced buoyant growth in the past two years.
- India’s agricultural exports are poised to scale a new peak in the financial year ending March 31, 2023. But so are imports, bringing down the overall farm trade surplus.
What are the Agri-Stats?
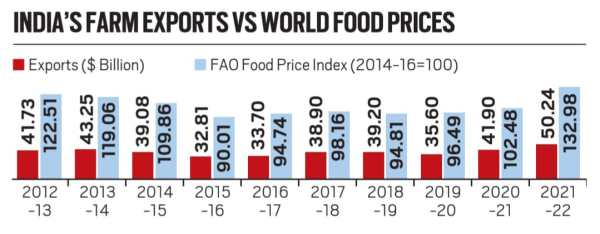
- The value of farm exports in April-December 2022 was 7.9% higher (USD 39 Billion) than the USD 36.2 bn for the corresponding period of the previous year.
- However, imports have grown 15.4% (USD 27.8 bn) in Apr-Dec 2022, over the USD 24.1 bn for Apr-Dec 2021.
- As a result, there has been a further shrinking of the surplus on the farm trade account.
- The two big contributors to India’s agri-export growth have been Rice and Sugar.
- Rice: India in 2021-22 shipped out an all-time-high 21.21 million tonnes (mt) of rice valued at USD 9.66 billion.
- That included 17.26 mt of non-basmati and 3.95 mt of basmati rice.
- Sugar: Sugar exports hit a record value of USD 4.60 billion in 2021-22, as against USD 2.79 billion in last fiscal.
- This fiscal has seen a further surge of 43.6%, from USD 2.78 billion in April-December 2021 to USD 3.99 billion in April-December 2022.
- Rice: India in 2021-22 shipped out an all-time-high 21.21 million tonnes (mt) of rice valued at USD 9.66 billion.
- However, exports of some big-ticket items have faltered or slowed, such as spices, wheat, buffalo meat etc.
What about the Imports?
- Vegetable Oil:
- According to the Solvent Extractors’ Association of India, India’s total edible oil imports rose from 13.13 mt in 2020-21 to 14.03 mt in the 2021-22 oil year (Nov-Oct), and increased further by 30.9% from 2.36 mt in Nov-Dec 2021 to 3.08 mt in Nov-Dec 2022.
- Cotton:
- India has turned from a net exporter to a net importer of cotton.
- Exports collapsed to USD 512.04 million in April-December, 2022 (from USD 1.97 billion in April-December 2021) and imports have also soared from USD 414.59 million to USD 1.32 billion for the same period.
- Cashew:
- During April-December 2022, imports have posted a 64.6% rise to USD 1.64 billion from USD 996.49 million in April-December 2021, even as exports of cashew products have plummeted from USD 344.61 million to USD 259.71 million for the same period.
What are the Related Initiatives?
How India’s Farm Performance is Linked to International Commodity Prices?
- The UN Food and Agriculture Organization’s (FAO) Food Price Index — having a base value of 100 for the 2014-16 period — averaged 122.5 points in 2012-13 and 119.1 points in 2013-14.
- Those were the years when India’s agri-exports were at USD 42-43 billion.
- As the index crashed to 90-95 points in 2015-16 and 2016-17, so did exports to USD 33-34 billion.
- The FAO index peaked at 159.7 points in March 2022, just after the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Since then, it has fallen every month, with the latest reading of 131.2 points for January 2023 the lowest after the 129.2 points of September 2021.
- More than a general export slowdown, it’s the growth in imports that should be cause for concern.
- Going by past correlation i.e., when the index was high, exports were high, and when it was low, exports were low. Currently, the index has been falling, which may lead to a slowdown in India's farm exports and an increase in imports.
- In the event, the focus of policymakers too, may have to shift from being pro-consumer (to the extent of banning/ restricting exports) to pro-producer (providing tariff protection against unbridled imports).
Way Forward
- Clearly, the effects of not allowing new genetic modification (GM) technologies after the first-generation Bt cotton are showing, and impacting exports as well. A proactive approach is required in edible oils as well, where planting of GM hybrid mustard has been permitted with great reluctance — and which is now a matter before the Supreme Court.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Among the following, which one is the largest exporter of rice in the world in the last five years? (2019)
(a) China
(b) India
(c) Myanmar
(d) Vietnam
Ans: (b)
- India has been the world’s top rice exporter since the beginning of this decade primarily owing to the lift of ban on export of non-basmati varieties of rice by GoI in 2011.
- India replaced Thailand in 2011-12 to become the largest rice exporter of the world.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Q2. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- The quantity of imported edible oils is more than the domestic production of edible oils in the last five years.
- The Government does not impose any customs duty on all the imported edible oils as a special case.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)


International Relations
Canada’s Indo-Pacific Strategy
Prelims: Early Progress Trade Agreement (EPTA), Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)
Mains: India-Canada Relations, Roadblocks in India-Canada Relations, significance of Canada’s Indo Pacific Policy on India’s Interests.
Why in News?
Recently, India-Canada Foreign minister’s Bilateral meeting as ‘India-Canada strategic Dialogue’ took place ahead of G20 Foreign ministers’ meeting in March in New Delhi.
- India welcomed the announcement of Canada’s Indo-Pacific Strategy given the shared vision of a free, open and inclusive Indo pacific.
What are the Highlights of the Meeting?
- The Ministers discussed strengthening the economic partnership, advancing security cooperation, facilitating migration and mobility, and growing our strong people-to-people ties.
- Canadian FM termed India as a critical partner for Canada in the Indo- Pacific. In return, Canada can be a reliable supplier of critical minerals, a strong partner in the green transition and a major investor.
What is the Significance of the Meeting?
- Candian FM’s visit is expected to pave the way for a continued reset in India-Canada ties after a freeze between 2020-2022.
- Freeze was over a number of issues including attacks on Indian-origin people and establishments by Khalistani groups in Canada, Canadian comments over India’s farmer protests and India’s cancellation of diplomatic talks in response.
- In 2022, New Delhi objected to Canada permitting a Khalistani secessionist “referendum” and hit back with an advisory against travel in Canada that warned against hate crimes.
- Apart from encouraging investment from Canadian funds, both the countries look forward to the ‘Early Progress Trade Agreement (EPTA)’ as a first step towards ‘Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)’.
- The issue of Khalistani activities in Canada, which has contributed to the strained relationship between Canada and India, was not addressed in any official statements.
- As India's economy grows, its strategic importance will only increase, providing a greater opportunity for Canada and India to strengthen their relationship.
- Both countries share a suspicion of China and are seeking to expand trade ties, improve supply chain resilience, and encourage greater exchange of people between their countries.
What is Canada’s Indo Pacific Policy?
- About:
- Canada released a new Indo-Pacific strategy, focusing on four regions: China, India, the North Pacific (Japan and Koreas), and ASEAN.
- The Indo-Pacific region is home to the largest diaspora in Canada, with 1 in 5 Canadians having family ties to the region and 60% of Canada's international students.
- The strategy contains strong words on China's challenge to the international rules-based order and human rights, while expressing a positive view of India's shared tradition of democracy and pluralism.
- However, Canada also acknowledges its dependence on China as its main export destination and recognizes the need for cooperation with China on issues such as climate change and health.
- Canada released a new Indo-Pacific strategy, focusing on four regions: China, India, the North Pacific (Japan and Koreas), and ASEAN.
- Funding:
- Canada's strategy includes a funding commitment of $1.7 billion over five years, including infrastructure projects, enhanced military presence, and expanded participation in regional military exercises.
- Objectives:
- Promote peace, resilience and security.
- Expand trade, investment and supply chain resilience.
- Invest in and connect people.
- Build a sustainable and green future.
- Be an active and engaged partner to the Indo-Pacific.
How are India- Canada Relations?
- Political:
- India and Canada share commonalities in Parliamentary structure and procedures. After the general election in October 2019, Mr Raj Saini, MP from the House of Common has been appointed as the Chair of the Canada-India Parliamentary Association.
- In India, Canada is represented by the High Commission of Canada in New Delhi.
- India is represented in Canada by a High Commission in Ottawa and by consulates in Toronto and Vancouver.
- Economic:
- Bilateral trade between India and Canada stands at USD 6.4 billion in 2020. In 2021, India was Canada's 14th largest export market, and 13th largest trading partner overall.
- More than 400 Canadian companies have a presence in India, and more than 1,000 companies are actively pursuing business in the Indian market.
- Indian companies in Canada are active in the field such as Information Technology, software, steel, natural resources and banking sectors.
- India’s exports to Canada include pharma, iron and steel, chemicals, gem and jewelry, nuclear reactors and boilers.
- Canada has one of the world’s largest resources of uranium, natural gas, oil, coal, minerals and advanced technologies in hydropower, mining, renewable energy and nuclear energy.
- Science and Technology:
- Primary focus has been on promoting Industrial R&D (Research and Development) and development of new IP (Intellectual property) processes, prototypes or products.
- Department of Biotechnology under IC-IMPACTS program implements joint research projects in health care, agri-biotech and waste management.
- IC-IMPACTS (the India-Canada Centre for Innovative Multidisciplinary Partnerships to Accelerate Community Transformation and Sustainability) is the first, and only, Canada-India Research Centre of Excellence.
- Department of Earth Science and Polar Canada have started a programme for exchange of knowledge and scientific research on Cold Climate (Arctic) Studies.
- Space:
- ISRO and Canadian Space Agency (CSA) have signed MOUs in the field of exploration and utilization of outer space.
- -ANTRIX, the Commercial arm of ISRO, has launched several nanosatellites from Canada.
- ISRO in its 100th Satellite PSLV launched in 2018, also flew Canadian first LEO (Low earth Orbit) satellite, from Indian spaceport Sriharikota.
- Security and Defence:
- India and Canada collaborate closely in international fora particularly through the UN, Commonwealth and G-20.
- A Statement of Intent (SoI) on Cooperation between DRDO and Canada’s Defence Research and Development Council has been signed in 2015.
- The security cooperation was further enhanced with the Framework for Cooperation between India and Canada on Countering Terrorism in 2018.
- There is substantial engagement on counter terrorism issues particularly through the framework of the Joint Working Group (JWG) on Counter Terrorism.
What are the Key Facts about Canada?
- Canada is the second largest country in the world in area (after Russia), occupying roughly the northern two-fifths of the continent of North America.
- Canada is a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary democracy,
- Constitutional Monarchy means that the British monarch is the head of state, but her role is mainly symbolic and ceremonial, while the actual governing of the country is carried out by elected representatives and government officials.
- The border between the United States and Canada is primarily defined by the 49th parallel north.
- Canada has a number of lakes including Great bear lake, Great slave lake, Winnipeg lake and 5 great lakes on USA Border namely: Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which among the following has the world’s largest reserves of Uranium? (2009)
(a) Australia
(b) Canada
(c) Russian Federation
(d) USA
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- As per the latest available data of OECD-NEA (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development – Nuclear Energy Agency)/IAEA (International Atomic Energy Agency), World Nuclear Association – Australia has 30% of reserves, Kazakhstan (14%), Canada (8%), Russia (8%) and USA (1%). Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.


Indian Economy
Protecting Investors from Market Volatility
Prelims: Market Volatility, SEBI, Supreme Court, RBI.
Mains: Protecting Investors from Market Volatility.
Why in News?
Recently, the SC (Supreme Court) asked the SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) and the government about the existing regulatory framework in place to protect Indian middle-class investors.
- This comes after the Adani Group was accused of stock manipulation and accounting fraud by the American firm Hindenburg Research.
- Earlier, a number of small investors lost lakhs of crores due to rapid market volatility following a collapse in the value of the shares of the Adani Group.
What is the SC’s Observation?
- The stock market is no longer a place for just “high value investors”, rather it is a place now where a whole wide spectrum of the middle class is investing due to changes in the financial and tax regimes.
- Therefore, there is a need for circuit-breakers like in other areas, so that market volatility does not cost much.
- Stock market goes entirely by sentiment, Capital is moving seamlessly, funds are flowing in and out of India, making it imperative to devise robust mechanisms in place to protect Indian investors.
What is Market Volatility?
- About:
- The stock markets sometimes experience sharp and unpredictable price movements, either down or up. These movements are often referred to as a “volatile market” and can occur over a period of days, weeks, or months.
- Causes:
- Surprising economic news that differs from the expectations of investors.
- A sudden change in monetary policy, such as the Federal Reserve announcing plans to.
- Political developments including unexpected election results, an event such as a government shutdown or passage of key legislation designed to give the economy a boost.
- Geopolitical events such as an outbreak of a military conflict or flaring tensions between powerful nations that could have economic ramifications.
- Events specific to markets, such as stocks becoming overvalued.
- This occurred in 2000 when a number of overpriced “dot-com” stocks faced a sudden and dramatic selloff as investors became concerned that prices had outdistanced underlying company fundamentals.
How can Market Volatility be Dealt with?
- Monetary Policy:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) can adjust interest rates to influence the supply of money and credit in the economy, which can have an impact on market sentiment and stability. The stock market and the interest rates have an inverse relationship.
- For example, a rate cut can help calm investor concerns and boost market confidence.
- Fiscal Policy:
- Governments can use fiscal measures such as tax cuts, spending increases, and targeted subsidies to boost economic activity and provide support to affected industries and individuals.
- Regulatory Measures:
- Governments and regulatory authorities can introduce measures to increase transparency and stability in financial markets.
- This may include increased disclosure requirements for companies, stricter standards for financial institutions, and greater oversight of hedge funds and other speculative investors.
- International Cooperation:
- In a globalized financial system, sudden market volatility can spread quickly across borders.
- Coordination among central banks and regulatory authorities can help mitigate the impact of market volatility and prevent financial contagion.
- Financial Education and Literacy:
- Encouraging financial education and literacy among the public can help reduce the risk of market speculation and improve overall financial stability.
- Diversification:
- By spreading investments across different assets and markets, investors can reduce the impact of market volatility on their portfolios.
What are the Investor Protection Measures?
- Investor protection legislation is implemented under the Section 11(2) of the SEBI Act. The measures are as follows:
- Stock Exchange and other securities market business regulation.
- Registering investment schemes like Mutual fund & venture Capital funds, and regulating their functioning.
- Promotion and controlling of self-regulatory companies.
- Investor Education and Protection Fund (IEPF):
- Government of India established IEPF under the 1956 Company Act.
- According to the act, the company which has completed seven years in the business should hand over all the unclaimed fund dividends, matured deposits, and Debentures, share application money etc. to the Government through IEPF.
- Investor Protection Fund:
- IPF is set up by Inter-connected Stock Exchange (ISE) in accordance with the guidelines issued by the Ministry of Finance for investor protection, in order to compensate the claims of investors against the members of exchanges (brokers) who have defaulted or failed to pay.
What is a Capital Market?
- Capital market is a market where securities, such as stocks and bonds, are bought and sold.
- It provides a platform for companies, governments, and other entities to raise capital by issuing securities and for investors to invest in these securities with the expectation of earning a return.
- The capital market can be divided into two main segments, the Primary Market and the Secondary Market.
- The primary market is where new securities are issued and sold directly to investors.
- The secondary market is where securities that have already been issued are bought and sold among investors.
- Capital markets play a critical role in the functioning of the economy by connecting savers with borrowers and facilitating the flow of capital to its most productive uses. Capital markets also provide investors with the opportunity to diversify their portfolios, manage risk, and potentially earn higher returns.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which of the following is issued by registered foreign portfolio investors to overseas investors who want to be part of the Indian stock market without registering themselves directly? (2019)
(a) Certificate of Deposit
(b) Commercial Paper
(c) Promissory Note
(d) Participatory Note
Ans: (d)


Important Facts For Prelims
Micro-LEDs
Why in News?
Apple is reportedly working on a new display technology called microLEDs, which is considered the next big thing in the display industry.
- MicroLEDs are self-illuminating diodes that have brighter and better colour reproduction than Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) display technology.
What are MicroLEDs ?
- About:
- MicroLED technology is based on the use of sapphires, which are known for their ability to shine on their own indefinitely.
- The technology involves the use of tiny light-emitting diodes (LEDs) that are packed tightly together to create a bright and high-quality display.
- Unlike OLED displays, microLED displays use inorganic material such as gallium nitride.
- A microLED is as small as cutting a centimetre of hair into 200 smaller pieces. Each of these microLEDs are semiconductors that receive electric signals.
- Once these microLEDs are gathered, they form a module. Several modules are then combined to form screens.
- MicroLED technology is based on the use of sapphires, which are known for their ability to shine on their own indefinitely.
- Benefits:
- Brighter screens with better colour reproduction and viewing angles.
- Limitless scalability, as microLED displays are resolution-free, bezel-free, ratio-free, and even size-free.
- The ability to freely resize the screen in any form for practical usage.
- Self-emissive microLEDs that individually produce red, green, and blue colours without needing backlighting or colour filters.
- Challenges:
- Manufacturing Complexity: The process of manufacturing microLEDs is highly complex, and it requires precise control over many variables to produce high-quality displays.
- Cost: The cost of manufacturing microLED displays is currently very high, and it may take some time for the technology to become affordable enough for widespread adoption.
- Power Consumption: MicroLEDs require a lot of power to operate, which can make them less energy-efficient than other display technologies.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. With reference to street lighting, how do sodium lamps differ from LED lamps? (2021)
- Sodium lamps produce light in 360 degrees but it is not so in the case of LED lamps.
- As street lights, sodium lamps have a longer lifespan than LED lamps.
- The spectrum of visible light from sodium lamps is almost monochromatic while LED lamps offer significant colour advantages in street lighting.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q2. Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs) are used to create digital display in many devices. What are the advantages of OLED displays over Liquid Crystal displays? (2017)
- OLED displays can be fabricated on flexible plastic substrates.
- Roll-up displays embedded in clothing can be made using OLEDs.
- Transparent displays are possible using OLEDs.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None
Mains
Q. The Nobel Prize in Physics of 2014 was jointly awarded to Akasaki, Amano and Nakamura for the invention of Blue LEDs in 1990s. How has this invention impacted the everyday life of human beings? (2021)


Important Facts For Prelims
H5N1- Avian Influenza
Why in News?
Recent reports of H5N1 (subtype of avian influenza) being transmitted between mammals have raised concerns about its potential to cause a human pandemic.
- Scientists are investigating a potential spillover event after a mass mortality event that killed over 700 seals along the Caspian Sea coast where a H5N1 variant was detected in wild birds a few months ago.
What is H5N1 Avian Influenza?
- About:
- Avian influenza or bird flu refers to the disease caused by infection with avian influenza Type A viruses.
- Infrequently, the virus can infect mammals from birds, a phenomenon called spillover, and rarely can spread between mammals.
- H5N1, a subtype of avian influenza, has the potential to infect other mammals such as minks, ferrets, seals, domestic cats, and others through contact with infected birds, their faeces, or infected bird carcasses.
- Avian influenza or bird flu refers to the disease caused by infection with avian influenza Type A viruses.
- Symptoms in Humans:
- Range from mild to severe influenza-like illnesses such as fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting.
- People can also develop severe respiratory illness (e.g., difficulty breathing, pneumonia, acute respiratory distress, viral pneumonia) and altered mental status, seizures etc.
- Avian Influenza in India:
- In 2019, India has been declared free from Avian Influenza (H5N1), which has also been notified to the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE).
- However, in December 2020 and early 2021, outbreaks of avian influenza H5N1 and H5N8 were reported in poultry in 15 states in India.
- In 2019, India has been declared free from Avian Influenza (H5N1), which has also been notified to the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE).
- Treatment:
- Evidence suggests that some antiviral drugs can reduce the duration of viral replication and improve prospects of survival, however ongoing clinical studies are needed.
- Concerns:
- The widespread H5N1 outbreaks have substantial economic impact, resulting in significant losses to the poultry industry and threatening food and vaccine security, apart from raising animal welfare and environmental concerns.
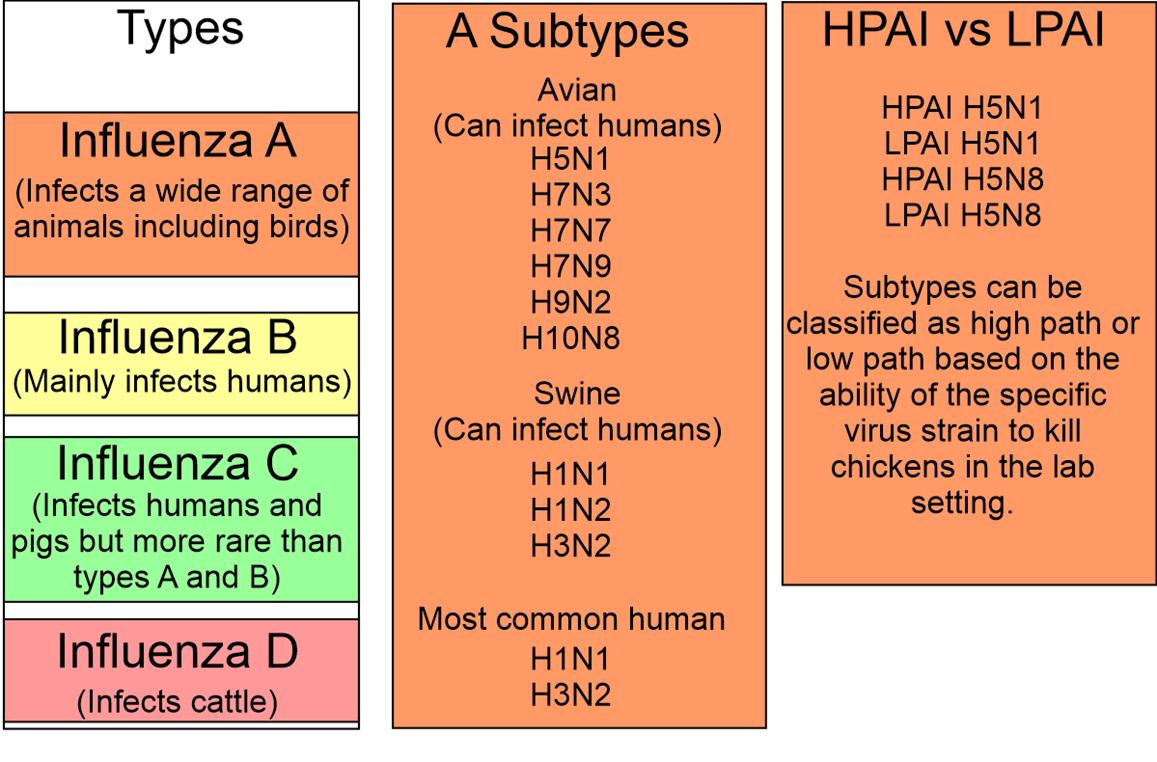
Types of Influenza Virus
- There are four types of influenza viruses: influenza A, B, C, and D
- Influenza A and B are the two types of influenza that cause epidemic seasonal infections nearly every year.
- Influenza C mainly occurs in humans, but has been known to also occur in dogs and pigs.
- Influenza D is found mainly in cattle. It’s not known to infect or cause illness in humans yet.
Avian influenza Type A Viruses
- Type A viruses are classified based on two proteins on their surfaces – Hemagglutinin (HA) and Neuraminidase (NA). There are about 18 HA subtypes and 11 NA subtypes.
- Several combinations of these two proteins are possible e.g., H5N1, H7N2, H9N6, H17N10, H18N11 etc.
- All known subtypes of influenza A viruses can infect birds, except subtypes H17N10 and H18N11, which have only been found in bats.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. H1N1 virus is sometimes mentioned in the news with reference to which one of the following diseases? (2015)
(a) AIDS
(b) Bird flu
(c) Dengue
(d) Swine flu
Ans: (d)


Important Facts For Prelims
Diyodar Meteorite
Why in News?
Scientists from Physical Research Laboratory (PRL), Ahmedabad, are claiming that the meteorite that crashed in two villages in Banaskantha, Gujarat on August 17, 2022, has been identified as an aubrite.
- The PRL group used a gamma-ray spectrometer to determine the mineral composition of aubrite. The group also classified the meteorite as a monomict breccia.
What are the Major Highlights Related to Aubrite?
- Aubrite meteorite is a coarse-grained igneous rock that formed in oxygen-poor conditions and contains exotic minerals not found on Earth.
- For example, the mineral heideite was first described in the Basti meteorite.
- India has seen hundreds of meteorite crashes, but this is only the second recorded crash of an aubrite. The meteorite has been named the Diyodar meteorite after the taluka in which the villages are located.
- The last crash of an aubrite before this was in Basti, Uttar Pradesh on December 2, 1852.
- Around 90% of the meteorite was composed of orthopyroxene. Pyroxenes are silicates consisting of single chains of silica tetrahedra (SiO 4); orthopyroxenes are pyroxenes with a certain structure.
- Pyroxenes such as diopside and jadeite have been used as gems. Spodumene was historically used as lithium ore. Rocks with pyroxene have also been used to make crushed stone that is used in construction.
- Aubrites have crashed in at least 12 locations worldwide since 1836, including 3 in Africa and 6 in the U.S.
What is a Meteorite?
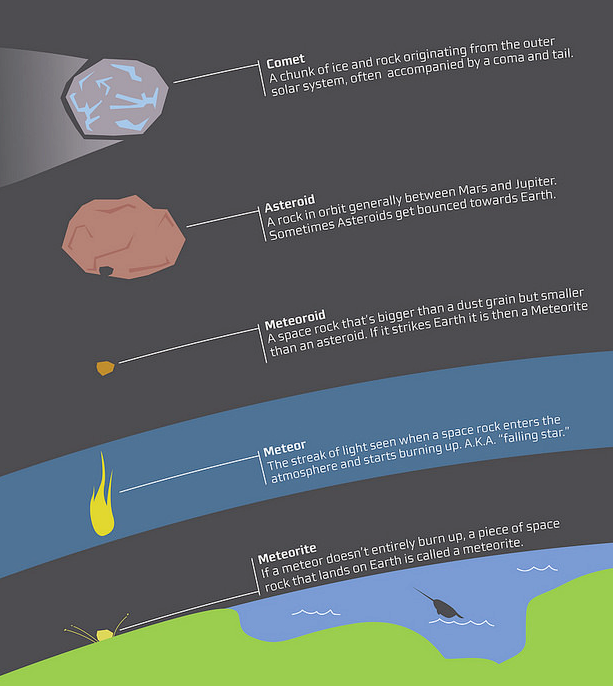
- About:
- A meteorite is a solid piece of debris from space that survives its passage through the Earth's atmosphere and lands on the Earth's surface.
- Difference between Meteor, Meteorite and Meteoroid:
- The difference between a meteor, meteorite and meteoroid is nothing but where the object is.
- Meteoroids are objects in space that range in size from dust grains to small asteroids.
- But when meteoroids enter the Earth’s atmosphere, they are called meteors.
- But if a meteoroid enters the Earth’s atmosphere and hits the ground, it is called a meteorite.
What is a Gamma Ray Spectrometer?
- Gamma ray spectrometers are scientific instruments used to measure the energy distribution of gamma rays emitted by radioactive materials.
- They consist of a detector, electronics, and software to analyse the data.
- The resulting gamma ray spectrum can be used to identify the radioactive isotopes present and their relative abundance.
- Gamma ray spectrometers are used in a variety of applications, including environmental monitoring, geology, and nuclear physics.
- They can be used to detect and measure the radiation emitted by natural sources, such as rocks and soils, as well as anthropogenic sources, such as nuclear power plants and medical facilities.


Important Facts For Prelims
Black Soldier Fly Larvae and Poultry Feed
Why in News?
India is among the top five chicken and egg producers in the world, but there are challenges to the business for small poultry farmers because of the quality, quantity and cost of feed.
- Black soldier fly, since it has a high nutritional value can be one of the substitutes to address these challenges.
What are the Challenges Related to Poultry Feed?
- Feeds account for up to 70% of the entire cost of poultry production. Besides, the conventional feed supplied to the poultry, majorly cereals and soya, competes with the food demands of a growing human population.
- In addition to rising cost, the feed resource availability is a major determinant of the sustainability of the poultry sector.
- One such alternative is brewers dried grains, a byproduct of the brewing industry.
- Though rich in protein and amino acid, its limitations include high moisture and fibre content.
- Rice bran is another economically viable alternative to wheat in certain parts of the country. It has a comparable apparent metabolisable energy as wheat.
- However, studies show that the laying performance of the chicks declined on incorporation of rice bran to the feed.
- The larvae of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens), for instance, have a high nutritional value and are easy to raise.
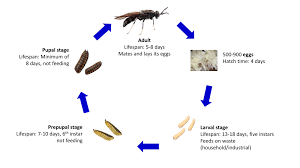
What is Black Soldier Fly?
- About:
- The black soldier fly is a fly (Diptera) of the Stratiomyidae family that is commonly found in many parts of the world.
- They are a dull, whitish color. They feed on a variety of organic matter, from rejected food waste to manure.
- They also have high waste-to-biomass conversion efficiency.
- This means, unlike hot-blooded mammals and birds, which use a lot of energy to keep themselves warm, insects are efficient converters of food into body mass.
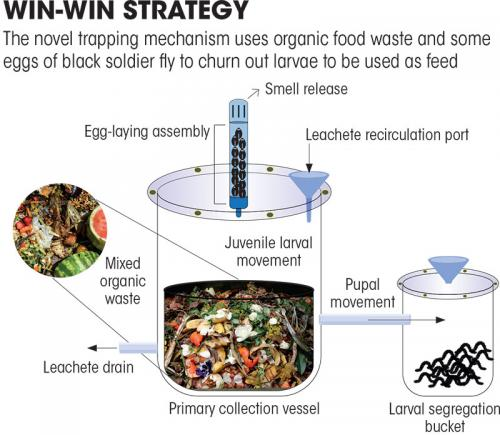
- Utility:
- They can be a low-cost, low footprint, eco-friendly as well as natural feed companion to poultry farmers.
- The larvae are capable of converting the organic waste into a wide range of useful vitamins and minerals.
- They are thus rich in calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, sodium, potassium, iron, zinc, copper, manganese and so on, which makes them a promising candidate for livestock feed.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Agricultural soils release nitrogen oxides into environment.
- Cattle release ammonia into environment.
- Poultry industry releases reactive nitrogen compounds into environment.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
World Radio Day
The Prime Minister of India greeted radio listeners and others associated with the broadcasting medium on ‘World Radio Day’.
It is celebrated on 13th February, every year. The theme for this year is “Radio and Peace”.
On 3rd November, 2011, the 36th session of UNESCO declared World Radio Day to be celebrated on 13th February, as UN Radio was established by the United Nations on 13th February, 1946. The day was later adopted by the UN General Assembly in 2012 as an International Day.
The day is observed every year to raise awareness among the public and the media about the importance of radio and to encourage access to information through radio.
India has around 479 radio stations making All India Radio one of the biggest broadcasters in the world. It covers around 99.19% of the Indian population.
Read More: Community Radio.
Khanan Prahari Mobile App
The Government of India has launched one mobile app namely “KhananPrahari” and one web app Coal Mine Surveillance and Management System (CMSMS) for reporting unauthorized coal mining activities.
The mobile app is developed by Ministry of Coal that enables citizens to report incidents of illegal coal mining using geo-tagged photos and textual information from the location of the incident.
Statutory measures taken in this regard include: Coal Mines (Nationalisation) Act, 1973, Mineral Concession Rules, 1960, Colliery Control Rules, 2004, Mines & Minerals (Development & Regulation) Act, 1957.
Further, concrete walls have been erected on the mouth of the abandoned mines to prevent access and illegal activities in these areas. Also, existing security/CISF personnel are being trained and Committees/task forces have been formed at different levels in some subsidiaries of CIL (Coal India Ltd.) to monitor different aspects of illegal mining.
Read More: Coal sector in India.
APEDA completes 37 years of its journey
The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA), which was established in 1986 through an Act of Parliament works under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry. It is mandated with export promotion of agricultural commodities. Additionally, APEDA has been entrusted with the responsibility to monitor import of sugar.
In line with ideas of ‘vocal for local’ and ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’, APEDA has been focusing on promotion of exports of locally sourced GI (Geographical Indications) tagged as well as indigenous, ethnic agricultural products.
India has become the world's eighth-largest exporter of agricultural products, with exports worth USD 24.77 billion in the 2021-22, based on WTO trade data.
Some of the recent initiatives of APEDA include Farmer Connect Portal, Varanasi Agri – Export Hub (VAEH); Millets Portal for promotion of millets, etc.
Read More: APEDA.
Nirman Se Shakti Initiative
Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC) presented an initiative named as ‘Nirman Se Shakti’ to modernize infrastructure.
The ‘Nirman Se Shakti’ initiative includes upgradation/modernization of ESI Scheme (ESIS) hospitals and dispensaries in a phased manner, formulation of standard design for 100/200/500 bedded hospitals with better modern facilities, online real-time dashboard for project monitoring/supervision, adoption of new building technologies to ensure quality of construction, elimination of delays, cost overrun, digitalization of land/property documents etc.
The Employees' State Insurance Scheme (ESI) is an integrated measure of social Insurance for worker population and immediate dependent or family embodied in the Employees' State Insurance Act, 1948.
Read More: ESIC.



.png)