Indian Economy
50th Meeting of GST Council
For Prelims: Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council, Online gaming, GST Appellate Tribunals, Prevention of Money Laundering Act, Enforcement Directorate , Financial Action Task Force
For Mains: Functions of GST Council, Regulation of Online Gaming in India.
Why in News?
At its 50th meeting, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council made changes to tax rates on various items and resolved the tax treatment for online gaming, casinos, and horse racing.
- The Council decided to levy a uniform 28% tax on the full face value of bets placed for online gaming, casinos and horse-racing.
What are the Major Highlights of the Meet?
- Changes in Tax Rates: The GST Council made the following revisions to the tax rates:
- Uncooked or Unfried Snack pellets and Fish Soluble Paste: The tax rate was reduced from 18% to 5%.
- Imitation Zari Threads or Yarn: The tax rate was reduced from 12% to 5%.
- Food and Beverages Consumed Inside Cinema Halls: The tax rate was set at 5% without input tax credits, as opposed to the previous 18% on cinema services.
- Tax Treatment of Online Gaming, Casinos, and Horse Racing:
- Regardless of whether they involve skill, chance, or a combination thereof (or neither), bets and wagers made on online gaming, casinos, and horse racing activities will now attract a 28% GST levy.
- The GST laws will be amended to explicitly include online gaming within the tax framework.
- Regardless of whether they involve skill, chance, or a combination thereof (or neither), bets and wagers made on online gaming, casinos, and horse racing activities will now attract a 28% GST levy.
- Exemption from GST:
- GST Council exempts cancer-related drugs, medicines for rare diseases, and food products for special medical purposes from GST
- Establishment of GST Appellate Tribunals:
- The Council examined proposals from states to establish 50 Benches of the GST Appellate Tribunals in the country.
- The initial Benches will be set up in state capitals and locations where High Courts have Benches.
- Concerns Raised on GST Network and PMLA:
- Some states expressed criticism regarding the recent decision to bring the GST Network (GSTN) under the purview of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), administered by the Enforcement Directorate (ED).
- Tamil Nadu, in particular, argued that this inclusion contradicts the interests of taxpayers and the objective of decriminalizing GST offenses.
- The Revenue Secretary assured the Council that it was in line with the requirements of the Financial Action Task Force.
- It was clarified that the ED will neither receive nor provide information from the GSTN, and the notification is aimed at empowering tax authorities to combat tax evasion and money laundering.
- Some states expressed criticism regarding the recent decision to bring the GST Network (GSTN) under the purview of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), administered by the Enforcement Directorate (ED).
What is GST Council?
- About:
- The GST Council is a constitutional body responsible for making recommendations on issues related to the implementation of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India.
- As per Article 279A (1) of the amended Constitution, the GST Council was constituted by the President.
Note: GST is a value-added tax system that is levied on the supply of goods and services in India. It is a comprehensive indirect tax that was introduced in India on 1st July 2017, through the 101st Constitution Amendment Act, 2016, with the slogan of ‘One Nation One Tax’.
- Members:
- The members of the Council include the Union Finance Minister (chairperson), the Union Minister of State (Finance) from the Centre.
- Each state can nominate a minister in-charge of finance or taxation or any other minister as a member.
- Functions:
- Under Article 279A (4), the Council makes recommendations to the Union and the States on important issues related to GST, like the goods and services that may be subjected or exempted from GST, model GST Laws, principles that govern place of supply, threshold limits, GST rates including the floor rates with bands, special rates for raising additional resources during natural calamities/disasters, special provisions for certain States, etc.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following items: (2018)
- Cereal grains hulled
- Chicken eggs cooked
- Fish processed and canned
- Newspapers containing advertising material
Which of the above items is/are exempted under GST (Good and Services Tax)?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Q2. What is/are the most likely advantages of implementing ‘Goods and Services Tax (GST)’? (2017)
- It will replace multiple taxes collected by multiple authorities and will thus create a single market in India.
- It will drastically reduce the ‘Current Account Deficit’ of India and will enable it to increase its foreign exchange reserves.
- It will enormously increase the growth and size of economy of India and will enable it to overtake China in the near future.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Explain the rationale behind the Goods and Services Tax (Compensation to States) Act of 2017. How has COVID-19 impacted the GST compensation fund and created new federal tensions? (2020)
Q. Enumerate the indirect taxes which have been subsumed in the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. Also, comment on the revenue implications of the GST introduced in India since July 2017. (2019)
Q. Explain the salient features of the Constitution (One Hundred and First Amendment) Act, 2016. Do you think it is efficacious enough “to remove cascading effect of taxes and provide for common national market for goods and services”? (2017)
Q. Discuss the rationale for introducing the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. Bring out critically the reasons for the delay in roll out for its regime. (2013)
Governance
Government Brings GSTN under PMLA Ambit
For Prelims: PMLA, GSTN, Financial Intelligence Unit , Goods and Services Tax(GST)
For Mains: Legal and regulatory framework in India to combat money laundering, Prevention of Money-Laundering Act (PMLA) and its objectives, Impact of money laundering on the economy.
Why in News?
Recently, the government has issued a notification, bringing the Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) under the ambit of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA).
- These changes have been made under Section 66 of the PMLA, which provides for disclosure of information.
Why has GSTN been Brought Under the PMLA Ambit?
- This move aims to enhance the fight against money laundering and strengthen efforts to combat Goods and Services Tax(GST) fraud.
- The notification amends a previous 2006 notification, allowing for improved information sharing between the GSTN, Enforcement Directorate (ED), and Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) under the provisions of the PMLA Act, 2002.
- Recently, over 69,600 suspected GST identification numbers were identified for physical verification by field tax officials in a two-month-long drive against fake registrations.
- Of these, over 59,000 were verified, and 25% were found to be non-existent.
What is Goods and Services Tax Network?
- GSTN has developed an Indirect Taxation platform for GST in India.
- The platform helps taxpayers in preparing, filing returns, making payments, and complying with indirect tax regulations.
- It provides IT infrastructure and services to the Central and State Governments, taxpayers, and other stakeholders.
- GSTN is a not for profit, limited by shares, Government Company. It was incorporated in 2013 under Section 25 of the Companies Act, 1956 (Now Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013).
- The company is headed by a chairman who is appointed by the Government.
- The Board of GSTN in its 49th Board Meeting held in June 2022 has approved the conversion of GSTN into Government Company and hence 100% of the shareholding being held by Government (50% with Union Government and 50% jointly with State Governments & UTs) in GSTN.
What is the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), 2002?
- Background:
- The PMLA was enacted in response to India’s global commitment (Vienna Convention) to combat the menace of money laundering. These include:
- United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances 1988
- Basle Statement of Principles, 1989
- Forty Recommendations of the Financial Action Task Force on Money Laundering, 1990
- Political Declaration and Global Program of Action adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in 1990.
- The PMLA was enacted in response to India’s global commitment (Vienna Convention) to combat the menace of money laundering. These include:
- About:
- It is a criminal law enacted to prevent money laundering and to provide for the confiscation of property derived from, or involved in, money-laundering and related matters.
- It forms the core of the legal framework put in place by India to combat Money Laundering.
- The provisions of this act are applicable to all financial institutions, banks (Including RBI), mutual funds, insurance companies, and their financial intermediaries.
- Objectives:
- Confiscate and seize proceeds of crime that are laundered, generated, or acquired through criminal activities.
- Establish a legal framework for the prevention of money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Strengthen and improve the mechanism for investigation and prosecution of money laundering offenses.
- Enhance international cooperation in the fight against money laundering and related crimes.
- Regulating Authorities:
- Directorate of Enforcement (ED):
- The ED is responsible for enforcing the provisions of the PMLA and investigating money laundering cases.
- Financial Intelligence Unit – India (FIU-IND):
- Unit of the Indian Government's Department of Revenue.
- Gathers financial intelligence on money laundering offenses.
- Operates under the PMLA, 2002.
- Sections 12 of PMLA require reporting entities to maintain transaction records, furnish information on prescribed transactions to the Director of FIU-IND, and verify the identity of clients and beneficial owners.
- Collaborates with enforcement agencies and foreign FIUs.
- Directorate of Enforcement (ED):
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q.1 What is/are the most likely advantages of implementing ‘Goods and Services Tax (GST)’? (2017)
- It will replace multiple taxes collected by multiple authorities and will thus create a single market in India.
- It will drastically reduce the ‘Current Account Deficit’ of India and will enable it to increase its foreign exchange reserves.
- It will enormously increase the growth and size of economy of India and will enable it to overtake China in the near future.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q.1 Discuss how emerging technologies and globalization contribute to money laundering. Elaborate measures to tackle the problem of money laundering both at national and international levels. (2021)
Q:2 Explain the rationale behind the Goods and Services Tax (Compensation to States) Act of 2017. How has COVID-19 impacted the GST compensation fund and created new federal tensions? (2020)
Geography
Marine Heatwave and its Impacts
For Prelims: Marine Heatwave its Impact, Bay of Bengal, Coral Bleeching, Ocean Currents, El Nino, Somali Jet.
For Mains: Marine Heatwave its Impact.
Why in News?
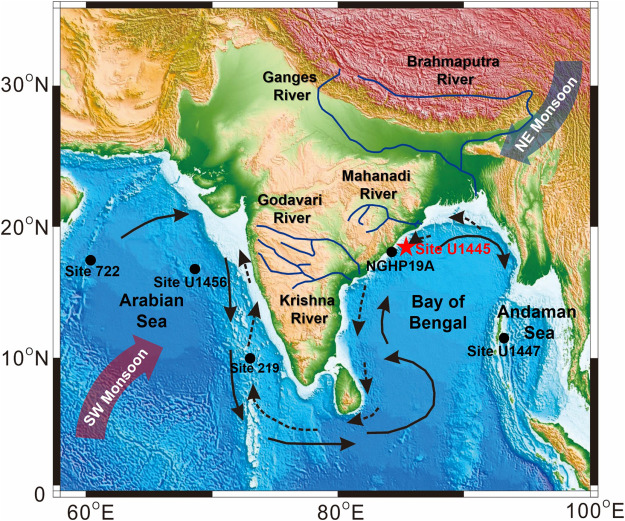
The northern Bay of Bengal has been experiencing an intense Marine Heatwave since 28th June 2023, leading to India’s usually arid northwest receiving extreme rainfall.
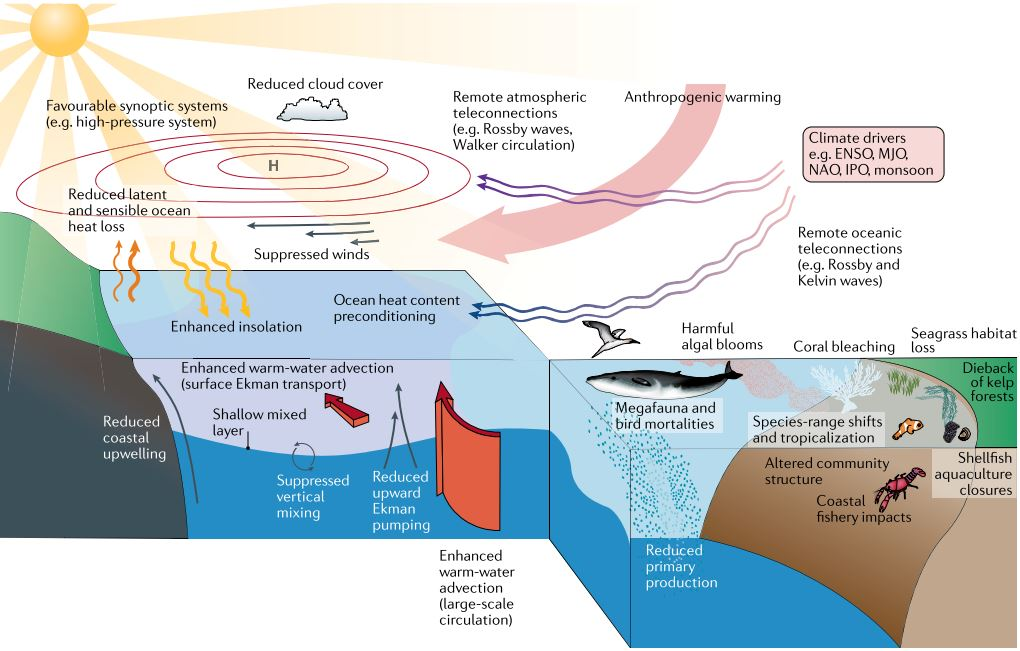
What is Marine Heatwave?
- Marine Heatwaves are prolonged periods of anomalously high Sea Surface Temperature (SST).
- These events are linked to coral bleaching, seagrass destruction, and loss of kelp forests, affecting the fisheries sector adversely.
- The most common drivers of marine heatwaves include ocean currents which can build up areas of warm water and air-sea heat flux or warming through the ocean surface from the atmosphere.
- Winds can enhance or suppress the warming in a marine heatwave, and climate modes like El Niño can change the likelihood of events occurring in certain regions.
How does Marine Heatwave Impact Rainfall in Northwest India?
- The marine heatwave in the Bay of Bengal increased sea surface temperatures, causing higher evaporation rates and a greater moisture supply in the atmosphere. This surplus of moisture contributed to above-average rainfall in northwest India.
- The marine heatwave likely influenced the formation and behavior of depressions in the Bay of Bengal, which may have contributed to an increase in the frequency and intensity of depressions, particularly on faster timescales (3-10 days).
- Depressions, which are low-pressure systems, play a significant role in the monsoon and rainfall patterns.
- The marine heatwave, along with changing timescales of depressions, affected the path and trajectory of these weather systems. Depressions tended to move more towards northwest India rather than north-central India, causing a higher concentration of rainfall in the northwest region, leading to above-average rainfall in that area.
What are the other Impacts of Marine Heatwaves?
- Affect Ecosystem Structure:
- Marine heat waves affect ecosystem structure, by supporting certain species and suppressing others.
- It has been associated with the mass mortality of marine invertebrates and may force species to change behaviour in a way that puts wildlife at increased risk of harm.
- Change Habitat Ranges of Certain Species:
- Marine heatwaves can change the habitat ranges of certain species, such as the spiny sea urchin off southeastern Australia which has been expanding southward into Tasmania at the expense of kelp forests which it feeds upon.
- Economic Losses:
- Marine heatwaves can cause economic losses through impacts on fisheries and aquaculture.
- Affect Biodiversity:
- Biodiversity can be drastically affected by marine heatwaves.
- A study from 2020 (Genesis and Trends in Marine Heatwaves Over the Tropical Indian Ocean and Their Interaction With the Indian Summer Monsoon) reveals that a previous marine heatwave led to bleaching of 85% of corals in the Gulf of Mannar near the Tamil Nadu coast.
- Biodiversity can be drastically affected by marine heatwaves.
- Increase the Risk of Deoxygenation and Acidification:
- Often, they occur alongside other stressors such as ocean acidification, deoxygenation, and overfishing.
- In such cases, MHWs not only further damage habitats, but also increase the risk of deoxygenation and acidification.
How does the Bay of Bengal Impact Monsoon?
- Moisture Source:
- The warm and humid air mass over the Bay of Bengal provides the necessary moisture that is carried by the monsoon winds towards the Indian subcontinent.
- Heat Exchange:
- The Bay of Bengal has warm sea surface temperatures, especially in its northern part. During the monsoon season, the landmass of the Indian subcontinent gets heated up, creating a low-pressure area. The warm air rises, and cooler air from the Bay of Bengal rushes in to replace it, causing a pressure gradient. This pressure gradient helps draw in moisture-laden winds from the Bay of Bengal, contributing to the monsoon rainfall.
- U-Turn of Monsoon Currents:
- The monsoon winds blowing from the southwest over the Arabian Sea cross over into the Bay of Bengal. When they reach the Bay of Bengal, they make a U-turn and start moving towards the northeast, eventually bringing rainfall to different parts of India.
- The warm temperatures in the Bay of Bengal facilitate this U-turn and the transport of moisture to the Indian subcontinent.
- Low-Level Jet Stream:
- The Bay of Bengal also influences the formation and intensity of the low-level jet stream, known as the Somali Jet.
- This jet stream plays a crucial role in the transport of moisture from the equatorial Indian Ocean to the Indian subcontinent.
- The warm sea surface temperatures in the Bay of Bengal contribute to the strengthening of this low-level jet, enhancing the moisture supply during the monsoon season.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains:
Q: How far do you agree that the behaviour of the Indian monsoon has been changing due to humanizing landscape? Discuss. (2015)
Indian Polity
Supreme Court on Tenure Extensions of Enforcement Directorate Chief
For Prelims: Foreign Exchange Management Act,1999 (FEMA), Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA), Supreme Court, Enforcement Directorate, Central Vigilance Commission Act, 2003, Delhi Special Police Establishment Act, 1946, Mandamus, Money laundering.
For Mains: Structure and Function of Enforcement Directorate (ED)
Why in News?
The Supreme Court of India has declared the two tenure extensions granted to the Director of the Enforcement Directorate (ED), beyond the fixed cut-off date as "not valid in law."
- While the court allowed the director to continue on the post until July 31, it cut short his overall tenure.
What is the Background and Current Status of the Issue?
- The current director was appointed in November 2018, for a period of two years. In November 2020, his tenure was extended to three years, which was subsequently challenged through petition.
- On September 8, 2021, the Supreme Court dismissed the petition but issued a specific mandamus prohibiting further extensions.
- The government later amended the Central Vigilance Commission Act, 2003, and the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act, 1946, to grant itself powers for three tenure extensions.
- The amendments were challenged, arguing that they contradicted a previous directive from the Supreme Court that advocated for fixed tenures for top officials like the CBI chief (Vineet Narayan Case).
- The court ruled that the amendments themselves were constitutional but declared the specific extensions given to the director of ED as invalid, as they violated the earlier mandamus.
Note: The ED Director is appointed under Section 25 of the CVC Act, 2003. The Central Government appoints a Director of ED on the recommendation of a selection committee. The committee consists of the CVC Chairperson, Vigilance Commissioners, Secretaries to the Ministry of Home Affairs, the Ministry of Personnel and the Ministry of Finance in the Central Government.
What is Mandamus?
- Mandamus refers to a writ or order issued by a court to a public body, tribunal, corporation or lower court, directing them to perform a specific legal duty that they are obligated to carry out.
- It is derived from the Latin word meaning “we command”.
- In India, it is used to enforce the fundamental rights of citizens when they are violated by the state or its agencies. It is also used to prevent the abuse of power or discretion by the authorities.
- It is only issued by the Supreme Court or the High Courts in India under Article 32 and Article 226 of the Constitution respectively
What is Enforcement Directorate (ED)?
- About:
- ED is a multi-disciplinary organization mandated with investigation of offences of money laundering and violations of foreign exchange laws.
- It operates under the jurisdiction of the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance, Government of India.
- Establishment:
- In 1956, an ‘Enforcement Unit’ was formed, in the Department of Economic Affairs, for handling Exchange Control Laws violations under,
- In 1957, this Unit was renamed as ‘Enforcement Directorate’.
- In 1960, the administrative control of the Directorate was transferred from the Department of Economic Affairs to the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance, Government of India.
- Enforcement:
- ED enforces the following laws:
- Foreign Exchange Management Act,1999 (FEMA)
- Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 (PMLA)
- The Fugitive Economic Offenders Act, 2018 (FEOA): This law was enacted to deter economic offenders from evading the process of Indian law by remaining outside the jurisdiction of Indian courts.
- ED enforces the following laws:
- Structure:
- The Directorate of Enforcement, with its headquarters at New Delhi, is headed by the Director of Enforcement.
- There are five regional offices at Mumbai, Chennai, Chandigarh, Kolkata and Delhi headed by Special Directors of Enforcement.
Social Justice
Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana
For Prelims: Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana, Issues Related to Elderly, IPSrC, RVY, BPL, NPOL.
For Mains: Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana.
Why in News?
The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, Government of India has been working towards creating an inclusive and equitable society for all its citizens and Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana (AVYAY) is one of the Schemes in that direction.
What is Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana?
- About:
- Earlier the AVYAY, was known as National Action Plan for Senior Citizen (NAPSrc), which was revamped, renamed as Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana in April 2021.
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme aimed at empowering senior citizens in India.
- Objective:
- This scheme recognizes the invaluable contribution made by the elderly to society and seeks to ensure their well-being and social inclusion.
- By recognizing the invaluable contributions of the elderly to society, the government aims to empower and uplift them, ensuring their active participation and inclusion in all aspects of life.
- Components:
- Integrated Programme for Senior Citizens (IPSrC): It provides financial assistance to eligible organization’s for running and maintenance of Senior Citizen Homes/ Continuous Care Homes to improve the quality of life of the senior citizens, especially indigent senior citizens by providing basic amenities etc.
- Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana (RVY): It provides eligible senior citizens suffering from any of the age-related disability/ infirmity, with assisted living devices which can restore near normalcy in their bodily functions, overcoming the disability/ infirmity manifested such as low vision, hearing impairment, loss of teeth and loco-motor disabilities.
- Financial criteria for beneficiaries are either the Senior Citizen belongs to ‘Below Poverty Line’ (BPL) category, or he/ she has income up to Rs. 15,000 (Rupees Fifteen Thousand) per month.
- Achievements:
- Nearly 1.5 lakh beneficiaries are staying in the Senior Citizen homes.
- 361 districts across the country have been covered.
- During the last 3 financial years a total of Rs. 288.08 crore grants in aid released and number of beneficiaries is 3,63,570.
- Under RVY a total of 269 camps have been held and the Number of beneficiaries of this camp is over 4 lakhs. Under this scheme, a total amount of Rs. 140.34 crore has been released during the last 3 financial years and a total number of 8,48,841 devices were distributed to 1,57,514 beneficiaries in 130 camps.
- Significance:
- The AVYAY stands as a testament to the government's commitment to the well-being and empowerment of senior citizens in India.
- By addressing their financial, healthcare, and social needs, the scheme aims to empower the elderly, ensuring their active participation and inclusion in society.
- Through this initiative, the government strives to create an environment where senior citizens can live a life of dignity, respect, and fulfilment, acknowledging their invaluable contributions to the nation.
What are the Initiatives Related to Elderly in India?
Economy
Social Entrepreneurship
For Prelims: Social Entrepreneurship, Social Trailblazer Programme, ESG, Impact Investors Council.
For Mains: Need for Social Entrepreneurship in India and related Challenges.
Why in News?
The Union Minister of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship, while addressing a Social Enterprise Conclave organized by Institute of Rural Management, Anand (IRMA) in partnership with LIC Housing Finance Limited has launched the 2nd edition of the Social Trailblazer Program, aiming to boost the Social Entrepreneurship Ecosystem in India.
What is the Social Trailblazer Programme?
- About:
- It is a programme for Social Enterprises and Entrepreneurs Development, which nurtures early-stage rural, social, and collective enterprises.
- The program aims to nurture the evolving ecosystem of Indian Social Enterprises.
- Objective:
- The goal is to promote the Social Enterprise programme so as to promote the development of social enterprise and social investment to help address entrenched social and environmental problems.
- Focus Areas:
- Agriculture
- Green Technology
- Finance Technology
- Education
- Renewable Energy
- Healthcare & Life sciences
- Human Resources
- Marketing
- Social Impact
- Waste Management
- Key Incentives: A financial award Upto INR 25,00,000 in the form of Equity Funding and upto INR 5,00,000 in the form of Grant Funding top 10-12 selected startups
- 1 year of personalized incubation and acceleration support at IRMA ISEED Foundation
- Top-up Incentives: Upto INR 50,00,000 follow-on investment from IRMA ISEED'S Networks.
- Upto USD 1000 worth of AWS (Amazon Web Services) credits and technology support.
What is Social Entrepreneurship?
- About:
- Social Entrepreneurship is the practice of using business models to address social and environmental problems.
- Social entrepreneurs, also known as social innovators, bring about positive change through innovative ideas. They aim to create social impact while also generating revenue and profits.
- They identify problems and create solutions to make a difference. Social entrepreneurship aligns with trends like Socially Responsible Investment and Environment, Social and Governance (ESG) investing.
- Examples: Educational programs or providing banking services in underserved areas and helping children orphaned by epidemic disease.
- Types:
- Community Initiative:
- A community initiative is a small-scale project aimed at addressing a specific issue within a community. It is particularly beneficial for marginalized and underprivileged communities that are disconnected from the larger economy.
- Non-Profit Organization:
- A non-profit organization is a group that is established with the intention of not making a profit, and in which no part of the organization’s revenue is given to its directors, officials, or members.
- Social Enterprise:
- An organization that uses commercial tactics to optimize advances in monetary, social, and environmental well-being is referred to as a social enterprise. This can entail increasing both social impact and profits for co-owners.
- Co-Operative:
- A co-operative is a free-standing group of people who come together voluntarily to work for the same economic, social, and cultural goals through a democratically run, collectively owned business.
- Social Conscious Business:
- Social consciousness is regarded as having a sensitivity to and sense of responsibility for injustice and social issues. The awareness of individuals within society is related to consciousness.
- Community Initiative:
- Achievements:
- According to the Impact Investors Council (IIC) report, over USD 9 billion has been invested in over 600 impact firms in India that have a positive impact on 500 million lives.
- Besides improving education for more than 226 million children and teenagers, these social entrepreneurs have helped reduce more than 192 million tonnes of CO2.
- They have promoted social inclusion for over 25 million individuals and assisted more than 100 million people gain access to electricity.
What is the Need for More Social Entrepreneurs?
- Tackling Social Problems:
- Social impact entrepreneurs have the ability to drive significant social change on a large scale. Unlike traditional approaches, they are open to taking risks.
- They utilize their business expertise and innovative thinking to develop sustainable solutions that benefit society.
- Promoting Inclusive Growth:
- India's economic growth has been impressive in recent years, but it has not been inclusive. There is a significant gap between the rich and poor, and many marginalized communities are left behind.
- Social Entrepreneurs can play a vital role in promoting inclusive growth by creating opportunities for marginalized communities.
- Tackling Environmental Challenges:
- India faces significant environmental challenges, including air and water pollution, deforestation, and climate change. Social entrepreneurs can create sustainable solutions to address these challenges.
- For example, they can create ventures that promote renewable energy, reduce waste, or promote sustainable agriculture. By doing so, they can help protect the environment and promote sustainable development.
- Bridging the Gap between Public and Private Sectors:
- Social Entrepreneurs can work with the government to create sustainable solutions to social and environmental problems.
- By doing so, they can leverage public resources and policies to create a more significant social impact.
- They can also work with the private sector to access capital, technology, and expertise, leading to more innovative and effective solutions.
- Social Entrepreneurs can work with the government to create sustainable solutions to social and environmental problems.
What are the Challenges of Social Entrepreneurship in India?
- Future Issues and Hypothetical Concerns:
- Social entrepreneurs tackle possible future issues such as overpopulation and sustainable energy sources, which makes it harder to attract investors who are more inclined towards safer, profit-driven projects.
- Business Strategy:
- Social entrepreneurs also face the challenge of developing a strong business strategy. They need support from professionals like attorneys, accountants, and experienced entrepreneurs to create a solid business plan that aligns with market realities and customer needs.
- Lack of Funding:
- Unlike traditional businesses, social enterprises often have to balance financial returns with social outcomes, which can make them less attractive to investors or donors. Moreover, they may face higher costs, risks, and uncertainties due to the complex and dynamic nature of the social problems they address.
- Lack of Balance:
- Social entrepreneurship can be very demanding and stressful, as it involves dealing with complex and urgent issues, facing multiple pressures and expectations, and making sacrifices and trade-offs.
- This can lead to burnout, exhaustion, or loss of motivation, which can affect their well-being and effectiveness.
Way Forward
- Social entrepreneurship has evolved over the years and has given innovative and profitable ideas that address social problems.
- The social entrepreneurship ecosystem in India is among the most developed in the world. It provides numerous opportunities to collaborate with local partners, learn from their experiences, and pursue creative solutions to some of the country’s many social problems in the areas of education, agriculture, healthcare, renewable energy, manufacturing, and skill development.
- The need of the hour is a nourishing ecosystem for social entrepreneurs to take up programmes, bridge pandemic-induced gaps, scale-up existing initiatives, and be part of the mainstream response system.
Important Facts For Prelims
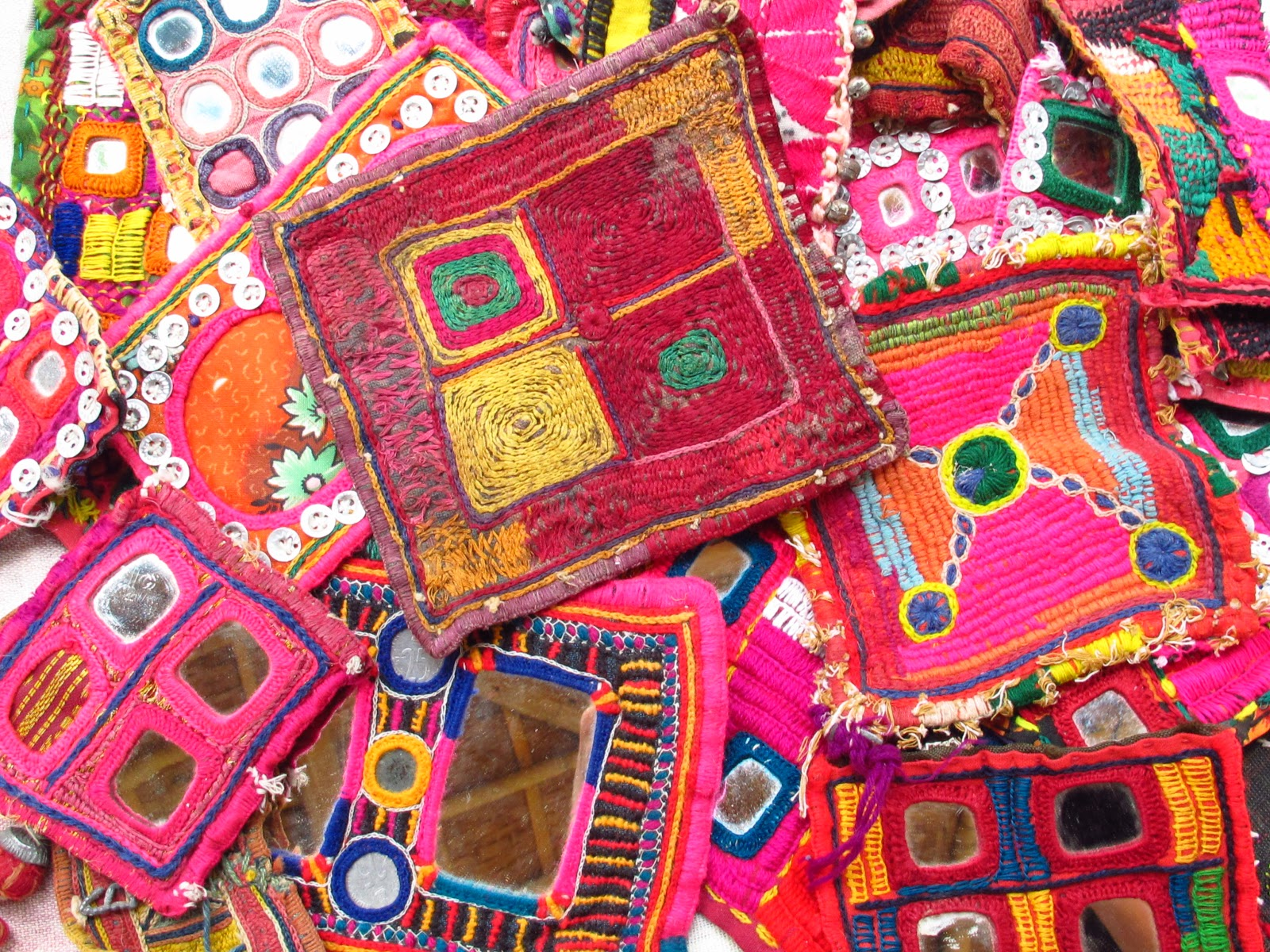
Lambani Art
Why in News?
The third G20 Culture Working Group (CWG) meeting in Hampi, Karnataka witnessed a historic moment as a Guinness World Record was established for the 'largest display of Lambani items’ in the event, titled 'Threads of Unity”.
- This achievement showcased the collective efforts of over 450 Lambani women artisans and cultural practitioners from the nomadic Lambani community in Karnataka.
- By supporting Lambani artisans, this initiative contributes to the economic independence of women. It aligns with the third priority of the CWG, 'Promotion of Cultural and Creative Industries and Creative Economy.
What is Lambani Art?
- Lambani art is a form of textile embellishment practised by the Lambani or Banjara community, a nomadic group inhabiting several states of India, especially Karnataka.
- It is characterised by colourful threads, mirror work, and a rich array of stitch patterns on loosely woven fabric.
- It involves skilfully stitching together small pieces of discarded fabric to create a beautiful patchwork.
- It is recognised as a sustainable practice that works on the principle of recycle and reuse.
- The Lambani embroidery techniques and aesthetics bear similarities with textile traditions in Eastern Europe, West Asia, and Central Asia, showcasing the interconnectedness of global textile arts
- Sandur Lambani embroidery, a specific type of Lambani art from the Sandur region of Karnataka, received a Geographical Indication tag in 2010.
G20 Culture Working Group
- The G20 Culture Ministers met for the first time in 2020 and highlighted culture’s cross-cutting contribution to advancing G20 agenda.
- Recognizing its impact on various aspects of development, culture was integrated into the G20 agenda as a Culture Working Group in 2021, acknowledging its synergies with other policy areas
- The G20 Culture Working Group stands among the 13 thematic Working Groups set up by the Indian Presidency to frame the G20 process in 2023 as part of the Sherpa Track.
- Priority Areas of CWC:
- Protection and Restitution of Cultural Property
- Harnessing Living Heritage for a Sustainable Future
- Promotion of Cultural and Creative Industries and Creative Economy
- Leveraging Digital Technologies for the Protection and Promotion of Culture
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 Consider the following statements about G-20: (2023)
- The G20 group was originally established as a platform for finance ministers and central bank governors to discuss international economic and financial issues.
- Digital public infrastructure is one of India's G-20 priorities
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: C
Important Facts For Prelims
Guillain-Barre Syndrome
Why in News?
Peru has declared a 90-day national health emergency in response to a recent surge in Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS) cases, raising concerns about the potential connection between GBS and Covid-19.
- Notably, Peru experienced a large outbreak of GBS in 2019 as well, with 683 suspected or confirmed cases during a specific period.
What is Guillain-Barre Syndrome?
- About: GBS is a serious autoimmune disorder that affects the peripheral nervous system. It initially presents weakness, tingling, and numbness in the limbs, which can progress to paralysis lasting 6-12 months or longer.
- The syndrome affects the nerves responsible for muscle movement, pain, temperature, and touch sensations.
- While more common in adults and males, GBS can occur in individuals of all ages.
- Cause: The exact cause of GBS is unknown, but as per the World Health Organisation (WHO), GBS is often preceded by an infection. This could be a bacterial or viral infection. This leads the immune system to attack the body itself.
- In rare cases, vaccinations and surgery may slightly increase the risk of developing GBS, but the likelihood of this happening is very low.
- Studies have shown that the risk of getting GBS from infections like the flu is much higher than the risk from vaccines, such as the flu vaccine.
- Treatment: GBS treatment involves procedures like plasmapheresis, which removes plasma and replaces it with other fluids.
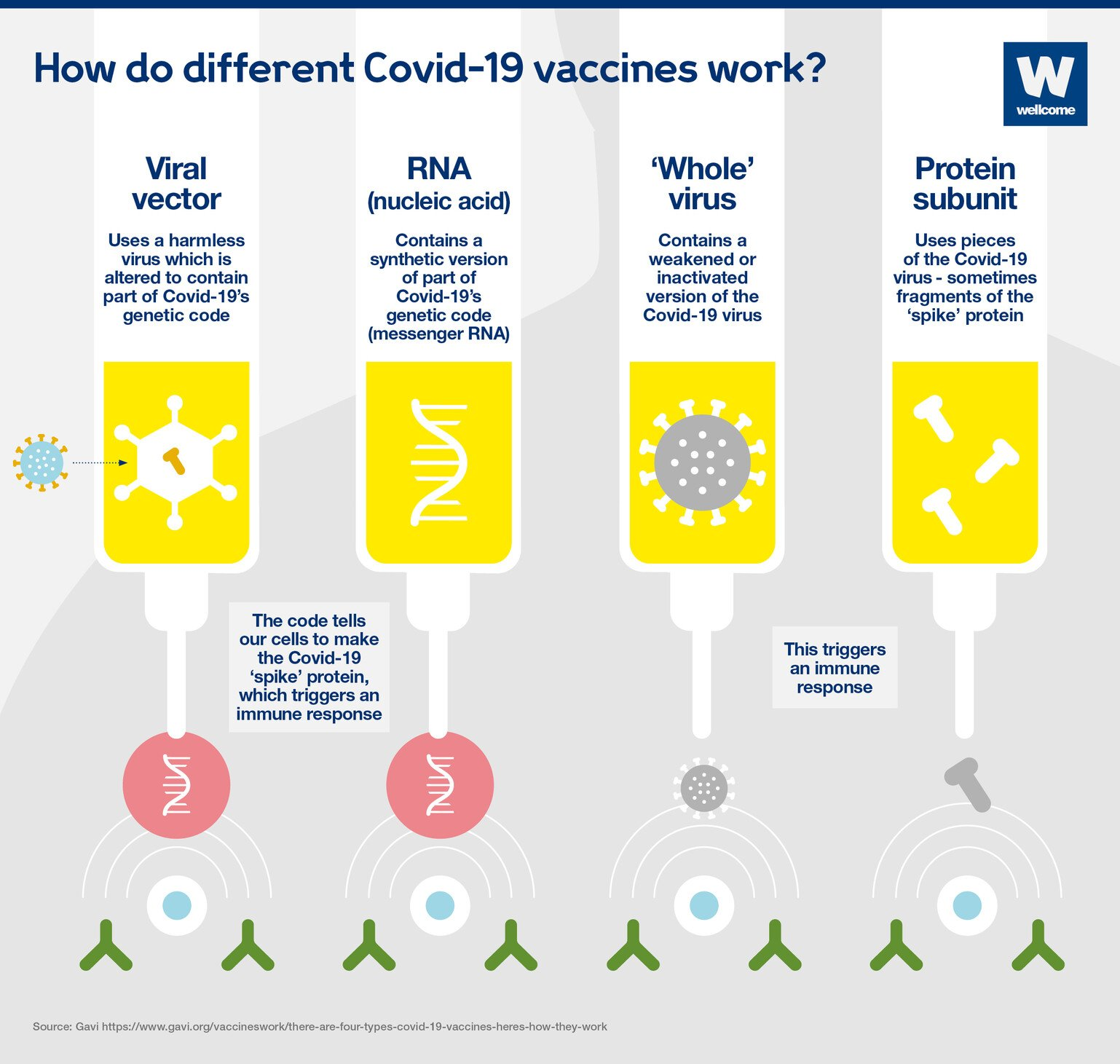
- GBS and Covid-19: GBS cases have been reported in both adults and children with Covid-19. Also, there have been concerns about cases of GBS following administration of Covid-19 vaccines.
- About 100 suspected cases of GBS were identified among the 12.8 million people who received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine (viral vector vaccine).
- Some cases of GBS have also been reported after receiving the Pfizer(mRNA vaccine) and AstraZeneca (viral vector vaccine) as well.
- A subcommittee of the WHO found that rare cases of GBS have been reported with adenovirus vector Covid-19 vaccines, but not with mRNA vaccines.
- However, recent studies suggest despite these potential side effects, the benefits of Covid-19 vaccination outweigh the risks.
- The incidence rate of GBS after SARS-CoV-2 infection or vaccination is low.
- About 100 suspected cases of GBS were identified among the 12.8 million people who received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine (viral vector vaccine).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. In the context of vaccines manufactured to prevent COVID-19 pandemic, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Serum Institute of India produced COVID-19 vaccine named Covishield using mRNA platform.
- Sputnik V vaccine is manufactured using vector-based platform.
- COVAXIN is an inactivated pathogen-based vaccine.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
BHARAT Campaign Launched to Boost Agri Infra Funding
Recently, the Ministry of Agriculture has called upon banks to actively promote the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF), a financing facility aimed at developing post-harvest infrastructure and community farm assets in the agricultural sector. With a target disbursement of Rs 1 lakh crore by 2025-26, the AIF will provide interest reduction and credit guarantee assistance until 2032-33. To accelerate the flow of funds, the ministry has launched the BHARAT (Banks Heralding Accelerated Rural & Agriculture Transformation) campaign, urging banks to participate actively in the promotion of the Agri Infra Fund. During the one-month campaign, banks are encouraged to achieve a target of Rs 7,200 crore. The involvement and support of over 100 banking executives from commercial banks, regional rural banks, small finance banks, NBFCs, and select cooperative banks have been sought.
Read more: Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)
India and EFTA Accelerate TEPA Negotiations
Recently, the Union Minister of Commerce & Industry, Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution and Textiles, concluded a successful meeting with the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) delegation in London. The discussions centered around advancing the Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA) negotiations between India and EFTA. The primary objective of these negotiations is to establish a fair, mutually beneficial, and comprehensive trade deal between India and EFTA.
EFTA is an intergovernmental organization that was established in 1960 as an alternative trade bloc for those European states that were unable or unwilling to join the European Union (EU). EFTA is India's 9th largest trading partner, accounting for about 2.5% of India's total merchandise trade in 2020-21.
The TEPA aims to create opportunities for trade and investment between India and EFTA by eliminating/reducing tariffs and non-tariff barriers on a wide range of products.
Read more: India and EFTA, India and EFTA states
GACL Initiates Domestic Production of Hydrazine Hydrate and Purified Phosphoric Acid
In a significant stride towards achieving self-reliance under the Atmanirbhar Bharat mission, Gujarat Alkalies and Chemicals Ltd (GACL), a leading chlor-alkali producer, has commenced the shipment of Hydrazine Hydrate. Furthermore, GACL has also addressed the scarcity of Purified Phosphoric Acid manufacturers in India by setting up a plant with a capacity of 33,870 MTA.
Hydrazine hydrate is a chemical compound with the formula N2H4·H2O. It is primarily used as a reducing agent in various chemical reactions, such as the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and agricultural chemicals.
Read more: Atmanirbhar Bharat Mission
Punjab Agricultural University Develops Nutrient-Rich Wheat Variety with Health Benefits
In a groundbreaking development, the Punjab Agricultural University (PAU) has successfully bred a new variety of wheat called PBW RS1, which contains high levels of amylose starch known to reduce the risks of type-2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
PBW RS1 has a total starch content similar to other wheat varieties (66-70%), but it boasts a remarkable 30.3% resistant starch content compared to the 7.5-10% found in other varieties. The variety not only offers nutritional benefits but also exhibits complete resistance to yellow rust and moderate resistance to brown rust fungal diseases.
Despite its nutritional advantages, PBW RS1 poses a challenge in terms of cultivation due to its lower average grain yield compared to other wheat varieties in Punjab.
Read more: Food security, Nutritional security, Diabetes, Cardiovascular diseases