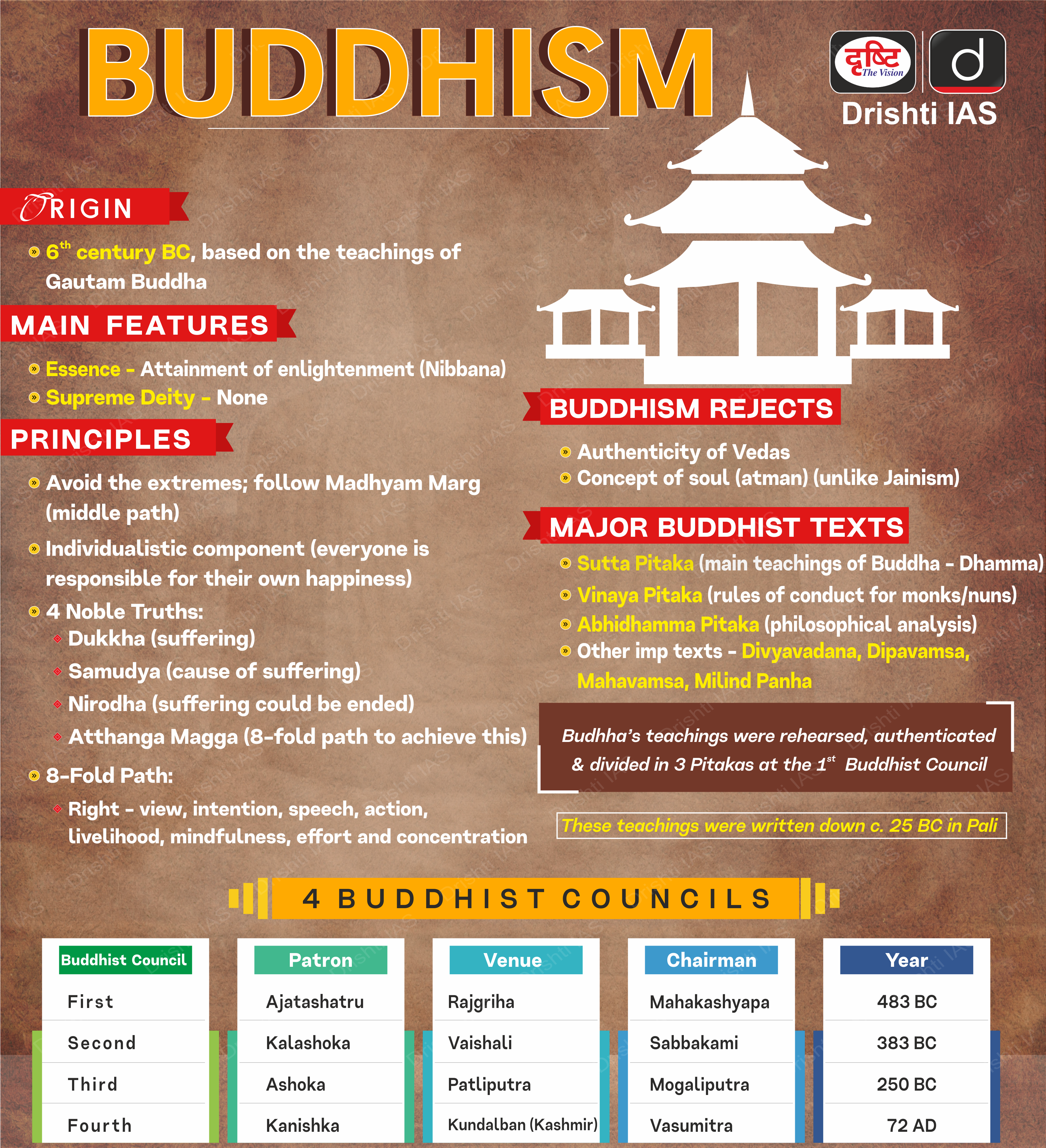
India-US Commercial Dialogue
Prelims: TPF, IPEF, iCET, Semiconductor, FDI, Climate Crisis.
Mains: India-US Commercial Dialogue.
Why in News?
Recently, India and the US have launched Joint Statement on their 5th Ministerial level Commercial Dialogue, discussing supply chain issues and agreeing on a semiconductor partnership initiative.
- In January 2023, the Union Minister of Commerce and Industry of India and the US Trade Representative Ambassador co-chaired the 13th Ministerial-level meeting of India – US Trade Policy Forum (TPF) in Washington D.C.
What are the Key Highlights of the Joint Statement?
- India-US Strategic Partnership:
- Both discussed India-US strategic partnership, as well as economic and commercial engagement between the two countries, including through the Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technology (iCET) and the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework (IPEF).
- MoU on Semiconductor Supply Chain:
- Both countries signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on semiconductor supply chain and innovation partnership to promote cooperation in the segment.
- Talent, Innovation and Inclusive Growth:
- Both countries recognized that small businesses and entrepreneurs are the lifeblood of the US and Indian economies and there is a need to facilitate collaboration between the SMEs of the two countries and to foster innovation ecosystems.
- In this context, both sides announced the launch of a new Working Group on Talent, Innovation and Inclusive Growth under the Commercial Dialogue.
- Travel and Tourism Working Group:
- They re-launched the Travel and Tourism Working Group to continue the progress from before the pandemic and to also address the many new challenges and opportunities to create a stronger travel and tourism sector.
- Standards and Conformance Cooperation Program:
- Both countries also launched the Standards and Conformance Cooperation Program that will be carried out in partnership between US’s American National Standard Institute (ANSI) and India’s Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) towards standards cooperation.
- Strategic Trade Dialogue:
- It will address export controls, explore ways of enhancing high technology commerce, and facilitate technology transfer between the two countries.
- Environmental Technology Business Development Mission:
- Also, the US will send a senior government official-led Clean Energy and Environmental Technology Business Development Mission to India in 2024.
- The trade mission would be an opportunity to further foster US-Indian business partnerships in grid modernization and smart grid solutions, renewable energy, energy storage, hydrogen, liquefied natural gas, and environmental technology solutions.
- Global Biofuels Alliance:
- Both sides also pledged to work together in the Global Biofuels Alliance and in the development and deployment of hydrogen technologies.
- US-India Energy Industry Network:
- The two sides made an announcement regarding US-India Energy Industry Network (EIN) as a broad platform for facilitating US industry involvement in the Clean EDGE Asia initiative, the US government’s signature initiative to grow sustainable and secure clean energy markets throughout the Indo-Pacific region.
- Telecommunications:
- Both sides expressed interest in working together in developing next generation standards in telecommunications, including 6G.
How are India’s Trade Ties with the US?
- India-US bilateral partnership today encompasses a whole host of issues including the response to Covid-19, economic recovery post-pandemic, the climate crisis and sustainable development, critical and emerging technologies, supply chain resilience, education, the diaspora, and defence and security.
- The bilateral goods and services trade between the two countries has almost doubled since 2014, exceeding US USD 191 billion in 2022.
- The United States has become India’s largest trading partner in 2022.
- The US is India’s largest exporter and trade partner, while India is the 9th largest trading partner for the US.
- Both nations aim to achieve bilateral trade of USD 500 billion by 2025.
- The US is also the third biggest investor in India with a cumulative Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) inflow of USD 56,753 million from April 2000 to September 2022.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q. ‘What introduces friction into the ties between India and the United States is that Washington is still unable to find for India a position in its global strategy, which would satisfy India’s National self-esteem and ambitions’. Explain with suitable examples. (2019)
Protecting Earth's Orbit from Space Debris
For Prelims: Space Debris, United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space, System for Safe and Sustainable Operations Management.
For Mains: Project NETRA, Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC), Clean Space Initiative of European Space Agency (ESA).
Why in News?
Since, United Nations agreed on a treaty to conserve and sustainably use the high seas beyond national boundaries, scientists are calling for a legally-binding agreement to protect the Earth's orbit from space debris.
- The United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space has laid out guidelines to mitigate space debris, but there is no international treaty that seeks to minimise it.
What is Space Debris?
- About:
- Space debris refers to the collection of artificial objects in orbit around the Earth that have lost their utility or are no longer in use.
- These objects include non-functional spacecraft, abandoned launch vehicle stages, mission-related debris, and fragmentation debris.
- Space debris refers to the collection of artificial objects in orbit around the Earth that have lost their utility or are no longer in use.
- Concern:
- The number of satellites orbiting Earth is expected to reach 60,000 by 2030, up from the current 9,000, and the amount of untracked debris is a cause for concern.
- Around 27,000 pieces of "space junk" are being tracked by NASA but over 100 trillion untracked pieces of old satellites circle the planet.
- Currently, companies are not incentivised to clean up orbits or to include de-orbiting functions in satellites.
- De-orbiting means bringing dead satellites back to Earth.
- The current Outer Space Treaty is hindered by ever-changing geopolitics, technology and commercial gain.
- Initiatives to Curb Space Debris:
- India:
- In 2022, ISRO set up the System for Safe and Sustainable Operations Management (IS 4 OM) to continually monitor objects posing collision threats.
- ‘Project NETRA’ is also an early warning system in space to detect debris and other hazards to Indian satellites.
- Global:
- India:
How Space Debris Can be Tackled?
- Space Treaty with Extended Producer Responsibility: A legally binding agreement is necessary to protect the Earth's orbit from space debris.
- The treaty should ensure that producers and users take responsibility for their satellites and debris and enforce collective international legislation with fines and other incentives to make countries and companies accountable for their actions.
- Incentivisation: Countries using the Earth's orbit should commit to global cooperation, and companies should be incentivized to clean up orbits and include de-orbiting functions in satellites.
- Reusable Launch Vehicles: Using reusable launch vehicles instead of single-use rockets can help reduce the number of new debris generated from launches.
Evolution of Women's Movements in India
For Prelims: Economic Survey 2022-23, SHG, Nationalist Movement, State-Led Movement for Economic Empowerment.
For Mains: Evolution of Women's Movement in India.
Why in News?
According to the Economic Survey 2022-23, there are about 1.2 crore Self Help Groups (SHG) in India, most of which are all-women. The Indian women's movement has been recognized globally for its vibrancy. However, the evolution of the movement has received less attention.
How the Women's Movement Evolved in India?
- Evolution:
- The movement has transformed over time from serving as a beacon for the nationalist movement to a rights-based civil society movement to a state-led movement for economic empowerment.
- Three Phases:
- Nationalist Movement (1936-1970s)
- Women were the face of the nationalist movement. The clarion call by Mahatma Gandhi to the 1936 All India Women’s Conference was the hallmark of a nationalist movement that relied on women to serve as its face.
- The movement aimed to give women political power. The political history of the Indian women’s movement was observed when women satyagrahis were arrested during the salt satyagraha and the Quit India movement.
- These movements set the stage for women's leadership in politics.
- Rights-Based Civil Society Movement (1970s-2000s)
- Women's groups were mobilised to sensitize women about their rights.
- The greatest success of this mobilisation came when the 73rd Amendment to the Constitution was passed, reserving one-third of seats in panchayat and leadership positions in local bodies for women.
- Chipko, one of the earliest ecofeminist movements in the world broadcasting pictures of women clinging to trees to protest logging.
- It was a non-violent agitation which originated in Uttar Pradesh’s Chamoli district (now Uttarakhand) in 1973.
- Also, Self Employed Women’s Association began to unionise women in the informal sector leading the advocacy for reforms in legal and social protection for women workers.
- Women's groups were mobilised to sensitize women about their rights.
- State-Led Movement for Economic Empowerment (2000s-present)
- The government invested heavily in building and supporting SHGs.
- SHGs function mainly as thrift and credit institutions.
- The movement aimed to enhance women's access to income-generating activities.
- The movement seeks to address the deficiency of vocational skills and entrepreneurship among women.
- Nationalist Movement (1936-1970s)
What are Self Help Groups?
- About:
- SHGs are informal associations of people who choose to come together to find ways to improve their living conditions.
- It can be defined as a self-governed, peer-controlled information group of people with similar socio-economic backgrounds and having a desire to collectively perform a common purpose.
- Objectives:
- SHG relies on the notion of “Self Help” to encourage self-employment and poverty alleviation.
- To build the functional capacity of the poor and the marginalized in the field of employment and income generating activities.
- To resolve conflicts through collective leadership and mutual discussion.
- To provide collateral free loans with terms decided by the group at the market driven rates.
- To work as a collective guarantee system for members who propose to borrow from organised sources.
Conclusion
The women's movement in India has evolved over time, with each phase addressing different aspects of women's lives. The future of the women's movement in India depends on how effectively the state-led movement can transform women's lives by taking economic empowerment programs to scale.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 Two of the schemes launched by the Government of India for Women’s development are Swadhar and Swayam Siddha. As regards the difference between them, consider the following statements: (2010)
- Swayam Siddha is meant for those in difficult circumstances such as women survivors of natural disasters or terrorism, women prisoners released from jails, mentally challenged women etc., whereas Swadhar is meant for holistic empowerment of women through Self Help Groups.
- Swayam Siddha is implemented through Local Self Government bodies or reputed Voluntary Organizations whereas Swadhar is implemented through the ICDS units set up in the states.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q.1 “Empowering women is the key to control population growth”. Discuss. (2019)
Q.2 Discuss the positive and negative effects of globalization on women in India? (2015)
Q.3 Male membership needs to be encouraged in order to make women’s organization free from gender bias. Comment. (2013)
CJI Urges SCO Member States to Strive for Judicial Cooperation
For Prelims: Chief Justice of India (CJI), Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), E-version of Supreme Court reports, Artificial intelligence, Shanghai Five, Overly Populated Prisons.
For Mains: Importance of Technology in Judiciary, SCO.
Why in News?
The Chief Justice of India (CJI) recently addressed the 18th meeting of the Chief Justices/Chairpersons of the Supreme Courts of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) member states.
- The conference provided an opportunity for member and observer states to reflect upon the challenges that are common to their jurisdictions and emphasised the need for mutual cooperation and sharing of experiences and wisdom gathered.
What are the Major Highlights of the Meeting?
- Smart and Accessible Judiciary:
- The CJI highlighted the need for judicial cooperation and adoption of new mechanisms to simplify and make the court processes more smart and accessible to the common people.
- Importance of Technology in Judiciary:
- The CJI also stressed the importance of technology in bridging the gap between citizens and the justice system.
- The CJI shared recent endeavours made by the Supreme Court of India, such as launching an e-version of Supreme Court reports, artificial intelligence-based live transcription of court proceedings, and translation of judgments in multiple regional languages, among others.
- Issues Highlighted:
- Also, various issues such as the overly populated prisons, access to quality legal representation, modern public judicial services, court work overload, limited judicial resources, high pendency of cases, and the need for adequate infrastructure facilities were highlighted.
What is SCO?
- About:
- The SCO is a regional intergovernmental organisation that promotes cooperation between its member states in the areas of security, economy, and culture.
- Genesis:
- Prior to the creation of SCO in 2001, Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia and Tajikistan were members of the Shanghai Five.
- Following the accession of Uzbekistan to the organisation in 2001, the Shanghai Five was renamed the SCO.
- India and Pakistan became members in 2017.
- Observer States: Iran and Belarus
- Iran will be the newest member of the largest regional organisation- the SCO, when it joins the forum in April 2023 under the chairmanship of India.
- Prior to the creation of SCO in 2001, Kazakhstan, China, Kyrgyzstan, Russia and Tajikistan were members of the Shanghai Five.
- Structure:
- Heads of State Council: The Supreme SCO body which decides its internal functioning and its interaction with other States & international organisations, and considers international issues.
- Heads of Government Council: Approves the budget, considers and decides upon issues related to economic spheres of interaction within SCO.
- Council of Ministers of Foreign Affairs: Considers issues related to day-to-day activities.
- Regional Anti-Terrorist Structure (RATS): Established to combat terrorism, separatism and extremism.
- Official language:
- The official working language of the SCO Secretariat is Russian and Chinese.
Conclusion
The member states agreed on shared goals for the future of their judiciary and entrusted the presidency for the next meeting of Chief Justices/Chairmans to Uzbekistan on rotation for the year 2024.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q.1 Consider the following: (2022)
- Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
- Missile Technology Control Regime
- Shanghai Cooperation Organisation
India is a member of which of the above?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q.1 Critically examine the Supreme Court’s judgement on ‘National Judicial Appointments Commission Act, 2014’ with reference to the appointment of judges of higher judiciary in India. (2017)
States Demand to Declare Lightning as a Natural Disaster
For Prelims: Natural Disasters, Lightning.
For Mains: Effects of lightning and lightning as a natural disaster and Natural Disaster
Why in the News?
Recently few States have demanded that “lightning” be declared as a “natural disaster” because deaths caused by it surpass any other disaster in India.
- According to present norms, cyclone, drought, earthquake, fire, flood, tsunami, hailstorm, landslide, avalanche, cloudburst, pest attack, frost and cold waves are considered as disasters that are covered under the State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF), 75% of which is funded by the Centre.
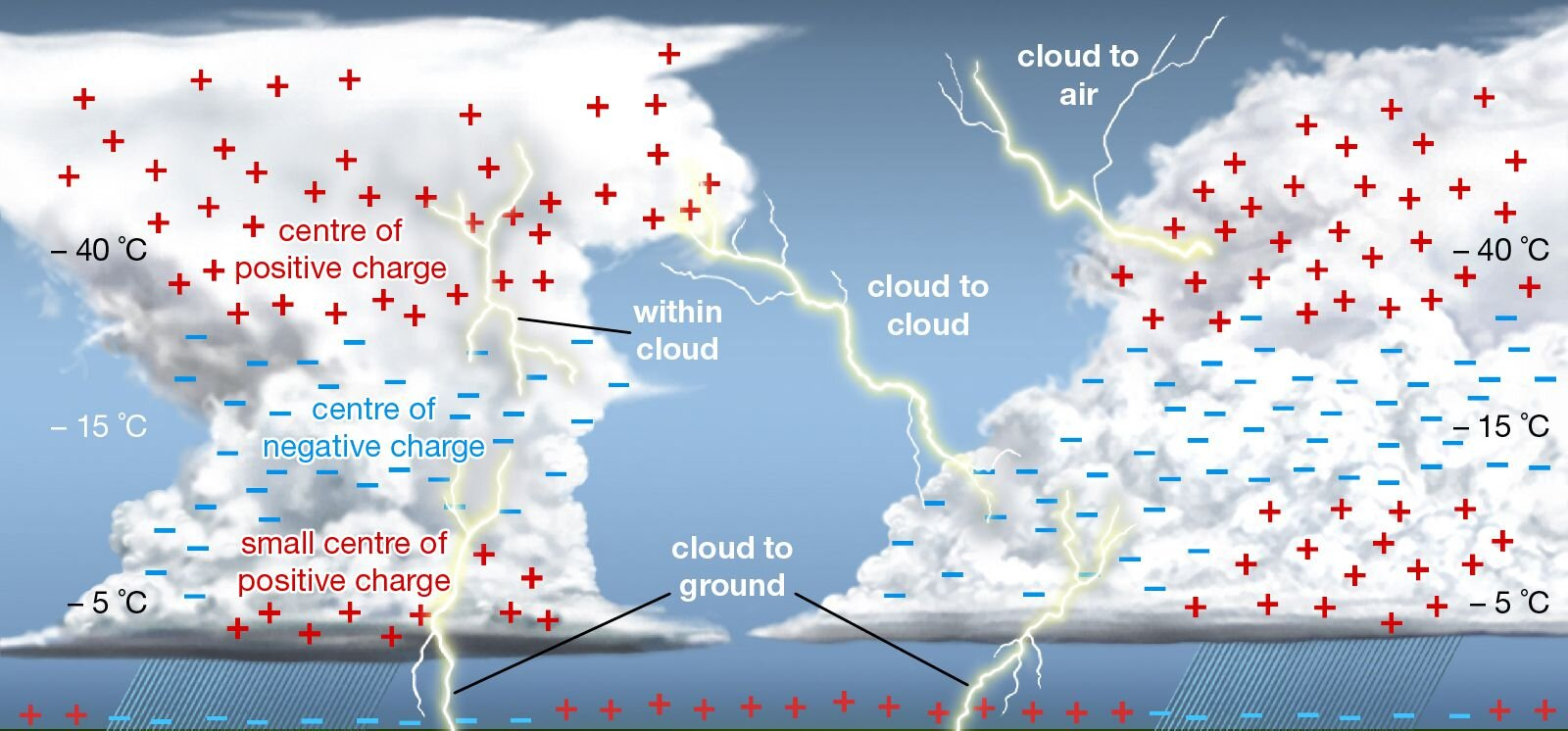
What is Lightning?
- About:
- It is the natural process of "an electrical discharge of very little duration and high voltage between a cloud and the ground or within a cloud," accompanied by a bright flash, a loud sound, and occasionally thunderstorms.
- Cloud-to-ground (CG) lightning is dangerous because it can electrocute people due to its high electric voltage and current. Inter- or intra-cloud lightning is visible and safe.
- Process of Lightning:
- Lightning is caused by a difference in electrical charge between the top and bottom of a cloud, which generates a huge current of electricity.
- Water vapor in the cloud condenses and rises, generating heat and pushing water molecules further up until they become ice crystals. Collisions between the ice crystals trigger the release of electrons, leading to a chain reaction that results in a positively charged top layer and negatively charged middle layer in the cloud.
- When the difference in charge becomes large enough, a huge current of electricity flows between the layers, producing heat that causes the air column to expand and produce shock waves that create thunder sounds.
- Lightning and the Climate Change:
- In a 2015 study from California University, the university cautioned that a rise in one degree Celsius would result in a 12% increase in the frequency of lightning strikes.
- Another study that was released in Geophysical Research Letters in March 2021 found connections between climate change and an increase in lightning strikes in the Arctic.
- Lightning Strikes in India:
- According to a newly published yearly report on lightning from the Lightning Resilient India Campaign (LRIC), India may have seen up to 18.5 million lightning strikes between April 2020 and March 2021.
- Each year, lightning claims the lives of more than 2,500 Indians.
- According to a study by the Delhi-based RMSI, a global leader in geospatial and engineering solutions, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, West Bengal, and Jharkhand have witnessed the maximum lightning strikes in recent years.
- According to government statistics, more than 100,000 individuals have died in the nation as a result of lightning strikes between 1967 and 2019. This represents more than a third of the deaths brought on by natural disasters throughout this time.
Way Forward
- Early Warning Systems: To warn people of impending thunderstorms and lightning strikes, India should invest in early warning systems. Weather radar, lightning detection networks, and smartphone applications are a few examples of these systems.
- Lightning Safety Measures: It is important to inform India's rural communities about quick and easy lightning safety precautions. This can involve putting lightning rods on homes, staying indoors during thunderstorms, and taking cover in secure structures.
- Research and Development: To better understand lightning and discover creative ways to lower the risk, the Indian government should support research and development projects.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q.1 During a thunderstorm, the thunder in the skies is produced by the (2013)
1. meeting of cumulonimbus clouds in the sky
2. lightning that separates the nimbus clouds
3. violent upward movement of air and water particles
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) None of the above produces the thunder
Ans: (d)
- Thunder is the sound produced by the rapid expansion of air, when it is heated by a lightning bolt.
- The air expands so quickly that it makes a loud sound called thunder.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
ESG and India
Prelims: CSR, Climate Change, UNPRI, BRSR, Poverty, Inequality.
Mains: ESG and India.
Why in News?
People across the world are embracing the idea that business should be measured on the Environment, Social and Governance (ESG) metric, however ESG laws and Regulations are still at a nascent stage in India, and much further to go in this direction.
What is ESG?
- About:
- ESG goals are a set of standards for a company’s operations that force companies to follow better governance, ethical practices, environment-friendly measures and social responsibility.
- Environmental criteria consider how a company performs as a steward of nature.
- Social criteria examine how it manages relationships with employees, suppliers, customers, and the communities where it operates.
- Governance deals with a company’s leadership, executive pay, audits, internal controls, and shareholder rights.
- It focuses on non-financial factors as a metric for guiding investment decisions wherein increased financial returns is no longer the sole objective of investors.
- Ever since the introduction of the United Nations Principles for Responsible Investing (UNPRI) in 2006, the ESG framework has been recognised as an inextricable link of modern-day businesses.
- ESG goals are a set of standards for a company’s operations that force companies to follow better governance, ethical practices, environment-friendly measures and social responsibility.
- Differing from CSR:
- India has a robust Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) policy that mandates that corporations engage in initiatives that contribute to the welfare of society.
- This mandate was codified into law with the passage of the 2014 and 2021 amendments to the Companies Act of 2013.
- The amendments require companies in any given financial year to spend at least 2% of their net profit over the preceding three years on CSR activities.
- Whereas ESG regulations differ in process and impact.
What is the Need for ESG in India?
- India faces significant environmental challenges, including air and water pollution, deforestation, and climate change, also there are significant social challenges such as poverty, inequality, discrimination, and human rights abuses, making the importance of investing in companies that are committed to addressing these issues and promoting social justice.
- India has a complex regulatory and legal environment, and companies operating in India may face challenges related to corruption, regulatory compliance, and corporate governance. Therefore, there is an increasing need for recognizing the companies with strong governance practices to mitigate these risks.
What are the Challenges related to ESG Compliance in India?
- Limited Awareness: Many companies in India may not be fully aware of the importance of ESG factors or may not have the resources to integrate ESG considerations into their business practices.
- Inadequate Data: In India, there may be limited publicly available data on ESG factors for companies, making it difficult for investors to evaluate ESG performance and make informed investment decisions.
- Weak Regulatory Environment: India's regulatory environment may not be fully developed or enforced to ensure ESG compliance by companies. This may lead to a lack of accountability and transparency in corporate practices.
- Cultural Factors: India has a diverse cultural landscape, and some traditional business practices may not align with ESG principles. Companies may need to navigate these cultural factors to implement ESG policies effectively.
- Limited ESG-focused Investment Options: Investors may have limited investment options that focus specifically on ESG factors in India, making it difficult to fully integrate ESG considerations into investment decision-making.
What Initiatives have been taken to Ensure ESG Compliance?
- One of the initial milestones towards identifying ESG disclosure requirements for companies was the release of the National Voluntary Guidelines on Social, Environmental and Economic Responsibilities of Business (NVGs) in 2011 by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
- In 2012, the SEBI formulated the Business Responsibility Reports (BRR) which mandated top 100 listed entities (which was extended to top 500 listed entities in 2015) by market capitalization to file BRR as part of their annual report.
- In 2021, SEBI replaced the existing BRR reporting requirement with a more comprehensive integrated mechanism, the Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR).
- It will be mandatorily applicable to the top 1,000 listed entities (by market capitalization) from FY 2022-23 onwards.
- The BRSR seeks disclosures from listed entities on their performance against the nine principles of the ‘National Guidelines on Responsible Business Conduct’ (NGBRCs).
Way Forward
- To promote ESG adoption in India, there needs to be increased awareness among companies, investors, and regulators about the importance of ESG factors for sustainable and responsible investing.
- Companies in India should provide more comprehensive and standardized disclosures on ESG factors to enable investors to evaluate their ESG performance more effectively.
- The regulatory environment in India should be strengthened to promote greater ESG compliance by companies. This could involve introducing more robust reporting requirements, establishing clearer ESG standards, and enforcing regulations more rigorously.
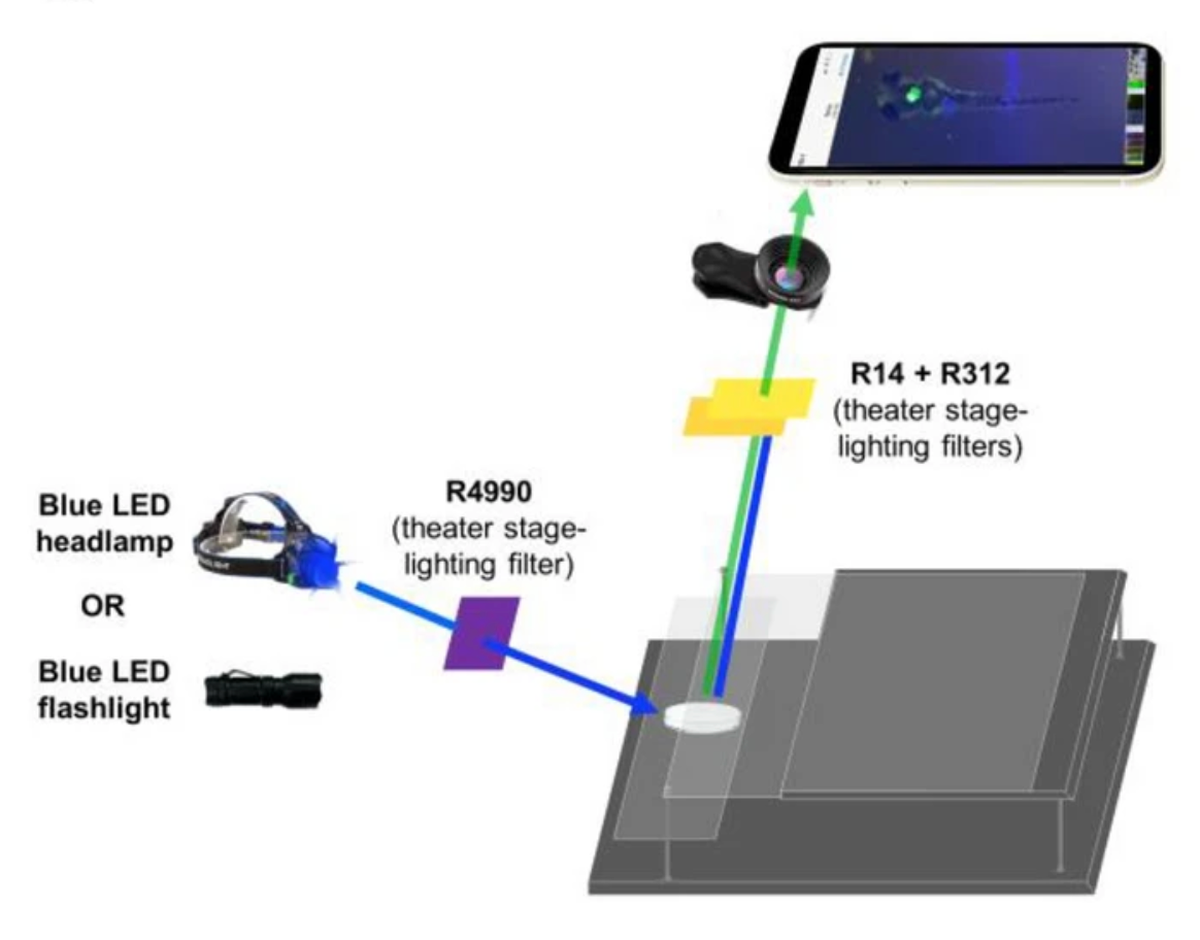
Glow Scope
Why in News?
Researchers at Winona State University, Minnesota, have created a design for a Glow Scope, a Fluorescence Microscope.
- With this setup, they were able to image the creatures’ brain, spinal cord, heart, and head and jaw bones.
- They were able to zoom in and out using the smartphone camera and the clip-on lens.
What is Fluorescence Microscopy?
- About:
- An optical microscope views an object by studying how it absorbs, reflects or scatters visible light.
- A fluorescent microscope views an object by studying how it reemits light that it has absorbed, i.e., how it fluoresces. This is its basic principle.
- The object is illuminated with light of a specific wavelength. Particles in the object absorb this light and reemit it at a higher wavelength. These particles are called fluorophores; the object is infused with them before being placed under the microscope.
Is the Glowscope Accessible?
- Using a ‘glowscope’ still requires access to fluorophores, suitable biological samples, the know-how to combine the two, and some knowledge of physics to work out which LED flashlight to buy.
- The Foldscope was truly remarkable because all its required components were simple to understand.
- In 2014, a group of scientists at Stanford University released Foldscope, a handheld microscope made almost entirely out of paper, which takes 30 minutes to put together, and which could capture images of cells.
- However, the fact that a simple fluorescent microscope can be set up for a few thousand rupees means, instead of being entirely out of reach, researchers can prepare samples and take them to schools, where students can observe them.
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
NASA’s Multi-Angle Imager for Aerosols (MAIA) missions
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and Italian Space Agency (Agenzia Spaziale Italiana :ASI) will build and launch the Multi-Angle Imager for Aerosols (MAIA) missions before 2024. The three-year mission will focus on 11 primary target areas including New Delhi from India.
MAIA is a satellite instrument that will collect data to examine the health effects of different types of air pollution. It will use measurements of sunlight reflecting off airborne particles to determine the abundance, size, chemical composition, and optical properties of pollutants in the atmosphere. The data will be collected from sensors on the ground and atmospheric models. These results will then be related to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, adverse reproductive outcomes, human birth, death and hospitalisation records to understand impacts of contaminated air we breathe.
The observatory will consist of the PLATiNO-2 satellite, which ASI will provide. The observatory’s science instrument contains a pointable spectropolarimetric camera, which captures digital images at multiple angles in the ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared and shortwave infrared portions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Read More: Aerosols
Indonesia’s Merapi Volcano Erupted
Merapi (Mountain of Fire) is the most active of more than 120 active volcanoes in Indonesia and has repeatedly erupted with lava and gas clouds recently. It rises to 2,911 metres and has steep slopes with dense vegetation on its lower sides. It is located near the centre of the island of Java and Indonesia’s cultural capital, Yogyakarta.Its last major eruption in 2010 killed 347 people and displaced 20,000 villagers.
Indonesia, an archipelago of 270 million people, is prone to earthquakes and volcanic activity because it sits along the “Ring of Fire,” a horseshoe-shaped series of seismic fault lines around the Pacific Ocean. An eruption in December 2021 of Mount Semeru, the highest volcano on Java island, left 48 people dead and 36 missing.
World’s Fastest Single-shot Laser Camera
Scientists from Germany and the US have built the world’s fastest single-shot laser camera – 1,000x faster than its predecessors at capturing extremely short-lived events. They used the camera to provide the most precise view yet of how a hydrocarbon flame produces soot.
The device’s technique is called laser-sheet compressed ultrafast photography (LS-CUP) combining laser sheet imaging with compressed sensing on a standard streak camera system. It “can resolve a plane of a three-dimensional object like a flame or spray or any turbid media and can “resolve physical or chemical processes” in space and time. It can capture images at 12.5 billion frames per second (fps).
Their device can also be used to photograph shockwaves in nuclear reactors, combustion of fine sprays, and an enigmatic process called sonoluminescence (sometimes, when excited by sound, bubbles in a liquid implode and release light at a temperature of ~10,000 K), all of which involve processes that happen in a few nanoseconds. However, the technology can be cost intensive.
Read More: Soot (Black Carbon)
Maritime Partnership Exercise (MPX) With French Navy
Indian Navy’s indigenously built guided missile frigate, INS Sahyadri participated in a Maritime Partnership Exercise (MPX) with French Navy (FN) ships in the Arabian Sea in March 2023.
The exercise witnessed a wide spectrum of evolutions at sea which included cross deck landings, boarding exercises and seamanship evolutions. The seamless conduct of the exercise reaffirmed the interoperability and high level of cooperation between the two navies.
INS Sahyadri is fitted with state-of-the-art weapons and sensors, which makes it capable of detecting and neutralising air, surface and sub-surface threats. The ship is a part of Indian Navy’s Eastern Fleet based at Visakhapatnam.
Also, India-France joint Military exercise FRINJEX-2023 was recently conducted in Kerala. Theme of the FRINJEX was ‘Humanitarian assistance and Disaster relief operations in contested environment.’
Other India France Exercises include Varuna (Naval exercise), Garuda (Air exercise), Shakti (Army exercise), Desert Knight-21 (Air exercise).