162nd Birth Anniversary of Swami Vivekananda
For Prelims: National Youth Day, Swami Vivekananda, National Youth Policy 2014, Ramakrishna Paramhansa, Vivekananda Rock Memorial, Vedanta, Yoga, Neo-Vedanta, Upanishads, Gita, Buddha, Ramakrishna Mission, Parliament of Religions, Sustainable Development Goals, National Education Policy 2020.
For Mains: Contributions of Swami Vivekananda. Role of youth in nation building
Why in News?
On National Youth Day (162nd birth anniversary of Swami Vivekananda), Prime Minister participated in the Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue 2025.
- The National Youth Day is celebrated on 12th January to commemorate the great spiritual leader, philosopher and thinker Swami Vivekananda.
- The National Youth Policy 2014 defines youth as the persons in the age group of 15-29 which constitute nearly 40% of India's total population.
What is the Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue?
- About: It is a platform aimed at engaging youth in nation-building, aligning with the Prime Minister’s Independence Day call to involve 1 lakh youth in politics without political affiliations.
- Participation: The event brings together 3,000 dynamic youth aged 15-29 years, selected through a merit-based, multi-stage process called the Viksit Bharat Challenge.
- Thematic Focus: Young leaders will present ideas on ten thematic areas critical to India's development, including technology, sustainability, women empowerment, manufacturing, and agriculture.
What are Key Facts Regarding Swami Vivekananda?
- About: Swami Vivekananda, born as Narendra Nath Datta on 12th January 1863, was a monk and the chief disciple of Ramakrishna Paramhansa.
- In 1893, upon the request of Maharaja Ajit Singh of the Khetri State, he took the name ‘Vivekananda’, changing from ‘Sachidananda’ that he used before.
- Enlightenment: In 1892, Swami Vivekananda was said to have swum to a rock (later named Vivekananda Rock Memorial) in the Indian Ocean from the shores of Kanyakumari for meditation.
- He spent three days and nights there, resulting in his enlightenment.
- Contributions:
- Philosophical: He introduced the world to the Indian philosophies of Vedanta and Yoga.
- He preached ‘neo-Vedanta’, an interpretation of Hinduism through a Western lens, and believed in combining spirituality with material progress.
- Spiritual: Vivekananda's message on human values draws from the Upanishads, the Gita, and the examples of Buddha and Jesus, emphasizing self-realization, compassion, and selfless service.
- He advocated the doctrine of service. Serving jiva (living beings) is considered worship of Shiva.
- He gave the four pathways of attaining moksha (liberation) from the worldly pleasure and attachment in his books- Raja-yoga, Karma-yoga, Jnana-yoga and Bhakti-yoga.
- Revivalism: He laid emphasis on education for the regeneration of our motherland. He advocated a man-making character-building education.
- Philosophical: He introduced the world to the Indian philosophies of Vedanta and Yoga.
- Core Values:
- Youth: He encouraged the youth to commit to their goals for success, stressing the importance of dedication in facing challenges.
- Swamiji urged them to develop both mental and physical strength, with 'muscles of iron' and 'nerves of steel’.
- Ethics: Ethics is a code of conduct that guides a person to be a good citizen, and purity, being our true divine Self or Atman, reflects our real nature.
- Religion: His view of religion sees it as a universal experience of transcendent reality, free from superstition, dogma, priestcraft, and intolerance..
- Education: Vivekananda emphasized education that reveals students' innate knowledge and power, focusing on character-building and making them self-reliant to face life's challenges.
- Rationality: He fully supported the methods and results of modern science and did not reject reason in favor of faith.
- Nationalism: His nationalism is based on Humanism and Universalism, the two cardinal features of Indian spiritual culture.
- His nationalism is based on concern for the masses, freedom, equality, and Karma Yoga — a path to political and spiritual freedom through selfless service.
- Youth: He encouraged the youth to commit to their goals for success, stressing the importance of dedication in facing challenges.
- Associated Organisations: He founded the Ramakrishna Mission in 1897 to propagate the ideals of service, education, and spiritual upliftment.
- In 1899, he established the Belur Math, which became his permanent abode.
- International Address: He addressed the Parliament of Religions held in Chicago in 1893, at which he represented Hinduism.
- In July, 1896, he addressed a conference of the London Hindu Association in London.
Views Related to Vivekananda
- No other religion preaches the dignity of humanity in such a lofty strain as Hinduism and no other religion on earth treads upon the poor and the low in such a fashion as Hinduism. —Swami Vivekananda.
- A country where millions have nothing to eat and where few thousand holy men and brahmins suck the blood of the poor and do nothing at all for them, is not a country but a living hell. Is this religion or a dance of death? —Swami Vivekananda
- Forget not that the lower classes, the ignorant, the poor, the illiterate, the cobbler, the sweeper are thy flesh and blood, thy brothers. —Swami Vivekananda.
- So far as Bengal is concerned Vivekananda may be regarded as the spiritual father of the modern nationalist movement. —Subash Chandra Bose.
National Youth Policy (NYP) 2014
- About NYP 2014: It is a policy framework by the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports to empower the youth of India to achieve their full potential and participate actively in the development of the country.
- About NYP 2024: The Government has reviewed and updated the NYP 2014, and has released a draft for the new NYP 2024.
- This draft outlines a ten-year vision for youth development in India, aligned with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- It focuses on five main areas: education, employment, youth leadership, health, and social justice, with a commitment to social inclusion.
- Key points include:
- A clear plan to achieve youth development goals by 2030.
- Alignment with the National Education Policy 2020 to improve career and life skills.
- Strengthening leadership and volunteering opportunities and using technology to empower youth.
- Enhancing healthcare, especially mental health and reproductive health, and promoting sports and fitness.
- Ensuring safety, justice, and support for marginalized youth.
Conclusion
The Viksit Bharat Young Leaders Dialogue and Swami Vivekananda’s teachings emphasize youth empowerment, ethical leadership, and holistic development. Aligning with national goals like NYP 2024, these initiatives aim to equip youth with education, self-reliance, and rationality to shape India’s sustainable future while honoring its spiritual and cultural heritage.
|
Drishti Mains Question: “A strong, rational, and ethical youth is the cornerstone of a developed India.” Comment in light of Vivekananda’s teachings. |
Community Notes Programme Against Fake News
For Prelims: Meta, Election, Deep Fake, Jana Gana Mana, Press Council Act, 1978, News Broadcasters Association, Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000, Community Notes Programme, User-Generated Context.
For Mains: Issues related to fake news, social media regulation in India
Why in News?
Meta, the parent company of Facebook and Instagram, has scrapped its 3rd-party professional fact-checking programme and replaced it with a Community Notes programme similar to X platform (formerly Twitter).
- Meta said that fact-checking organisations had behaved in a partisan way and added that the Community Notes programme would face fewer biases.
- Experts warn that replacing fact-checkers with a community-based network could lead to increased fake news and misinformation in India.
What is a Community Notes programme?
- About: It is an initiative of X, aimed at combating misinformation and enhancing content quality through user-generated context.
- It empowers users rather than relying solely on centralized moderation teams.
- Community Notes was first piloted as a programme called ‘Birdwatch’ by Twitter in 2021.
- Function: Users provide notes on posts that need clarification or additional context.
- Notes are visible only when a diverse group agrees on their accuracy and usefulness.
- Algorithmic Review: A rating system ensures that only the most balanced and widely supported notes appear publicly. This helps mitigate bias and ensure fairness.
- No Editorial Oversight: Unlike traditional fact-checking or moderation, the notes are not edited or curated by platform employees but are entirely community-driven.
Professional Fact Checkers
- About: Professional fact-checkers are individuals or organizations that verify public claims to combat misinformation in the digital age.
- Meta collaborates with 11 independent, certified fact-checking organisations covering content in 15 languages in India.
- Key Characteristics: Professional fact-checkers are trained, independent, and non-partisan, using evidence-based methods and ethical codes for transparent claim verification.
- Prominent Examples: International ones include PolitiFact, FactCheck.org, and Snopes, while India-specific platforms are Alt News, Factly, and Boom Live.
What are the Concerns Regarding the Community Notes Programme in India?
- Vulnerability to Misinformation: Without professional fact-checkers, untrained users may struggle to identify biases and misinformation.
- Without oversight, political or biased content may dominate, misleading large sections of the population.
- Shifting Responsibility to Users: User-flagged content may experience delays in addressing misinformation as companies shift responsibility to the public, resulting in inconsistencies and the potential spread of false information.
- Ideological Bias: Without neutral fact-checking, content may skew politically, contributing to manipulation and polarization, especially in politically charged environments that may enforce majoritarian views.
- Financial and Technical Challenges: Losing support from platforms like Meta could limit fact-checkers' scope, weakening fight against misinformation and leaving gaps in content verification.
- Diversity and Context: India's cultural and political diversity makes community-based fact-checking challenging, as interpretations may vary.
- Complex issues may require professional expertise to interpret accurately, which users may not provide.
Why is Fact-Checking Essential?
- Fair Journalism: Fact-checking ensures media credibility, fosters transparency, and combats misinformation, especially on social media, by correcting false claims and ensuring accurate news.
- Political Integrity: Fact-checking ensures election integrity by combating misinformation and verifying political claims to prevent misleading the electorate.
- Technological Innovations: The rise of deep fakes, viral rumors, and manipulated media requires professional journalists to investigate and verify content.
- Accountability: By scrutinizing and exposing exaggerations or falsehoods, fact-checkers ensure that those in power are held to high standards of truthfulness.
Popular Examples of Fake News from India
- Muzaffarnagar riots of 2013 caused by fake video fuelled communal passions
- UNESCO has declared ‘Jana Gana Mana’ best national anthem in the world (WhatsApp)
- GPS tracking nano chip in 2000 Rupee notes (Nov 2016)
- A Indian politician used photo of Russian streets to show LED-electrification of Indian streets
- Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) annual report used a picture of Spain-Morocco border to show Indian border floodlighting
What are Challenges in Tackling Fake News?
- Lack of Legal Definition: Most countries (including India), including those with robust free speech laws, lack a clear legal definition of fake news, complicating efforts to regulate it effectively.
- A study found that false information spreads 70% more quickly than accurate news on social media platforms.
- Balancing Regulation and Free Speech: Efforts to curb fake news often risk being perceived as censorship, leading to controversies over freedom of expression and content moderation practices.
- Passive Re-sharers: A significant number of users unknowingly share unverified content, amplifying misinformation without malicious intent, which is harder to address with punitive measures.
- Platform Accountability: Social media platforms have limited accountability due to safe harbor protections making it challenging to hold them liable for user-generated content.
- Language and Regional Diversity: India, with over 22 official languages and hundreds of dialects, faces unique challenges in combating fake news, as a BBC study (2019) revealed that misinformation often spreads faster in regional languages than in English or Hindi.
- Rise of Deepfakes: According to Deeptrace Labs (2019), the number of deepfake videos online doubled every 6 months, with 96% related to disinformation or exploitation.
- Deepfake tools are now widely accessible, lowering the barrier for malicious actors.
What are Provisions to Tackle Fake News in India?
- Press Council of India (PCI): The Press Council Act, 1978 allows the PCI to censure or warn media outlets for spreading fake news or professional misconduct.
- News Broadcasters Association (NBA): The NBA is a self-regulatory body that ensures better control over the quality and accuracy of content aired on private television news channels.
- Indian Penal Code (IPC): Sections 153 and 295 of the IPC (Bharatiya Nyay Sanhita) can be invoked to deal with fake news that incites violence, communal unrest, or insults religious sentiments.
- Defamation Laws: Defamed individuals can file a case under IPC Section 499, with criminal defamation under Section 500 carrying up to two years of imprisonment.
- Section 66 in IT Act, 2000: The Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000 penalizes cybercrimes such as identity theft (Section 66C), cheating by impersonation (Section 66D), privacy violations (Section 66E), transmitting obscene material (Section 67) etc.
Way Forward
- Multilingual Moderation: Develop AI-driven tools for detecting fake news in regional languages and dialects. Collaborate with linguists and local fact-checkers to improve monitoring of regional content.
- Platform Accountability: Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and WhatsApp must ensure accountability by investing in strong moderation systems to prevent the spread of fake news, especially during elections.
- Ethical Journalism: Implementing stringent editorial guidelines, independent audits of content, and holding journalists accountable for spreading fake news are crucial for maintaining trust in the media.
- Public Awareness: Governments and NGOs can run awareness campaigns to educate the public on the dangers of fake news and the importance of verifying information, helping reduce misinformation spread.
- Media Literacy Programs: Introduce media literacy and critical thinking as part of school curricula to cultivate a generation of responsible digital citizens.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What are the challenges India faces in implementing effective fact-checking mechanisms, and how can these challenges be addressed? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. In India, it is legally mandatory for which of the following to report on cyber security incidents? (2017)
- Service providers
- Data centres
- Body corporate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. What do you understand about the concept of “freedom of speech and expression”? Does it cover hate speech also? Why do the films in India stand on a slightly different plane from other forms of expression? Discuss. (2014)
Challenges and Developments Related with Denotified Tribes
For Prelims: Idate Commission report, Nomadic, Semi Nomadic, and De-Notified Tribes (NTs, SNTs, and DNTs) in India, National Commission for Schedule Tribes, Kanjar, Nat, Pardhi, and Sapera, Sixth Schedule.
For Mains: Issues related to Denotified Tribes (DNTs), Nomadic Tribes (NTs), and Semi-Nomadic Tribes (SNTs), Challenges and Measures.
Why in News?
The Denotified Tribes (DNTs), Nomadic Tribes (NTs), and Semi-Nomadic Tribes (SNTs) in India face numerous challenges, including denial of caste certificates in most states.
- Despite the Indian Government launching the Scheme for Economic Empowerment of DNTs scheme (SEED) for their upliftment, various other issues have led to growing discontent among these communities.
What are the Major Challenges faced by DNTs, NTs, and SNTs?
- Historical Injustice: These tribes were labeled criminal tribes under the Criminal Tribes Act,1871 during British rule, stigmatizing them for generations.
- Despite being denotified in 1952, the stigma persists, impacting their social and economic inclusion.
- Historically, Nomadic Tribes and De-notified Tribes never had access to private land or home ownership.
- Unclassified Communities: The Idate Commission (2017) identified a total of 1,526 DNT, NT and SNT communities.
- Out of these 1,526 identified communities, 269 communities are still unclassified under the categories of either SC, ST or OBC.
- Similarly, many individuals from these communities are unable to obtain caste certificates in 29 states, limiting their access to welfare schemes.
- Several estimates suggest a significant population of over 25 crore individuals, yet many lack basic identity recognition.
- Implementation Gaps: Recommendations of the Idate Commission, including a permanent commission and caste-census inclusion, remain unaddressed.
- The SEED scheme has seen limited success due to delays and lack of outreach. Overlapping benefits with SC/ST/OBC schemes lead to difficulties in beneficiary identification.
- Lack of Representation: Leadership positions remain scarce for DNT communities, with no full-time chairperson in the Union government’s Development and Welfare Board for DNTs, SNTs, and NTs (DWBDNC).
Idate Commission, 2014
- About: It was established in 2014 under the leadership of Bhiku Ramji Idate, to compile a statewide catalogue of Denotified, Nomadic, and Semi-Nomadic Tribes (DNTs).
- Mandate: It was mandated to recognize those excluded from Scheduled Castes (SC), Scheduled Tribes (ST) and Other Backward Classes (OBC) categories and recommend welfare measures for their well-being.
- Recommendations:
- Create a permanent commission with legal standing for the DNTs, SNTs, and NTs.
- Assign individuals not identified in the SCs/STs/OBCs list to the OBC category.
- Enhance legal and constitutional safeguards by incorporating a third schedule into the Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989 to prevent atrocities and restore the feeling of security amongst the members of the community.
- Form a distinct department to address the welfare of these communities in states with significant populations.
- Undertake a thorough survey of DNT families to determine their estimated numbers and distribution.
Note: Instead of establishing a permanent commission for De-notified Tribes (DNTs), the government set up the DWBDNC under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, citing that a permanent commission would conflict with the existing National Commissions for SCs, STs, and OBCs.
Who are DNTs, NTs, and SNTs?
- About: The term De-notified Tribes refers to communities that were once classified under the Criminal Tribes Acts,1871 which were implemented by the British Government.
- The Acts were abolished by the Government of India in 1952, leading to the De-Notification of these communities.
- A few of these communities which were listed as de-notified were also nomadic.
- Nomadic and semi-nomadic communities are defined as those who move from one place to another rather than living in one place all the time.
- While most DNTs are spread across the SC, ST and OBC categories, some DNTs are not covered in any of the SC, ST or OBC categories.
- Distribution: DNTs encompass a wide range of communities, each with unique cultural practices, languages, and socio-economic conditions. Communities include the Kanjar, Nat, Pardhi, and Sapera.
- South Asia is estimated to have the largest nomadic population in the world. In India, approximately 10% of the population comprises NTs, SNTs, and DNTs.
- While there are around 150 De-notified Tribes, the Nomadic Tribes population includes about 500 distinct communities.
- Major Committees/Commissions for DNTs, NTs, and SNTs Communities:
- The Criminal Tribes Inquiry Committee, 1947 constituted in the United Provinces (now Uttar Pradesh).
- Ananthasayanam Ayyangar Committee, 1949.
- Criminal Tribes Act, 1871 was repealed based on the recommendation of this committee.
- Kaka Kalelkar Commission (also called first OBC Commission), 1953.
- B P Mandal Commission, 1980.
- The commission also made some recommendations related to the issue of NTs, SNTs, and DNTs Communities.
- The National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution (NCRWC), 2002 held that DNTs have been wrongly stigmatised as crime prone and subjected to high handed treatment as well as exploitation by the representatives of law and order and general society.
- Renke Commission (2005): The commission had estimated their population to be around 10 to 12 crores at the time.
What is SEED?
- About: The Scheme for Economic Empowerment Denotified, Nomadic, Semi Nomadic communities was launched in February 2022 by the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment.
- Aim and Components: It aims to provide free competitive exam coaching to these students for Civil Services, entry to professional courses like medicine, engineering, MBA, etc.
- To provide health insurance to families, to uplift clusters of these communities through livelihood initiatives, and to provide financial assistance for housing.
- Health Insurance through PM Jan Arogya Yojana.
- Livelihoods through National and State Rural Livelihood Missions (NRLM and SRLMs).
- Land and Housing construction of houses through PM Awas Yojana.
- To provide health insurance to families, to uplift clusters of these communities through livelihood initiatives, and to provide financial assistance for housing.
- Features: It ensures expenditure of Rs.200 crore to be spent over five years beginning 2021-22.
- The DWBDNCs has been tasked with the implementation of this scheme.
What are India's Efforts Taken for DNTs, NTs, and SNTs?
- Dr Ambedkar Pre-Matric and Post-Matric Scholarship for DNTs: This Centrally Sponsored Scheme was launched in 2014-15 for the welfare of those DNT students who are not covered under SC, ST or OBC.
- The scheme of Pre-matric Scholarships for DNT students is helpful in spreading education amongst DNT children, especially the girl child.
- Nanaji Deshmukh Scheme of Construction of Hostels for DNT Boys and Girls: This Centrally Sponsored Scheme, launched in 2014-15, is implemented through State Governments/UT Administrations/Central Universities.
- The goal of the program is to offer hostel accommodations to DNT students who do not fall under the categories of SC, ST, or OBC.
Way Forward
- Policy Implementation: Expedite the classification process for DNT communities within SC/ST/OBC frameworks. Issue caste certificates alongside regular caste classifications. e.g. SC-DNT, ST-DNT.
- Strengthening SEED Scheme: Improve outreach through active Non-Governmental Organisation (NGO) participation and awareness drives.
- Simplify eligibility processes to ensure that all eligible families access education, housing, and livelihood support.
- Identity and Representation: Conduct a caste-based census to capture the actual population and socio-economic conditionvs of these communities.
- Encourage community representation in policy making through reserved leadership roles.
- Institutional Reforms: Establish a permanent commission with a clear mandate to oversee DNT welfare. Ensure district-level complaints committees to address grievances.
|
DRISHTI Mains Question: Critically examine the socio-economic issues faced by the Denotified and Nomadic Tribes communities and suggest policy measures for their upliftment. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to ‘Changpa’ community of India, consider the following statements:(2014)
- They live mainly in the State of Uttarakhand.
- They rear the Pashmina goats that yield a fine wool.
- They are kept in the category of Scheduled Tribes.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. What are the two major legal initiatives by the State since Independence addressing discrimination against Scheduled Tribes (STs). (2017)
Sovereign AI
Why in News?
The government is investing in semiconductors and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to ensure AI sovereignty as India's digital economy is aiming for USD 1 trillion by 2028.
What is Sovereign AI?
- About: Sovereign AI refers to a nation's ability to develop, control, and deploy artificial intelligence using its own infrastructure, data, workforce, and business networks.
- This includes developing AI models, infrastructure, and fostering talent within the country.
- Growth of AI: In 2018, a 340-million-parameter model was considered large (LLMs), while today, ChatGPT has 1.8 trillion parameters, Gemini has 1.5 trillion, and China’s DeepSeek has 240 billion.
- Parameters are internal variables that are adjusted during training to improve a model's performance.
- Key Aspects:
- National Control: Sovereign AI ensures alignment with national laws, regulations, and ethics.
- Data Sovereignty: It emphasizes data control within borders, safeguarding privacy and national security.
- AI in Governance: Generative AI is reshaping markets, governance, industries, and work dynamics, with AI-powered copilots assisting professionals.
- Ethical Considerations: Nations set security protocols and ethical standards for AI use.
- Strategic Autonomy: Sovereign AI reduces reliance on foreign technologies, promoting domestic AI development.
- Economic Competitiveness: AI is key to industrial innovation; without it, India risks falling behind globally.
- Various Applications: Sovereign AI is used in critical sectors like defense, healthcare, and transportation.
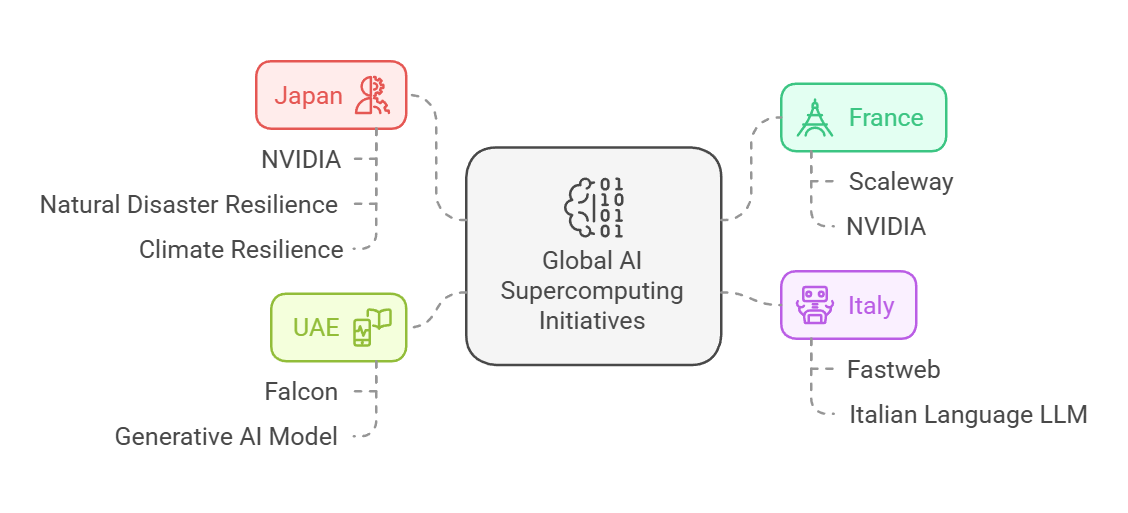
- India’s Position: Tata Group and Reliance are developing AI infrastructure and Large Language Models (LLMs) for India.
- India allocated USD 1.2 billion for a sovereign AI project, including an AI supercomputer with thousands of chips under IndiaAI Mission.
- Global AI Cooperation: A proposed Global AI Compact suggests that AI resources should be shared across nations, ensuring equitable access to critical technologies.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following?(2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Harvest Festivals
Why in News?
- The President of India has greeted citizens on the eve of Lohri, Makar Sankranti, Pongal and Magh Bihu.
- These are harvest festivals celebrated in diverse forms across the various regions of India.
What are the Harvest Festivals in India?
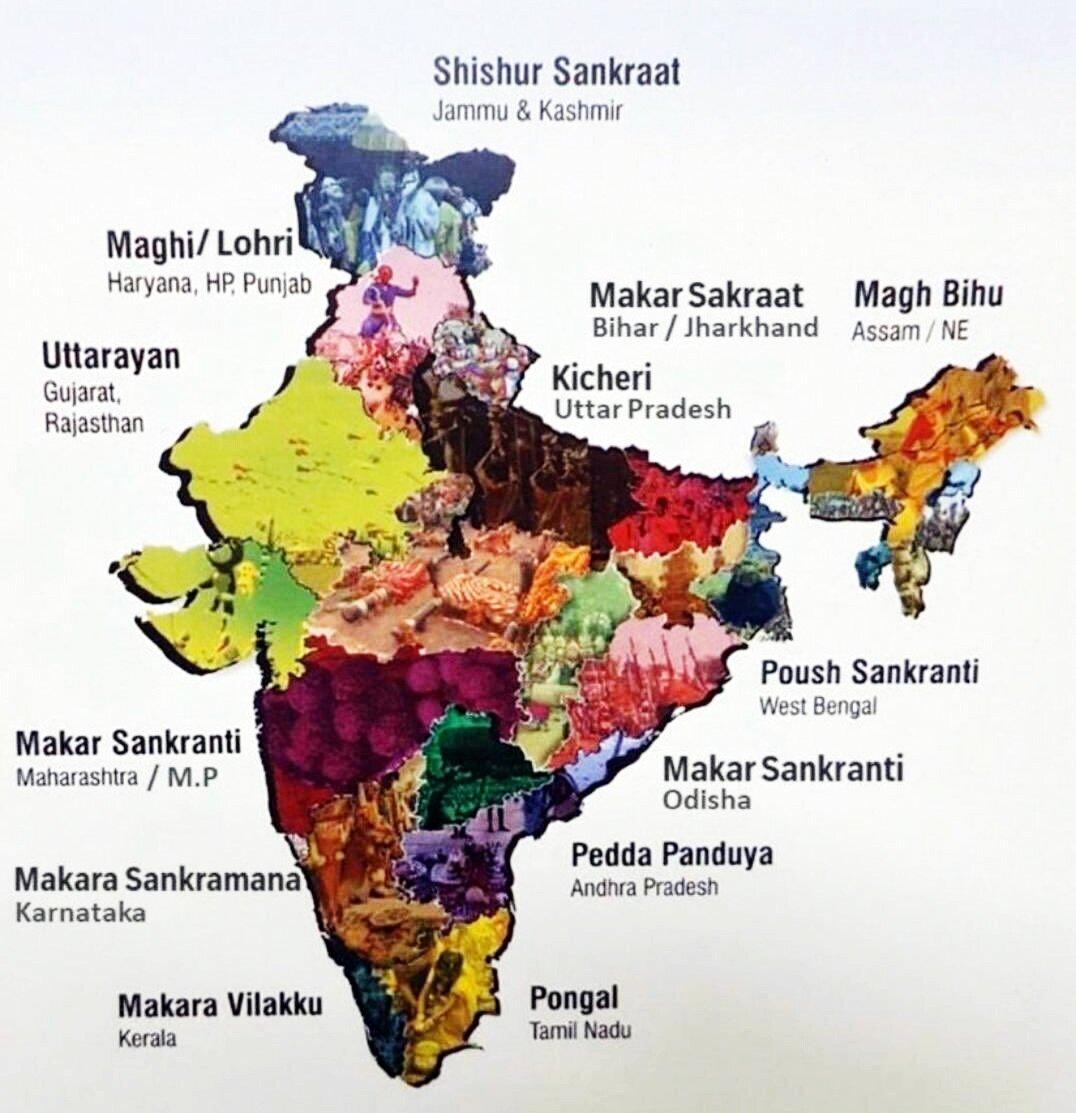
- About: They are celebrated to mark the end of the harvesting season across India under various names e.g., Makar Sankranti, Pongal, Magh Bihu, Lohri, etc.
- Astronomical Significance: It marks the transition of the Sun into the Capricorn (Makara) zodiac sign and the start of the Sun's northward journey (Uttarayan).
- It represents the shift from winter to warmer months, symbolizing the end of inactivity.
- Unlike festivals based on the lunar cycle, it follows the solar cycle, resulting in a fixed date of 14th January.
- Cultural Significance: Sankranti rituals, including bathing, offering Naivedhya (food) to Lord Surya, giving charity, performing Shraddha, and breaking fast, are performed during the day.
- Devotees often bathe in sacred rivers like the Ganga, Yamuna, Godavari, Krishna, and Cauvery.
- Regional Celebrations:
- Tamil Nadu (Pongal): The four-day festival marks the rice harvest, with Tamilians decorating their homes with traditional kolams made from rice powder.
- Karnataka: Locals have a tradition of sharing sesame and jaggery mixture symbolising harmony and goodwill.
- Farming communities dress their cattle in colorful costumes and jewels, making them jump over a fire pit in a display called ‘Kicchu Haisodu’.
- Punjab (Lohri): Lohri involves bonfires, folk songs, and offerings like groundnuts and popcorn to the fire.
- Bihar: A festival called ‘Khichdi’ is celebrated and a dish of the same name (rice and lentils) is prepared. Sesame and jaggery ladoos or chikkis are distributed.
- Rajasthan and Gujarat: Celebrated with kite-flying competitions and festivals, including the International Kite Festival in Ahmedabad.
- In the evening, sky lanterns light up the skies.
- Assam (Magh Bihu): Magh Bihu in Assam celebrates the annual harvest and marks the beginning of the Assamese new year.
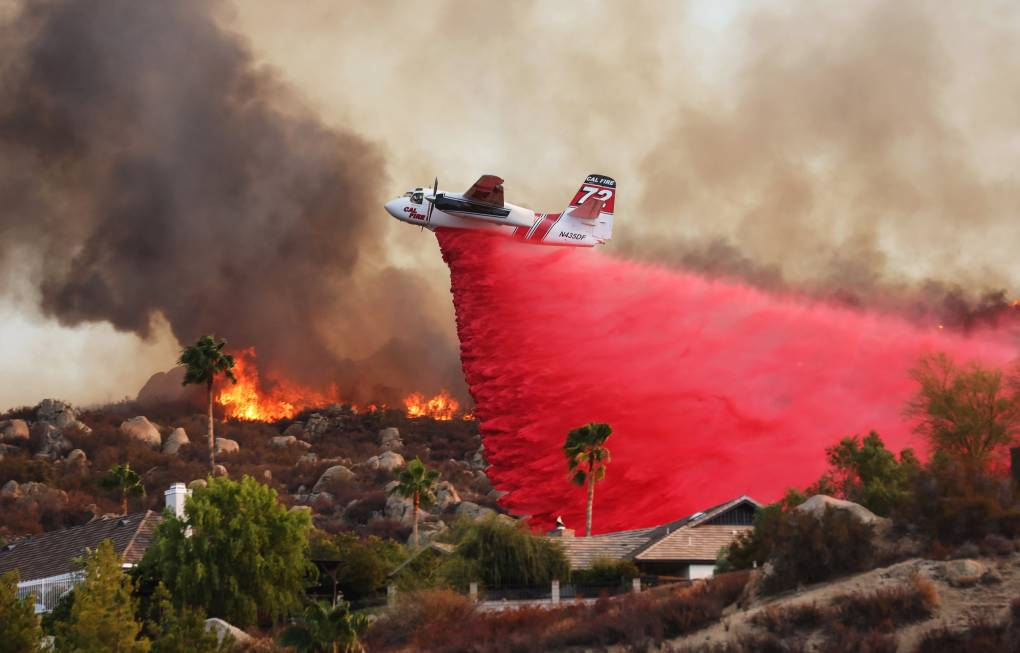
Wildfires in California
Why in News?
Los Angeles, California, is battling devastating wildfires, with fatalities and structural losses, as authorities deploy pink fire retardants to contain the flames.
- These wildfires have been occurring with increasing frequency and outside the usual wildfire season, prompting questions about their causes, the role of climate change, and potential solutions.
- Authorities are using pink fire retardants to control the wildfires.
Note: In India, as per the India State of Forest Report (ISFR) 2021 published by the Forest Survey of India (FSI), 35.47% of the forest cover is prone to fire.
What are the Causes and Impacts of Frequent Wildfires in California?
- Natural Causes:
- Lightning Strikes: Lightning Strikes ignite dry vegetation like trees and grass, triggering uncontrollable fires, especially when combined with strong winds. This is common during dry seasons.
- Climate Change: California, in the last two winters (2022 and 2023) saw heavy rainfall, promoting vegetation growth.
- The unusually dry winters of 2024-2025 have dried out vegetation in Los Angeles, turning it into fuel for wildfires.
- Global warming has also exacerbated dry and wet seasons, leading to prolonged droughts and reduced moisture in vegetation, which has led to a rise in frequency and severity of wildfires.
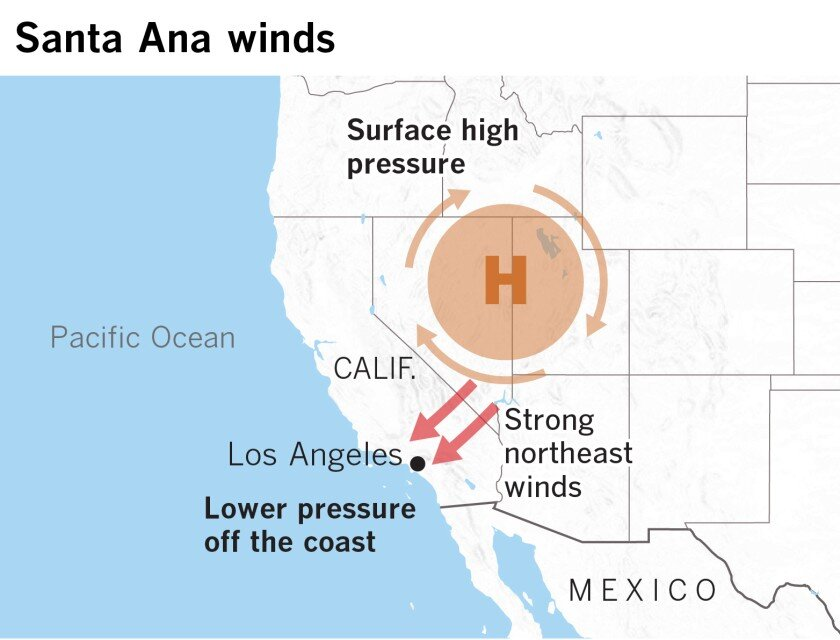
- Santa Ana Winds: The Santa Ana winds in California, typically strong between October and January, have been exceptionally powerful in 2025.
- The winds originate from high-pressure systems in the Great Basin and blow hot, dry air from east to west, flowing down towards the Pacific coast.
- As air descends the Sierra Nevada and Santa Ana mountains and passes through valleys, it gets compressed, which raises its temperature and reduces humidity.
- In Southern California, these winds exacerbate wildfires by rapidly spreading flames across dry vegetation, power lines, and buildings.
- Human Intervention: According to the US National Park Service, human activities account for approximately 85% of wildfires in the US.
- Campfires: Unattended or improperly extinguished campfires are major human-induced causes of wildfires.
- Roadside Ignition: Sparks from vehicles, such as dragging chains or malfunctioning catalytic converters, can ignite fires along highways.
- Power Lines: Faulty or wind-disturbed power lines often trigger wildfires.
- Other Human Activities: Equipment malfunctions, arson, and discarded cigarettes also contribute to wildfire outbreaks.
- Sometimes smugglers and wildlife traffickers ignite wildfires to divert the attention of security forces or to destroy the evidence of crime.
- Impact of Wildfires:
- Economic loss from destruction of life and property.
- Air pollution by small particulate matter and also acids, organic chemicals, and metals along with dust and allergens.
- Land degradation as high temperatures consume all nutrients and vegetation from a land, leaving it barren and infertile.
- Loss of biodiversity
What is Pink Fire Retardant?
- About:
- It is a chemical mix used to slow or extinguish wildfires.
- It primarily contains ammonium phosphate-based slurry with salts like ammonium polyphosphate and toxic metals like chromium and cadmium.
- A commonly used fire retardant in the US is Phos-Chek.
- Phos-Chek is a mixture of water, ammonium phosphate-based fertilizers (diammonium phosphate and ammonium polyphosphate), and a red dye (iron oxide) for visibility.
- It also includes thickening agents to enhance its stickiness and prevent drift during aerial application.
- Function: It is sprayed ahead of fire that coats vegetation to prevent oxygen from aiding combustion.
- Pink is chosen because it is highly visible, helping firefighters target fire lines more effectively.
- Concerns: Toxic metals like chromium and cadmium cause cancer and organ damage, and pose severe risks to aquatic life when they contaminate waterways.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following: (2019)
- Carbon monoxide
- Methane
- Ozone
- Sulphur dioxide
Which of the above are released into atmosphere due to the burning of crop/biomass residue?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)
Z-Morh Tunnel
The Prime Minister inaugurated the Z-Morh tunnel aimed at improving all-weather connectivity between Ladakh and Kashmir.
- Location: The 6.5 km Z-Morh tunnel, located at 8,650 feet in Ganderbal, Kashmir, bypasses avalanche-prone zones on the Srinagar-Leh highway (NH-1).
- It was built under the Thajiwas glacier and the tunnel has been renamed Sonamarg tunnel.
- Timeline: Built at Rs 2,400 crore, the project began in 2015 under BRO but later, it was developed by the National Highways and Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL).
- Strategic Partnership: Paired with the Zojila tunnel, it improves road access to Ladakh, reducing the route by 6 km between Srinagar and Ladakh.
- The Zoji La tunnel (14.15 Km), Asia's longest bi-directional tunnel, will ensure all-weather connectivity between Srinagar, Kargil, and Leh.
- Strategic Significance: Ensures year-round connectivity to Ladakh for military and civilian needs.
Read More: Z-Morh Tunnel
Cryo-Born Baby Corals
The world's first cryo-born baby corals have been successfully introduced into the Great Barrier Reef, marking a groundbreaking achievement in coral restoration and conservation.
- Australian scientists used cutting-edge cryopreservation to fertilize coral eggs with cryopreserved sperm collected from the Great Barrier Reef.
- Scientists grew the corals in the National Sea Simulator before transferring them to specially designed ‘coral cradles’ on the Reef.
- It aims to introduce heat-tolerant corals to protect reefs from climate change and rising ocean temperatures.
- The CryoDiversity Bank in Australia holds the world’s largest collection of frozen coral sperm from 32 species, collected annually since 2011.
- Coral Reefs: Corals are invertebrates from the class Anthozoa, phylum Cnidaria.
- Reefs are formed by colonies of polyps that secrete limestone skeletons and rely on symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae) for nutrition.
- Soft corals are species that do not produce the massive calcium carbonate skeletons needed to form coral reefs. Only hard corals make reefs.
Read More: World's Largest Deep Sea Coral Reef
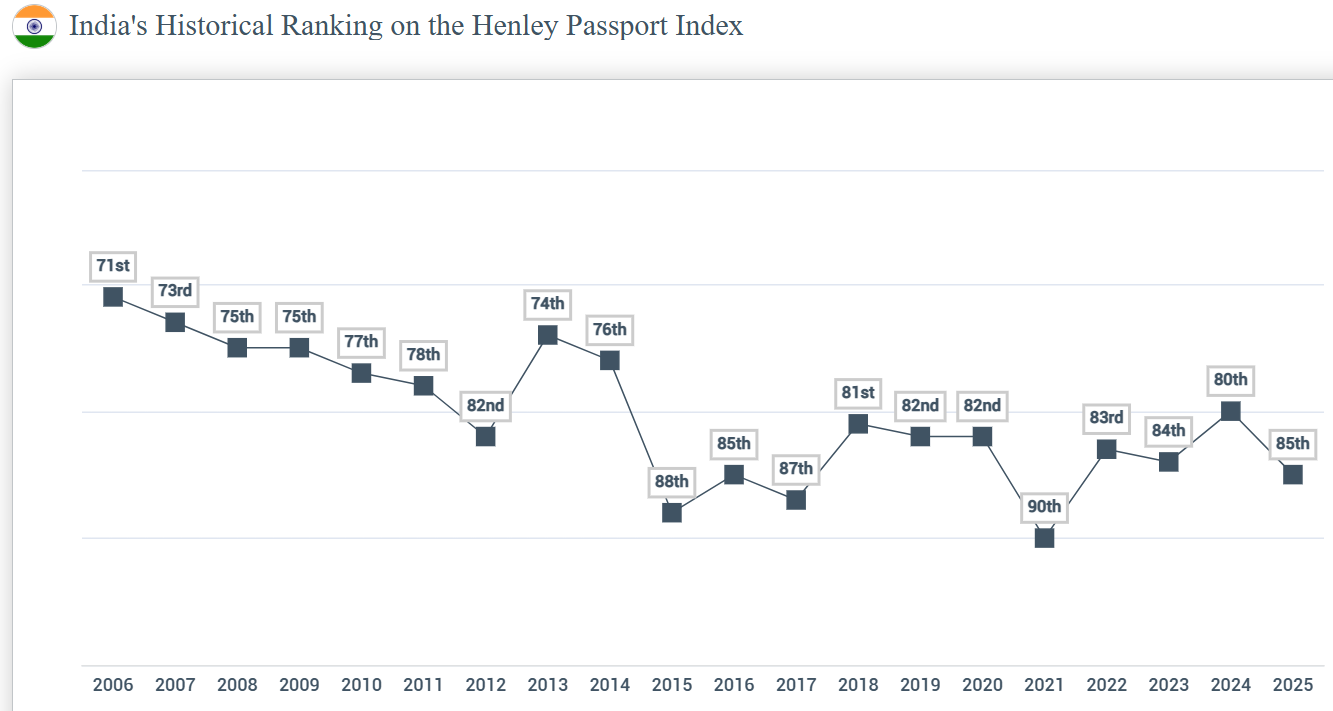
Henley Passport Index 2025
In the latest Henley Passport Index 2025, India's rank has dropped to 85th, down from 80th in 2024 giving its holders visa free access to 57 countries.
- India's ranking showed fluctuations over the years, with its highest being 71st in 2006 and lowest 90th in 2021 due to Covid-19 restrictions.
Henley Passport Index 2025
- About:
- The Henley Passport Index ranks 199 global passports (covers 227 travel destinations) based on the number of destinations their holders can travel to without a visa, with data sourced from the International Air Transport Association (IATA).
- It is compiled and published by Henley & Partners, a global citizenship and residence advisory firm.
- Key Highlights:
- Top Rankings: Singapore (195 destinations) leads, followed by Japan (193). Several EU countries and South Korea share 3rd place (192 destinations).
- Falling Rankings: The US (2nd to 9th), the UK (1st to 5th).
- Bottom Countries: Pakistan and Yemen (shared the 103rd position) followed by Iraq, Syria and Afghanistan.
- As per UK-based online platform "Compare the Market," 2024 data:
- Most Expensive Passports: Mexico, Australia, and the USA
- Cheapest Passports: UAE, India, and Hungary.
- India’s passport stands out for offering the best "cost per year" value, making it highly economical compared to other countries.
Read More: Henley Passport Index 2023
Unauthorized Railway E-ticket Declared Illegal
In the Mathew K Cherian Case, 2025, the Supreme Court held that unauthorised business of procuring and supplying railway e-tickets is a social crime which must be stopped.
- Section 143 of the Railways Act, 1989 addresses penalties for the unauthorized sale and procurement of railway tickets, both online and offline.
- The case referenced the English case of Comdel Commodities Ltd. v. Siporex Trade SA Case, 1990 to argue that legal provisions can extend to unforeseen technological advancements.
- The Kerala High Court had previously ruled that the provision applied only to offline ticket sales but was corrected by the Supreme Court.
- Mathew, the accused, created hundreds of unauthorized user IDs to circumvent ticketing limits set by IRCTC (12-24 ticket reservations per month), violating Section 143 of the Act.
- The Indian Railways is a keystone of India’s infrastructure that carries around 673 crore passengers annually.
Read More: Rerouting Indian Railways' Future
Mobile Connectivity at Maha Kumbh Mela 2025
The government is preparing to provide seamless mobile connectivity at the Maha Kumbh Mela 2025 in Prayagraj.
- Maha Kumbh Mela 2025 is expected to host 40 crore devotees over 44 days, averaging nearly 1 crore devotees per day expected to be the maximum tele-density in human history.
- Over 100 km of optical fibre has been laid, and each tower will be configured with higher radio capacities to ensure peak data capacity.
- 78 transportable towers and 150 small cell solutions will be deployed in crowded zones to maintain communication.
- Special centres will facilitate emergency communication, coordinated with local authorities.
- The Maha Kumbh Mela 2025, a sacred pilgrimage, will be held in Prayagraj from 13th January to 26th February 2025.
- It occurs every 12 years, rotating among four locations i.e., Prayagraj (UP), Haridwar (UK), Nashik (MH), and Ujjain (MP).
- The word Kumbh refers to a pot or vessel, which, in Hindu mythology, is said to have held the nectar of immortality (amrit).
- Uttar Pradesh has declared the Maha Kumbh area in Prayagraj as a new district called Maha Kumbh Mela for 4 months i.e., 1st December 2024 to 31st March 2025.
Read More: Maha Kumbh Mela 2025

.png)