Infographics
Nobel Prize-2023
Read More: Nobel Prize in Physics, Chemistry, Medicine, Economics, Peace and Literature


Biodiversity & Environment
Stratospheric Aerosol Intervention Impact on Global Food Production
For Prelims: Stratospheric Aerosol Intervention, Geoengineering Technique
For Mains: Application of Geoengineering Techniques and Concerns, Science and Technology- Developments and their Applications and Effects, Climate Change.
Why in News?
A recent study published in the journal Nature Food highlights the potential consequences of a geoengineering technique, stratospheric aerosol intervention (SAI), on global food production.
What are the Key Highlights of the Study?
- SAI as a Climate Intervention:
- SAI is considered a Plan B for addressing climate change if traditional mitigation strategies fail.
- SAI mimics volcanic eruptions by injecting sulphur dioxide into the stratosphere (layer of atmosphere extending from about 10 kilometres to 50 km in altitude), where it oxidises to form sulphuric acid, which then forms reflective aerosol particles.
- For example, Mount Pinatubo in the Philippines erupted in 2001 and injected about 15 million tonnes of sulphur dioxide into the stratosphere, which then formed aerosol particles.
- According to the National Aeronautics and Space Administration(NASA), it caused a drop in the average global temperature of about 0.6 degrees Celsius over the next 15 months.
- Diverse Impact on Agriculture:
- Reduction in temperature due to SAI affects agriculture differently based on factors like precipitation and solar radiation.
- Understanding the ideal global temperatures for crop production is crucial for informed decision-making.
- Researchers employ computer models to evaluate the effects of SAI scenarios on crops like maize, rice, soybean, and spring wheat.
- Under uncontrolled climate change, crop production thrives in cold, high-latitude areas like Canada and Russia.
- Moderate SAI levels could enhance food productivity in mid-latitude temperate regions like North America and Eurasia.
- Under large amounts of climate intervention, agricultural production in the tropics could see an increase.
- These regions include Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean and the top half of South America, most of Africa, parts of the Middle East, most of India, all of Southeast Asia, most of Australia and most of the island nations of Oceania.
- Different nations may opt for varying SAI levels to maximize crop production, considering their geographical location and climate conditions.
- Reduction in temperature due to SAI affects agriculture differently based on factors like precipitation and solar radiation.
- Comprehensive Impact Assessment:
- Beyond crop production, the study underscores the need to explore other consequences, such as effects on human health and ecosystems.
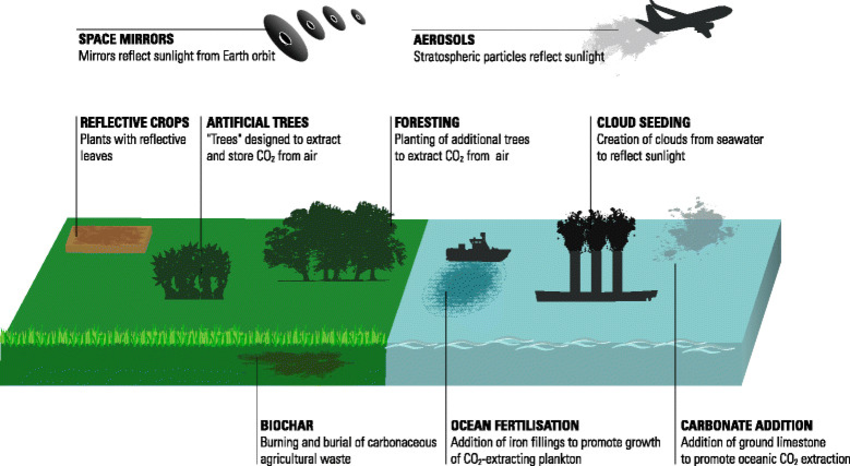
What is Stratospheric Aerosol Intervention (SAI)?
- SAI is a proposed method of solar geoengineering (or solar radiation modification) to reduce global warming.
- This would introduce aerosols into the stratosphere to create a cooling effect via global dimming and increased albedo, which occurs naturally from volcanic winter.
- However, some of the possible disadvantages of SAI are that it could have unintended consequences for the environment and human society, such as affecting the ozone layer, the hydrological cycle, the monsoon systems, and crop yields.
What is Geoengineering Technique?
- About:
- It is a term that refers to the deliberate large-scale intervention in the Earth’s climate system to combat climate change.
- These interventions generally fall into two categories: Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) and Solar Radiation Management(SRM).
- Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR):
- These techniques aim to remove excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, thereby reducing the greenhouse effect.
- Examples of CDR Techniques:
- Afforestation and Reforestation:
- Planting trees or restoring forests to increase the natural absorption of carbon dioxide by plants.
- Biochar:
- Converting biomass into charcoal and burying it in the soil to enhance its carbon storage capacity.
- Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS):
- Growing crops for biofuel production and capturing the carbon dioxide emitted during combustion and storing it underground or in the ocean.
- Ocean Fertilization:
- Adding nutrients such as iron or nitrogen to the ocean to stimulate the growth of phytoplankton that consume carbon dioxide and transfer it to the deep ocean.
- Afforestation and Reforestation:
- Solar Radiation Management (SRM):
- These techniques aim to reduce the amount of solar energy that reaches the Earth’s surface, thereby cooling the planet.
- Examples of SRM Techniques:
- Stratospheric Aerosol Intervention (SAI).
- Space-Based Reflectors (SBR):
- Placing mirrors or other devices in orbit around the Earth to deflect or block some of the incoming sunlight.
- Marine Cloud Brightening (MCB):
- Spraying sea water droplets or other substances into low-level clouds over the ocean to increase their reflectivity and albedo.
- Cirrus Cloud Thinning (CCT):
- Reducing the formation or persistence of high-level cirrus clouds that trap heat by cloud seeding them with ice crystals or other agents.
- Surface Albedo Modification (SAM):
- Changing the reflectivity of the land or sea surface by painting roofs white, covering deserts with reflective sheets, or increasing the ice cover.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. In the context of which of the following do some scientists suggest the use of cirrus cloud thinning technique and the injection of sulphate aerosol into stratosphere? (2019)
(a) Creating the artificial rains in some regions
(b) Reducing the frequency and intensity of tropical cyclones
(c) Reducing the adverse effects of solar wind on the Earth
(d) Reducing the global warming
Ans: (d)


Science & Technology
Emergence of Multimodal AIs
For Prelims: Emergence of Multimodal AIs, AI (Artificial Intelligence), Human-like Cognition, OpenAIs ChatGPT, Google's Gemini model.
For Mains: Emergence of Multimodal AIs and their implications, Developments and their applications and effects in everyday life
Why in News?
There has been a paradigm shift within AI (Artificial Intelligence) towards Multimodal Systems, allowing users to engage with AI through a combination of text, images, sounds, and videos.
- These systems aim to replicate human-like cognition by encompassing multiple sensory inputs.
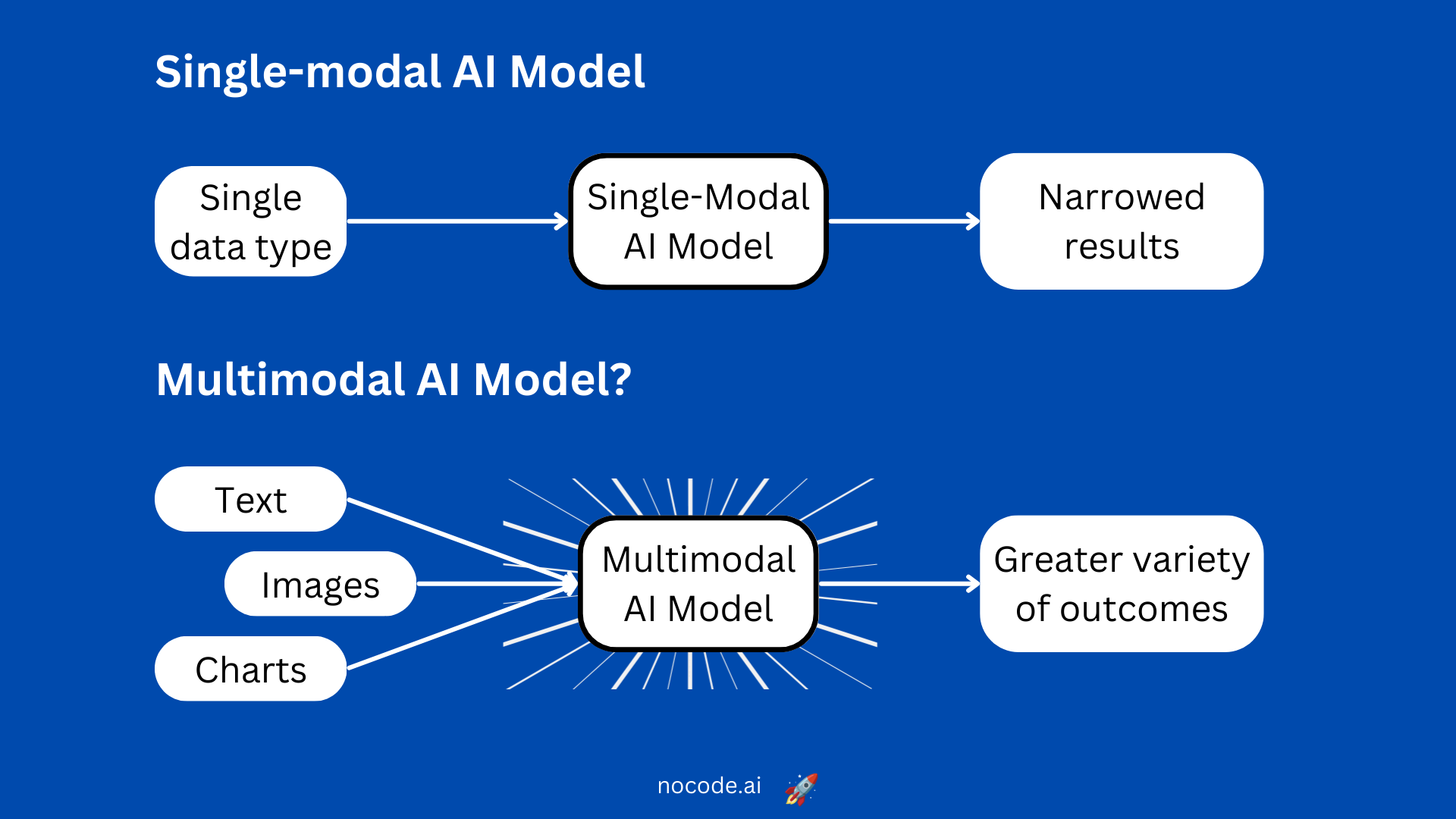
What are Multimodal AI Systems?
- About:
- Multimodal AI is artificial intelligence that combines multiple types, or modes, of data to create more accurate determinations, draw insightful conclusions or make more precise predictions about real-world problems.
- Multimodal AI systems train with and use video, audio, speech, images, text and a range of traditional numerical data sets.
- For Example: Multimodal audio systems follow similar principles, with Whisper, OpenAI's open-source speech-to-text translation model, serving as the foundation for GPT's voice processing capabilities.
- Recent Developments in Multimodal AI:
- OpenAIs ChatGPT: OpenAI announced enhancements to its GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 models, allowing them to analyze images and engage in speech synthesis, enabling more immersive interactions with users.
- It is working on a project named "Gobi," which aims to create a multimodal AI system from scratch, distinct from the GPT models.
- Google's Gemini Model:
- Another major player in the field is Google’ new yet-to-be-released multimodal large language model Gemini.
- Due to its huge collection of images and videos from its search engine and YouTube, Google had a clear edge over its rivals in the multimodal domain.
- It puts immense pressure on other AI systems to rapidly advance their multimodal capabilities.
- Another major player in the field is Google’ new yet-to-be-released multimodal large language model Gemini.
- OpenAIs ChatGPT: OpenAI announced enhancements to its GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 models, allowing them to analyze images and engage in speech synthesis, enabling more immersive interactions with users.
What are the Advantages of Multimodal AI over Unimodal AI?
- Multimodal AI, unlike unimodal AI, leverages diverse data types such as text, images, and audio, offering a richer representation of information.
- This approach enhances contextual understanding, resulting in more accurate predictions and informed decisions.
- By fusing data from multiple modalities, multimodal AI achieves better performance, increased robustness, and the ability to handle ambiguity effectively.
- It broadens applicability across various domains and enables cross-modal learning.
- Multimodal AI provides a more holistic and human-like understanding of data, paving the way for innovative applications and a deeper comprehension of complex real-world scenarios.
What are the Applications of Multimodal AI?
- It finds applications in diverse fields, including autonomous driving, robotics, and medicine.
- For example, In medical field, the analysis of complex datasets from CT Scans and identifying genetic variations, simplifying the communication of results to medical professionals is very crucial.
- Speech translation models, such as Google Translate and Meta's SeamlessM4T, also benefit from multimodality, offering translation services across various languages and modalities.
- Recent developments include Meta's ImageBind, a multimodal system capable of processing text, visual data, audio, temperature, and movement readings.
- The potential for integrating additional sensory data like touch, smell, speech, and brain MRI signals is explored, enabling future AI systems to simulate complex environments.
What are the Challenges of Multimodal AI?
- Data Volume and Storage:
- The diverse and voluminous data required for Multimodal AI poses challenges in terms of data quality, storage costs, and redundancy management, making it expensive and resource-intensive.
- Learning Nuance and Context:
- Teaching AI to understand nuanced meanings from identical input, especially in languages or expressions with context-dependent meanings, proves challenging without additional contextual cues like tone, facial expressions, or gestures.
- Limited and Incomplete Data:
- Availability of complete and easily accessible data sets is a challenge. Public data sets may be limited, costly, or suffer from aggregation issues, affecting data integrity and bias in AI model training.
- Missing Data Handling:
- Dependency on data from multiple sources can result in AI malfunctions or misinterpretations if any of the data sources are missing or malfunctioning, causing uncertainty in AI response.
- Decision-Making Complexity:
- Neural networks in Multimodal AI may be complex and challenging to interpret, making it difficult to understand how AI evaluates data and makes decisions. This lack of transparency can hinder debugging and bias elimination efforts.
Conclusion
- The advent of multimodal AI systems represents a significant advancement in the field of artificial intelligence.
- These systems have the potential to revolutionize various industries, enhance human-computer interactions, and address complex real-world problems.
- As AI continues to evolve, multimodality is poised to play a pivotal role in achieving artificial general intelligence and expanding the boundaries of AI applications.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Introduce the concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI). How does AI help clinical diagnosis? Do you perceive any threat to privacy of the individual in the use of AI in the healthcare? (2023)


Governance
World Habitat Day 2023 and India’s Urban Landscape
For Prelims: World Habitat Day, United Nations, UN-Habitat Scroll of Honour Award, Smart Cities, AMRUT Mission, Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban, HRIDAY, Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban, Aspirational district Programme
For Mains: Current Major Challenges Related to Urban Landscape in India, Role of Cities in Economic Recovery.
Why in News?
In 2023, World Habitat Day (WHD), was celebrated on 2nd October. This annual global observance has come a long way focusing on the evolution of urban development, sustainability, and the role of cities in economic growth.
What is World Habitat Day?
- About: The United Nations designated the first Monday of October of every year as World Habitat Day to reflect on the state of our habitats, and on the basic right of all to adequate shelter.
- The Day is also intended to remind the world that we all have the power and the responsibility to shape the future of our cities and towns.
- Origin: The origin of World Habitat Day can be traced back to Nairobi, Kenya, in 1986. The theme of the first celebration was 'Shelter is my Right,' addressing the acute problem of inadequate shelter in cities.
- Theme 2023: Resilient urban economies. Cities as drivers of growth and recovery.
- 2023 has been a particularly challenging year for Urban Economies. The global economy growth itself is declining to about 2.5% and, apart from the initial Covid-19 crisis in 2020 and the global financial crisis in 2009, this is the weakest growth experienced since 2001.
Note: The UN-Habitat Scroll of Honour Award was launched by the United Nations Human Settlements Programme in 1989. It is currently the most prestigious human settlements award in the world.
What is the Role of Cities in Economic Recovery?
- Economic Engines: Cities serve as economic engines, contributing significantly to a nation's GDP.
- Urban areas are the productive hubs of economies, generating more than 75 % of the world's GDP, attracting businesses, talent, and investments, thereby stimulating economic growth.
- Employment Opportunities: Cities offer diverse job opportunities, drawing in a skilled and diverse workforce.
- In times of economic recovery, cities become critical in reducing unemployment rates, and improving the overall well-being of their residents.
- Innovation and Technology Hubs: Many cities are epicenters of innovation and technology.
- They house research centers, universities, and tech companies that drive technological advancements, further fostering economic recovery through innovation-led growth.
- Infrastructure Development: Cities often receive substantial infrastructure investments during economic recovery phases.
- These investments in transportation, utilities, and public services not only boost immediate job creation but also enhance long-term productivity and quality of life.
- Cultural and Creative Industries: Cultural and creative industries thrive in cities, contributing to the local economy through tourism, arts, entertainment, and design.
- These sectors not only generate revenue but also make cities attractive and competitive on a global scale.
What is the Current Urban Landscape in India?
- Status:
- India is one of the fastest growing economies in the world, and its growth is propelled by its cities.
- Cities contribute 66% to the national GDP, a number expected to rise to 80% by 2050.
- India is one of the fastest growing economies in the world, and its growth is propelled by its cities.
- Current Major Challenges:
- Overpopulation and Rapid Urbanization:
- India is the world's most populous country, with a significant portion of the population migrating from rural to urban areas.
- This rapid urbanization exerts immense pressure on urban resources and infrastructure.
- India is the world's most populous country, with a significant portion of the population migrating from rural to urban areas.
- Inadequate Infrastructure:
- Housing: The shortage of affordable housing results in the growth of slums and informal settlements, where living conditions are often substandard.
- Water Supply and Sanitation: Many Indian cities struggle to provide clean and safe drinking water and proper sanitation facilities to their residents.
- This leads to health issues and the contamination of water bodies.
- Transportation: Congested roads and lack of efficient public transportation systems contribute to traffic congestion, pollution, and increased travel time.
- Environmental Degradation:
- Air Pollution: Many Indian cities suffer from high levels of air pollution, leading to respiratory diseases and reducing the quality of life for residents.
- Water Pollution: Industrial discharges, sewage, and improper waste disposal contaminate water bodies, affecting public health and the environment.
- Inequality and Social Disparities:
- Economic Disparities: Urban areas in India witness stark income inequality, with a growing gap between the rich and poor.
- Access to Services: Many urban residents lack access to basic services like healthcare and education, leading to disparities in well-being and quality of life.
- Inadequate Waste Management: Urban India alone generates nearly 0.15 million tonnes per day of Municipal Solid Waste.
- According to GOI, almost 78% of the sewage generated in India remains untreated and is disposed of in rivers, lakes, or sea.
- The volume of waste is projected to reach 165 million tonnes by 2031 and 436 million tonnes by 2050, if existing policies, programmes and management strategies are not adequately addressed.
- Water Scarcity: Urbanization and industrialization are leading to the over-extraction of groundwater, causing water scarcity in many cities, especially during dry seasons.
- Climate Change Vulnerability: Urban areas are particularly susceptible to the adverse effects of climate change, such as extreme temperatures, flooding, and intensified heat islands, which can exacerbate environmental and health issues.
- Overpopulation and Rapid Urbanization:
What are Government Initiatives Related to Urban Development?
Way Forward
- Integrated Urban Planning: There is a need to develop comprehensive urban plans that consider long-term sustainability, resilience to climate change, and the balanced use of resources.
- Also, promote mixed land use, efficient land management, and zoning regulations that encourage smart growth.
- Innovative Financing for Urban Development: Cities can explore innovative financing methods like municipal bonds for raising resources.
- Through the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) mission, the government has encouraged cities to raise capital investment.
- To date, 12 cities have raised more than Rs. 4,384 crores through municipal bonds.
- Urban Employment Guarantee: Urban areas need a scheme similar to MGNREGA to provide basic living standards to urban poor.
- The Indira Gandhi Urban Employment Guarantee Scheme has been rolled out in Rajasthan is a good step in this direction.
- Proper Waste Management: There is a need to emphasize strict segregation of waste at the source and promote formal recycling and composting practices.
- Also, investing in waste-to-energy technologies and modern landfill management to reduce the environmental impact of waste disposal.
- Inclusive Development: There is a need to prioritize the needs of marginalized and vulnerable populations by providing them with access to basic services, quality healthcare, and education.
- The data of migrants needs to be compiled and used in city development activities in the interest of migrant workers.
- Also, promoting social housing and slum redevelopment projects to improve living conditions.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the Indian economy after the 1991 economic liberalization, consider the following statements: (2020)
- Worker productivity (Rs. per worker at 2004-05 prices) increased in urban areas while it decreased in rural areas.
- The percentage share of rural areas in the workforce steadily increased.
- In rural areas, the growth in the non-farm economy increased.
- The growth rate in rural employment decreased.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 4 only
Ans: (b)
Q. As per the Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016 in India, which one of the following statements is correct? (2019)
(a) Waste generators have to segregate waste into five categories.
(b) The Rules are applicable to notified urban local bodies, notified towns and all industrial townships only
(c) The Rules provide for exact and elaborate criteria for the identification of sites for landfills and waste processing facilities.
(d) It is mandatory on the part of the waste generator that the waste generated in one district cannot be moved to another district.
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. The frequency of urban floods due to high intensity rainfall isincreasing overthe years. Discussing the reasons for urban floods, highlight the mechanisms for preparedness to reduce the risk during such events. (2016)
Q. Do government’s schemes for up-lifting vulnerable and backward communities by protecting required social resources for them, lead to their exclusion in establishing businesses in urban economies? (2014)


Governance
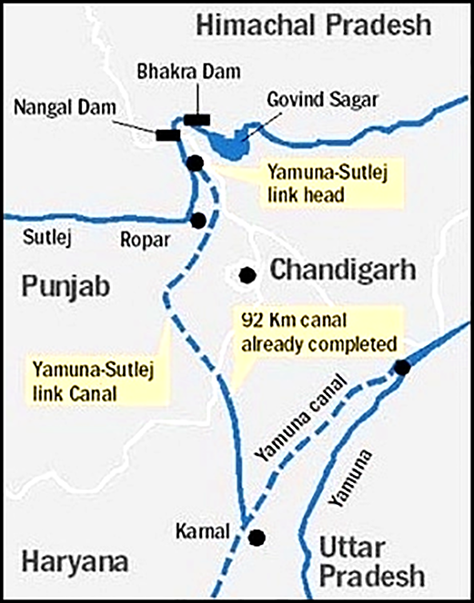
Sutlej-Yamuna Link Canal Dispute
For Prelims: Sutlej-Yamuna Link Canal Dispute, Indus Water Treaty, Supreme Court (SC), Article 143.
For Mains: Sutlej-Yamuna Link Canal Dispute, and its Implications, Changes in critical geographical features (including water bodies and ice-caps) and in flora and fauna and the effects of such changes, Statutory, regulatory, and various quasi-judicial bodies.
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court has ordered the Punjab Government to complete Sutlej-Yamuna Link (SYL) canal, warning the Government to comply with its orders.
- The court directed the Union Government to oversee talks between Punjab and the Haryana governments on this topic; the Haryana government has completed construction of its half of the canal.
- The Issue stems from a controversial 1981 water-sharing agreement drawn up when Haryana was carved out of Punjab in 1966.
What is the Background?
- 1960:
- The dispute can be traced back to the Indus Water Treaty between India and Pakistan, allowing the former ‘free and unrestricted use’ of Ravi, Beas and Sutlej.
- 1966:
- Creation of Haryana from the old (undivided) Punjab presented the problem of giving Haryana its share of river waters.
- For Haryana to get its share of the waters of the Sutlej and its tributary Beas, a canal linking the Sutlej with the Yamuna was planned (SYL Canal).
- Punjab refused to share waters with Haryana stating it was against the riparian principle which dictates that the water of a river belongs only to the State and country or States and countries through which the river in question flows.
- Creation of Haryana from the old (undivided) Punjab presented the problem of giving Haryana its share of river waters.
- 1981:
- Both states mutually agreed for the re-allocation of water.
- 1982:
- Construction of the 214-km SYL was launched in Kapoori village, Punjab.
- Agitations, protests and assassinations were carried out in protest creating the environment of terrorism in the state and making the issue of national security.
- 1985:
- Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi and then Akali Dal chief Sant signed an accord agreeing for a new Tribunal to assess the water.
- The Eradi Tribunal headed by Supreme Court Judge V Balakrishna Eradi was set up to reassess availability and sharing of water.
- In 1987, the tribunal recommended an increase in the shares of Punjab and Haryana to 5 MAF and 3.83 MAF, respectively.
- 1996:
- Haryana moved the Supreme Court (SC) seeking directions to Punjab to complete the work on the SYL.
- 2002 and 2004:
- SC directed Punjab to complete the work in its territory.
- 2004:
- Punjab Assembly passed the Punjab Termination of Agreements Act, terminating its water-sharing agreements and thus jeopardizing the construction of SYL in Punjab.
- 2016:
- SC started hearings into a presidential reference (Article 143) to decide on the legality of the 2004 Act and declared that Punjab backed out of its promise to share the waters of rivers. Thus, the act was termed constitutionally invalid.
- 2020:
- SC directed the Chief Ministers of both states to negotiate and settle the SYL canal issue at the highest political level to be mediated by the Centre.
- Punjab has asked for a tribunal for fresh time-bound assessment of the water availability.
- Punjab holds that there has been no adjudication or scientific assessment of river waters in the state till date.
- The availability of Ravi-Beas water has also come down from the estimated 17.17 MAF in 1981 to 13.38 MAF in 2013. A fresh tribunal would ascertain all this.
What is the Argument of Punjab and Haryana?
- Punjab:
- Punjab vehemently opposes sharing any additional water with neighboring states. They stress that Punjab lacks surplus water and highlights the reduction in their water allocation over the years.
- Many areas in Punjab may go dry after 2029 and the state has already over-exploited its groundwater for irrigation purposes as it fills granaries of the Centre by growing wheat and paddy worth Rs 70,000 crore every year.
- Water in about 79% of the state’s area is over-exploited and in such a situation, the government says sharing water with any other state is impossible.
- Haryana:
- Haryana strongly advocates for the canal's completion, citing a looming water crisis and asserting that Punjab has been utilizing Haryana's share of water.
- It says that providing irrigation is tough for the state and there was a problem of drinking water in southern parts of Haryana, where groundwater has depleted up to 1,700 feet.
- Haryana has been citing its contribution to the central food pool and arguing that it is being denied its rightful share in the water as assessed by a tribunal.
What is the Significance of Satluj Yamuna Link Canal?
- Facilitating Equitable Water Sharing:
- The SYL Canal aims to facilitate the equitable sharing of river waters between Haryana and Punjab. Once completed, the canal would enable the distribution of waters from the Ravi and Beas rivers, which are vital water sources in the region. This is crucial for both states to ensure fair access to water resources and prevent potential conflicts arising from unequal distribution.
- Addressing Historical Water Disputes:
- It can address long standing water disputes between Haryana and Punjab. By providing a defined pathway for water transfer, it aims to settle disagreements related to water allocation and usage, which have persisted for decades and at times led to legal battles and political tensions.
- Enhancing Agricultural Productivity:
- The SYL Canal, by facilitating better water distribution, can contribute to enhanced agricultural productivity and sustainability.
- It can support farmers in cultivating their lands effectively, leading to better yields and socio-economic development.
- Socio-Economic Development:
- The SYL Canal can play a significant role in promoting overall socio-economic development in both states.
- Reliable access to water is fundamental for industrial development, urbanization, and overall growth, benefiting various sectors and improving the quality of life for the residents.
What are the Reasons of Water Sharing Issues Among Various States?
- Water sharing issues among various states, not only in India but in many parts of the world, are complex and multifaceted, often involving several factors. Some common reasons that contribute to water sharing issues among states:
- Geographical Variation in Water Availability: Different states have varying levels of access to water resources due to their geographical location, topography, and proximity to rivers, lakes, or other sources of water.
- Some states may naturally have more abundant water resources, while others may face water scarcity.
- Climate Change and Global Warming: Climate change and global warming are altering weather patterns and affecting precipitation levels, leading to changes in the availability and distribution of water.
- Erratic rainfall, prolonged droughts, and changing monsoon patterns can exacerbate water scarcity issues and create conflicts over water sharing.
- Unequal Distribution of Rivers and Water Sources: The distribution of rivers and other water sources across states is often unequal, causing disputes over access and utilization.
- States located upstream may have control over the source of a river, while downstream states may face challenges in securing their fair share of water.
- Construction of Dams and Reservoirs: The construction of dams and reservoirs for various purposes can significantly alter the flow of rivers and affect water availability downstream.
- Population Growth and Increased Demand: Rapid population growth in certain states increases the demand for water for various purposes, including agriculture, industry, and domestic use.
- This heightened demand puts pressure on available water resources, leading to conflicts over allocation and sharing.
- Political and Inter-State Relations: Political factors, interstate relations, and differing priorities among states can influence negotiations and agreements related to water sharing.
- Political considerations, power dynamics, and electoral interests can complicate the resolution of water disputes.
- Geographical Variation in Water Availability: Different states have varying levels of access to water resources due to their geographical location, topography, and proximity to rivers, lakes, or other sources of water.
What are the Sustainable Solution for Water Sharing Issues?
- Water Conservation and Efficiency Measures:
- Implementing water-saving technologies and promoting water conservation practices in agriculture, industry, and households can significantly reduce water demand.
- Modernizing Irrigation Systems:
- Upgrading irrigation infrastructure to more efficient systems like drip irrigation can minimize water wastage in agriculture, a sector that consumes the majority of water resources.
- Real-time Monitoring and Forecasting:
- Utilizing technology for real-time monitoring of reservoir levels, river flows, and weather patterns can aid in effective water management and timely decision-making, especially during climatic uncertainties.
- Conflict Resolution Mechanisms:
- Establishing efficient conflict resolution mechanisms, possibly outside the legal framework, can help states resolve water-sharing disputes more expediently and collaboratively.
- An atmosphere of cooperation and understanding among neighboring states is necessary to address water disputes amicably.
- Establishing efficient conflict resolution mechanisms, possibly outside the legal framework, can help states resolve water-sharing disputes more expediently and collaboratively.
- River Basin Ecosystem Restoration:
- Focusing on restoring and preserving river basin ecosystems can enhance the sustainability of water resources. Healthy ecosystems contribute to the quality and availability of water.
- Ensuring comprehensive EIAs (Environmental Impact Assessment) before initiating any water-related project can prevent or mitigate adverse effects on water sources and ecosystems.
Way Forward
- The water disputes can be solved or balanced by having a permanent tribunal established with appellate jurisdiction of the Supreme Court established over the tribunal’s decision.
- The immediate target of any Constitutional Government should be amendment to Article 262 (Adjudication of disputes relating to waters of inter State rivers or river valleys) and amendment to Inter-State Water Disputes Act and its implementation at the equal note.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Recently, linking of which of the following rivers was undertaken? (2016)
(a) Cauvery and Tungabhadra
(b) Godavari and Krishna
(c) Mahanadi and Sone
(d) Narmada and Tapti
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. Not many years ago, river linking was a concept but it is becoming a reality in the country. Discuss the advantages of river linking and its possible impact on the environment. (2017)
Q. In what way can floods be converted into a sustainable source of irrigation and all-weather inland navigation in India? (2017)
Q. How will the melting of Himalayan glaciers have a far-reaching impact on the water resources of India? (2020)
Q. The interlinking of rivers can provide viable solutions to the multi-dimensional inter-related problems of droughts, floods, and interrupted navigation. Critically examine. (2020)
Q. Suggest measuresto improve waterstorage and irrigation system to make itsjudicious use under depleting scenario. (2020)


International Relations
India Tanzania Relations
For Prelims: Bordering Countries of Tanzania, Lake Victoria, Ngorongoro Crater, Mount Kilimanjaro, Lake Tanganyika.
For Mains: Areas of Cooperation Between India and Tanzania, Bilateral Groupings & Agreements, Global Biofuels Alliance
Why in News?
Recently, India welcomed the President of Tanzania at the India Tanzania Investment Forum in New Delhi.
- India and Tanzania have upgraded their bilateral relations to the level of a strategic partnership.
What are the Key Takeaways from the Visit?
- Both nations inked six agreements to strengthen cooperation across various vital domains.
- It encompasses cooperation in the digital domain, culture, sports, maritime industries, and white shipping information sharing.
- These agreements lay the foundation for fostering technological and cultural exchange between the two nations.
- Both nations are promoting trade between the Indian Rupee and Tanzanian Shilling by enabling authorized banks in India to open Special Rupee Vostro Accounts of correspondent banks in Tanzania.
- Efforts to address concerns and ensure the sustainability of this currency trade mechanism are underway.
- The newly established five-year defense roadmap sets the stage for expanded cooperation in military training, maritime collaboration, capacity building, and the defense industry.
- Both nations expressed their intent to enhance cooperation in maritime security in the Indian Ocean region.
- The success of the first-ever India-Tanzania joint Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) surveillance exercise in July, 2023 was a positive step in this direction.
- Tanzanian President Samia Suluhu Hassan received an honorary doctorate from Jawaharlal Nehru University in Delhi.
- She is the first woman to receive this honor for her role in promoting economic diplomacy, regional integration, and multilateralism between India and Tanzania.
- The Government of Tanzania also announced that they would be joining the International Big Cat Alliance and the Global Biofuel Alliance.
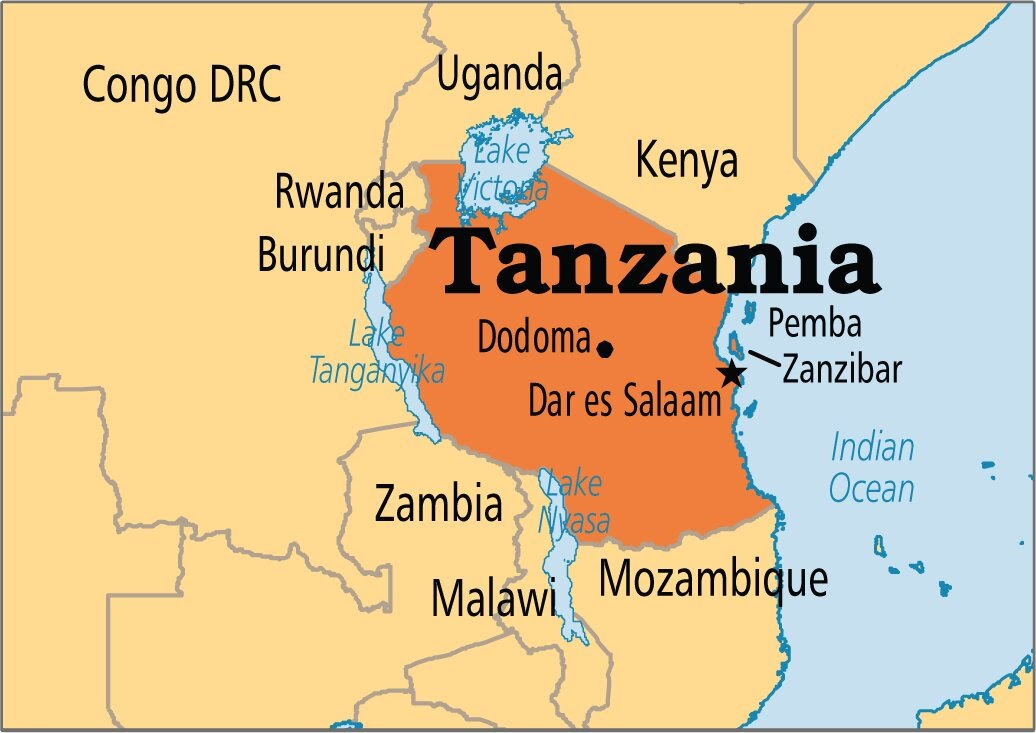
What are the Key Facts Related to Tanzania?
- About: Tanzania is the largest country in East Africa. With eight neighbors, it is among the top 10 countries in the world with the most international borders.
- The islands of Zanzibar, Pemba and Mafia are also a part of Tanzania.
- Capital: Dar es Salaam is the administrative capital of the country while Dodoma is the legislative capital.
- Currency: Tanzanian shilling
- Landform:
- Its northern region has the southern part of Lake Victoria, which is the source of the River Nile.
- Also, in the north is the World famous Ngorongoro Crater, which is the world’s largest intact volcanic caldera.
- The Northeastern part of the country is mountainous. This region is home to Mount Meru, an active volcano, and Mount Kilimanjaro, the tallest mountain in Africa and the highest single free-standing mountain in the world.
- In the west lies Lake Tanganyika, the world’s second deepest lake.
- The eastern region has coastal lowlands along the Indian Ocean.
- Its northern region has the southern part of Lake Victoria, which is the source of the River Nile.
What are the Other Areas of Cooperation Between India and Tanzania?
- About:
- India sees Tanzania as a valuable partner in the Indo-Pacific region, reflecting the broader geopolitical context.
- Tanzania plays an important role in overall India-Africa relations.
- India sees Tanzania as a valuable partner in the Indo-Pacific region, reflecting the broader geopolitical context.
- Economic Cooperation:
- India is the largest destination for Tanzania’s exports and two-way trade was worth USD 6.4 billion in 2022-23, including Indian exports of USD 3.9 billion.
- India is the fifth largest investor in Tanzania.
- India’s Major Exports to Tanzania: Petroleum products, Pharmaceutical products, Machinery, nuclear reactors, boilers, Electrical, electronic equipment, Sugars and sugar confectionery
- Tanzania’s Major Exports to India: Gold ore, cashew nuts, spices (mainly cloves), ores and metal scrap, gemstones, etc.
- India is the largest destination for Tanzania’s exports and two-way trade was worth USD 6.4 billion in 2022-23, including Indian exports of USD 3.9 billion.


Governance
Accredited Social Health Activists
For Prelims: Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHA) , National Health Mission
For Mains: Role and Significance of ASHA in India's healthcare system, Issues Relating to the Management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health and Human Resources,
Why in News?
Recently, a study published in the journal Social Science and Medicine has unveiled the hidden struggles faced by Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHA) in India.
- The study exposes a significant research gap, with over 50% of prior articles solely focusing on the health system's perspective, overlooking ASHA workers' individual struggles. It engaged 59 ASHA workers in six focus groups, allowing them to openly discuss their work-related stress, encompassing workload, gender, caste discrimination, and relationship dynamics.
What are the Key Findings from the Study?
- Caste Discrimination:
- Many ASHAs recounted instances where they were discriminated against based on their caste.
- ASHA workers were not allowed inside the homes of residents belonging to a higher social caste. In some instances they were permitted entry but denied a seat on the chair.
- Many ASHAs recounted instances where they were discriminated against based on their caste.
- Gender-Based Disrespect:
- ASHA workers experienced derogatory comments and discriminatory behaviour from community members when seen in public with men who were not their family members.
- These incidents also extended to their interactions with male relatives of patients or counselling male clients on reproductive health and family planning.
- ASHA workers experienced derogatory comments and discriminatory behaviour from community members when seen in public with men who were not their family members.
- Toxic Work Relationships:
- ASHA workers described their interactions with supervisors, auxiliary nurse midwives (ANMs), medical officers, and hospital staff as unhealthy, bordering on toxic. Instances of insensitivity and lack of support were common.
- Domestic Conflicts:
- Balancing their work and domestic responsibilities often led to conflicts at home, sometimes to the extent of divorce threats.
- Many ASHA workers had to grapple with the pressure of fulfilling their familial duties while performing their demanding jobs.
- Balancing their work and domestic responsibilities often led to conflicts at home, sometimes to the extent of divorce threats.
- The Need for Support and Coping Mechanisms:
- The study suggests that with appropriate support and coping mechanisms, ASHA workers can better manage their stress.
What is Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHA)?
- About:
- The ASHA program was launched in 2005-06 as part of the National Rural Health Mission, initially in rural areas.
- It was later extended to urban settings with the introduction of the National Urban Health Mission in 2013.
- The ASHA programme was introduced as a key component of the community process intervention and now it has emerged as the largest community health worker programme in the world and is considered a critical contribution to enabling people's participation in health.
- As of June 2022, there are over 10.52 Lakh ASHAs in all states/UTs (except Goa).
- The ASHA program was launched in 2005-06 as part of the National Rural Health Mission, initially in rural areas.
- Role of ASHA:
- ASHA is a community-level worker whose role is to function as a health care facilitator, and a service provider and to generate awareness on health issues.
- Besides delivering key services to maternal child health and family planning, they also render important services under the National Disease Control Programme.
- ASHA workers, all women, serve populations of approximately 1,000 in rural areas and 2,000 in urban settings, with room for local adjustments.
- Generally, there is “1 ASHA per 1000 population”. However, this norm can be relaxed in tribal, hilly and desert areas to “1 ASHA per habitation” depending upon the workload.
- Selection of ASHA:
- ASHA must primarily be a woman resident of the village married/ widowed/ divorced, preferably in the age group of 25 to 45 years.
- She should be a literate woman with due preference in selection to those who are qualified up to 10 standard wherever they are interested and available in good numbers. This may be relaxed only if no suitable person with this qualification is available.
- ASHA workers are not recognized as the government's "workers", but are instead classified as holding an "honorary/volunteer" position.
Way Forward
- Establish mentorship initiatives to provide ASHAs with emotional support and guidance. Empower them to navigate the complexities they face.
- Strengthen advocacy efforts to address caste and gender discrimination, ensuring ASHAs are treated with dignity and respect in their communities.
- Create open channels of communication between ASHAs and their supervisors to encourage constructive dialogue, understanding, and collaboration.
- Educate ASHAs' families about the significance of their work, fostering support and understanding. Highlight how their efforts benefit the entire community.
- Explore flexible working arrangements to help ASHAs balance their work and family responsibilities effectively.
- Promote community-wide recognition of ASHAs' contributions, instilling a sense of pride and appreciation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the National Rural Health Mission, which of the following are the jobs of ‘ASHA’, a trained community health worker? (2012)
- Accompanying women to the health facility for antenatal care checkup
- Using pregnancy test kits for early detection of pregnancy
- Providing information on nutrition and immunisation.
- Conducting the delivery of baby
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
Dancing Frogs
Why in News?
Recently, the Wildlife Trust of India has assessed the 2nd edition of the Global Amphibian Assessment coordinated by the Amphibian Specialist Group of the IUCN Species Survival Commission, which shows that the Dancing Frogs that are endemic to the Western Ghats are the most threatened amphibian genus of India.
- Of the 24 species of the frogs belonging to the Micrixalus genus that were assessed, two were found to be critically endangered and 15 were endangered. This makes them the most threatened of all Indo-Malayan genera.
- It is also the fifth most threatened genus in the world with 92% of its species in the threatened category.
What are Dancing Frogs?
- About:
- Dancing frogs, specifically from the Micrixalus genus, are a group of frogs.
- Behavior and Mating Display:
- Dancing frogs exhibit a unique mating behavior characterized by foot flagging, where males extend their hind legs and wave their webbed toes.
- This visual display helps in attracting female mates and signaling to rival males.
- Habitat Preference:
- They prefer habitats with a thick canopy cover, typically around 70-80 %, and are often found near slow-moving perennial streams within the Western Ghats.
- Threats:
- The population of dancing frogs is threatened by various anthropogenic factors, including invasive species like the Mosquito Fish, land use change, temperature and humidity variations, extreme weather events, infectious diseases, water pollution, light pollution, and infrastructure projects such as dams.
- Protecting the natural habitats and maintaining optimal living conditions are crucial for the survival of these species. However, globally, amphibian populations are declining, with a significant percentage categorized as threatened with extinction.
- Conservation Efforts:
- Conservation initiatives, such as the Wildlife Trust of India’s Amphibian Recovery Project, are actively working to address challenges that pose a risk of extinction to amphibian specis.
- These efforts include threat mitigation, conservation action planning, capacity development, training, advocacy, and information sharing.


Important Facts For Prelims
Asia-Pacific Institute for Broadcasting Development
Why in News?
Recently, in an unprecedented development, India has been elected president of the Asia-Pacific Institute for Broadcasting Development (AIBD) General Conference (GC) for the third successive term.
- This was the first in the history of AIBD as this reflects the confidence of broadcasting organizations worldwide in India's capabilities in guiding and innovating in the field of broadcasting.
What is Asia-Pacific Institute of Broadcasting Development (AIBD)?
- About:
- The Asia-Pacific Institute for Broadcasting Development (AIBD) was established in 1977 under the aegis of United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
- It is a unique regional intergovernmental organization servicing countries of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UN-ESCAP) in the field of electronic media development.
- Its secretariat is situated in Kuala Lumpur and is hosted by the Government of Malaysia.
- Objective:
- The AIBD is mandated to achieve a vibrant and cohesive electronic media environment in the Asia-Pacific region through policy and resource development.
- Founding Members:
- The International Telecommunication Union (ITU), the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), and the UNESCO and the Asia-Pacific Broadcasting Union (ABU) are founding organizations of the Institute and they are non-voting members of the General Conference.
- Members:
- The AIBD currently has 92 member organizations from across 44 countries, including 26 government members (countries) represented by 48 broadcasting authorities and broadcasters, and 44 affiliates (organizations) represented by 28 countries and regions in Asia, Pacific, Europe, Africa, Arab States and North America.
- Asia Media Summit:
- Asia Media Summit is the annual conference organized by (AIBD) in collaboration with its partners and international organizations.
- The Conference is attended by Decision makers, media professionals, scholars, and stakeholders of news and programming from Asia, Pacific, Africa, Europe, Middle East, and North America.
- Secretariat:
- Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
- India and AIBD:
- India is one of the founding members of AIBD.
- Prasar Bharati, India’s public service broadcaster, is the representative body of the Ministry of Information & Broadcasting, Government of India, at AIBD.
Prasar Bharti
- Prasar Bharati is a statutory autonomous body.
- It is the Public Service Broadcaster of the country.
- It was established under the Prasar Bharati Act in 1997.
- The Prasar Bharati Corporation’s main objective is to provide autonomy to Doordarshan and Akashvani in order to “educate and entertain the public.


Important Facts For Prelims
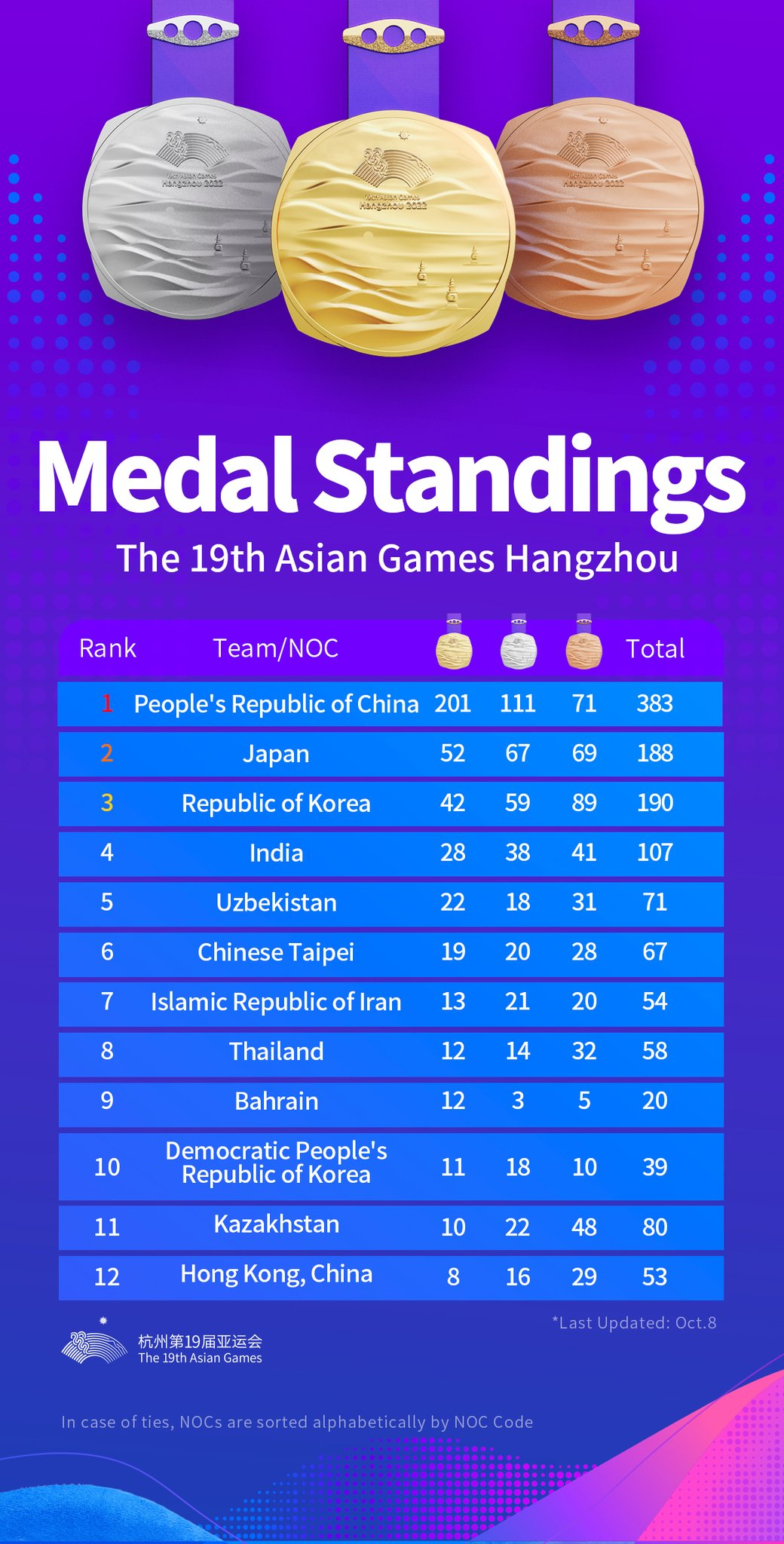
Asian Games 2023
Why in News?
Recently, the 19th Asian Games (of 2022, held in 2023) came to a close at the Hangzhou Olympic Sports Centre Stadium (also called Big Lotus) in China. Hockey player PR Sreejesh was India’s flagbearer at the parade of athletes.
- The 20th Asian Games will be held in Japan in 2027.
What are the Key Highlights of Asian Games 2023?
- India’s Milestones:
- India’s Medals Tally:
- With an unprecedented haul of 107 medals (28 gold, 38 silvers and 41 bronze), India set a new benchmark for themselves at the Asian Games 2023 in Hangzhou, the People’s Republic of China.
- At the 2018 Asian Games in Jakarta, India performed well and returned with 70 medals, including a haul of 16 gold medals.
- It was the first time in Asian Games history that India’s medals tally crossed the three-figure mark. By doing so, they became the only fourth country after China (383), Japan (188) and the Republic of Korea (190) to win 100 or more medals in a single edition of the Asian Games.
- With an unprecedented haul of 107 medals (28 gold, 38 silvers and 41 bronze), India set a new benchmark for themselves at the Asian Games 2023 in Hangzhou, the People’s Republic of China.
- Athletes Performance:
- Athletics turned out to be the most productive sport with a total of 29 medals - six gold, 14 silver and nine bronze.
- Hockey:
- The India men's hockey team won an Asian Games gold and booked a Paris Olympics berth with a 5-1 thrashing of Japan.
- India’s Medals Tally:
- Introduction of New Sports:
- 2023 Games saw two medal sports make their debut: e-Sports and Breakdancing.
- Apart from them, Cricket, and board games - Go, Xiangqi, and Chess returned to Asian Games in this edition after not featuring in the 2018 Asiad.
What are the Asian Games ?
- About:
- The Asian Games is the biggest sports competition in Asia, held once every four years. The symbol for the Asian Games is the rising sun with interlocking rings.
- It is recognised by the International Olympic Committee.
- The Asian Games is the biggest sports competition in Asia, held once every four years. The symbol for the Asian Games is the rising sun with interlocking rings.
- Background and Inauguration:
- After the Second World War, many Asian countries gained independence and the Indian International Olympic Committee proposed the idea of Asian Games as a sporting event, where all Asian nations can be represented.
- The first-ever Asian Games were held in New Delhi in 1951.
- Regulation:
- Asian Games were regulated by the Asian Games Federation from 1951 to 1978. Since 1982, the Olympic Council of Asia has regulated the Asian Games.
- India as a Host:
- India is a founder member of Asian Games and also the host of the first Asian Games.
- The 9th edition of the Asian Games was also held in New Delhi in November and December 1982.
- Appu, the Indian elephant, was the first mascot to be used for the Asian Games.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Consider the following statements in respect of the 32nd Summer Olympics: (2021)
- The official motto for this Olympics is ‘A New World’.
- Sport Climbing, Surfing, Skateboarding, Karate and Baseball are included in this Olympics.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Q. Consider the following statements in respect of the Laureus World Sports Award which was instituted in the year 2000: (2021)
- American golfer Tiger Woods was the first winner of this award.
- The award was received mostly by ‘Formula One’ players so far.
- Roger Federer received this award the maximum number of times compared to others.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Loknayak Jayaprakash Narayan Birth Anniversary
Recently, the Prime Minister of India has paid tributes to Loknayak Jayaprakash Narayan on his birth anniversary.
- Jayaprakash Narayan born on 11th October 1902, in Sitabdiara, Bihar, popularly referred to as JP or Lok Nayak (People’s Leader), was an Indian Independence activist, social reformer and political leader.
- Influenced by both Marxist ideas in the US and Gandhian ideology.
- Joined the Indian National Congress in 1929 and participated in the civil disobedience movement and Quit India Movement.
- Devoted his life to the Bhoodan Yajna Movement, advocating land redistribution to the landless, inspired by Vinoba Bhave.
- He led the movement against the Indira Gandhi Regime in response to electoral law violations, promoting a program of 'Sampoorna Kranti' or total revolution in 1974.
- The 'Total Revolution' had seven components: political, social, economic, cultural, ideological, educational, and spiritual.
- His objective was to bring about societal change in line with the ideals of Sarvodaya, a Gandhian philosophy emphasizing progress for all.
- Jayaprakash Narayan was posthumously awarded the Bharat Ratna in 1999. Died: 8th October, 1979.
Read more: Birth Anniversaries of Jayaprakash Narayan and Nanaji Deshmukh
Nanaji Deshmukh Birth Anniversary
Recently, the Prime Minister of India has paid tributes to Nanaji Deshmukh on his birth anniversary.
- Nanaji Deshmukh, born on 11th October 1916 in Maharashtra's Hingoli district, was a prominent social activist, politician, and a key figure in India's political landscape.
- Active participant in Acharya Vinoba Bhave's Bhoodan Movement.
- Played a pivotal role in Jayaprakash Narayan's agitation for total revolution.
- Focused on social reform, health, education, and rural self-reliance.
- Contributed significantly to anti-poverty and minimum needs programs.
- Established Chitarkoot Gramoday Vishwavidyalaya, India's first rural university, and served as its Chancellor.
- Nominated to the Rajya Sabha in 1999 in recognition of his services to the nation.
- Awarded Padma Vibhushan in 1999 and was posthumously honoured with the Bharat Ratna by the President of India in 2019.
- Death: 27th February, 2010.
Read more: Birth Anniversaries of Jayaprakash Narayan and Nanaji Deshmukh
World Sight Day
World Sight Day is a global event held every second Thursday in October to raise awareness about blindness and vision impairment.
- In 2023, it falls on 12th October, and the theme is "Love your eyes at work."
- The emphasis this year is on educating people about safeguarding their vision in the workplace.
- Globally, at least 1 billion people have near or distance vision impairment that could be prevented or has yet to be addressed (WHO).
Read more: World Sight Day
India Launches Operation Ajay for Citizens' Safe Return from Israel
India has initiated "Operation Ajay" to assist its citizens who wish to return from Israel. Special charter flights and arrangements are being organized for their safe repatriation.
- A 24-hour Control Room has been established in the Ministry of External Affairs to monitor the situation in Israel and Palestine and provide information and assistance.
- The announcement was made concurrently with Israel's ongoing military operations targeting Hamas militants in the Gaza Strip.
- These actions were undertaken in response to a severe and violent attack that occurred within the borders of Israel.
Read more: Israel-Palestine Conflict
REC Limited Launches 'SUGAM REC' Mobile App for Bond Investors
REC Limited, a Maharatna Central Public Sector Enterprise under the Ministry of Power, has introduced a mobile application called 'SUGAM REC,' designed exclusively for current and prospective investors in REC's 54EC Capital Gain Tax Exemption Bonds.
- This app offers comprehensive information about investments in REC 54EC Bonds, a type of fixed income financial instrument that provides tax exemptions on capital gains under Section 54EC of the Income Tax Act.
- The term capital gain refers to any profit or gain that is received from the sale of a capital asset.
- REC Limited, established in 1969, operates as an non-banking finance company (NBFC) with a focus on financing and developing the power sector across India.
Read more: Capital Gain Tax