Maps
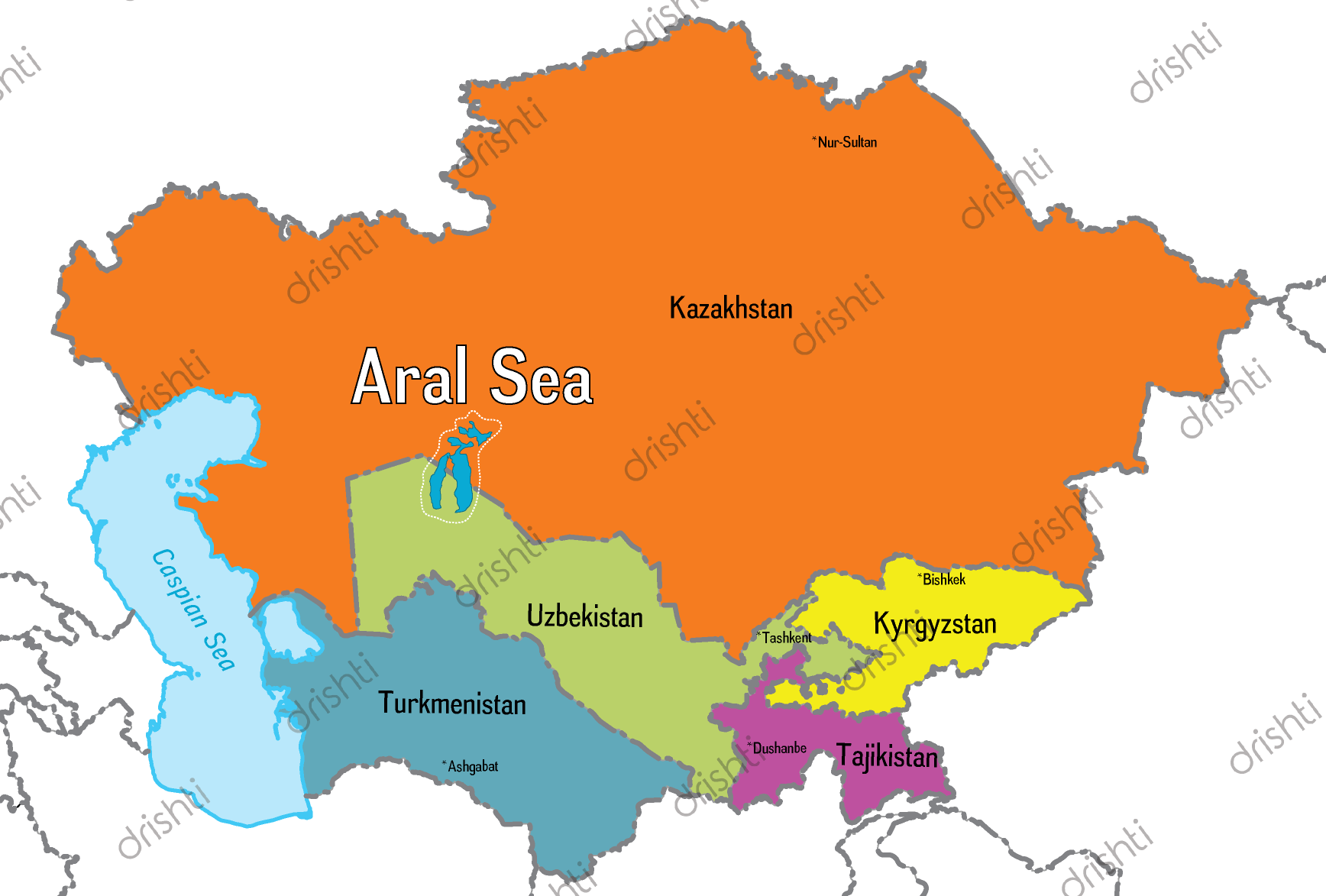
Aral Sea
Key Points
- Physical Geography:
- A once-large saltwater lake of Central Asia.
- Bordering Countries: Kazakhstan (north) and Uzbekistan (south).
Infographics
Indian Polity
Democratic Decentralisation in India
For Prelims: Panchayati Raj Institutions, 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments
For Mains: Democratic Decentralisation in India
Why in News?
It has been almost 30 years since the 73rd and 74th constitutional amendment Acts were passed to facilitate democratic decentralisation in India, but very little and actual progress has been made in this direction.
What is Democratic Decentralisation?
- About:
- Democratic decentralization is the process of devolving the functions and resources of the state from the Centre to the elected representatives at the lower levels so as to facilitate greater direct participation of citizens in governance.
- Devolution, envisioned by the Indian Constitution, is not mere delegation.
- It implies that precisely defined governance functions are formally assigned by law to local governments, backed by adequate transfer of a basket of financial grants and tax handles, and they are given staff so that they have the necessary wherewithal to carry out their responsibilities.
- Related Constitutional Provisions:
- Local government, including panchayats, is a state subject in the Constitution, and consequently, the devolution of power and authority to panchayats has been left to the discretion of states.
- The Constitution mandates that panchayats and municipalities shall be elected every five years and enjoins States to devolve functions and responsibilities to them through law.
- The 73rd and 74th Amendments, by constitutionally establishing Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) in India, mandated the establishment of panchayats and municipalities as elected local governments.
- These amendments added two new parts to the Constitution, namely, Part IX titled “The Panchayats” (added by 73rd Amendment) and Part IXA titled “The Municipalities” (added by 74th Amendment).
- The 11th Schedule contains the powers, authority and responsibilities of Panchayats.
- The 12th Schedule contains the powers, authority and responsibilities of Municipalities.
- Article 40: Organization of a village panchayat
What are the Major Achievements of the Local Bodies?
- Rising Women Representation:
- The proportion of elected women representatives has been steadily rising since the enactment of the 73rd Amendment Act.
- Currently, India has 260,512 Panchayats with 3.1 million elected representatives, of which a record 1.3 million are women.
- While there is merely 7–8% representation in Parliament and State Assemblies for women, an astounding 49% of elected local representatives (in states like Odisha it has crossed 50%) are women.
- Created Healthy Competition among Various States:
- The passage of the 73rd and 74th Amendments has created healthy competition among various states regarding devolution (the 3Fs: funds, functions, and functionaries).
- For instance:
- Kerala has devolved 29 of its functions to Panchayats.
- Rajasthan took the inspiration from Kerala to devolve many key departments such as health, education, women, and agriculture to PRIs.
- Similarly, Bihar came out with the idea of “Panchayat Sarkar” and states such as Odisha have increased 50% seats for women
What are the Issues with Local Governments in India?
- Insufficient Funding: The money given to the local governments is inadequate to meet their basic requirements.
- A number of conditions constrain the use of money, including inflexibility in spending the allocated budget.
- There is little investment in enabling and strengthening local governments to raise their own taxes and user charges.
- Infrastructural Challenges:
- Some of the Gram Panchayats (GPs) do not have their own building and they share space with schools, Anganwadi centres and other places.
- Some have their own building but without basic facilities like toilets, drinking water, and electricity connection.
- While GPs have internet connections, they are not functional in many cases. For any data entry purposes, panchayat officials have to visit Block Development offices which delay the work.
- Some of the Gram Panchayats (GPs) do not have their own building and they share space with schools, Anganwadi centres and other places.
- Lack of Staff:
- Local governments do not have the staff to perform even basic tasks.
- Furthermore, as most staff are hired by higher level departments and placed with local governments on deputation, they do not feel responsible to the latter; they function as part of a vertically integrated departmental system.
- Untimely and Delayed Elections:
- States often postpone the elections and violate the constitutional mandate of five yearly elections to local governments.
- Downgraded Role of Local Government:
- Local governments are merely acting as an implementation machinery rather than a policy-making body for local development. Technology-enabled schemes have further downgraded their role.
- Corruption:
- Criminal elements and contractors are attracted to local government elections, tempted by the large sums of money now flowing to them. Thus, forming a market chain of corruption operates, involving a partnership between elected representatives and officials at all levels.
- However, there is no evidence to show that corruption has increased due to decentralisation.
Way Forward
- Revitalisation of Gram Sabhas:
- Gram Sabhas and wards committees in urban areas have to be revitalised to achieve the objective of people’s participation in real terms.
- Strengthening Organisational Structure:
- Local government organisational structures have to be strengthened with sufficient manpower.
- Serious efforts should be made towards recruitment and appointment of support and technical staff to ensure the smooth functioning of panchayats.
- Comprehensive Mechanism for Taxation:
- Devise a comprehensive mechanism for taxation at the local levels. Without local taxation, Gram Panchayats cannot be held accountable.
- Funding:
- The Ministry of Panchayati Raj should monitor the release and expenditure of Finance Commission grants to ensure that there is no delay in their release.
- It should also be ensured that grants are utilised in a proper and effective manner.
- Panchayats should also be encouraged to carry out local audits regularly so that Finance Commission grants are not delayed.
- The Ministry of Panchayati Raj should monitor the release and expenditure of Finance Commission grants to ensure that there is no delay in their release.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. The Constitution (Seventy-Third Amendment) Act, 1992, which aims at promoting the Panchayati Raj Institutions in the country provides for which of the following? (2011)
- Constitution of District Planning Committees.
- State Election Commissions to conduct all panchayat elections.
- Establishment of State Finance Commissions.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Article 243ZD of the 74th Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992 related to municipalities provides that every State at the district level shall constitute a District Planning Committee, which would be responsible for consolidation of development plans prepared by the Panchayats and the Municipalities through proposing a development plan for the district as a whole. Hence, 1 is not correct.
- Article 243K of the 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992 mandates that superintendence, direction and control of the preparation of electoral rolls for, and the conduct of, all elections to the Panchayats shall be vested in a State Election Commission. Hence, 2 is correct.
- Article 243I of the 73rd Constitutional Amendment Act, 1992 says that at the expiration of every fifth year; the Governor shall constitute a State Finance Commission to review the financial position of the Panchayats. It will make recommendations to the Governor in matters of distribution and possible allocation/ appropriation of the net proceeds of the taxes, duties, tolls and fees between the State and the Panchayats and the grants-in-aid to the Panchayats from the Consolidated Fund of the State. Hence, 3 is correct. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q2. The fundamental object of Panchayati Raj system is to ensure which among the following? (2015)
- People’s participation in development
- Political accountability
- Democratic decentralization
- Financial mobilization
Select the correct answer using the code given below
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- The most fundamental objective of the Panchayati Raj system is to ensure people’s participation in development and democratic decentralization. Hence, 1 and 3 are correct.
- Establishment of Panchayati Raj Institutions does not automatically lead to political accountability. Hence, 2 is not correct.
- Financial mobilization is not the fundamental objective of Panchayati Raj, although it seeks to transfer finances and resources to the grass root government. Hence, 4 is not correct. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q3. Local self-government can be best explained as an exercise in (2017)
(a) Federalism
(b) Democratic decentralisation
(c) Administrative delegation
(d) Direct democracy
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Democracy means decentralisation of power and giving more and more power to the people. Local self governments are looked upon as instruments of decentralisation and participatory democracy.
- To examine the working of the Community Development Programme (1952) and the National Extension Service (1953) and to suggest measures for their better working, the GoI appointed a committee in January, 1957 under the chairmanship of Balwant Rai G Mehta.
- The committee submitted its report in November, 1957 and recommended the establishment of the scheme of ‘democratic decentralisation’, which ultimately came to be known as Panchayati Raj or unit of Local Self Government. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. Assess the importance of the Panchayat system in India as a part of local government. Apart from government grants, what sources can the Panchayats look out for financing developmental projects? (2018)
Q. To what extent, in your opinion, has the decentralisation of power in India changed the governance landscape at the grassroots? (2022)


Governance
Revised Beti Bachao Beti Padhao Scheme
For Prelims: Govt schemes for Womens and Girls, Beti Bachao Beti Padhao’ scheme (BBBP), Women in STEM, STEM, Ministry of Women & Child Development (MW&CD)
For Mains: Non-traditional livelihoods for Girls, Girls in STEM, Women related issues, Women and Atmanirbhar Bharat
Why in News?
The Central Government, expanding the mandate of its flagship scheme - ‘Beti Bachao Beti Padhao' (BBBP Scheme) announced the inclusion of skilling of girls in non-traditional livelihood (NTL) options.
- At the national conference on skilling in non-traditional livelihoods for girls, Ministries of Women and Child Development MW&CD emphasises the importance of convergence between various departments for providing quality education to empower girls.
What is BBBP Scheme?
- About:
- The Scheme was launched by Prime Minister on January 22, 2015 to addresses the declining Child Sex Ratio (CSR) and related issues of women’s empowerment over a life-cycle continuum.
- It is a Tri-ministerial effort of the Ministries of Women and Child Development (MW&CD), Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MH&FW), and Ministry of Education.
- Main Objectives:
- Prevention of gender-biased sex-selective elimination.
- Ensuring survival & protection of the girl child.
- Ensuring education and participation of the girl child.
- Protecting rights of Girl children.
- Innovative Interventions under BBBP: Innovations that have created a positive ecosystem/ enabling environment for girls include:
- Guddi-Gudda Boards: (Display of Birth Statistics (number of Girls born vis-à-vis number of Boys) in public). Example: Jalgaon district, Maharashtra has installed digital Guddi-Gudda Display Boards.
- Breaking Gender Stereotypes & Challenging Son-centric Rituals: Celebration of birth of the girl child, dedicating special day on value of girl child, plantation drives symbolizing nurturing and care for girl child. Example: Cuddalore (Tamil Nadu), Selfie with Daughters (Jind district, Haryana).
What are the New Changes in the BBBP Scheme?
- Some of the new aims in the revised BBBP scheme include:
- Ensuring 1% increment in enrolment at the secondary level particularly in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) subjects.
- Skilling of girls and women every year (mainly in non-traditional livelihoods)
- Raising awareness about safe menstrual hygiene
- Promulgating elimination of child marriages
- Other Changes to the Scheme:
- The MW&CD also emphasised the convergence between various departments for providing quality education (including vocational) to empower girls.
- A MoU was signed between the MW&CD and Ministries Skill Development and Entrepreneurship, and Minority Affairs to ensure adolescents complete their education, build skills, and enter the workforce in a diverse range of professions.
- A national committee headed by the Secretary of MW&CD, formed under the larger Mission Shakti will review the implementation of the BBBP scheme with states and UTs.
What are the Other Initiatives to Support Girl Children?
What are Non-Traditional Livelihoods (NTL)?
- “Non-Traditional Livelihoods” (NTLs) – sectors and jobs where participation of women is and has historically been conventionally low or absent. Like STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) subjects due to gender-based categorization of the work, in the society.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. What are the continued challenges for Women in India against time and space? (2019)
Q. Women empowerment in India needs gender budgeting. What are the requirements and status of gender budgeting in the Indian context? (2016)


Governance
India’s First 24x7 Solar-Powered Village
For Prelims: India’s first solar-powered village, Ground Mounted Solar power plant, Rooftop solar systems, Battery Energy storage systems (BESS)
For Mains: India's achievements in the renewable energy sector and India’s Solar Power Capacity
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister declared Modhera, a village in the Mehsana district of Gujarat as India's first solar-powered village.
What are the Key Highlights of India’s First Solar Powered Village?
- About Modhera Village: Modhera is famous for its Sun temple, a protected ancient site, which is situated on the river Pushpavati. It was built by King Bhima-I of the Chalukya dynasty in 1026-27.
- The temple will acquire a 3-D projection facility which will inform tourists about the history of Modhera.
- Solar Power Generation: The solar power village would be self-sufficient in solar energy generation, as it will utilise 1000 solar panels that have been installed on the village houses, generating electricity round the clock for the villagers.
- It is developed through Ground Mounted Solar power plant and more than 1300 Rooftop solar systems on residential and Government buildings, all integrated with Battery Energy storage systems (BESS).
- A BESS is a type of energy storage system that uses batteries to store and distribute energy in the form of electricity.
- It is developed through Ground Mounted Solar power plant and more than 1300 Rooftop solar systems on residential and Government buildings, all integrated with Battery Energy storage systems (BESS).
- Benefits:
- The project will demonstrate how India's renewable energy prowess can empower people at the grassroots.
- The people in the village wouldn't pay for electricity, rather they could start selling it and earn from energy produced by the solar panel by selling it to the government grid.
- It will generate employment at the village level, and ultimately improve the standard of living.
- It will enhance the sustainable implementation of various welfare projects in the area.
- Residents of the area will be able to save 60-100% of their electricity bills.
- It will reduce the drudgery among rural women and girls engaged in the collection of fuel wood from long distances and cooking in smoky kitchens.
- It will also result in minimization of the risks of contracting lung and eye ailments.
- The project will demonstrate how India's renewable energy prowess can empower people at the grassroots.
What is the Status of Solar Energy in India?
- About: The installed solar energy capacity has increased by 19.3 times in the last 8 years and stands at 56.6 GW.
- Further, India has set an ambitious target to achieve a capacity of 175 GW worth of renewable energy by the end of 2022, which expands to 500 GW by 2030. This is the world’s largest expansion plan for renewable energy.
- India was the second-largest market in Asia for new solar PV capacity and third globally. It ranked fourth for total installations (60.4 GW), overtaking Germany (59.2 GW) for the first time.
- As of June 2022, Rajasthan and Gujarat were the top states for large-scale solar, accounting for 53% and 14% of installations, respectively, followed by Maharashtra with 9%.
- Related Initiatives:
- Solar Park Scheme: The Solar Park Scheme plans to build a number of solar parks, each with a capacity of nearly 500 MW, across several states.
- Rooftop Solar Scheme: The Rooftop Solar Scheme aims to harness solar power by installing solar panels on the roof of houses.
- Atal Jyoti Yojana (AJAY): The AJAY scheme was launched in September 2016 for the installation of solar street lighting (SSL) systems in states with less than 50% of households covered with grid power (as per Census 2011).
- National Solar Mission: It is a major initiative of the Government of India and State Governments to promote ecologically sustainable growth while addressing India's energy security challenge.
- SRISTI Scheme: Sustainable rooftop implementation of Solar transfiguration of India (SRISTI) scheme to promote rooftop solar power projects in India.
What are the Challenges Related to Solar Energy in India?
- Heavy Dependence on Imports: India doesn't have enough module and PV cell manufacturing capacity.
- The current solar module manufacturing capacity is limited to 15 GW per year, whereas the domestic production is around 3.5 GW only.
- Further, out of the 15 GW of module manufacturing capacity, only 3-4 GW of modules are technologically competitive and worthy of deployment in grid-based projects.
- The current solar module manufacturing capacity is limited to 15 GW per year, whereas the domestic production is around 3.5 GW only.
- Raw Material Supply: The silicon wafer, the most expensive raw material, is not manufactured in India.
- It currently imports 100% silicon wafers and around 80% cells.
- Further, other key raw materials, such as silver and aluminium metal pastes for making electrical contacts, are also almost 100% imported.
- It currently imports 100% silicon wafers and around 80% cells.
- Inefficiencies in Solar PV cells: The utility-scale solar PV sector continues to face challenges like land costs, high T&D losses and other inefficiencies, and grid integration challenges.
- Issues related to Biodiversity: There have also been conflicts with local communities and biodiversity protection norms.
- Pricing issue: while India has achieved record low tariffs for solar power generation in the utility-scale segment, this has not translated into cheaper power for end-consumers.
Way Forward
- India is making significant progress in the development of solar PV modules, but for it to become a manufacturing hub, it will require more policy interventions like developing home-grown technologies which could, in the short-term, work with the industry to provide them with trained human resource, process learnings, root-cause analysis through right testing and, in the long term, develop India’s own technologies.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
- The International Solar Alliance was launched at the United Nations Climate Change Conference in 2015.
- The Alliance includes all the member countries of the United Nations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- India and France launched the International Solar Alliance (ISA) to boost solar energy in developing countries. z It was launched at the United Nations Climate Change Conference in Paris in November 2015 by the Indian Prime Minister and French President. Its secretariat is located in Gurugram, India. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- At initial stage ISA was opened to membership of countries lying fully or partly between the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn (torrid zone).
- In 2018, the membership of ISA was opened for all the UN members. However, all the member countries of the UN are not its members. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Currently, 80 countries have signed and ratified the ISA Framework Agreement while 98 countries have signed the ISA Framework Agreement. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. India has immense potential of solar energy though there are regional variations in its developments. Elaborate (2020)


Indian Heritage & Culture
Shri Mahakal Lok Corridor
For Prelims: Shri Mahakal Lok Corridor, Mahakal Temple of Ujjain, Kashi Vishwanath Corridor, Temple Architecture.
For Mains: Temple Architecture of India, Shri Mahakal Lok Corridor and its Significance.
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister inaugurated the first phase of the ‘Shri Mahakal Lok’ corridor in Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh.
- After Vishwanath temple in Varanasi and the Kedarnath shrine in Uttarakhand, Mahakal temple is the third ‘jyotirlinga’ site to see a major upliftment exercise.
- The Rs 800-crore Mahakal corridor is four times the size of the Kashi Vishwanath Corridor.
What is the Shri Mahakal Lok Corridor?
- About:
- Mahakal Maharaj Mandir Parisar Vistar Yojna is a plan for the expansion, beautification, and decongestion of the Mahakaleshwar temple and its adjoining area in Ujjain district.
- Under the plan, the Mahakaleshwar temple premises of around 2.82 hectares is being increased to 47 hectares, which will be developed in two phases by the Ujjain district administration.
- This will include the 17 hectares of Rudrasagar lake.
- The project is expected to increase annual footfall in the city from the current 1.50 crore to nearly three crores.
- First Phase:
- One of the aspects of the Vistar Yojna’s first phase is a visitor plaza with two entrances or Dwaars i.e., the Nandi Dwaar and the Pinaki Dwaar.
- The visitor plaza can hold up to 20,000 pilgrims at a time.
- A circulation plan to reduce congestion has also been developed, keeping in mind the entry of visitors into the city and their movement up to the temple.
- A 900-metre pedestrian corridor has been constructed, connecting the plaza to the Mahakal temple, dotted with 108 murals and 93 statues depicting stories related to Lord Shiva, such as Shiv Vivah, Tripurasur Vadh, Shiv Puran, and Shiv Tandav Swaroop.
- There are also 128 convenience points, eateries and shopping joints, florists, handicraft stores, etc. along this pedestrian corridor.
- One of the aspects of the Vistar Yojna’s first phase is a visitor plaza with two entrances or Dwaars i.e., the Nandi Dwaar and the Pinaki Dwaar.
- Second Phase:
- This includes expansion of the eastern and northern fronts of the temple.
- It also includes development of various areas of Ujjain city, such as Maharajwada, Mahal Gate, Hari Phatak Bridge, Ramghat façade, and Begam Bagh Road.
- Buildings in Maharajwada will be redeveloped and connected to the Mahakal temple campus, while a heritage dharamshala and Kumbh museum will be built.
- It also includes development of various areas of Ujjain city, such as Maharajwada, Mahal Gate, Hari Phatak Bridge, Ramghat façade, and Begam Bagh Road.
- The second phase is being developed with funding from Agence Francaise de Development (AFD) under the City Investments to Innovate, Integrate and Sustain (CITIIS) programme.
- This includes expansion of the eastern and northern fronts of the temple.
What is the Significance of Shri Mahakal Lok Corridor?
- Immense Cultural Beliefs: The temple is believed to be governed by Mahakaleshwar, which means the ‘Lord of time’ i.e., Lord Shiva. As per Hindu mythology, the temple was constructed by Lord Brahma and is presently located alongside the holy river Kshipra.
- Only Jyotirlinga Facing South: Mahakaleshwar Jyotirlinga in Ujjain is one of the 12 jyotirlingas considered the most sacred abodes of Shiva. The shrine is revered as one the 18 Maha Shaktia Peeth in India.
- It is the only jyotirlinga facing the south, while all the others face east. This is because the direction of death is believed to be the south.
- In fact, people worship Mahakaleshwar to prevent an untimely death.
- According to the Puranas, Lord Shiva pierced the world as an endless pillar of light, called the jyotirlinga.
- Besides Mahakal, these include Somnath and Nageshwar in Gujarat, Mallikarjuna in Andhra Pradesh, Omkareshwar in Madhya Pradesh, Kedarnath in Uttarakhand, Bhimashankar, Triyambakeshwar and Grishneshwar in Maharashtra, Viswanath at Varanasi, Baidyanath in Jharkhand, and Rameswaram in Tamil Nadu.
- It is the only jyotirlinga facing the south, while all the others face east. This is because the direction of death is believed to be the south.
- Mention in Ancient Texts: The Mahakal temple finds a mention in several ancient Indian poetic texts. In the early part of the Meghadutam (Purva Megha) composed in the 4th century, Kalidasa gives a description of the Mahakal temple.
- It is described as one with a stone foundation, with the ceiling on wooden pillars. There would be no shikharas or spires on the temples prior to the Gupta period.
- Destruction and Rebuilt of Temple: During the medieval period, Islamic rulers used to give donations to priests for offering prayers here.
- In the 13th century, the temple complex was destroyed by Turk ruler Shams-ud-din Iltutmish during his raid on Ujjain.
- The present-day five-storeyed structure was built by the Maratha general Ranoji Shinde in 1734, in the Bhumija, Chalukya and Maratha styles of temple architecture.
What is the Historical Significance of the City of Ujjain?
- The city of Ujjain was one of the primary centres of learning for Hindu scriptures, called Avantika in the 6th and 7th centuries BC.
- Later, astronomers and mathematicians such as Brahmagupta and Bhaskaracharya made Ujjain their home.
- In the 18th century, an observatory was built here by Maharaja Jai Singh II, known as the Vedh Shala or Jantar Mantar, comprising 13 architectural instruments to measure astronomical phenomena.
- Also, as per the Surya Siddhanta, one of the earliest available texts on Indian astronomy dating back to the 4th century, Ujjain is geographically situated at a spot where the zero meridian of longitude and the Tropic of Cancer intersect.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to Chausath Yogini Temple situated near Morena, consider the following statements: (2021)
- It is a circular temple built during the reign of Kachchhapaghata Dynasty.
- It is the only circular temple built in India.
- It was meant to promote the Vaishnava cult in the region.
- Its design has given rise to a popular belief that it was the inspiration behind the Indian Parliament building.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- The Chausath Yogini temple is in Mitaoli village, near Padhaoli in Morena district 40 km from Gwalior. The Archaeological Survey of India has declared the temple an ancient and historical monument.
- According to an inscription dated to 1323 AD, the temple was built by the Kachchhapaghata king Devapala (reigned 1055 – 1075). It is said that the temple was the venue of providing education in astrology and mathematics based on the transit of the Sun. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- The Chausath Yogini Temple is also known as Ekattarso Mahadeva Temple. Standing atop an isolated hill of about a hundred feet high, this circular temple commands a splendid view of the cultivated fields below and is one among the very few such temples in India. This temple is so named because of the presence of a multitude of shiva lingas inside its cells. This is a yogini temple dedicated to sixty-four yoginis. Hence, statements 2 and 3 are not correct.
- It is externally circular in shape with a radius of 170 feet and within its interior part it has 64 small chambers. Within the main central shrine there are slab coverings which have perforations in them to drain rainwater to a large underground storage. The pipe lines from the roof leading the rain water to the storage are also visible.
- Many of the curious visitors have compared this temple with the Indian Parliament building (Sansad Bhawan) as both are circular in style. Many have drawn conclusions that this temple was the inspiration behind the Sansad Bhawan. Hence, statement 4 is correct.
- Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. The rock-cut architecture represents one of the most important sources of our knowledge of early Indian art and history. Discuss. (2020)


Indian History
Birth Anniversaries of Jayaprakash Narayan and Nanaji Deshmukh
For Prelims: Jayaprakash Narayan and his contributions, Bhoodan Movement, Nanaji Deskhmukh and his contributions
For Mains: Post independence role of Jayaprakash Narayan, Nanaji Deshmukh and his contributions to Bhoodan Movement
Why in News?
The Prime Minister of India has paid tributes to Loknayak Jayaprakash Narayan and Nanaji Deshmukh on their birth anniversary.
Who was Jayprakash Narayan?
- About:
- Birth: 11th October, 1902 in Sitabdiara, Bihar.
- Influenced By: Marxist ideas in the USA and Gandhian ideology.
- Contribution to Freedom Struggle:
- In 1929, he joined the Indian National Congress.
- In 1932, he was imprisoned for a year for participation in the civil disobedience movement.
- In 1939, he was imprisoned again for his opposition to Indian participation in World War II on the side of Britain but escaped.
- He played a key role in the formation of the Congress Socialist Party (1934), a left-wing group within the Congress Party.
- In 1929, he joined the Indian National Congress.
- Post-Independence Role:
- In 1948, he left the Congress Party and initiated an anti-Congress Campaign.
- In 1952, he formed the Praja Socialist Party (PSP).
- In 1954, he devoted his life exclusively to the Bhoodan Yajna Movement, of Vinoba Bhave, which demanded land redistribution to the landless.
- In 1959, he argued for a “reconstruction of Indian polity” by means of a four-tier hierarchy of village, district, state, and union councils (Chaukhamba Raj).
- Total Revolution: He led the movement against Indira Gandhi Regime as she was found guilty of violating electoral laws by the Allahabad High Court.
- He advocated a program of social transformation which he termed ‘Sampoorna Kranti' (total revolution) in 1974 against corruption in public life.
- Total Revolution has seven component revolutions, namely- political, social, economic, cultural, ideological or intellectual, educational and spiritual.
- The objective was to bring in a change in the existing society that is in tune with the ideals of the Sarvodaya (Gandhian philosophy- progress for all).
- In 1948, he left the Congress Party and initiated an anti-Congress Campaign.
- Awarded Bharat Ratna: Jayaprakash Narayan was posthumously conferred with India's highest civilian award, the Bharat Ratna (1999), for his "invaluable contribution to the freedom struggle and upliftment of the poor and downtrodden".
Who was Nanaji Deshmukh?
- About:
- Birth: 11th October 1916 in Maharashtra’s Hingoli district.
- Influenced by: Lokamanya Tilak and his nationalist ideology and Dr. Keshav Baliram Hedgewar, founding Sarsangha-chalak(head) of the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS).
- Participation in Movements: He actively participated in Acharya Vinoba Bhave’s Bhoodan Movement.
- Deshmukh was the main force behind Jayaprakash Narayan's agitation for total revolution.
- Social Activism: He was a social reformer with focus on health, education and rural self-reliance.
- He established Chitarkoot Gramoday Vishwavidyalaya in Chitrakoot - India’s first rural University and served as its Chancellor.
- He did great work towards the anti-poverty and minimum needs programme.
- Electoral Politics: He was one of the main architects of the Janata Party.
- He won in the 1977 Lok election from Balrampur (UP) Lok Sabha constituency.
- He was nominated to Rajya Sabha in 1999 in recognition of his services to the nation.
- Death: 27th February, 2010.
- Awards: He was awarded Padma Vibhushan in 1999.
- In 2019, the President of India, conferred the Bharat Ratna upon him (posthumously) for his services to the nation.


Important Facts For Prelims
THE World University Rankings 2023
Why in News?
Recently, the Times Higher Education (THE) rankings 2023 were released.
- Earlier, QS World University Ranking 2023 was released.
What is Times Higher Education?
- THE, formerly known as The Times Higher Education Supplement (THES), is a magazine reporting specifically on news and issues related to higher education.
- The Times Higher Education World University Rankings include 1,799 universities across 104 countries and regions, making them the largest and most diverse university rankings to date.
- This is based on 13 performance indicators that measure an institution’s performance across four areas: teaching, research, knowledge transfer and international outlook and is trusted worldwide by students, teachers, governments and industry experts.
What are the Key Highlights of the Ranking?
- Parameters:
- The parameters based on which the institutes are ranked are teaching (30%), research (30%), citations (30%), international outlook (7.5%), and industry outcome (2.5%). In teaching and research, 15% weightage each is based on a reputational survey.
- Global Top Performer:
- The University of Oxford has emerged as the best institute among 1,799 universities from 104 countries.
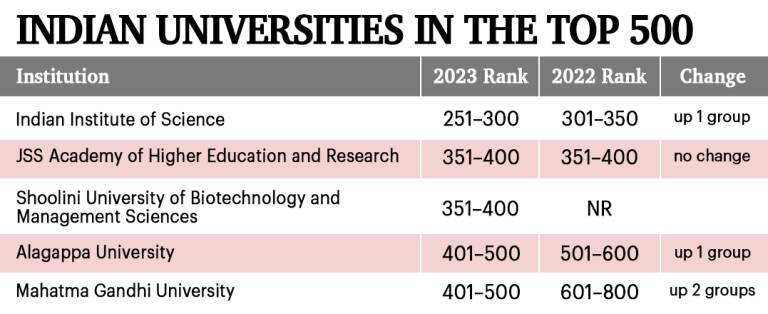
- Indian Institutions:
- Rankings: India is the sixth most represented country in the 2023 rankings with 75 ranked universities.
- The Indian Institute of Science (IISc) is at the top position among Indian institutes, for its performance score for teaching and research.
- Globally, the IISc is placed in the 251-300 band.
- IISc was the top-ranking Indian Institute in the 2022 rankings as well.
- The second position among Indian institutions has been taken by Himachal Pradesh based Shoolini University of Biotechnology and Management Sciences (351-400 overall), which made its debut in the rankings.
- IIT Ropar which was the second highest ranking Indian institute in 2022 rankings, slipped to 6th position.
- The third position is backed by Tamil Nadu’s Algappa University, a public institution.
- The Indian Institute of Science (IISc) is at the top position among Indian institutes, for its performance score for teaching and research.
- Response from IITs: It has been boycotted by most Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) for the third consecutive year over transparency concerns.
- The last time major IITs participated in the rankings was in 2019 when IIT Bombay and IIT Delhi were placed in the 401-500 overall band behind IIT Ropar and IIT Indore.
- Rankings: India is the sixth most represented country in the 2023 rankings with 75 ranked universities.
What are the Related Indian Initiatives?
- Institutions of Eminence (IoE) Scheme: Institutions of Eminence (IoE) Scheme is a government scheme to provide the regulatory architecture for setting up or upgrading 20 Institutions (10 from the public sector and 10 from the private sector) as world-class teaching and research institutions called ‘Institutions of Eminence’.
- National Education Policy, 2020: National Education Policy, 2020 aims to introduce several changes in the Indian education system - from school to college- and make India a global knowledge superpower.
- Impacting Research Innovation and Technology (IMPRINT): Impacting Research Innovation and Technology (IMPRINT) is a first-of-its-kind Pan-IIT and IISc joint initiative to develop a new education policy and a roadmap for research to solve major engineering and technology challenges that India must address and champion to enable, empower and encourage the nation for inclusive growth and self-reliance.
- Uchhatar Avishkar Yojana (UAY): Uchhatar Avishkar Yojana (UAY) was announced with a view to promote innovation of a higher order that directly impacts the needs of the industry and thereby improves the competitive edge of Indian manufacturing.


Important Facts For Prelims
Indian Foreign Service (IFS)
Why in News?
Every year, Indian Foreign Service (IFS) Day is celebrated on 9th October.
Why is Indian Foreign Service (IFS) Day Celebrated?
- About:
- Indian Foreign Service Day is celebrated to commemorate the day the Indian Cabinet created the Foreign Service.
- Origin:
- The Indian government established the Indian Foreign Service for India's diplomatic, consular and commercial representation overseas on 9th October 1946.
- With independence, there was a near-complete transition of the Foreign and Political Department into what then became the new Ministry of External Affairs.
- The origin of the Indian Foreign Service can be traced back to British rule when the Foreign Department was created to conduct business with the "Foreign European Powers".
- Offices under IFS:
- Ambassador, High Commissioner, Consul General, Permanent Representative of India to the United Nations and Foreign Secretary are some of the offices held by the members of the Indian Foreign Service.
How do Foreign Service Officers Contribute to the Country?
- As a career diplomat, the Foreign Service Officer is required to project India’s interests, both at home and abroad on a wide variety of issues.
- These include bilateral political and economic cooperation, trade and investment promotion, cultural interaction, press and media liaison as well as a whole host of multilateral issues.
- During the Russia-Ukraine war, the splendid manner in which officers rose to the challenges of Operation Ganga was recognised by the entire nation.
- Operation Ganga was an evacuation operation by India to evacuate the Indian citizens amidst the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, who had crossed over to neighboring countries.
- Under the Vande Bharat Mission, lakhs of Indians have been brought back by air, sea and land across multiple borders.
- Over the years IFS has produced President and Vice President of India, Speaker of Lok Sabha, Ministers, Parliamentarians, noted authors, scholars, historians and international public servants from its ranks.


Important Facts For Prelims
Marathon
Why in News?
Kenya’s Eliud Kipchoge, who is regarded as the world’s greatest marathon runner, broke his own world record by 30 seconds at the Berlin Marathon.
- It was a major improvement over his 2:01:39 set four years ago in Berlin.
- The Berlin marathon course is considered the fastest in the world because of the flat smooth roads.
What is a Marathon?
- Origin:
- The word marathon comes from a Greek legend that tells the story of Pheidippides, who ran from the Plains of Marathon all the way to Athens in 490 BCE to spread the news of the Greeks’ victory over the Persian army.
- The running race based on the story was first introduced at the Olympic Games in 1896.
- About:
- It is a race in which people run on roads over a distance of 42 kilometres or about 26 miles.
- It is an activity that takes a long time to complete and needs a lot of energy and determination.
- Another Important Athlete:
- One of the greatest marathon runners of all time was Abebe Bikila of Ethiopia.
- He became the first black African to win Olympic gold by winning the marathon in a world record time at the 1960 Rome Games.
- Four years later he became the first man in history to successfully defend the title.
- One of the greatest marathon runners of all time was Abebe Bikila of Ethiopia.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Consider the following statements in respect of the Laureus World Sports Award which was instituted in the year 2000:
- American golfer Tiger Woods was the first winner of this award.
- The award was received mostly by ‘Formula One’ players so far.
- Roger Federer received this award maximum number of times compared to others.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- The Laureus World Sports Awards is the premier global sporting awards. First held in 2000, the annual event honours the greatest and most inspirational sporting triumphs of the year and showcases the work of Laureus Sport for Good.
- American golfer Tiger Woods was the first winner of this award. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- The award has been received mostly by Men’s Football Team (6 times) players so far. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Roger Federer (5 times) has received this award, the maximum number of times compared to others followed by Usain Bolt (4 times) and Novak Djokovic (4 times). Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q2. Consider the following statements in respect of the 32nd Summer Olympics:
- The official motto for this Olympics is ‘A New World’.
- Sport Climbing, Surfing, Skateboarding, Karate and Baseball are included in this Olympics.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- The Games of the 32nd Summer Olympiad (Tokyo 2020) were held from 23 July to 8 August 2021. The Olympics have been held every four years since 1948. However, Tokyo Olympic 2020 was not held after four years as it was postponed for 2021, because of Covid pandemic.
- The official motto for Olympics 2020 was “United by Emotion”. The motto emphasised the power of sport to bring together people from diverse backgrounds of every kind and allow them to connect and celebrate in a way that reaches beyond their differences. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- A total of 46 Olympic Sports were contested at the Tokyo 2020 Games including Rugby, Sport Climbing, Fencing, Football, Skateboarding, Handball, Surfing, Karate, Baseball, among others. Hence, statement 2 is correct. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Q3. Consider the following statements in respect of the ICC World Test Championship:
- The finalists were decided by the number of matches they won.
- New Zealand was ranked ahead of England because it won more matches than England.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans : (d)
Exp:
- The 2021–2023 ICC World Test Championship is the second edition of the ICC World Test Championship. It started on 4 August 2021 and is scheduled to finish on 31 March 2023.
- Revamped Point System
- The ICC announced in 2020, that the finalists would be decided by percentage of points earned. The amount of points available per Test has been made uniform. This system allows the relative performance of teams to be compared at any point in time, meaning the cancellation of any matches or series for any reason does not directly impact the points table. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- New Zealand was the first team to qualify for the inaugural final. It was ahead of England due to its ratings, i.e., points (126) after playing 22 matches. On the other hand, England after playing 35 matches has got a 107 rating. Hence, statement 2 is not correct. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.