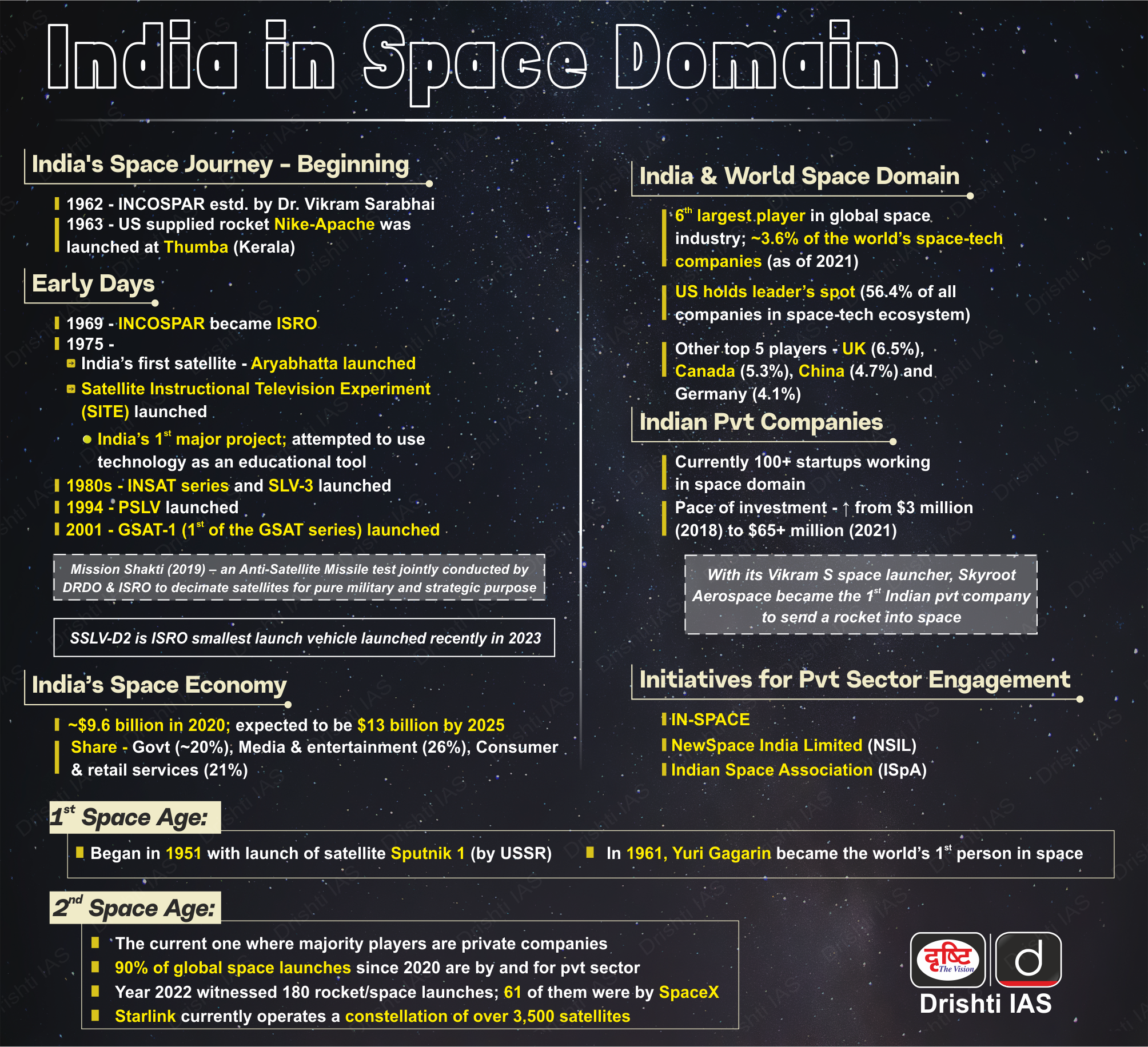
Western Disturbance Threatens India's Wheat Crop
For Prelims: Food inflation, Wheat, Food Crops.
For Mains: Effects of Weather in Food Production, Foodgrain Security.
Why in News?
Recent inclement weather conditions, including an unusual rise in mercury in February and untimely spells of widespread rain, gusty winds, and hails during March under the influence of western disturbances in key wheat-producing states have left farmers worried about a potential drop in yield, output, and quality of wheat.
What is the Impact of Untimely Rains and Winds on Wheat Crops in India?
- Impact of Untimely Rains and Winds:
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) reported that the rains, along with stormy winds between 40-50 kilometers per hour, could be detrimental to the crop's health, especially if they occur close to the ripening and harvesting stage. Unfortunately, there have been instances of crop flattening and waterlogging in fields, which could further damage the ready-to-harvest wheat crop.
- Impact on Production:
- According to the researchers, with the recent untimely rains, India's wheat production in the agriculture year 2022-23 is likely to be 102.9 MT, which is less than the Union government's estimate of 112 MT. However, the Centre remains optimistic that wheat production will be close to 112 MT due to increased acreage and better yield this season, despite a slight production loss due to recent adverse weather conditions.
- Impact on Price and Foodgrain Security:
- If India's wheat production drops below the government's estimate, it could lead to a hike in the prices of wheat and wheat-based products in the domestic market.
- Additionally, any decline in wheat production could lead to a potential foodgrain security issue.
What are the Key Points related to Wheat?
- About:
- This is the second most important cereal crop in India after rice.
- It is the main food crop, in the north and north-western part of the country.
- Wheat is a rabi crop that requires a cool growing season and bright sunshine at the time of ripening.
- Success of the Green Revolution contributed to the growth of Rabi crops, especially wheat.
- Temperature:
- Between 10-15°C (Sowing time) and 21-26°C (Ripening & Harvesting) with bright sunlight.
- Rainfall:
- Around 75-100 cm.
- Soil Type:
- Well-drained fertile loamy and clayey loamy (Ganga-Satluj plains and black soil region of the Deccan).
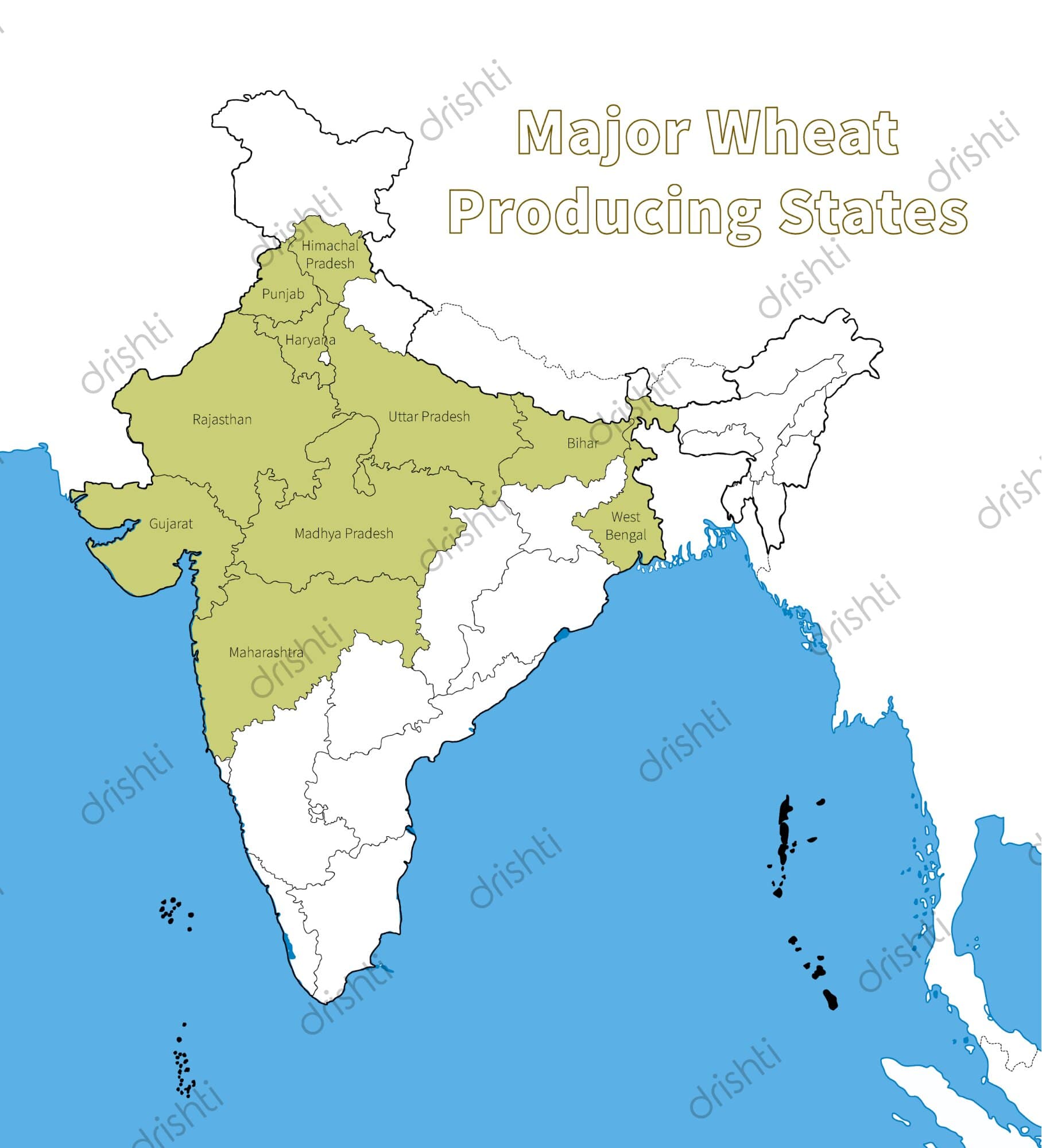
- Top Wheat Producing States:
- Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Bihar, Gujarat.
- Status of Indian Wheat Production and Export:
- India is the world's second-biggest wheat producer after China. But it accounts for less than 1% of the global wheat trade. It keeps a lot of it to provide subsidised food for the poor.
- Its top export markets are Bangladesh, Nepal and Sri Lanka - as well as the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
- Government Initiatives:
- Macro Management Mode of Agriculture, National Food Security Mission and Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana are few government initiatives to support wheat cultivation.
What are Western Disturbances?
- Western disturbances are storms that originate in the Caspian or Mediterranean Sea, and bring non-monsoonal rainfall to northwest India, according to the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- They are labelled as an extra-tropical storm originating in the Mediterranean, is an area of low pressure that brings sudden showers, snow and fog in northwest India.
- It arrives with rain and snow in Pakistan and northern India. The moisture which WDs carry with them comes from the Mediterranean Sea and/or from the Atlantic Ocean.
- WD brings winter and pre-monsoon rain and is important for the development of the Rabi crop in the Northern subcontinent.
- The WDs are not always the harbingers of good weather. Sometimes WDs can cause extreme weather events like floods, flash floods, landslides, dust storms, hailstorms and cold waves killing people, destroying infrastructure and impacting livelihoods.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following crops:
- Cotton
- Groundnut
- Rice
- Wheat
Which of these are Kharif crops?
(a) 1 and 3
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
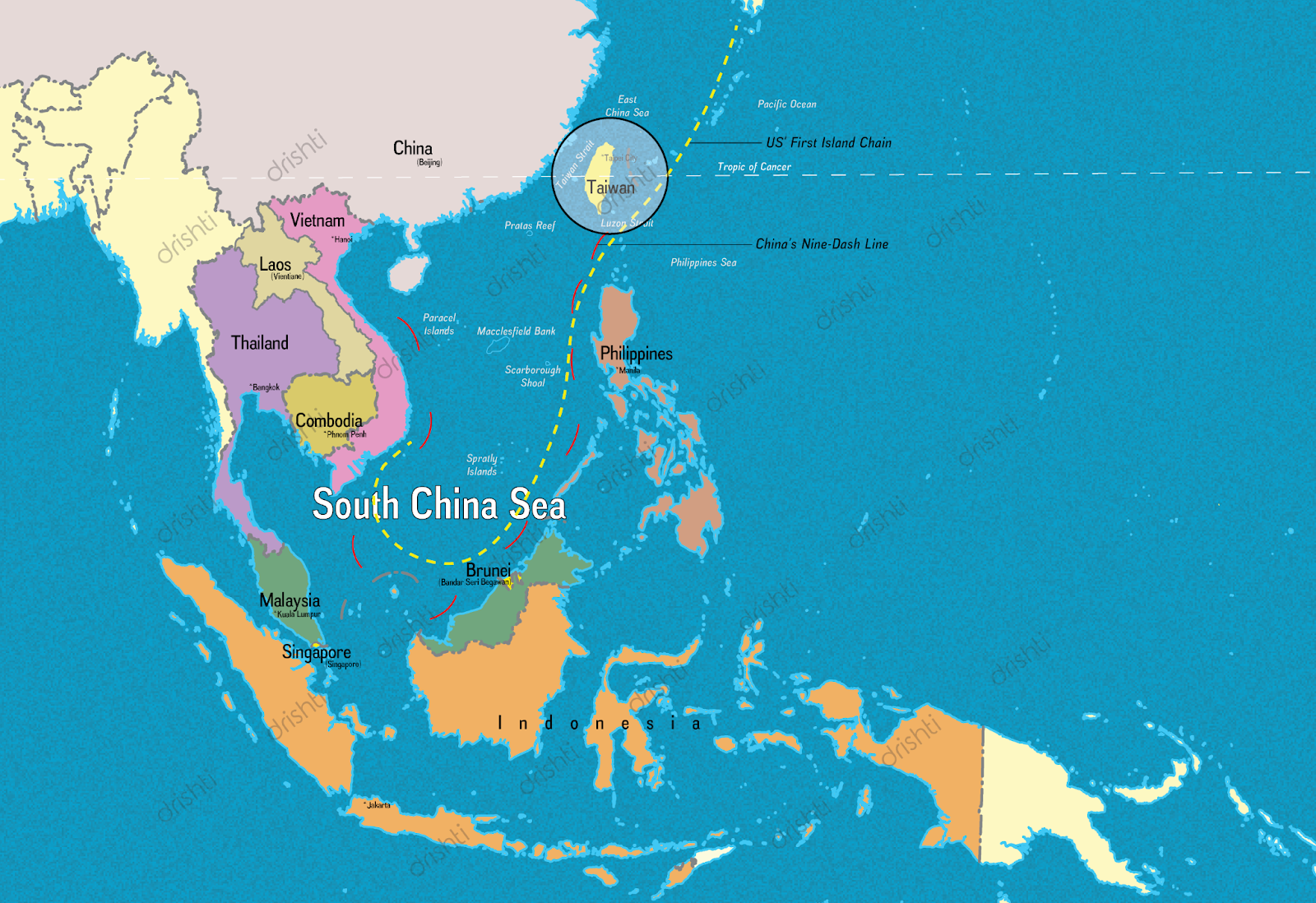
China Taiwan Conflict
For Prelims: China-Taiwan Conflict, South China Sea,Taiwan Relations Act, One China Polic.
For Mains: Significance of Taiwan, Stand of India on the Taiwan Issue, India's Act East Foreign Policy.
Why in News?
China has announced that it is prepared to fight against any attempt to achieve Taiwan's independence or any foreign interference.
- China conducted military exercises simulating a "seal off" of Taiwan, in response to the visit of Taiwan's President to the United States.
- Largely unrecognized by other nations, Taiwan sees itself as a sovereign country. However, China considers it to be a breakaway state and is determined to bring the island under its control.
What is the Point of Contention?
- Background:
- Taiwan came under Chinese control during the Qing dynasty but was given to Japan after China lost the first Sino-Japanese war in 1895.
- China regained control of Taiwan in 1945 after Japan lost World War II, but the civil war between the nationalists and communists led to the nationalists fleeing to Taiwan in 1949.
- The Kuomintang party, led by Chiang Kai-shek, ruled Taiwan for many years and is still a prominent political party. China claims Taiwan as a Chinese province, but Taiwan argues that it was never part of the People's Republic of China (PRC).
- Currently, only 13 countries recognize Taiwan as a sovereign country due to China's diplomatic pressure.
- The US backs Taiwan’s independence, maintains ties with Taipei, and sells weapons to it — but officially subscribes to PRC’s “One China Policy”, which means there is only one legitimate Chinese government
- Escalation:
- In the 1950s, the PRC bombed islands under Taiwan's control, drawing in the US, which passed the Formosa (Old Name of Taiwan) Resolution to defend Taiwan's territory.
- In 1995-96, China's testing of missiles in the seas around Taiwan led to the biggest US mobilization in the region since the Vietnam War.
- Recent Developments:
- The 2016 election of President Tsai marked the beginning of a sharp pro-independence phase in Taiwan, which has been intensified by her re-election in 2020.
- The island now has significant economic interests, including investments in China.
- Pro-independence groups worry that this economic dependence may hinder their goals, while pro-reunification groups in Taiwan, as well as China, hope that increasing people-to-people contacts will eventually wear down the pro-independence lobbies.
- Taiwan has been able to maintain its independence, but the situation remains volatile. As Taiwan continues to develop economically, it is likely that tensions will continue to rise between China and Taiwan, making it crucial to monitor the situation in the region closely.
What is the Strategic Significance of Taiwan?
- Taiwan is situated in a strategically important location in the western Pacific Ocean, adjacent to China, Japan, and the Philippines. Its location provides a natural gateway to Southeast Asia and the South China Sea, which are critical for global trade and security.
- It is a major producer of high-tech electronics, including semiconductors, and is home to some of the world's largest technology companies.
- Taiwan produces over 60% of the world's semiconductors and over 90% of the most advanced ones.
- Taiwan has a modern and capable military that is focused on defending its sovereignty and territorial integrity.
- Taiwan is a major focus of regional and global geopolitics, with the potential to influence the balance of power in the Asia-Pacific region and beyond.
What is the US’ Interest in Taiwan?
- Taiwan anchors a chain of islands which includes a list of US-friendly territories that the US is planning to use as a place of leverage for countering China’s expansionist plans.
- The US does not have official diplomatic ties with Taiwan but is bound by US law (Taiwan Relations Act, 1979) to provide the island with the means to defend itself.
- It is by far the largest arms dealer for Taiwan and follows a ‘strategic ambiguity’ policy.
What has been the Stand of India on the Taiwan Issue?
- India-Taiwan Ties:
- India-Taiwan Ties have been gradually improving over the years, as a part of India's Act East Foreign Policy. India has sought to cultivate extensive ties with Taiwan in trade and investment, as well as developing cooperation in science & technology, environment issues, and people-to-people exchange.
- Despite not having formal diplomatic relations, India and Taiwan have maintained representative offices in each other's capitals since 1995 that function as de facto embassies. These offices have facilitated high-level visits and helped deepen the economic and cultural ties between the two countries.
- One China Policy:
- India follows the One China policy which recognizes Taiwan as part of China.
- However, India also expects China to recognize India's sovereignty over territories like Jammu and Kashmir.
- India has recently stopped mentioning its adherence to the One China policy. Although India's engagement with Taiwan is restricted due to its ties with China, it sees Taiwan as an important economic partner and strategic ally.
- India's increasing ties with Taiwan are viewed as a move to counter China's growing influence in the region.
Way Forward
- The Chinese economy is far more interconnected with the global economy than Russia's Economy. Thus, China will look to mind the gap very carefully if they want to launch an invasion of Taiwan, especially so close to the Ukraine crisis.
- After all, the Taiwan issue is not just about a moral question of allowing the destruction of a successful democracy, or about international ethics, the day after China's invasion of Taiwan will mark a very different Asia, regardless of what happens.
- In addition, India can rethink the One China Policy and separate its relationship with mainland China from that with Taiwan just as China is expanding its involvement in Pakistan occupied Kashmir (PoK) through its ambitious project China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. “China is using its economic relations and positive trade surplus as tools to develop potential military power status in Asia”. In the light of this statement, discuss its impact on India as her neighbour. (2017)
Debt of Emerging Markets & Developing Economies Rose
For Prelims: Sovereign Debt, External commercial borrowings.
For Mains: factors contributing to debt crisis, impact of sovereign debt on countries
Why in News?
The report from Debt Relief for a Green and Inclusive Recovery (DRGR) Project states that the sovereign debt of emerging markets and developing economies (EDME) increased by 178% from USD 1.4 trillion to USD 3.9 trillion between 2008-2021, indicating a looming debt crisis in the Global South.
- The G20’s "Common Framework" created to provide debt relief has shortcomings, as it failed to bring all creditors, including private and commercial creditors, on board and link debt relief with development and climate goals.
Note: An emerging market economy is the economy of a developing nation that is becoming more engaged with global markets as it grows. Countries classified as emerging market economies are those with some, but not all, of the characteristics of a developed market such as India, Mexico, Russia, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, China, and Brazil.
What are the Factors and Impacts of the Debt Crisis?
- EDMEs are Experiencing Weakened Economic Growth due to:
- Slow recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic,
- High food and energy prices, and
- Russia's war in Ukraine.
- Escalating climate impacts
- Strong US dollar and depreciating currencies for many EMDEs.
- Impacts on Vulnerable Countries:
- Countries vulnerable to climate change tend to face the most significant debt distress.
- Higher climate vulnerability is linked to lower sovereign borrowing space.
- High debt service payments, forcing countries to set aside a significant portion of their foreign reserves to pay off debt.
- Providing immediate debt relief to EDMEs could free up their fiscal and borrowing, allowing them to pursue a low-carbon, socially inclusive, and resilient future.
What are the Proposed Solutions?
- The report calls for a reform of the Common Framework and proposes three pillars to address the issue.
- The first pillar involves public creditors granting significant cuts in debts to bring a distressed country back to debt sustainability and also helping it achieve development and climate goals.
- The second pillar involves private and commercial creditors granting debt reductions comparable to public creditors.
- For the remaining debt, the government should issue new bonds for private creditors, backed by a guaranteed fund.
- The last pillar is for countries not at risk of debt distress, for which international financial institutions can provide credit enhancement.
- Debt Restructuring: The report also calls for the restructuring of USD 812 billion of debt owed by 61 countries that are in or at high risk of debt distress.
- At least USD30 billion in debt should be suspended over the next five years for 55 of the most debt-distressed countries, the authors calculated.
What is G20 Common Framework?
- The Common Framework for debt treatment beyond the Debt Service Suspension Initiative (DSSI) is an initiative endorsed by the G20 in 2020, together with the Paris Club, to support, in a structural manner, Low Income Countries with unsustainable debt.
- The framework is aimed at providing a coordinated and comprehensive approach to addressing the debt vulnerabilities of low-income countries (LICs) that are facing the most severe debt challenges, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Note: DRGR Project is a collaboration between the Boston University Global Development Policy Center, Heinrich-Böll-Stiftung and the Centre for Sustainable Finance at SOAS University of London.
Preventive Detention
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court (SC) of India observed that preventive detention laws in India are a colonial legacy that confers arbitrary power to the state.
- The Court warned that these laws are extremely powerful and have the potential to provide the state with free discretion.
What are the Implications of the SC's Judgment on Preventive Detention Laws?
- The Supreme Court's judgment is a significant development in the protection of civil liberties in India. The Court's warning about the arbitrary power conferred on the state through preventive detention laws emphasizes the importance of ensuring checks and balances on government power.
- The judgment's emphasis on analyzing cases with extreme caution and excruciating detail sets a high standard for the government to follow every procedure of law while exercising preventive detention powers against individuals.
- The Supreme Court's judgment underscores the importance of protecting individual and civil liberties while balancing the need to maintain public order and national security.
- The judgment highlights the importance of judicial oversight and review to ensure that preventive detention laws are not misused to suppress dissent or violate individual rights.
- The Court's emphasis on protecting civil liberties is a significant development in safeguarding fundamental rights and ensuring the rule of law in India.
What is Preventive Detention?
- About:
- Preventive detention means detention of a person without trial and conviction by a court. Its purpose is not to punish a person for a past offence but to prevent him from committing an offence in the near future.
- The detention of a person cannot exceed three months unless an advisory board reports sufficient cause for extended detention.
- Protection:
- Article 22 grants protection to persons who are arrested or detained.
- Article 22 has two parts—the first part deals with the cases of ordinary law and the second part deals with the cases of preventive detention law.
- Article 22 grants protection to persons who are arrested or detained.
- Two Types of Detentions:
- Preventive detention is when a person is held in police custody only on the basis of a suspicion that they would conduct a criminal act or cause harm to society.
- The police have the authority to hold anyone they suspect of committing a criminal offence and also to make arrests without a warrant or a magistrate’s authorization in certain cases.
- Punitive detention, which means detention as a punishment for a criminal offence. It occurs after an offence is actually committed, or an attempt has been made towards the commission of that crime.
- Preventive detention is when a person is held in police custody only on the basis of a suspicion that they would conduct a criminal act or cause harm to society.
State Energy Efficiency Index 2021-22
Why in News?
Recently, the State Energy Efficiency Index (SEEI) 2021-22 has been released by the Union Minister of Power and New & Renewable Energy.
What is the State Energy Efficiency Index?
- About:
- The index is developed by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), a statutory body under the Ministry of Power, in association with Alliance for an Energy-Efficient Economy (AEEE).
- It assesses the annual progress of states and UTs in energy efficiency (energy savings and reduction in emission intensity).
- The updated framework of 50 indicators is aligned with national priorities, and program-specific indicators are included to track outcomes and impacts of state-level energy efficiency initiatives.
- Based on the progress and accomplishments of states in energy efficiency implementation, they have been classified into four categories: Front Runner, Achiever, Contender, and Aspirant.
- Significance:
- India is committed to achieving NDC goals and transitioning to a net-zero economy by 2070.
- This requires collaboration between central and state governments, judicious resource allocation, policy alignment, and regular progress tracking.
- SEEI tracks progress in managing states' and India's energy footprint, driving energy efficiency policies and programs at the state and local levels.
- India is committed to achieving NDC goals and transitioning to a net-zero economy by 2070.
What are the Key Findings from SEEI 2021-22?
- Front Runner Category (>60 points):
- Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Rajasthan, and Telangana.
- Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Assam, and Chandigarh are the top-performing states in their respective state groups, while Telangana and Andhra Pradesh showed the most improvement since the last index.
- Achiever Category (50-60 points):
- Assam, Haryana, Maharashtra, and Punjab.
What are the Recommendations for States?
- Enabling fiscal assistance for energy efficiency in the focus sectors
- Developing institutional capacity in states and UTs to address emerging needs and challenges in energy efficiency implementation
- Enhancing cross-functional collaborations across financial institutions, energy service companies, and energy professionals in large-scale energy efficiency implementation in states
- Mainstreaming energy data reporting and monitoring across sectors
What is the Bureau of Energy Efficiency?
- About:
- BEE was established on March 1st, 2002, under the provisions of the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
- The mission of BEE is to assist in developing policies and strategies for energy efficiency with the primary objective of reducing the energy intensity of the Indian economy.
- Functions of BEE:
- BEE is responsible for regulatory and promotional functions as outlined in the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
- It recognizes, identifies, and utilizes existing resources and infrastructure to perform its functions. BEE works with state governments and utilities to improve energy efficiency implementation.
- BEE's focus on energy efficiency contributes to India's climate commitments and a sustainable future.
RBI's Decision to Pause Interest Rate Hikes
Why in News?
Recently, The RBI's Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) decided to pause interest rate hikes and assess the impact of previous hikes.
- Since May 2021, RBI had been consistently raising interest rates to reduce inflation, which was far above its target level of 4%.
What is Inflation Targeting?
- About:
- Inflation targeting in India is a monetary policy framework that was adopted by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in 2016.
- Under this framework, the RBI sets a target for the inflation rate and uses monetary policy instruments to achieve it.
- Currently, RBI's primary objective is to achieve the 4% inflation target. RBI has a comfort zone of +/- 2% within which inflation must remain. This means that the RBI aims to keep the inflation rate between 2% and 6%.
- The last two readings of inflation (January and February 2023) were 6.5% and 6.4%, respectively.
- Inflation targeting in India is a monetary policy framework that was adopted by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in 2016.
- Reasons to Pause Interest Rate Hikes:
- RBI's strategy of hiking interest rates to control inflation has limitations. According to the RBI, under the current circumstances, monetary measures alone may not be sufficient to control inflation.
- Fiscal policy (government's taxes and spending) may be more effective in bringing down current inflation.
- RBI's strategy of hiking interest rates to control inflation has limitations. According to the RBI, under the current circumstances, monetary measures alone may not be sufficient to control inflation.
- Advantages:
- Increased central bank transparency and accountability.
- Allows investors and the public to anticipate interest rate changes.
- Lowers inflation expectations.
- Limitations of RBI’s Inflation Targeting:
- Limited Impact on Supply-side Factors: Inflation targeting can only control demand-side factors, such as money supply and interest rates, and may not be effective in addressing supply-side shocks such as crop failures, natural disasters, and global commodity price shocks due to disturbed geopolitics.
- Limited Impact on Structural Issues: Inflation targeting may not be able to address structural issues that contribute to inflation, such as inefficient distribution systems, inadequate infrastructure, and bureaucratic hurdles.
- Conflict with Other Objectives: Inflation targeting may conflict with other macroeconomic objectives, such as economic growth, employment, and income distribution.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2010)
- The Wholesale Price Index (WPI) in India is available on a monthly basis only.
- As compared to Consumer Price Index for Industrial Workers (CPI(IW)), the WPI gives less weight to food articles.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Q2. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The weightage of food in Consumer Price Index (CPI) is higher than that in Wholesale Price Index (WPI).
- The WPI does not capture changes in the prices of services, which CPI does.
- The Reserve Bank of India has now adopted WPI as its key measure of inflation and to decide on changing the key policy rates.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
C R Rao will Receive the 2023 International Prize in Statistics
Why in News?
Calayampudi Radhakrishna Rao, a prominent Indian-American mathematician and statistician, will be awarded the 2023 International Prize in Statistics, the equivalent of a Nobel Prize in the field.
What are the Works of C R Rao?
- Background:
- Rao's remarkable paper, published in 1945 in the Bulletin of the Calcutta Mathematical Society, demonstrated three fundamental results that paved the way for the modern field of statistics and provided statistical tools heavily used in science today.
- Theory:
- The Cramer-Rao Lower Bound:
- Provides a means of knowing when a method for estimating a quantity is as good as any method can be.
- The Rao-Blackwell Theorem:
- Provides a means of transforming an estimate into an optimal estimate. Together, these results form a foundation on which much of statistics is built.
- The Information Geometry:
- Provided insights that pioneered a new interdisciplinary field that has flourished as "information geometry.
- Information geometry is the study of the geometrical structure of families of probability distributions.
- Provided insights that pioneered a new interdisciplinary field that has flourished as "information geometry.
- The Cramer-Rao Lower Bound:
What is the Significance of Rao’s Contribution?
- His work on information geometry has aided the understanding and optimization of Higgs boson measurements at the Large Hadron Collider, and contributed to advancements in artificial intelligence, data science, signal processing, shape classification, and image segregation.
- The Rao-Blackwell process has been applied to stereology, particle filtering, and computational econometrics, among others.
- The Cramer-Rao lower bound is of great importance in diverse fields such as signal processing, spectroscopy, radar systems, multiple image radiography, risk analysis, and quantum physics.
What Other Awards Conferred to C R Rao?
- Padma Bhushan in1968.
- Padma Vibhushan in 2001.
International Prize in Statistics
- The International Prize in Statistics is awarded every two years by a collaboration among five leading international statistics organizations.
- The prize recognizes a major achievement by an individual or team in the statistics field, particularly an achievement of powerful and original ideas that have led to practical applications and breakthroughs in other disciplines.
- The prize is modeled after the Nobel prizes, Abel Prize, Fields Medal, and Turing Award.
United Nations Democracy Fund
Why in News?
India is the fourth highest donor to the UN Democracy Fund (UNDEF), which funds at least 68 projects worldwide linked to George Soros’s Open Society Foundation.
- India has put George Soros’s NGO on watchlist in 2016.
What is UNDEF?
- About:
- UNDEF was established in 2005 by UN Secretary-General Kofi A. Annan as a United Nations General Trust Fund to support democratization efforts around the world.
- It was welcomed by the General Assembly in the Outcome Document of the 2005 World Summit.
- UNDEF plays a unique role in complementing the UN's other work with governments to strengthen democratic governance around the world.
- UNDEF was established in 2005 by UN Secretary-General Kofi A. Annan as a United Nations General Trust Fund to support democratization efforts around the world.
- UNDEF's Mandate and Projects:
- UNDEF funds projects that empower civil society, promote human rights, and encourage the participation of all groups in democratic processes.
- The majority of UNDEF funds go to local civil society organizations (CSOs).
- The Advisory Board of the UNDEF offers policy guidance and funding guidelines, considers proposals for funding, and recommends funding proposals for approval by the Secretary-General.
- UNDEF provides grants ranging from USD 100,000 to USD 300,000.
- In 15 rounds of funding so far, UNDEF has supported over 880 two-year projects in more than 130 countries.
- India's Support for UNDEF:
- India has contributed over USD 32 million since its inception (2005).
- Top three donors are US, Sweden, and Germany.
- In 2022, when India contributed USD 150,000 to the fund, it was the fourth highest among 45 donors, after
- India has consistently supported UNDEF’s mission of promoting democratic governance worldwide through funding of projects carried out by local and international CSOs and NGOs.
- India has contributed over USD 32 million since its inception (2005).
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
National Party
The Election Commission of India has recognized the Aam Aadmi Party (AAP) as a national party. The decision was made based on a review of the parties’ poll performances, including the 2014 and 2019 Lok Sabha polls and 21 state assembly polls since 2014. With this recognition, AAP joins the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), Indian National Congress (INC), Bahujan Samaj Party (BSP), CPI(M), and National People’s Party (NPP) as the sixth national party in the country. This status ensures that the party’s symbol is reserved for its candidates across the country, and it gets land for an office in the national capital.
In contrast, the Trinamool Congress (TMC), Nationalist Congress Party (NCP), and Communist Party of India (CPI) have lost their national party status. The EC's decision was based on the criteria stipulated in the Election Symbols (Reservation and Allotment) Order, of 1968. Among other conditions, a national party must get at least a 6% vote share in four or more states in the last Lok Sabha or Assembly elections and have at least four MPs in Lok Sabha. In its review, the EC found that the TMC did not contest the 2019 Lok Sabha elections from Arunachal Pradesh and Manipur, while the NCP lost its state party status in Goa, Manipur, and Meghalaya. The CPI had its status as a state party withdrawn in West Bengal and Odisha.
Read more: National and State Parties
Guru Tegh Bahadur Parkash Purab
Guru Tegh Bahadur Parkash Purab 2023 is celebrated to mark the birth of the Ninth Guru of Sikhism, Guru Tegh Bahadur, and to remember his life and teachings. This year it is being observed on April 11, 2023. Tegh Bahadur was born on the 21st of April 1621 in Amritsar. He was raised under the guidance of his father, Guru Hargobind, who was known for raising an army against the Mughals and promoting the concept of warrior saints. Tegh Bahadur's contribution to Sikhism is immense. His poetic hymns are housed in the sacred text of Sikhism, 'Guru Granth Sahib.' He founded the town of Chak-Nanki in Punjab during one of his missions, which later became a part of Punjab's Anandpur Sahib.
Unfortunately, Guru Tegh Bahadur was executed in Delhi in 1675 under the orders of the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb. He is remembered as a saint and martyr who sacrificed his life to uphold the principles of freedom of religion and justice.
Read more: Guru Tegh Bahadur, Sikhism
Mahatma Jyotiba Phule
The Prime Minister has paid tribute to the great social reformer, philosopher, and writer Mahatma Jyotirao Phule on his birth anniversary. Jyotirao Phule was born on 11th April 1827 in Maharashtra, India. He belonged to the Mali caste of gardeners and vegetable farmers. Phule was greatly influenced by Thomas Paine’s book ‘The Rights of Man’, which led him to advocate for liberty, egalitarianism, and socialism. He believed in the enlightenment of women and lower-caste members as the only solution to combat social evils. Phule was a prolific writer, and his major publications include ‘Tritiya Ratna,’ ‘Gulamgiri,’ and ‘Shetkarayacha Aasud.’
Phule established the Satyashodhak Samaj in 1873, which meant ‘Seekers of Truth’ and aimed to attain equal social and economic benefits for lower castes in Maharashtra. In 1848, Phule and his wife Savitribai opened the first indigenously run school for girls in Pune, where they both taught. Phule was a believer in gender equality and involved his wife in all his social reform activities. He established an ashram for young widows and became an advocate for the idea of Widow Remarriage. He worked towards abolishing untouchability and the caste system in Maharashtra. Phule’s activism inspired the likes of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar and Mahatma Gandhi. He passed away on 28th November 1890, and his memorial is built in Phule Wada, Pune, Maharashtra. It is believed that he was the first person to use the term ‘Dalit’ for the depiction of oppressed masses often placed outside the ‘varna system’.
Read more: Jyotirao Phule
Unified Licensing Portal
The Central Bureau of Narcotics has launched a unified portal aimed at streamlining the licensing and authorization process for the pharma and chemical industry in India. The portal has been developed with the goal of instilling efficiency, transparency, and accountability in the department's operations while boosting the economy for "Aatma Nirbhar Bharat" and ensuring the availability of essential narcotic drugs and medicines to patients and their families.
The portal will benefit drug exporters, importers, and manufacturers with easy and secure transactions, simplified processes, and contactless operations. The portal is designed to be integrated with other government services, including Bharat Kosh, GST, PAN-NSDL validation, e-Sanchit, and UIDAI, providing single-point services for obtaining licenses from the Central Bureau of Narcotics. The portal is an effective tool for striking a balance between the availability of these substances for medicinal, scientific, and industrial use while ensuring compliance with the law and preventing their diversion for illicit use.
Central Bureau of Narcotics is a central government organization dealing with the international trade of Narcotic Drugs, Psychotropic Substances, and Precursor Chemicals under the ambit of various United Nations Conventions and the provisions of NDPS Act, 1985.
Read more: Narcotics Control Bureau