Geography
Rock Glaciers
For Prelims: Jhelum, Rock Glaciers, Glacial lake outburst floods, Landslides, Thermokarst, Batagaika crater
For Mains: Potential Consequences of Rock Glaciers, Factors Influence Glacial Dynamics, Impact of Glacial Retreat
Why in News?
A recent study has shed light on the presence of over 100 active permafrost structures in the Jhelum basin of the Kashmir Himalayas. These structures, known as rock glaciers, have significant implications for the region's hydrology and pose potential risks as the climate warms.
What are Rock Glaciers?
- About:
- Rock glaciers are a type of landform that consists of a mixture of rock fragments and ice.
- Rock glaciers typically form in mountainous regions where there is a combination of permafrost, rock debris, and ice.
- Permafrost is a permanently frozen layer on or under Earth's surface. It consists of soil, gravel, and sand, usually bound together by ice.
- One common scenario involves a pre-existing glacier that accumulates debris and rocks as it moves. Over time, if the glacier recedes or thaws, the debris-covered ice can transform into a rock glacier.
- These rock glaciers occur in highly elevated regions with steep slopes.
- To the naked eye, the rock glaciers look like regular ground, they require a geomorphological view for proper identification.
- Classification:
- They are classified as active or relict, depending on whether they have ice and movement or not. Active rock glaciers are more dynamic and hazardous, while relict rock glaciers are more stable and inert.
- Importance:
- Rock glaciers are important indicators of mountain permafrost, which is the permanently frozen ground that underlies many high-altitude regions.
- Rock glaciers also store significant amounts of water in their frozen cores, which could be a valuable resource in the face of water scarcity and glacial retreat.
What are the Potential Impacts of the Active Rock Glaciers on the Region?
- Glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs):
- These are sudden and catastrophic floods that occur when a glacial lake bursts its natural or artificial dam, releasing large volumes of water and debris downstream.
- The active rock glaciers could increase the risk of GLOFs by destabilizing the slopes or the dams of glacial lakes.
- Rock glaciers near glacial lakes, such as Chirsar Lake and Bramsar Lake, increase the risk of GLOFs.
- These are sudden and catastrophic floods that occur when a glacial lake bursts its natural or artificial dam, releasing large volumes of water and debris downstream.
- Landslides:
- These are the rapid movements of soil, rock, or snow down a slope, often triggered by earthquakes, rainfall, or human activities.
- The active rock glaciers could cause landslides by weakening the slope stability or by melting and releasing water that could lubricate the sliding mass.
- The melting permafrost makes these areas unstable, posing risks to nearby settlements and critical infrastructure.
- For example, the Nunavik area in Quebec was mostly built on permafrost ground many years ago. In the last decades, the ice in the underlying layers began to melt due to global warming, increasing the frequency of mudslides and other dangers.
- These are the rapid movements of soil, rock, or snow down a slope, often triggered by earthquakes, rainfall, or human activities.
- Thermokarst:
- This is a type of terrain that is characterized by irregular surfaces of marshy hollows and small hummocks (ridges), formed by the thawing of ice-rich permafrost.
- The active rock glaciers could lead to the formation of thermokarst features, such as ponds or lakes, that could alter the hydrology, ecology, and carbon cycle of the region.
- The presence of water bodies near Kulgam town, Jammu and Kashmir suggests the existence of permafrost underground, resembling 'thermokarst lakes', which can pose further risks.
- The melting of ice underneath the earth’s surface is a high risk of collapse. The collapse leads to formation of a landscape whose features are sinkholes, hummocks, caverns, and tunnels.
- The Batagaika crater is an example of thermokarst, it is the biggest permafrost crater in the world, it belongs to the Sakha Republic, Russia.
- This is a type of terrain that is characterized by irregular surfaces of marshy hollows and small hummocks (ridges), formed by the thawing of ice-rich permafrost.
Jhelum Basin of the Kashmir Himalayas
- The Jhelum basin is drained by the upper Jhelum River, which originates from a deep spring at Vernag at Anantnag, situated at the base of the Pir Panjal range in the Kashmir Valley, the river passes through Srinagar and Wular Lake before entering Pakistan.
- As a tributary of the Indus River, the Jhelum contributes to the larger river system in the Indian subcontinent.
- The river flows through Jammu and Kashmir and into Pakistan, where it joins the Chenab River.
- The primary tributary is the Kishenganga (Neelum) River. The Kunhar River, another significant tributary, connects Pakistan-occupied Kashmir and Pakistan via the Kohala Bridge in the Kanghan Valley.
Way Forward
- The study highlights the critical role of permafrost research in understanding and mitigating the impacts of climate change in the Himalayan region.
- Allocate resources for further studies on the hydrological potential of active rock glaciers, exploring ways to harness the stored water for sustainable use in regions facing water scarcity.
- Develop and implement early warning systems in regions with identified active rock glaciers to alert communities and authorities about potential disasters.
- Integrate findings from permafrost studies into regional and national climate change adaptation plans, considering the specific challenges posed by the transition from glaciers to rock glaciers.
- There is a need to raise awareness among local communities, planners, and policymakers about the risks associated with permafrost degradation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the Indus river system, of the following four rivers, three of them pour into one of them which joins the Indus directly. Among the following, which one is such a river that joins the Indus direct? (2021)
(a) Chenab
(b) Jhelum
(c) Ravi
(d) Sutlej
Ans: (d)
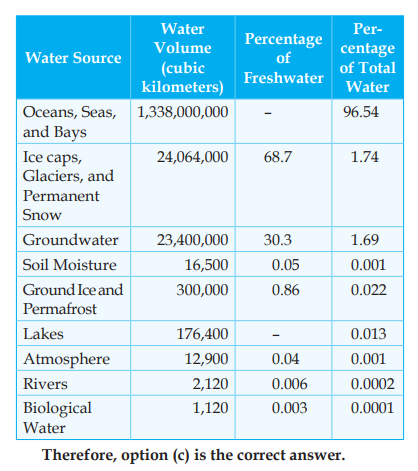
Q. On the planet earth, most of the freshwater exists as ice caps and glaciers. Out of the remaining freshwater, the largest proportion (2013)
(a) is found in atmosphere as moisture and clouds
(b) is found in freshwater lakes and rivers
(c) exists as groundwater
(d) exists as soil moisture
Ans: C
Exp:
Mains:
Q. How does the cryosphere affect global climate? (2017)


Indian Economy
Navigating GST Challenges
For Prelims: Goods and Services Tax, Economic recovery curves, National Statistical Office, Input Tax Credit, 101st Constitution Amendment Act, 2016.
For Mains: Current Major Challenges Related to GST in India, GST Council
Why in News?
The recent Goods and Services Tax (GST) revenue data paints a concerning picture: consumption growth is not uniform across Indian states, revealing a potential dissonance in national economic recovery.
What are the Major Takeaways From the Recent GST Related Data?
- Overall GST Collections: It grew by 11.7% in the first nine months of 2023-24 compared to the 2022-23.
- State GST collections grew at a higher rate (15.2%) compared to Central GST, suggesting differential consumption patterns across states.
- Sharp Disparities Among States: Some states like Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Karnataka showed robust growth in state GST revenues (17% to 18.8%), while others like Gujarat, West Bengal, and Andhra Pradesh lagged behind with single-digit growth or even contraction.
- Lowest Private Consumption Expansion: National Statistical Office (NSO) estimates project private final consumption expenditure (PFCE) growth for the year at only 4.4%, the slowest since 2002-03 (excluding pandemic times).
- The PFCE is defined as the expenditure incurred by the resident households and non-profit institutions serving households (NPISH) on final consumption of goods and services, whether made within or outside the economic territory.
What is Goods and Services Tax?
- About: GST is a value-added tax system that is levied on the supply of goods and services in India.
- It is a comprehensive indirect tax that was introduced in India on 1st July 2017, through the 101st Constitution Amendment Act, 2016, with the slogan of ‘One Nation One Tax’.
- Tax Slabs: The primary GST slabs for regular taxpayers are currently 0% (nil-rated), 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%.
- There are a few GST rates that are less commonly used, such as 3% and 0.25%.
- Benefits of GST:
- Simplified Tax Regime: GST replaced a multitude of indirect taxes, making compliance easier and reducing paperwork for businesses.
- Increased Transparency: The online GST portal simplifies tax administration and promotes transparency in the system.
- Reduced Tax Burden: Lower prices due to the elimination of cascading taxes benefit consumers.
- Boosted Economic Growth: By removing tax barriers and improving efficiency, GST is expected to contribute to higher economic growth and job creation.
- GST Council: The GST Council is a constitutional body responsible for making recommendations on issues related to the implementation of the GST in India.
- As per Article 279A (1) of the amended Constitution, the GST Council was constituted by the President.
What are the Current Major Challenges Related to GST in India?
- Complexity and Compliance Burden: GST in India has a complex structure with multiple tax slabs, leading to increased compliance requirements.
- This complexity poses a challenge for businesses, especially smaller enterprises, in understanding and adhering to the diverse regulations.
- Technology and Infrastructure Readiness: The successful implementation of GST relies heavily on robust technological infrastructure. Issues such as lack of technological readiness among businesses, and disparities in technology adoption can hinder the seamless functioning of the GST network.
- Input Tax Credit (ITC) Verification: The government authorities have recently identified and busted more than 29,000 bogus firms involved in evading GST dues.
- Multiple Registrations Across States: Businesses operating in multiple states must register separately in each state for GST compliance.
- This multiplicity of registrations adds administrative burden and increases compliance costs for businesses with a pan-India presence, contributing to logistical challenges.
Way Forward
- Simplify and Rationalize Tax Structure: Simplifying the GST tax structure by reducing the number of tax slabs.
- A more straightforward and uniform tax system would ease compliance for businesses and promote a clearer understanding of tax obligations.
- Streamline Compliance Procedures: Work towards simplifying and streamlining compliance procedures to reduce the administrative burden on businesses. This could involve harmonizing return filing processes, ensuring timely refunds, and implementing user-friendly interfaces for tax filings.
- Focus on Anti-Evasion Measures: Strengthen measures to curb tax evasion, especially through fake invoices and fraudulent activities.
- Utilizing advanced data analytics and technology to identify suspicious transactions, and implement stringent penalties for non-compliance to deter fraudulent practices.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following items: (2018)
- Cereal grains hulled
- Chicken eggs cooked
- Fish processed and canned
- Newspapers containing advertising material
Which of the above items is/are exempted under GST (Good and Services Tax)?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Q2. What is/are the most likely advantages of implementing ‘Goods and Services Tax (GST)’? (2017)
- It will replace multiple taxes collected by multiple authorities and will thus create a single market in India.
- It will drastically reduce the ‘Current Account Deficit’ of India and will enable it to increase its foreign exchange reserves.
- It will enormously increase the growth and size of economy of India and will enable it to overtake China in the near future.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Explain the rationale behind the Goods and Services Tax (Compensation to States) Act of 2017. How has COVID-19 impacted the GST compensation fund and created new federal tensions? (2020)
Q. Enumerate the indirect taxes which have been subsumed in the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. Also, comment on the revenue implications of the GST introduced in India since July 2017. (2019)
Q. Explain the salient features of the Constitution (One Hundred and First Amendment) Act, 2016. Do you think it is efficacious enough “to remove cascading effect of taxes and provide for common national market for goods and services”? (2017)
Q. Discuss the rationale for introducing the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. Bring out critically the reasons for the delay in roll out for its regime. (2013)


Economy
World Economic Situation and Prospects Report for 2024
For Prelims: United Nations, Inflation, Headline Inflation, El Nino, Net-zero-emissions, Artificial Intelligence, Loss and Damage Fund
For Mains: World Economic Situation and Prospects, Impact of Climate Change on Global GDP
Why in News?
A recent United Nations report titled World Economic Situation and Prospects report for 2024 forecasts a decline in global inflation in 2024, but warns of a simultaneous rise in food inflation, particularly in developing nations.
- The implications of this phenomenon, coupled with climate-related challenges and geopolitical tensions, pose threats to food security, poverty alleviation, and economic growth.
What are the Key Highlights of the World Economic Situation and Prospects Report for 2024?
- Global GDP Growth:
- The report forecasts a deceleration in global gross domestic product (GDP) growth, from an estimated 2.7% in 2023 to 2.4% in 2024.
- Developing economies, in particular, are struggling to recover from pandemic-induced losses, with many facing high debt and investment shortfalls.
- It is anticipated that many low-income and vulnerable nations will experience only moderate growth in the upcoming years.
- The reasons are persistently high-interest rates, escalating geopolitical conflicts, slow international trade and an increase in climate-related calamities.
- India’s Perspective:
- South Asia grew by an estimated 5.3% in 2023 and is projected to increase by 5.2% in 2024, driven by a robust expansion in India, which remains the fastest-growing large economy in the world.
- India is projected to grow by 6.2% in 2024, supported by domestic demand and growth in manufacturing and services.
- Inflation:
- Global inflation, a key concern over the past two years, shows signs of easing.
- Global headline inflation fell from 8.1% in 2022 to an estimated 5.7% in 2023 and is projected to decline to 3.9% in 2024.
- Headline inflation measures the total inflation within an economy, which includes commodities like food and energy prices.
- The decline in inflation was attributed to ongoing moderation in international commodity prices and a decrease in demand due to monetary tightening by the UN.
- Global headline inflation fell from 8.1% in 2022 to an estimated 5.7% in 2023 and is projected to decline to 3.9% in 2024.
- However, food price inflation remains critical, exacerbating food insecurity and poverty, particularly in developing countries.
- An estimated 238 million people experienced acute food insecurity in 2023, an increase of 21.6 million from 2022.
- Weak local currencies, climate-related shocks and limited pass-through from international prices to local prices will be the causes of this ongoing increase in food inflation.
- The resurgence of El Nino can disrupt climate patterns, leading to both excessive and insufficient precipitation affecting food production.
- An estimated 238 million people experienced acute food insecurity in 2023, an increase of 21.6 million from 2022.
- Global inflation, a key concern over the past two years, shows signs of easing.
- Climate Change:
- 2023 experienced extreme weather conditions, leading to devastating wildfires, floods, and droughts worldwide.
- These events have direct economic impacts, such as damage to infrastructure, agriculture, and livelihoods.
- Studies project significant economic losses due to climate change.
- Estimates suggest a potential 10% reduction in global GDP by 2100, considering events like the Greenland ice shelf collapse.
- Without mitigation, models indicate a potential 23% decrease in average global incomes by 2100.
- IPCC estimates predict a range of 10 to 23% global GDP losses by 2100 due to temperature impacts alone.
- 2023 experienced extreme weather conditions, leading to devastating wildfires, floods, and droughts worldwide.
- Investment:
- Global investment growth is expected to remain low due to economic uncertainties, high debt burdens, and rising interest rates.
- Developed nations prioritize sustainable sectors like green energy and digital infrastructure.
- Developing countries grapple with capital flight and reduced foreign direct investment.
- Geopolitical tensions impact regional investment flows, contributing to low global investment growth amid economic uncertainties and rising interest rates.
- Investment in the energy sector, especially in clean energy, is growing but not at a pace sufficient to meet the net-zero-emissions goal by 2050.
- Report estimates USD 150 trillion needed by 2050 for energy transition and infrastructure, requiring USD 5.3 trillion annually for the global energy sector alone.
- Despite this, climate finance falls short of requirements, emphasizing the crucial need for massive scaling up.
- The report calls for effective operationalization of the Loss and Damage Fund and increased financing commitments to aid vulnerable countries facing climate disasters.
- Global investment growth is expected to remain low due to economic uncertainties, high debt burdens, and rising interest rates.
- Labour Market:
- The global labour market displays divergent trends between developed and developing countries post-pandemic.
- Developed Countries:
- Experienced a robust recovery with low unemployment rates, notably 3.7% in the US and 6.0% in the EU in 2023, coupled with rising nominal wages and narrowing wage inequality.
- However, real income losses and labour shortages pose challenges.
- Developing Countries:
- Mixed progress with varied unemployment trends (e.g., China, Brazil, Türkiye, Russia report declines).
- Persistent issues are informal employment, gender gaps, and high youth unemployment.
- Globally, the decline in female labor force participation to 47.2% in 2023 (compared to 48.1% in 2013).
- Artificial Intelligence(AI) Impact on Global Employment:
- Since ChatGPT's introduction in 2022, AI adoption has rapidly advanced.
- One-third of global firms now use generative AI, with 40% planning to expand AI investment.
- AI could reduce demand for low-skilled jobs, disproportionately impacting women and lower-income countries. Also, there’s a significant gender gap in AI professions.
- One-third of global firms now use generative AI, with 40% planning to expand AI investment.
- Since ChatGPT's introduction in 2022, AI adoption has rapidly advanced.
- Developed Countries:
- The global labour market displays divergent trends between developed and developing countries post-pandemic.
- Trade:
- Global trade growth weakened to 0.6% in 2023, anticipated to recover to 2.4% in 2024.
- The report points to a shift in consumer spending from goods to services, rising geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and the lingering effects of the pandemic as factors impeding global trade.
- Global trade growth weakened to 0.6% in 2023, anticipated to recover to 2.4% in 2024.
- International Finance and Debt:
- Rising external debt and increased interest rates hinder developing countries' access to international capital markets.
- Decline in official development assistance and foreign direct investment compounds financial constraints for low-income nations.
- Debt sustainability becomes a critical concern, necessitating debt restructuring and relief efforts to manage escalating financial burdens effectively.
- Multilateralism and Sustainable Development:
- The 2024 WESP report emphasizes the need for strengthened global cooperation, particularly in areas like climate action, sustainable development financing, and addressing the debt sustainability challenges of low- and middle-income countries.
- The report underscores the critical role of multilateralism in navigating the complex global economic landscape and achieving the UN-mandated Sustainable Development Goals (SDG).


Important Facts For Prelims
Darjeeling Zoo’s Conservation Breeding Programme for Snow Leopards
Why in News?
The Padmaja Naidu Himalayan Zoological Park (PNHZP), West Bengal also commonly known as Darjeeling zoo has achieved international recognition from the World Association for Zoos and Aquariums (WAZA) for its successful conservation breeding programme (CBC) for snow leopards.
- This recognition is a testament to the zoo's dedication to wildlife conservation and the preservation of endangered species.
What is the World Association for Zoos and Aquariums (WAZA)?
- WAZA is the global alliance of regional associations, national federations, zoos and aquariums, dedicated to the care and conservation of animals and their habitats around the world.
- The membership consists of nearly 400 leading institutions and organisations around the world, and this number continues to grow.
What are the Conservation Efforts of Snow Leopards in the Darjeeling Zoo?
- About:
- Darjeeling Zoo has the only conservative breeding programme for snow leopards in India.
- Apart from snow leopards, it has conservative breeding programmes for red pandas, mountain orals and pheasants.
- Darjeeling zoo is the largest high altitude zoo in India.
- Conservation Breeding Programme:
- The first ex-situ conservation breeding program started in 1986 as a Snow Leopard conservation breeding project.
- The CBC at Darjeeling Zoo recorded the first birth of a snow leopard in 1989. Since then, 77 snow leopards have been born at the zoo, marking a remarkable achievement in wildlife conservation.
- The zoo's success in breeding snow leopards can be attributed to careful pairing of male and female snow leopards, creating a natural environment within the enclosures, and using a wide genetic pool to avoid inbreeding.
- Before pairing, the snow leopards are kept in adjoining enclosures to develop courtship. Once their compatibility is observed, they are paired and kept in the same enclosure.
- Pregnant female leopards are separated and kept under 24X7 CCTV surveillance, with regular blood tests and monitoring of body weight.
- The zoo practices the highest biosecurity protocols for all captive animals, including regular screening for parasites, deworming, and advanced veterinary facilities.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following: (2012)
- Black-necked crane
- Cheetah
- Flying squirrel
- Snow leopard
Which of the above are naturally found in India?
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
President of India Presents Sports and Adventure Awards 2023
Why in News?
Recently, the President of India presided over a ceremony at Rashtrapati Bhavan to bestow the prestigious National Sports and Adventure Awards 2023.
- The awards are administered by the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports, Government of India.
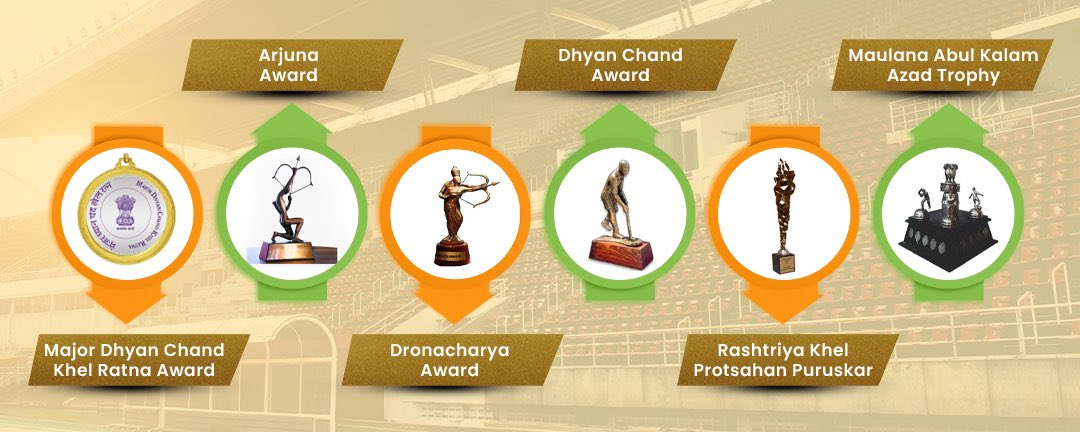
What Awards Were Included in the Ceremony?
- Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award:
- India's highest sporting honor established in 1991-92.
- Named after hockey legend Major Dhyan Chand.
- Given for outstanding performances over 4 years.
- Notable awardees include MC Mary Kom, PV Sindhu, Sachin Tendulkar, and Virat Kohli.
- 2023: Chirag Shetty and Satwik Sairaj Rankireddy (badminton).
- Arjuna Award:
- Instituted in 1961, it was India’s highest sporting honor before the Khel Ratna came into being.
- Named after the Mahabharata character Arjuna.
- Awarded for consistent good performance over 4 years.
- Winners receive a statuette of Arjuna, a certificate, and a cash prize.
- First awarded to football Olympian PK Banerjee in 1961.
- First woman awardee: Hockey player Anna Lumsden.
- 2023: Aditi Gopichand Swami (archery), Mohammed Shami (cricket), Aishwary Pratap Singh Tomar (shooting), among others.
- Dronacharya Award:
- India's highest sports honor for coaches, instituted in 1985.
- Named after Dronacharya, Arjuna's coach in Mahabharata.
- Awardees receive a bronze statue of Dronacharya, a certificate, and a cash prize.
- First woman awardee: Athletics coach Renu Kohli in 2002.
- Given for both recent accomplishments and lifetime contributions.
- 2023:
- Regular Category: Lalit Kumar (wrestling), RB Ramesh (chess) among others.
- Lifetime Category:Jaskirat Singh Grewal (golf), Bhaskaran E (kabaddi) among others.
- 2023:
- Major Dhyan Chand Award:
- Instituted in 2002, honors lifetime achievements in sports.
- Recognizes contributions to the promotion of sports in an individual capacity.
- First awardees include Olympian boxer Shahuraj Birajdar and hockey player Ashok Diwan.
- 2023: Manjusha Kanwar (badminton), Vineet Kumar Sharma (hockey), Kavitha Selvaraj (kabaddi).
- Maulana Abul Kalam Azad Trophy (MAKA):
- Oldest National Sports Award in India, instituted in 1956–1957.
- Given to an institution or university for top performance in inter-university tournaments.
- Award comprises a rolling MAKA Trophy and a cash prize.
- First awarded to Bombay University in 1956-57.
- 2023: Guru Nanak Dev University, Amritsar (overall winner university); Lovely Professional University, Punjab (first runner -up); Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra (second runner-up).
- Rashtriya Khel Protsahan Puraskar:
- Instituted in 2009.
- Awarded to organizations and individuals for sports promotion and development.
- Categories include talent identification, corporate social responsibility, employment of sportspersons, and sports for development.
- 2023: JAIN (Deemed-to-be-University), Odisha Mining Corporation Limited.
- Tenzing Norgay National Adventure Award:
- It has been presented since 1993-1994 and is named after Tenzing Norgay, one of the first two individuals to reach the summit of Mount Everest along with Edmund Hillary in 1953.
- The recipients are honored for their "outstanding achievement in the field of adventure activities on land, sea and air" over the last three years.
- The status of this award is considered to be equivalent to the Arjuna Award conferred in the field of sport.
- 2022: Late Ms. Savita Kanswal (land), Shri Tulsi Chaitanya Mothukuri(water), Shri Anshu Kumar Tiwari (air).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question: (2023)
Q. Consider the following pairs with regard to sports awards:
- Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award- For the most spectacular and outstanding performance by a sportsperson over period of last four years
- Arjuna Award- For the lifetime achievement by sportsperson
- Dronacharya Award- To honor eminent coaches who have successfully trained sportspersons or teams
- Rashtriya Khel Protsahan Puraskar- To recognize the contribution made by sports persons even after their retirement
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
Atal Setu Nhava Sheva Sea Link
Why in News?
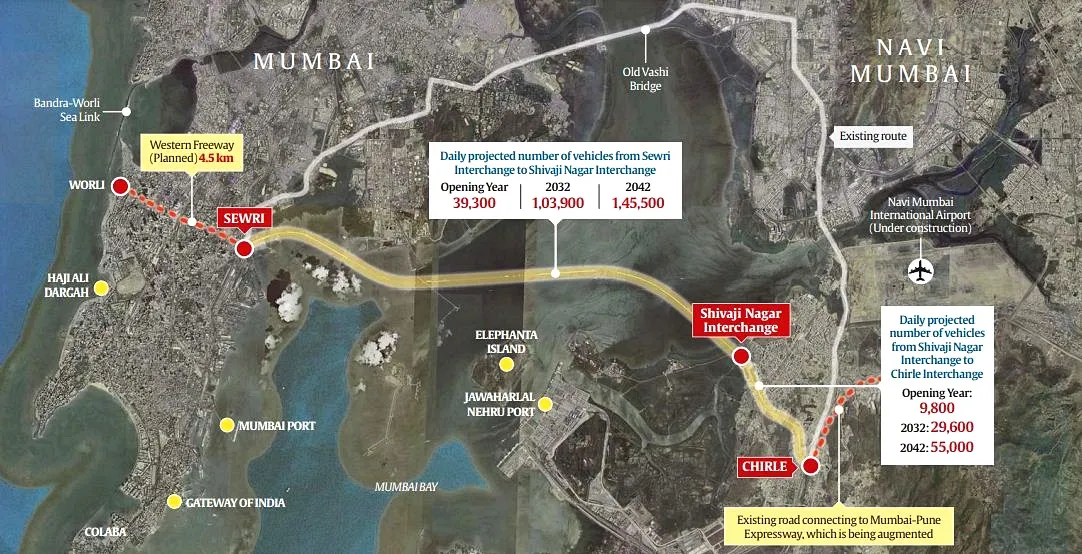
The Prime Minister of India inaugurated the Mumbai Trans Harbour Link (MTHL) officially known as Atal Setu Nhava Sheva Sea Link, a monumental 22 km sea bridge.
- This mega-infrastructure project aims to revolutionize travel between Sewri and Chirle, promising a significant reduction in travel time.
What are the Key Highlights of MTHL?
- About:
- Atal Setu is the longest bridge in India and also the longest sea bridge in the country.
- The bridge is about 21.8 km long six-lane bridge having about 16.5 km length over sea and about 5.5 km on the land.
- The bridge has been named after former prime minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee.
- The bridge originates from Sewri in Mumbai and ends at Nhava Sheva in Uran taluka in Raigad district.
- The project is financed by the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), covering 80% of the total project cost, while the remaining portion is shared between the state and central governments.
- Atal Setu is the longest bridge in India and also the longest sea bridge in the country.
Note
- Earlier Dr. Bhupen Hazarika Bridge was the longest bridge in India, over the River Brahmaputra, in Assam. The 9.15 Km long river bridge.
- Technologies Incorporated:
- MTHL incorporates various innovative technologies, such as Reverse Circulation Drilling (RCD) piling, Orthotropic Steel Deck (OSD) bridge girders, and Open Road Tolling (ORT) system.
- RCD is used for the first time in India, an innovative technology employed for pile foundation laying, it minimizes noise disturbances compared to the traditional vertical drilling method.
- OSD is a construction method that combines strength and flexibility. This technology allows the bridge's steel deck to withstand heavy loads, such as vehicles, while maintaining a lightweight structure.
- MTHL became the country's first project to adopt the ORT method of collecting tolls without requiring vehicles to stop or slow down.
- MTHL incorporates various innovative technologies, such as Reverse Circulation Drilling (RCD) piling, Orthotropic Steel Deck (OSD) bridge girders, and Open Road Tolling (ORT) system.
- Benefits:
- According to a study conducted by Mumbai Metropolitan Region Development Authority (MMRDA) and JICA, the MTHL will bring down the average travel time between Sewri and Chirle from 61 minutes currently to less than 16 minutes.
- Close to 40,000 vehicles are expected to use the link every day in the opening year (2024).
- The project is expected to facilitate greater economic integration of Navi Mumbai with Mumbai, with benefits extending to Panvel, Alibaug, Pune, and Goa.
- The bridge also reduces the distance between Mumbai and Pune Expressway.


Rapid Fire
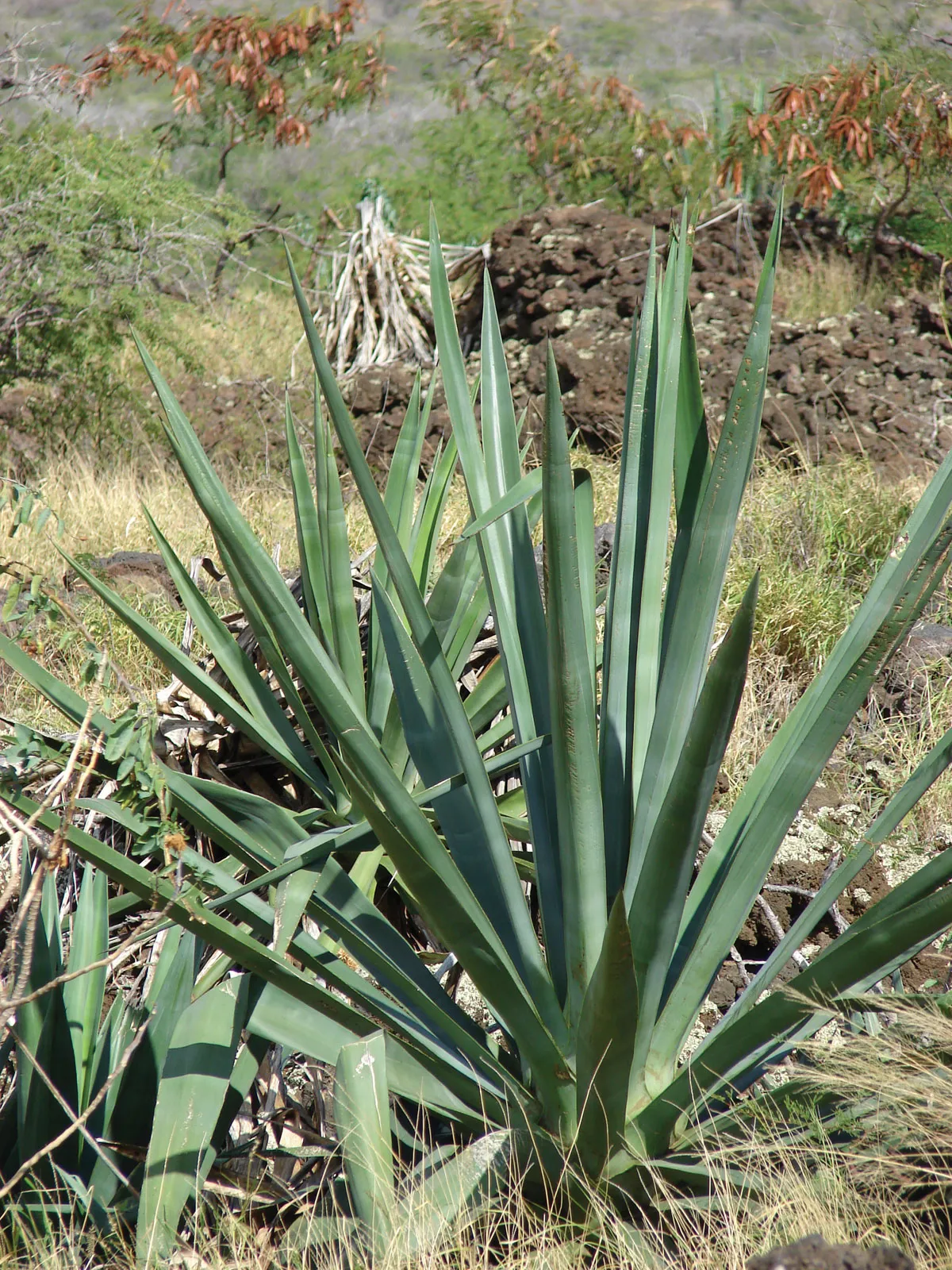
Sisal Leaves: A Green Revolution in Menstrual Hygiene
Recently, scientists at Stanford University have devised an innovative method utilizing sisal leaves to create a highly absorbent material, potentially replacing cotton, wood pulp, and chemical absorbents in sanitary napkins.
- This environmentally-friendly approach boasts higher absorption capacity than commercial alternatives, while the cultivation of sisal requires significantly less water compared to cotton.
- Sisal is a xerophytic, semi-perennial leaf fiber producing plant. Leaves are thick, fleshy and often covered with a waxy layer.
Read more: Addressing the Menstrual Health & Hygiene


Rapid Fire
Impact of Wind Turbines on Forest Bats
A recent study conducted by scientists from Germany, has revealed the impact of wind turbines on the activity of forest bats.
- Three foraging groups of bat species were studied: narrow-space, open-space(hunt in open areas with few obstacles), and edge-space(specialized on hunting prey close to background objects), within a radius of 80 to 450 meters under variable wind conditions.
- Narrow-space foraging bats, which are particularly reliant on forest habitat, showed a 77% decline in activity as wind speed increased in operational wind turbines.
- The avoidance behavior was not observed in edge-space and open-space foraging bats, indicating a habitat-specific response.
- The noise emitted by wind turbine rotors was identified as a significant cause of the avoidance behavior.
- Wind turbines, a key element in national climate strategies, are increasingly erected in forest sites worldwide, posing potential challenges to bat populations.
- The study, initially focusing on short-term impacts, suggests potential long-term effects on bat activity near operational wind turbines, particularly if noise emissions are the cause.
Read more: Bamboo-Dwelling Bat


Rapid Fire
National Youth Day 2024
- India celebrates the National Youth Day, on 12th January every year on the occasion of Swami Vivekananda’s birth anniversary.
- Since 1984, the nation has marked the day by urging the youth to live up to the values, principles and beliefs that Vivekananda embraced.
- As a part of National Youth Day celebrations, India organizes an annual National Youth Festival from January 12 to 16.
- The theme of this year’s festival is “Viksit Bharat@ 2047: Yuva ke liye, yuva ke dwara”.
- Swami Vivekananda is considered one of the great Indian monks who enlightened the Western world about Hinduism.
- As a disciple of Sri Ramakrishna Paramahamsa, he pushed for national integration in colonial India and is credited with reviving Hinduism in the nation.
Read More: Swami Vivekananda


Rapid Fire
Startups for Railways
Recently, Indian Railways has taken an important initiative in the field of innovation through participation of start-ups and other entities.
- “Startups for Railways" initiative was launched by the Ministry of Railways and Indian Railways Innovation Portal is a part of this initiative.
- Its objective is to leverage innovative technologies developed by Indian Startups/MSMEs/Innovators/Entrepreneurs to improve operational efficiency and safety on Indian Railways.
- The Ministry of Railways aims to address quality, reliability and maintainability related issues of the Indian Railways.
- Under the policy, the Startup/MSME/Innovator/Entrepreneur will have exclusive ownership of Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) created in the project.
Read more: Indian Railway Innovation Policy