Land Restoration and Afforestation
For Prelims: Nagar Van Yojana, National Forest Policy of 1988,National Mission for a Green India (GIM)
For Mains: Role of afforestation and sustainable land management in achieving India's climate resilience goals. Initiatives related to Land Restoration and Afforestation
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister of State for Environment, Forest and Climate Change, in a written reply in the Lok Sabha, shed light on the pivotal initiatives taken by India to combat land degradation and promote afforestation.
- The Nagar Van Yojana (Urban Forest Scheme), a progressive initiative the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, has gained significant traction as its progress continues to illuminate India's commitment to creating vibrant urban green spaces.
What is Nagar Van Yojana( NVY)?
- About:
- The NVY was introduced in the year 2020 with a visionary objective – the creation of 1000 Nagar Vans (urban forests) in cities equipped with Municipal Corporations, Municipal Councils, Municipalities, and Urban Local Bodies (ULBs).
- This ambitious initiative is designed to foster not only a holistic and healthy living environment for city residents but also to contribute significantly to the growth of cleaner, greener, and more sustainable urban centres.
- Key Features:
- Creating green space and aesthetic environment in an urban set-up.
- Creating awareness about plants and biodiversity and developing environment stewardship.
- Facilitating in-situ conservation of important flora of the region.
- Contributing to environmental improvement of cities by pollution mitigation, providing cleaner air, noise reduction, water harvesting and reduction of heat islands effect.
- Extending health benefits to residents of the city and helping cities become climate resilient.
- Progress and Impact of NVY:
- Since its inception, the NVY has gained remarkable momentum, with 385 projects sanctioned across the country.
- This impressive progress underscores India's dedication to transforming its cities into thriving, eco-conscious communities.
What are the Initiatives to Combat Land Degradation and Promote Afforestation?
- Government Initiatives to Boost Forest Cover:
- National Forest Policy (NFP) 1988:
- The NFP 1988 sets a national goal of achieving a minimum of one-third of the total land area under forest or tree cover.
- The aim is to maintain ecological balance, conserve natural heritage, and prevent soil erosion in river, lake, and reservoir catchment areas.
- National Mission for a Green India (GIM):
- It is under the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) and aims to increase forest and tree cover, restore degraded ecosystems, and enhance biodiversity.
- Forest Fire Protection & Management Scheme (FFPM):
- This scheme focuses on preventing and managing forest fires, contributing to the overall health of forests.
- Compensatory Afforestation Fund:
- This approach involves utilizing funds collected for diverting forest land for non-forest purposes to undertake afforestation and reforestation projects, thus restoring forest cover.
- Utilized by States/UTs for compensatory afforestation to offset forest land diversion for developmental projects.
- 90% of the Compensatory Afforestation Fund money is to be given to the states while 10% is to be retained by the Centre.
- This approach involves utilizing funds collected for diverting forest land for non-forest purposes to undertake afforestation and reforestation projects, thus restoring forest cover.
- National Coastal Mission Programme:
- Under the National Coastal Mission Programme on ‘Conservation and Management of Mangroves and Coral Reefs’, annual Management Action Plan (MAP) for conservation and management of mangroves are formulated and implemented in all the coastal States and Union Territories.
- State Specific Initiatives:
- Mission Haritha Haram:
- It is a flagship programme of the Telangana government to increase the green cover of the State from the present 25.16 to 33% of the total geographical area.
- Green Wall:
- It is an initiative launched by the Haryana government to restore and protect the Aravalli range.
- It is an ambitious plan to create a 1,400km long and 5km wide green belt buffer around the Aravali Mountain range covering the states of Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat and Delhi.
- Mission Haritha Haram:
- Afforestation Achievements:
- Twenty Point Programme Reporting:
- Over the period from 2011-12 to 2021-22, approximately 18.94 million hectares of land have been covered through afforestation efforts.
- These achievements result from concerted efforts by both the State Governments and central and state-specific schemes.
- Multi-Sectoral Approach:
- Afforestation activities are undertaken collaboratively across various sectors, involving departments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), civil society groups, and corporate entities. This multi-faceted approach ensures a holistic effort to combat land degradation.
- Twenty Point Programme Reporting:
- National Forest Policy (NFP) 1988:
- Measures to Combat Land Degradation:
- Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas:
- Published by the Space Applications Centre (SAC) of the Indian Space Research Organisation, this atlas provides critical data on the extent of land degradation and desertification in India. It helps in planning restoration efforts based on accurate information.
- Centre of Excellence at ICFRE:
- The establishment of a Centre of Excellence at the Indian Council for Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE) in Dehradun promotes South-South Cooperation.
- It facilitates knowledge exchange, best practice sharing, and capacity building for sustainable land management.
- The establishment of a Centre of Excellence at the Indian Council for Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE) in Dehradun promotes South-South Cooperation.
- Bonn Challenge Pledge:
- India committed to restoring 26 million hectares of degraded and deforested land by 2030 as part of the voluntary Bonn Challenge. This global initiative focuses on restoring degraded lands for enhanced ecosystem services and biodiversity.
- UNFCCC COP and UNCCD COP14:
- India's participation in the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) Conference of the Parties (COP) and the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) COP14 demonstrates the country's commitment to global efforts in land restoration and combating desertification.
- Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas:
What are the Challenges Associated With Land Degradation and Afforestation?
- Challenges Associated with Land Degradation:
- Soil Erosion:
- Intense rain and wind remove topsoil, reducing soil fertility.
- Improper agricultural practices and deforestation contribute to erosion.
- Climate change disrupts soil health through shifting precipitation patterns and rising temperatures. Altered weather conditions, such as intense rainfall exceeding soil absorption capacity, accelerate erosion, causing runoff and degradation.
- Desertification:
- Arid and semi-arid areas experience soil degradation and loss of vegetation cover.
- Overgrazing and unsustainable land use exacerbate desertification.
- Industrialization and Urbanization:
- Urban expansion and industrial activities lead to soil sealing, impeding water infiltration and nutrient cycling.
- Pollution from industries can contaminate soil and water resources.
- Land Pollution and Contamination:
- Improper disposal of waste and hazardous materials leads to soil contamination and reduced soil productivity.
- Landfills and improper waste management contribute to land degradation.
- Soil Erosion:
- Challenges Associated with Afforestation:
- Species Selection:
- Choosing suitable tree species that thrive in the local ecosystem.
- Invasive species may outcompete native vegetation.
- Survival and Growth:
- Ensuring newly planted trees survive harsh conditions and grow successfully.
- Water availability, soil quality, and climate influence tree establishment.
- Competing Land Uses:
- Conflicts arise when afforestation competes with agriculture, urbanization, or other land uses.
- Balancing conservation goals with economic activities is challenging.
- Ecosystem Imbalance:
- Rapid afforestation without considering native species and ecosystems may disrupt natural balances.
- Planting monocultures can lead to biodiversity loss.
- Community Participation:
- Engaging local communities in afforestation efforts is crucial for long-term success.
- Inadequate community involvement may lead to resistance or unsustainable practices.
- Species Selection:
Way Forward
- Integrated Landscape Management:
- Develop holistic land-use plans integrating afforestation with other activities.
- Implement sustainable land management practices to prevent erosion and desertification.
- Science-Based Species Selection and Agroforestry:
- Conduct research to select suitable tree species for local ecosystems.
- Promote agroforestry models for enhanced biodiversity and productivity.
- Bio-Engineering Solutions:
- Harness bio-engineering techniques like soil bio-remediation and bio-fencing to restore land health and prevent erosion.
- Traditional Ecological Wisdom:
- Collaborate with indigenous communities to revive traditional agroforestry practices, integrating local knowledge into modern restoration strategies.
- Eco-Entrepreneurship:
- Encourage community-led afforestation enterprises, creating sustainable livelihoods and nurturing a sense of ownership.
- Sustainable Financing Mechanisms:
- Mobilize funds from budgets, international sources, and public-private partnerships.
- Ensure transparent allocation for afforestation projects.
- Monitoring, Research, and Innovation:
- Develop robust monitoring systems for progress and impact assessment.
- Invest in research and innovation for climate-resilient afforestation techniques.
Initiatives Under National Education Policy 2020
For Prelims: National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, PARAKH, PM-SHRI , National Credit Framework , NIPUN Bharat Mission, Scheme for Promotion of Academic and Research Collaboration.
For Mains: Salient Features of National Education Policy (NEP) 2020
Why in News?
Recently, the Minister of State for Education provided valuable insights into the initiatives taken up under National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 for the transformation of Education Sector in India during a written reply in the Lok Sabha.
What is NEP 2020?
- About:
- The NEP 2020 aims at making “India a global knowledge superpower”. It is only the 3rd major revamp of the framework of education in India since independence.
- The two earlier education policies were brought in 1968 and 1986.
- The NEP 2020 aims at making “India a global knowledge superpower”. It is only the 3rd major revamp of the framework of education in India since independence.
- Salient Features:
- Ensuring Universal Access at All Levels of schooling from pre-primary school to Grade 12.
- Ensuring quality early childhood care and education for all children between 3-6 years.
- New Curricular and Pedagogical Structure (5+3+3+4) corresponds to the age groups of 3-8, 8-11, 11-14, and 14-18 years respectively.
- It covers four stages of schooling: Foundational Stage (5 years), Preparatory Stage (3 years), Middle Stage (3 years), and Secondary Stage (4 years).
- No hard separations between arts and sciences, between curricular and extra-curricular activities, between vocational and academic streams;
- Emphasis on promoting multilingualism and Indian languages
- Setting up of a new National Assessment Centre, PARAKH (Performance Assessment, Review, and Analysis of Knowledge for Holistic Development)
- A separate Gender Inclusion fund and Special Education Zones for disadvantaged regions and groups
What are the Major Initiatives Taken Under NEP 2020?
- PM Schools for Rising India (SHRI): PM-SHRI scheme aims to provide high-quality education in an equitable, inclusive, and joyful school environment.
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme launched in September 2022 for upgradation and development of more than 14500 Schools across the country.
- Rs. 630 crore has been allocated to upgrade schools under the PM SHRI initiative.
- NIPUN Bharat: The vision of National Initiative for Proficiency in Reading with Understanding and Numeracy(NIPUN) Bharat Mission is to create an enabling environment to ensure the universal acquisition of foundational literacy and numeracy, so that every child achieves the desired learning competencies in reading, writing, and numeracy by the end of Grade 3, by 2026-27.
- PM e-VIDYA: The initiative aimed to promote online education and digital learning by providing various e-learning platforms like DIKSHA and offering e-books and e-contents to students across the country.
- NCF FS and Jadui Pitara: Launch of National Curriculum Framework for Foundational Stage (NCF FS) and Jadui Pitara for play-based learning teaching material tailored for children between the age group of 3 to 8 years
- NISHTHA: The National Initiative for School Heads' and Teachers' Holistic Advancement (NISHTHA) is a capacity-building program for teachers and school principals in India.
- NDEAR: National Digital Education Architecture (NDEAR), an architectural blueprint, that lays down a set of guiding principles and building blocks to enable the creation of digital technology-based applications pertaining to education.
- Academic Frameworks: Introduction of National Credit Framework (NCrF) and National Higher Education Qualification Framework (NHEQF) to facilitate credit transfer and academic flexibility.
- Increased Investment in Education: The policy advocates for both the Central government and State Governments to allocate a combined 6% of GDP to education.
- In alignment with this vision, the Ministry of Education has witnessed a budget of Rs. 1,12,899 crore in 2023-24, indicating a 13.68% increment from 2020-21.
- International Campuses and Partnerships: NEP 2020 supports Indian universities in establishing campuses abroad and inviting foreign institutions to operate in India.
- Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) have been signed for the establishment of IIT campuses in Zanzibar and Abu Dhabi, reflecting India's global educational outreach.
- Educational Innovation in GIFT City:
- NEP 2020's innovative approach extends to Gujarat's GIFT City, where world-class foreign universities and institutions are permitted to offer specialized courses.
- This move, free from domestic regulations, aims to nurture high-end human resources for financial services and technology.
- NEP 2020's innovative approach extends to Gujarat's GIFT City, where world-class foreign universities and institutions are permitted to offer specialized courses.
What are the Other Related Initiatives?
- World-Class Institutions Scheme: The World Class Institutions Scheme, initiated in 2017, aims to create affordable, top-notch academic and research facilities.
- The scheme designates "Institutions of Eminence" (IoEs) to promote academic excellence.
- To date, 12 institutions, including eight public and four private ones, have been identified as IoEs, a testament to India's commitment to providing world-class education.
- Global Initiative for Academic Network (GIAN) and SPARC: GIAN focuses on tapping the expertise of scientists and entrepreneurs, including those of Indian origin, to bolster India's academic resources.
- The Scheme for Promotion of Academic and Research Collaboration (SPARC) enhances research ecosystems by fostering collaborations between Indian and foreign institutions.
- These initiatives contribute to elevating research quality and promoting knowledge exchange.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following provisions of the Constitution does India have a bearing on Education? (2012)
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Rural and Urban Local Bodies
- Fifth Schedule
- Sixth Schedule
- Seventh Schedule
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 2 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans- (d)
Mains
Q1. How have digital initiatives in India contributed to the functioning of the education system in the country? Elaborate on your answer. (2020)
Q2. Discuss the main objectives of Population Education and point out the measures to achieve them in India in detail. (2021)
Dam Safety and Water Resource Management in India
For Prelims: Dam Safety Act, 2021, National Hydrology Project (NHP)
For Mains: Related issues with the Dam Safety, Dams Construction and environmental challenges, Ageing of dams in India, Measures that can be taken to ensure dam safety.
Why in News?
Recently, the Minister of State for Jal Shakti has shed light on India's significant strides in the realm of dam safety and water resource management.
What are the Highlighted Initiatives for Dam Safety Water Resource Management in India?
- Dam Safety Act, 2021: A Regulatory Framework:
- Enactment of the Dam Safety Act, 2021, by the Union Government.
- Focuses on proper surveillance, inspection, operation, and maintenance of specified dams.
- Aims to prevent dam failure-related disasters and establish an institutional mechanism for safe functioning.
- Institutional Mechanism:
- National Committee on Dam Safety (NCDS):
- Formation of the National Committee on Dam Safety at the national level.
- Responsible for evolving dam safety policies and recommending essential regulations.
- Provides a strategic platform for ensuring uniform safety standards.
- National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA):
- Creation of the National Dam Safety Authority as a regulatory body.
- Tasks include implementing policies of the National Committee on Dam Safety.
- Offers technical assistance to State Dam Safety Organisations (SDSO) and resolves inter-state disputes.
- Creation of the National Dam Safety Authority as a regulatory body.
- State-level Dam Safety Measures:
- Empowerment of State Governments to establish State Committee on Dam Safety.
- Creation of State Dam Safety Organisations responsible for enforcing dam safety standards.
- Renders crucial instructions to dam owners regarding safety protocols and remedial actions.
- National Committee on Dam Safety (NCDS):
- National Hydrology Project (NHP):
- National Hydrology Project (NHP) is designed with four major components: Water Resources Monitoring System, Water Resources Information System, Water Resources Operations and Planning System, and Institutional Capacity Enhancement.
- The project aims to enhance water resource management capabilities across the country.
- Supports studies related to flood forecasting undertaken by Implementing agencies.
What is the State of Indian Dams?
- India has 5745 numbers of dams (5334 are completed and 411 are under construction).
- India is ranked third in the world in terms of building large dams.
- Tehri Dam in Uttarakhand is the highest dam in India built on the Bhagirathi River.
- Hirakud Dam in Odisha built on river Mahanadi is the longest dam in India.
- Kallanai Dam in Tamil Nadu is the oldest dam in India. It is built on the Kaveri river and is about 2000 years old.
What are the Other Related Water Resource Management Initiatives?
- Swachh Bharat Mission.
- Jal Jeevan Mission.
- National Water Policy, 2012.
- Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana.
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan- Catch the Rain Campaign.
- Atal Bhujal Yojana.
- Sujalam 2.0.
- Amrit Sarovar Mission.
What are the Challenges Associated with Dam Safety and Water Resource Management?
- Geological and Geotechnical Challenges:
- Many regions in India are seismically active, which poses a risk of earthquakes that could impact dam stability.
- Poor soil quality and unstable geological conditions in certain areas also contribute to challenges in ensuring dam safety.
- Ageing Infrastructure:
- Several dams in India are aging and may not meet modern safety standards. Maintenance and rehabilitation of these older structures are essential to prevent potential failures.
- Climate Change and Extreme Weather Events:
- Changing climate patterns and increasing instances of extreme weather events, such as heavy rainfall and floods, can strain dams and their reservoirs, potentially leading to overtopping or dam failure.
- Interstate and International Cooperation:
- Many rivers in India are shared with neighbouring states or countries, requiring coordinated efforts for dam safety and water management. Disputes and lack of cooperation can impact effective dam management.
- Emergency Response Infrastructure:
- Developing and maintaining effective communication networks, evacuation plans, and emergency shelters in the vicinity of dams is essential to manage potential disasters.
- Community Resettlement and Rehabilitation:
- In cases where dam construction or operation requires the displacement of local communities, ensuring their proper resettlement and rehabilitation presents challenges.
Way Forward
- Develop a dynamic and adaptable project plan that incorporates real-time monitoring, eco-friendly technologies, disaster preparedness, and ecosystem restoration, ensuring long-term environmental and social sustainability.
- Integrate climate change considerations into dam design and management, anticipating shifts in weather patterns and implementing adaptive measures to withstand extreme events.
- Continue organizing training programs to equip dam safety professionals with skills and knowledge.
- Strengthen cooperation with neighbouring countries/states to ensure effective management of shared river systems, and resolve conflicts.
- Prioritize meaningful engagement with local ethnic communities, valuing their input, cultural heritage, and concerns to foster a harmonious project coexistence and ensure their well-being.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Suppose the Government of India is thinking of constructing a dam in a mountain valley bound by forests and inhabited by ethnic communities. What rational policy should resort to in dealing with unforeseen contingencies? (2018)
Connection Between Dinosaurs and Birds
For Prelims: Connection Between Dinosaurs and Birds, Cranial Evolution, Endothermic Animals, Theropod Lineage.
For Mains: Connection Between Dinosaurs and Birds.
Why in News?
Recently, a study published in the journal Royal Society Open Science, suggests a connection between Birds and Dinosaurs.
What is the Methodology of Research?
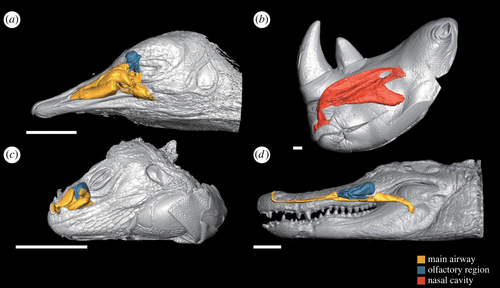
- The Researchers employed cutting-edge techniques, including Computed Tomography (CT) scans and 3D reconstruction, to analyze the nasal cavities of 51 present-day species.
- These species encompassed birds, mammals, reptiles (including crocodiles and turtles), and lizards. Additionally, the researchers digitally reconstructed the nasal cavity of a velociraptor, a type of theropod dinosaur, based on fossils.
- They focussed primarily on the nasal cavity to enhance understanding of the cranial evolution (changes in organism's skull over time) from dinosaurs to birds.
- They explored the possibility that the nasal cavity played a crucial role in brain cooling and regulation.
What are the Key Findings of the Study?
- Nasal Cavity Size and Warm-Bloodedness:
- Endothermic (Warm-blooded) animals, including birds and mammals, had larger nasal cavities relative to their head sizes compared to cold-blooded animals.
- This size difference indicated a potential link between warm-bloodedness and nasal cavity dimensions.
- Respiratory Turbinates and Brain Cooling:
- Warm-blooded animals exhibited a complex structure known as the respiratory turbinate within their nasal cavities. One of the primary functions of this structure was brain cooling.
- This discovery challenged the previously held belief that larger nasal cavities primarily facilitated whole-body metabolism.
- Warm-blooded animals exhibited a complex structure known as the respiratory turbinate within their nasal cavities. One of the primary functions of this structure was brain cooling.
- Evolutionary Implications for Dinosaurs and Birds:
- The cooling mechanism might have provided an advantage for warm-blooded creatures, including birds and mammals, influencing their evolution.
- In contrast, the reconstructed nasal cavity of the velociraptor indicated a lack of a developed cooling system, suggesting differences in thermoregulation between theropod dinosaurs and modern birds.
- Influence of Maxilla on Nasal Passage:
- The shape of the nasal passage in the velociraptor was influenced by the maxilla, the lower jaw bone.
- They proposed that a reduction in the maxilla in the theropod lineage led to the nasal cavity becoming a crucial apparatus for their thermal regulation strategy.
What is the Significance of the Study?
- While the study provided novel insights into the potential function of respiratory turbinates in brain cooling, the researchers emphasized the need for more comprehensive research to validate their hypotheses.
- Understanding the complex interplay between anatomical adaptations and environmental factors remains a key focus for future studies.
What are Warm Blooded and Cold Blooded Animals?
| Aspect | Warm-Blooded Animals (Endotherms) | Cold-Blooded Animals (Ectotherms) |
| Metabolism | High metabolic rate | Low metabolic rate |
| Body Temperature | Maintain a relatively constant body temperature independent of the environment | Body temperature varies with the external environment |
| Energy Source | Rely on internal heat production (metabolism) to maintain body temperature | Depend on external sources of heat for thermoregulation |
| Activity Levels | Can be active in a wide range of environmental conditions | Activity levels influenced by temperature; often more active in warmer conditions |
| Adaptability to Environments | Can inhabit diverse environments due to their ability to regulate body temperature | Limited in their habitat choices by temperature preferences |
| Reproductive Rate | Generally have lower reproductive rates due to high energy demands | May have higher reproductive rates due to lower energy demands |
| Examples | Mammals (including humans), birds | Reptiles (such as snakes, lizards), amphibians, most fish, invertebrates (except some insects) |
What is the Theory of Evolution by Charles Darwin?
- About:
- Charles Darwin's theory of evolution is a foundational concept in biology that explains how species change over time and how new species arise.
- Darwin's ideas revolutionized the understanding of life on Earth and provided a comprehensive explanation for the diversity of species.
- Key Elements:
- Descent with Modification: Darwin proposed that all species share common ancestors and that species change gradually over time through a process called descent with modification, meaning that new species arise from existing ones.
- Natural Selection: The central mechanism of Darwin's theory is natural selection. He observed that in every generation, more offspring are produced than can survive due to limited resources, leading to a struggle for survival.
- Variation: Within any population, there is variation in traits among individuals. Some of these variations are heritable, meaning they can be passed down to offspring.
- Adaptation: As natural selection acts on the variations in a population, individuals with traits that are better suited to their environment become more successful at surviving and reproducing.
- Speciation: Over long periods of time and through the accumulation of gradual changes, populations can become so different from each other that they can no longer interbreed. This leads to the formation of new species.
What is Computed Tomography (CT)?
- It is a medical imaging technique that uses X-rays and advanced computer processing to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body.
- Like an X-ray, it shows structures inside the body. But instead of creating a flat, 2D image, a CT scan takes dozens to hundreds of images of the body.
- Healthcare providers use CT scans to see things that regular X-rays can’t show.
- For example, body structures overlap on regular X-rays and many things aren’t visible.
- A CT shows the details of each of the organs for a clearer and more precise view.
Nuclear Rocket for Space Travel
For Prelims: NASA, Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations, Project Orion, Atomic bomb, Perseverance Rover - NASA, India’s Mars Orbiter Mission, UAE’s Hope Mars Mission
For Mains: Significance of DRACO, Nuclear Propulsion System
Why in News?
NASA in collaboration with the United States Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is seeking a nuclear propulsion system that could potentially cut down the travel time to Mars by half.
- This ambitious initiative, known as the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations (DRACO) and the launch is scheduled for late 2025 or early 2026.
What is DRACO?
- About: The DRACO project is offering the prospect of shorter travel times between celestial bodies and improved fuel efficiency. Central to DRACO's vision is a nuclear reactor that utilizes the energy derived from the fission of uranium atoms.
- Significance: DRACO hold the potential to revolutionize space travel in numerous ways:
- Acceleration and Speed: Unlike traditional rocket engines that rely on chemical reactions (fuel like hydrogen or methane with oxygen), nuclear reactions generate far more energy, enabling the spacecraft to accelerate continuously throughout its journey.
- This acceleration could significantly shorten travel times to distant destinations like Mars.
- Enhanced Fuel Efficiency: Nuclear propulsion systems yield greater fuel efficiency, reducing the need to carry excessive propellant.
- This advantage can drastically lower the duration of interplanetary voyages.
- Minimized Exposure: Expedited travel times translate to reduced exposure of astronauts to the harsh conditions of deep space.
- The potential risks associated with extended space travel, such as radiation exposure and isolation, could be mitigated through quicker journeys.
- Military Applications: Beyond its application in space exploration, DARPA's involvement hints at the potential for nuclear propulsion to facilitate rapid maneuvers of military satellites in Earth's orbit.
- Acceleration and Speed: Unlike traditional rocket engines that rely on chemical reactions (fuel like hydrogen or methane with oxygen), nuclear reactions generate far more energy, enabling the spacecraft to accelerate continuously throughout its journey.
- Concern:
- Safety Concerns: One of the primary concerns with using nuclear fuel in space is the potential for accidents or malfunctions that could release radioactive material into space or back to Earth.
- Such incidents could have severe environmental and health consequences.
- Launch Risks: Launching spacecraft with nuclear fuel on board presents risks, as there is always a chance of a launch failure or explosion, leading to the dispersion of radioactive material over a wide area.
- Safety Concerns: One of the primary concerns with using nuclear fuel in space is the potential for accidents or malfunctions that could release radioactive material into space or back to Earth.
What is the Historical Context of Nuclear Propulsion and How DRACO is Different?
- Projects like Orion, Rover, and NERVA explored nuclear-powered propulsion systems, although these initiatives were not fully realized.
- Notably, Project Orion considered using atomic bomb explosions for acceleration, while Project NERVA aimed to develop nuclear-thermal engines akin to the DRACO engine.
- DRACO marks a significant evolution from its predecessors due to several key differentiators:
- Fuel Enrichment: Unlike Project NERVA, which used weapons-grade uranium, DRACO employs a less-enriched form of uranium.
- This shift enhances safety and minimizes the risks associated with the use of radioactive materials.
- In-Space Activation: The nuclear reactor within the DRACO engine remains dormant until it reaches space.
- This precautionary measure mitigates the potential for radioactive accidents during launch or on Earth.
- Fuel Enrichment: Unlike Project NERVA, which used weapons-grade uranium, DRACO employs a less-enriched form of uranium.
Note:
- Atomic Bomb Explosions: Atomic bomb explosions involve the rapid and uncontrolled release of nuclear energy through a chain reaction of nuclear fission.
- The core of the bomb contains fissile material, like uranium-235 or plutonium-239.
- Nuclear-Thermal Engines: Nuclear-thermal engines are propulsion systems that use a nuclear reactor to heat a propellant, usually hydrogen, to high temperatures.
- The heated propellant is then expelled through a nozzle at high velocity, creating thrust according to Newton's third law of motion.
Mars
- About: Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in our solar system. It is often referred to as the "Red Planet" due to its reddish appearance caused by iron oxide (rust) on its surface.
- Atmosphere: Mars has a thin atmosphere primarily composed of carbon dioxide (95.3%), with traces of nitrogen and argon.
- Major Surface Features:
- Olympus Mons: The largest known volcano in the solar system.
- Valles Marineris: A massive canyon system.
- Polar Ice Caps: Ice caps made of water and frozen carbon dioxide (dry ice) at the poles.
- Dusty Surface: The surface is covered in fine dust and rocks.
- Liquid Water: Liquid water is rare, but evidence suggests past liquid flows.
What are the Major Mars Missions?
- Perseverance Rover - NASA
- India’s Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) or Mangalyaan (2013)
- ExoMars rover (2021) (European Space Agency)
- Tianwen-1: China's Mars Mission (2021)
- UAE’s Hope Mars Mission (UAE’s first-ever interplanetary mission) (2021)
- Mars 2 and Mars 3 (1971) (Soviet Union)
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO
- is also called the Mars Orbiter Mission
- made India the second country to have a spacecraft orbit the Mars after USA
- made India the only country to be successful in making its spacecraft orbit the Mars in its very first attempt
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
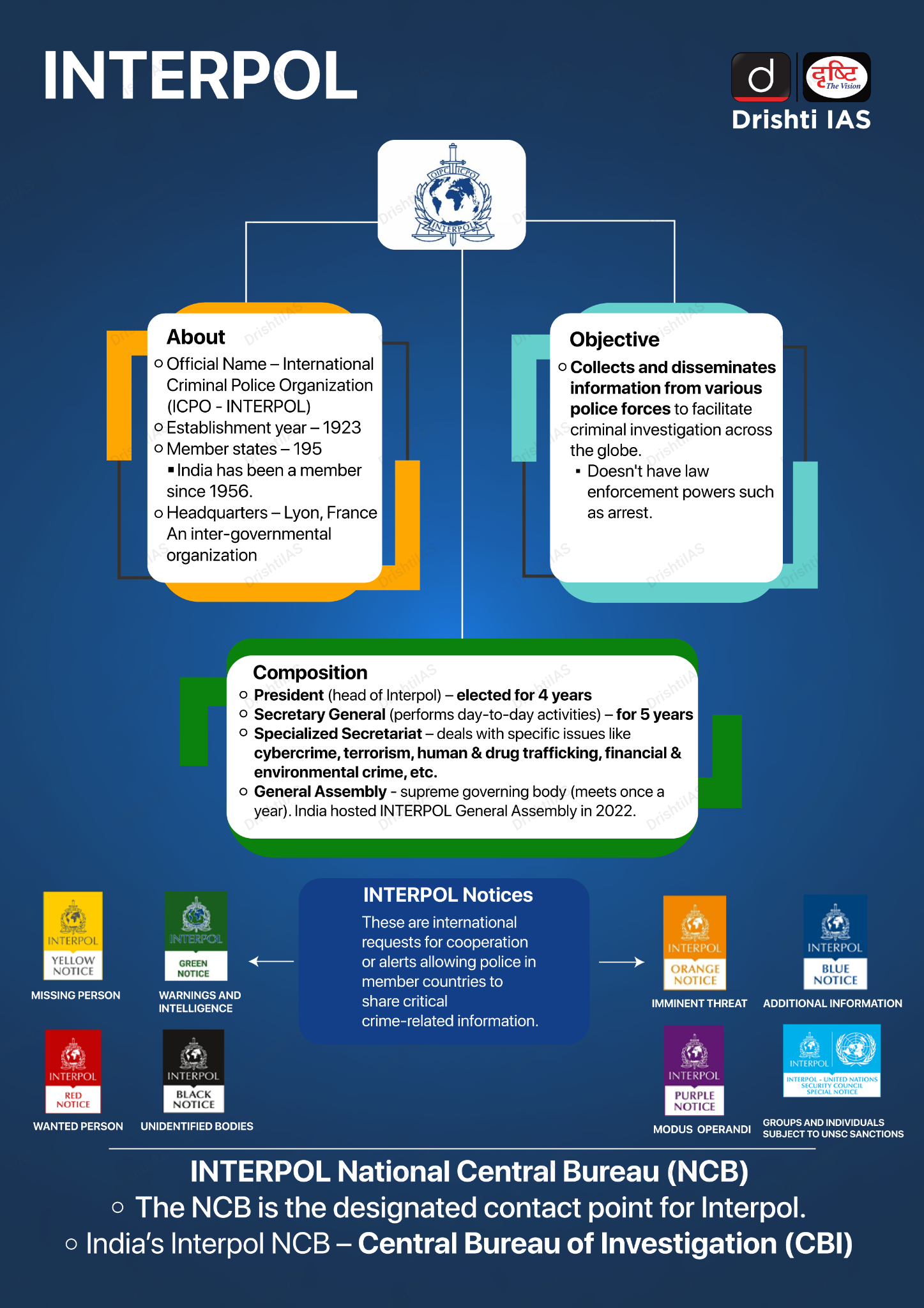
CBI Academy Joins Interpol Global Academy Network
Why in News?
The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) Academy, a key player in crime investigation and law enforcement training, has joined the Interpol Global Academy Network as its 10th member.
- This significant move enhances the academy's global influence and paves the way for impactful joint initiatives and capacity building.
What is the Interpol Global Academy Network?
- It is an initiative launched by Interpol in 2019 to support Interpol in leading a global approach to law enforcement training.
- The network aims to foster academic collaboration among law enforcement training institutions by developing and delivering joint training programmes and research projects, sharing best practices and resources, and facilitating the exchange of expertise and knowledge.
- The network also seeks to promote academic excellence and innovation in law enforcement training by establishing quality standards, accreditation mechanisms, and recognition systems.
What is the CBI Academy?
- The CBI Academy is a training institution for the CBI, which is the premier investigative agency of India.
- The CBI Academy was established in 1996 and is located in Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh.
- It aims to attain higher levels of professionalism, impartiality, uprightness, and dedication to the service of the nation.
- It conducts various training programmes on topics such as cybercrime, financial crime, counter-terrorism, environmental crime, anti-corruption, human rights, forensic science, etc.
- It collaborates with foreign agencies and international organisations such as US Department of Homeland Security, French Embassy, and Interpol for joint training programmes and research project.
- It has also established three Regional Training Centres (RTCs) at Kolkata, Chennai, and Mumbai to expand its training infrastructure and outreach.
Central Bureau of Investigation
- The CBI was established in 1963 by a resolution of the Ministry of Home Affairs and later transferred to the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions, currently functioning as an attached office.
- Its establishment was recommended by the Santhanam Committee on Prevention of Corruption.
- The CBI operates under the Delhi Special Police Establishment (DSPE) Act, 1946. It is neither a constitutional nor a statutory body.
- It investigates cases related to bribery, governmental corruption, breaches of central laws, multi-state organized crime, and multi-agency or international cases.
World Lion Day
Why in News?
World Lion Day is celebrated every year on 10th August to raise awareness about the conservation of lions and their habitats. It was first established in 2013 by Big Cat Rescue, the world’s largest accredited sanctuary dedicated to lions.
- Recent studies have revealed that lions were once present in the Arabian Peninsula, significantly influencing Arab culture.
- It is noted that Arabic dialects and literature contain an extensive array of almost 700 distinct names or expressions referring to the lion.
What does the Recent Research Suggest?
- Lions, often associated with the vast savannas of East and Southern Africa, and the Gir forest in Kathiawar, India but they were once an integral part of the deserts of the Arabian Peninsula.
- The evidence of the lion's presence, though now extinct, resounds through historical accounts, archaeological findings, and linguistic nuances.
- Research reveals that lions occupied a vast and diverse range spanning the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, Eurasia, and parts of India.
- The lion's habitat extended from latitudes as far south as 15°N (Yemen) to 18°N (Mali, Chad) and as far north as 45-48°N (Bulgaria, Ukraine, Hungary).
- It is noteworthy that lions thrived in various environments, including deserts, steppes, and maritime coasts.
- Lions exhibited remarkable adaptability, dwelling in the arid deserts of the Arabian Peninsula, including Sinai, Sahara, and Yemen.
- This presence is supported by Neolithic rock engravings found in Saudi Arabia and Oman.
- By the early 20th century, evidence of the lion's presence had faded. Observations in 1920 showed no records of lions in Afghanistan, Balochistan, or southern Arabia.
What are the Major Facts About Lions?
- Scientific Name: Panthera leo
- The lion is divided into two subspecies: the African lion (Panthera leo leo) and the Asiatic lion (Panthera leo persica).
- Characteristics:
- Lions are known for their distinctive appearance, including a tawny coat, a tufted tail, and a prominent mane in males.
- They are social animals and live in groups called prides. A pride typically consists of multiple females, their offspring, and a few adult males.
- Distribution and Habitat:
- Lions are found in sub-Saharan Africa and a small population exists in the Gir Forest National Park in the Indian state of Gujarat.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List:
- African Lion: Vulnerable (Globally)
- Asiatic Lion: Endangered.
- CITES: Appendix I for populations of India, all other populations are included in Appendix II.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972: Schedule I
- IUCN Red List:
- Conservation Efforts in India:
- Project Lion
- Asiatic Lion Conservation Project
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Asiatic lion is naturally found in India only.
- Double-humped camel is naturally found in India only.
- One-horned rhinoceros is naturally found in India only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
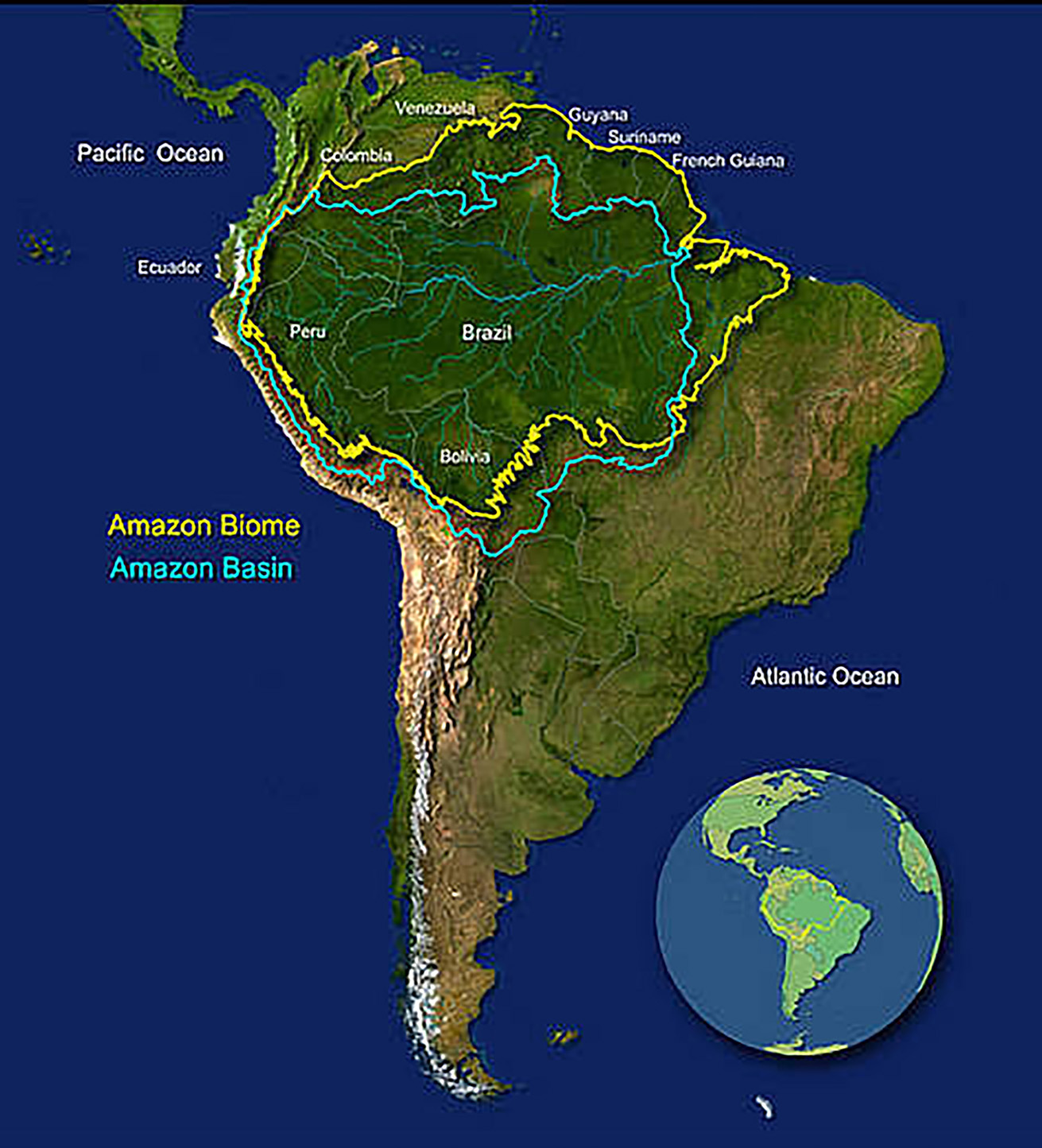
Amazon Summit by the Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization
- Amazon Cooperation Treaty Organization (ACTO) is an international organization “aimed at the promotion of sustainable development of the Amazon Basin”.
- Colombia at the Amazon summit proposed that 80% of the Amazon should be protected from deforestation and degradation by 2025 but did not find support from all the members.
- Scientists have warned for long that if the combined deforestation and degradation of the Amazon crosses a 20-25% threshold, the forest could reach an irreversible tipping point that may result in the dieback of the entire ecosystem.
- The Belem Declaration released during the Amazon Summit recognises Indigenous knowledge as a condition for biodiversity conservation and calls for ensuring full and effective participation of Indigenous Peoples in decision-making and public policy formulation processes.
Read more: Amazon Rainforest
Jeevan Pramaan
- The Department of Pension & Pensioners’ Welfare (DoPPW) has taken proactive steps to enhance the ease of living for Central Government pensioners through the widespread promotion of Digital Life Certificates (DLC), known as Jeevan Pramaan.
- Pensioners must submit DLC every November (with a provision for those aged 80 years and above in October) to ensure continuous pension disbursement.
- Initially, the submission of DLCs involved biometric methods. Subsequently, in collaboration with MeitY, the department introduced a pioneering Face Authentication technology system linked to the Aadhar database.
- This innovation enables pensioners to generate their Life Certificates via any Android-based smartphone. This reduces reliance on external biometric devices, rendering the process more accessible and affordable, especially for the broader population.
- To ensure the success of the campaign, detailed guidelines have been issued These guidelines include :
- Nodal officers nominated for the campaign.
- Awareness through banners, posters, and ATMs.
- Utilization of technology during doorstep banking and branch visits.
- Camps for easy submission, and home visits for bedridden pensioners.
Read more: Jeevan Pramaan
GeM: Transforming India's Public Procurement Landscape
Government e-Marketplace (GeM) marks its 7th Foundation Day as a landmark in India's procurement landscape.
- The GeM is an online platform launched by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India in 2016 to facilitate procurement of goods and services by various government departments and organisations.
- GeM has saved over ₹45,000 crore since 2016.
- It is open to all government departments, public sector undertakings, autonomous bodies and other organizations.
- GeM has surpassed the achievements of renowned public procurement platforms such as South Korea's KONEPS and Singapore's GeBIZ.
Read more: Government e-Marketplace
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis cases have been surging in India during the monsoon season, as the high humidity and rainfall create a favorable environment for the transmission of the infection
- Also known as "pink eye," conjunctivitis is an eye condition characterized by inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin membrane that covers the white part of the eye and lines the inner eyelids.
- It leads to redness, itching, discharge and pain in the affected eye.
- It can be caused by viruses, bacteria, allergens or other factors.
- Viral and bacterial conjunctivitis can spread through direct contact with contaminated hands or surfaces.
- Allergic conjunctivitis is not contagious and results from exposure to allergens.
- To prevent conjunctivitis, one should wash hands frequently, avoid touching or rubbing eyes, not share personal items with others, wear sunglasses or protective eyewear, and stay away from people who have conjunctivitis.