UNEP's Action Plan for Cooling Sector
For Prelims: United Nations Environment Programme, Conference of Parties(COP28), Global Cooling Pledge, Kigali Amendment, India Cooling Action Plan (ICAP)
For Mains: Importance Reducing Emissions from the Cooling Sector, Green Cooling Strategies for Sustainable Development, Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has proposed an action plan aimed at significantly reducing emissions from the global cooling sector in its recent report titled “Keeping it Chill: How to meet cooling demands while cutting emissions.”
- This initiative carries the potential to make a substantial impact on the predicted 2050 greenhouse gas emissions, reducing them by 60%.
- The report is released in support of the Global Cooling Pledge, a joint initiative between the United Arab Emirates as host of the Conference of Parties(COP28) and the Cool Coalition.
Note
- The Cool Coalition is a global network of partners working to provide efficient, climate-friendly cooling for all.
- The UNEP launched the Cool Coalition at the First Global Conference on Synergies between the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development Goals and the Paris Agreement.
- India is a member of the Cool Coalition.
What is UNEP's Proposed Action Plan for Sustainable Cooling?
- Nature-Based Solutions:
- Recommendations include passive cooling measures like shading, ventilation, insulation, green roofs, and reflective surfaces, and reintroducing nature to urban areas.
- Passive cooling can reduce the need for mechanical cooling and save energy and emissions.
- Efficiency Standards:
- Emphasizes the importance of higher energy efficiency technologies and practices for cooling equipment, such as air conditioners, refrigerators, and fans.
- Higher-energy efficiency cooling can reduce the energy consumption and emissions of cooling devices and lower the costs for users and utilities.
- Emphasizes the importance of higher energy efficiency technologies and practices for cooling equipment, such as air conditioners, refrigerators, and fans.
- Phasedown of Refrigerants:
- This refers to the use of alternative substances to cool devices, such as hydrocarbons, ammonia, or carbon dioxide, instead of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which are potent greenhouse gases.
- HFCs are a group of synthetic gases primarily used for cooling and refrigeration. HFCs, classified as "super-pollutants," possess potent greenhouse gas properties, capable of trapping heat hundreds to thousands of times more than carbon dioxide.
- Despite their significant impact, they are short-lived climate pollutants, with an average atmospheric lifespan of 15 years.
- Low-global warming potential refrigerants can reduce the direct emissions of cooling devices and contribute to the phase-down of HFCs under the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol.
- Urges a faster phasedown of climate-warming refrigerants and air conditioning.
- This refers to the use of alternative substances to cool devices, such as hydrocarbons, ammonia, or carbon dioxide, instead of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which are potent greenhouse gases.
Why Address the Cooling Sector?
- The cooling sector plays a crucial role in combating rising temperatures, ensuring food safety, industrial cooling processes, and driving productive economies.
- However, without intervention, the growing demand for cooling equipment could lead to a substantial increase in electricity consumption and emissions.
- The cooling sector accounts for a substantial 20% of global electricity consumption.
- If current policies continue, the installed capacity of cooling equipment globally will triple, resulting in a more than doubling of electricity consumption by 2050.
- This could lead to emissions between 4.4 billion and 6.1 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) in 2050, accounting for over 10% of global projected emissions that year.
What are the Benefits of Sustainable Cooling?
- Passive cooling techniques and efficient cooling equipment can save consumers USD 17 trillion between 2022 and 2050.
- It is projected to reduce peak power requirements by 1.5-2 terawatts (TW), avoiding substantial power generation investments.
- Increasing the adoption of low-global warming potential technologies in new equipment and effectively managing refrigerant life cycles can reduce HFC emissions by 50% in 2050.
- Decarbonizing the power grid can further reduce sectoral emissions by 96%.
What are the Initiatives Related to Sustainable Cooling?
- Global:
- National Cooling Action Plans (NCAPs):
- Presently, more than 40 countries, including India, have developed NCAPs, and 25 others are at various stages of preparing theirs as well.
- Though India and China have included implementation mechanisms in their NCAPs, the rollout has been slow.
- Global Cooling Pledge:
- At the bthe United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, the host country United Arab Emirates and the Cool Coalition launched the Global Cooling Pledge.
- Over 60 countries signed up to the Pledge with commitments to reduce the climate impact of the cooling sector.
- At the bthe United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, the host country United Arab Emirates and the Cool Coalition launched the Global Cooling Pledge.
- Kigali Amendment Acceleration:
- The Kigali Amendment is an international agreement to reduce the production and consumption of HFCs.
- The amendment is part of the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer.
- The Kigali Amendment aims to reduce HFC production and consumption by 80–85% by 2047.
- This is expected to prevent the emissions of up to 105 billion tonnes of CO2 of greenhouse gases, avoiding up to 0.5 degree Celsius of global temperature rise by 2100.
- National Cooling Action Plans (NCAPs):
- India:
Critical Minerals
For Prelims: Critical Minerals, Mining Sector, Rare Earth Metals, Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957, Geological Survey of India (GSI), Mineral Security Partnership.
For Mains: Critical Minerals, Significance of Critical Minerals for India, Mineral Distribution in India.
Why in News?
Recently, Government of India has made a significant move in the Mining Sector by launching the first-ever auction of critical minerals, offering 20 blocks for sale to Private Sectors.
What are the Key Features of the First Auction of Critical Minerals?
- This is the first time that rights related to the mining of lithium ore are being auctioned to private sectors. Other minerals in the blocks include nickel, copper, molybdenum, and rare earth elements (REEs).
- The mineral blocks are spread across eight states, with Tamil Nadu having the most blocks (seven). Rights for these blocks vary; four blocks are auctioned for Mining Licences (ML), enabling immediate mining operations, while the remaining 16 blocks are auctioned for Composite Licences (CL), allowing geological exploration before mining.
What is the Background of the First Auction of Critical Minerals?
- The ongoing auction follows the government's declaration of 30 minerals as "critical" and amendments to mining laws.
- In July 2023, the government identified 30 minerals as Critical Minerals by amending the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957, through the MMDR Amendment Act, 2023, empowering the Central Government to auction blocks of these minerals.
- The 30 critical minerals are Antimony, Beryllium, Bismuth, Cobalt, Copper, Gallium, Germanium, Graphite, Hafnium, Indium, Lithium, Molybdenum, Niobium, Nickel, PGE, Phosphorous, Potash, REE, Rhenium, Silicon, Strontium, Tantalum, Tellurium, Tin, Titanium, Tungsten, Vanadium, Zirconium, Selenium and Cadmium.
- The bidding is based on the highest percentage of mineral dispatch value quoted by bidders. Post this auction, a second tranche of critical mineral block auctions is anticipated.
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) is actively exploring critical mineral reserves across the country.
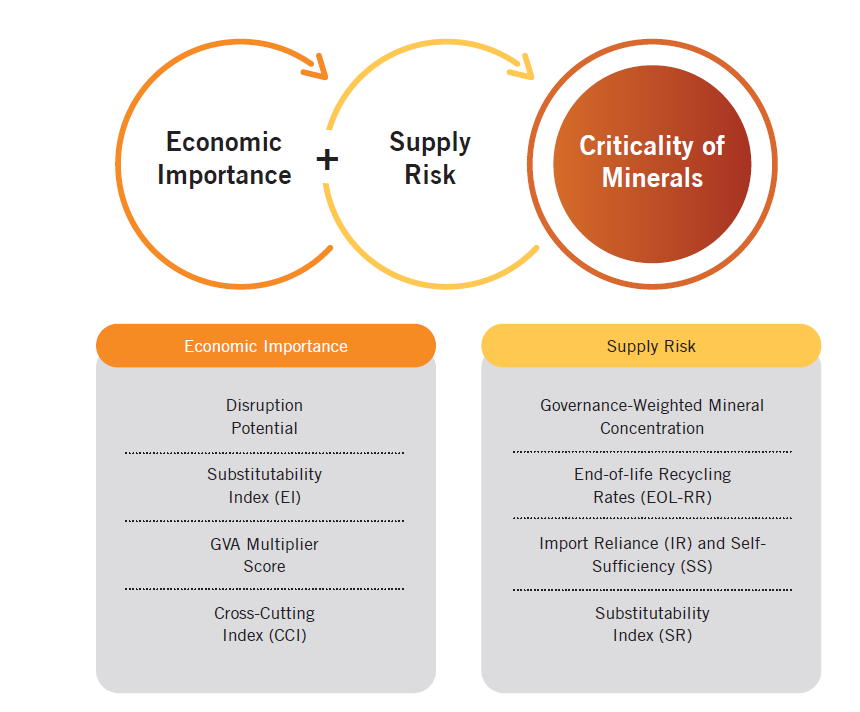
What are Critical Minerals?
- Critical Minerals:
- Critical minerals are those minerals that are essential for economic development and national security, the lack of availability of these minerals or concentration of extraction or processing in a few geographical locations may lead to supply chain vulnerabilities and even disruption of supplies.
- Declaration of Critical Minerals:
- It is a dynamic process, and it can evolve over time as new technologies, market dynamics, and geopolitical considerations emerge.
- Different countries may have their own unique lists of critical minerals based on their specific circumstances and priorities.
- The US has declared 50 minerals critical in light of their role in national security or economic development.
- Japan has identified a set of 31 minerals as critical for their economy.
- The UK considers 18 minerals critical, EU (34) and Canada (31).
What is the Significance of Critical Minerals for India?
- Economic Development:
- Industries such as high-tech electronics, telecommunications, transport, and defense heavily rely on these minerals.
- Additionally, critical minerals are essential for green technologies like solar panels, wind turbines, batteries, and electric vehicles.
- Given India's significant domestic demand and potential in these sectors, their growth can lead to job creation, income generation, and innovation.
- National Security:
- These minerals are vital for defense, aerospace, nuclear, and space applications, necessitating the use of high-quality and reliable materials capable of withstanding extreme conditions and performing complex functions.
- Environmental Sustainability:
- They are integral to the transition toward clean energy and a low-carbon economy, enabling the reduction of India's reliance on fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions.
- With a commitment to attaining 450 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030, these minerals are essential for achieving India's green objectives.
What are the Challenges for India Related to Critical Minerals?
- Implications of the Russia-Ukraine Conflict:
- Russia is a significant producer of various critical minerals, while Ukraine possesses reserves of lithium, cobalt, graphite, and rare earth elements.
- The ongoing war between the two countries affects these critical mineral supply chains.
- Limited Domestic Reserves:
- India has limited reserves of critical minerals such as lithium, cobalt, and other rare earth elements.
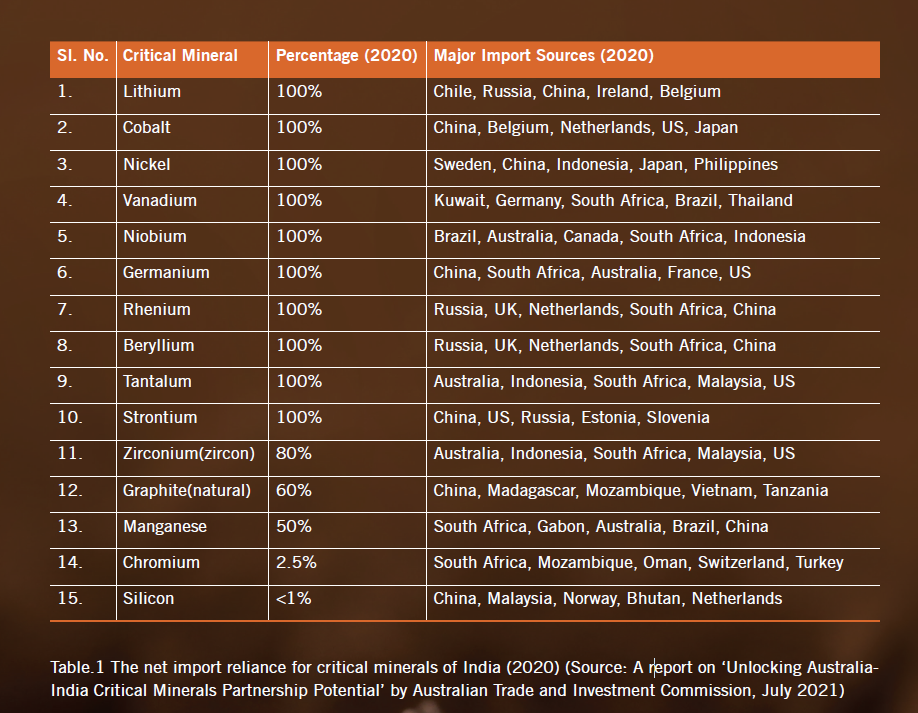
- Most of these minerals are imported, making India heavily dependent on other countries for its supply. This reliance on imports can create vulnerability in terms of price fluctuations, geopolitical factors, and supply disruptions.
- India heavily relies on imports for critical minerals like lithium and nickel, with 100% import reliance for lithium and nickel, and 93% for copper.
- Increasing Demand for Minerals:
- The manufacturing of renewable energy technologies and the transition to electric vehicles necessitate larger quantities of minerals such as copper, manganese, zinc, lithium, cobalt, and rare earth elements.
Conclusion
- India has an opportunity to strengthen its international cooperation and partnerships through the strategic management of critical minerals. By participating in initiatives like the Mineral Security Partnership (MSP) led by the United States, India can contribute to the establishment of global critical mineral supply chains.
- Bilateral agreements with countries such as Australia, Canada, Japan, and South Africa can further enhance India's position in critical mineral exploration, development, processing, and trade.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. Despite India being one of the countries of Gondwanaland, its mining industry contributes much less to its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in percentage. Discuss. (2021)
Q. “In spite of adverse environmental impact, coal mining is still inevitable for development”. Discuss. (2017)
Jammu and Kashmir Reservation Bill and J&K Reorganisation (Amendment) Bill 2023
For Prelims: Jammu and Kashmir Reservation Bill And J&K Reorganisation (Amendment) Bill, Lok Sabha, Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK), Revocation of Article 370, Delimitation.
For Mains: Jammu and Kashmir Reservation Bill And J&K Reorganisation (Amendment) Bill.
Why in News?
Recently, the Lok Sabha has passed the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation (Amendment) Bill, 2023 and the Jammu and Kashmir Reservation (Amendment) Bill, 2023.
- The Bill seeks to represent those who became refugees in their own country and also reserves one seat in the Jammu and Kashmir Assembly for people who have been displaced from Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK).
What is the Background?
- Before the Revocation of Article 370, Jammu and Kashmir had distinct rules for delimiting Lok Sabha and Assembly seats.
- Post the abrogation of Article 370 and the region's transition into a Union Territory, a Delimitation Commission was formed in March 2020.
- This commission was tasked not only with delimiting J&K's seats but also those of Assam, Manipur, Arunachal Pradesh, and Nagaland, aiming to finish within a year.
- Recently, the commission concluded its delimitation process, resulting in an increase in J&K's legislative assembly seats from 107 to 114, facilitated by the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation (Amendment) Bill, 2023.
What are These Two Bills?
- What is the Jammu & Kashmir Reservation (Amendment) Bill, 2023:
- It seeks to amend Section 2 of the Jammu and Kashmir Reservation Act, 2004.
- The Jammu and Kashmir Reservation Act, 2004 provided reservation in jobs and admission in professional institutions to Scheduled Castes (SCs), Scheduled Tribes (STs), and other socially and educationally backward classes.
- The amendment Bill suggests a change in the nomenclature of a section of people who were earlier described as “weak and underprivileged classes (social castes)" to "other backward classes'.
- It seeks to amend Section 2 of the Jammu and Kashmir Reservation Act, 2004.
- Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation (Amendment) Bill, 2023:
- It seeks to amend the 2019 Act and provide representation in the Legislative Assembly to the Kashmiri Migrants and displaced persons from the PoK.
- It seeks to nominate two members from the Kashmiri migrant community, with one nominee being a woman and the power of the lieutenant governor to nominate one person representing the displaced persons from Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK) to the Legislative Assembly.
- This bill proposes to increase the total number of seats in the Jammu and Kashmir legislative assembly from 107 to 114, of which 7 would be reserved for scheduled caste members and 9 seats for legislators from scheduled tribes.
- As per the Bill, 24 seats of the Assembly will remain vacant until the occupation in Pakistan-occupied Kashmir ceases.
- Therefore, the effective strength of the Assembly is 83, which the amendment seeks to increase to 90.
How is the Zero Terror Plan Linked with the Abrogation of Article 370?
- The Zero Terror Plan refers to a comprehensive strategy initiated by the Indian government to eradicate terrorism from Jammu and Kashmir. This plan has been in effect for the past three years and is slated for full implementation by 2026.
- Since the abrogation of Article 370, which granted special status to Jammu and Kashmir, there has been a noticeable decline in terrorism in the region.
What is Delimitation?
- Delimitation is the act of fixing or redrawing the limits or boundaries of territorial constituencies (Assembly or Lok Sabha seat) in a country or a province having a legislative body, as per the Election Commission.
- The delimitation exercise is carried out by an independent high-powered panel known as the Delimitation Commission whose orders have the force of law and cannot be questioned by any court.
- Delimitation Commissions have been set up four times — 1952, 1963, 1973 and 2002 under the Acts of 1952, 1962, 1972 and 2002.
- The exercise has been carried out over the years to redefine the area of a constituency-based on its population size (based on the last Census).
- Aside from changing the limits of a constituency, the process may result in a change in the number of seats in a state.
- This exercise also involves reservation of Assembly seats for SC & ST in accordance with the Constitution.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the Delimitation Commission consider the following statements: (2012)
The orders of the Delimitation Commission cannot be challenged in a Court of Law.
When the orders of the Delimitation Commission are laid before the Lok Sabha or State Legislative Assembly, they cannot effect any modification in the orders.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: C
Q. Which one of the following is the largest (areawise) Lok Sabha constituency? (2008)
(a) Kangra
(b) Ladakh
(c) Kachchh
(d) Bhilwara
Ans: (b)
Q. Siachen Glacier is situated to the (2020)
(a) East of Aksai Chin
(b) East of Leh
(c) North of Gilgit
(d) North of Nubra Valley
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. To what extent is Article 370 of the Indian Constitution, bearing marginal note “Temporary provision with respect to the State of Jammu and Kashmir”, temporary? Discuss the future prospects of this provision in the context of Indian polity. (2016)
Q. The banning of ‘Jamaat-e-Islami’ in Jammu and Kashmir brought into focus the role of over-ground workers (OGWs) in assisting terrorist organizations. Examine the role played by OGWs in assisting terrorist organizations in insurgency-affected areas. Discuss measures to neutralize the influence of OGWs. (2019)
Decoding Online Gaming Ethics
For Prelims: Internet and Mobile Association of India (IAMAI), Know-Your-Customer (KYC), Information Technology Act of 2000, Sections 67, 67A, and 67B of the IT Act
For Mains: The influence of the voluntary code of ethics on the online gaming sector and its legal implication.
Why in News?
Recently, the online gaming industry has voluntarily entered into a code of ethics.
- This move signifies an attempt to self-regulate and create a more stable environment for the industry.
- Responsibility for online gaming matters has been assigned to the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology by the Government of India.
What is the Code of Ethics Adopted by the Gaming Industry?
- To govern itself and address growing concerns, three prominent lobby groups Internet and Mobile Association of India (IAMAI), E-Gaming Federation (EGF), and All India Gaming Federation (AIGF) have voluntarily co-signed a code of ethics.
- The code of ethics is entirely voluntary, in nature. Despite its non-binding nature, the code aims to foster responsible practices within the industry and is viewed as a step towards self-regulation.
- The code endeavors to safeguard the interests of consumers by empowering them to make informed decisions regarding the online games they choose.
- According to the code, online gaming companies are required to undertake know-your-customer (KYC) procedures in accordance with applicable laws.
- Additionally, companies must disclose on their platforms the criteria for determining winners, fees charged, and ensure that deposits are solely utilized for playing games on the platform.
- It also strives to create a "healthy environment" for online games in India, focusing on aspects such as transparency, fairness, and responsible gaming.
What is Online Gaming?
- About:
- Online gaming involves playing games through the internet, facilitating player connections and collaborative gameplay irrespective of their physical locations.
- It is accessible on various devices, including computers, and mobile phones.
- Difference Between Gambling and Online Gaming:
- Gambling is the practice of placing bets on events with uncertain outcomes, primarily aimed at winning money or material possessions.
- Various forms of gambling exist, such as casino games, sports betting, and lotteries.
- Unlike online gaming, gambling carries the risk of losing money or valuable items.
- In India, games of chance fall under the category of gambling and are generally prohibited, while games of skill, falling outside the ambit of gambling are usually exempted.
- In RMD Chamarbaugawala v. Union of India, the Supreme Court relied on the 'skill test' to decide whether an activity is gambling or not.
- The court held that competitions that substantially involve skills are not gambling activities.
- Gambling is the practice of placing bets on events with uncertain outcomes, primarily aimed at winning money or material possessions.
How Does the Code Align With Government Regulations on Online Gaming?
- Public Gambling Act, 1867:
- The act primarily addresses physical gambling activities. However, its relevance extends to online gaming, providing a legal framework for regulation.
- Information Technology Act, 2000:
- The Information Technology Act of 2000 plays a pivotal role in regulating online activities, including gaming. Section 66 of the IT Act deals with computer-related offenses, providing a legal basis for addressing cyber crimes associated with online gaming.
- Sections 67, 67A, and 67B of the IT Act empower authorities to formulate laws related to online gaming, recognizing the need for discretion in regulating activities that involve elements of chance, gambling, and betting.
- This recognition aligns with the constitutional division of responsibilities, placing gambling and betting within the state's jurisdiction.
- Self-Regulatory Bodies:
- The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology has introduced rules that permit the establishment of self-regulatory bodies within the online gaming industry.
- Inter-Ministerial Task Force Recommendations:
- The government's proactive approach is evident in the recommendations put forth by the inter-ministerial task force, contributing to the formulation of rules for online gaming.
- These recommendations reflect a collaborative effort aimed at striking a balance between industry growth and consumer protection.
- The government's proactive approach is evident in the recommendations put forth by the inter-ministerial task force, contributing to the formulation of rules for online gaming.
Way Forward
- Technology Integration for Compliance:
- Invest in technology solutions that facilitate seamless implementation of the code's provisions, such as robust KYC procedures and transparent disclosure mechanisms.
- Leverage blockchain or other secure technologies to enhance transparency in winner determination and financial transactions, ensuring a fair and accountable gaming environment.
- Regular Audits and Reporting:
- Establish a system for periodic audits by independent bodies to assess compliance with the code's stipulations.
- Mandate online gaming companies to publish regular reports on their platforms, detailing the manner of determining winners, platform fees, and the utilization of deposits, promoting transparency and accountability.
- Consumer Feedback Mechanism:
- Implement a robust feedback mechanism that allows players to express concerns and provide input on the industry's adherence to the code.
- Use consumer feedback to continually improve the code, address emerging issues, and enhance the overall gaming experience.
- International Best Practices Adoption:
- Stay informed about global best practices in online gaming ethics and consider adopting relevant measures that have proven successful in other jurisdictions.
- Participate in international forums to share insights and learn from the experiences of the global gaming community.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Q. Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centres within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centres.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Article 99 of the UN Charter
Why in News?
Recently, the United Nations(UN) Secretary-General Antonio Guterres invoked Article 99 of the UN Charter.
- This move was intended to warn the UN Security Council about the danger caused by Israel's actions in Gaza. This step is meant to draw attention to the pressing need to prevent a major humanitarian disaster in the area.
What is Article 99 of the UN Charter?
- Article 99 is a provision within the United Nations Charter, serving as the U.N.'s constitution.
- It empowers the secretary-general to bring attention to the Security Council about matters that, in their opinion, could threaten international peace and security.
- Article 99 is considered discretionary, allowing the Secretary-General to highlight critical issues, and it requires the Security Council's attention when invoked.
- This article has been sparingly used, with previous invocations including addressing the upheaval in the Republic of the Congo in 1960, Tunisia's complaint against France's military actions in 1961, and the creation of Bangladesh in 1971.
Charter of the United Nations
- The Charter of the UN is the founding document of the UN. It was signed on 26th June 1945, in San Francisco and came into force on 24th October 1945.
- The UN can take action on a wide variety of issues due to its unique international character and the powers vested in its Charter, which is considered an international treaty.
- As such, the UN Charter is an instrument of international law, and UN Member States are bound by it.
- The International Court of Justice (ICJ), the primary judicial body of the United Nations, operates by its Statute, annexed to the UN Charter as an integral part.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question
Prelims
Q. The Security Council of UN consists of 5 permanent members, and the remaining 10 members are elected by the General Assembly for a term of (2009)
(a) 1 year
(b) 2 years
(c) 3 years
(d) 5 years
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. What are the main functions of the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)? Explain different functional commissions attached to it. (2017)
India Offers Agricultural Line of Credit to Kenya
Why in news?
Recently, India has announced a USD 250 million line of credit to Kenya for modernisation of its agricultural sector during the recent visit of Kenya’s President to India.
- A line of credit (LOC) is a predetermined borrowing limit that is accessible whenever necessary. The borrower can withdraw funds as required until reaching the established limit, and once repaid, the funds can be borrowed again in the case of an open line of credit.
What are the Key Highlights of the Recent Visit of Kenya’s President?
- India and Kenya signed five pacts providing for cooperation in a range of areas including sports, education and digital solution, and unveiled a joint vision document to scale up maritime engagement in the Indian Ocean region.
- India also raised the issue of two Indian nationals who went missing in the east African country last year.
- Both sides agreed to strengthen bilateral ties in the field of defense, trade, energy, digital public infrastructure and healthcare.
- Both sides deliberated on defense cooperation and emphasized on military exercises, capacity building as well as linking the defense industries of both the countries .
- Kenya invited Indian companies to take advantage of the conducive and attractive environment to invest in Kenya, especially in agriculture, manufacturing, pharmaceutical, health, green energy and green mobility sectors.
- Terrorism is the most serious challenge and both sides have decided to increase counter-terror cooperation
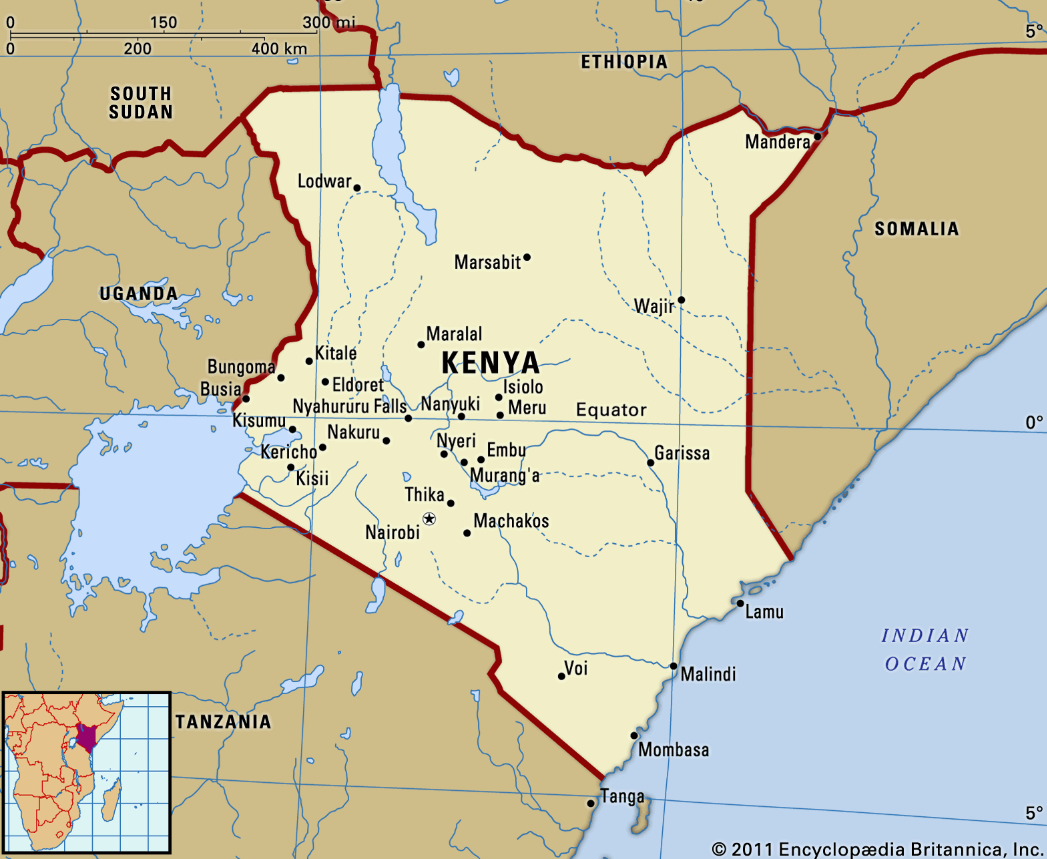
What are the Key Points Related to Kenya?
- Kenya is located in East Africa. Its terrain rises from a low coastal plain on the Indian Ocean to mountains and plateaus at its center.
- Kenya's location between the Indian Ocean and Lake Victoria means that people from all over Africa and the Middle East have traveled and traded across it for centuries.
- This has created a diverse culture with many ethnic groups and languages.
- The bones of one of the earliest human ancestors ever found were discovered in Kenya's Turkana Basin.
- Lake Turkana, the world's largest desert lake, is part of the Omo-Turkana basin, which stretches into four countries: Ethiopia, Kenya, South Sudan and Uganda.
- UN-Habitat maintains its headquarters at the United Nations Office at Nairobi, Kenya.
New Regulation of AICTE
Why in News?
Recently, the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) has announced new regulations for undergraduate courses like Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) and Bachelor of Computer Application (BCA) starting from 2024-25.
What are the Key Highlights of the New Regulations?
- Regulation Expansion:
- Undergraduate (UG) courses in Computer Applications (BCA) and Management (BBA/BMS) will come under the umbrella of AICTE to ensure coordinated development in technical and management education.
- Engineering colleges are now permitted to offer BBA and BCA programs, expanding their scope beyond traditional engineering disciplines.
- Institutional Flexibility:
- Well-performing institutions will be given provision for Extension of Approval up to 3 years for well-performing institutions.
- Presently, every technical education institute has to reapply for approval every year.
- Career Advancement for Working Professionals:
- Flexible study timings are introduced for selected institutes, allowing working professionals, such as diploma graduates, to pursue lateral entry into engineering degrees. This accommodates their work commitments by allowing extended study durations.
- Professional Upgradation Initiatives:
- AICTE has identified and selected over 300 institutes nationwide offering limited seats in diploma, engineering UG, and PG degrees for working professionals seeking educational upgrades.
- Relaxation in ranking criteria is provided for regions lacking suitable institutes.
- Regional Language Emphasis:
- AICTE has published academic textbooks, including engineering, in 13 regional languages, promoting regional language education in technical fields.
- Polytechnic Autonomy and Industry Collaborations:
- AICTE is granting autonomy to polytechnic colleges and encouraging collaborations with industries for degree issuance, focusing on employability and facilitating placements.
What is All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE)?
- The All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) is a statutory body, and a national-level council for technical education, under Ministry of Education, Government of India.
- It was set up in November 1945 as a national-level apex advisory body.
Ban on Sugarcane Juice for Ethanol
The Centre's recent ban on using sugarcane juice and sugar syrup for ethanol production in the 2023-24 supply year aims to maintain adequate sugar availability for domestic consumption and stabilize prices. However, the government has permitted the use of B-molasses for ethanol production.
- The Indian Sugar Mills Association (ISMA) forecasts a 9% reduction in gross sugar production for the 2023-24 marketing year, further complicating the situation.
- India has emerged as the world's largest producer and consumer of sugar as well as the world's 2nd largest exporter of sugar after Brazil, in Sugar Season (Oct-Sep) 2021-22.
Read more: Sugar Industry
Advancements in TB Care
The Union World Conference on Lung Health in 2023 heralded an optimistic turn in the fight against tuberculosis (TB) with the unveiling of four new improved drug regimens, promising to reduce treatment time for drug-resistant TB by up to two-thirds.
- The long duration of treatment, and subsequent drug toxicity, leads to patients being unable to tolerate drugs, and also causes non compliance with treatment schedules. This ultimately leads to drug resistant TB.
- With a mission to offer more effective treatment, these regimens exhibit similar efficacy and safety to conventional treatments but significantly reduce treatment time.
- TB is an infectious disease that most often affects the lungs and is caused by the bacteria- Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It spreads through the air when infected people cough, sneeze or spit.
- According to WHO, Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) remains a public health crisis and a health security threat. Only about 2 in 5 people with drug resistant TB accessed treatment in 2022.
Hanukkah
Hanukkah, also known as the Festival of Lights or Chanukah,commences at sundown on 7th December, 2023.
- It is an eight-day Jewish holiday that commemorates the rededication of the Second Temple in Jerusalem during the second century BCE.
- The festival begins on the 25th day of the Jewish month of Kislev and usually falls in late November to late December in the Gregorian calendar.
- Hanukkah celebrates the miracle of a small quantity of oil, which lasted for eight days, lighting the Temple's menorah (candelabrum) at the time of the Maccabean revolt, despite there being only enough oil for one day.
- The Hanukkah menorah is a nine-branched candelabrum that is lit during the eight-day holiday of Hanukkah.
Central Tribal University in Telangana
Recently, a bill seeking to establish a Central Tribal University in Telangana was passed by the Lok Sabha. This legislation, meeting the obligations of the Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2014, earmarks ₹889.7 crore for the university.
- The bill amends Central Universities Act, 2009 and the new university will be called Sammakka Sarakka Central Tribal University. It will be set up in Mulugu district in Telangana.
- The university's focus on tribal art, culture, technology, and traditional knowledge aims to advance education, research, and development while functioning akin to other Central Universities.