Social Justice
Global TB Report 2023
For Prelims: Global TB Report 2023, Tuberculosis (TB), Covid-19, Multidrug-Resistant TB (MDR-TB), United Nations (UN), World Health Organization (WHO), Universal Health Coverage (UHC).
For Mains: Global TB Report 2023, Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes.
Why in News?
Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO) has released the Global Tuberculosis (TB) report 2023, highlighting the high burden of TB worldwide in 2022.
- India accounted for the highest number of TB cases in the world in 2022, with 2.8 million TB cases, representing 27% of the global burden.
What are the Key Findings of the Global TB Report 2023?
- Burden of TB:
- It was the world's second leading cause of death from a single infectious agent in 2022, following Covid-19.
- TB caused almost twice as many deaths as Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)/Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome stage (AIDS). More than 10 million people continue to fall ill with TB every year.
- 30 high burden TB countries collectively accounted for 87% of the world's TB cases in 2022.
- Among the top eight high burden countries, in addition to India, are Indonesia, China, the Philippines, Pakistan, Nigeria, Bangladesh, and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- Increase in TB Diagnosis:
- In 2022, 7.5 million people were diagnosed with TB, marking the highest figure recorded since WHO began global TB monitoring in 1995.
- High Mortality Without Treatment:
- Without treatment, the death rate from TB disease is high, at about 50%.
- However, with treatments currently recommended by WHO (a 4–6 months course of anti-TB drugs), about 85% of people with TB can be cured.
- Global Recovery in TB Diagnosis and Treatment:
- There is a positive global recovery in the number of people diagnosed with TB and treated in 2022, following two years of Covid-19-related disruptions.
- Countries like India, Indonesia, and the Philippines, accounted for over 60% of the global reductions.
- TB Incidence Rate:
- The TB incidence rate, which measures new cases per 100,000 population per year, increased by 3.9% between 2020 and 2022.
- This increase reversed the declining trend of about 2% per year that had been observed for most of the past two decades.
What are the Findings Related to India?
- TB Case Fatality Ratio in India:
- India reported a case fatality ratio of 12%, indicating that 12% of TB cases in the country resulted in death.
- The report estimates that 3,42,000 TB-related deaths occurred in India in 2022, with 3,31,000 among HIV-negative individuals and 11,000 among those with HIV.
- Multidrug-Resistant TB (MDR-TB):
- India recorded 1.1 lakh cases of multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) in 2022, highlighting the continued challenge of MDR-TB as a public health crisis.
What are the Recommendations of the Report?
- Urgent action is required to end the global TB epidemic by 2030, a goal that has been adopted by all Member States of the United Nations (UN) and the WHO.
- Universal Health Coverage (UHC) is essential to ensure that all people who need treatment for TB disease or infection can access these treatments.
- Multisectoral action is also needed to address TB determinants such as poverty, undernourishment, HIV infection, smoking, and diabetes to reduce the number of people acquiring infection and developing TB disease.
What is Tuberculosis?
- About:
- Tuberculosis is an infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It can practically affect any organ of the body. The most common ones are lungs, pleura (lining around the lungs), lymph nodes, intestines, spine, and brain.
- Transmission:
- It is an airborne infection that spreads through close contact with the infected, especially in densely populated spaces with poor ventilation.
- Symptoms:
- Common symptoms of active lung TB are cough with sputum and blood at times, chest pains, weakness, weight loss, fever and night sweats.
- Treatment:
- TB is a treatable and curable disease. It is treated with a standard 6-month course of 4 antimicrobial drugs that are provided with information, supervision and support to the patient by a health worker or trained volunteer.
- Anti-TB medicines have been used for decades and strains that are resistant to 1 or more of the medicines have been documented in every country surveyed.
- Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR-TB):
- It is a form of TB caused by bacteria that do not respond to isoniazid and rifampicin, the 2 most powerful, first-line anti-TB drugs.
- MDR-TB is treatable and curable by using second-line drugs such as Bedaquiline.
- Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB) is a more serious form of MDR-TB caused by bacteria that do not respond to the most effective second-line anti-TB drugs, often leaving patients without any further treatment options.
What are the Initiatives to Combat TB?
- Global Efforts:
- The WHO has launched a joint initiative “Find. Treat. All. #EndTB” with the Global Fund and Stop TB Partnership.
- WHO also releases the Global Tuberculosis Report.
- India’s Efforts:
- National Strategic Plan (NSP) for Tuberculosis Elimination (2017-2025), The Nikshay Ecosystem (National TB information system), Nikshay Poshan Yojana (NPY- financial support), TB Harega Desh Jeetega Campaign.
- Currently, two vaccines VPM (Vaccine Projekt Management) 1002 and MIP (Mycobacterium Indicus Pranii) have been developed and identified for TB, and are under Phase-3 clinical trial.
- In 2018 Nikshay Poshan Yojna was launched, which aimed to support every Tuberculosis (TB) Patient by providing a Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) of Rs 500 per month for nutritional needs.


Biodiversity & Environment
8-Point Plan in NCR and Nearby Regions under GRAP Stage-IV
For Prelims: Commission for Air Quality Management in NCR & Adjoining Areas, Graded Response Action Plan, PM2.5 emissions, Light Commercial Vehicles, System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research, National Air Quality Monitoring Programme
For Mains: Stages of Graded Response Action Plan, Indian Government Initiatives Related to Air Pollution.
Why in News?
Commission for Air Quality Management in National Capital Region(NCR) and Adjoining Areas has invoked an eight-point action plan aligning with Stage-IV of the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP), aiming to avert any additional decline in the region's air quality.
What is the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP)?
- About:
- The GRAP consists of emergency measures designed to prevent the deterioration of air quality after reaching specific thresholds in the Delhi-NCR region.
- The Ministry of Environment, Forests & Climate Change (MoEF&CC) notified the GRAP in 2017.
- Commission for Air Quality Management in NCR & Adjoining Areas (CAQM) implements the GRAP.
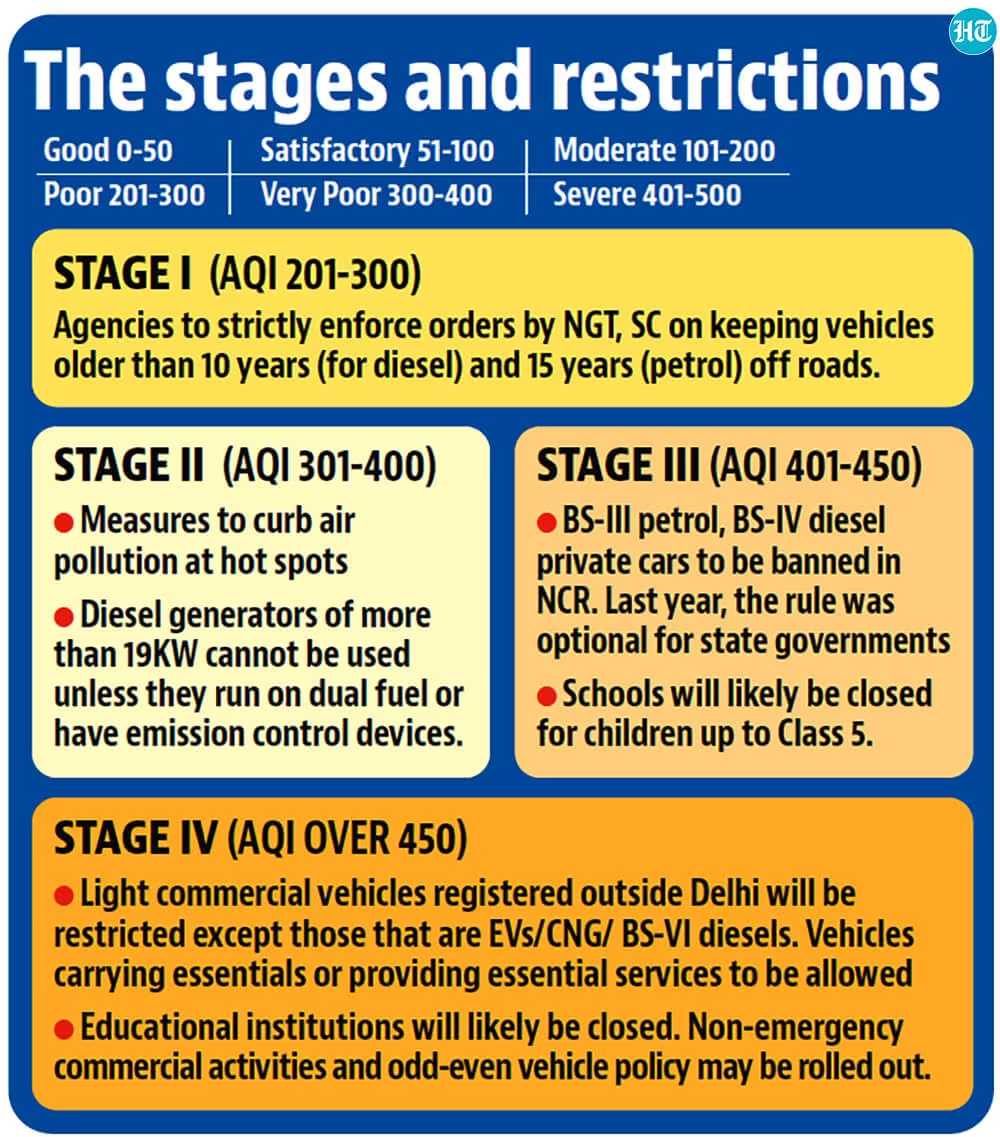
- Implementation: It is implemented under four stages:
- GRAP is incremental in nature and thus, when the air quality dips from ‘poor’ to ‘very poor,’ measures listed under both sections have to be followed.
What is the Eight Point Action Plan as per Stage-IV of GRAP?
- Prohibiting the entry of truck traffic into Delhi, except for those transporting essential goods and services, along with LNG/CNG/electric trucks.
- Restricting non-Delhi-registered Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs) to enter Delhi, unless they are EVs/CNG/BS-VI diesel, except for essential service carriers.
- Banning the operation of Delhi-registered diesel Medium Goods Vehicles (MGVs) and Heavy Goods Vehicles (HGVs), except for those transporting essential items.
- Imposing a prohibition on construction and demolition (C&D) activities in linear public projects like highways, roads, flyovers, power transmission, and pipelines.
- Advising NCR State Governments and GNCTD to transition physical classes for grades VI to IX, XI to online mode.
- Directing NCR State Governments/GNCTD to consider allowing 50% capacity in public, municipal, and private offices, with the remainder working remotely.
- Empowering the Central Government to decide on work-from-home protocols for employees in Central Government offices.
- Encouraging State Governments to contemplate additional emergency measures such as the closure of educational institutions, non-essential commercial activities, and implementing an odd-even vehicle registration number scheme.
What are the Main Causes and Sources of Air Pollution in Delhi-NCR Region?
- Stubble burning: Burning crop residue by farmers in the nearby states of Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh though significantly reduced but still stands as a primary cause of heightened air pollution brought by north-westerly winds in the national capital during October and November.
- According to SAFAR, stubble burning contributed 25% to Delhi's pollution in 2021.
- SAFAR stands for System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research. It is a national initiative introduced by the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) to provide location-specific information on air quality in near real time.
- According to SAFAR, stubble burning contributed 25% to Delhi's pollution in 2021.
- Vehicle Emissions: The vehicular emissions from the large number of cars, trucks, buses, and two-wheelers plying on the roads of Delhi and the NCR are another significant source of air pollution.
- As per a research paper published in the Observer Research Foundation, the transport sector is the main source of PM2.5 emissions in Delhi (28% of all PM2.5 emissions).
- Industrial Emissions: The presence of multiple industries in and around the NCR region releases harmful emissions into the atmosphere. Industries emit various pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter, contributing substantially to air pollution.
- Construction Activities: Construction sites, especially brick kilns in the outskirts, generate high levels of pollutants.
- Lack of compliance with environmental regulations, inadequate waste management, and insufficient timelines for construction projects compound the problem.
- Waste Burning and Landfills: Improper disposal of waste, including open burning of garbage and landfill sites, emits harmful gases and particulate matter into the air, significantly affecting air quality.
- Example: The Ghazipur landfill site.
- Geographical and Meteorological Factors: The geographical location of the NCR region, along with specific meteorological conditions such as temperature inversion during winters, contributes to trapping pollutants close to the ground, leading to the exacerbation of pollution levels.
- October 2023 witnessed the highest pollution levels since 2020 in Delhi-NCR, partly due to minimal rainfall.
- Rain typically aids in settling particulate matter and dust, thereby enhancing the Air Quality Index .
- October 2023 witnessed the highest pollution levels since 2020 in Delhi-NCR, partly due to minimal rainfall.
Note
Global research connects air pollution to acute myeloid leukemia, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma in children, primarily due to pollutants like benzene, NOx, and particulate matter. Delhi stands out with high numbers of leukemia and lymphoma cases in children compared to regions with lower pollution levels.
What are the Indian Government Initiatives Related to Air Pollution?
- System of Air Quality and Weather Forecasting and Research (SAFAR) Portal.
- Air Quality Index
- For Reducing Vehicular Pollution:
- BS-VI Vehicles,
- Push for Electric Vehicles (EVs),
- Odd-Even Policy as an emergency measure (for Delhi).
- Subsidy to farmers for buying Turbo Happy Seeder (THS) Machine for reducing stubble burning.
- National Air Quality Monitoring Programme (NAMP)
Way Forward
- Strict Emission Control Policies: Stricter enforcement of emission norms for industries, vehicles, and construction activities to limit pollutants released into the atmosphere.
- Public Transport and Traffic Management: Encouraging and enhancing the use of public transportation to reduce vehicular emissions. Expanding and improving public transport networks can alleviate congestion and emissions.
- The recent initiative in Delhi including increased number of electric buses and Delhi Metro’s additional trips is a significant step in the direction.
- Waste Management and Regulation: Strict regulations and effective enforcement in waste management to minimize open waste burning and landfill emissions.
- Encouraging recycling, composting, and waste-to-energy initiatives to decrease the volume of waste that is openly burnt.
- Crop Residue Management: Addressing crop burning by providing farmers with sustainable and cost-effective alternatives for residue management like Happy Seeder.
- Incentivizing and promoting these methods can significantly reduce the need for burning.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. In the cities of our country, which among the following atmospheric gases are normally considered in calculating the value of Air Quality Index? (2016)
- Carbon dioxide
- Carbon monoxide
- Nitrogen dioxide
- Sulfur dioxide
- Methane
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Describe the key points of the revised Global Air Quality Guidelines (AQGs) recently released by the World Health Organisation (WHO). How are these different from its last update in 2005? What changes in India’s National Clean Air Programme are required to achieve revised standards? (2021)


Science & Technology
Deepfakes
For Prelims: Deepfake technology, Deep synthesis technology, Artificial Intelligence technology, blockchain technology
For Mains: Impact of Deepfake Technology, Dealing with deepfakes, Ethical concerns,
Why in News?
A Deepfake video showing an Indian actress has sparked outrage and concern over the misuse of artificial intelligence (AI) to create realistic but fake videos, aso known as deepfakes.
What are Deepfakes?
- About:
- Deepfakes are synthetic media that use AI to manipulate or generate visual and audio content, usually with the intention of deceiving or misleading someone.
- Deepfake Creation:
- Deepfakes are created using a technique called generative adversarial networks (GANs), which involve two competing neural networks: a generator and a discriminator.
- The generator tries to create fake images or videos that look realistic, while the discriminator tries to distinguish between the real and the fake ones.
- The generator learns from the feedback of the discriminator and improves its output until it can fool the discriminator.
- Deepfakes require a large amount of data, such as photos or videos, of the source and the target person, which are often collected from the internet or social media without their consent or knowledge.
- The generator tries to create fake images or videos that look realistic, while the discriminator tries to distinguish between the real and the fake ones.
- Deepfakes are a part of Deep Synthesis, which uses technologies, including deep learning and augmented reality, to generate text, images, audio and video to create virtual scenes.
- Deepfakes are created using a technique called generative adversarial networks (GANs), which involve two competing neural networks: a generator and a discriminator.
- Positive Applications of Deep Learning:
- Deep learning technology has enabled positive advancements, such as restoring lost voices and recreating historical figures.
- Deep learning techniques have been applied in comedy, cinema, music, and gaming to enhance artistic expression.
- Synthetic avatars of people with physical or mental disabilities will help express themselves online.
- It enhances medical training and simulation by generating diverse and realistic medical images. It also creates virtual patients and scenarios for simulating medical conditions and procedures, improving training efficiency.
- It can also be used to enhance the interaction and immersion of augmented reality (AR) and gaming applications.
- Concerns Regarding the Deepfakes:
- Deepfakes are a problem because they can be used for various malicious purposes, such as
- Spreading propaganda, and fake news;
- Influencing elections and public opinion;
- Blackmailing and extortion individuals or organizations;
- Damaging the reputation and credibility of celebrities, politicians, activists, and journalists; and
- Creating non-consensual pornography and revenge porn.
- Deepfakes can cause various harms, such as eroding trust in institutions, media, and democracy, and undermining the rule of law and human rights.
- Deepfake technology can violate the privacy, dignity, and reputation of individuals, and harm the mental health and well-being of the victims, especially women, who are often the targets of such malicious manipulation.
- Deepfakes are a problem because they can be used for various malicious purposes, such as
- Detection:
- Look for visual and audio inconsistencies in the media.
- Use reverse image search to find the original source or similar images.
- Use AI-based tools to analyze the quality, consistency, and authenticity of the images or videos.
- Using digital watermarking or blockchain to verify the source and integrity of the media.
- Educate oneself and others about deepfake technology and its implications.
What are the Global Approaches Related to Deepfake Regulation?
- India:
- India does not have specific laws or regulations that ban or regulate the use of deepfake technology.
- India has called for a global framework on the expansion of “ethical” AI tools.
- Existing laws such as Sections 67 and 67A of the Information Technology Act (2000) have provisions that may be applied to certain aspects of deep fakes, such as defamation and publishing explicit material.
- Section 500 of the Indian Penal Code (1860) provides punishment for defamation.
- The Digital Personal Data Protection Act, provides some protection against the misuse of personal data.
- The Information Technology Rules, 2021, mandate the removal of content impersonating others and artificially morphed images within 36 hours.
- India needs to develop a comprehensive legal framework specifically targeting deepfakes, considering the potential implications for privacy, social stability, national security, and democracy.
- Global:
- The recent world’s first ever AI Safety Summit 2023 involving 28 major countries, including the US, China, and India, agreed on the need for global action to address AI's potential risks.
- The Bletchley Park Declaration declaration at the summit acknowledged the risks of intentional misuse and the loss of control over AI technologies.
- European Union:
- The European Union's Code of Practice on Disinformation requires tech companies to counter deep fakes and fake accounts within six months of signing up to the Code.
- If found non-compliant, tech companies can face fines up to 6% of their annual global turnover
- The European Union's Code of Practice on Disinformation requires tech companies to counter deep fakes and fake accounts within six months of signing up to the Code.
- United States:
- The U.S. introduced the bipartisan Deepfake Task Force Act to assist the Department of Homeland Security in countering deepfake technology.
- China:
- China introduced comprehensive regulation on deep synthesis, effective from January 2023.
- Aimed at curbing disinformation, the regulation requires clear labelling and traceability of deep synthesis content.
- The Regulations impose obligations on the providers and users of so-called “deep synthesis technology”.
- China introduced comprehensive regulation on deep synthesis, effective from January 2023.
- The recent world’s first ever AI Safety Summit 2023 involving 28 major countries, including the US, China, and India, agreed on the need for global action to address AI's potential risks.
- Tech Companies:
- Big tech companies like Meta and Google have announced measures to address the issue of deep fake content.
- However, there are still vulnerabilities in their systems that allow the dissemination of such content.
- Google has introduced tools for identifying synthetic content, including watermarking and metadata.
- Watermarking embeds information directly into content, making it resistant to editing, while metadata provides additional context to original files.
- Big tech companies like Meta and Google have announced measures to address the issue of deep fake content.
Way Forward
- Developing and implementing comprehensive laws and regulations that specifically target the creation and dissemination of deepfakes, while balancing the freedom of speech and expression.
- Enhancing the public awareness and media literacy of the potential risks and impacts of deepfakes, and encouraging critical thinking and verification of the sources and content of media.
- Creating and adopting technical solutions and standards that can detect, prevent, and remove deepfakes, such as digital watermarks, and blockchain.
- Promoting ethical and responsible use of deep learning technology and synthetic media, and establishing codes of conduct and best practices for the creators and users of deepfakes.
- Fostering collaboration and coordination among various stakeholders, such as governments, media, civil society, academia, and industry, to address the challenges and opportunities posed by deepfakes.
Legal Insight: Indian Laws Safeguarding Society against Deepfake Technology
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. What are the main socio-economic implications arising out of the development of IT industries in major cities of India? (2022)


Important Facts For Prelims
Radiative Cooling Paint
Why in News?
Researchers at the Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research (JNCASR) Bengaluru, an autonomous institute of the Department of Science and Technology, have introduced an innovative paint that utilizes radiative cooling.
- In the wake of escalating global temperatures and the pressing need for sustainable cooling solutions, this new, cost-effective, and eco-friendly radiative cooling technology stands as an effective solution.
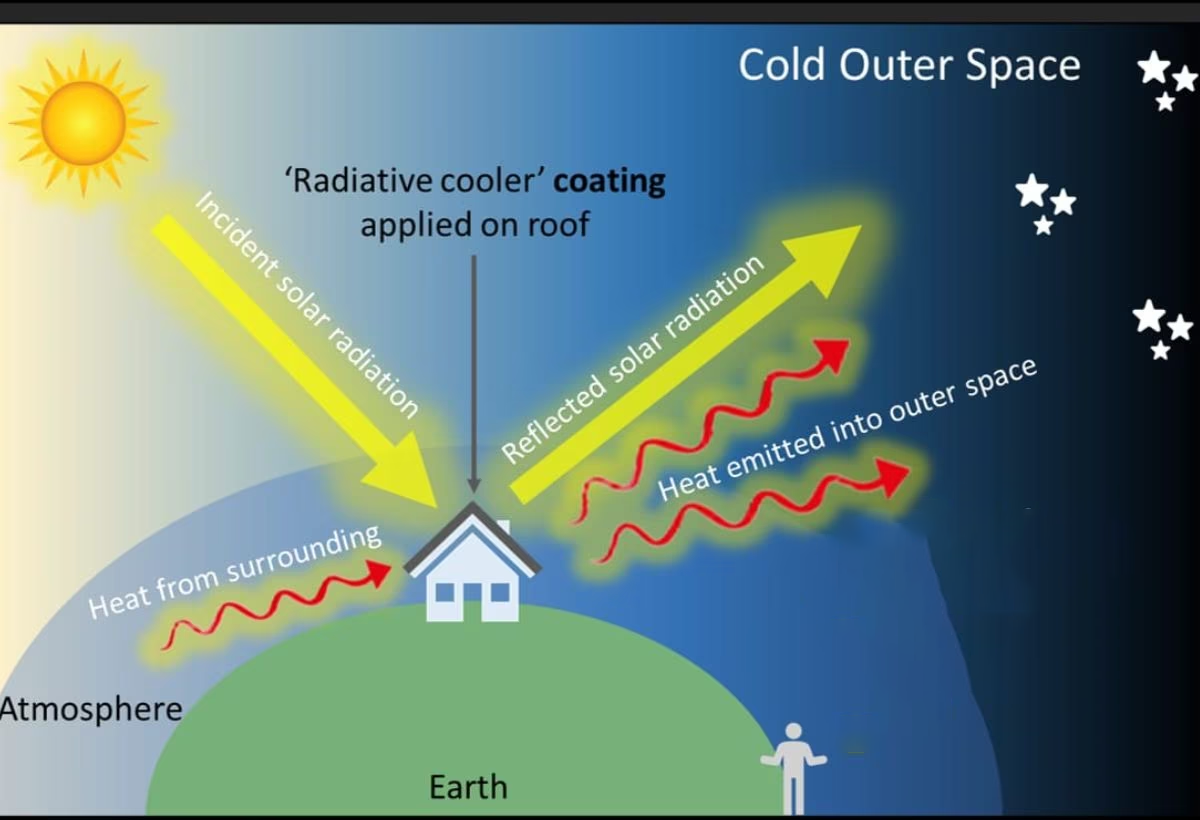
What is Radiative Cooling Technology?
- About:
- Radiative cooling technology is a method designed to dissipate heat from an object by emitting thermal radiation into the atmosphere, allowing the object to become cooler.
- It leads to creation of cool surfaces by emitting thermal radiation directly into the extremely cold universe (around 3 Kelvin), using the atmospheric transmission window (8 - 13 µm).
- Notably, this process occurs without any reliance on electricity.
- Need:
- Increased global warming and urban heat island effects have accentuated the necessity for effective cooling technologies.
- Conventional active cooling devices like air-conditioners, fans, and refrigerators demand substantial electrical energy, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and elevated surface temperatures.
- Radiative cooling technology addresses these challenges by emitting thermal radiation without electricity consumption, through the atmospheric transmission window.
- Increased global warming and urban heat island effects have accentuated the necessity for effective cooling technologies.
- Radiative Cooling Paint:
- It is derived from a novel magnesium oxide (MgO)-polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) polymer nanocomposite prepared from materials that are earth abundant, cheap, non-toxic and non-harmful.
- It showcases remarkable cooling capabilities with high solar reflectivity and infrared thermal emissivity.
- The MgO-PVDF with dielectric nanoparticles resulted in high solar reflectance (96.3%) and exceptional thermal emission (98.5%).
- Tailored to counter escalating heat impact on buildings, this paint minimizes electricity usage and provides crucial cooling during sweltering summer days.
- With outstanding optical features, it lowers surface temperatures by about 10°C in strong sunlight, outperforming standard white paints.
- Its water-resistant, hydrophobic nature guarantees effortless application on diverse surfaces, ensuring consistent coverage and strong adhesion.
- It is derived from a novel magnesium oxide (MgO)-polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) polymer nanocomposite prepared from materials that are earth abundant, cheap, non-toxic and non-harmful.


Important Facts For Prelims
Pusa-2090 Alternative to Pusa-44
Why in News?
With the Supreme Court emphasizing the need to cease stubble burning in states like Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Rajasthan, the discussion surrounding Pusa-2090 rice variety from its ability to provide an alternative to the problematic long-duration Pusa-44 variety.
What is Pusa-44 and Pusa-2090?
- Pusa-44:
- Pusa-44, a long-duration paddy variety bred by the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI), has been a key contributor to stubble burning.
- Its growth cycle of 155-160 days, from nursery sowing to harvesting, leads to late October maturity, leaving a short window for field preparation for the next crop.
- Due to time constraints, farmers resort to burning the stubble, causing severe environmental issues.
- Despite its longer duration, the high-yielding nature of Pusa-44, averaging 35-36 quintals an acre, makes it popular among farmers.
Note: In the current kharif season, Pusa-44 covers a significant portion of the paddy cultivation in Punjab, especially in non-basmati varieties. Whereas, basmati varieties, producing softer straw, contribute less to stubble burning, but their cultivation area is relatively smaller.
- Pusa-2090: A Potential Solution
- IARI has developed Pusa-2090, an improved version derived from a cross between Pusa-44 and CB-501, an early-maturing Japonica rice line.
- It matures in a shorter duration of 120-125 days while maintaining comparable yields, addressing the core issue of stubble burning.
- It combines the high yield attributes of Pusa-44 with the quicker maturation cycle of CB-501, making it a promising alternative.
- It has undergone testing at the All-India Coordinated Rice Improvement Project and has been identified for cultivation in regions like Delhi and Odisha.
- Farmers in regions where Pusa-2090 has been tested have reported promising yield results.
What can be the Alternatives to Stubble Burning?
- PUSA Decomposers: The decomposers are in the form of capsules made by extracting fungi strains that help the paddy straw to decompose at a much faster rate.
- Happy Seeder: It is a tractor-mounted device offering an eco-friendly alternative to stubble burning.
- It works by cutting and lifting rice straw, simultaneously sowing wheat into the exposed soil and depositing the straw over the sown area as protective mulch.
- Palletisation: Paddy straw, when dried and transformed into pellets, becomes a viable alternative fuel source.
- When mixed with coal, these pellets can be utilized in thermal power plants and industries, potentially saving coal usage and lowering carbon emissions.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following agricultural practices: (2012)
- Contour bunding
- Relay cropping
- Zero tillage
In the context of global climate change, which of the above helps/help in carbon sequestration/storage in the soil?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None of them
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
Kavach System
Why in News?
The recent collision between two passenger trains in Andhra Pradesh’s Vizianagaram district drew attention to the absence of the Traffic Collision Avoidance Systems (TCAS), specifically the indigenously developed system called 'Kavach,' which, if installed, could have averted the tragic incident.
What is Kavach?
- About:
- Kavach is a cab signaling train control system with anti-collision features developed by the Research Design and Standards Organisation (RDSO) in association with three Indian vendors.
- It has been adopted as our National Automatic Train Protection (ATP) System.
- It adheres to Safety Integrity Level-4 (SIL-4) standards and acts as a vigilant watchdog over the existing signaling system, alerting the loco pilot when approaching a 'red signal' and applying automatic brakes if necessary to prevent overshooting the signal.
- The system also relays SoS messages during emergency situations.
- It features centralized live monitoring of train movements through the Network Monitor System.
- The Indian Railways Institute of Signal Engineering & Telecommunications (IRISET) in Secunderabad, Telangana hosts the 'Centre of Excellence' for Kavach.
- Kavach is a cab signaling train control system with anti-collision features developed by the Research Design and Standards Organisation (RDSO) in association with three Indian vendors.
- Components of Kavach:
- Within the Kavach setup, designated railway stations along the intended route for deployment consist of three essential components.
- First Component: The first component involves the incorporation of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology into the tracks.
- RFID employs radio waves to identify objects or individuals and utilizes electromagnetic fields to automatically read wireless device information from a distance without physical contact or line of sight.
- Second Component: The locomotive, serving as the driver's cabin, is equipped with RFID readers, a computer, and brake interface equipment, comprising the second component.
- Third Component: It encompasses radio infrastructure, such as towers and modems, strategically installed at railway stations to support the system's functionality.
- First Component: The first component involves the incorporation of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology into the tracks.
- Within the Kavach setup, designated railway stations along the intended route for deployment consist of three essential components.
- Challenges in Deployment:
- Its deployment cost is ₹50 lakh per kilometer, with limited coverage of approximately 1,500 km currently, posing a challenge in comprehensive implementation across the 68,000 km rail network.
Note: Presently, the Indian Railways has designated ₹4,000 crore within the Signalling and Telecom budget section, encompassing ₹2,000 crore allocated under the Rashtriya Rail Sanraksha Kosh (RRSK) specifically for implementing Kavach.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:
Q. Consider the following communication technologies: (2022)
- Closed-circuit Television
- Radio Frequency Identification
- Wireless Local Area Network
Which of the above are considered Short-Range devices/technologies?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Need For Policy to Distribute Sanitary Napkins in Schools
The Supreme Court tells Centre to set down a national model for the number of girls’ toilets per femalepopulation across government-aided and residential schools in the country and place on record an “optimum”menstrual hygiene policy with focus on the distribution of sanitary napkins.
- It was held that certain States had already been implementing their own schemes for distribution of sanitary
napkins.- In Tamil Nadu, 18 packets with six napkins each were given to girls.
- Northeastern States had also shown progressiveness with their own schemes.
- The latest National Family Health Survey 5 (NFHS-5) found a significant improvement in the percentage of
women aged 15-24 who use a hygienic method of protection during their menstrual cycle, rising from 58% in
NFHS-4 to 78%.
Read More: World Menstrual Hygiene Day, Swachh Bharat guidelines
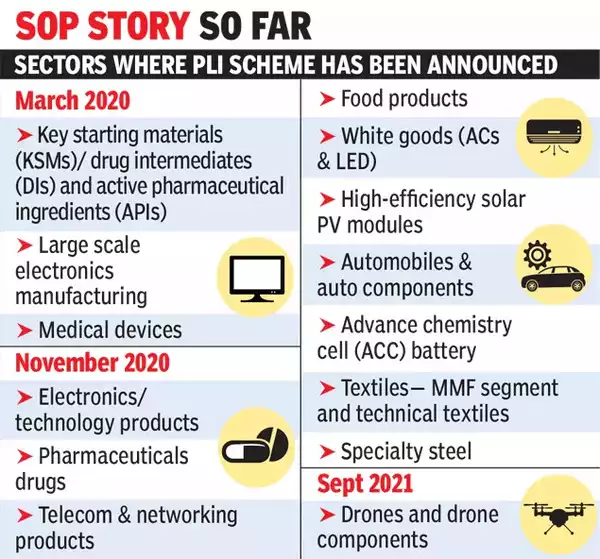
80% of Semiconductor Manufacturing Funds Remain Untouched
An official from the Industry Ministry stated that out of the USD 10 billion allocated for semiconductor
production through the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme by the Union government, about USD 8 billion
remains unclaimed.
- In 2021, India announced its roughly USD 10 billion dollar PLI scheme to encourage semiconductor and display
manufacturing in the country. - The PLI scheme was launched by the Government of India to boost the domestic manufacturing sector and to
reduce the dependence on imports.- The scheme offers financial incentives to companies that manufacture products in India.
- It covers 14 key sectors:
Read more: India Semiconductor Mission
Aadhaar Authentication: Reinforcing Prison Security
The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has proposed an initiative to implement Aadhaar authentication for inmates and visitors in around 1,300 jails across the nation.
- The integration of Aadhaar services with the ePrisons system developed by the National Informatics Centre (NIC) is aimed at accurately verifying inmates and visitors, thereby reducing identity fraud within the prison system and enhancing administrative processes related to prisoner management.
- As per the MHA notification, the authentication process will be voluntary, with the onus on the States and Union Territories to adhere to relevant guidelines.
Read more: Safeguarding Aadhaar Data
Uttarakhand State Foundation Day
Annually, 9th November is celebrated as Uttarakhand State Foundation Day, as on this day Uttarakhand became India's 27th state on November 9, 2000, when it was carved out of northern Uttar Pradesh.
- The state was originally named Uttaranchal, but was renamed Uttarakhand in 2007. The name Uttarakhand comes from the Sanskrit dialect and means "northern city"
- Uttarakhand is a land of natural beauty, cultural diversity, and religious significance. It is home to the Char Dham, the four sacred Hindu pilgrimage sites of Badrinath, Kedarnath, Gangotri, and Yamunotri.
- Uttarakhand is home to two UNESCO Heritage sites, Valley of Flowers and Nanda Devi National Park.
Read more: Statehood Demand